Содержание
- Mean, median and mode in Excel
- How to calculate mean in Excel
- How to find median in Excel
- How to calculate mode in Excel
- Mean vs. median: which is better?
- How to find the arithmetic mean in Excel?
- How to find the arithmetic mean?
- Average value by condition
- How to calculate the weighted average price in Excel?
- The standard deviation: the formula in Excel
- How to Find Mean in Excel
- Introduction to Mean in Excel
- Examples on How to Find Mean in Excel
- Example #1 – How to Calculate the Basic Mean in Excel
- Example #2 – How to Calculate Mean if Text Value Exists in the Data Set
- Example #3 – How to Calculate Mean for Different Set of Data
- Things to Remember About How to Find Mean in Excel
- Recommended Articles

When analyzing numerical data, you may often be looking for some way to get the «typical» value. For this purpose, you can use the so-called measures of central tendency that represent a single value identifying the central position within a data set or, more technically, the middle or center in a statistical distribution. Sometimes, they are also classified as summary statistics.
The three main measures of central tendency are Mean, Median and Mode. They all are valid measures of central location, but each gives a different indication of a typical value, and under different circumstances some measures are more appropriate to use than others.
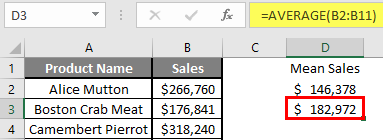
How to calculate mean in Excel
Arithmetic mean, also referred to as average, is probably the measure you are most familiar with. The mean is calculated by adding up a group of numbers and then dividing the sum by the count of those numbers.
For example, to calculate the mean of numbers <1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 6>, you add them up, and then divide the sum by 6, which yields 3: (1+2+2+3+4+6)/6=3.
In Microsoft Excel, the mean can be calculated by using one of the following functions:
- AVERAGE- returns an average of numbers.
- AVERAGEA — returns an average of cells with any data (numbers, Boolean and text values).
- AVERAGEIF — finds an average of numbers based on a single criterion.
- AVERAGEIFS — finds an average of numbers based on multiple criteria.
For the in-depth tutorials, please follow the above links. To get a conceptual idea of how these functions work, consider the following example.
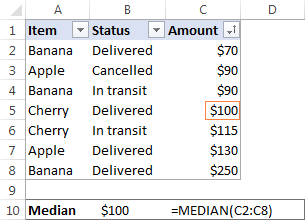
In a sales report (please see the screenshot below), supposing you want to get the average of values in cells C2:C8. For this, use this simple formula:
To get the average of only «Banana» sales, use an AVERAGEIF formula:
=AVERAGEIF(A2:A8, «Banana», C2:C8)
To calculate the mean based on 2 conditions, say, the average of «Banana» sales with the status «Delivered», use AVERAGEIFS:
=AVERAGEIFS(C2:C8,A2:A8, «Banana», B2:B8, «Delivered»)
You can also enter your conditions in separate cells, and reference those cells in your formulas, like this: 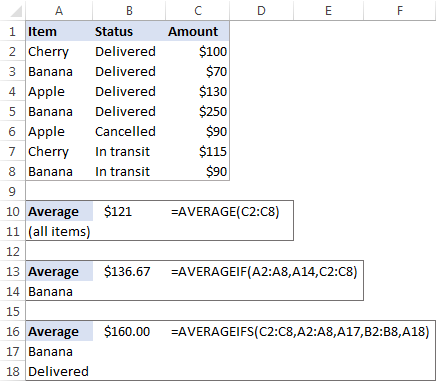
Median is the middle value in a group of numbers, which are arranged in ascending or descending order, i.e. half the numbers are greater than the median and half the numbers are less than the median. For example, the median of the data set <1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9>is 3.
This works fine when there are an odd number of values in the group. But what if you have an even number of values? In this case, the median is the arithmetic mean (average) of the two middle values. For example, the median of <1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 6>is 2.5. To calculate it, you take the 3rd and 4th values in the data set and average them to get a median of 2.5.
In Microsoft Excel, a median is calculated by using the MEDIAN function. For example, to get the median of all amounts in our sales report, use this formula:
To make the example more illustrative, I’ve sorted the numbers in column C in ascending order (though it is not actually required for the Excel Median formula to work):
In contrast to average, Microsoft Excel does not provide any special function to calculate median with one or more conditions. However, you can «emulate» the functionality of MEDIANIF and MEDIANIFS by using a combination of two or more functions like shown in these examples:
How to calculate mode in Excel
Mode is the most frequently occurring value in the dataset. While the mean and median require some calculations, a mode value can be found simply by counting the number of times each value occurs.
For example, the mode of the set of values <1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 6>is 2. In Microsoft Excel, you can calculate a mode by using the function of the same name, the MODE function. For our sample data set, the formula goes as follows:
=MODE(C2:C8)
In situations when there are two or more modes in your data set, the Excel MODE function will return the lowest mode.
Generally, there is no «best» measure of central tendency. Which measure to use mostly depends on the type of data you are working with as well as your understanding of the «typical value» you are attempting to estimate.
For a symmetrical distribution (in which values occur at regular frequencies), the mean, median and mode are the same. For a skewed distribution (where there are a small number of extremely high or low values), the three measures of central tendency may be different.
Since the mean is greatly affected by skewed data and outliers (non-typical values that are significantly different from the rest of the data), median is the preferred measure of central tendency for an asymmetrical distribution.
For instance, it is generally accepted that the median is better than the mean for calculating a typical salary. Why? The best way to understand this would be from an example. Please have a look at a few sample salaries for common jobs:
- Electrician — $20/hour
- Nurse — $26/hour
- Police officer — $47/hour
- Sales manager — $54/hour
- Manufacturing engineer — $63/hour
Now, let’s calculate the average (mean): add up the above numbers and divide by 5: (20+26+47+54+63)/5=42. So, the average wage is $42/hour. The median wage is $47/hour, and it is the police officer who earns it (1/2 wages are lower, and 1/2 are higher). Well, in this particular case the mean and median give similar numbers.
But let’s see what happens if we extend the list of wages by including a celebrity who earns, say, about $30 million/year, which is roughly $14,500/hour. Now, the average wage becomes $2,451.67/hour, a wage that no one earns! By contrast, the median is not significantly changed by this one outlier, it is $50.50/hour.
Agree, the median gives a better idea of what people typically earn because it is not so strongly affected by abnormal salaries.
This is how you calculate mean, median and mode in Excel. I thank you for reading and hope to see you on our blog next week!
Источник
How to find the arithmetic mean in Excel?
There are many functions in order to find the average in Excel (although it does not matter what kind of value it is: numerical, textual, percentage or other). And each of them has its own peculiarities and advantages. After all, certain conditions can be put in this task.
For example, the average in Excel is counting using statistical functions. You can also manually enter your own formula. Consider the various options.
How to find the arithmetic mean?
It is necessary to add all the numbers in the set and divide the sum by the number in order to find the arithmetic mean. For example, the student’s marks in computer science: 3, 4, 3, 5, 5. The average rating is 4 for a quarter. We found the arithmetic mean using the formula: =(3 + 4 + 3 + 5 + 5) / 5.
How can you quickly do this with Excel functions? Take for example a number of random numbers in a row:
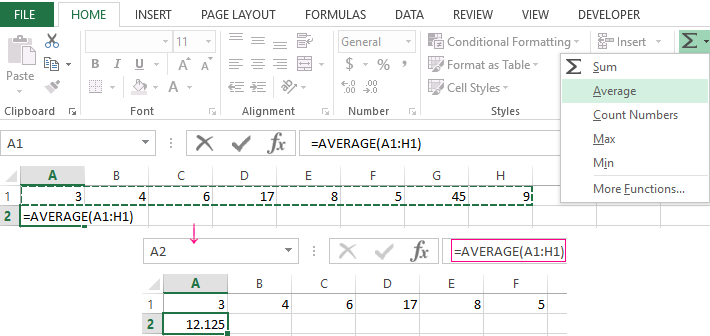
- We put the cursor in cell A2 (under a set of numbers). In the menu – «HOME»-«Editing»-«AutoSum»-«Average» button. A formula appears after clicking in the active cell. Select the range: A1: H1 and press ENTER.
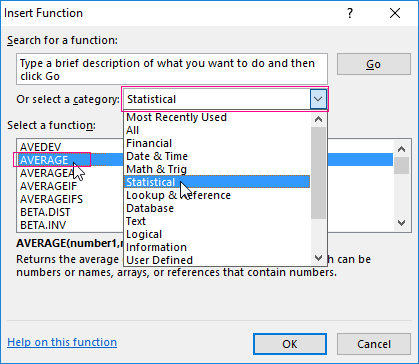
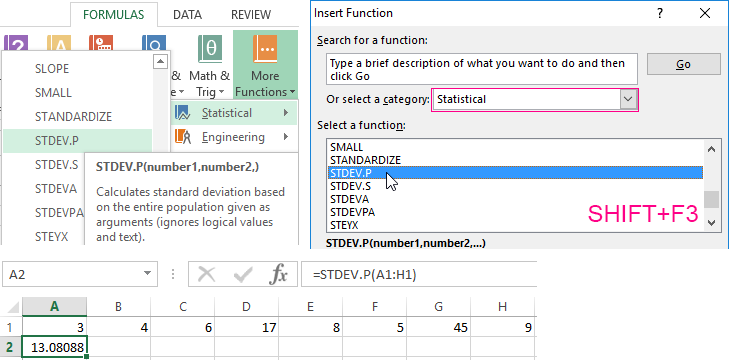
- The second method is based on the same principle of finding the arithmetic mean. But we will call the function AVERAGE differently. Using the function wizard (use fx button or key combination SHIFT + F3).
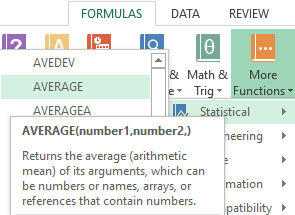
- The third way to call the AVERAGE function from the panel: «FORMULAS»-«More Function»-«Statistical»-«AVERAGE».
Or you can make cell to be active and just manually enter the formula: =AVERAGE(A1:A8).
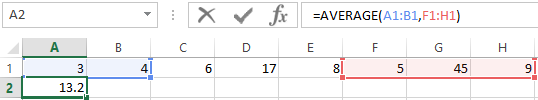
Now let’s see what the AVERAGE function be able to:
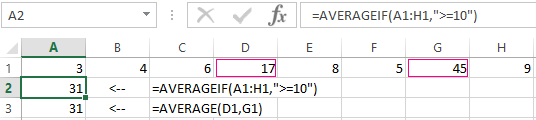
Let us find the arithmetic mean of the first two and three last numbers. Formula: =AVERAGE(A1:B1,F1:H1).
Average value by condition
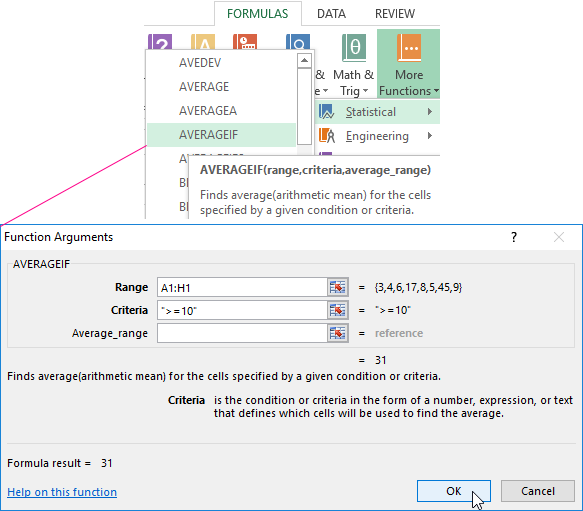
A numerical criterion or a textual criterion can be the condition for finding the arithmetic mean. We will use the function: = AVERAGEIF().
Find the arithmetic mean for numbers that are greater or equal to 10.
The result of using the function «AVERAGEIF» by the condition «>=10» is next:
The third argument «Averaging Range» is omitted. Firstly, it is not necessary. Secondly, the range analyzed by the program contains ONLY numeric values. In the cells specified in the first argument, the search will be performed according to the condition specified in the second argument.
Attention! You can specify the search criteria in the cell. And in the formula make a reference to it.
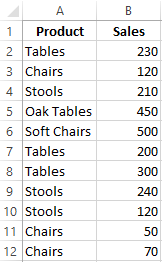
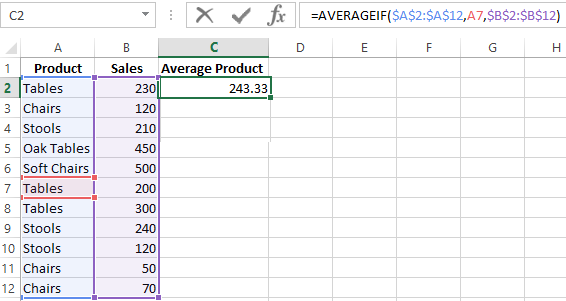
Let’s find the average value of numbers by the text criterion. For example, the average sales of goods «Tables».
The function will look like this:
Range is a column with the names of goods. Search criteria is a link to a cell with the word «Tables» (you can insert the word «Tables» instead of the A7 link). The averaging range is the cells from which data will be taken to calculate the arithmetic mean.
We get the following value as a result of calculating using the function:
Attention! It is mandatory to point the averaging range for the text criterion (condition).
How to calculate the weighted average price in Excel?
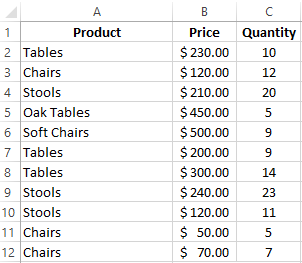
How to calculate the average percentage in Excel? For this purpose, the SUMPRODUCTS and SUM functions are suitable. Table for an example:
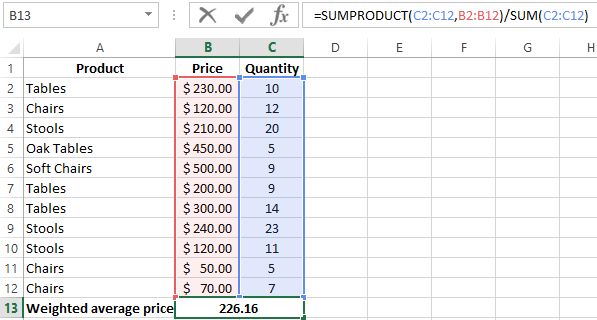
How did we know the weighted average price?
Using the formula =SUMPRODUCT() we learn the total revenue after the realization of the entire quantity of goods. And the =SUM() function sums the goods quantity. We found a weighted average price having divided the total revenue from the sale of goods by the total number of units of the goods. This indicator takes into account the «weight» of each price and its share in the total mass of values.
The standard deviation: the formula in Excel
There is a standard deviation in the entire population and in the sampling. In the first case, this is the square root of the general variance. In the second, this is a square root of the sampling variance.
A dispersion formula is compiled to calculate this statistical indicator. The square root is extracted from it. But in Excel, there is a ready-made function for finding the root-mean-square deviation.
The root-mean-square deviation is related to the scope of the initial data. This is not enough for a figurative representation of the variation of the analyzed range. The coefficient of variation is calculated to obtain the relative level of the data variability.
standard deviation / arithmetic mean
The formula in Excel is as follows:
STDEV.P (range of values) / AVERAGE (range of values).
The coefficient of variation is considered as a percentage. Therefore, set the percentage format in the cell set.
Источник
How to Find Mean in Excel
How to Find Mean in Excel (Table of Content)
Introduction to Mean in Excel
The average function is used to calculate the Arithmetic Mean of the given input. It is used to do sum of all arguments and divide it by the count of arguments where the half set of the number will be smaller than the mean, and the remaining set will be greater than the mean. It will return the arithmetic mean of the number based on provided input. It is an in-built Statistical function. A user can give 255 input arguments in the function.
Excel functions, formula, charts, formatting creating excel dashboard & others
As an example, suppose there is 4 number 5,10,15,20 if a user wants to calculate the mean of the numbers then it will return 12.5 as the result of =AVERAGE (5, 10, 15, 20).
The formula of Mean: It is used to return the mean of the provided number where a half set of the number will be smaller than the number, and the remaining set will be greater than the mean.
The argument of the Function:
- number1: It is a mandatory argument in which functions will take to calculate the mean.
- [number2]: It is an optional argument in the function.
Examples on How to Find Mean in Excel
Here are some examples of how to find mean in excel with the steps and the calculation
Example #1 – How to Calculate the Basic Mean in Excel
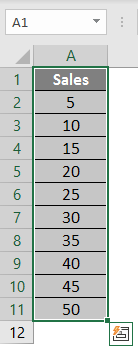
Let’s assume there is a user who wants to perform the calculation for all numbers in Excel. Let’s see how we can do this with the average function.
Step 1: Open MS Excel from the start menu >> Go to Sheet1, where the user has kept the data.
Step 2: Now create headers for Mean where we will calculate the mean of the numbers.
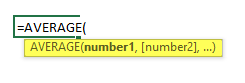
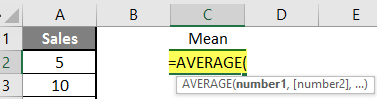
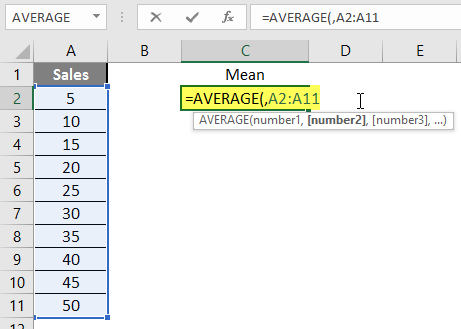
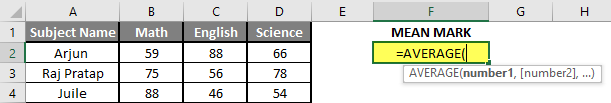
Step 3: Now calculate the mean of the given number by average function>> use the equal sign to calculate >> Write in cell C2 and use average>> “=AVERAGE (“
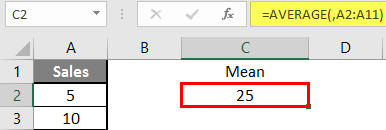
Step 3: Now, it will ask for a number1, which is given in column A >> there are 2 methods to provide input either a user can give one by one or just give the range of data >> select data set from A2 to A11 >> write in cell C2 and use average>> “=AVERAGE (A2: A11) “
Step 4: Now press the enter key >> Mean will be calculated.
Summary of Example 1: As the user wants to perform the mean calculation for all numbers in MS Excel. Easley everything calculated in the above excel example, and the Mean is 27.5 for sales.
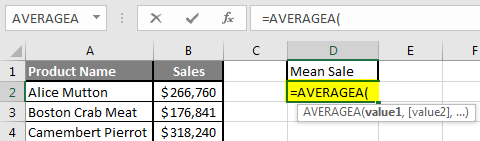
Example #2 – How to Calculate Mean if Text Value Exists in the Data Set
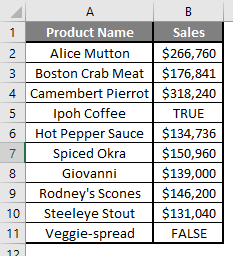
Let’s calculate the Mean if there is some text value in the Excel data set. Let’s assume a user wants to perform the calculation for some sales data set in Excel. But there is some text value also there. So, he wants to use count for all, either its text or number. Let’s see how we can do this with the AVERAGE function. Because in the normal AVERAGE function, it will exclude the text value count.
Step 1: Open MS Excel from the start menu >> Go to Sheet2, where the user has kept the data.
Step 2: Now create headers for Mean where we will calculate the mean of the numbers.
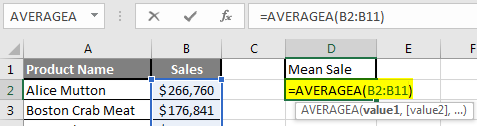
Step 3: Now calculate the mean of the given number by average function>> use the equal sign to calculate >> Write in cell D2 and use AVERAGEA>> “=AVERAGEA (“
Step 4: Now, it will ask for a number1, which is given in column B >> there is two open to provide input either a user can give one by one or just give the range of data >> select data set from B2 to B11 >> write in D2 Cell and use average>> “=AVERAGEA (D2: D11) “
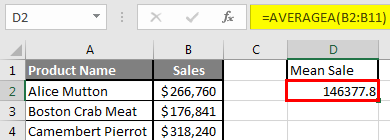
Step 5: Now click on the enter button >> Mean will be calculated.
Step 6: Just to compare the AVERAGEA and AVERAGE, in normal average, it will exclude the count for text value so mean will high than the AVERAGE MEAN.
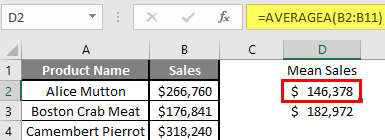
Summary of Example 2: As the user wants to perform the mean calculation for all number in MS Excel. Easley, everything calculated in the above excel example and the Mean is $146377.80 for sales.
Example #3 – How to Calculate Mean for Different Set of Data
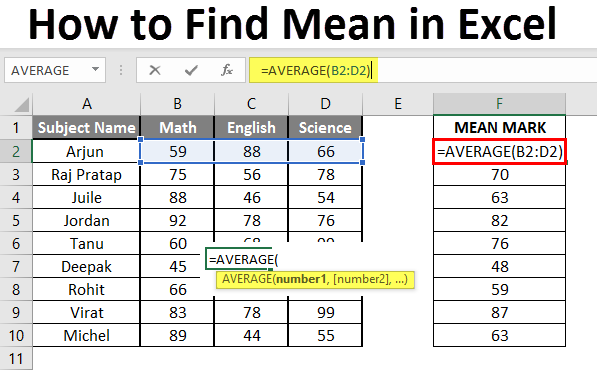
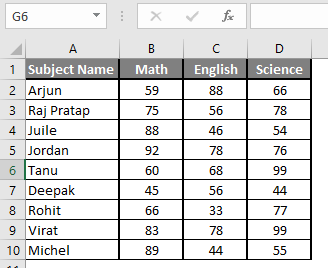
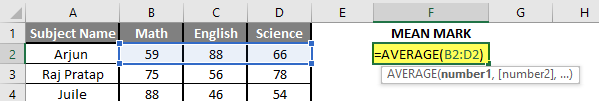
Let’s assume a user wants to perform the calculation for some student’s mark data set in MS Excel. There are ten student marks for Math, English, and Science out of 100. Let’s see How to Find Mean in Excel with the AVERAGE function.
Step 1: Open the MS Excel from the start menu >> Go to Sheet3, where the user kept the data.
Step 2: Now create headers for Mean where we will calculate the mean of the numbers.
Step 3: Now calculate the mean of the given number by average function>> use the equal sign to calculate >> Write in F2 Cell and use AVERAGE >> “=AVERAGE (“
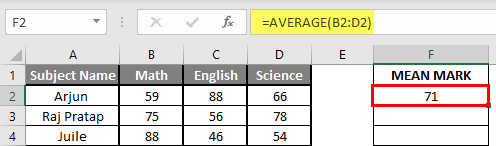
Step 3: Now, it will ask for number1 which is given in B, C, and D column >> there is two open to provide input either a user can give one by one or just give the range of data >> Select data set from B2 to D2 >> Write in F2 Cell and use average >> “=AVERAGE (B2: D2) “
Step 4: Now click on the enter button >> Mean will be calculated.
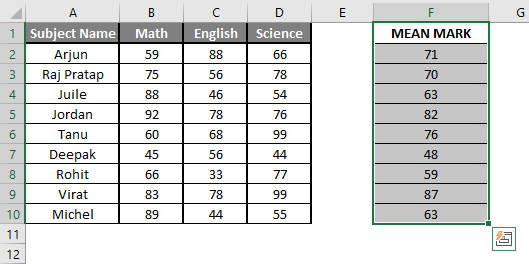
Step 5: Now click on the F2 cell and drag and apply to another cell in the F column.
Summary of Example 3: As the user wants to perform the mean calculation for all number in MS Excel. Easley, everything calculated in the above excel example and the Mean is available in the F column.
Things to Remember About How to Find Mean in Excel
- Microsoft Excel’s AVERAGE function used to calculate the Arithmetic Mean of the given input. A user can give 255 input arguments in the function.
- Half the set of a number will be smaller than the mean, and the remaining set will be greater than the mean.
- If a user calculating the normal average, it will exclude the count for a text value, so AVERAGE Mean will bigger than the AVERAGE MEAN.
- Arguments can be number, name, range or cell references that should contain a number.
- If a user wants to calculate the mean with some condition, then use AVERAGEIF or AVERAGEIFS.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to How to Find Mean in Excel. Here we discuss How to Find Mean along with examples and a downloadable excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –
Источник
This tutorial will explain and elaborate on how to calculate Mean in Excel along with easy steps and examples. Indeed Microsoft excel is designed to analyze and organize numerical data quickly.
For this reason measure of central tendency is a big part thus basically used to represent and identify the central position within the data provided or, more technically, the middle or center in a statistical distribution. Sometimes, they are also classified as summary statistics.
The three main measures of central tendency are Mean, Median and Mode. They all are valid measures of a central location, but each gives a different indication of a typical value, and under different circumstances, some measures are more appropriate to use than others.
Particularly, we will be focused on how to get the MEAN of supplied data
Mean formula in Excel
The mean function is one of the three main measure of central tendency. It is basically known as average of cells was calculated by adding up all the collection of data sets and dividing it by the number of counts.
These mathematical terms including median and mode have different ways of examining the set of data or numbers. Consequently, Excel provides built-in function determining these terms except range, which requires formula to obtain the output.
Furthermore, MEAN is one of the crucial functions in terms of analyzing data. Therefore it is not a waste when you know how to use it. It is helpful considering instances of finalizing the students’ grades or even product sales.
One more thing that MEAN or average function can do is to ignore cells omitting numbers and empty cells. But if you want to include empty cells or values specified as zero, you can use AVERAGEA function which is more likely the same.
The good thing about finding MEAN is that the function you’re gonna use is still available on the following; excel for Microsoft 365, excel 2010, excel 2016, excel 2019, and excel 2021.
Syntax of Mean
=Average(value1,[value2]...)
Return Value
Average of the set of numerical values
Arguments
value1: required its the values needed to calculate MEAN.value2:Optional.Values to calculate.
There are bunches of ways to calculate the MEAN of your data in your spreadsheet, it will depend on what data you are trying to exercise. So here are the simple steps to find your mean.
- Create the data you will use in your workbook.
Open your Microsoft Excel, and analyze what data you need. You can have any data such as order sales, student grades, employee salaries, or whatever suits your perspective. Make use of the columns and rows as it is favorable when doing hands-on take advantage to create your design and creativity.
- Reorganize your Excel spreadsheet as needed
If you imported data in your workbook reorganize those data and format it according to the requirements. Actually, this step is not required to finish since you are at hand making your data; it is up to you how you would like to rearrange the data.
- Select an empty cell to enter the mean formula
Calculating MEAN in your excel spreadsheet could be done on the same worksheet you’re analyzing. Select an empty cell so you will not lose any data in the worksheet. You can prefer to be at the bottom of the column or at the right side depending on what is easy for you.
- Press Enter to the formula to find the mean
After you created a formula, just hit enter key to completely see the Mean of your data.
As we have probably known the arithmetic mean is also understood as average. Thus let’s see how to calculate the average, will give few example formulas and instances to clearly understand it.
Basically, to get the mean of a group of numbers: {2,4,6,7, 8,10,12}.
Add them up and then divide the sum by the total number of set: {2,4,6,7, 8,10,12}/7=6
Take a look at this another sample:
Supposedly you are going to get the mean of Smith’s subjects’ scores.

- To get the Mean use this formula: =AVERAGE(B2:E2)

To get the average of only “Kivell” grades, use an AVERAGEIF formula:
=AVERAGEIF(A2:A10,"Kivell",C3:E3)

To calculate the mean of all the student’s averages

You can also enter your conditions in separate cells, and reference those cells in your formulas, like this:
=AVERAGEIF(A2:A44,A31,F2:F44)

Reminders for Specifying MEAN calculation criteria
There are more often that you need to meet certain criteria in order to obtain the mean of data. Here are circumstances you will use more specific mean formulas to acquire specified information needed in the calculation.
- AVERAGEA: If you need to include text or zero value in your calculations.
- AVERAGEIF: Utilize this formula if you want to get the mean which needs to meet a single criterion of certain information. For instance, you need to find the cells that do not meet a quota or the passing average.
- AVERAGE IF: Finding MEAN which meets multiple criteria. This scenario implies two or more requirements need to find the MEAN of a sample data, thus use this formula to find the mean of a certain range.
What does ref mean on excel?
The #REF error you encountered when applying your formula is because the formula refers to a cell that is not valid. It always occurs when your cells used as references are pasted or deleted.
Summary
Recap on this tutorial How To Calculate Mean on Excel there are several ways to calculate MEAN from single criteria to two or more, including text values. Finding MEAN is similar to average and it uses the same function. Besides, it is beneficial in analyzing data in business, study, and daily activities.
There we have already done what MEAN is. For further clarification and suggestions feel free to leave your comment!
Thank you for reading!
How to Find Mean in Excel (Table of Content)
- Introduction to Mean in Excel
- Example of Mean in Excel
Introduction to Mean in Excel
The average function is used to calculate the Arithmetic Mean of the given input. It is used to do sum of all arguments and divide it by the count of arguments where the half set of the number will be smaller than the mean, and the remaining set will be greater than the mean. It will return the arithmetic mean of the number based on provided input. It is an in-built Statistical function. A user can give 255 input arguments in the function.
As an example, suppose there is 4 number 5,10,15,20 if a user wants to calculate the mean of the numbers then it will return 12.5 as the result of =AVERAGE (5, 10, 15, 20).
The formula of Mean: It is used to return the mean of the provided number where a half set of the number will be smaller than the number, and the remaining set will be greater than the mean.
The argument of the Function:
- number1: It is a mandatory argument in which functions will take to calculate the mean.
- [number2]: It is an optional argument in the function.
Examples on How to Find Mean in Excel
Here are some examples of how to find mean in excel with the steps and the calculation
You can download this How to Find Mean Excel Template here – How to Find Mean Excel Template
Example #1 – How to Calculate the Basic Mean in Excel
Let’s assume there is a user who wants to perform the calculation for all numbers in Excel. Let’s see how we can do this with the average function.
Step 1: Open MS Excel from the start menu >> Go to Sheet1, where the user has kept the data.
Step 2: Now create headers for Mean where we will calculate the mean of the numbers.
Step 3: Now calculate the mean of the given number by average function>> use the equal sign to calculate >> Write in cell C2 and use average>> “=AVERAGE (“
Step 3: Now, it will ask for a number1, which is given in column A >> there are 2 methods to provide input either a user can give one by one or just give the range of data >> select data set from A2 to A11 >> write in cell C2 and use average>> “=AVERAGE (A2: A11) “
Step 4: Now press the enter key >> Mean will be calculated.
Summary of Example 1: As the user wants to perform the mean calculation for all numbers in MS Excel. Easley everything calculated in the above excel example, and the Mean is 27.5 for sales.
Example #2 – How to Calculate Mean if Text Value Exists in the Data Set
Let’s calculate the Mean if there is some text value in the Excel data set. Let’s assume a user wants to perform the calculation for some sales data set in Excel. But there is some text value also there. So, he wants to use count for all, either its text or number. Let’s see how we can do this with the AVERAGE function. Because in the normal AVERAGE function, it will exclude the text value count.
Step 1: Open MS Excel from the start menu >> Go to Sheet2, where the user has kept the data.
Step 2: Now create headers for Mean where we will calculate the mean of the numbers.
Step 3: Now calculate the mean of the given number by average function>> use the equal sign to calculate >> Write in cell D2 and use AVERAGEA>> “=AVERAGEA (“
Step 4: Now, it will ask for a number1, which is given in column B >> there is two open to provide input either a user can give one by one or just give the range of data >> select data set from B2 to B11 >> write in D2 Cell and use average>> “=AVERAGEA (D2: D11) “
Step 5: Now click on the enter button >> Mean will be calculated.
Step 6: Just to compare the AVERAGEA and AVERAGE, in normal average, it will exclude the count for text value so mean will high than the AVERAGE MEAN.
Summary of Example 2: As the user wants to perform the mean calculation for all number in MS Excel. Easley, everything calculated in the above excel example and the Mean is $146377.80 for sales.
Example #3 – How to Calculate Mean for Different Set of Data
Let’s assume a user wants to perform the calculation for some student’s mark data set in MS Excel. There are ten student marks for Math, English, and Science out of 100. Let’s see How to Find Mean in Excel with the AVERAGE function.
Step 1: Open the MS Excel from the start menu >> Go to Sheet3, where the user kept the data.
Step 2: Now create headers for Mean where we will calculate the mean of the numbers.
Step 3: Now calculate the mean of the given number by average function>> use the equal sign to calculate >> Write in F2 Cell and use AVERAGE >> “=AVERAGE (“
Step 3: Now, it will ask for number1 which is given in B, C, and D column >> there is two open to provide input either a user can give one by one or just give the range of data >> Select data set from B2 to D2 >> Write in F2 Cell and use average >> “=AVERAGE (B2: D2) “
Step 4: Now click on the enter button >> Mean will be calculated.
Step 5: Now click on the F2 cell and drag and apply to another cell in the F column.
Summary of Example 3: As the user wants to perform the mean calculation for all number in MS Excel. Easley, everything calculated in the above excel example and the Mean is available in the F column.
Things to Remember About How to Find Mean in Excel
- Microsoft Excel’s AVERAGE function used to calculate the Arithmetic Mean of the given input. A user can give 255 input arguments in the function.
- Half the set of a number will be smaller than the mean, and the remaining set will be greater than the mean.
- If a user calculating the normal average, it will exclude the count for a text value, so AVERAGE Mean will bigger than the AVERAGE MEAN.
- Arguments can be number, name, range or cell references that should contain a number.
- If a user wants to calculate the mean with some condition, then use AVERAGEIF or AVERAGEIFS.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to How to Find Mean in Excel. Here we discuss How to Find Mean along with examples and a downloadable excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –
- FIND Function in Excel
- Excel Find
- Excel Average Formula
- Excel AVERAGE Function
To find the mean in Excel, you start by typing the syntax =AVERAGE or select AVERAGE from the formula dropdown menu. Then, you select which cells will be included in the calculation. For example: Say you will be calculating the mean for column A, rows two through 20. Your formula will look like this: =AVERAGE(A2:A20).
Contents
- 1 What is mean function in Excel?
- 2 How do you find the mean?
- 3 How do you find the mean median and mode?
- 4 How does mean work?
- 5 How do you solve a mean problem?
- 6 How do you find the mean of the following data?
- 7 What is a mean in a data set?
- 8 How do you calculate mean with examples?
- 9 Is mean the same as average?
- 10 When to use median vs mean?
- 11 How do you find the mean of two means?
- 12 How do you find the mean of grouped data?
- 13 How do I find the mean shortcut method?
- 14 How do you find the sample mean of a data set?
- 15 How do you find the mean of two sets of data?
- 16 How do you find mean in a table?
- 17 How do you calculate mean manually?
- 18 What are the three methods to find mean?
- 19 What does a mean score mean?
- 20 What is the difference between mean and means?
What is mean function in Excel?
The mean or the statistical mean is essentially means average value and can be calculated by adding data points in a setand then dividing the total, by the number of points. Excel’s AVERAGE function does exactly this: sum all the values and divides the total by the count of numbers.
The mean is the same as the average value of a data set and is found using a calculation. Add up all of the numbers and divide by the number of numbers in the data set.
How do you find the mean median and mode?
The arithmetic mean is found by adding the numbers and dividing the sum by the number of numbers in the list. This is what is most often meant by an average. The median is the middle value in a list ordered from smallest to largest. The mode is the most frequently occurring value on the list.
How does mean work?
The mean is the total of the numbers divided by how many numbers there are. To find the mean, add all the numbers together then divide by the number of numbers.
How do you solve a mean problem?
It is easy to calculate: add up all the numbers, then divide by how many numbers there are. In other words it is the sum divided by the count.
How do you find the mean of the following data?
To find the mean of a data set, add all the values together and divide by the number of values in the set. The result is your mean!
What is a mean in a data set?
average
The mean of a set of numbers, sometimes simply called the average , is the sum of the data divided by the total number of data. Example 1 :There are 8 numbers in the set. Add them all, and then divide by 8 .
How do you calculate mean with examples?
For example, take this list of numbers: 10, 10, 20, 40, 70. The mean (informally, the “average“) is found by adding all of the numbers together and dividing by the number of items in the set: 10 + 10 + 20 + 40 + 70 / 5 = 30.
Is mean the same as average?
Average, also called the arithmetic mean, is the sum of all the values divided by the number of values. Whereas, mean is the average in the given data. In statistics, the mean is equal to the total number of observations divided by the number of observations.
When to use median vs mean?
Mean is the most frequently used measure of central tendency and generally considered the best measure of it. However, there are some situations where either median or mode are preferred. Median is the preferred measure of central tendency when: There are a few extreme scores in the distribution of the data.
How do you find the mean of two means?
A combined mean is a mean of two or more separate groups, and is found by : Calculating the mean of each group, Combining the results.
To calculate the combined mean:
- Multiply column 2 and column 3 for each row,
- Add up the results from Step 1,
- Divide the sum from Step 2 by the sum of column 2.
How do you find the mean of grouped data?
To calculate the mean of grouped data, the first step is to determine the midpoint of each interval or class. These midpoints must then be multiplied by the frequencies of the corresponding classes. The sum of the products divided by the total number of values will be the value of the mean.
How do I find the mean shortcut method?
To calculate mean deviation about mean by shortcut method, *First take an appropriate ‘Assumed Mean’ A. *calculate the sum of the frequencies, ∑i=1nfi . *calculate ∑i=1nfidi where, di=xi−A .
How do you find the sample mean of a data set?
The following steps will show you how to calculate the sample mean of a data set: Add up the sample items. Divide sum by the number of samples. The result is the mean.
How do you find the mean of two sets of data?
How to Find the Mean: Overview. To find the arithmetic mean of a data set, all you need to do is add up all the numbers in the data set and then divide the sum by the total number of values.
How do you find mean in a table?
It is easy to calculate the Mean: Add up all the numbers, then divide by how many numbers there are.
How do you calculate mean manually?
The mean, or average, is calculated by adding up the scores and dividing the total by the number of scores.
The mean is calculated in the following manner:
- 3 + 4 + 6 + 6 + 8 + 9 + 11 = 47.
- 47 / 7 = 6.7.
- The mean (average) of the number set is 6.7.
What are the three methods to find mean?
There are three methods for finding the mean from a grouped frequency table.
- Method 1: Direct method.
- Method 2: Assumed Mean method.
- Method 3: Step Deviation method.
What does a mean score mean?
A mean scale score is the average performance of a group of students on an assessment. Specifically, a mean scale score is calculated by adding all individual student scores and dividing by the number of total scores. It can also be referred to as an average.
What is the difference between mean and means?
Mean is the base form and means is the fifth form of verb ‘mean’. In other way,we can also say that mean is plural and means is singular.
-
1
Open Microsoft Excel. Click or double-click the Excel app icon, which resembles a green «X» on a green-and-white background.
- If you already have an Excel document that contains your data, double-click the document to open it in Excel 2007, then skip ahead to finding the mean.
-
2
Select a cell for your first data point. Click once the cell in which you want to enter your first number.
- Be sure to select a cell in a column that you want to use for the rest of your points.
Advertisement
-
3
Enter a number. Type in one of your data points’ numbers.
-
4
Press ↵ Enter. Doing so will both enter the number into your selected cell and move your cursor down to the next cell in the column.
-
5
Enter each of the rest of your data points. Type in a data point, press Enter, and repeat until you’ve entered all of your data points in the same column. This will make it easier to calculate the mean and the standard deviation of the list.
Advertisement
-
1
Click an empty cell. Doing so places your cursor in the cell.
-
2
Enter the «mean» formula. Type =AVERAGE( ) into the cell.[1]
-
3
Place your cursor in between the parentheses. You can press the left arrow key once to do this, or you can click in between the two parentheses in the text box at the top of the document.
-
4
Add your data range. You can input a range of data cells by typing the name of the first cell in the list of data, typing a colon, and typing in the last cell name in the column. For example, if your list of numbers goes from cell A1 through cell A11, you would type in A1:A11 in between the parentheses.
- Your completed formula should look something like this: =AVERAGE(A1:A11)
- If you want to calculate the mean of a few numbers (not a whole range), you can type each number’s cell name between the parentheses and separate the names with commas. For example, to find the mean of A1, A3, and A10, you would type in =AVERAGE(A1,A3,A10).
-
5
Press ↵ Enter. Doing so will run your formula, causing the mean of your selected values to display in your currently selected cell.
Advertisement
-
1
Click an empty cell. Doing so places your cursor in the cell.
-
2
Enter the «standard deviation» formula. Type =STDEV( ) into the cell.[2]
-
3
Place your cursor in between the parentheses. You can press the left arrow key once to do this, or you can click in between the two parentheses in the text box at the top of the document.
-
4
Add your data range. You can input a range of data cells by typing the name of the first cell in the list of data, typing a colon, and typing in the last cell name in the column. For example, if your list of numbers goes from cell A1 through cell A11, you would type in A1:A11 in between the parentheses.
- Your completed formula should look something like this: =STDEV(A1:A11)
- If you want to calculate the standard deviation of a few numbers (not a whole range), you can type each number’s cell name between the parentheses and separate the names with commas. For example, to find the standard deviation of A1, A3, and A10, you would type in =STDEV(A1,A3,A10).
-
5
Press ↵ Enter. Doing so will run your formula, causing the standard deviation value for your selected values to display in your currently selected cell.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
If the data set has 0 in it, should we include that when calculating mean? What about if the data set has blank cells; will these be considered zeroes when calculating mean?
If there is a 0 among your data set, it should be included when calculating the mean. Blank cells are not considered as zeroes in Excel, even if they are not excluded from the data range.
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
-
Changing a value in one of your data range’s cells will cause any connected formulas to refresh with an updated solution.
-
You can actually use the above instructions in any more-recent version of Excel (e.g., Excel 2016) as well.
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
-
Double-check your list of data points before attempting to calculate mean or standard deviation.
Advertisement
About This Article
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 895,394 times.