Family (from Latin: familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideally, families offer predictability, structure, and safety as members mature and learn to participate in the community.[1] Historically, most human societies use family as the primary locus of attachment, nurturance, and socialization.[2][3]
Anthropologists classify most family organizations as matrifocal (a mother and her children), patrifocal (a father and his children), conjugal (a wife, her husband, and children, also called the nuclear family), avuncular (a man, his sister, and her children), or extended (in addition to parents and children, may include grandparents, aunts, uncles, or cousins).
The field of genealogy aims to trace family lineages through history. The family is also an important economic unit studied in family economics. The word «families» can be used metaphorically to create more inclusive categories such as community, nationhood, and global village.
[edit]
One of the primary functions of the family involves providing a framework for the production and reproduction of persons biologically and socially. This can occur through the sharing of material substances (such as food); the giving and receiving of care and nurture (nurture kinship); jural rights and obligations; and moral and sentimental ties.[5][6] Thus, one’s experience of one’s family shifts over time. From the perspective of children, the family is a «family of orientation»: the family serves to locate children socially and plays a major role in their enculturation and socialization.[7] From the point of view of the parent(s), the family is a «family of procreation», the goal of which is to produce, enculturate and socialize children.[8] However, producing children is not the only function of the family; in societies with a sexual division of labor, marriage, and the resulting relationship between two people, it is necessary for the formation of an economically productive household.[9][10][11]
C. C. Harris notes that the western conception of family is ambiguous and confused with the household, as revealed in the different contexts in which the word is used.[12] Olivia Harris states this confusion is not accidental, but indicative of the familial ideology of capitalist, western countries that pass social legislation that insists members of a nuclear family should live together, and that those not so related should not live together; despite the ideological and legal pressures, a large percentage of families do not conform to the ideal nuclear family type.[13]
Size[edit]
Mennonite siblings, Montana, United States, 1937
The total fertility rate of women varies from country to country, from a high of 6.76 children born/woman in Niger to a low of 0.81 in Singapore (as of 2015).[14] Fertility is low in most Eastern European and Southern European countries, and high in most sub-Saharan African countries.[14]
In some cultures, the mother’s preference of family size influences that of the children through early adulthood.[15] A parent’s number of children strongly correlates with the number of children that their children will eventually have.[16]
Types[edit]
A German mother with her children in the 1960s
Although early western cultural anthropologists and sociologists considered family and kinship to be universally associated with relations by «blood» (based on ideas common in their own cultures) later research[5] has shown that many societies instead understand family through ideas of living together, the sharing of food (e.g. milk kinship) and sharing care and nurture. Sociologists have a special interest in the function and status of family forms in stratified (especially capitalist) societies.[17]
According to the work of scholars Max Weber, Alan Macfarlane, Steven Ozment, Jack Goody and Peter Laslett, the huge transformation that led to modern marriage in Western democracies was «fueled by the religio-cultural value system provided by elements of Judaism, early Christianity, Roman Catholic canon law and the Protestant Reformation».[18]
Much sociological, historical and anthropological research dedicates itself to the understanding of this variation, and of changes in the family that form over time. Levitan claims:
Times have changed; it is more acceptable and encouraged for mothers to work and fathers to spend more time at home with the children. The way roles are balanced between the parents will help children grow and learn valuable life lessons. There is [the] great importance of communication and equality in families, in order to avoid role strain.[19]
Multigenerational family[edit]
Historically, the most common family type was one in which grandparents, parents, and children lived together as a single unit. For example, the household might include the owners of a farm, one (or more) of their adult children, the adult child’s spouse, and the adult child’s own children (the owners’ grandchildren). Members of the extended family are not included in this family group. Sometimes, «skipped» generation families, such as a grandparents living with their grandchildren, are included.[20]
In the US, this arrangement declined after World War II, reaching a low point in 1980, when about one out of every eight people in the US lived in a multigenerational family.[20] The numbers have risen since then, with one in five people in the US living in a multigenerational family as of 2016.[21] The increasing popularity is partly driven by demographic changes and the economic shifts associated with the Boomerang Generation.[20]
Multigenerational households are less common in Canada, where about 6% of people living in Canada were living in multigenerational families as of 2016, but the proportion of multigenerational households was increasing rapidly, driven by increasing numbers of Aboriginal families, immigrant families, and high housing costs in some regions.[22]
Conjugal (nuclear) family[edit]
The term «nuclear family» is commonly used to refer to conjugal families. A «conjugal» family includes only the spouses and unmarried children who are not of age.[23][failed verification] Some sociologists[which?] distinguish between conjugal families (relatively independent of the kindred of the parents and of other families in general) and nuclear families (which maintain relatively close ties with their kindred).[24][25]
A father with his children in the United States in the 1940s
Other family structures – with (for example) blended parents, single parents, and domestic partnerships – have begun to challenge the normality of the nuclear family.[26][27][28]
Single-parent family[edit]
A single-parent family consists of one parent together with their children, where the parent is either widowed, divorced (and not remarried), or never married.[29] The parent may have sole custody of the children, or separated parents may have a shared-parenting arrangement where the children divide their time (possibly equally) between two different single-parent families or between one single-parent family and one blended family. As compared to sole custody, physical, mental and social well-being of children may be improved by shared-parenting arrangements and by children having greater access to both parents.[30][31] The number of single-parent families have been[when?] increasing, and about half of all children in the United States will live in a single-parent family at some point before they reach the age of 18. Most single-parent families are headed by a mother, but the number of single-parent families headed by fathers is increasing.[32][33]
Matrifocal family[edit]
A «matrifocal» family consists of a mother and her children.[34] Generally, these children are her biological offspring, although adoption of children occurs in nearly every society. This kind of family occurs commonly where women have the resources to rear their children by themselves, or where men are more mobile than women. As a definition, «a family or domestic group is matrifocal when it is centred on a woman and her children. In this case, the father(s) of these children are intermittently present in the life of the group and occupy a secondary place. The children’s mother is not necessarily the wife of one of the children’s fathers.»[35] The name, matrifocal, was coined in Guiana but it is defined differently in other countries. For Nayar families, the family have the male as the «center» or the head of the family, either the step-father/father/brother, rather than the mother.[34]
Extended family[edit]
Extended family with roots in Cape Town, Kimberley and Pretoria, South Africa
The term «extended family» is also common, especially in the United States. This term has two distinct meanings:
- It serves as a synonym of «consanguinal family» (consanguine means «of the same blood»).
- In societies dominated by the conjugal family, it refers to «kindred» (an egocentric network of relatives that extends beyond the domestic group) who do not belong to the conjugal family.
These types refer to ideal or normative structures found in particular societies. Any society will exhibit some variation in the actual composition and conception of families.[36]
Historically, extended families were the basic family unit in the Catholic culture and countries (such as Southern Europe and Latin America),[37] and in Asian, Middle Eastern and Eastern Orthodox countries.[37]
Family of choice[edit]
The term family of choice, also sometimes referred to as «chosen family» or «found family», is common within the LGBT community, veterans, individuals who have suffered abuse, and those who have no contact with biological «parents». It refers to the group of people in an individual’s life that satisfies the typical role of family as a support system. The term differentiates between the «family of origin» (the biological family or that in which people are raised) and those that actively assume that ideal role.[38]
The family of choice may or may not include some or all of the members of the family of origin. This family is not one that follows the «normal» familial structure like having a father, a mother, and children. This is family is a group of people that rely on each other like a family of origin would.[39] This terminology stems from the fact that many LGBT individuals, upon coming out, face rejection or shame from the families they were raised in.[40] The term family of choice is also used by individuals in the 12 step communities, who create close-knit «family» ties through the recovery process.
As a family system, families of choice face unique issues. Without legal safeguards, families of choice may struggle when medical, educational or governmental institutions fail to recognize their legitimacy.[40] If members of the chosen family have been disowned by their family of origin, they may experience surrogate grief, displacing anger, loss, or anxious attachment onto their new family.[40]
Blended family[edit]
The term blended family or stepfamily describes families with mixed parents: one or both parents remarried, bringing children of the former family into the new family.[41] Also in sociology, particularly in the works of social psychologist Michael Lamb,[42] traditional family refers to «a middle-class family with a bread-winning father and a stay-at-home mother, married to each other and raising their biological children,» and nontraditional to exceptions to this rule. Most of the US households are now non-traditional under this definition.[43] Critics of the term «traditional family» point out that in most cultures and at most times, the extended family model has been most common, not the nuclear family,[44] though it has had a longer tradition in England[45] than in other parts of Europe and Asia which contributed large numbers of immigrants to the Americas. The nuclear family became the most common form in the U.S. in the 1960s and 1970s.[46]
In terms of communication patterns in families, there are a certain set of beliefs within the family that reflect how its members should communicate and interact. These family communication patterns arise from two underlying sets of beliefs. One being conversation orientation (the degree to which the importance of communication is valued) and two, conformity orientation (the degree to which families should emphasize similarities or differences regarding attitudes, beliefs, and values).[47]
Blended families is complex, ranging from stepfamilies to cohabitating families (an individual living with guardians who are not married with step or half siblings). While it’s not too different from stepfamilies, cohabiting families pose a prevalent psychological effect on youths.[48] Some adolescents would be prone to «acts of delinquency,» and experiencing problems in school ranging from a decrease in academic performance to increased problematic behavior. It coincides with other researches on the trajectories of stepfamilies where some experienced familyhood, but others lacking connection. Emotional detachment from members within stepfamilies contributes to this uncertainty, furthering the tension that these families may establish.[49] The transition from an old family to a new family that falls under blended families would also become problematic as the activities that were once performed in the old family may not transfer well within the new family for adolescents.[50]
Monogamous family[edit]
A monogamous family is based on a legal or social monogamy. In this case, an individual has only one (official) partner during their lifetime or at any one time (i.e. serial monogamy).[51] This means that a person may not have several different legal spouses at the same time, as this is usually prohibited by bigamy laws, (the act of entering into a marriage with one person while still legally married to another[52]) in jurisdictions that require monogamous marriages.
Polygamous family[edit]
Chinese immigrant with his three wives and fourteen children, Cairns, Australia, 1904
Polygamy is a marriage that includes more than two partners.[53][54] When a man is married to more than one wife at a time, the relationship is called polygyny; and when a woman is married to more than one husband at a time, it is called polyandry. If a marriage includes multiple husbands and wives, it can be called polyamory,[55] group or conjoint marriage.[54]
Polygyny is a form of plural marriage, in which a man is allowed more than one wife .[56] In modern countries that permit polygamy, polygyny is typically the only form permitted. Polygyny is practiced primarily (but not only) in parts of the Middle East and Africa; and is often associated with Islam, however, there are certain conditions in Islam that must be met to perform polygyny.[57]
Polyandry is a form of marriage whereby a woman takes two or more husbands at the same time.[58] Fraternal polyandry, where two or more brothers are married to the same wife, is a common form of polyandry. Polyandry was traditionally practiced in areas of the Himalayan mountains, among Tibetans in Nepal, in parts of China and in parts of northern India. Polyandry is most common in societies marked by high male mortality or where males will often be apart from the rest of the family for a considerable period of time.[58]
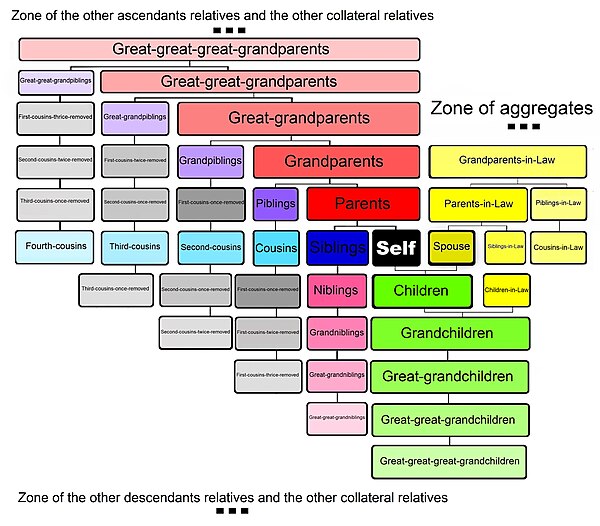
Kinship terminology[edit]
Degrees of kinship[edit]
Family in a wagon, Lee County, Mississippi, United States, August 1935.
A first-degree relative is one who shares 50% of your DNA through direct inheritance, such as a full sibling, parent or progeny.
There is another measure for the degree of relationship, which is determined by counting up generations to the first common ancestor and back down to the target individual, which is used for various genealogical and legal purposes.[59]
| Kinship | Degree of relationship by coefficient |
Coefficient of relationship |
Degree of relationship by counting generations to common ancestor |
|---|---|---|---|
| identical twins | 0 | 100%[60] | second-degree |
| sister / brother | first-degree | 50% (2×2−2) | second-degree |
| mother / father / daughter / son[61] | first-degree | 50% (2−1) | first-degree |
| half-sister / half-brother | second-degree | 25% (2−2) | second-degree |
| grandmother / grandfather / granddaughter / grandson | second-degree | 25% (2−2) | second-degree |
| aunt / uncle / niece / nephew | second-degree | 25% (2×2−3) | third-degree |
| half-aunt / half-uncle / half-niece / half-nephew | third-degree | 12.5% (2−3) | third-degree |
| first-cousin | third-degree | 12.5% (2×2−4) | fourth-degree |
| half-first-cousin | fourth-degree | 6.25% (2−4) | fourth-degree |
| great-grandmother / great-grandfather / great-granddaughter / great-grandson | third-degree | 12.5% (2−3) | third-degree |
| first-cousin-once-removed | fourth-degree | 6.25% (2⋅2−5) | fifth-degree |
| second-cousin | fifth-degree | 3.125% (2−6+2−6) | sixth-degree |
Terminologies[edit]
Family tree with some family members.
Family tree with other family members.
Swedish family eating, 1902
In his book Systems of Consanguinity and Affinity of the Human Family, anthropologist Lewis Henry Morgan (1818–1881) performed the first survey of kinship terminologies in use around the world. Although much of his work is now considered dated, he argued that kinship terminologies reflect different sets of distinctions. For example, most kinship terminologies distinguish between sexes (the difference between a brother and a sister) and between generations (the difference between a child and a parent). Moreover, he argued, kinship terminologies distinguish between relatives by blood and marriage (although recently some anthropologists have argued that many societies define kinship in terms other than «blood»).
Morgan made a distinction between kinship systems that use classificatory terminology and those that use descriptive terminology. Classificatory systems are generally and erroneously understood to be those that «class together» with a single term relatives who actually do not have the same type of relationship to ego. (What defines «same type of relationship» under such definitions seems to be genealogical relationship. This is problematic given that any genealogical description, no matter how standardized, employs words originating in a folk understanding of kinship.) What Morgan’s terminology actually differentiates are those (classificatory) kinship systems that do not distinguish lineal and collateral relationships and those (descriptive) kinship systems that do. Morgan, a lawyer, came to make this distinction in an effort to understand Seneca inheritance practices. A Seneca man’s effects were inherited by his sisters’ children rather than by his own children.[62] Morgan identified six basic patterns of kinship terminologies:
- Hawaiian: only distinguishes relatives based upon sex and generation.
- Sudanese: no two relatives share the same term.
- Eskimo: in addition to distinguishing relatives based upon sex and generation, also distinguishes between lineal relatives and collateral relatives.
- Iroquois: in addition to sex and generation, also distinguishes between siblings of opposite sexes in the parental generation.
- Crow: a matrilineal system with some features of an Iroquois system, but with a «skewing» feature in which generation is «frozen» for some relatives.
- Omaha: like a Crow system but patrilineal.
Table of degrees of kinship.
Roles[edit]
Group photograph of a Norwegian family by Gustav Borgen ca. 1900: Father, mother, three sons and two daughters.
Father and child, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Most Western societies employ Eskimo kinship terminology.[63] This kinship terminology commonly occurs in societies with strong conjugal, where families have a degree of relative mobility. Typically, societies with conjugal families also favor neolocal residence; thus upon marriage, a person separates from the nuclear family of their childhood (family of orientation) and forms a new nuclear family (family of procreation). Such systems generally assume that the mother’s husband is also the biological father. The system uses highly descriptive terms for the nuclear family and progressively more classificatory as the relatives become more and more collateral.
Nuclear family[edit]
The system emphasizes the nuclear family. Members of the nuclear family use highly descriptive kinship terms, identifying directly only the husband, wife, mother, father, son, daughter, brother, and sister. All other relatives are grouped together into categories. Members of the nuclear family may be lineal or collateral. Kin, for whom these are family, refer to them in descriptive terms that build on the terms used within the nuclear family or use the nuclear family term directly.
Nuclear family of orientation
- Brother: the male child of a parent.
- Sister: the female child of a parent.
- Father: a male parent.
- Grandfather: the father of a parent.
- Mother: a female parent.
- Grandmother: the mother of a parent.
Nuclear conjugal family
- Husband: a male spouse.
- Wife: a female spouse.
- Son: a male child of the parent(s).
- Grandson: a child’s son.
- Daughter: a female child of the parent(s).
- Granddaughter: a child’s daughter.
Nuclear non-lineal family
- Spouse: husband or wife
- Stepparent: a spouse of a parent that is not a biological parent
- Sibling: sister or brother
- Half-sibling: a sibling with whom the subject shares only one biological parent
- Step-sibling: a child of a parent that is not a biological parent
Collateral relatives[edit]
A sibling is a collateral relative with a minimal removal. For collateral relatives with one additional removal, one generation more distant from a common ancestor on one side, more classificatory terms come into play. These terms (Aunt, Uncle, Niece, and Nephew) do not build on the terms used within the nuclear family as most are not traditionally members of the household. These terms do not traditionally differentiate between a collateral relatives and a person married to a collateral relative (both collateral and aggregate). Collateral relatives with additional removals on each side are Cousins. This is the most classificatory term and can be distinguished by degrees of collaterality and by generation (removal).
When only the subject has the additional removal, the relative is the subject’s parents’ siblings, the terms Aunt and Uncle are used for female and male relatives respectively. When only the relative has the additional removal, the relative is the subjects siblings child, the terms Niece and Nephew are used for female and male relatives respectively. The spouse of a biological aunt or uncle is an aunt or uncle, and the nieces and nephews of a spouse are nieces and nephews. With further removal by the subject for aunts and uncles and by the relative for nieces and nephews the prefix «grand-» modifies these terms. With further removal the prefix becomes «great-grand-,» adding another «great-» for each additional generation. For large numbers of generations a number can be substituted, for example, «fourth great-grandson», «four-greats grandson» or «four-times-great-grandson».
When the subject and the relative have an additional removal they are cousins. A cousin with minimal removal is a first cousin, i.e. the child of the subjects uncle or aunt. Degrees of collaterality and removals are used to more precisely describe the relationship between cousins. The degree is the number of generations subsequent to the common ancestor before a parent of one of the cousins is found, while the removal is the difference between the number of generations from each cousin to the common ancestor (the difference between the generations the cousins are from).[64][65]
Cousins of an older generation (in other words, one’s parents’ first cousins), although technically first cousins once removed, are often classified with «aunts» and «uncles».
Aggregate relatives[edit]
English-speakers mark relationships by marriage (except for wife/husband) with the tag «-in-law». The mother and father of one’s spouse become one’s mother-in-law and father-in-law; the wife of one’s son becomes one’s daughter-in-law and the husband of one’s daughter becomes one’s son-in-law. The term «sister-in-law» refers to two essentially different relationships, either the wife of one’s brother, or the sister of one’s spouse. «Brother-in-law» is the husband of one’s sister, or the brother of one’s spouse. The terms «half-brother» and «half-sister» indicate siblings who share only one biological parent. The term «aunt-in-law» is the wife of one’s uncle, or the aunt of one’s spouse. «Uncle-in-law» is the husband of one’s aunt, or the uncle of one’s spouse. «Cousin-in-law» is the spouse of one’s cousin, or the cousin of one’s spouse. The term «niece-in-law» is the wife of one’s nephew, or the niece of one’s spouse. «Nephew-in-law» is the husband of one’s niece, or the nephew of one’s spouse. The grandmother and grandfather of one’s spouse become one’s grandmother-in-law and grandfather-in-law; the wife of one’s grandson becomes one’s granddaughter-in-law and the husband of one’s granddaughter becomes one’s grandson-in-law.
In Indian English a sibling in law who is the spouse of your sibling can be referred to as a co-sibling (specificity a co-sister[66] or co-brother[67]).
Types of kinship[edit]
Patrilineal[edit]
Patrilineality, also known as the male line or agnatic kinship, is a form of kinship system in which an individual’s family membership derives from and is traced through his or her father’s lineage.[68] It generally involves the inheritance of property, rights, names, or titles by persons related through male kin.
A patriline («father line») is a person’s father, and additional ancestors that are traced only through males. One’s patriline is thus a record of descent from a man in which the individuals in all intervening generations are male. In cultural anthropology, a patrilineage is a consanguineal male and female kinship group, each of whose members is descended from the common ancestor through male forebears.
Matrilineal[edit]
Matrilineality is a form of kinship system in which an individual’s family membership derives from and is traced through his or her mother’s lineage.
It may also correlate with a societal system in which each person is identified with their matriline—their mother’s lineage—and which can involve the inheritance of property and titles. A matriline is a line of descent from a female ancestor to a descendant in which the individuals in all intervening generations are mothers – in other words, a «mother line».
In a matrilineal descent system, an individual is considered to belong to the same descent group as her or his mother. This matrilineal descent pattern is in contrasts to the more common pattern of patrilineal descent pattern.
Bilateral descent[edit]
Bilateral descent is a form of kinship system in which an individual’s family membership derives from and is traced through both the paternal and maternal sides. The relatives on the mother’s side and father’s side are equally important for emotional ties or for transfer of property or wealth. It is a family arrangement where descent and inheritance are passed equally through both parents.[69] Families who use this system trace descent through both parents simultaneously and recognize multiple ancestors, but unlike with cognatic descent it is not used to form descent groups.[70]
Traditionally, this is found among some groups in West Africa, India, Australia, Indonesia, Melanesia, Malaysia and Polynesia. Anthropologists believe that a tribal structure based on bilateral descent helps members live in extreme environments because it allows individuals to rely on two sets of families dispersed over a wide area.[71]
History of theories[edit]
Early scholars of family history applied Darwin’s biological theory of evolution in their theory of evolution of family systems.[72] American anthropologist Lewis H. Morgan published Ancient Society in 1877 based on his theory of the three stages of human progress from Savagery through Barbarism to Civilization.[73] Morgan’s book was the «inspiration for Friedrich Engels’ book» The Origin of the Family, Private Property and the State published in 1884.[74]
Engels expanded Morgan’s hypothesis that economical factors caused the transformation of primitive community into a class-divided society.[75] Engels’ theory of resource control, and later that of Karl Marx, was used to explain the cause and effect of change in family structure and function. The popularity of this theory was largely unmatched until the 1980s, when other sociological theories, most notably structural functionalism, gained acceptance.
The nuclear family in industrial society[edit]
Family arrangements in the United States have become more diverse with no particular household arrangement representing half of the United States population.[76]
Contemporary society generally views the family as a haven from the world, supplying absolute fulfillment. Zinn and Eitzen discuss the image of the «family as haven … a place of intimacy, love and trust where individuals may escape the competition of dehumanizing forces in modern society».[77]
During industrialization, «[t]he family as a repository of warmth and tenderness (embodied by the mother) stands in opposition to the competitive and aggressive world of commerce (embodied by the father). The family’s task was to protect against the outside world.»[78] However, Zinn and Eitzen note, «The protective image of the family has waned in recent years as the ideals of family fulfillment have taken shape. Today, the family is more compensatory than protective. It supplies what is vitally needed but missing in other social arrangements.»[78]
«The popular wisdom», according to Zinn and Eitzen, sees the family structures of the past as superior to those today, and families as more stable and happier at a time when they did not have to contend with problems such as illegitimate children and divorce. They respond to this, saying, «there is no golden age of the family gleaming at us in the far back historical past.»[79] «Desertion by spouses, illegitimate children, and other conditions that are considered characteristics of modern times existed in the past as well.»[79]
The postmodern family[edit]
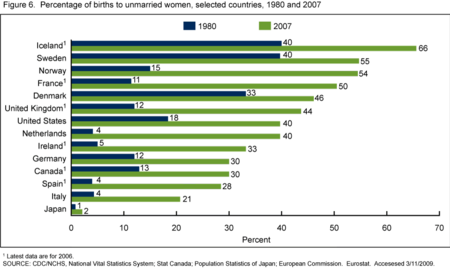
Percentage of births to unmarried women, selected countries, 1980 and 2007[80]
Others argue that whether or not one views the family as «declining» depends on one’s definition of «family». «Married couples have dropped below half of all American households. This drop is shocking from traditional forms of the family system. Only a fifth of households were following traditional ways of having married couples raising a family together.»[81] In the Western World, marriages are no longer arranged for economic, social or political gain, and children are no longer expected to contribute to family income. Instead, people choose mates based on love.[82] This increased role of love indicates a societal shift toward favoring emotional fulfilment and relationships within a family, and this shift necessarily weakens the institution of the family.[83]
Margaret Mead considers the family as a main safeguard to continuing human progress. Observing, «Human beings have learned, laboriously, to be human», she adds: «we hold our present form of humanity on trust, [and] it is possible to lose it» … «It is not without significance that the most successful large-scale abrogations of the family have occurred not among simple savages, living close to the subsistence edge, but among great nations and strong empires, the resources of which were ample, the populations huge, and the power almost unlimited»[84]
Many countries (particularly Western) have, in recent years, changed their family laws in order to accommodate diverse family models. For instance, in the United Kingdom, in Scotland, the Family Law (Scotland) Act 2006 provides cohabitants with some limited rights.[85] In 2010, Ireland enacted the Civil Partnership and Certain Rights and Obligations of Cohabitants Act 2010. There have also been moves at an international level, most notably, the Council of Europe European Convention on the Legal Status of Children Born out of Wedlock[86] which came into force in 1978. Countries which ratify it must ensure that children born outside marriage are provided with legal rights as stipulated in the text of this convention. The convention was ratified by the UK in 1981 and by Ireland in 1988.[87]
In the United States, one in five mothers has children by different fathers; among mothers with two or more children the figure is higher, with 28% having children with at least two different men. Such families are more common among Blacks and Hispanics and among the lower socioeconomic class.[88]
However, in western society, the single parent family has been growing more accepted and has begun to make an impact on culture. Single parent families are more commonly single mother families than single father.[89] These families sometimes face difficult issues besides the fact that they have to rear their children on their own, for example, low income making it difficult to pay for rent, child care, and other necessities for a healthy and safe home.
Furthermore, there are families that consist of two mothers, two fathers, non-binary, trans, and queer folks raising children. This is made possible due to surrogacy, IVF, IUI, adoption, and other processes.
Domestic violence[edit]
Domestic violence (DV) is violence that happens within the family. The legal and social understanding of the concept of DV differs by culture. The definition of the term «domestic violence» varies, depending on the context in which it is used.[90] It may be defined differently in medical, legal, political or social contexts. The definitions have varied over time, and vary in different parts of the world.
The Convention on preventing and combating violence against women and domestic violence states that:[91]
«domestic violence» shall mean all acts of physical, sexual, psychological or economic violence that occur within the family or domestic unit or between former or current spouses or partners, whether or not the perpetrator shares or has shared the same residence with the victim.
In 1993, the United Nations Declaration on the Elimination of Violence against Women identified domestic violence as one of three contexts in which violence against women occurs, describing it as:[92]
Physical, sexual and psychological violence occurring in the family, including battering, sexual abuse of female children in the household, dowry-related violence, marital rape, female genital mutilation and other traditional practices harmful to women, non-spousal violence and violence related to exploitation.
Family violence[edit]
Family violence is a broader definition, often used to include child abuse, elder abuse, and other violent acts between family members.[93]
Child abuse is defined by the WHO as:[94]
Child maltreatment, sometimes referred to as child abuse and neglect, includes all forms of physical and emotional ill-treatment, sexual abuse, neglect, and exploitation that results in actual or potential harm to the child’s health, development or dignity. Within this broad definition, five subtypes can be distinguished – physical abuse; sexual abuse; neglect and negligent treatment; emotional abuse; and exploitation.
There exists legislation to prevent and punish the occurrence of these offences. There are laws regarding familial sexual activity, which states that it is a criminal offence to have any kind of sexual relationship between one’s grandparent, parent, sibling, aunt or uncle.[95][96]
Elder abuse is, according to the WHO: «a single, or repeated act, or lack of appropriate action, occurring within any relationship where there is an expectation of trust which causes harm or distress to an older person».[97]
Parental abuse of children (child abuse)[edit]
Child abuse is the physical, sexual or emotional maltreatment or neglect of a child or children.[98] In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Department for Children and Families (DCF) define child maltreatment as any act or series of acts of commission or omission by a parent or other caregiver that results in harm, potential for harm, or threat of harm to a child.[99] Child abuse can occur in a child’s home, or in the organizations, schools or communities the child interacts with. There are four major categories of child abuse: neglect, physical abuse, psychological or emotional abuse, and sexual abuse.
Parental abuse by children[edit]
Abuse of parents by their children is a common but under reported and under-researched subject. A factor why this subject is under-researched is because of the overshadowing effect caused by parents abusing their children instead. Parents are quite often subject to levels of childhood aggression in excess of normal childhood aggressive outbursts, typically in the form of verbal or physical abuse. Parents feel a sense of shame and humiliation to have that problem, so they rarely seek help and it is usually little or no help available anyway.[100][101]
Elder abuse[edit]
Elder abuse is «a single, or repeated act, or lack of appropriate action, occurring within any relationship where there is an expectation of trust, which causes harm or distress to an older person».[102] This definition has been adopted by the World Health Organization from a definition put forward by Action on Elder Abuse in the UK. Laws protecting the elderly from abuse are similar to, and related to, laws protecting dependent adults from abuse.
The core element to the harm of elder abuse is the «expectation of trust» of the older person toward their abuser. Thus, it includes harms by people the older person knows or with whom they have a relationship, such as a spouse, partner or family member, a friend or neighbor, or people that the older person relies on for services. Many forms of elder abuse are recognized as types of domestic violence or family violence.
Forced and child marriage[edit]
Forced and child marriages are practiced in certain regions of the world, particularly in Asia and Africa, and these types of marriages are associated with a high rate of domestic violence.[103][104][105][106]
A forced marriage is a marriage where one or both participants are married without their freely given consent.[107] The line between forced marriage and consensual marriage may become blurred, because the social norms of many cultures dictate that one should never oppose the desire of one’s parents/relatives in regard to the choice of a spouse; in such cultures it is not necessary for violence, threats, intimidation etc. to occur, the person simply «consents» to the marriage even if he/she doesn’t want it, out of the implied social pressure and duty. The customs of bride price and dowry, that exist in parts of the world, can lead to buying and selling people into marriage.[108][109]
A child marriage is a marriage where one or both spouses are under 18.[110][103] Child marriage was common throughout history but is today condemned by international human rights organizations.[111][112][113] Child marriages are often arranged between the families of the future bride and groom, sometimes as soon as the girl is born.[111] Child marriages can also occur in the context of marriage by abduction.[111]
The concept of family honour[edit]
Family honor is an abstract concept involving the perceived quality of worthiness and respectability that affects the social standing and the self-evaluation of a group of related people, both corporately and individually.[114][115] The family is viewed as the main source of honor and the community highly values the relationship between honor and the family.[116] The conduct of family members reflects upon family honor and the way the family perceives itself, and is perceived by others.[115] In cultures of honor maintaining the family honor is often perceived as more important than either individual freedom, or individual achievement.[117] In extreme cases, engaging in acts that are deemed to tarnish the honor of the family results in honor killings. An honor killing is the homicide of a member of a family or social group by other members, due to the perpetrators’ belief that the victim has brought shame or dishonor upon the family or community, usually for reasons such as refusing to enter an arranged marriage, being in a relationship that is disapproved by their relatives, having sex outside marriage, becoming the victim of rape, dressing in ways which are deemed inappropriate, or engaging in homosexual relations.[118][119][120][121][122]
Economic issues[edit]
A family is often part of a sharing economy with common ownership.
Dowry, bride price and dower[edit]
A traditional, formal presentation of the bride price at a Thai engagement ceremony.
Dowry is property (money, goods, or estate) that a wife or wife’s family gives to her husband when the wife and husband marry.[123] Offering dowry was common in many cultures historically (including in Europe and North America), but this practice today is mostly restricted to some areas primarily in the Indian subcontinent.
Bride price, (also bride wealth or bride token), is property paid by the groom or his family to the parents of a woman upon the marriage of their daughter to the groom. It is practiced mostly in Sub-Saharan Africa, parts of South-East Asia (Thailand, Cambodia), and parts of Central Asia.
Dower is property given to the bride herself by the groom at the time of marriage, and which remains under her ownership and control.[124]
Property regimes and taxation[edit]
In some countries married couples benefit from various taxation advantages not available to a single person or to unmarried couples. For example, spouses may be allowed to average their combined incomes. Some jurisdictions recognize common law marriage or de facto relations for this purposes. In some jurisdictions there is also an option of civil partnership or domestic partnership.
Different property regimes exist for spouses. In many countries, each marriage partner has the choice of keeping their property separate or combining properties. In the latter case, called community property, when the marriage ends by divorce each owns half. In lieu of a will or trust, property owned by the deceased generally is inherited by the surviving spouse.
Rights and laws[edit]
Reproductive rights[edit]
Reproductive rights are legal rights and freedoms relating to reproduction and reproductive health. These include the right to decide on issues regarding the number of children born, family planning, contraception, and private life, free from coercion and discrimination; as well as the right to access health services and adequate information.[125][126][127][128] According to UNFPA, reproductive rights «include the right to decide the number, timing and spacing of children, the right to voluntarily marry and establish a family, and the right to the highest attainable standard of health, among others».[129] Family planning refers to the factors that may be considered by individuals and couples in order for them to control their fertility, anticipate and attain the desired number of children and the spacing and timing of their births.[130][131]
The state and church have been, and still are in some countries, involved in controlling the size of families, often using coercive methods, such as bans on contraception or abortion (where the policy is a natalist one—for example through tax on childlessness) or conversely, discriminatory policies against large families (e.g., China’s one-child policy in place from 1978 to 2015) or even forced abortions. Forced sterilization has often targeted ethnic minority groups, such as Roma women in Eastern Europe,[132][133] or indigenous women in Peru (during the 1990s).[134]
Parents’ rights[edit]
The parents’ rights movement is a movement whose members are primarily interested in issues affecting parents and children related to family law, specifically parental rights and obligations. Mothers’ rights movements focus on maternal health, workplace issues such as labor rights, breastfeeding, and rights in family law. The fathers’ rights movement is a movement whose members are primarily interested in issues related to family law, including child custody and child support, that affect fathers and their children.[135]
Children’s rights[edit]
Children’s rights are the human rights of children, with particular attention to the rights of special protection and care afforded to minors, including their right to association with both parents, their right to human identity, their right to be provided in regard to their other basic needs, and their right to be free from violence and abuse.[136][137][138]
Marriage rights[edit]
Each jurisdiction has its own marriage laws. These laws differ significantly from country to country; and these laws are often controversial. Areas of controversy include women’s rights as well as same-sex marriage.
Legal reforms[edit]
Legal reforms to family laws have taken place in many countries during the past few decades. These dealt primarily with gender equality within marriage and with divorce laws. Women have been given equal rights in marriage in many countries, reversing older family laws based on the dominant legal role of the husband. Coverture, which was enshrined in the common law of England and the US for several centuries and throughout most of the 19th century, was abolished. In some European countries the changes that lead to gender equality were slower. The period of 1975–1979 saw a major overhaul of family laws in countries such as Italy,[139][140] Spain,[141] Austria,[142] West Germany,[143][144] and Portugal.[145] In 1978, the Council of Europe passed the Resolution (78) 37 on equality of spouses in civil law.[146] Among the last European countries to establish full gender equality in marriage were Switzerland. In 1985, a referendum guaranteed women legal equality with men within marriage.[147][148] The new reforms came into force in January 1988.[149] In Greece, in 1983, legislation was passed guaranteeing equality between spouses, abolishing dowry, and ending legal discrimination against illegitimate children.[150][151] In 1981, Spain abolished the requirement that married women must have their husbands’ permission to initiate judicial proceedings[152] the Netherlands,[153][154] and France[note 1] in the 1980s. In recent decades, the marital power has also been abolished in African countries that had this doctrine, but many African countries that were former French colonies still have discriminatory laws in their marriages regulations, such regulations originating in the Napoleonic Code that has inspired these laws.[152] In some countries (predominantly Roman Catholic) divorce was legalized only recently (e.g. Italy (1970), Portugal (1975), Brazil (1977), Spain (1981), Argentina (1987), Ireland (1996), Chile (2004) and Malta (2011)) although annulment and legal separation were options. The Philippines still does not allow divorce. (see Divorce law by country). The laws pertaining to the situation of children born outside marriage have also been revised in many countries (see Legitimacy (family law)).
Health[edit]
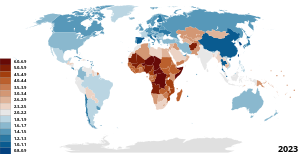
Global maternal mortality rate per 100 000 live births, (2010)[157]
Family medicine[edit]
Family medicine is a medical specialty devoted to comprehensive health care for people of all ages; it is based on knowledge of the patient in the context of the family and the community, emphasizing disease prevention and health promotion.[158] The importance of family medicine is being increasingly recognized.[159]
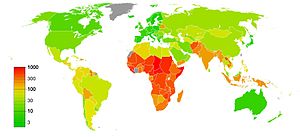
World infant mortality rates in 2012[160]
Maternal mortality[edit]
Maternal mortality or maternal death is defined by WHO as «the death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective of the duration and site of the pregnancy, from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregnancy or its management but not from accidental or incidental causes.»[161] Historically, maternal mortality was a major cause of women’s death. In recent decades, advances in healthcare have resulted in rates of maternal mortality having dropped dramatically, especially in Western countries. Maternal mortality however remains a serious problem in many African and Asian counties.[161][162]
Infant and child mortality[edit]
Infant mortality is the death of a child less than one year of age. Child mortality is the death of a child before the child’s fifth birthday. Like maternal mortality, infant and child mortality were common throughout history, but have decreased significantly in modern times.[163][164]
Politics[edit]
Parents with child statue, Hrobákova street, Petržalka, Bratislava
While in many parts of the world family policies seek to promote a gender-equal organization of the family life, in others the male-dominated family continues to be the official policy of the authorities, which is also supported by law. For instance, the Civil Code of Iran states at Article 1105: «In relations between husband and wife; the position of the head of the family is the exclusive right of the husband».[165]
In some parts of the world, some governments promote a specific form of family, such as that based on traditional family values. The term «family values» is often used in political discourse in some countries, its general meaning being that of traditional or cultural values that pertain to the family’s structure, function, roles, beliefs, attitudes, and ideals, usually involving the «traditional family»—a middle-class family with a breadwinner father and a homemaker mother, raising their biological children. Any deviation from this family model is considered a «nontraditional family».[166] These family ideals are often advanced through policies such as marriage promotion. Some jurisdictions outlaw practices which they deem as socially or religiously unacceptable, such as fornication, cohabitation or adultery.
Work–family balance[edit]
Work–family balance is a concept involving proper prioritizing between work/career and family life. It includes issues relating to the way how work and families intersect and influence each other. At a political level, it is reflected through policies such maternity leave and paternity leave. Since the 1950s, social scientists as well as feminists have increasingly criticized gendered arrangements of work and care, and the male breadwinner role, and policies are increasingly targeting men as fathers, as a tool of changing gender relations.[167]
Protection of private and family life[edit]
Article 8 of the European Convention on Human Rights provides a right to respect for one’s «private and family life, his home and his correspondence», subject to certain restrictions that are «in accordance with law» and «necessary in a democratic society».[168]
Article 8 – Right to respect for private and family life
1. Everyone has the right to respect for his private and family life, his home and his correspondence.
2. There shall be no interference by a public authority with the exercise of this right except such as is in accordance with the law and is necessary in a democratic society in the interests of national security, public safety or the economic well-being of the country, for the prevention of disorder or crime, for the protection of health or morals, or for the protection of the rights and freedom of others.
Criticism[edit]
An early opponent of the family was Socrates whose position was outlined by Plato in The Republic.[169] In Book 5 of The Republic, Socrates tells his interlocutors that a just city is one in which citizens have no family ties.[170][171]
The family being such a deep-rooted and much-venerated institution, few intellectuals have ventured to speak against it. Familialism has been atypically defined as a «social structure where … a family’s values are held in higher esteem than the values of the individual members of the family». Favoritism granted to relatives regardless of merit is called nepotism.
The Russian-American rationalist and individualist philosopher, novelist and playwright Ayn Rand compared partiality towards consanguinity with racism, as a small-scale manifestation of the latter.[172] «The worship of the family is merely racism, like a crudely primitive first installment on the worship of the tribe. It places the accident of birth above a man’s values and duty to the tribe above a man’s right to his own life.»[173] Additionally, she spoke in favor of childfree lifestyle, while following it herself.[172]
The family and social justice[edit]
One of the controversies regarding the family is the application of the concept of social justice to the private sphere of family relations, in particular with regard to the rights of women and children. Throughout much of the history, most philosophers who advocated for social justice focused on the public political arena, not on the family structures; with the family often being seen as a separate entity which needed to be protected from outside state intrusion. One notable exception was John Stuart Mill, who, in his work The Subjection of Women, advocated for greater rights for women within marriage and family.[174] Second wave feminists argued that the personal is political, stating that there are strong connections between personal experiences and the larger social and political structures. In the context of the feminist movement of the 1960s and 1970s, this was a challenge to the nuclear family and family values, as they were understood then.[175] Feminists focused on domestic violence, arguing that the reluctance—in law or in practice—of the state to intervene and offer protection to women who have been abused within the family, is in violation of women’s human rights, and is the result of an ideology which places family relations outside the conceptual framework of human rights.[176]
Global trends in family composition[edit]
Statistics from an infographic by Olivier Ballou showed that,[177]
In 2013, just over 40% of US babies were born outside marriage. The Census bureau estimated that 27% of all children lived in a fatherless home. Europe has seen a surge in child-free adults. One in five 40-something women are childless in Sweden and in Switzerland, in Italy one in four, in Berlin one in three. So-called traditional societies are seeing the same trend. About one-sixth of Japanese women in their forties have never married and about 30% of all women that age are childless.
However, Swedish statisticians reported in 2013 that, in contrast to many countries, since the 2000s, fewer children have experienced their parents’ separation, childlessness had decreased in Sweden and marriages had increased. It had also become more common for couples to have a third child suggesting that the nuclear family was no longer in decline in Sweden.[178]: 10
See also[edit]
- Childlessness
- Familialism
- Family economics
- Household
- Nepotism
- Parent
- Stepfamily
- Voluntary childlessness
Notes[edit]
- ^ Although married women in France obtained the right to work without their husbands’ permission in 1965,[155] and the paternal authority of a man over his family was ended in 1970 (before that parental responsibilities belonged solely to the father who made all legal decisions concerning the children), it was only in 1985 that a legal reform abolished the stipulation that the husband had the sole power to administer the children’s property.[156]
References[edit]
Citations[edit]
- ^ Donald Collins; Catheleen Jordan; Heather Coleman (2010). An Introduction to Family Social Work. Brooks/Cole, Cengage Learning. pp. 28–29. ISBN 978-0-495-80872-5. Archived from the original on 2020-07-31. Retrieved 2019-08-13.
- ^ Alhussain, Khalid, Shah, Drishti, Thornton, James, Kelly, Kimberly. Familial Opioid Misuse and Family Cohesion: Impact on Family Communication and Well-being. Addictive Disorders & Their Treatment 2019;18(4):194–204. doi:10.1097/ADT.0000000000000165.
- ^ Lander L, Howsare J, Byrne M. The impact of substance use disorders on families and children: from theory to practice. Soc Work Public Health. 2013;28:194–205.
- ^ Jás Elsner (2007). «The Changing Nature of Roman Art and the Art Historical Problem of Style,» in Eva R. Hoffman (ed), Late Antique and Medieval Art of the Medieval World, 11–18. Oxford, Malden & Carlton: Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4051-2071-5, p. 17, Figure 1.3 on p. 18.
- ^ a b Schneider, David 1984 A Critique of the Study of Kinship. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press. p. 182
- ^ Deleuze-Guattari (1972). Part 2, ch. 3, p. 80
- ^ Russon, John, (2003) Human Experience: Philosophy, Neurosis, and the Elements of Everyday Life, Albany: State University of New York Press. pp. 61–68.
- ^ George Peter Murdoch Social Structure p. 13
- ^ Wolf, Eric. 1982 Europe and the People Without History. Berkeley: University of California Press. 92
- ^ Harner, Michael 1975 «Scarcity, the Factors of Production, and Social Evolution,» in Population, Ecology, and Social Evolution, Steven Polgar, ed. Mouton Publishers: the Hague.
- ^ Rivière, Peter 1987 «Of Women, Men, and Manioc», Etnologiska Studier (38).
- ^ «We have seen that people can refer to their relatives as ‘the family.’ ‘All the family turned up for the funeral… But of course, my brother didn’t bring his family along— they’re much too young.’ Here the reference is to the offspring (as distinct from ‘all’ the family). The neighbors were very good, too. ‘The Jones came, and their two children. It was nice, the whole family turning up like that.’ Here the usage is more restricted than ‘relatives’ or ‘his relatives,’ but includes just both parents and offspring. ‘Of course, the children will be leaving home soon. It’s always sad to see the family break up like that.’ Here the reference is not only to parents and children but to their co-residence, that is, to the household.»The Family and Industrial Society», 1983, George Allen Unwin, London, p. 30
- ^ Olivia Harris. Kate Young; Carol Wolkowitz; Roslyn McCullagh (eds.). Of Marriage and the Market: Women’s Subordination Internationally and its Lessons. London: Routeledge. p. 138.
- ^ a b «The World Factbook – Central Intelligence Agency». Cia.gov. Archived from the original on 28 October 2009. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ Axinn, William G.; Clarkberg, Marin E.; Thornton, Arland (1994). «Family Influences on Family Size Preferences». Demography. 31 (1): 65–79. doi:10.2307/2061908. ISSN 0070-3370. JSTOR 2061908. PMID 8005343. S2CID 7787872.
- ^ Murphy, Michael (2013). «Cross-National Patterns of Intergenerational Continuities in Childbearing in Developed Countries». Biodemography and Social Biology. 59 (2): 101–126. doi:10.1080/19485565.2013.833779. ISSN 1948-5565. PMC 4160295. PMID 24215254.
- ^ Little, William (2014-11-06). «Chapter 1. An Introduction to Sociology». Archived from the original on 2022-07-15. Retrieved 2022-07-15.
- ^ «The Collapse of Marriage by Don Browning – The Christian Century». Religion-online.org. February 7, 2006. pp. 24–28. Archived from the original on September 30, 2007. Retrieved 2007-07-10.
- ^ Levitan, Sara (2010). «Working wives and mothers: what happens to family life?» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on August 19, 2013. Retrieved January 8, 2014.
- ^ a b c «The Return of the Multi-Generational Family Household». Pew Research Center’s Social & Demographic Trends Project. 2010-03-18. Archived from the original on 2021-02-28. Retrieved 2021-02-20.
- ^ «Record 64 million Americans live in multigenerational households». Pew Research Center. 2018-04-05. Archived from the original on 2021-02-21. Retrieved 2021-02-20.
- ^ «The Daily — Families, households and marital status: Key results from the 2016 Census». Statistics Canada. 2017-08-02. Archived from the original on 2021-04-15. Retrieved 2021-02-20.
- ^ Smith, Court. «Definitions of Anthropological Terms». Oregonstate.edu. Archived from the original on 7 February 2015. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ Compare: Scott, John, ed. (2014). A Dictionary of Sociology. Oxford paperback reference (4 ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 237. ISBN 978-0-19-968358-1. Archived from the original on 2020-08-01. Retrieved 2018-06-30.
The conjugal family refers to a family system of spouses and their dependent children. […] The term nuclear family is used to refer to a unit consisting of spouses and their dependent children. […]
- ^ Compare: Lee, Gary R. (1999). «4: Comparative Perspectives». In Sussman, Marvin B.; Steinmetz, Suzanne K.; Peterson, Gary W. (eds.). Handbook of Marriage and the Family (2 ed.). New York: Springer Science & Business Media (published 2013). p. 96. ISBN 978-1-4757-5367-7. Archived from the original on 2020-08-01. Retrieved 2018-06-30.
[…] the nuclear family (consisting of parents and dependent children) […] the conjugal family (defined as nuclear in structure) […].
- ^ «Fewer than half of U.S. kids today live in a ‘traditional’ family». Pewresearch.org. 22 December 2014. Archived from the original on 11 April 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ Staff writers (March 2014). «The Kids will be alright, even without the Nuclear Family». Pacific Standard magazine. Archived from the original on 30 July 2022. Retrieved 22 April 2017.
- ^ Bryant, L.E. (March 2016). «Nuclear Families». The Wiley-Blackwell Encyclopedia of Family Studies. pp. 1–3. doi:10.1002/9781119085621.wbefs490. ISBN 978-0-470-65845-1.
- ^ Dowd, Nancy E (1997). In Defence of Single Parent Families. New York and London: New York University Press. ISBN 0-8147-1869-8. Retrieved 19 November 2022.
- ^ Sanford L. Braver and Michael E. Lamb, Shared Parenting After Parental Separation: The Views of 12 Experts, Journal of Divorce & Remarriage, April 2018: «The empirical evidence currently available supports the view that children of divorce, on average, benefit substantially from SP [shared parenting] arrangements in which they live with each parent at least 35% of the time. Findings from well over 50 individual studies indicate that children whose parents have SP fare better than those with sole physical custody […].»
- ^ Baude, Amandine; Pearson, Jessica; Drapeau, Sylvie (27 June 2016). «Child Adjustment in Joint Physical Custody Versus Sole Custody: A Meta-Analytic Review». Journal of Divorce & Remarriage. 57 (5): 338–360. doi:10.1080/10502556.2016.1185203. S2CID 147782279.
- ^ American Psychological Association, Single parenting and today’s family Archived 2019-01-30 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Kathryn M. Feltey, Single-Parent Families Archived 2019-01-31 at the Wayback Machine, International Encyclopedia of Marriage and Family
- ^ a b Randolph, Richard R. (1964). «The «Matrifocal Family» as a Comparative Category». American Anthropologist. 66 (3): 628–631. doi:10.1525/aa.1964.66.3.02a00130. ISSN 0002-7294. JSTOR 668860.
- ^
Godelier, Maurice, trans. Nora Scott, The Metamorphoses of Kinship (London: Verso, 2011 (ISBN 978-1-84467-746-7)), p. 568 (Glossary, entry matrifocal) (trans. from Métamorphoses de la parenté (Librarie Arthème Fayard (apparently), 2004)) (author prof. anthropology, École des hautes études en sciences sociales, Paris). - ^ Little, William (2014-11-06). «Chapter 4. Society and Social Interaction». Archived from the original on 2022-05-21. Retrieved 2022-07-18.
- ^ a b Pritchard, Colin Pritchard (2006). Mental Health Social Work: Evidence-Based Practice. Routledge. p. 111. ISBN 9781134365449.
in cultures with stronger ‘extended family traditions’, such as Asian and Catholic countries
- ^ «ALGBTICAL LGBT Glossary of Terminology». ALGBTICAL Association for Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, and Transgender Issues in Counseling of Alabama. 2005–2006. Archived from the original on May 6, 2016. Retrieved May 4, 2016.
- ^ Dewaele, Alexis; Cox, Nele; Van den Berghe, Wim; Vincke, John (February 2011). «Families of Choice? Exploring the Supportive Networks of Lesbians, Gay Men, and Bisexuals1: FAMILIES OF CHOICE». Journal of Applied Social Psychology. 41 (2): 312–331. doi:10.1111/j.1559-1816.2010.00715.x. Archived from the original on 2022-05-04. Retrieved 2022-05-04.
- ^ a b c Stitt, Alex (2020). ACT For Gender Identity: The Comprehensive Guide. London: Jessica Kingsley Publishers. pp. 372–376. ISBN 978-1785927997. OCLC 1089850112.
- ^ Blended and Blessed Archived 2017-11-04 at the Wayback Machine – Encouraging Step-Families, blendedandblessed.com
- ^ «Department of Social and Developmental Psychology: PPSIS Faculty, Academic Profile». Sdp.cam.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 2011-11-25. Retrieved 2011-03-26.
- ^ Civil Action No. 1:09-cv-10309 Archived 2010-12-25 at the Wayback Machine paragraph 17
- ^ «Parenting Myths And Facts». NPR.org. Archived from the original on 2019-04-13. Retrieved 2018-05-14.
- ^ see History of the family § Evolution of household
- ^ «The Evolution of American Family Structure». Concordia University, St. Paul Online. 2015-06-23. Archived from the original on 2021-06-10. Retrieved 2021-06-10.
- ^ McCornack, Steven (2010). Reflect & Relate an introduction to interpersonal communication. Boston/NY: Bedford/St. Martin’s. pp. 369–370.
- ^ Portrie, Torey; Hill, Nicole R. (October 2005). «Blended Families: A Critical Review of the Current Research». The Family Journal. 13 (4): 445–451. doi:10.1177/1066480705279014. ISSN 1066-4807. S2CID 32353012. Archived from the original on 2022-05-04. Retrieved 2022-05-04.
- ^ Braithwaite, Dawn; Olson, Loreen; Golish, Tamara; Soukup, Charles; Turman, Paul (2001-01-01). ««Becoming a family»: developmental processes represented in blended family discourse». Journal of Applied Communication Research. 29 (3): 221–247. doi:10.1080/00909880128112. ISSN 0090-9882. S2CID 14220043.
- ^ Braithwaite, Dawn O.; Baxter, Leslie A.; Harper, Anneliese M. (1998-06-01). «The role of rituals in the management of the dialectical tension of «old» and «new» in blended families». Communication Studies. 49 (2): 101–120. doi:10.1080/10510979809368523. ISSN 1051-0974. Archived from the original on 2022-07-30. Retrieved 2022-05-04.
- ^ Cf. «Monogamy» in Britannica World Language Dictionary, R.C. Preble (ed.), Oxford-London 1962, p. 1275:1. The practice or principle of marrying only once. opp. to digamy now rare 2. The condition, rule or custom of being married to only one person at a time (opp. to polygamy or bigamy) 1708. 3. Zool. The habit of living in pairs, or having only one mate; The same text repeats The Shorter Oxford English Dictionary, W. Little, H.W. Fowler, J. Coulson (ed.), C.T. Onions (rev. & ed.,) Oxford 1969, 3rd edition, vol. 1, p. 1275; OED Online. March 2010. Oxford University Press. 23 Jun. 2010 Cf. Monogamy Archived 2015-06-23 at the Wayback Machine in Merriam-Webster Dictionary
- ^ «bigamy». Merriam-Webster Dictionary.
- ^ «Opening Up: Challenging Myths about Consensual Non-Monogamy – Science of Relationships». Scienceofrelationships.com. 2012-08-17. Archived from the original on 2017-04-04. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ a b Zeitzen, Miriam Koktvedgaard (2008). Polygamy: a cross-cultural analysis. Berg. p. 3. ISBN 978-1-84520-220-0. Archived from the original on 2020-08-01. Retrieved 2015-11-19.
- ^ McCullough, Derek; Hall, David S. (February 27, 2003). «Polyamory – What it is and what it isn’t». Electronic Journal of Human Sexuality. 6. Archived from the original on December 10, 2020. Retrieved March 14, 2015.
- ^ Zeitzen, Miriam K. (2008). Polygamy: A Cross-Cultural Analysis. Oxford: Berg. p. 9.
- ^ «Archived copy». study.com. Archived from the original on 2022-07-30. Retrieved 2022-07-18.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ a b Starkweather, Katherine E.; Hames, Raymond (June 2012). «A survey of non-classical polyandry». Human Nature. 23 (2): 149–172. doi:10.1007/s12110-012-9144-x. PMID 22688804. S2CID 2008559. Archived from the original on 2019-12-04. Retrieved 2018-11-14.
- ^ w3we.com. «Family — w3we». hy.w3we.com (in Armenian). Archived from the original on 2022-07-18. Retrieved 2022-07-18.
- ^ By replacement in the definition of the notion of «generation» by meiosis». Since identical twins are not separated by meiosis, there are no «generations» between them, hence n=0 and r=1. See genetic-genealogy.co.uk Archived 2021-02-24 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ «Kin Selection». Benjamin/Cummings. Archived from the original on 2015-05-17. Retrieved 2007-11-25.
- ^ Tooker, Elisabeth. «Another View of Morgan on Kinship.» Archived 2018-09-22 at the Wayback Machine Current Anthropology 20, no. 1 (March 1979): 131–134.
- ^ «Systematic Kinship Terminologies». www.umanitoba.ca. Archived from the original on 2019-12-24. Retrieved 2022-07-18.
- ^ A Dictionary of Genetics. Oxford University Press. 2013. 8.
- ^ «Definition of Cousin». Merriam-Webster. Archived from the original on 2021-02-01. Retrieved 2020-04-20.
- ^ «Co-Sister». Cambridge Dictionary. Cambridge Dictionary. Archived from the original on 13 January 2021. Retrieved 18 April 2020.
- ^ «Co-Brother». Cambridge Dictionary. Cambridge Dictionary. Archived from the original on 25 February 2021. Retrieved 18 April 2020.
- ^ Benokraitis, N.V. Marriages and Families. 7th Edition, Pearson Education, Inc., 2011
- ^ Shepard, Jon; Greene, Robert W. (2003). Sociology and You. Ohio: Glencoe McGraw-Hill. p. A-22. ISBN 978-0-07-828576-9. Archived from the original on 2010-03-08.
- ^ Stone, Linda (2006). Kinship and Gender: An Introduction. Boulder, Colorado: Westview Press. pp. 168–169. ISBN 978-0-8133-4302-0.
- ^ Ezzell, Carol (June 2001). «The Himba and the Dam». Scientific American. 284 (6): 80–90. Bibcode:2001SciAm.284f..80E. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0601-80. PMID 11396346. Archived from the original on 2007-10-12. Retrieved 2015-07-12.
- ^ «Sociology/Founding the discipline». Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 2009-12-23. Retrieved 2009-07-26.
- ^ Morgan 1877
- ^ «Cultural Anthropology». Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on 2009-08-15. Retrieved 2009-07-22.
- ^ «The Marxists Internet Archive». Archived from the original on 2006-04-25. Retrieved 2009-07-17.
- ^ Williams, Brian; Sawyer, Stacey C.; Wahlstrom, Carl M. (2005). Marriages, Families & Intimate Relationships. Boston, MA: Pearson. 0-205-36674-0.
- ^ Zinn, Maxine Baca; Eitzen, D. Stanley (2002). Diversity in families (6 ed.). Allyn and Bacon. p. 557. ISBN 978-0-205-33522-0. Archived from the original on 2013-03-29. Retrieved 2012-01-06.
This ‘family as haven’ image of a refuge from an impersonal world characterizes the family as a place of intimacy, love, and trust in which individuals may escape the competition of dehumanizing forces in modern society. Christopher Lasch (1977:8) has named this image a ‘haven in a heartless world’ and described it as a glorification of private life made necessary by the deprivations experienced in the public world.
- ^ a b Zinn and Eitzen (1987) Diversity in American families Archived 2016-05-29 at the Wayback Machine, p. 3
- ^ a b Zinn and Eitzen (1987) Diversity in American families Archived 2016-05-18 at the Wayback Machine, p. 8
- ^ «Changing Patterns of Nonmarital Childbearing in the United States». CDC/National Center for Health Statistics. May 13, 2009. Archived from the original on September 6, 2011. Retrieved September 24, 2011.
- ^ Tavernise, Sabrina (2011). «Married Couples Are No Longer a Majority, Census Finds». The New York Times. Archived from the original on March 25, 2014. Retrieved January 8, 2014.
- ^ «The Family Revolution». Greater Good. Archived from the original on 2022-03-15. Retrieved 2022-05-04.
- ^ Coontz, Stephanie. 2005. Marriage, A History: How Love Conquered Marriage. New York: Viking/Penguin Books.
- ^ Male and Female, New York, 1949. pp. 193–194
- ^ Scottish Government, Scottish Government, Edinburgh (27 April 2006). «Family Matters – Couples – Cohabitation». Scotland.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 24 October 2014. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «Full list». Coe.int. Archived from the original on 2 October 2000. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «Full list». Coe.int. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «1 in 5 US moms have kids with multiple dads, study says». Nbcnews.com. 1 April 2011. Archived from the original on 22 June 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «American Children’s Family Structure: Single-Parent Families». Bowling Green State University. Archived from the original on 2021-06-20. Retrieved 2022-05-04.
- ^ «Definitions of Domestic Violence – Child Welfare Information Gateway». Childwelfare.gov. Archived from the original on 15 December 2014. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ «Full list». Coe.int. Archived from the original on 23 September 2015. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «A/RES/48/104. Declaration on the Elimination of Violence against Women». United Nations. 20 December 1993. Archived from the original on 16 August 2019. Retrieved 28 June 2017.
- ^ Wallace, p. 2
- ^ «Child maltreatment». World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 17 October 2017. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ Roffee, James A. (2015). «When Yes Actually Means Yes». Roffee, James (2015). When Yes Actually Means Yes in Rape Justice. 72–91. doi:10.1057/9781137476159.0009. ISBN 978-1-137-47615-9.
- ^ Roffee, J. A. (2014). «No Consensus on Incest? Criminalisation and Compatibility with the European Convention on Human Rights» (PDF). Human Rights Law Review. 14 (3): 541–572. doi:10.1093/hrlr/ngu023. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-10-30. Retrieved 2018-10-30.
- ^ «Elder abuse». World Health Organization. Archived from the original on October 26, 2007. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ «Child abuse – definition of child abuse by the Free Online Dictionary, Thesaurus and Encyclopedia». Thefreedictionary.com. Archived from the original on 9 June 2019. Retrieved 15 September 2010.
- ^ Leeb, R.T.; Paulozzi, L.J.; Melanson, C.; Simon, T.R.; Arias, I. (1 January 2008). «Child Maltreatment Surveillance: Uniform Definitions for Public Health and Recommended Data Elements». Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Archived from the original on 16 October 2008. Retrieved 20 October 2008.
- ^ «Parenting and Family Support – Family Lives (Parentline Plus)». Parentlineplus.org.uk. Archived from the original on 21 December 2010. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «WHEN FAMILY LIFE HURTS: Family experience of aggression in children – Parentline plus 31 October 2010» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on June 19, 2012.
- ^ elderabus.org.uk Archived 2019-08-20 at the Wayback Machine, accessed October 12, 2007.
- ^ a b «Q & A: Child Marriage and Violations of Girls’ Rights». Hrw.org. 14 June 2013. Archived from the original on 20 June 2013. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «WHO – Child marriages: 39 000 every day». Who.int. Archived from the original on March 14, 2013. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «I have a right to – BBC World Service». Bbc.co.uk. Archived from the original on 6 April 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ Finsgate, Switchboard: +44300 777 9777 Plan International UK; London, 5-7 Cranwood Street; Uk, Ec1v 9lh. «Ending child marriage». Plan International UK. Archived from the original on March 12, 2014.
- ^ «Ethics – Forced Marriages: Introduction». Bbc.co.uk. Archived from the original on 3 September 2015. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «Ethics – Slavery: Modern slavery». Bbc.co.uk. Archived from the original on 6 January 2014. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ Gulnara Shahinian. «Report of the Special Rapporteur on contemporary forms of slavery, including its causes and consequences» (PDF). Ohchr.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ «Child marriage». Unicef.org. Archived from the original on 7 September 2018. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ a b c «I have a right to». Bbc.co.uk. Archived from the original on 6 April 2017. Retrieved 7 October 2014.
- ^ «Factsheet: Child Marriage» (PDF). GirlUp. United Nations Foundation. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-09-09. Retrieved 2014-07-20.
- ^ «Child marriages: 39 000 every day». Who.int. Archived from the original on March 14, 2013. Retrieved 7 October 2014.
- ^ Malina, Bruce J. (15 February 2001). The New Testament world: insights from cultural anthropology. Westminster John Knox Press. p. 42. ISBN 978-0-664-22295-6. Archived from the original on 25 December 2018. Retrieved 7 November 2011.
- ^ a b Mosquera, Patricia M.R.; Manstead, Antony S.R.; Fischer, Agneta H. (January 2002). «Honor in the Mediterranean and Northern Europe». Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology. 33 (1): 16–36. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.1006.591. doi:10.1177/0022022102033001002. S2CID 55174724. Archived from the original on 25 December 2018. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ Berns, Roberta (2007). Child, family, school, community: socialization and support. Thompson Learning. p. 139. ISBN 978-0-495-00758-6. Archived from the original on 2021-04-15. Retrieved 2020-10-31.
- ^ McGoldrick, Monica; Giordano, Joseph; Garcia-Preto, Nydia (18 August 2005). Ethnicity and family therapy. Guilford Press. p. 445. ISBN 978-1-59385-020-3. Archived from the original on 16 March 2015. Retrieved 24 October 2011.
- ^ «Ethics: Honour Crimes». BBC. 1 January 1970. Archived from the original on 19 June 2014. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
- ^ «Honor killing: Definition and More from the Free Merriam-Webster Dictionary». Merriam-webster.com. 31 August 2012. Archived from the original on 22 December 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
- ^ «Honor killing definition». Dictionary.reference.com. Archived from the original on 2 December 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2013.
- ^ «Shocking gay honor killing inspires movie». Edition.cnn.com. Archived from the original on 29 September 2013. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Iraqi immigrant convicted in Arizona ‘honor killing’ awaits sentence». Edition.cnn.com. 23 February 2011. Archived from the original on 29 September 2013. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Definition of DOWRY». Merriam-webster.com. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ Goody, Jack (1976). Production and Reproduction: A Comparative Study of the Domestic Domain. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 8.
- ^ «Gender, equity, human rights». Who.int. Archived from the original on August 29, 2003. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «State of World Population 2005». UNFPA – United Nations Population Fund. Archived from the original on 1 March 2014. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «WHO – Gender and human rights». Who.int. Archived from the original on 23 December 2018. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «Get Involved». Amnesty.org. Archived from the original on 17 January 2015. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «Supporting the Constellation of Reproductive Rights». UNFPA – United Nations Population Fund. Archived from the original on 30 July 2013. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «Family planning». Who.int. Archived from the original on 18 March 2016. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «Family planning». UNFPA – United Nations Population Fund. Archived from the original on 30 March 2019. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «Forced/Coerced Sterilization». Stopvaw.org. Archived from the original on 13 December 2014. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «Czech regret over sterilisation». BBC News. 2009-11-24. Archived from the original on 2018-10-13. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ Cabitza, Mattia (6 December 2011). «Peru women fight for justice over forced sterilisation». BBC News. Archived from the original on 8 July 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ Collier & Sheldon, 2006, pp. 1–26.
- ^ «Protecting children’s rights». Unicef.org. Archived from the original on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ «Children’s Rights». Hrw.org. Archived from the original on 6 April 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «Children and human rights». Amnesty International. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ «The Policy on Gender Equality in Italy» (PDF). Europarl.europa.eu. Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ Rashida Manjoo. «Report of the Special Rapporteur on violence against women, its causes and consequences» (PDF). Ohchr.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ Solsten, Eric; Meditz, Sandra W., eds. (1988). «Social Values and Attitudes». Spain: A Country Study. Washington: Government Printing Office for the Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 2011-05-20. Retrieved 2016-02-26.
- ^ Contemporary Western European Feminism, by Gisela Kaplan, p. 133
- ^ Reconciliation Policy in Germany 1998–2008, Construing the ‘Problem’ of the Incompatibility of Paid Employment and Care Work, by Cornelius Grebe; p. 92: «However, the 1977 reform of marriage and family law by Social Democrats and Liberals formally gave women the right to take up employment without their spouses’ permission. This marked the legal end of the ‘housewife marriage’ and a transition to the ideal of ‘marriage in partnership’.»[1] Archived 2017-04-16 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Further reforms to parental rights law in 1979 gave equal legal rights to the mother and the father. Comparative Law: Historical Development of the Civil Law Tradition in Europe, Latin America, and East Asia, by John Henry Merryman, David Scott Clark, John Owen Haley, p. 542
- ^ Women in Portugal, by Commission of the European Communities, Directorate-General Information, p. 32
- ^ «On Equality of Spouses in Civil Law» (PDF). Wcd.coe.int. Archived from the original on 21 January 2016. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ «Switzerland profile». Bbc.com. 24 July 2017. Archived from the original on 17 June 2018. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ Switzerland, Markus G. Jud, Lucerne. «The Long Way to Women’s Right to Vote in Switzerland: a Chronology». History-switzerland.geschichte-schweiz.ch. Archived from the original on 21 November 2019. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ Women’s movements of the world: an international directory and reference guide, edited by Sally Shreir, p. 254
- ^ «AROUND THE WORLD; Greece Approves Family Law Changes». The New York Times. 23 October 1983. Archived from the original on 16 June 2012. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ Demos, Vasilikie. (2007) «The Intersection of Gender, Class and Nationality and the Agency of Kytherian Greek Women.» Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Sociological Association. August 11
- ^ a b International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/The World Bank (2013). «Women, Business and the Law 2014: Removing Restrictions to Enhance Gender Equality» (PDF). London: Bloomsbury Publishing Plc. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-08-24. Retrieved 2014-08-25.
- ^ «Dutch gender and LGBT-equality policy : 2013 – 2016» (PDF). Rm.coe.int. Archived from the original on 12 June 2018. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ «2015 Review Report of the Netherlands Government in the context of the twentieth anniversary of the Fourth World Conference on Women and the adoption of the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action» (PDF). Unece.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 October 2015. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ «Virtual Special Issue: Modern & Contemporary France: Women in France» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2016-04-03.
- ^ Ferrand, Frédérique. «National Report: France» (PDF). Commission on European Family Law. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2014-08-11. Retrieved 2016-02-26.
- ^ Country Comparison: Maternal Mortality Rate Archived 2015-04-18 at the Wayback Machine in The CIA World Factbook.
- ^ «What is Family Medicine?». Uchicago.edu – Department of Family Medicine. Archived from the original on 7 May 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «The rising importance of family medicine». Who.int. Archived from the original on March 7, 2014. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ Infant Mortality Rates in 2012 Archived July 14, 2014, at the Wayback Machine, UNICEF, 2013.
- ^ a b «Maternal mortality ratio (per 100 000 live births)». Who.int. Archived from the original on May 7, 2013. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «Maternal mortality». Who.int. Archived from the original on 30 September 2015. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «Infant mortality». Who.int. Archived from the original on March 24, 2014. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «Children: reducing mortality». Who.int. Archived from the original on 18 April 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «The Civil Code of the Islamic Republic of Iran» (PDF). 11 March 2017. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 March 2017. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ N, Panasenko (2013). «Czech and Slovak Family Patterns and Family Values in Historical, Social and Cultural Context». Journal of Comparative Family Studies. 44 (1): 79–98. doi:10.3138/jcfs.44.1.79.
- ^ Bjørnholt, M. (2014). «Changing men, changing times; fathers and sons from an experimental gender equality study» (PDF). The Sociological Review. 62 (2): 295–315. doi:10.1111/1467-954X.12156. S2CID 143048732. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-10-21. Retrieved 2014-09-11.
- ^ «Art. 8 ECHR Right to private life – Introduction». ECHR online. Archived from the original on 2014-10-21. Retrieved 2014-10-20.
- ^ «Abolition of the Family for The Guardians and the Use of War (457b-471c)» (PDF). Homepages.gac.edu. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 May 2018. Retrieved 23 October 2017.
- ^ «SparkNotes: The Republic: Book V». Sparknotes.com. Archived from the original on 26 April 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ «The Republic Book 5 Summary & Analysis». Litcharts.com. LitCharts – The creators of SparkNotes. Archived from the original on 17 April 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ a b Heller, Anne C. (2009). Ayn Rand and the World She Made. New York: Doubleday. pp. 320–321. ISBN 978-0-385-51399-9. OCLC 2290274371. Said in one of the lectures Archived 2015-07-03 at the Wayback Machine Ayn Rand delivered.
- ^ Said in one of the public lectures Archived 2015-07-03 at the Wayback Machine Ayn Rand delivered
- ^ Satz, Debra (1 January 2017). Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Archived from the original on 18 March 2019. Retrieved 12 April 2017 – via Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy.
- ^ Angela Harutyunyan, Kathrin Hörschelmann, Malcolm Miles (2009) Public Spheres After Socialism pp. 50–51 Archived 2022-03-13 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Patel, Vibhuti. «Domestic Violence: A Violation of Human Rights of Women by Dr. Vibhuti Patel, Director, P.G.S.R.» Academia.edu. Archived from the original on 17 April 2022. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ^ Nicholas Eberstadt (February 23, 2015), The global flight from the family, Washington: American Enterprise Institute, archived from the original on September 8, 2015, retrieved February 26, 2017,
keywords Economic Development, Foreign and Defense Policy, International Economics, Infographic by Olivier Ballou global trends in family composition
- ^
Sources[edit]
- Race, Class, & Gender: An Anthology, 9th edition. Editors: Margaret L. Anderson and Patricia Hill Collins. Cengage Learning.
Bibliography[edit]
- Monica McGoldrick; Nydia A. Garcia Preto; Betty A. Carter (12 June 2015). The Expanding Family Life Cycle: Individual, Family, and Social Perspectives. Pearson Education. ISBN 978-0-205-96806-0. Archived from the original on 17 February 2017. Retrieved 15 February 2017.
- Daly, Mary (2011). «What adult worker model? A critical look at recent social policy reform in Europe from a gender and family perspective». Social Politics. 18 (1): 1–23. doi:10.1093/sp/jxr002. PMID 21692242. S2CID 21306624.
- Daly, Mary; Lewis, Jane (2000). «The concept of social care and the analysis of contemporary welfare states». British Journal of Sociology. 51 (2): 281–98. doi:10.1111/j.1468-4446.2000.00281.x. PMID 10905001. Archived from the original on 2019-06-29. Retrieved 2019-06-25.
- Esping-Andersen, Gøsta (2009). The incomplete revolution: Adapting welfare states to women’s new roles. Cambridge: Polity Press.
- Ferragina, Emanuele; Seeleib-Kaiser, Martin (2015). «Determinants of a Silent (R)evolution:Understanding the Expansion of Family Policy in Rich OECD Countries». Social Politics. 22 (1): 1–37. doi:10.1093/sp/jxu027.
- Forbes, Scott, A Natural History of Families, (Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2005), ISBN 0-691-09482-9
- Foucault, Michel (1978). The History of Sexuality: Volume I: An Introduction. (New York: Vintage Books). ISBN 978-0-679-72469-8
- Gilroy, Paul «Identity Belonging and the Critique of Pure Sameness» in Gilroy, Paul (2000) Against Race: Imagining Political Culture Beyond the Color Line, (Cambridge, Mass.: Belknap Press of Harvard University Press), Ch. I.3, pp. 97–133
- Goody, Jack The Development of the Family and Marriage in Europe Archived 2016-05-19 at the Wayback Machine (Cambridge University Press, 1980); translated into Spanish, French, Italian, Portuguese.
- Mock, Douglas W., More Than Kin and Less Than Kind, (Belknap Press, 2004), ISBN 0-674-01285-2
- Schneider, David M., American Kinship: a cultural approach (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1980).
- Tabak, I.; Mazur, J.; Granado, M.C.; Örkenyi, Á.; Zaborskis, A.; Aasvee, K.; Moreno, C. (2012). «Examining trends in parent-child communication in Europe over 12 years». The Journal of Early Adolescence. 32 (1): 26–54. doi:10.1177/0272431611419509. S2CID 206496782.
- Chevallier, Denis (1985). «Famille et parenté: une bibliographie». Terrain (in French) (4): 77–82. doi:10.4000/terrain.2874. Archived from the original on July 24, 2008. Retrieved January 8, 2014.
External links[edit]
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Family.
Look up family in Wiktionary, the free dictionary.
Wikiquote has quotations related to Family.
- «Family» . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 10 (11th ed.). 1911.
Noun
The disappearance of decent-paying low-skilled jobs over the last 30 years makes it virtually impossible for a young high-school dropout to successfully support a family on a legitimate income.
—
A defendant in a racketeering trial was described yesterday as a Mafia captain who had carried out a plot to kill three rivals in the Bonanno crime family.
—
Nobody ever came to the farm—through «the big gate,» a mile off on the pike—except kin and a family named Rawls: a widow with two daughters and a son, my only playmate.
—
It was quite an understood thing in the family that Lord Fawn must marry money.
—
There were a lot of families at the circus.
The show is fun for the whole family.
a death in the family
There are several doctors on his mother’s side of the family.
She wants to spend more time with her family.
After his father’s death he became the head of the family.
She’s a friend of the family.
He spent a quiet evening at home with family.
trying to find a balance between work and family
He’s devoted to his wife and family.
See More
Recent Examples on the Web
The area also ranked nationally with high rates of unsheltered homelessness for multiple populations including unaccompanied youth, families with children, chronically homeless individuals and veterans.
—
So many lives had been claimed by 2016, touching countless families.
—
It is owned by the billionaire Magnier family, who dominate the Irish stud industry (Queen Elizabeth once visited their nearby breeding operation, Coolmore Stud), and equine activities predominate at the property.
—
More:’Wrap our arms around these families‘: Beshear, Greenberg react to Louisville mass shooting The other shooting victims Monday were Jim Tutt Jr., 64; Josh Barrick, 40; Juliana Farmer, 45; and Deana Eckert, 57.
—
Alabama’s defense has lost eight starters to the NFL draft and was without four others Friday because of injuries to inside linebackers Deontae Lawson, outside linebackers Dallas Turner and Chris Braswell, and the absence of cornerback Kool-Aid McKinstry for a family matter.
—
The 35-year-old actress dropped several pics of herself and her family on Instagram—including husband Ryan Reynolds, her mom, and her mother-in-law—hanging out in and around a beach, looking all kinds of blissed out.
—
Tucson police announced Monday that officers arrested a man after finding a woman dead inside her family home from a gunshot wound last week.
—
The young men may have recently turned 18 and now qualify, or have cleared up family obligations that previously stopped them from joining.
—
Almost 30,000 single- and multi-family homes and businesses could benefit if approved in the coming months.
—
City Council members unanimously supported the ordinance, which changed property use in an area previously zoned for retail and multi-family homes.
—
The residence is a multi-family home with five bedrooms and two bathrooms, according to a Zillow listing.
—
The fire took place in a multi-family home in Detroit, allegedly caused by the downstairs tenants’ kids lighting up a mattress in the bedroom.
—
The code changes also would not affect the city’s nearly 140,000 existing multi-family homes, where owners or managers can decide whether to voluntarily install EV charging.
—
Four Meriden firefighters and one occupant of a multi-family home in Meriden were hospitalized after a three-alarm fire this weekend, city officials said Sunday.
—
Three of the people who died lived above the third floor of multi-family dwellings, county officials said.
—
Priorities for the state grants include rural and underserved areas not eligible for the NEVI grants, as well as low- to moderate-income areas and those with high ratios of multi-family dwellings like apartment complexes.
—
See More
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word ‘family.’ Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Family. It’s not just any other word lost in the pages of a vast dictionary. ‘Family’ is an emotion. Just the mere mention of this word can invoke the most innate feelings of love and belonging in you. Love and belonging is a true family definition. Everyone, even the most solitary soul needs someone they can call a family because family is the one humane aspect that makes a house a home. And that’s why we must know the true meaning of family.

A family doesn’t necessarily mean your parents, your siblings or your immediate blood relatives. Family can mean your best friends, your classmates, your teachers, your pet, or even that one person you always wave to at your local coffee shop.
In fact, a family can mean anyone who gives you that comforting feeling of familiarity. Family is the group of people who you know accepts you for you. You feel comfortable, safe, special, that you matter and that your voice matters. Family is that which can make you happy as soon as you see them. They are the ones who stand by you through thick and thin. They are your entire support system. Moreover, keep you going forward in life.
Family Definition – How Do You Define Your Family?

To be a part of a family is a beautiful phenomenon. It gives us a sense of belonging and love we all crave. But your family isn’t always limited to just your parents, grandparents or siblings. Your family can also be your closest friends, your teachers or your mentors -your chosen family. The true definition of family lies not in blood relations, but it is measured in the amount of love and respect people hold for each other.
The definition of a true family is just this. A group of people who have each other’s back and are willing to go to the ends of the earth to bring a smile to the others’ face. Call it a true family or a real family—the true family definition is the sense of loyalty, selflessness, love, and genuine care and concern for others.
Strengthen Your Ties
It is difficult to find people who want the best for you without any ulterior motives. However, once you do, make sure you fight for them to stay no matter what. There will be hurdles along the way, and huge fights where your relationship may seem too fragile to hold on to. But remember this, overcoming these hurdles together will only strengthen your ties. After all, at the end of the day, the true meaning and definition of family lies in how much you care for one another.
Sometimes your chosen family, vis-a-vis your friends, co-workers, mentors, or teachers may seem more helpful in rising above yourself but never forget your family too. After all, they have known you your entire life and have loved and cared for you since the very beginning, no matter what.
So go out there into the real world and find your chosen family. Those who will stand by you no matter what, and will always support you no matter what. But make sure you never forget where you came from because that is where you will always truly belong.
The Importance Of A Family

When we talk about the basic necessities required to sustain life, we focus mainly on food, clothing, and shelter. However, we forget to talk about human interaction. Believe it or not, all human beings require some sort of human association. Without it, we cannot survive. We slip into extreme depression or resort to suicide as a cure to the loneliness we feel due to the lack of this human feeling. Therefore, we require exposure to our own species. Man cannot survive in a solitary unit.
Family is your primary exposure to the same species as you. It is the most basic level of human recognition. A child begins to develop a sense of self-concept by comparing himself to his family. Therefore, a family is essential for the very building of your personality. Family teaches you your first lessons in everything, be it responsibility, forgiveness, letting go of petty fights or caring about others. One cannot stress the importance of having a family anymore. And this is the true meaning of family.
Family Bond Matters
Man is a social animal. Ever since the beginning of time, man has required an association with emotional make-up designed similarly to their own. Basically, we all have an innate need to connect with our own species. Family is one of the major factors that fulfill this necessity.
The need for love and validation is literally a human necessity. Family is that one body that will willingly fulfil those needs. A family with an unbreakable bond can be challenged but never severed. No matter how bad the times are, your true family will be within a mere arm’s reach. They’ll stand ready to help you fight your battles and guide you on the long path of life. After all, a family is what helps a person make their life worth living, and we should value the true meaning of family. For many people, the best approach to life when it comes to the importance of family is a family approach or being family-oriented. So what is family oriented meaning?
Family Oriented Meaning

A family-oriented person thinks profoundly about each family member and cares for them; besides ensuring that his family holds importance in his life, they make them feel seen and heard and accept them for who they are. In other words, family-oriented means putting your family first. In a family-oriented system, you value your family’s feelings, decisions, and, most importantly, thoughts. Always appreciate your bond with them and put them first on your priority list. Moreover, a family-oriented approach is important for personal well-being. It helps to grow professionally, spiritually, physically, and emotionally. So when you make a decision, you ensure that you made your decision while considering your parents’ and families’ feelings. A family-oriented system teaches respect and cares toward family members; it provides support in difficult times. Again, it is a positive trait that enhances personal beliefs and morals.
What Does It Mean To Be “Family-Oriented” In Today’s World?

The traditional concept of family-oriented work has evolved as both men and women work and devote time to their families. The family-oriented concept was different a few decades ago than it is now. Women at the time had strong family ties and preferred not to work, stay at home, looking after all household chores; their primary objective was to take care of their family. In contrast, family-oriented men worked to support their families. However, with time, the family-oriented concept has changed; now, both men and women work to support their families, sharing the load equally. Today’s men have surpassed the socially perceived meaning of family-oriented; they work, look after their kids when needed, and treat their partners equally. Women are balancing both home and work, maintaining their work-life balance, and proving that their professional life will not affect their values towards the family.
Are You Family-Oriented? What Does It Mean To Be Family-Oriented To You?

The family-oriented concept may vary depending on a person’s values, ideas, and way of thinking. A family-oriented person places their family and close relationships first and foremost. They strongly rely on the family to make decisions, and they prioritize their family’s needs over their own. Furthermore, these people emphasize family values and morals more than anything else. In my opinion, it’s good to be family-oriented. Prioritizing your family first is nothing to be ashamed of, so always prioritize your family. For this reason, always consider ways to become more family-oriented. If your family has grown estranged from you, express your love and appreciation to them before it’s too late.
How To Build A Strong Relationship Within Your Family

Every relationship blossoms on the basis of trust. If your child begins to trust you fully and completely at an early stage, the odds are, they’ll still be that connected to you in their teenage stage.
Build Trust
Getting someone as pure as a little child to trust you is easy. What makes it hard is to maintain that trust as they grow up. That means their secrets should remain secrets, no matter how silly they may seem. That means you should be able to make time to hear them out, no matter how bad the work is. This also means being able to trust your child to tell the truth, no matter how fishy things may seem.
Trust is like a spider’s web. You invest all your time and effort trying to build it up, and one small mistake may ruin it all. Trust is fragile and complicated and when you try to build it up again, it won’t ever be the same. Something as delicate and exquisite as trust must be protected and treasured. Apart from this, there are certain things you should do as parents in order to create smooth compatibility within your family. All you need to do to set the gears going is to facilitate contact among the different members of your family.
Spend Time
Sit together and plan to spend quality time with your family; organize family get-togethers, family dinners, karaoke nights, and family game nights where you all sit and sing together or play a board game and whatnot. This will help the family get to know each other better.
You can also have daily talk sessions where you all leave everything aside and just talk to each other about any random thing for at least 15 minutes. This will help you think of the people in your family as individual people and not just members of a family. For example, kids think of their mothers only as mothers and they often fail to recognize that their mother is a separate entity, who has certain likes, dislikes, opinions, or problems. It helps family members to disengage from their own personal bubbles and step into others’ shoes.
How Does A Family Affect Teenagers?

Most teenagers stop feeling this sense of familiarity with their parents once they start growing up. They lose that confidence and trust that they once had in their parents and begin to search for a family amongst their peers. While this is healthy, “normal”, one might say, it does play a major role in a teenager’s life. Making friends that seem as close as a family is a great thing, but not when you begin to push away people who truly care about you.
All of us experienced that one stage in life, where your own family embarrassed or irritated you. Most of these experiences are direct results of parents attempting to connect with their children. While they mean well, the method they use to make this connection can often result in uncomfortable situations for teenagers.
Parents try to adhere to teenage trends thinking that by doing so, their children will be more receptive to their attention. Parents should try to dress, talk and behave in such a way that give a sense of belonging and understanding to the children. In an attempt to befriend their children, parents lose out on their primary goal: preparing their children for the tough future they have to face.
However, this usually has negative consequences, wherein children start to think of their parents as a source of embarrassment, rather than someone they look up to.
A strong connection can be maintained among parents and their children if there is an undisputed understanding within them. Parents and children can be the best of friends if they trust and understand each other, it should be the parents’ duty to rebuke as well as reform.
Also Read: For every single person in the world, a family is everything!. Celebrate your family love with these family quotes.
A group of people, usually of the same blood (but do not have to be), who genuinely love, trust, care about, and look out for each other. REAL family is a bondage that cannot be broken by any means.
————
I’m angry. I’m bitter. I’m sad. I’m heartbroken.
The best part? They aren’t. They’re fine…
After my grandfather died in November, I lost people I considered family.
They decided that money and objects were more important than keeping in touch and love.
So the word “family” has an entirely different meaning to me now.
I used to be close with one of my Uncles until my Grandfather grew ill. This fear… these ideas.. spread in his mind that my Mother would some how take everything from him after their father died. I still don’t understand how this even started. I guess there was a distrust between the siblings, which spread to the cousins, which intern leaves me abandoned. My Mother’s side of the “family” no longer is what you’d call a family. Just because they are blood does not mean they are family. Sure, I have a blood relation to them through genetics, but family? No. They’ve lied to me, said they’d keep in touch, finish writing Christmas cards, invite me to their weddings, but I’m still empty. They’ve blocked me on Instagram and Facebook, cut contact and I’m still so incredibly heartbroken.
I wish I could ask them what I did wrong.. what did I do to deserve this excommunication. A cousin once told me, “we are not our parents. what’s going on with them is their own and we have our own lives.” This statement is incredibly true, too bad she didn’t stay true to her own words. I understand her parents are important to her, but apparently their influence and anger has lead her to ditch me. This is true for my other cousins as well. I’m the only only-child on both sides of my family. All my cousins have siblings. So my cousins, growing up, to me were like brothers and sisters. I’ve lost them all.
I’ve tried so fucking hard to stay in touch, update them about our grandparents, see them whenever I could, let them know whats going on, wish them a happy birthday or a Merry Christmas. But not anymore. There will be none of that.
I was the better person the day of my Grandfather’s funeral. I was the one who approached them, hugged them, cried with them, mourned with them. It was all a front on their part because after the funeral, and they all went back home, I was no one to them.
I’m working through this in therapy. It’s still hard. It’s been months. Especially since I’m still mourning the loss of my Grandparents.
Through all of this, I learned that you get the pick your family.
You get to decide who your family is.
My family are my best friends. The ones who’ve been with me since my grandmother died, the ones who came to visit me while I was in the hospital, the ones who were with me when my fiance was in the hospital, the ones who knew when something was wrong just by the look on my face, the ones who can celebrate life with me, my family. I can count them on two hands. That’s how small and how close my new and real family is.
The word family means trust, love, loyalty, compassion, unconditional.
Fuck the rest.
Sociologists do not agree on one standard definition of ‘the family’.
Functionalist sociologists traditionally used narrow definitions of the family, in which the family unit had to consist of a man and a woman in a committed sexual relationship living together with their children.
More contemporary Postmodern sociologists prefer much broader definitions of the family which extend the concept to include anyone an individual thinks of as being ‘part of the family’, such as friends or even pets.
There is no ‘right’ or ‘wrong’ definition of the family, but you do need to know how sociologists define the family to really understand their perspective on the family, and to be able to evaluate the different perspectives.
The rest of this introductory post explores how the concept of ‘the family’ has been used by different sociologists, and aims to get you thinking about what the family is.
It has been written as an introduction the Families and Households module for A-level sociology, AQA focus.
The Functionalist definition of the family
Functionalist Sociologist George Peter Murdock used the following definition of the family as a starting point in his classic cross national study of families in more than 250 societies.
‘A social group characterised by common residence, economic cooperation and reproduction. It includes adults of both sexes, at least two of whom maintain a socially approved sexual relationship, and one or more children, own or adopted, of the sexually cohabiting adults’ (Murdock, 1949).

Today, many Sociologists criticise the above definition of the family as being too narrow because (both today and historically) too many groups of people who regard themselves as a family would not be included in the above definition, such as reconstituted or step-families and same sex families.
For example, The Oxford English Dictionary defines ‘the family’ as ‘a group consisting of one or two parents and their children’. (1)
The above definition includes step-families, single parent families and doesn’t even mention sex or sexual orientation of the parents, so includes same-sex families too.
One way around the problem of defining a family is to distinguish carefully between different ‘family arrangements’ when we discuss them. It is also generally good practice to define your concepts tightly when writing and essay or before conducting research.
There is nothing wrong with limiting your research or analysis to just one specific type of family below, you just need to make sure you are clear about limiting your discussion. (It’s often necessary to focus more tightly just for the sake of time!)
Different types of family
Some of the most common family types in modern Britain include.
The Nuclear Family – two parents with biological children living in one household.
The reconstituted family – two partners living in one household sharing parental duties for one or more children, but only one of them is the biological parent.
The single parent family – one adult with one or more children living in one household
The extended family – where relatives such as uncles/ aunts or grandparents reside permanently in the same household as those making up the nuclear family.
Postmodern definitions of the family
Because of the diversity within family life in contemporary Britain, post-modern thinkers suggest that it is better to use a broader definition of ‘the family’, which includes a range of family types – one suggested definition of the family is ‘a group of people who are related by either blood or marriage/ similar form of committed relationship’
Because of the problems of defining the family it is often easier to analyse families in terms of households (NB – The module you’re all studying is called families and households, we just tend to abbreviate it to the ‘families’ module)
A household is much easier to define than a family – A household is simply a group of people who share a residence in common and share such things as meals, bills, facilities or chores, or one person living alone. Of course, families can spread themselves across many households!
Case study: the Rainbow Family of Light
Have a look at the case study below, do you think this group of people is a ‘family’?

The Rainbow Family was created out of the Vortex gathering in Oregon from August 28 to September 3, 1970. Inspired in large part by the first Woodstock Festival.
Those who attend Rainbow Gatherings usually share an interest in intentional communities, ecology and new age spirituality. Attendees refer to one another as “brother”, “sister”, or the gender neutral term, “sibling.” Attendance is open to all interested parties and decisions are reached through group meetings leading to some form of group consensus.
The organization is a loose, international affiliation of individuals who have a stated goal of trying to achieve peace and love on earth. There are no official leaders or structure, no official spokespersons, and no formalized membership. Strictly speaking, the only goals are set by each individual, as no individual can claim to represent all Rainbows in word or deed.
You might also like this video…
I think it shows one of the activities these people get up to during their gatherings, a good old sing song!
Question: is the family rainbow of light a family?
Think carefully about this – if you do then it means that practically any group of friends with close emotional ties should be called a family, but is this really what me mean when we use the term ‘family’? Or should sociologists limit themselves to studying families in the more traditional sense of the word?
Defining the family… why it matters…
You can only really get your head around perspectives on the family if you understand how different perspectives define the family differently!
Ultimately, how you define the family will determine how you conclude any essay within the families and households module!
Sources
(1) The Oxford English Dictionary definition of the family.
I ran into a stranger as he passed by,
«Oh excuse me please,» was my reply.
He said, «Please excuse me too;
I wasn’t watching for you.»
We were very polite, this stranger and I.
We went on our way saying good-bye.
But at home a difference is told,
How we treat our loved ones, young and old.
Later that day, cooking the evening meal,
My son stood beside me very still.
As I turned, I nearly knocked him down.
«Move out of the way,» I said with a frown.
He walked away, his little heart broken.
I didn’t realize how harshly I’d spoken.
While I lay awake in bed,
God’s still small voice came to me and said,
«While dealing with a stranger, common courtesy you use,
But the children you love, you seem to abuse.
Go and look on the kitchen floor,
You’ll find some flowers there by the door.
Those are the flowers he brought for you.
He picked them himself: pink, yellow and blue.
He stood very quietly not to spoil the surprise,
And you never saw the tears that filled his little eyes.»
By this time, I felt very small,
And now my tears began to fall.
I quietly went and knelt by his bed;
«Wake up, little one, wake up,» I said.
«Are these the flowers you picked for me?»
He smiled, «I found ’em, out by the tree.
I picked ’em because they’re pretty like you.
I knew you’d like ’em, especially the blue.»
I said, «Son, I’m very sorry for the way I acted today;
I shouldn’t have yelled at you that way.»
He said, «Oh, Mom, that’s okay.
I love you anyway.»
I said, «Son, I love you too,
And I do like the flowers, especially the blue.»
Are you aware that if we died tomorrow, the company that we are working for could easily replace us in a matter of days. But the
family we left behind will feel the loss for the rest of their lives?
And come to think of it, we pour ourselves more into work than to our own family; an unwise investment indeed, don’t you think?
So what is behind the story? Do you know what the word FAMILY means?
FAMILY = (F)ATHER (A)ND (M)OTHER, (I) (L)OVE (Y)OU!
Pass this on to everyone that you care about.
Stories / Articles 2001
More Stories For Life
Princeton’s WordNetRate this definition:4.0 / 4 votes
-
family, household, house, home, menagenoun
a social unit living together
«he moved his family to Virginia»; «It was a good Christian household»; «I waited until the whole house was asleep»; «the teacher asked how many people made up his home»
-
family, family unitnoun
primary social group; parents and children
«he wanted to have a good job before starting a family»
-
class, category, familynoun
a collection of things sharing a common attribute
«there are two classes of detergents»
-
family, family line, folk, kinfolk, kinsfolk, sept, phratrynoun
people descended from a common ancestor
«his family has lived in Massachusetts since the Mayflower»
-
kin, kinsperson, familynoun
a person having kinship with another or others
«he’s kin»; «he’s family»
-
familynoun
(biology) a taxonomic group containing one or more genera
«sharks belong to the fish family»
-
syndicate, crime syndicate, mob, familynoun
a loose affiliation of gangsters in charge of organized criminal activities
-
family, fellowshipnoun
an association of people who share common beliefs or activities
«the message was addressed not just to employees but to every member of the company family»; «the church welcomed new members into its fellowship»
WiktionaryRate this definition:3.7 / 6 votes
-
familynoun
A father, mother and their sons and daughters; also called nuclear family.
Our family lives in town.
-
familynoun
A group of people related by blood, marriage, law, or custom.
crime family, Mafia family
-
familynoun
A kin, tribe; also called extended family.
-
familynoun
A rank in the classification of organisms, below order and above genus; a taxon at that rank.
Magnolias belong to the family Magnoliaceae.
-
familynoun
A group of people who live together, or one that is similar to one that is related by blood, marriage, law, or custom, or members of one’s intimate social group.
-
familynoun
Any group or aggregation of things classed together as kindred or related from possessing in common characteristics which distinguish them from other things of the same order.
-
familynoun
A group of instrument having the same basic method of tone production.
-
familynoun
A group of languages believed to have descended from the same ancestral language.
-
familyadjective
Suitable for children and adults.
-
familyadjective
Conservative, traditional.
The cultural struggle is for the survival of family values against all manner of atheistic amorality.
-
familyadjective
Homosexual.
I knew he was family when I first met him.
-
Etymology: familia, from famula.
Samuel Johnson’s DictionaryRate this definition:0.0 / 0 votes
-
Familynoun
Etymology: familia, Latin; famille, French.
1. Those who live in the same house; household.
The night made little impression on myself; but I cannot answer for my whole family; for my wife prevailed on me to take somewhat.
Jonathan Swift.2. Those that descend from one common progenitor; a race; a tribe; a generation.3. A class; a tribe; a species.
There be two great families of things, sulphureous and mercurial, inflammable and not inflammable, mature and crude, oily and watry.
Francis Bacon, Natural History, №. 354.
WikipediaRate this definition:5.0 / 1 vote
-
Family
In the context of human society, a family (from Latin: familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth), affinity (by marriage or other relationship), or co-residence (as implied by the etymology of the English word «family») or some combination of these. The purpose of families is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideally, families would offer predictability, structure, and safety as members mature and participate in the community. In most societies, it is within families children acquire socialization for life outside the family. Additionally, as the basic unit for meeting the basic needs of its members, it provides a sense of boundaries for performing tasks in a heterosexual environment, ideally builds a person into a functional adult, transmits culture, and ensures continuity of humankind with precedents of knowledge.
Anthropologists generally classify most family organizations as matrifocal (a mother and her children); conjugal (a wife, her husband, and children, also called the nuclear family); avuncular (for example, a grandparent, a brother, his sister, and her children); or extended (parents and children co-reside with other members of one parent’s family).
Members of the immediate family may include spouses, parents, grandparents, brothers, sisters, sons, and daughters. Members of the extended family may include aunts, uncles, cousins, nephews, nieces, and siblings-in-law. Sometimes these are also considered members of the immediate family, depending on an individual’s specific relationship with them. Sexual relations among the members are regulated by rules concerning incest such as the incest taboo.
The word «families» can be used metaphorically to create more inclusive categories such as community, nationhood, global village, and humanism.
The field of genealogy aims to trace family lineages through history.
The family is also an important economic unit studied in family economics.
Webster DictionaryRate this definition:3.7 / 3 votes
-
Familyverb
the collective body of persons who live in one house, and under one head or manager; a household, including parents, children, and servants, and, as the case may be, lodgers or boarders
-
Familyverb
the group comprising a husband and wife and their dependent children, constituting a fundamental unit in the organization of society
-
Familyverb
those who descend from one common progenitor; a tribe, clan, or race; kindred; house; as, the human family; the family of Abraham; the father of a family
-
Familyverb
course of descent; genealogy; line of ancestors; lineage
-
Familyverb
honorable descent; noble or respectable stock; as, a man of family
-
Familyverb
a group of kindred or closely related individuals; as, a family of languages; a family of States; the chlorine family
-
Familyverb
a group of organisms, either animal or vegetable, related by certain points of resemblance in structure or development, more comprehensive than a genus, because it is usually based on fewer or less pronounced points of likeness. In zoology a family is less comprehesive than an order; in botany it is often considered the same thing as an order
-
Etymology: [L. familia, fr. famulus servant; akin to Oscan famel servant, cf. faamat he dwells, Skr. dhman house, fr. dhto set, make, do: cf. F. famille. Cf. Do, v. t., Doom, Fact, Feat.]
FreebaseRate this definition:0.0 / 0 votes
-
Family
In human context, a family is a group of people affiliated by consanguinity, affinity, or co-residence. In most societies it is the principal institution for the socialization of children. Anthropologists most generally classify family organization as matrilocal; conjugal; and consanguineal in which parents and children co-reside with other members of one parent’s family.
There are also concepts of family that break with tradition within particular societies, or those that are transplanted via migration to flourish or else cease within their new societies. As a unit of socialization the family is the object of analysis for sociologists of the family. Genealogy is a field which aims to trace family lineages through history. In science, the term «family» has come to be used as a means to classify groups of objects as being closely and exclusively related. In the study of animals it has been found that many species form groups that have similarities to human «family»—often called «packs.» Sexual relations among family members are regulated by rules concerning incest such as the incest taboo.
Chambers 20th Century DictionaryRate this definition:4.0 / 1 vote
-
Family
fam′i-li, n. the household, or all those who live in one house under one head, including parents, children, servants: the children of a person: the descendants of one common progenitor: race: honourable or noble descent: a group of animals, plants, languages, &c. more comprehensive than a genus.—ns. Fam′ilism, the family feeling; Fam′ilist, one of the 16th-cent. mystical sect known as the Family of Love, which based religion upon love independently of faith.—Family Bible, a large Bible for family worship, with a page for recording family events; Family coach, a large carriage able to carry a whole family; Family man, a man with a family: a domesticated man.—Be in the family way, to be pregnant; In a family way, in a domestic manner. [L. familia—famulus, a servant.]
U.S. National Library of MedicineRate this definition:0.0 / 0 votes
-
Family
A social group consisting of parents or parent substitutes and children.
The Foolish Dictionary, by Gideon WurdzRate this definition:5.0 / 1 vote
-
FAMILY
Originally a wife and several children, a matter of pride to the possessor. Now obsolete among the careful, or confined to the wife, a bull pup and a canary bird.
Editors ContributionRate this definition:0.0 / 0 votes
-
family
A group of people who live at a house, dwelling or property as a group or unit.
Family can take so many forms in 2020, what is important is that they act and feel like a family.
Submitted by MaryC on February 16, 2020
-
Family
Family is a group of people by blood, adoption, marriage and friends
Monogamy
Polygamy etcSubmitted by Lazolk on October 15, 2020
EntomologyRate this definition:0.0 / 0 votes
-
Family
a division of classification including a number of genera agreeing in one or a set of characters and so closely related that they are apparently descended from one stem: opinionative and indicated by the termination idae.
Matched Categories
-
- Association
- Biology
- Collection
- Lineage
- Organized Crime
- Taxonomic Group
British National Corpus
-
Spoken Corpus Frequency
Rank popularity for the word ‘Family’ in Spoken Corpus Frequency: #234
-
Written Corpus Frequency
Rank popularity for the word ‘Family’ in Written Corpus Frequency: #511
-
Nouns Frequency
Rank popularity for the word ‘Family’ in Nouns Frequency: #36
How to pronounce Family?
How to say Family in sign language?
Numerology
-
Chaldean Numerology
The numerical value of Family in Chaldean Numerology is: 9
-
Pythagorean Numerology
The numerical value of Family in Pythagorean Numerology is: 3
Examples of Family in a Sentence
-
Abdul Baseer Nomand:
Everyone is missing his family, his country, and this is very hard, (It’s) so difficult for people far away from their country, from their neighbors, from their relatives.
-
Minnesota Sen. Amy Klobuchar:
Bernie Sanders makes me nervous, but all the young people in my family love Bernie Sanders.
-
William James:
A genius is the man in whom you are least likely to find the power of attending to anything insipid or distasteful in itself. He breaks his engagements, leaves his letters unanswered, neglects his family duties incorrigibly, because he is powerless to turn his attention down and back from those more interesting trains of imagery with which his genius constantly occupies his mind.
-
Nenegale Diallo:
But Nash locked the door again and hit her with a chair during one point in the struggle, DNAInfo reported. Police told the website that Nenegale’s sister helped pull Nash off of her and she was able to grab her phone in the struggle, calling her husband, who took around 20 minutes to return home. I took my phone and see my husband’s number first. I pressed the number. I made a loud noise, screaming,’ Please, help me ! Help me ! Call the police !’ then Nenegale Diallo slapped me again. The phone is falling, but I was making noise so my husband could hear the noise. Nash tried to flee the scene, Nenegale Diallo said, but then was attacked by Nenegale Diallo, police said. Nash later died at a hospital. Defense attorney Anthony Michaels said in court this was an attack on Diallo’s family in Nenegale Diallo home. Nenegale Diallo had been arrested once before, but records on the case were sealed, police told DNAInfo. Nenegale Diallo’s Nenegale Diallo. Nenegale Diallo’s been in this country 27 years and never had a problem.
-
Anthony Liccione:
Everyone needs a house to live in, but a supportive family is what builds a home.
Popularity rank by frequency of use
Translations for Family
From our Multilingual Translation Dictionary
- аҭаацәаAbkhaz
- familieAfrikaans
- ቤተሰብ, ዘመድ አዝማድ, ቤተሰቦችAmharic
- familhaAragonese
- أَقَارِب, عَائِلَة, أَهْل, أُسْرَة, أسرةArabic
- পৰিয়ালAssamese
- fəsilə, ailəAzerbaijani
- ғаиләBashkir
- радзі́на, сям’я́Belarusian
- рода, семейство, семеен, семе́йство, групаBulgarian
- পরিবারBengali
- familh, kerentiezh, kerentiad, tiegezhBreton
- família, marieta, familiarCatalan, Valencian
- доьзалChechen
- famigliaCorsican
- rodinný, čeleď, rodinaCzech
- teuluWelsh
- familie, æt, familie-Danish
- Familie, vom anderen Ufer seinGerman
- އާއިލާDivehi
- ƒomeEwe
- οικογένειαGreek
- familia, familioEsperanto
- familia, familiarSpanish
- perekond, pereEstonian
- عائله, خاندان, نزدیکان, همنوا, فامیل, گونه, شاخه, خانوادَه, خویشان, خانوادهPersian
- perhe, suku, heimoFinnish
- ættFaroese
- familleFrench
- teaghlach, dream, fineIrish
- teaghlachScottish Gaelic
- familia, familiarGalician
- પરિવારGujarati
- lught thie, mooinjerManx
- IyaliHausa
- משפחה, משפחתיHebrew
- परिवार, ख़ानदान, बाल-बच्चेHindi
- fanmiHaitian Creole
- család, családi, háziHungarian
- ընտանիքArmenian
- familia, familiarInterlingua
- keluarga, famili, kerabatIndonesian
- ꏤNuosu
- familioIdo
- ættingjar, fjölskylda, skyldmenni, ætt, afkvæmi, ættingiIcelandic
- famigliaItalian
- משפחהHebrew
- 親類, 家庭, 科, 親戚, 家族, 親族Japanese
- brayatJavanese
- ოჯახიGeorgian
- семья, от басы, әулетKazakh
- គ្រួសារ, អំបូរKhmer
- ಆವಳಿ, ಕುಟುಂಬKannada
- 가정, 가족, 家族, 家庭, 친척Korean
- malbatîKurdish
- үй-бүлө, бүлөKyrgyz
- familiaLatin
- amakaGanda
- ຄອບຄົວLao
- šeimyna, šeima, giminėLithuanian
- saime, ģimene, dzimtaLatvian
- род, фамилија, се́мејство, семејство, фами́лија, фамилија́рен, семеенMacedonian
- തറവാട്Malayalam
- овог, гэр бүл, айлMongolian
- परिवारMarathi
- keluarga, famili, rumpunMalay
- familja, familjiMaltese
- မိသားစုBurmese
- परिबारNepali
- familie, gezinDutch
- skeiv, familieNorwegian
- hakʼéí, bił kééhashtʼíinii, hooghan hazʼą́Navajo, Navaho
- familhaOccitan
- ପରିବାରOriya
- бинонтӕOssetian, Ossetic
- ਪਰਿਵਾਰPanjabi, Punjabi
- rodzinny, rodzinaPolish
- کورنۍPashto, Pushto
- família, familiarPortuguese
- famigliaRomansh
- familie, familiarRomanian
- семе́йный, семе́йство, семья́, род, фами́лия, семьяRussian
- कुल, कुलःSanskrit
- خاندانSindhi
- породица, pòrodica, обитељ, obiteljSerbo-Croatian
- පවුලSinhala, Sinhalese
- rodinný, rodinaSlovak
- družina, družinskiSlovene
- familjeAlbanian
- familj, börd, bög, hushållSwedish
- குடும்பம், குடும்பTamil
- వంశ పరంపర, కుటుంబము, కుటుంబంTelugu
- оила, хонавода, хонадонTajik
- ครอบครัวThai
- maşgalaTurkmen
- pamilya, kamag-anakanTagalog
- familya, aile, ocakTurkish
- гаилә, семьяTatar
- ئائىلەUyghur, Uighur
- сім’я́, роди́на, familyUkrainian
- خاندان, پروارUrdu
- oila, xonadonUzbek
- gia tộc, 家庭, gia đinhVietnamese
- famül, familiaVolapük
- famileWalloon
- משפּחה, מישפּאָכעYiddish
Get even more translations for Family »
Translation
Find a translation for the Family definition in other languages:
Select another language:
- — Select —
- 简体中文 (Chinese — Simplified)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese — Traditional)
- Español (Spanish)
- Esperanto (Esperanto)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Deutsch (German)
- العربية (Arabic)
- Français (French)
- Русский (Russian)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- עברית (Hebrew)
- Gaeilge (Irish)
- Українська (Ukrainian)
- اردو (Urdu)
- Magyar (Hungarian)
- मानक हिन्दी (Hindi)
- Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Italiano (Italian)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- Türkçe (Turkish)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ภาษาไทย (Thai)
- Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
- Čeština (Czech)
- Polski (Polish)
- Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Românește (Romanian)
- Nederlands (Dutch)
- Ελληνικά (Greek)
- Latinum (Latin)
- Svenska (Swedish)
- Dansk (Danish)
- Suomi (Finnish)
- فارسی (Persian)
- ייִדיש (Yiddish)
- հայերեն (Armenian)
- Norsk (Norwegian)
- English (English)