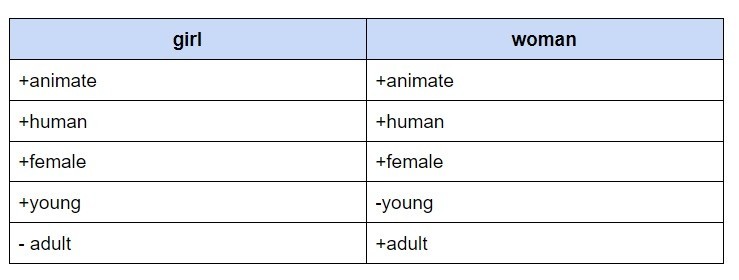
The
definition of the word meaning
presents no less difficulty than the definition of the word itself.
The word meaning
renders the emotion or the concept in the mind of the speaker which
he wants to convey to the listener in the process of
communication. By
concept we understand any discrete unit of human cognition. The
word being a unit of language enters a number of combinations with
other units stands in functional relations to other linguistic signs.
Thus the meaning of the word not only fixes concepts by way of
generalizing and reflecting reality, but it is realized on contexts
and combinations. The meaning of the word is not homogeneous. It is
closely connected with the object it names and the concept it fixes.
It is also connected with the sound form besides it is realized in
different relations with other concepts. There are two main
approaches to word meaning: 1. relative approach, according to which
each linguistic sign (word) gets its meaning only in some semantic
field or paradigmatic relations. 2. the referential or denotational
approach, according to which the meaning of the word is autonomous,
it’s an integral part of the word, though is realized in contexts
and this approach is shown as a triangle (symbol – the word,
concept – thought; referent – object, denoted by the word).
28 Word meaning and motivation.
The
relationship between morphemic structure and meaning is termed
morphological motivation. The main criteria in morphological
motivation is the relationship between morphemes. All one-morpheme
words (look, eat) are non-motivated. Such words as writer, worker are
described as motivated. Phonetic motivation is represented by such
words as swish, boom, splash. Beside grammatical and lexical meanings
some linguists also distinguish the co-called structural meaning,
i.e. words in a sentence are joined together according to some
specific rules (a diggled-boggle, a boggled diggle). Motivation is
the relationship existing between the morpheme or phonemic
composition and the structural pattern of the word, on the one hand,
and its meaning on the other. The words are motivated: 1.
Structurally (a shoe-maker), but sometimes due to the character of
the lexical meaning of a morphological motivation becomes rather
relevant or weak (flower-girl); 2. Phonetically (swish, boom); 3.
Semantically (the dawn of life). Sometimes motivation of the words
may be lost: a) one of the elements of compound words dropped out of
usage (mermaid – русалка,
mere – море);
b) the loss of the primary meaning of the word (spoon – щепка).
34
Homonyms.
Definition, formal classification. Homonyms
are words
which are identical in sound and spelling, or, at least, in one of
these aspects, but different in their meaning.E. g. bank, n. —a
shore,bank, n. —an
institution for receiving, lending, exchanging, and safeguarding
money. ball, n. —a
sphere; any spherical body,ball, n. —a
large dancing party. Homonyms which are the same in sound and
spelling are traditionally termed homonyms
proper. Bean, n.
and been, Past
Part, of to
be are
homophone- they
are the same in sound but different in spelling. Homographs- words
which are the same in spelling but different in sound(lead v – show
smb the way, lead n – a heavy, rather soft metal). When analysing
different cases of homonymy we find that some words are homonymous in
all their forms, i.e. we observe full h. of the paradigms of two or
more different words, e.g., in seal1 —‘a
sea animal’ and seal2 —‘a
design printed on paper by means of a stamp’. When only some of the
word-forms(seal, seals, etc.) are homonymous, whereas others(sealed,
sealing) are not, we can speak of partial
h. — find,
found, found, and found, founded, founded.
.lexico-grammatical
classification of homonyms. Homonyms
may be also classified by the type of meaning into lexical,
lexico-grammatical and grammatical homonyms.
In seal1 n and seal2 n, e.g.,
the part-of-speech meaning of the word and the grammatical meanings
of all its forms are identical (seal [si:l] Common Case Singular,
seal’s [si:lz] Possessive Case Singular for both seal1 and
seal2). The
difference is confined to the lexical meaning only: seal1 denotes
‘a sea animal’,‘the fur of this animal’,etc., seal2—‘a
design printed on paper,the stamp by which the design is made’etc.
So we can say that seal2 and
seal1 are
lexical homonyms because they differ in lexical
meaning.If
we compare seal1—‘a
sea animal’, and (to) seal3—‘to
close tightly, we shall observe not only a difference in the lexical
meaning of their homonymous word-forms but a difference in their
grammatical meanings as well. Identical sound-forms, i.e.
seals[si:lz] (Common Case Plural of the noun) and (he) seals[si:lz]
(third person Singular of the verb) possess each of them different
grammatical meanings. As both grammatical and lexical meanings differ
we describe these homonymous word-forms as lexico-grammatical. Modern
English abounds in homonymic word-forms differing in grammatical
meaning only. e.g. brother’s —brothers —the
Possessive Case Singular and the Common Case Plural. It
may be easily observed
that grammatical
homonymy is
the homonymy of different
word-forms of one and the same word.
Sources
of homonyms. The
two main sources of h. are:1.diverging
meaning development
of a polysemantic word. This process can be observed when different
meanings of the same word move so far away from each other that they
come to be regarded as two separate units.
Ex.: flower and flour originally
were one wordmeaning ‘the flower’ and ‘the finest part of
wheat’.2.convergent
sound development of
two or more different words. Ex, OE. ic
and OE. еаzе have
become identical in pronunciation(ME. I
and eye). A number of lexico-grammatical homonyms appeared as a
result of convergent sound development of the verb and the noun
(MnE.love — (to)
love and OE. lufu
— lufian). Words
borrowed from other languages may through phonetic convergence become
homonymous. ONorse. ras
and Fr. race
are homonymous in Modern English (race1 [reis]
— ‘running’ and race2 [reis] —
‘a distinct
ethnical stock’).
35
Types of
Synonyms. The role of synonyms it the development of the
vocabulary.The
only existing classification system for synonyms was established by
Academician Vinogradov, the famous Russian scholar. In his
classification system there are three types of
synonyms: ideographic (which
he defined as words conveying the same concept but differing in
shades of meaning), stylistic (differing
in stylistic characteristics) and absolute (coinciding
in all their shades of meaning and in all their stylistic
characteristics) A more modern and a more effective approach to the
classification of synonyms may be based on the definition describing
synonyms as words differing in connotations.
36
The themantic
groups and semantic fields. Classification
of vocabulary items into thematic
groups is
based on the co-occurrence of words in certain repeatedly used
contexts. In linguistic contexts co-occurrence maу be
observed on different levels. On the level of word-groups the
word question, for
instance, is often found in collocation with the verbs raise,
put forward, discuss, etc.,
with the adjectives urgent,
vital, disputable and
so on. The verb
accept occurs
in numerous contexts together with the nouns proposal,
invitation, plan and
others.As a rule, thematic groups deal with contexts on the level of
the sentence. Words in thematic groups are joined together by common
contextual associations within the framework of the sentence and
reflect the interlinking of things or events. Common contextual
association of the words,
e.g. tree—grow—green;journey—train—taxi—bags—ticket
or sunshine—brightly—blue—sky, is
due to the regular co-occurrence of these words in a number of
sentences. Words making up a thematic group belong to different parts
of speech and do not possess any common denominator of meaning.
Contextual associations formed by the speaker of a language are
usually conditioned by the context of situation which necessitates
the use of certain words. When watching a play, for example, we
naturally speak of the actors who act the
main parts, of
good (or bad)
staging of
the play, of the wonderful scenery and
so on. When we go shopping it
is usual to speak of the prices, of the
goods we buy, of the
shops. Words
may be classified according to the concepts underlying their meaning.
This classification is closely connected with the theory of
conceptual or semantic
fields.
By the term “semantic fields” we understand closely knit sectors
of vocabulary each characterised by a common concept. For example,
the words blue,
red, yellow, black, etc.
may be described as making up the semantic field of colours, thewords
mother, father, brother, cousin, etc.
— as members of the semantic field.In
practical lang. learning thematic groups are often listed under
various headings, e. g. “At the Theatre”, “At School”,
“Shopping”, and are often found in textbooks and courses of
conversational English.The members of the semantic fields are not
synonyms but all of them are joined together by some common semantic
component — the
concept of colours or the concept of kinship, etc. It is argued that
we cannot possibly know the exact meaning of the word if we do not
know the structure of the SF to which the word belongs, the number of
the members and the concepts covered by them.It should also be
pointed out that different meanings of polysemantic words make it
possible to refer the same word to different lexico-semantic groups.
Thus, e.g. make in
the meaning of ‘construct’ is naturally a member of the same
lexico-semantic group as the verbs produce,
manufacture, etc , whereas
in the meaning of compel it
is regarded as a member of a different lexico-semantic group made up
by the verbs force,
induce.
37
Semantic
contrasts and antonymy. General problems(contrast, contradiction)The
term antonyms indicate words of the same category of parts of speech
which have contrasting meanings. And nearly identical in distribution
associated and used together so that their implication aspects render
contrary or contradictory notion:love-hate, early-late. The
opposition here is obvious, each component means the opposite of the
other. Almost every word can have synonyms comparatativly, few have
antonyms. Antonyms apposition is characterized of a)qualitative
adj-s:new-old, big-little. b)word derived from word qualitative
adj-s:gladly-sadly, sadness-gladness. c)words concern with feeling or
state and their derivatives:triumph-disaster, hope-dispair. d)words
denoting directions and position in space: up-down, far-near.
Polysemantic words may have antonyms in some of their meanings and
none in the others. E.g.a shot/long story, a short/tall man. Not so
many years ago antonymy was not universally accepted as a linguistic
problem, and the opposition within antonymic pairs was regarded as
purely logical and finding no reflection in the semantic structures
of these words. The contrast between heat and cold or big and small,
said most scholars, is the contrast of things opposed by their very
nature. Nowadays most scholars agree that in the semantic structures
of all words, which regularly occur in antonymic pairs, a special
antonymic connotation can be singled out. We are so used to coming
across hot and cold together, in the same contexts, that even when we
find hot alone, we cannot help subconsciously registering it as not
cold, that is, contrast it to its missing antonym. Contradictions
represent the type of semnantic relantions that exist between pairs
like dead and alive) single and married.
Classification
of antonyms. Depending
on the type of polarity ant-s are usually classified into absolute
and derivational. Absolute ant-s are words regularly contrasted as
homogeneous members connected by copulative, disjunctive and
adversative conjunctions or parallel constructions: good or bad,
right or wrong. Derivational a. are formed with the help of affixes
dis, un, less, ful:selfish-unselfish, useless-useful. The
contradiction is expressed morphologically and symantically too.
Absolute ant-s can be arranged into a series according to increasing
difference in one of the qualities:young-middle aged-old;
love-resentment-hate. A-s mostly form pairs not groups.
38
Connotations
of synonyms.I.The
connotation of degree
or intensity can
be traced in such groups of synonyms as to surprise — to astonish —
to amaze — to astound; to shout — to yell — to bellow — to roar.
IIconnotation of duration:
to stare — to glare — to gaze — to glance — to peep — to peer. all
the synonyms except to glance denote a lasting act of looking at smb
or smth, whereas to glance describes a brief, passing look. IIIThe
synonyms to stare — to glare — to gaze are differentiated from the
other words of the group by emotive connotations,
and from each other by the nature of the emotion they
imply. In the group alone — single — lonely — solitary, the adjective
lonely also has an emotive connotation. IV.
The evaluative connotation
conveys the speaker’s attitude towards the referent, labelling it as
good or bad. So in the group well-known — famous — notorious —
celebrated, the adjective notorious bears a negative evaluative
connotation and celebrated a positive one. V.The causativeconnotation
can be illustrated by the examples to sparkle and to glitter given
above: one’s eyes sparkle with positive emotions and glitter with
negative emotions. VI.The connotation of manner can
be singled out in some groups of verbal synonyms. The verbs to stroll
— to stride — to trot — to pace — to swagger — to stagger — to
stumble all denote different ways and types of walking,. VII.The
verbs to peep and to peer is the connotation of attendant
circumstances.
VIII.The synonyms pretty, handsome, beautiful have been mentioned as
the ones which are more or less interchangeable. Yet, each of them
describes a special type of human beauty: beautiful is mostly
associated with classical features and a perfect figure, handsome
with a tall stature, a certain robustness and fine pro portions,
pretty with small delicate features and a fresh complexion. This
connotation may be defined as the connotation of attendant
features.
IX.Stylistic connotations.
Examples :Meal. Snack, bite (coll.), snap (dial.), repast,
refreshment, feast (formal).
39
Sources
of synonyms. Euphemisms. 1)borrowings:
to ask(eng)-to question(fr)-interrogate(lat); to
gather(eng)-assemble(fr)-collect(lat) 2)dialects or
variations(amer)radio-(british)wireless; (irish)lass-(eng)girl; 3)new
formations with a post positive: to postphone-to put off, to
return-to come back, to betray-to give a way; 4)word-building by
means of :a)synonymas, affixes:changeable-changefull; b) composition
and affixation:trader-tradesman; c)affixation and
conversion:saying-say; 5) by means of shortening:microfone-mike,
doctor-doc; 6) a special groups of synonymas is comprised by the
Euphemisms. There are words in every language which people
instinctively avoid because they are considered indecent, indelicate,
rude, too direct or impolite. As the «offensive» referents,
for which these words stand, must still be alluded to, they are often
described in a round-about way, by using substitutes called
euphemisms. The
word lavatory has
produced many euphemisms:powder
room,washroom,restroom,retiring room,(public) comfort station,
ladies’ (room),gentlemen’s (room),water-closet,w.c., public
conveniences and
even Windsor. Pregnancy: in
an interesting condition,in a delicate condition,in the family
way,with a baby coming,(big) with child,expecting. Drunk:
intoxicated (form.),under the influence (form.),tipsy,mellow, fresh,
high, merry, flustered, overcome, full (coll.), drunk as a lord
(coll.), drunk as an owl (coll.), boiled (sl.), fried (sl.), tanked
(sl.), tight (sl.), stiff (sl.), pickled (sl.), soaked (sl.), three
sheets to the wind (sl.), high as a kite (sl.), half-seas-over (sl.),
etc. All the euphemisms that have been described so far are used to
avoid the so-called social taboos. Their use is inspired by social
convention. Euphemisms
may be:a) based on some social or ethical standard of behavior not to
hurt other people’s feelinfs: poor-underprivilaged
disaipled-invalid; 2) the requinment of style:to die-to join the
majority, to pass away, to go west; 3)religious taboo:the name of
God-good heavens.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Every teacher wonders how to teach a word to students, so that it stays with them and they can actually use it in the context in an appropriate form. Have your students ever struggled with knowing what part of the speech the word is (knowing nothing about terminologies and word relations) and thus using it in the wrong way? What if we start to teach learners of foriegn languages the basic relations between words instead of torturing them to memorize just the usage of the word in specific contexts?
Let’s firstly try to recall what semantic relations between words are. Semantic relations are the associations that exist between the meanings of words (semantic relationships at word level), between the meanings of phrases, or between the meanings of sentences (semantic relationships at phrase or sentence level). Let’s look at each of them separately.
Word Level
At word level we differentiate between semantic relations:
- Synonyms — words that have the same (or nearly the same) meaning and belong to the same part of speech, but are spelled differently. E.g. big-large, small-tiny, to begin — to start, etc. Of course, here we need to mention that no 2 words can have the exact same meaning. There are differences in shades of meaning, exaggerated, diminutive nature, etc.
- Antonyms — semantic relationship that exists between two (or more) words that have opposite meanings. These words belong to the same grammatical category (both are nouns, adjectives, verbs, etc.). They share almost all their semantic features except one. (Fromkin & Rodman, 1998) E.g.
- Homonyms — the relationship that exists between two (or more) words which belong to the same grammatical category, have the same spelling, may or may not have the same pronunciation, but have different meanings and origins. E.g. to lie (= to rest) and to lie (= not to tell the truth); When used in a context, they can be misunderstood especially if the person knows only one meaning of the word.
Other semantic relations include hyponymy, polysemy and metonymy which you might want to look into when teaching/learning English as a foreign language.
At Phrase and Sentence Level
Here we are talking about paraphrases, collocations, ambiguity, etc.
- Paraphrase — the expression of the meaning of a word, phrase or sentence using other words, phrases or sentences which have (almost) the same meaning. Here we need to differentiate between lexical and structural paraphrase. E.g.
Lexical — I am tired = I am exhausted.
Structural — He gave the book to me = He gave me the book.
- Ambiguity — functionality of having two or more distinct meanings or interpretations. You can read more about its types here.
- Collocations — combinations of two or more words that often occur together in speech and writing. Among the possible combinations are verbs + nouns, adjectives + nouns, adverbs + adjectives, etc. Idiomatic phrases can also sometimes be considered as collocations. E.g. ‘bear with me’, ‘round and about’, ‘salt and pepper’, etc.
So, what does it mean to know a word?
Knowing a word means knowing all of its semantic relations and usages.
Why is it useful?
It helps to understand the flow of the language, its possibilities, occurrences, etc.better.
Should it be taught to EFL learners?
Maybe not in that many details and terminology, but definitely yes if you want your learners to study the language in depth, not just superficially.
How should it be taught?
Not as a separate phenomenon, but together with introducing a new word/phrase, so that students have a chance to create associations and base their understanding on real examples. You can give semantic relations and usages, ask students to look up in the dictionary, brainstorm ideas in pairs and so on.
Let us know what you do to help your students learn the semantic relations between the words and whether it helps.
Download Article
Download Article
Maybe you are in the middle of an exam and suddenly come across a word that makes absolutely no sense. This is usually a cue for most people to panic if a dictionary is not handy. But don’t worry! There are several steps you can take to help you figure out the meaning of a word without a dictionary.
-
1
Read the entire sentence. It can be very frustrating to have your reading interrupted by an unknown word. If you are in the middle of an exam or an assignment for school or work, it can also be very stressful. If you can’t reach for a dictionary, take other steps to figure out what the word means.
- Your first step is to go back and re-read the entire sentence. You probably lost track of what your were reading when you stumbled upon the new word.
- Think about the content of the sentence. Do you understand the sentence without using the new word? Or is it incomprehensible?
- Try underlining the unknown word. This will help you separate it from the rest of the sentence.
-
2
Identify words you do understand. You can often use other words in the sentence to help you define the unknown word. Think about what else is happening in the sentence. Hopefully, this will help you figure out whether the unknown word is a noun, verb, or adjective.
- For example, maybe you are looking at a sentence that says, «It was a very sultry day in the middle of the summer.» You probably understand each word except for «sultry».
- Think about what you know about the summer. It is likely that «sultry» has something to do with weather.
- Maybe your biology exam has this sentence, «Many members of the canine family are predators, looking for other animals to eat.» You can surmise that «predators» prey on other animals.
Advertisement
-
3
Look for illustrative examples. Once you have examined the other words in that sentence, you can move on. Start looking at the sentences that follow the unknown word. An author will often give descriptions that can help you figure out the meaning of an unknown word.[1]
- For example, take the sentence, «It was a very sultry day in the middle of summer.» It could be followed by the sentence, «The heat and humidity made it appealing to sit in the shade and drink lemonade.»
- You can now more confidently define «sultry». The descriptive words such as «heat» and «humidity» are further clues that it is a description of the weather.
- Sometimes, the descriptive examples will be right in the original sentence. For example, it could say, «Sultry days are so damp and hot.»
-
4
Think logically. Sometimes, the context clues will not be as clear. You will have to use logic to figure out the word. You can also use experience, or prior knowledge, of the topic.[2]
- For example, maybe a sentence says, «In the antebellum South, many plantation owners kept slaves.» It is likely that «antebellum» is the unknown word.
- The sentence itself does not offer many clues. However, the following sentences are, «But after the Civil War, slavery was outlawed. This was a major change between the two periods.»
- Think about what you know now. You are reading information about two different time periods, right? Before the Civil War and after the Civil War.
- You can now make a pretty logical assumption about the word «antebellum». Based on your experience and reading the following sentences, you know it probably means «before the war».
-
5
Use other context clues. Sometimes an author will offer other types of clues. Look for restatement. This is where the meaning of the word is restated in other words.
- Here is an example of «restatement»: «The pig squealed in pain. The high-pitched cry was very loud.»
- You can also look for «appositives». This is where an author highlights a specific word by placing a further description between two commas.
- This is an example of the use of an appositive: «The Taj Mahal, which is a massive white marble mausoleum, is one of the most famous landmarks in India.
- You may not know the words «Taj Mahal», but the use of appositives makes it clear that it is a landmark.
Advertisement
-
1
Look for a prefix. Etymology is the study of the meanings of words. It also looks at the origins of words, and how they have changed over time. By learning about etymology, you can find new ways to define unknown words without using a dictionary.
- Start by looking at each part of the word in question. It is very helpful to look to see if the word has a common prefix.
- Prefixes are the first part of the word. For example, a common prefix is «anti».
- «Anti» means «against». Knowing this should help you figure out the meanings of words such as «antibiotic» or «antithesis».
- «Extra» is a prefix that means «beyond». Use this to figure out words such as «extraterrestrial» or «extracurricular».
- Other common prefixes are «hyper», «intro», «macro» and «micro». You can also look for prefixes such as «multi», «neo» and «omni».
-
2
Pay attention to the suffix. The suffix are the letters at the end of the word. There are several suffixes in the English language that are common. They can help you figure out what kind of word you are looking at.
- Some suffixes indicate a noun. For example, «ee» at the end of the word almost always indicates a noun. Some examples are «trainee» and «employee».
- «-ity» is also a common suffix for a noun. Examples include «electricity» and «velocity».
- Other suffixes indicate verbs. For example, «-ate». This is used in words such as «create» and «deviate».
- «-ize» is another verb suffix. Think about the words «exercise» and «prioritize».
-
3
Identify root words. A root word is the core word, without a prefix or suffix. Most words in the English language come from either a Latin or Greek root word.[3]
- By learning common root words, you can begin to identify new words more easily. You will also be able to recognize words that have had a prefix or suffix added.
- An example of a root word is «love». You can add many things to the word: «-ly» to make «lovely».
- «Bio» is a Greek root word. It means «life, or living matter». Think about how we have adapted this root word to become «biology», «biography», or «biodegradable».
- The root word mater- or matri- comes from the Latin word mater, meaning mother. By understanding this root, you can better understand the definitions of words like matron, maternity, matricide, matrimony, and matriarchal.
Advertisement
-
1
Keep notes. If you can increase the size of your vocabulary, you will find yourself less likely to encounter unknown words. There are several steps you can take to effectively build your vocabulary. For example, you can start by writing notes.
- Every time you encounter an unfamiliar word, write it down. Then later, when you have access to a dictionary, you can look it up for a precise definition.
- Keep a small pack of sticky notes with you while you read. You can write the unfamiliar word on a note and just stick it on the page to return to later.
- Start carrying a small notebook. You can use it to keep track of words that you don’t know and new words that you have learned.
-
2
Utilize multiple resources. There are a lot of tools that you can use to help you build your vocabulary. The most obvious is a dictionary. Purchase a hard copy, or book mark an online dictionary that you find useful.
- A thesaurus can also be very helpful. It will give you synonyms for all of the new words you are learning.
- Try a word of the day calendar. These handle desk tools will give you a new word to learn each day. They are available online and at bookstores.
-
3
Read a lot. Reading is one of the best ways to increase the size of your vocabulary. Make it a point to read each day. Both fiction and non-fiction will be helpful.
- Novels can expose you to new words. For example, reading the latest legal thriller will likely expose you to some legal jargon you’ve never heard before.
- Read the newspaper. Some papers even have a daily feature that highlights language and explores the meanings of words.
- Make time to read each day. You could make it a point to scroll through the news while you drink your morning coffee, for example.
-
4
Play games. Learning can actually be fun! There are many enjoyable activities that can help you to build your vocabulary. Try doing crossword puzzles.
- Crossword puzzles are a great way to learn new words. They will also stretch your brain by giving you interesting clues to figure out the right word.
- Play Scrabble. You’ll quickly learn that unusual words can often score the most points.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
Is there a list of prefixes/suffixes, or a simple etymology handbook, that I can obtain from the Internet or someplace else?
I’m sure there are many! Check websites like Amazon, Barnes and Noble, or other booksellers who might sell grammar handbooks. You could also try checking your local book stores.
-
Question
How does one find out and understand the formation of words?
If you can recognize the prefixes, suffixes, and anything else that might alter the root word, then you’ll know how the root is being altered. For example, ‘amuse’ is made up of ‘a’ as in ‘not’ and ‘muse’ referring to ponderous thought. Even if you don’t recognize the root ‘muse’ because it’s a more archaic term, you know that the ‘a’ inverses it’s meaning.
-
Question
How can I know the exact meaning of a word using dictionaries from many leanings given?
Substitute each meaning into the sentence where you encountered the word, and see which definition makes the most sense within the context of that sentence.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
-
Keep a notebook. This could be useful if you come across a word that you want to learn later, if you want to list any words that share suffixes or prefixes (both of which are known as «roots», which also include anything that goes into the middle.)
-
Read etymology dictionaries. They are found online and presumably in bookstores if you look hard enough.
-
Make your own notes in your personal English notebook to remember important points later on.
Advertisement
References
About This Article
Article SummaryX
To understand a word without a dictionary, try re-reading the entire sentence to see if the context helps you to find out what the word means. If it’s unclear, try to figure it out by thinking about the meaning of the words you’re familiar with, since the unknown word might have a similar meaning. Additionally, look for common prefixes in words, such as «anti,» which means against, or «extra,» which means beyond. Next, check the following sentences for clues, such as the topic the word is related to. Alternatively, keep a list of unknown words so you can check them in a dictionary at a later date. For tips on how to identify root words and how to learn words by doing crossword puzzles, read on!
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 215,260 times.
Reader Success Stories
-
Aaron Junior
Jul 26, 2016
«This article has really helped me especially finding the meaning of the word using prefixes, suffixes, and word…» more
Did this article help you?
Предложения с «different understandings of»
|
Yes, some people have different understandings of the word country. |
Да, некоторые люди по — разному понимают слово страна. |
|
Our purpose in this dialogue today is to try to do something about that, to try to have a different kind of conversation, to do some listening, some thinking, some understanding . |
Давайте попытаемся сегодня сдвинуть ситуацию с мёртвой точки, попробуем наладить диалог, где участники слышат друг друга, относятся с пониманием . |
|
I mean, it feels like we need a different kind of conversation, one that’s based on — I don’t know, on reason, listening, on understanding , on a broader context. |
Мне кажется, что нам нужен качественно новый диалог, который будет строиться на здравом смысле и понимании более широкого контекста. |
|
And I’m a teacher and a lecturer, and I can actually use this to teach something, because when I give someone else another story, a metaphor, an analogy, if I tell a story from a different point of view, I enable understanding . |
Я учитель и преподаватель, и я действительно могу применить эту методику в преподавании, потому что когда я рассказываю кому — то историю, метафору, аналогию с другой точки зрения, я включаю понимание . |
|
The subject of love is one that has inspired poets, writers, those lucky in love and those who have been passed over by Cupid…Love has been defined as wise, silly, profound, bitter, funny…It seems as if each and one of us has a different understanding of love, or at least the attitude to love varies greatly from person to person. |
Тема любви является той, которая вдохновляла поэтов, писателей, тех, кому везло в любви, и тех, которые были переданы Амуром , Любовь определяется как мудрая, глупая, глубокая, горькая, смешная , Кажется, как будто каждый из нас имеет своё понимание любви, или по крайней мере, отношение к любви сильно варьируется от человека к человеку. |
|
It just means that love has different dimensions, different sides that reflect our understanding of life. |
Это просто означает, что любовь имеет разные размеры, разные стороны, которые отражают наше понимание жизни. |
|
Neuroscientists don’t even have a clear idea of just how many different cell types exist, which is crucial to understanding how they work together. |
Нейробиологи даже не имеют четкого представления о том, сколько существует разных типов нейронов; ответ на этот вопрос важен для понимания совместной работы этих клеток. |
|
If you saw the genome for a mouse or for a human it would look no different than this, but what scientists are doing now is they’re understanding what these do and what they mean. |
Если бы вы увидели геном мыши или человека, он бы вряд ли отличался от этого, но чем сейчас занимаются ученые, они пытаются понять, как это устроено и как это работает. |
|
From these disagreements, there are three viable visions that reflect a different understanding of NATO’s geographic and functional dimensions. |
Из — за этих разногласий есть три разных взгляда, отражающих географические и функциональные пределы НАТО. |
|
Understanding how water molecules arrange themselves on average at different temperatures could shed light on the workings of how they interact in biological systems. |
Если понять, как молекулы воды в среднем ведут себя при разных температурах, можно прояснить, как они взаимодействуют в биологических системах. |
|
As a way to get acquainted with this new world, let’s take a look at all the different ways that yesterday’s announcement could change our understanding of the cosmos. |
Чтобы познакомиться с этим новым миром, давайте взглянем на то, как вчерашнее объявление может изменить наши представления о космосе. |
|
By analyzing the impact driven by different view lengths of your video ad, you get a better understanding of what view lengths offer the best value for driving desired responses. |
Сопоставив продолжительность просмотра видео с его воздействием на зрителя, вы сможете понять, какая продолжительность просмотра обеспечивает желаемый результат. |
|
After the five-hour talks were over, no documents were signed and it appeared that the parties had emerged with a different understanding of what was agreed. |
По результатам пятичасовых переговоров не было подписано никаких документов и создалось впечатление, что стороны по — разному понимают то, о чем они договорились. |
|
Understanding how the stochastic is formed is one thing, but knowing how it will react in different situations is more important. |
Очень важно понимать , как формируется Стохастик, и знать, как он будет реагировать в различных ситуациях. |
|
It is my understanding the great circle transported us to a different world. |
Я считаю, что большое кольцо переносит нас в совсем другой мир. |
|
They trusted you on understanding the language completely and speaking it idiomatically and having a knowledge of the different places. |
Тебе доверяют потому, что ты отлично понимаешь язык и говоришь без запинки и во многих местах побывал в этой стране. |
|
You feel their pain as if its your own pain. But you do have a hard time understanding someone whose approaching from a different perspective. |
Ты чувствуешь их боль как свою, но тебе очень трудно понять кого — то, у кого другая точка зрения. |
|
That seem to be so different , but they can come to an understanding and they can actually work together. |
Они кажутся такими разными, но они могут придти к пониманию и даже могут работать вместе. |
|
Knowing something is different from understanding it. |
Знать и понимать – разные вещи. |
|
But these will finally give way, eventually, to the final phase of acceptance an understanding that what has been lost can never return, and that life can continue although it may be very different . |
Но в конце концов, это приводит к финальной фазе согласия с действительностью.. …главное понять, то, что потеряно, уже не вернуть, и жизнь продолжается, хотя многое изменилось. |
|
In addition to different subjects, rationalists sometimes vary the strength of their claims by adjusting their understanding of the warrant. |
В дополнение к различным предметам рационалисты иногда варьируют силу своих притязаний, корректируя свое понимание ордера. |
|
Rationalists also have different understanding and claims involving the connection between intuition and truth. |
Рационалисты также по — разному понимают и утверждают связь между интуицией и истиной. |
|
I’m having trouble understanding why a default edit summary would ask a user to respond or comment on a different website. |
У меня возникли проблемы с пониманием того, почему резюме редактирования по умолчанию попросит пользователя ответить или прокомментировать другой веб — сайт. |
|
The CMM has thus been used by different organizations as a general and powerful tool for understanding and then improving general business process performance. |
Таким образом, ШМ используется различными организациями в качестве общего и мощного инструмента для понимания и последующего повышения эффективности общих бизнес — процессов. |
|
Other examples may suggest contact between different cultures that is hard to account for with conventional historical understanding . |
Другие примеры могут предполагать контакт между различными культурами, который трудно объяснить с помощью традиционного исторического понимания . |
|
The second major area in semantic analysis is the understanding of how different sentence and textual elements fit together. |
Второй важной областью семантического анализа является понимание того, как различные предложения и текстовые элементы сочетаются друг с другом. |
|
Below are six derivations, all of which are very different and lead to different ways of understanding and extending this theory. |
Ниже приведены шесть выводов, все из которых очень различны и ведут к различным путям понимания и расширения этой теории. |
|
The common modern understanding of a political community as a modern state is quite different from Aristotle’s understanding . |
Общепринятое современное понимание политической общности как современного государства сильно отличается от понимания Аристотеля. |
|
Education aims to help students acquire knowledge and develop skills which are compatible with their understanding and problem-solving capabilities at different ages. |
Образование направлено на то, чтобы помочь студентам приобрести знания и развить навыки, которые совместимы с их пониманием и способностью решать проблемы в разных возрастах. |
|
As SPR biosensors facilitate measurements at different temperatures, thermodynamic analysis can be performed to obtain a better understanding of the studied interaction. |
Поскольку биосенсоры SPR облегчают измерения при различных температурах, термодинамический анализ может быть выполнен для лучшего понимания изучаемого взаимодействия. |
|
I, and many other commenters, have found that the list of Largest Urban Areas does not in fact reflect common understanding of different cities’ sizes. |
Я и многие другие комментаторы обнаружили, что список крупнейших городских районов на самом деле не отражает общего понимания размеров различных городов. |
|
Similarly, other studies illustrate how students construct different understandings from explanation in isolation versus having a first experience with the material. |
Аналогичным образом, другие исследования показывают, как студенты строят различные понимания от объяснения в изоляции по сравнению с первым опытом работы с материалом. |
|
Although the riots were perceived in different aspects, Alvarez argues it brought a greater sense of understanding between Hispanics and blacks. |
Хотя беспорядки воспринимались по — разному, Альварес утверждает, что они принесли большее понимание между латиноамериканцами и черными. |
|
Within the Star Wars narrative, the Jedi and Sith naturally have different self-understandings. |
В рамках повествования о Звездных войнах джедаи и ситы, естественно, имеют разное самопонимание. |
|
This understanding is a hypothesis for why the outcomes later in life are so starkly different . |
Это понимание является гипотезой, объясняющей, почему результаты в дальнейшей жизни так резко отличаются. |
|
An explanation is often underpinned by an understanding or norm that can be represented by different media such as music, text, and graphics. |
Объяснение часто подкрепляется пониманием или нормой, которые могут быть представлены различными средствами массовой информации, такими как музыка, текст и графика. |
|
This method does not give an easy or straightforward understanding of whether a twist rate is relatively slow or fast when bores of different diameters are compared. |
Этот метод не дает простого и однозначного представления о том, является ли скорость закручивания относительно медленной или быстрой при сравнении отверстий разного диаметра. |
|
More generally, teaching a subject forces its evaluation from different perspectives and can provide a deeper understanding . |
В более общем плане преподавание предмета заставляет оценивать его с разных точек зрения и может обеспечить более глубокое понимание . |
|
Potter brought a different understanding of parish life. |
Поттер привнес иное понимание приходской жизни. |
|
The latter emphasizes different realities, while authors like Gregorio Morales are more interested in understanding humankind. |
Последний подчеркивает различные реальности, в то время как авторы, подобные Грегорио Моралесу, больше заинтересованы в понимании человечества. |
|
For an understanding of the different ionising effects of these radiations and the weighting factors applied, see the article on absorbed dose. |
Для понимания различных ионизирующих эффектов этих излучений и применяемых весовых коэффициентов см. статью о поглощенной дозе. |
|
It also involves understanding the different cultures, languages and customs of people from other countries. |
Она также включает в себя понимание различных культур, языков и обычаев людей из других стран. |
|
My understanding is that the rules are different in BritEng, which adds a complication, but not a sufficient complication to justify those edits. |
Я понимаю , что правила отличаются в Бритенге, что добавляет сложность, но не достаточную сложность, чтобы оправдать эти изменения. |
|
This model was later used by David Keirsey with a different understanding from Jung, Briggs and Myers. |
Эта модель позже была использована Дэвидом Кирси с иным пониманием , чем Юнг, Бриггс и Майерс. |
|
With Specification by example, different roles participate in creating a single source of truth that captures everyone’s understanding . |
С помощью спецификации на примере различные роли участвуют в создании единого источника истины, который захватывает понимание каждого. |
|
Imperial control, territorial and cultural, is justified through discourses about the imperialists’ understanding of different spaces. |
Имперский контроль, территориальный и культурный, оправдывается дискурсами о понимании империалистами различных пространств. |
|
Learners with different skills and backgrounds should collaborate in tasks and discussions to arrive at a shared understanding of the truth in a specific field. |
Учащиеся с различными навыками и опытом должны сотрудничать в выполнении заданий и проведении дискуссий, чтобы прийти к общему пониманию истины в конкретной области. |
|
I considered merging the two articles initially but the understanding of the term register between the two articles is so different I doubt this is possible. |
Первоначально я рассматривал возможность объединения двух статей, но понимание термина регистр между двумя статьями настолько различно, что я сомневаюсь, что это возможно. |
|
Argumentation theory provides a different approach to understanding and classifying fallacies. |
Теория аргументации предлагает иной подход к пониманию и классификации ошибок. |
|
Maharishi Vedic Approach to Health uses a model for understanding health and disease that is fundamentally different from that of modern medicine. |
Ведический подход Махариши к здоровью использует модель понимания здоровья и болезни, которая принципиально отличается от модели современной медицины. |
|
Therefore, the key to a comprehensive understanding of development at any stage requires the ·interaction of different factors and not only one. |
Поэтому ключ к всестороннему пониманию развития на любом этапе требует * взаимодействия различных факторов, а не только одного. |
|
The Christian bible is different for Catholics and Protestants owing to understanding and custom. |
Христианская Библия отличается для католиков и протестантов в силу понимания и обычая. |
|
People should come away from this article understanding the conflict, the different perspectives, why they exist, and how everything got to be the way it is now. |
Люди должны уйти от этой статьи, понимая конфликт, различные точки зрения, почему они существуют, и как все стало таким, как сейчас. |
|
Such research has been done in pursuit of a better understanding of animal locomotion, including the factors that different gaits seek to optimize. |
Такие исследования были проведены в поисках лучшего понимания локомоции животных, включая факторы, которые различные походки стремятся оптимизировать. |
|
The term Hearing impaired is often contrasted to the term Deaf to indicate two different models of understanding hearing loss. |
После долгой и бесплодной переписки с ЦКБ он в конце концов принял меры, по совпадению в тот день, когда о’Донован Росса умер в Нью — Йорке. |
|
Epigenetic modifications have given insight into the understanding of the pathophysiology of different disease conditions. |
Эпигенетические модификации дали представление о понимании патофизиологии различных состояний болезни. |
|
As seen previous to this section, many different cultures around the world use divination as a way of understanding the future. |
Как было показано ранее в этом разделе, многие различные культуры во всем мире используют гадание как способ понимания будущего. |
|
It also led to a different understanding of the eightfold path, since this path does not end with insight, but rather starts with insight. |
Это также привело к другому пониманию восьмеричного пути, поскольку этот путь не заканчивается прозрением, а скорее начинается с прозрения. |
|
Several different iterations of MGCM have led to an increased understanding of Mars as well as the limits of such models. |
Несколько различных итераций MGCM привели к более глубокому пониманию Марса, а также пределов таких моделей. |
|
I don’t think there is any difficulty in understanding that what is written is the article title in different forms — what else would it be? |
Я не думаю, что есть какие — то трудности в понимании того, что то, что написано, является названием статьи в разных формах — что еще это может быть? |
На основании Вашего запроса эти примеры могут содержать грубую лексику.
На основании Вашего запроса эти примеры могут содержать разговорную лексику.
иное понимание
разное понимание
разное представление о
иное представление о
разное понятие
различное понимание
другое понимание
иного понимания
различные понимания
разном понимании
различном понимании
разным пониманием
разного понимания
различного понимания
другим пониманием
He gave her a rush of new energy and a different understanding of art; she inspired him and helped him to settle.
Он ей дал порыв новой энергии и иное понимание искусства; она его вдохновила и помогла ему обосноваться.
And a completely different understanding of their professional and civic responsibility.
И совершенно иное понимание своей профессиональной и гражданской ответственности.
And also describes different understanding of human soul in a context of transcendental and existential philosophical systems.
А также описывает разное понимание человеческой души в контексте трансцендентальных и экзистенциальных философских систем.
As in other religions, people have different understanding of the situation, different political views.
Как и в других конфессиях, у нас люди имеют разное понимание ситуации, разные политические взгляды.
However, the two countries’ governments clearly had a different understanding of «open access» to the global net.
Тем не менее, правительства двух стран явно имеют разное представление о том, что такое «открытый доступ» к глобальной сети.
And so, when you study it, you realize that different people of the world have a different understanding of the world.
Поэтому при её изучении становится ясно, что разные народы имеют разное представление о мире.
They bring a different understanding of that culture and a different lived experience.
Они привносят иное понимание культуры и другой жизненный опыт.
This period created a different understanding of a human and measures of its value than antiquity.
Средневековье создало иное понимание человека и меры его ценности, чем античность.
It seems that there are some manufacturers who have a different understanding of this issue.
У некоторых изготовителей, по всей видимости, имеется иное понимание этого вопроса.
Different people have different understanding of the word ‘religion’.
Battling considerable intellectual resistance, I’ve gradually developed an entirely different understanding of the universe, of the psyche, and of human nature.
Преодолевая значительное интеллектуальное сопротивление, у меня постепенно сложилось совершенно иное понимание вселенной, психики и человеческой природы.
One can observe different understanding of the law requirements in different local governments when they entrust commercial companies with some of their functions.
Разное понимание требований закона наблюдаема в разных самоуправлениях и в тех случаях, когда они делегируют некоторые из своих функций коммерсантам.
However, it is a deep ecology with a fundamentally different understanding of life.
А вот глубинная экология предлагает принципиально иное понимание.
Different people have a different understanding of love.
He was teasing me, but I was pleased because it reflected a fundamentally different understanding of alignment.
Он дразнил меня, но я был доволен, потому что это отразило принципиально иное понимание согласованности.
With the «Rockefellers», among other things, their hatred and a different understanding of the prospects for globalization.
С «рокфеллерами», среди прочего, их рознит и разное понимание перспективы глобализации.
[Healing with ayahuasca] presumes a completely different understanding of illness and medicine than what we are accustomed to in the West.
Исцеление аяуаской предполагает совершенно иное понимание болезни и медицины, чем то, к которому мы привыкли на Западе.
Moldova seems to have a different understanding of the question.
China and Europe have a different understanding of multilateralism, but it will not hinder their multilateral cooperation.
У Китая и Европы разное понимание многостороннего подхода, но это не мешает их многостороннему сотрудничеству.
I had a different understanding of football with Olga Smorodskaya and Ilya Herkus.
О КИКНАДЗЕ У меня было разное понимание футбола с Ольгой Смородской и Ильей Геркусом.
Результатов: 197. Точных совпадений: 197. Затраченное время: 138 мс
Documents
Корпоративные решения
Спряжение
Синонимы
Корректор
Справка и о нас
Индекс слова: 1-300, 301-600, 601-900
Индекс выражения: 1-400, 401-800, 801-1200
Индекс фразы: 1-400, 401-800, 801-1200