Interrogative sentences in Past Simple: rules and examples
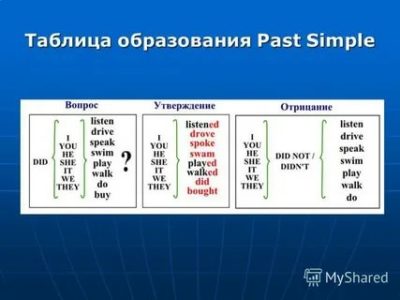
As mentioned in the first lesson of this topic, interrogative sentences in Past Simple are formed using an auxiliary verb did.
General question
General question — this is a question for the whole proposal. In all grammatical tenses of the English language in general at the first place to be an auxiliary verb, on the second — subject, on the third place there is a predicate in the form of an infinitive, then there are minor members of the sentence.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Did | I | make | a mistake | in the last | test? |
| We | |||||
| you | want__ | to buy | a dog? | ||
| They | |||||
| She | listen__ | to the teacher | Attentively? | ||
| He | |||||
| It | rain | hard | yesterday |
A short answer to a general question is constructed in the same way as in Present Simple:
Did you have a good time? — Yes, I did.
Did they buy anything? — No, they didn’t/ No, they did not.
Special Issues
Special questions are asked in order to clarify in detail any details. The structure of the special question is almost the same as the general one — in the first place is the interrogative word, in the second is the auxiliary verb, in the third place is the subject, in the fourth place is the predicate in the form of the infinitive.
Typical of the past simple tense is a special question starting with When.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| What | did | I | do | yesterday? | ||
| We | ||||||
| Where | you | spend | your | last | holidays? | |
| They | ||||||
| When | he | pass | the exams? | |||
| She | ||||||
| Why | it | happen__ | to | me? |
Question to the subject
The subject question is a special case of a special question. A feature of this question is the absence of a clearly expressed subject (object of the question) and an auxiliary verb.
The subject is the question word itself who/what… And since there is no auxiliary verb in the question, then the semantic verb (predicate) retains the current tense form, in this case the form of the past simple tense.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Who | helped | you | about | the house? |
| What | went | Wrongs | With | the concert? |
Note
If there is a compound verb predicate in a sentence, then its first part has the form of the current grammatical tense, and the second — the form of an infinitive with a particle to.
Did you to play soccer?
What did you do to become so clever?
Negative questions
Any of the above questions can be made negative by simply adding the particle Note after the auxiliary verb. As a rule, in negative questions, a short form of denial is used, in this case it is did not.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| What | did not | you | do | on holiday? |
| Why | did not | she | talk | is it me? |
| Who | did not | hear | the question? | |
| Didnt | you | get | my hint? |
Source: https://www.study.ru/courses/elementary/did
Simple past tense in English
Past Simple expressed by the second form of the semantic verb. Verbs are divided into right and wrong depending on how the past tense is formed. The forms of irregular verbs need to be looked at in the table of irregular verbs and memorized.
Regular verbs.
Unlike present tense verbs, past tense verbs have only one conjugation for all persons. In the form of a simple past tense to regular verbs ending is added ed.
examples:
| to help | helped |
| to look | Looked |
| to call | called |
| to visit | visited |
| to move | moved |
| I looked at two apartments, but they were too expensive. | I looked at two apartments, but they were too expensive. |
| Linda called the apartment managers. | Linda called the manager. |
| Mario and Laura visited Acapulco for their honeymoon. | Mario and Laura went to Acapulco on their honeymoon. |
Irregular Verbs.
Irregular Verbs form simple past tense forms no nо general scheme (by adding the ending «ed»).
There is no rule according to which the forms of irregular verbs would be formed, they just need remember. There is a table of irregular verbs. Refer to it as needed until you learn it by heart.
As with regular verbs, the forms of irregular verbs are the same in all persons.
Compare:
| Currently, | Past tense |
| I usually come to this restaurant on Tuesdays. | I came here last spring. |
| I usually come to this restaurant on Tuesdays. | I came here last spring. |
| To get there, I take the train every morning. | Today I took the bus, and I was late to work. |
| I take the train every morning to get here. | Today I took the bus and was late for work. |
| Tony goes to Central Park every morning. | Mary went to the park with her family last week. |
| Tony goes to Central Park every day. | Mary went to the park with her family last week. |
Conjugation forms of simple past tenseare usually the same for all persons except past tense of the verb to be.
examples:
| I lived in Washington. | |
| You lived in Washington. | |
| He lived in Washington. | |
| She lived in Washington. | |
| It lived in Washington. | |
| We lived in Washington. | |
| They lived in Washington. |
To be.
. Verb to be means “to be”, “to be”, “to be” and is usually implied but not translated literally into Russian.
The verb to be conjugated like this:
| I was |
| you were |
| he, she, it was |
| we were |
| they were |
examples:
| I was in San Diego. |
| You were in San Diego. |
| He was in San Diego. |
| She was in San Diego. |
| It was in San Diego. |
| We were in San Diego. |
| They were in San Diego. |
Asking questions in the simple past tense.
Question in simple past tense formed using the past tense form of the auxiliary verb to do (did).
| Did I live in Washington? | |
| Did you live in Washington? | |
| Did He live in Washington? | |
| Did She live in Washington? | |
| Did It live in Washington? | |
| Did We live in Washington. | |
| They live in Washington? |
The answer can be short or long.
examples:
| Did Mark move already? | Yes, he did. |
| Mark has already moved? | Yes. |
| Did you find an apartment? | No, I didn’t find an apartment. |
| Have you found an apartment? | No, I haven’t found an apartment. |
| Did you call your sister? | No, I didn’t. |
| Have you called your sister? | No. |
| Did John buy this apartment or rent it? | Did John buy this apartment or rent it? |
| He bought it. | He bought it. |
| Were they students at the university? | Were they students at the university? |
| No, they weren’t. | No, they were not. |
| Was your grandfather a doctor? | Was your grandfather a doctor? |
| No, he was a lawyer. | No, he was a lawyer. |
Negation in the simple past tense.
Just as for present tense negation, past tense negation occurs using the auxiliary verb to do… Past tense conjugation uses did + not (abbreviated didn’t) + infinitive… The forms in the simple past tense are the same for all grammatical persons.
examples:
| I didn’t live in Washington. |
| You didn’t live in Washington. |
| He didn’t live in Washington. |
| She didn’t live in Washington. |
| It didn’t live in Washington. |
| We didn’t live in Washington. |
| They didn’t live in Washington. |
Past simple spelling of regular verbs
If the infinitive of a regular verb ends in a consonant, add «Ed» for formations of the past.
examples:
| to call | called |
| to work | worked |
| to paint | painted |
If the infinitive ends with «E», added simply «D».
examples:
| to move | moved |
| to decide | Decided |
| to live | lived |
However, individual verbs can change… If the verb ends a consonant (except for «w» and «x») preceded by a single vowelthen this the consonant is doubled and «ed» is added.
examples:
| to stop | stopped |
| to occur | happened |
| to prefer | preferred |
PLEASE NOTEthat when the stress is not on the last syllable, the last consonant is not doubled.
examples:
| to open | opened |
| to visit | visited |
| to travel | traveled |
If the verb ends in y, in front of which is consonant , then y changing to «I» and added «Ed».
examples:
| to study | Studied |
| to worry | worried |
EXCEPTION: past tense form to play (play) will played.
Using the simple past tense
1. Actions that took place in the past and have nothing to do with the present moment. At the time of the commission, the words can indicate: yesterday, ago, last week, the other day, etc.
Example:
I saw him yesterday. I saw him yesterday.
2. Sequences of actions when describing the development of events in the past.
Example:
| I finished work, walked to the beach, and found a nice place to swim. | I finished work, went to the beach, and found a great place to swim. |
3. An action that has lasted for a period of time in the past and is now over.
Example:
I lived in Brazil for two years. I have lived in Brazil for two years.
4. Common repetitive actions that can be indicated by the words: every (day, week), usually, regularly, often, always.
Example:
| They never went to school, they always skipped class. | They never went to school, they always skipped classes. |
Source: http://enjoy-eng.ru/grammatika/prostoe-proshedshee-vremia-v-angliiskom-iazyke
What is simple past tense, rules and its uses with examples: Simple past tense is very easy to use in English grammar. If you know about simple present tense then simple past tense becomes easier to understand. Simple Past tense is also called “Preterite tense”. Let’s us discuss about simple past tense and its rules with examples.
What is simple past tense, rules and its uses with examples?
Simple Past Tense: Simple past tense is used to express any action that started or completed in the past. Or in other words, simple past tense describes any action that happened in the past. For example,” Joolie visited market yesterday”. In this example, Joolie visited the market in the past time. The action happened in the past.
According to the rules of English grammar, we can also define simple past tense as: any sentence that uses second for as its main verb called simple past tense. Simple past tense is made up of three of its main parts that are: Subject, Main verb (Second Form of Verb) and Object.
Simple Past Tense= Subject + 2nd form of verb + Object

Positive Sentence
In positive sentences, we simply make the sentences according to Simple past tense rules.
For Example
- He reviewed my website yesterday.
- I repaired this computer last month.
- She met the Prime minister two week ago.
- Mark saved me from those hurdles of life.
- You taught me this lesson yesterday.
- She always lied to me.
Negative Sentences in the Simple past tense
When we make negative sentences, we normally add auxiliary verb did + not before main verb.
Negative Simple Past tense = Subject+ did+ not + 1st form of Verb +Object
For example
- Steve did not finish his work.
- I did not attend his class yesterday.
- Mark did not pass GMAT exam last year.
- They did not go to America this year.
- I did not comment on him yesterday.
Yes/No Questions in the Simple past tense
When you make any question that can be answered as yes or no, then you should start it with auxiliary verb did followed by the subject and the 1st form of base verb.
Yes/No Sentences = Did + Subject + 1st form of Verb +Object?
For example
- Did she work in that company?
- Did she go to the market?
- Did you complete the task?
- Did we win the match yesterday?
- Did she come last week?
Wh- Questions in the Simple past tense
When you make any question that starts with wh word, then you should start it from wh word and then add auxiliary verb did, after that subject followed by the 1st form of base verb.
Wh words are when, why, who, where, whom, how, what, how much, how many.
WH Sentences = Wh word + did+ Subject + 1st form of Verb+ Object?
For example
- Where did she live in England?
- What did you say about her?
- When did you meet the CEO?
- Why did he work for that hotel?
- Why did she wash the clothes?
Tag Questions in the Simple past tense
Tag questions are those questions which are answered at the end of the sentence. They can be simply made by adding auxiliary verbs.
For examples
- I visited the market, did not you?
- You can also use tag questions in positive sentences
- She read news paper yesterday, did she?
More Examples to unfold some other aspects
- Why did you not say anything to her?
- Did he not visit at your home yesterday?
- He did not want me to be there?
- Did you just waste his time?
These were the structures of simple past tense. Now let us discuss about the rules and use of simple past tense.
Rules and Uses of Simple past tense
- Yesterday/ Last/Ago
- Past habit
- Anything happened once in the past
- Past fact or truths
- Past duration
- Since/When clause
Yesterday/ Last/Ago
Simple past tense is used when these words like “Yesterday/ Last/Ago” are used in the sentence or any sentences that gives a sense of past time.
For example
- I visited cinema yesterday.
- She came here last month.
- I left my country two years ago.
- We went to the college yesterday.
- You played very well.
Past habit
Simple past tense is used to describe any action that contains past habit.
For example
- I played too much cricket in my childhood.
- We always enjoyed working with him.
- They never went to the college
- They worked for each other daily.
Anything happened once in the past
Any action happened in the past but only once. In this situation, we use simple past tense.
For example
- I met my friend in 2000.
- We went to England for our picnic.
- She ate all the food last night.
- He broke this table yesterday.
Past fact or truths
Sentences expressing past truth or facts can be used in simple past tense.
For Example
- Man walked on the moon in 1969.
- Swami Vivekananda always spoke the truth.
- Mark Zuckerberg invented Facebook.
- I was born in 1994.
Past duration
When you describe any action that contains a past duration then we use simple past tense.
For example
- I lived in England for three years.
- They stood in the market all day.
- We studied in the library for thirty minutes.
- She stared me entire time in the party.
Since/When clause
In any sentences when “since” is used as an adverb then it is of past tense form. Also with “when clause” we use past tense.
For example
- It is two hours since the bus left the station.
- He is living with me since he came from London.
- We are getting in problems since he joined our group.
- When I paid him money, he gave me the ice-cream.
- When I was a child, I went to the school every day.
So these were the rules and the uses of simple past tense with examples.
I hope you have enjoyed this article and get what you wanted. So this is the What is simple past tense, rules and its uses with examples. If you feel any problem regarding this topic then comment below so that we can solve out your problems.
Also Read
Simple Present Tense
Present Continuous Tense
Present Perfect Tense
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Simple Past Tense
Past Continuous Tense
Past Perfect Tense
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Simple Future Tense
Future Continuous Tense
Future Perfect Tense
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
https://careersplay.com/what-is-simple-past-tense-rules-and-its-uses-with-examples/What is simple past tense, rules and its uses with exampleshttps://careersplay.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/simple-past-tense.jpghttps://careersplay.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/simple-past-tense-150×150.jpg2014-04-03T04:08:28+00:00Sumit ThakurImprove Englishsimple past tense,simple past tense examples,simple past tense rules,simple past tense uses,what is simple past tenseWhat is simple past tense, rules and its uses with examples: Simple past tense is very easy to use in English grammar. If you know about simple present tense then simple past tense becomes easier to understand. Simple Past tense is also called “Preterite tense”. Let’s us discuss about…Sumit ThakurSumit
Thakursumitsssrt@gmail.comAdministratorHello,I am Sumit Thakur. I am here to help you regarding all your problems related to career. We are three members of this website including me, Virender SIngh and Shreya Thakur.Our motto is to help all the friends who are seeking for the best future 🙂CareersPlay.com
Содержание
Прошедшая неопределённая форма глагола (past indefinite form of the verb [pɑ:st ɪn’defɪnɪt]), или прошедшее неопределённое время(1) (past indefinite tense) — это форма глагола неопределенного аспекта в прошедшем времени (далее просто «прошедшее неопределённое«).
Часто в практических грамматиках английского языка помимо термина «прошедшее неопределённое» (past indefinite) используется термин «простое прошедшее (время)» (simple past (tense) [‘sɪmpl]), получивший своё название благодаря более простому формообразованию по сравнению с другими аспектными формами глагола (см. Аспект).
Форма глагола в прошедшем неопределённом образуются от основы инфинитива (даётся в словарях) при помощи окончания -ed или -d (подробнее см. «Прошедшее время глагола»).
Отрицательная форма глагола в прошедшем неопределённом образуется при помощи вспомогательного глагола «do» в форме прошедшего времени «did» [dɪd] и отрицания «not», при этом смысловой глагол употребляется в форме инфинитива (без частицы «to»):
-
I did not study English in school. – Я не изучал английский в школе.
Вместо глагола с отрицанием «did not» может употребляться его сокращённая форма «didn’t» [dɪdnt]:
-
I didn’t watch TV. – Я не смотрел телевизор.
Вопросительная форма прошедшего времени неопределённого аспекта образуется при помощи вспомогательного глагола «do» (в соответствующей форме). Вспомогательный глагол ставится перед подлежащим, а смысловой глагол в форме инфинитива (без частицы «to») после подлежащего:
-
Did you watch television? – Вы смотрели телевизор?
В вопросительно-отрицательной форме прошедшего неопределённого, частица «not» ставится после подлежащего, исключением являются сокращённая форма вспомогательного глагола, которая целиком ставится перед подлежащим:
-
Did you not know? ⇒ Didn’t you know? – (Разве) Вы не знали?
Отрицательная и вопросительная форма глагола «be» в прошедшем неопределённом образуется без помощи вспомогательного глагола «do»:
-
He was not at home. – Он не был дома.
-
Was he at home? – Он был дома?
При употреблении собственно модальных глаголов отрицательная и вопросительная форма глаголов образуются с помощью самих модальных глаголов без вспомогательного глагола «do»:
-
How did you do it? – Как Вы это делали?
-
How could you do it? – Как Вы могли это делать?
-
I did not do it. – Я не делал этого.
-
I could not do it. – Я не мог этого делать.
Употребление прошедшего неопределённого
Формы прошедшего времени неопределённого аспекта употребляется в следующих случаях:
-
для выражения повторяющегося действия или констатации постоянного признака характеризующего объект в прошлом:
-
I learned English on my own. – Я учил английский язык самостоятельно.
-
He was my neighbor. – Он был моим соседом.
-
-
для выражения цепи последовательных действий в прошлом:
-
I took my favourite book, opened it and began reading it. – Я взял свою любимую книгу, открыл её и стал читать.
-
-
для указания на однократное действие в прошлом:
-
You threw away your future. – Ты отказался от своего будущего.
-
-
для выражения вежливого, скромного, ненавязчивого обращения, пожелания или вопроса:
-
I wanted to have a word with you. – Я бы хотел с вами поговорить.
-
I wondered if he comes. – Мне хотелось бы знать, придёт ли он.
-
Did you help me, please? – Вы не поможете мне, пожалуйста?
-
-
для образования форм глагола сослагательного наклонения II: при выражении события, которое рассматривается как нереальное:
-
If I came tomorrow, it would be late. – Если бы я пришёл завтра, было бы уже поздно.
-
I wish she were here now. – Как бы мне хотелось, чтобы она сей час была здесь.
-
Примечания

Using different verb tenses correctly can be difficult. Especially past tense English verbs. This post will explain the basic rules of this verb grammar and teach you 50 Irregular Verbs.
Past tense verbs describe actions that have finished at some time before now “I played soccer yesterday.”
or things that once existed. “There was a dog outside this morning.”
Regular verbs end with the letters _ed – “played”
Irregular verbs do not – “was”
This post will be a great resource for you to master the English past tense verb form. The 50 Irregular verb examples will follow a story to make them easier to remember.
Table of Contents
- How do you make past tense verbs?
- Regular verbs
- Irregular verbs
- Simple past tense rules
- What are the 4 types of past tense?
- Simple Past
- Past Progressive (continuous)
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Progressive (continuous)
- 50 Irregular Past Tense verbs
- Printable 50 Irregular Past Tense Verbs PDF
How do you make past tense verbs?
Regular verbs
The past tense of regular verbs will end in _ed
pick picked – “Last fall we picked apples and pears at my grandfather’s orchard.”
work worked – “My father worked for my grandfather when she was in high school.”
If the verb ends in the letter E we just add _d
move moved – “We moved a lot when I was younger.”
debate debated – “The politicians debated for 3 hours.”
Verbs ending with a consonant and the letter Y will change to I before adding _ed
apply applied – “I applied for three jobs this summer.”
deny denied – “The bank denied his loan application.”
Verbs ending with a vowel and the letter Y add _ed
play played – “I played in the park near my house when I was young.”
stay stayed – “We stayed in a luxury hotel for 2 weeks.”
Regular verb writing rules. If the word…
| …ends with e | – add the letter d | move – moved |
| …ends with a vowel + y | – add ed | stay – stayed |
| …ends with a consonant + y | – change the y to an i and add ed | apply – applied |
| …is 1 syllable ending with 1 vowel before 1 consonant | – we must double the last letter before adding ed | stop – stopped |
I found an awesome video to explain the 1:1:1 rule. (One syllable, one vowel, one consonant)
Irregular verbs
In English, there are many verbs whose past tense doesn’t end with _ed. These are called irregular verbs. Some examples:
- bought (this is the past tense of the verb BUY)
“I bought a new computer last week.” - saw (this is the past tense of the verb SEE)
“Daisy saw the movie on opening night.” - wrote (this is the past tense of the verb WRITE)
“Mark Twain wrote many popular books.”
Irregular verbs do not follow any pattern. The only way to learn which verbs are irregular is to memorize them.
A great way to memorize them is to see them used in real sentences, sentences that are part of a longer story are even better.
I created a list of 50 irregular verbs with example sentences that follow a simple story just for you. You can find those examples here>> 50 irregular verbs
You can also download a FREE PDF of the list at the bottom of the post.
Simple past tense rules
| Questions use the auxiliary verb did. | Did you play soccer last week? |
| Negative statements use the negative auxiliary did not. (didn’t) | I didn’t play soccer last week. |
| Questions – Do is the main verb Did (subject) do? |
Did you do your homework? |
| Negative statements – Do is the main verb Didn’t do. |
I didn’t do my homework. |
Negative verb forms and questions in the past tense use did, the past tense of the auxiliary verb do. The main verb in the sentence will be in the simple present tense.
Negative past tense statements use did not, didn’t.
- Mark Twain didn’t go to university. (Not didn’t
went) - The computer sale is over soon so I didn’t want to wait. (Not didn’t
wanted)
Past tense questions use did you? – did he/she/it etc.
- Did Mark Twain live in Australia? (Not did he
lived?) - Did you buy a Mac or a PC? (Not did you
bought?)
When do is the main verb we will use this grammar:
Did do. Didn’t do.
A: “What did you do on Saturday?”
B: “I didn’t do anything.”
A: “Did you finally ask Heather for a date? You have been talking about her for 2 weeks!”
B: “I didn’t do it yet. I’m shy when I’m around her.”
A: “I’m so mad today! I’m going to tell the boss what I really think of him!”
B: “Don’t do it! Please wait until you calm down, you will regret it if you do it now.”
What are the 4 types of past tense?
- Simple Past “I played soccer this morning.”
- Past Progressive (continuous) “I was playing soccer this morning.”
- Past Perfect “If I had woken up on time today, I wouldn’t have been late.”
- Past Perfect Progressive (continuous) “I had been playing soccer when she called.”
How to use the four different types of past tense verbs.
Simple Past
We use the Simple Past for actions that have stopped, they no longer continue.
I like to compare the Simple Present tense with the Simple Past tense to explain how to use it. My private students in Japan find this helpful.
The present simple describes an activity that we do regularly.
Present simple – “I walk to school every day.”
I have walked to school in the past and I will continue to walk to school in the future.
The past simple describes an activity that is finished.
Past simple – “I walked to school yesterday.”
The sentence describes an action that no longer continues. This sentence may be used to show that we walked to school yesterday but it is not something that we do regularly.
Past Progressive (continuous)
The Past Progressive is a past form of the verb To BE – was, were – plus the continuous tense of a verb. (Verb + ~ing)
We used the Past Progressive to talk about an action that was happening during a certain time in the past. It is commonly used to describe an action that happened at the same time another action was happening.
“I saw Karen when I was walking to school.”
I saw Karen at the same time as I was walking to school.
*When you use the past continuous tense to connect to another action, that verb will be in the simple past tense.
“The delivery came as I was cooking dinner.”
I heard the door at the same time as I was cooking dinner.
We connect the ideas with conjunctions like as, while, or when.
“The phone rang while I was washing the dog so I couldn’t answer it. My hands are all wet.
The past continuous can be the first action in our sentence.
“I was driving the car while Evan looked at the map.”
“I was cooking dinner when the delivery came.”
How to use FOR, DURING, and WHILE (Over 20 examples + Quiz + Audio)
Past Perfect
The Past Perfect is HAD + the past participle of a verb.
“I had driven 80 kilometers before I noticed the warning light on my dashboard.”
We use the Past Perfect to describe the sequence of past actions. We clearly want to show that one past action happened before another past action.
“My mother had just finished mopping the floor when my little brother came inside with his muddy rain boots.”
First, my mother cleaned the floor and next my brother came inside with dirty boots. The order of these actions is important to the story.
The Past Perfect can also describe the reason for a situation.
“Wendy was hungry because she hadn’t eaten all morning.”
Situation: Wendy was hungry.
Reason: She had not eaten all morning.
“I had never been there before so I didn’t know what to expect.”
*NOTE – In our example sentences the verbs driven, finished, eaten, and been are all in the past participle form.
Use Past Participles The Right Way (25 examples + PDF list)
Past Perfect Progressive (continuous)
We’ll use the past perfect progressive to talk about an action that started, continued, and ended at a specific point in the past.
“Kyle had been doing well at school until last semester when he started missing classes.”
(The specific point in the past is last semester.)
The Past Perfect Progressive is had been + the continuous tense of a verb.
“Ben had been working at a bakery for 10 years before finally opening his own cake shop.”
(The specific point in the past is before he opened his own shop.)
This grammar is often used with conjunctions like before, when, for, etc.
<< PDF download at the bottom of this list >>
1. say said
- “Nancy said she would be here by 6:00.”
2. make made
- “I hope she gets here soon, I made reservations for 6:30 at the restaurant.”
3. go went
- “Maybe she went to the bank after work?”
4. take took
- “If she took the local streets she will be late. The roads are always crowded around this time.”
5. come came
- “Last week she came here after work and the traffic was fine.”
6. see saw
- “I just saw her pull into the driveway.”
7. know knew
- “I knew Nancy would be here on time!”
8. get got
- “I got an email from Peter this morning, he’s back from his vacation.”
9. give gave
- “Yes, he gave me a call from the airport last night when he arrived. I went there to pick him up.”
10. find found
- “The airport was so busy! I finally found him after 15 minutes of searching.”
11. think thought
- “I thought Peter would be on vacation for 3 weeks.”
12. tell told
- “He told me that he would only stay for 12 days.”
13. become became
- “He just became a division manager so he can’t be away from the office for too long.”
14. show showed
- “On the drive home from the airport, he showed some photos from his trip.”
*Show is an irregular verb because the past participle is shown not showed. Other regular verbs whose past tense is _ed use the same form for the past participle.
Learn more about the Past Participle verb form here – Use Past Participles The Right Way (25 examples + PDF list)
15. leave left
- “Hawaii is so beautiful, You must have been sad when you left.”
16. feel felt
- “I felt sad every time I left the beach! Relaxing on the beach is my favorite thing to do.”
17. put put
- “Peter had to buy an extra duffel bag for all the souvenirs he bought for his staff. First, he put them in his suitcase, but then his clothes wouldn’t fit!”
18. bring brought
- “He is so kind! He brought back a lot of treats for his co-workers.”
19. begin began
- “After working for 6 hours without a break, Lisa began to get very hungry.”
20. keep kept
- “We kept telling her to relax a little, but Lisa really wants to finish this project.”
21. hold held
- “Our boss held a meeting to explain how important this project is to the company.”
22. write wrote
- “As the project manager, Lisa wrote a 3-page memo detailing everyone’s tasks.”
23. stand stood
- “At the meeting, Lisa stood behind our boss taking notes.”
24. hear heard
- “She heard everything he said very clearly.”
25. let let
- “She works hard, so this morning I let her have the last donut in the staff break room.”
26. mean meant
- “Sorry, I meant to say danish, not donut.”
27. meet met
- “After the meeting, the team met at a local restaurant to have dinner together.”
28.set set
- “The whole project team was at the restaurant, the staff set the table for 18 people. It was a big table!”
29. run ran
- “It was a big dinner so I ran home to burn some calories.”
30. pay paid
- “It was a great dinner, and our company paid for everything!”
31. sit sat
- “Eric was very quiet during dinner. He sat in the corner and didn’t say anything.”
32. speak spoke
- “Almost every member of the team spoke about their contribution to the project.”
33. lie lay
- “3 nights ago I lay in bed thinking about what I would say at the meeting.”
34. lead led
- “It was my first time in Tokyo, so I was happy to have a guide. He led the way during my trip.”
35. read read
- “I read 6 books about Tokyo before my trip.”
*Be careful, the spelling for the past tense is the same as the present tense but they are pronounced differently.
Learn more about the verb To READ here – Past tense of READ and Past Participle of READ (Audio, Quiz, and PDF)
36. grow grew
- “No one took care of my garden while I was away and weeds grew everywhere.”
37. lose lost
- “My favorite team lost an important game last night. I’m sad today.”
38. fall fell
- “I was so nervous watching the game I fell off my chair!”
39. send sent
- “My friend sent me a message right after the game to tease me. (He likes the other team!)”
40. build built
- “I wish my local team had more support from the community. They built a new arena last summer but not enough people are coming to live games.”
41. understand understood
- “I tried to explain to my friends that it’s important to support the team, but I don’t think they understood why.”
42. draw drew
- “I drew a picture for my student to help explain the meaning of the new word.”
43. break broke
- “I pressed the pencil so hard that I broke it!”
44. spend spent
- “I spent the next 5 minutes trying to find a new pencil.”
45. cut cut
- “I reached into my desk looking for a pencil and I cut my finger on a utility knife.”
46. rise rose
- “I shouted ‘ouch!’ and my student rose from her desk to see what was wrong.”
47. drive drove
- “I didn’t have any bandages so we drove to the pharmacy to buy some.”
48. buy bought
- “I bought a big box of band-aids.”
49. wear wore
- “It was raining so I wore a rain jacket to the pharmacy.”
50. choose chose
- “I chose a family size box, it has 50 band-aids in 4 different shapes.
Printable 50 Irregular Past Tense Verbs PDF
Download your printable 50 Irregular Past Tense Verbs PDF E-below. (It’s FREE!)↓
Was this post helpful for you? Which Irregular Past Tense Verb will you use next? Tell me in the comments!
For negatives and questions in the past simple tense, we use the auxiliary verb did — the past of «do».
Compare:
I don’t like tomatoes. → I didn’t like tomatoes.
Do you live in London? → Did you live in London?
did + not = didn’t
In the negative sentences, we normally use the short word «didn’t» instead of «did not».
If there is an auxiliary verb, it takes over the indication of the tense. The main verb comes in its infinitive form. In the negative and question sentences in the past simple, «did» takes over the tense, exactly like «does» in the present simple.
How to make negatives and questions in the past simple
Negative: subject + didn’t + infinitive
Question: (question word) + did + subject + infinitive
| Infinitive | Past simple positive | |
|---|---|---|
| look | I you she he it we they |
looked |
| want | wanted | |
| go | went | |
| buy | bought | |
| do | did |
| Past simple negative | ||
|---|---|---|
| I you she he it we they |
didn’t (did not) |
look |
| want | ||
| go | ||
| buy | ||
| do |
| Past simple question | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Why What Where When … |
did | I you she he it we they |
look? |
| want? | |||
| go? | |||
| buy? | |||
| do? |
Examples
I didn’t go to the cinema last night.
Olivia didn’t buy new clothes last month.
Did you like the film yesterday?
What did he do five years ago?
Short answers
You can give a short answer to a «yes/no» question in the past simple: «Yes, I did» or «No, I didn’t».
Examples
A: Did you call me yesterday afternoon? B: Yes, I did.
A: Did Alex sell his car last month? B: No, he didn’t.
A: Did you see Pete yesterday? B: No, we didn’t.
A: Did the students get good test scores? B: Yes, they did.