Home / Excel Basics / How to Open Dialog Box in Excel
In Excel, to get to more options of any option category you can open the dialog box and use those options directly from the dialog box. Apart from this, there are a few options that need to be used directly from a dialog box.

In this tutorial, we will look at how to open and use a dialog box use an option.
Open a Dialog Boxes from the Ribbon
- Go to the Tab from where you want to open the option.
- Move to the options group.
- Hover your cursor on the small arrow at the bottom right.
- Click on it to open the options dialog box.

The moment you click on it, Excel will open the dialog box for that option. And, when you click on the arrow from the font group, it opens the format dialog box and opens the font tab from there.

On the ribbon, you have multiple tabs, but not all the tabs have that down arrows in the options groups to open the dialog box.
Dialog Box Options
As I said, there are a few options that you need to use directly from a dialog box. For example, the find and replace option. When press the keyboard shortcut (Ctrl + F) it gives you a dialog box where you need to enter the value that you want to find.

Excel Options Dialog Box
Excel Options also have a dialog box. When you open the options, File ⇢ More ⇢ Options. You will get a large dialog box with all the options that you can make a change to in your Excel environment.

In this post, you will learn more about Dialog Boxes in Excel and how to use them with-in your Excel spread she
What is the use of dialog boxes?
A dialog box is a temporary window, where an application creates to retrieve user input. An application typically uses dialog boxes to prompt the user for additional information for menu items.
The following are the ways to use the dialog boxes.
- First, prepare an excel sheet with the required details in it.
Types of Dialog boxes
- When a Typical dialog box displays on the screen, it will remain until the user dismisses it. By clicking on the ok button, the task selected from the dialog box will be performed, and by clicking on the Cancel button, the dialog box will close without taking any action.
- The image below is an example for Typical dialog box.
- Navigating dialog boxes is very easy, click the command that you want to use. Although dialog boxes were designed for mouse users, you can also use the keyboard. Every dialog box button has also a text name on the button.
- The image below is an example for Navigating Dialog Boxes.
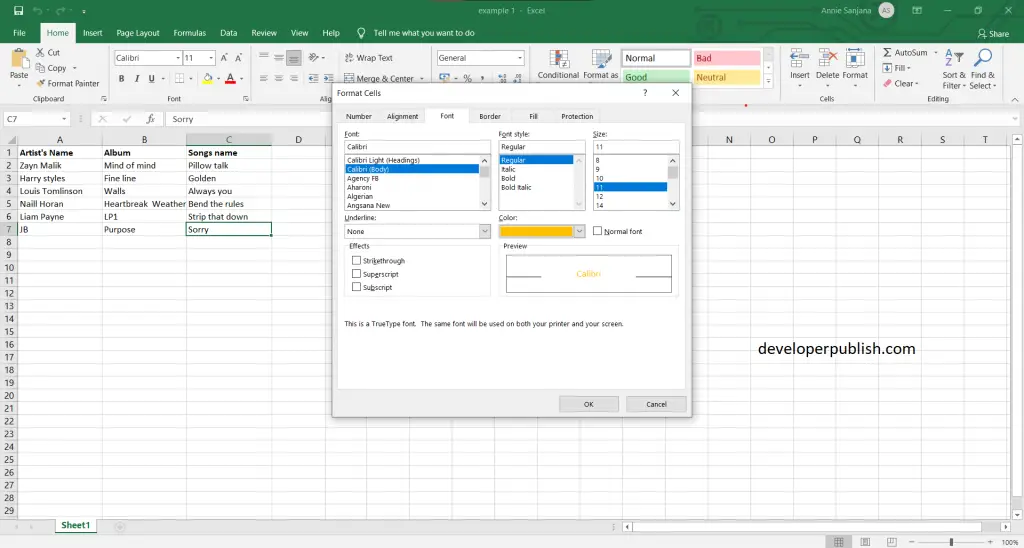
- Several Excel dialog boxes are tabbed dialog boxes. When you select a tab, a panel with relevant commands is visible. Tabbed dialog boxes are highly convenient because you can make several changes in a single dialog box. After you have made all your setting changes, click OK.
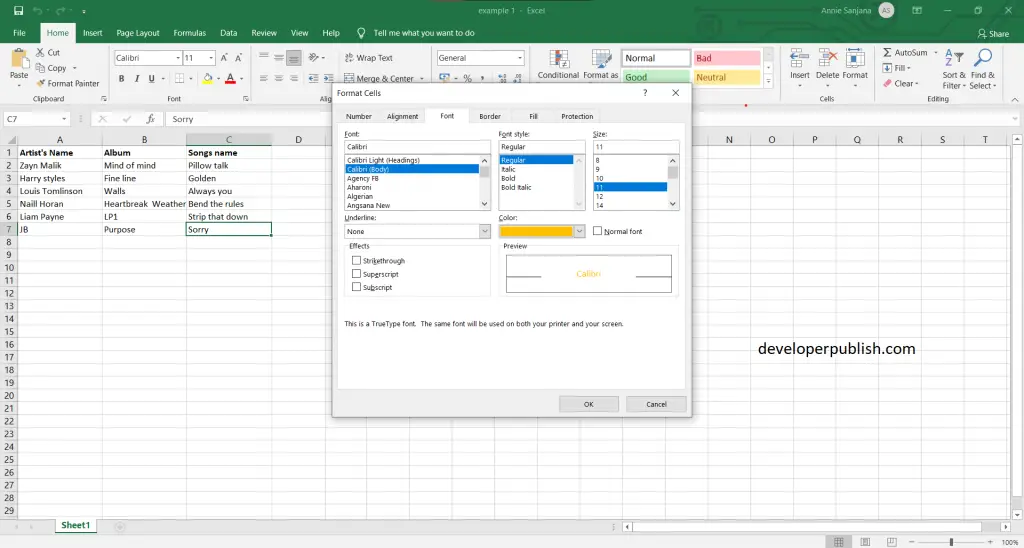
We will hope that this article was useful and understandable.
Author: Oscar Cronquist Article last updated on February 08, 2023
A dialog box is an excellent alternative to a userform, they are built-in to VBA and can save you time because you don’t need to code and build a userform. Some of these dialog boxes also have built-in validation. This article shows you what you can and can’t do with dialog boxes.
Table of contents
- How to create a Message box (VBA)
- Message box arguments
- Message box buttons
- vbOKOnly
- vbOKCancel
- vbAbortRetryIgnore
- vbYesNoCancel
- vbYesNo
- vbRetryCancel
- How to display Message box icons
- vbCritical
- vbQuestion
- vbExclamation
- vbinformation
- Combine buttons and icons
- Default buttons
- Messagebox return value
- Helpfile
- Working with text in a message box
- Input box (vba)
- How to set the default value for an input box?
- Input box (Excel)
- Number
- Range
- Combine data types
- DataForm
- FileDialog
- msoFileDialogFilePicker
- msoFileDialogFolderPicker
- msoFileDialogOpen
- msoFileDialogSaveAs
- GetOpenFilename
- GetSaveAsFilename
1. How to create a Message box (VBA)
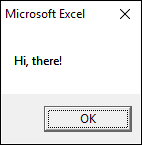
The most basic dialog box you probably have seen many times is the message box. In its most simple form, it gives the user a message you specify and an OK button.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Hi, there!" End Sub
It is a great tool for quickly troubleshooting a subroutine or a custom function. The message box has more options than displaying text or variables, these are the arguments:
Back to top
1.1 Message box arguments
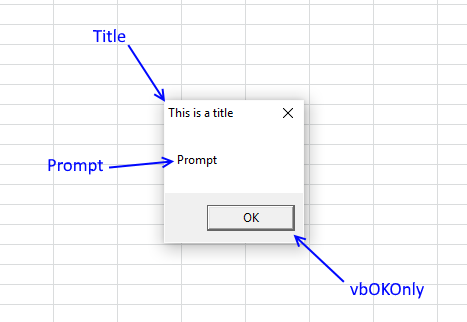
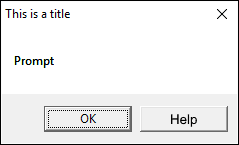
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbOKOnly, "This is a title" End Sub
Prompt — Text shown in message box
Buttons — You can select of a variety of different buttons and icons. If you can’t find the buttons you need, a user form is required.
vbOKOnly — 0
vbOKCancel — 1
vbAbortRetryIgnore — 2
vbYesNoCancel — 3
vbYesNo — 4
vbRetryCancel — 5
vbCritical — 16
vbQuestion — 32
vbExclamation — 48
vbInformation — 64
vbDefaultButton1 — 0
vbDefaultButton2 — 256
vbDefaultButton3 — 512
vbDefaultButton4 — 768
Title — Text at the very top of the message box. (Optional)
Helpfile — Path to your helpfile. (Optional)
Context — A numerical expression. (Optional, required if you specify a helpfile)
Back to top
1.2 How to configure buttons on a message box
There are six different button setups. The most basic message box shows a text string or a variable and an OK button.
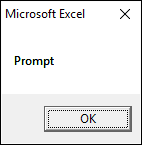
1.2.1 vbOKOnly
The dialog box demonstrated in the image above shows a single «OK» button, the VBA code below shows how to create the dialog box.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbOKOnly End Sub
You don’t even need to specify the vbOKOnly argument to show the above dialog box.
Back to top
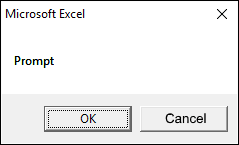
1.2.2 vbOKCancel
The dialog box demonstrated in the image above shows an «OK» and «Cancel» button, the VBA code below shows how to create the dialog box.
vbOKCancel argument displays OK and Cancel buttons.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbOKCancel End Sub
Back to top
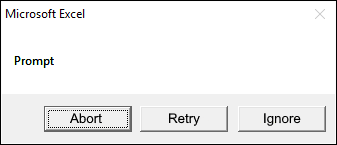
1.2.3 vbAbortRetryIgnore
The dialog box demonstrated in the image above shows an «Abort», «Retry», and «Ignore» button, the VBA code below shows how to create the dialog box.
vbAbortRetryIgnore argument shows three buttons, abort, retry and ignore on the dialog box.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbAbortRetryIgnore End Sub
Back to top
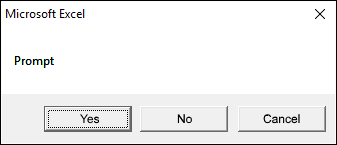
1.2.4 vbYesNoCancel
The dialog box demonstrated in the image above shows a «Yes», «No», and «Cancel» button, the VBA code below shows how to create the dialog box.
vbYesNoCancel argument also shows three buttons, however, they are named, Yes, No, and Cancel.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbYesNoCancel End Sub
Back to top
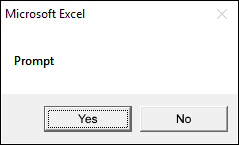
1.2.5 vbYesNo
The dialog box demonstrated in the image above shows a «Yes» and «No» button, the VBA code below shows how to create the dialog box.
vbYesNo argument diplays Yes and No buttons.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbYesNo End Sub
Back to top
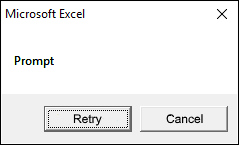
1.2.6 vbRetryCancel
vbRetryCancel argument shows Retry and Cancel buttons.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbRetryCancel End Sub
Back to top
1.3 Icons
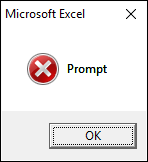
1.3.1 vbCritical
vbCritical shows this icon on the message box, see the image above.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbCritical End Sub
Back to top
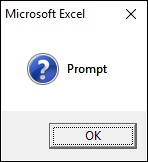
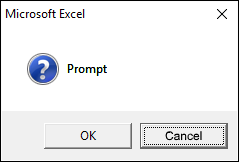
1.3.2 vbQuestion
vbQuestion shows this query icon, see the image above.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbQuestion End Sub
Back to top
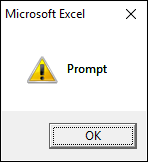
1.3.3 vbExclamation
vbExclamation shows a warning icon, see the image above.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbExclamation End Sub
Back to top
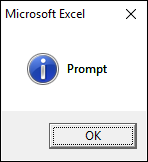
1.3.4 vbinformation
vbinformation shows an information icon, see the image above.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbInformation End Sub
Back to top
1.3 Combine buttons and icons
If you look at the message box arguments at the beginning of this post, you will see a number next to each constant. Combining for example an OK and Cancel button with a query icon you simply add the numbers for those constants. OK and Cancel has value 1 and the query icon has value 32.
1 + 32 = 33
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", 33 End Sub
You can combine constants intead of values, if you prefer that. See macro below, it produces the same result as the macro above.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbOKCancel + vbQuestion End Sub
Back to top
1.4 Default buttons
You can change the default button for a message box, see the arguments in the beginning of this post. The following message box has the OK button as the default button, it has a dotted line around the text «OK».
You can change it to the second button by adding 256 to the second argument. 33 + 256 = 289
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", 289 End Sub
If you prefer you can add the constants to the second argument, as well. This macro shows the same message box as above.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbOKCancel + vbQuestion + vbDefaultButton2 End Sub
Back to top
1.5 Messagebox return value
The message box returns one of these values depending on which button was press with left mouse button oned on by the user.
vbOK — 1
vbCancel — 2
vbAbort — 3
vbRetry — 4
vbIgnore — 5
vbYes — 6
vbNo — 7
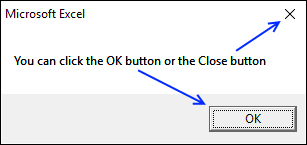
This message box allows you to press with left mouse button on the OK button or the Close button. Both buttons result in the value 1 or vbOK.
Sub Macro1()
Dim btt
btt = MsgBox("You can press with left mouse button on the OK button or the Close button", vbOKOnly)
MsgBox btt
End Sub
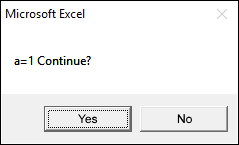
The following macro allows you to continue or stop a loop using a message box. If you press with left mouse button on No the macro ends.
Sub Macro1()
Dim a As Integer
For a = 1 To 10
If MsgBox("a=" & a & " Continue?", vbYesNo) = vbNo Then Exit For
Next a
End Sub
Back to top
1.6 Help file
Here is an example of how to use a msgbox with a helpfile.
<href=»https://www.get-digital-help.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/dialog-boxes-help-file-1.png»>
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "Prompt", vbMsgBoxHelpButton, "This is a title", "c:temphelpfile.chm", 7 End Sub
How to build a chm file
Back to top
1.7 Working with text in a message box
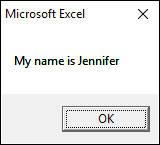
The following macro shows you how to concatenate text and a variable.
Sub Macro1() Dim nm As String nm = "Jennifer" MsgBox "My name is " & nm End Sub
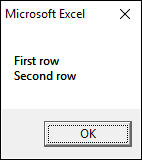
This macro shows you how to put text on two rows.
Sub Macro1() MsgBox "First row" & vbNewLine & "Second row" End Sub
You can also show data with a delimiting tab.
Sub Macro1() Dim a As Integer, result As String For a = 1 To 8 result = result & a & vbTab Next a MsgBox result End Sub
Back to top
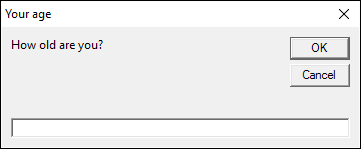
2. Input box (VBA)
An input box asks the user for a value, you can specify the text and the title in the inputbox. You also have the option where to show the input box on screen and a default input value.
prompt — text in input box
title — Text at the very top of the input box
default — default value shown in the input box
xpo,ypos — specify where you want the input box on the screen from the upper-left corner.
helpfile — path to help file
context — A numerical value
Back to top
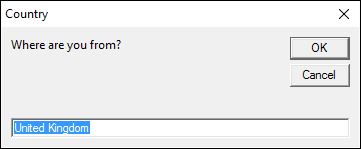
2.1 How to set the default value for an input box?
This macro asks where you are from. The default value is «United Kingdom».
Sub Macro1()
Dim Country
Country = InputBox("Where are you from?", "Country", "United Kingdom")
MsgBox Country
End Sub
Note, the Input box returns nothing if you press with left mouse button on the Cancel button.
Back to top
3. Input box (Excel)
Excel input box is more versatile, it will do basic validation for you and the user can select a cell range on a worksheet. You have also the option to select one or multiple data types returned by the input box.
prompt — text in input box
title — Text at the very top of the input box
default — default value shown in the input box
left, top — specify where you want the input box from the upper-left corner of the screen.
helpfile — path to help file
HelpContextID — A numerical value
Type — A number representing the data type returned
0 — Formula
1 — Number
2 — Text
4 — Logical value, True or False
8 — A cell reference
16 — Error value
64 — An array of values
Back to top
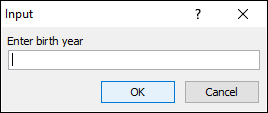
3.1 Number
Sub Macro1()
Dim cd
cd = Application.InputBox("Enter birth year", , , , , , , 1)
MsgBox "Your birth year is " & cd
End Sub
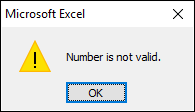
Excel provides basic data validation, if you type a text string excel gives you this warning message.
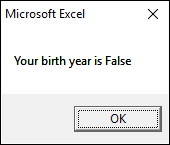
If you press with left mouse button on «Cancel» button excel returns «False».
Back to top
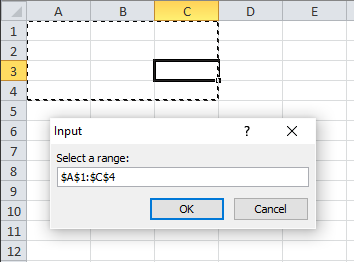
3.2 Range
Data type 8 (Cell reference) lets the user select a cell range.
Sub Macro1()
Dim rngAs Range
Set rng = Application.InputBox("Select a range: ", , , , , , , 8)
MsgBox "You selected " & rng.Address
End Sub
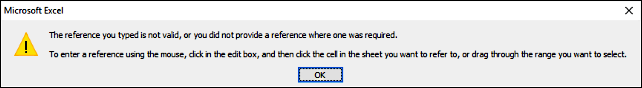
If the user enters something else than a cell reference excel gives this message until a valid cell reference is entered:
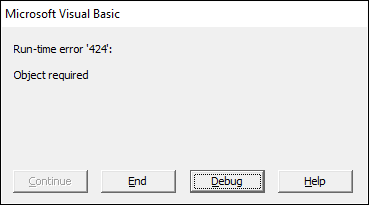
Press with left mouse button oning on «Cancel» button makes excel error out:
Back to top
3.3 Combine data types
If you combine data types by adding their corresponding value, like this 1+2 = 3 the user is allowed to enter both numbers and text.
Sub Macro1()
Dim cd
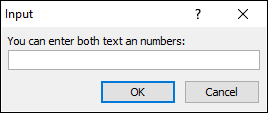
cd = Application.InputBox("You can enter both text an numbers: ", , , , , , , 3)
MsgBox "You entered " & cd
End Sub
Back to top
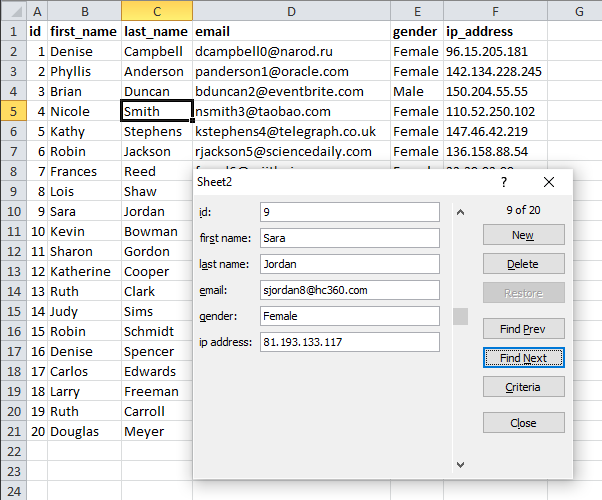
4. Data Form
Data in this table is made up and random.
The data form is a smart dialog box, it analyzes your table and customizes the dialog box using table headers.
Make sure you have a cell selected in the table you want to work with before running this macro:
Sub Macro1() ActiveSheet.ShowDataForm End Sub
Back to top
5. FileDialog
FileDialog property lets you prompt the user for a directory or open/save/select a file
fileDialogType — Choose between 4 constants, see below.
msoFileDialogFilePicker — Select a file
msoFileDialogFolderPicker — Select a folder
msoFileDialogOpen — Open a file
msoFileDialogSaveAs — Save a file
5.1 msoFileDialogFilePicker
Allows the user to select a file. The following macro prompts the user for a file o multiple files and then a message box returns the path and file name for each file.
Sub Macro1() Dim i As Integer With Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogFilePicker) .Show For i = 1 To .SelectedItems.Count MsgBox .SelectedItems(i) Next i End With End Sub
5.2 msoFileDialogFolderPicker
The following macro lets the user pick a folder. A message box displays the path and folder name.
Sub Macro1() Dim i As Integer With Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogFolderPicker) .Show MsgBox .SelectedItems(1) End With End Sub
5.3 msoFileDialogOpen
The macro below asks the user for a file to open. A message box displays the path and file name. Note, it doesn’t open the file.
Sub Macro1() Dim i As Integer With Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogOpen) .Show MsgBox .SelectedItems(1) End With End Sub
5.4 msoFileDialogSaveAs
This macro lets the user pick a folder and a save name. A message box displays the path and file name. It doesn’t save the file
Sub Macro1() Dim i As Integer With Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogOpen) .Show MsgBox .SelectedItems(1) End With End Sub
Back to top
6. GetOpenFilename
Filefilter — Filter criteria (Optional)
FilterIndex — Index number of default filter (Optional)
Title — title of dialog box (Optional)
Multiselect — Enables the user to select multiple filenames (Optional)
The following macro asks for a file to open, filters used are *.xlsx and *.xlsm. The second filter is the default value. Keep in mind, the macro doesn’t open the file it just returns a file name and path.
Sub Macro1()
Dim txt
txt = Application.GetOpenFilename("Excel Files (*.xlsx), *.xlsx, Excel macro files (*.xlsm),*.xlsm", 2)
MsgBox txt
End Sub
If the user press with left mouse button ons «Cancel» a False is returned.
Back to top
7. GetSaveFilename
Filefilter — Filter criteria (Optional)
FilterIndex — Index number of default filter (Optional)
Title — title of dialog box (Optional)
Sub Macro1()
Dim txt
txt = Application.GetSaveAsFilename("Excel Files (*.xlsx), *.xlsx, Excel macro files (*.xlsm),*.xlsm", 2)
MsgBox txt
End Sub
This macro does not save the file, it only returns the selected path and name.
Back to top
Input information and make choices about Excel worksheet features
Updated on October 14, 2019
A dialog box in Excel is a screen where you input information and make choices about different aspects of the current worksheet or its content, such as data, charts, and graphic images.
The information in this article applies to Excel versions 2019, 2016, 2013, 2010, and Excel for Mac.
Find the Dialog Box Launcher
One way to open dialog boxes is to use the dialog box launcher. The launcher is a small downward-pointing arrow located in the bottom right corner of individual groups or boxes on the ribbon.
Examples of groups with a dialog box launcher include:
- The Font and Number groups on the Home tab
- The Charts group on the Insert tab
- The Page Setup and Sheet Options groups on the Page Layout tab
Access Function Dialog Boxes
Not all dialog box launchers in Excel are found in the corner of ribbon groups. Some, such as those found under the Formulas tab, are associated with individual icons on the ribbon.
The dialog box makes it easy to enter information related to the function’s arguments, such as the location of data and other input options.
The Formulas tab in Excel contains groups of functions that have similar purposes in the Function Library. Each group name has a dialog box launcher associated with it. When you select these down arrows, a drop-down menu opens and displays individual function names. Selecting a function’s name in the list opens its dialog box.
Work With Non-Dialog Box Options
It is not always necessary to access features and options in Excel through a dialog box. For example, many of the formatting features found on the Home tab of the ribbon, such as the bold feature, are found on single choice icons. Select these icons once to activate the feature and select a second time to turn the feature off.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe
Хитрости »
19 Октябрь 2014 101399 просмотров
Работа с диалогами
Несомненно каждый разработчик делает работу простого пользователя хоть немного, но проще. И конечно, порой просто необходима обратная связь от пользователя при выполнении некоторых программ. О ней и хочу сегодня рассказать.
Что я имею ввиду: есть ситуации, когда необходимо:
- сообщить пользователю о выполнении кода;
- получить от пользователя подтверждение на выполнение того или иного действия;
- запросить какие-то данные(число, текст для поиска, диапазон поиска и т.п.).
Простейшие запросы и подтверждения можно сделать при помощи уже встроенных диалоговых окон.
Из основных можно выделить три типа:
MsgBox — окно информирования пользователя с возможностью запроса действия (Да, Нет, Отмена и т.п.);
InputBox — окно запроса текстовой информации от пользователя (текст для поиска, дата, число и т.п.);
Application.InputBox — чуть более расширенная версия InputBox с возможностью указания не только текста и чисел, но и выделения диапазона ячеек (например для указания ячеек, в которых осуществлять поиск значения или которые необходимо закрасить).
- Информационный диалог MsgBox
- MsgBox, автоматически закрываемый по истечении указанного времени
- Диалог ввода информации пользователем InputBox
- Диалог выбора диапазона Application.InputBox
Самый простой тип. Используется для информирования пользователя. Как правило применяется по окончании выполнения кода:
MsgBox Promt, [Buttons], [Title], [HelpFile], [Context]
Обязательным к указанию является только первый параметр —
Promt
, в котором указывается непосредственно сообщение для вывода:
MsgBox "Обработка завершена"
Все остальные параметры указывать не обязательно, но их использование несколько расширяет возможности данного диалогового окна.
Buttons — указывается тип выводимых кнопок и стиль окна. По умолчанию применяется vbOKOnly — одна только кнопка Ок:
'показываем окно с кнопкой по умолчанию и типом важного сообщения MsgBox "Обработка завершена", vbCritical
Доступны значения:
| Значение | Числовая константа | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| vbOKOnly | 0 | Отображает только кнопку OK |
| vbOKCancel | 1 | Отображает кнопки ОК и Отмена |
| vbAbortRetryIgnore | 2 | Отображает кнопки Прервать, Повтор и Пропустить |
| vbYesNoCancel | 3 | Отображает кнопки Да, Нет и Отмена |
| vbYesNo | 4 | Отображает кнопки Да и Нет |
| vbRetryCancel | 5 | Отображает кнопки Повтор и Отмена |
| vbCritical | 16 | Отображает значок важного сообщения |
| vbQuestion | 32 | Отображает значок важного запроса |
| vbExclamation | 48 | Отображает значок предупреждающего сообщения |
| vbInformation | 64 | Отображает значок информационного сообщения |
| vbDefaultButton1 | 0 | По умолчанию выделена первая кнопка |
| vbDefaultButton2 | 256 | По умолчанию выделена вторая кнопка |
| vbDefaultButton3 | 512 | По умолчанию выделена третья кнопка |
| vbDefaultButton4 | 768 | По умолчанию выделена четвертая кнопка |
| vbApplicationModal | 4098 | Все приложения приостанавливают свою работу до момента, пока пользователь ответит на запрос в окне сообщения (работает не во всех случаях) |
| vbMsgBoxHelpButton | 16384 | Показываются кнопки Ок и Help |
Константы Buttons могут быть объединены между собой. Ниже приведен код, который показывает диалоговое окно с возможностью выбора одного из трех вариантов — Прервать, Повтор, Пропустить:
'--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ' Procedure : test ' DateTime : 19.10.2014 19:24 ' Author : The_Prist(Щербаков Дмитрий) ' WebMoney - R298726502453; Яндекс.Деньги - 41001332272872 ' http://www.excel-vba.ru ' Purpose : Процедура показывает диалоговое окно с возможностью выбора одного из трех вариантов: ' Прервать, Повтор, Пропустить ' По умолчанию выделена кнопка Прервать, т.к. иное не указано '--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Sub test() Dim lRetVal As Long 'для получения выбранного значения Retry_: lRetVal = MsgBox("Обработка завершена", vbAbortRetryIgnore + vbQuestion) Select Case lRetVal Case vbAbort '3/Прервать/Abort Exit Sub 'выходим из процедуры Case vbRetry '4/Повтор/Retry GoTo Retry_ 'переход на метку Retry_ Case vbIgnore '5/Пропустить/Ignore End Select End Sub
Следующий код показывает то же окно, но по умолчанию выделяет кнопку Пропустить
'--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ' Procedure : test ' DateTime : 19.10.2014 19:24 ' Author : The_Prist(Щербаков Дмитрий) ' WebMoney - R298726502453; Яндекс.Деньги - 41001332272872 ' http://www.excel-vba.ru ' Purpose : Процедура показывает диалоговое окно с возможностью выбора одного из трех вариантов: ' Прервать, Повтор, Пропустить ' По умолчанию выделена кнопка Пропустить(3-я по счету - значит vbDefaultButton3) '--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Sub test() Dim lRetVal As Long 'для получения выбранного значения Retry_: lRetVal = MsgBox("Обработка завершена", vbAbortRetryIgnore + vbQuestion + vbDefaultButton3) Select Case lRetVal Case vbAbort '3/Прервать/Abort Exit Sub 'выходим из процедуры Case vbRetry '4/Повтор/Retry GoTo Retry_ 'переход на метку Retry_ Case vbIgnore '5/Пропустить/Ignore End Select End Sub
Вместо текстового представления констант можно применить их числовые значения:
Sub test() Dim lRetVal As Long 'для получения выбранного значения Retry_: lRetVal = MsgBox("Обработка завершена", 2 + 32 + 512) Select Case lRetVal Case 3 'vbAbort Exit Sub 'выходим из процедуры Case 4 'vbRetry GoTo Retry_ 'переход на метку Retry_ Case 5 'vbIgnore End Select End Sub
Нетрудно после этого предположить, что можно указать просто сумму данных чисел:
MsgBox "Обработка завершена", 546
Доступные константы значений возврата:
| Константа | Значение | Нажатая кнопка |
|---|---|---|
| vboK | 1 | ОК |
| vbCancel | 2 | Отмена |
| vbAbort | 3 | Прервать |
| vbRetry | 4 | Повтор |
| vblgnore | 5 | Пропустить |
| vbYes | 6 | Да |
| vbNo | 7 | Нет |
Title — указывается текст заголовка окна. Например, можно указать либо что это ошибка, либо имя своего приложения:
MsgBox "Обработка завершена", vbOKOnly, "Мое приложение"
HelpFile — указывается имя файла-справки в формате HLP. Применяется, если параметр Buttons указан как vbMsgBoxHelpButton. Файл справки должен существовать.
Context — целое число. Указывается индекс страницы файла-справки, которую необходимо открыть. Указывается только если указан параметр HelpFile.
Небольшой практический пример применения простого диалогового окна MsgBox.
Цель процедуры(макроса): очистить все ячейки листа.
Согласитесь, что неплохо бы перед этим запросить у пользователя решение — он согласен с этим и это является обдуманным решением или случайностью?
'--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ' Procedure : ClearRange ' DateTime : 19.10.2014 20:06 ' Author : The_Prist(Щербаков Дмитрий) ' WebMoney - R298726502453; Яндекс.Деньги - 41001332272872 ' http://www.excel-vba.ru ' Purpose : '--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Sub ClearRange() Dim lRetVal As Long 'для получения выбранного значения lRetVal = MsgBox("Все данные выделенных ячеек будут удалены." & _ Chr(10) & "Действительно хотите продолжить?", _ vbYesNo + vbQuestion, "Запрос на выполнение") If lRetVal = vbNo Then Exit Sub 'выходим из процедуры без выполнения End If Selection.Clear End Sub
Так же на странице Полезные программы для Excel и VBA можно найти программу MsgBox Generator, которая просто и наглядно формирует коды показа MsgBox.
Диалог MsgBox удобен, если надо проинформировать пользователя о каких-то событиях или предоставить ему выбор Да или Нет. Но в тоже время есть один недостаток: этот диалог не закроется, пока пользователь не нажмет хоть какую-то кнопку. Но бывает необходимо просто проинформировать и закрыть окно независимо от реакции пользователя. Показали окно, подождали секунд 5-7 и даже если пользователь ничего не нажал — закрыли окно и продолжили выполнение кода. Стандартно такой опции в MsgBox нет. Однако можно использовать функции API(это встроенные в ОС Windows функции, которые можно вызывать из любого языка программирования).
Код такого диалога:
Declare Function MessageBoxTimeOut Lib "User32" Alias "MessageBoxTimeoutA" _ (ByVal hwnd As Long, ByVal lpText As String, _ ByVal lpCaption As String, ByVal uType As VbMsgBoxStyle, _ ByVal wLanguageId As Long, ByVal dwMilliseconds As Long) As Long Sub AutoCloseMsgBox() Const lSeconds As Long = 5 MessageBoxTimeOut 0, "Отчет сформирован. Это окно закроется автоматически через 5 секунд", "www.excel-vba.ru", _ vbInformation + vbOKOnly, 0&, lSeconds * 1000 End Sub
Основную роль здесь играет строка:
Declare Function MessageBoxTimeOut Lib "User32" Alias "MessageBoxTimeoutA" _ (ByVal hwnd As Long, ByVal lpText As String, _ ByVal lpCaption As String, ByVal uType As VbMsgBoxStyle, _ ByVal wLanguageId As Long, ByVal dwMilliseconds As Long) As Long
это и есть сама функция, создающая MsgBox.
Главное: эта строка должна располагаться в самом верху стандартного модуля(в области объявлений, перед всеми процедурами и функциями).
Так же следует помнить, что это функция API и в некоторых версиях Excel именно в таком виде может не работать — вся строка будет подсвечена красным. Если проявился такой эффект, то можно просто добавить ключевое слово PtrSafe, отвечающее за совместимость функции с 64-битными ОС:
Declare PtrSafe Function MessageBoxTimeOut Lib "User32" Alias "MessageBoxTimeoutA" _ (ByVal hwnd As Long, ByVal lpText As String, _ ByVal lpCaption As String, ByVal uType As VbMsgBoxStyle, _ ByVal wLanguageId As Long, ByVal dwMilliseconds As Long) As Long
Помимо очевидного текста сообщения и заголовка, который можно заменить на свой, главное внимание уделим константе lSeconds. Она отвечает за количество секунд показа сообщения. В примере выше сообщение будет показано на 5 секунд, после чего закроется само собой, если ранее не была нажата кнопка Ок.
Если необходимо показать сообщение на 10 секунд, то надо лишь заменить 5 на 10:
Const lSeconds As Long = 10
Параметр uType работает точно так же, как параметр Buttons у стандартного MsgBox. Т.е. можно комбинировать различные виды кнопок и использовать этот MsgBox как стандартный, но при этом закрыть его автоматически, если пользователь случайно «уснул» или ему лень/некогда что-то нажимать:
Sub AutoCloseMsgBox() Const lSeconds As Long = 10 Dim retval retval = MessageBoxTimeOut(0, "Файлы обработаны. Вывести список?" & vbNewLine & _ "Если действие не будет выбрано окно закроется через 10 секунд", "www.excel-vba.ru", _ vbInformation + vbYesNo, 0&, lSeconds * 1000) If retval = 6 Then 'была нажата кнопка Да(Yes) 'выводим отчет Else 'была нажата кнопка Нет(No) или окно закрылось само 'другое действие End If End Sub
InputBox
позволяет запросить от пользователя любую текстовую информацию.
InputBox Promt, [Title], [DefaultValue], [XPos], [YPos], [HelpFile], [Context]
Так же как и с MsgBox обязательным аргументом для указания является только
Promt
— это тот текст, который будет расположен непосредственно на самой форме диалога. Как правило это пояснение, что должен ввести пользователь.
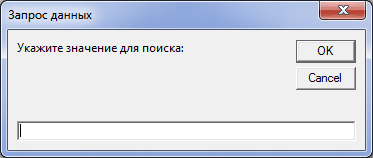
Dim vRetVal 'для получения выбранного значения vRetVal = InputBox("Укажите значение для поиска:", "Запрос данных", "") If vRetVal = "" Then Exit Sub 'завершаем процедуру, если строка пуста
Title — текст, отображаемый в заголовке окна. В приведенном выше примере это «Запрос данных».
DefaultValue — значение, которое будет показано в поле ввода до указания значения пользователем. Как правило оно указывается в случаях, когда требуемое значение изменяется редко по запросу пользователя, но возможность такую оставить все же требуется.
Пример: необходимо по нажатию кнопки удалять всегда столбец 5. Но иногда столбец в отчете смещается и требуется запрашивать у пользователя реальный номер столбца:
Sub DelCols() Dim vRetVal 'для получения выбранного значения vRetVal = InputBox("Укажите номер столбца для удаления(целое число):", "Запрос данных", 5) 'используем Val для преобразования текста vRetVal в число 'Val() преобразует число как текст в число. 'Если указан текст(например "третий") - он будет преобразован в 0 vRetVal = Val(vRetVal) If Val(vRetVal) = 0 Then MsgBox "Номер столбца должен быть целым числом больше нуля!", vbCritical, "DelCols" Exit Sub End If Columns(vRetVal).Delete End Sub
Важно знать: InputBox всегда возвращает только текст. Даже если указать — 5 — он вернет «5». В некоторых случаях это может привести к ошибке типов данных, поэтому я привел выше один из примеров преобразования типов данных к нужному.
Так же по прошествии какого-то времени появится вопрос, как отследить нажатие кнопки Отмена. Ведь ориентир на vRetVal = «» не всегда верен, иногда надо принять пустое значение(в случаях, скажем, замены значений) и отследить именно нажатие Отмена. Сделать это можно так:
vRetVal = InputBox("Укажите номер столбца для удаления(целое число):", "Запрос данных", "") If StrPtr(vRetVal) = 0 Then MsgBox "Нажата кнопка Отмена. Процедура прервана", vbCritical, "DelCols" Exit Sub End If
Больше всего вопросов здесь явно вызовет StrPtr. Эта специальная функция VBA, которая указывает, что переданы некие строковые данные. Если никаких данных не передавалось(а в случае с нажатием кнопки Отмена так и есть) указатель вернет 0. Если какие-то данные были переданы или нажата кнопка Ок(автоматом будет передана строка нулевой длины) — указатель StrPtr вернет значение отличное от нуля.
XPos — положение окна InputBox в твипах по горизонтали относительно левого края экрана. Следует учитывать, что именно относительно экрана, а не окна Excel.
YPos — положение окна InputBox в твипах по вертикали относительно верхнего края экрана.
HelpFile — указывается имя файла-справки в формате HLP. В отличие от MsgBox указание файла допускается при любых значениях. При этом к уже имеющимся в InputBox кнопкам добавляется еще одна — Help, которая и отвечает за вызов справки.
Context — целое число. Указывается индекс страницы файла-справки, которую необходимо открыть при нажатии кнопки Help. Указывается только если указан параметр HelpFile.
В дополнение приведу классический пример применения InputBox — выполнение процедуры только после введения пароля:
Sub ClearAllCells() Dim vRetVal vRetVal = InputBox("Введите пароль:", "Авторизация", "") If StrPtr(vRetVal) = 0 Then 'Нажата кнопка Отмена Exit Sub End If 'если пароль неверный - завершаем процедуру без выполнения действий If vRetVal <> "1234" Then MsgBox "Введенный пароль неверный", vbCritical, "ClearAllCells" Exit Sub End If 'будет выполнено только если введен правильный пароль - 1234 'полная очистка всех ячеек активного листа ActiveSheet.Cells.Clear End Sub
А вот еще один пример применения — запрос имени пользователя и запись его в лист LOG, чтобы можно было отследить кто и когда открывал файл. При этом если пользователь нажал Отмена, то книга закроется, а если не укажет имя пользователя — появится сообщение и заново запрос. И так до тех пор, пока имя пользователя не будет введено или не будет нажата кнопка Отмена:
Private Sub Workbook_Open() 'ThisWorkbook - Обращение к книге с кодом 'Но из модуля самой книги можно обращаться и проще - Me ThisWorkbook.Visible = False Dim user As String, lastrow As Long 'цикл, пока не будут указаны данные пользователя Do While user = "" user = InputBox("Введите имя пользователя:", "Авторизация", "") If StrPtr(user) = 0 Then MsgBox "Приложение будет закрыто", vbCritical, "Авторизация" ThisWorkbook.Close Exit Sub End If If user = "" Then MsgBox "Не указано имя пользователя!", vbCritical, "Авторизация" End If Loop With ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("LOG") 'получаем последнюю заполненную ячейку на листе "LOG" lastrow = .Cells(.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row 'записываем имя пользователя .Cells(lastrow + 1, 1) = user 'записываем время входа .Cells(lastrow + 1, 2) = Now End With End Sub
Что важно: этот код записывается в модуль ЭтаКнига(ThisWorkbook) и тогда при любом открытии книги будет появляться запрос на имя пользователя.
Так же некоторые примеры применения InputBox можно найти в статьях на сайте. Например:
Как удалить строки по условию?
Как массово изменить гиперссылки?
ДИАЛОГ ВВОДА ИНФОРМАЦИИ ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЕМ — APPLICATION.INPUTBOX
В общем-то данный диалог мало отличается от обычного InputBox, за исключением типов возвращаемых данных. У данного диалога намного богаче функционал определения типов данных.
InputBox Promt, [Title], [DefaultValue], [Left], [Top], [HelpFile], [HelpContextID], [Type]
почти все параметры аналогичны таким же параметрам в InputBox.
Promt — текст, отображаемый на самой форме. Иначе говоря — сама суть показа диалога.
Title — текст, отображаемый в заголовке окна. В приведенном выше примере это «Запрос данных».
DefaultValue — значение, которое будет показано в поле ввода до указания значения пользователем.
Left — положение окна InputBox в поинтах по горизонтали относительно левого края экрана. В отличие от простого InputBox положение определяется на основании расположения самого окна Excel, а не экрана.
Top — положение окна InputBox в твипах по вертикали относительно верхнего края экрана.
HelpFile — указывается имя файла-справки в формате HLP. В отличие от MsgBox указание файла допускается при любых значениях. При этом к уже имеющимся в InputBox кнопкам добавляется еще одна — Help, которая и отвечает за вызов справки. Сам вызов справки осуществляется путем нажатия на иконку со знаком вопроса в заголовке диалога.
HelpContextID — целое число. Указывается индекс страницы файла-справки, которую необходимо открыть при нажатии кнопки Help. Указывается только если указан параметр HelpFile.
Type — целое число. Указывается одно из предустановленных значений, указывающих диалогу Application.InputBox тип данных, которые предполагается получить от пользователя. Ниже приведен листинг кода, демонстрирующий запрос данных всех типов с описанием ограничений и нюансов.
Dim vRetVal 'для получения выбранного значения 'запрос формулы - Type:=0 'возвращает либо произвольный текст, указанный в поле или ссылку на указанную ячейку в стиле R1C1 vRetVal = Application.InputBox("Укажите формулу:", "Запрос данных", "", Type:=0) 'запрос числа - Type:=1 'возвращает число. Не даст ввести текст, выдав сообщение об ошибке vRetVal = Application.InputBox("Укажите любое число:", "Запрос данных", "", Type:=1) 'запрос текст - Type:=2 'возвращает указанный текст. При указании числа оно будет в виде текста: 1="1" vRetVal = Application.InputBox("Укажите любой текст:", "Запрос данных", "", Type:=2) 'запрос логического значения True или False - Type:=4 'значение указывает в текущей локализации офиса 'для русской это ИСТИНА или ЛОЖЬ 'так же можно указать универсальные числовые константы - 1 или 0. 1 - ИСТИНА; 0 - ЛОЖЬ 'Не даст ввести иные значения, выдав сообщение об ошибке 'возвращает указанное логическое значение в английской локализации vRetVal = Application.InputBox("Укажите ИСТИНА или ЛОЖЬ:", "Запрос данных", "", Type:=4) 'запрос диапазона - Type:=8 'возвращает ссылку на диапазон 'При получении такого значения обязательно следует использовать оператор Set 'В противном случае вернет значение массива(Array), содержащего значения указанных ячеек 'при указании через Set и нажатии Отмена будет ошибка VBA Set vRetVal = Application.InputBox("Укажите диапазон для очистки ячеек:", "Запрос данных", "", Type:=8) 'запрос значения ошибки #Н/Д - Type:=16 'всегда возвращает значение ошибки #Н/Д независимо от введенного значения vRetVal = Application.InputBox("Укажите диапазон для очистки ячеек:", "Запрос данных", "", Type:=16) 'запрос диапазона ячеек для создания массива - Type:=64 'возвращает массив ячеек с границами начала от 1(Option Base 1) 'если указать всего одну ячейку vRetVal будет содержать значение этой ячейки, а не массив vRetVal = Application.InputBox("Укажите диапазон для создания массива:", "Запрос данных", "", Type:=64)
Конечно, чаще всего используют Type:=8, т.к. это избавляет от необходимости рисования своих форм и прочих заморочек для запроса указания диапазона от пользователя. Еще раз обращаю внимание, что для Type:=8 необходим ключевой оператор присвоения Set, т.к. в результате необходимо получить именно диапазон(т.е. объект). Ниже приведена процедура, которая запрашивает диапазон для очистки и корректно обрабатывает ситуацию при нажатии кнопки Отмена(т.е. не показывает никаких ошибок пользователю, а просто не выполняется). Стандартно при нажатии Отмена процедура завершается с ошибкой VBA вида Type Mismatch, что не очень грамотно с точки зрения взаимодействия с пользователем — он не должен видеть внутренние ошибки:
'--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ' Procedure : ClearCells ' DateTime : 19.10.2014 22:53 ' Author : The_Prist(Щербаков Дмитрий) ' WebMoney - R298726502453; Яндекс.Деньги - 41001332272872 ' http://www.excel-vba.ru ' Purpose : ' Запрашиваем диапазон ячеек для очистки. ' По умолчанию заносится диапазон выделенных на момент запуска ячеек '--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Sub ClearCells() Dim vRetVal 'для получения выбранного значения On Error Resume Next Set vRetVal = Application.InputBox("Укажите диапазон для очистки ячеек:", "Запрос данных", Selection.Address, Type:=8) If vRetVal Is Nothing Then 'нажата кнопка Отмена - диапазон не выбран MsgBox "Отмена выполнения", vbCritical, "Нет данных" Exit Sub 'завершаем процедуру, т.к. ячейки не выбраны End If 'диапазон выбран - очищаем ячейки vRetVal.Clear End Sub
Статья помогла? Поделись ссылкой с друзьями!
Видеоуроки
Поиск по меткам
Access
apple watch
Multex
Power Query и Power BI
VBA управление кодами
Бесплатные надстройки
Дата и время
Записки
ИП
Надстройки
Печать
Политика Конфиденциальности
Почта
Программы
Работа с приложениями
Разработка приложений
Росстат
Тренинги и вебинары
Финансовые
Форматирование
Функции Excel
акции MulTEx
ссылки
статистика
Return to VBA Code Examples
In this Article
- Message Box
- Syntax
- Simple Message Box
- YesNo Message Box
- Adding a Title
- Input Box
This article will demonstrate how to use Dialog Boxes in VBA.
Dialog Boxes are used to return information to the user. The most common dialog box that is used is the Message Box, but we can also use the Input Box.
Message Box
Syntax
The syntax of the Message Box is as follows:
|
Argument |
Explanation |
| Prompt |
Message returned to the user – required |
|
Buttons |
Visual Basic buttons – defaults to OK if omitted |
|
Title |
Title of Message box – optional |
|
HelpFile |
Helpfile – optional |
| Context |
Context – optional |
Simple Message Box
A simple message box just requires the prompt – the message you are returning to your user. The OK button will automatically be displayed.
Sub SimpleBox ()
MsgBox "Hello everybody!"
End SubYesNo Message Box
Adding in buttons can make you message box more flexible.
We can select the type of box from a drop down list of VB constants.
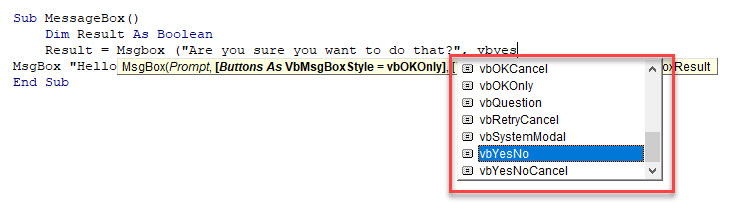
Sub MessageBox ()
Dim Result As Integer
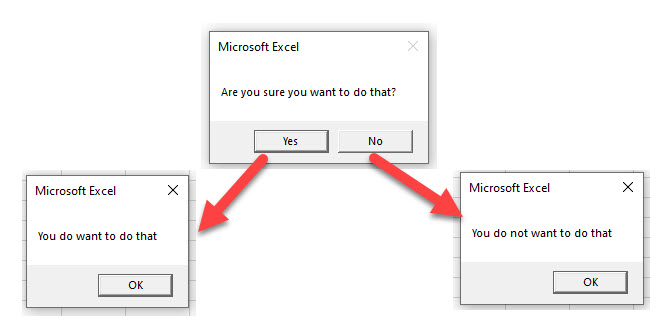
Result = MsgBox("Are you sure you want to do that?", vbYesNo)
If Result = vbYes Then
MsgBox ("You do want to do that")
Else
MsgBox ("You do not want to do that")
End If
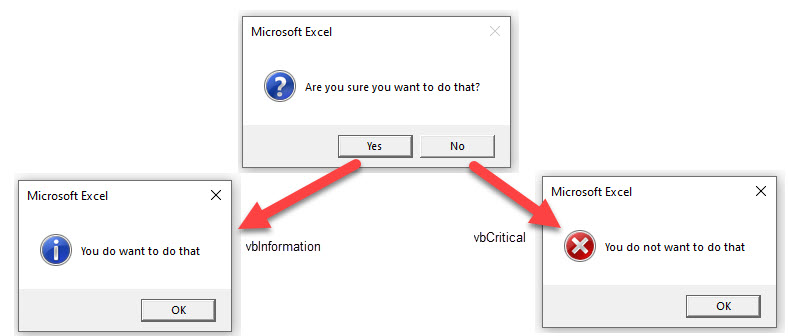
End SubAs well as the Yes/No button, we can icons to display in our message box to indicate to the user what type of message is being displayed.
Sub MessageBox ()
Dim Result As Integer
Result = MsgBox("Are you sure you want to do that?", vbYesNo + vbQuestion)
If Result = vbYes Then
MsgBox "You do want to do that", vbInformation
Else
MsgBox "You do not want to do that", vbCritical
End If
End SubNOTE: if you do not select a button constant, but do select an information constant, you need to omit the brackets from around the message box arguments.
Adding a Title
We can also fill in the title argument.
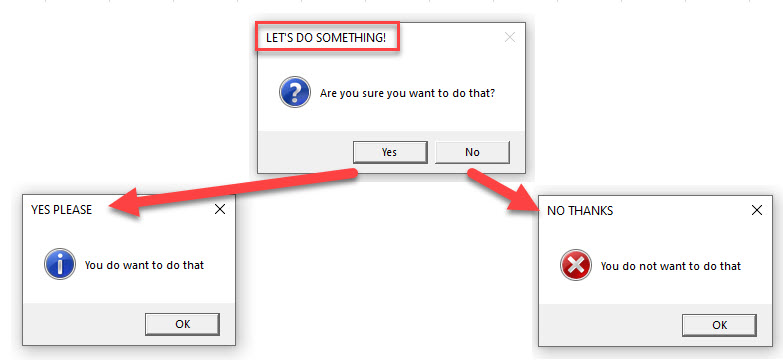
Sub MessageBox ()
Dim Result As Integer
Result = MsgBox("Are you sure you want to do that?", vbYesNo + vbQuestion, "LET'S DO SOMETHING!")
If Result = vbYes Then
MsgBox "You do want to do that", vbInformation, "YES PLEASE"
Else
MsgBox "You do not want to do that", vbCritical, "NO THANKS"
End If
End SubFor a more detailed article about Message Boxes, click here.
Input Box
An input box is a Dialog Box that asks the user a question, and returns a result.
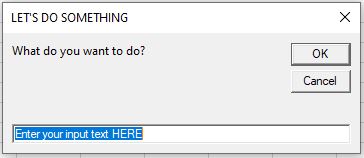
Sub TestInputBox ()
Dim Result As String
Result = InputBox("What do you want to do?", "LET'S DO SOMETHING", "Enter your input text HERE")
MsgBox Result
End SubFor a more detailed article about Input Boxes, click here.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!