|
Является ли диаграмма объектом в ООП для VBA |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
||||||||
Ответить |
Создание диаграммы с диапазонами и фиксированное имя
Графики могут быть созданы путем непосредственной работы с объектом Series который определяет данные диаграммы. Чтобы перейти к Series без диаграммы exisitng, вы создаете ChartObject на данном Worksheet а затем получаете объект Chart из него. Поверхность работы с объектом « Series заключается в том, что вы можете установить Values и XValues , обратившись к объектам Range . Эти свойства данных будут правильно определять Series со ссылками на эти диапазоны. Недостатком этого подхода является то, что при настройке Name не обрабатывается одно и то же преобразование; это фиксированное значение. Он не будет корректироваться с базовыми данными в исходном Range . Проверка формулы SERIES и очевидно, что имя исправлено. Это необходимо обработать, создав формулу SERIES напрямую.
Код, используемый для создания диаграммы
Обратите внимание, что этот код содержит объявления дополнительных переменных для Chart и Worksheet . Они могут быть опущены, если они не используются. Они могут быть полезны, однако, если вы изменяете стиль или любые другие свойства диаграммы.
Sub CreateChartWithRangesAndFixedName()
Dim xData As Range
Dim yData As Range
Dim serName As Range
'set the ranges to get the data and y value label
Set xData = Range("B3:B12")
Set yData = Range("C3:C12")
Set serName = Range("C2")
'get reference to ActiveSheet
Dim sht As Worksheet
Set sht = ActiveSheet
'create a new ChartObject at position (48, 195) with width 400 and height 300
Dim chtObj As ChartObject
Set chtObj = sht.ChartObjects.Add(48, 195, 400, 300)
'get reference to chart object
Dim cht As Chart
Set cht = chtObj.Chart
'create the new series
Dim ser As Series
Set ser = cht.SeriesCollection.NewSeries
ser.Values = yData
ser.XValues = xData
ser.Name = serName
ser.ChartType = xlXYScatterLines
End Sub
Исходные данные / диапазоны и итоговая Chart после Chart кода
Обратите внимание, что формула SERIES включает в себя "B" для названия серии вместо ссылки на Range который ее создал.

Создание пустой диаграммы
Отправной точкой для подавляющего большинства графического кода является создание пустой Chart . Обратите внимание , что эта Chart является предметом шаблона диаграммы по умолчанию , который является активным и не может на самом деле быть пустым (если шаблон был изменен).
Ключ к ChartObject определяет его местоположение. Синтаксис вызова — ChartObjects.Add(Left, Top, Width, Height) . После создания ChartObject вы можете использовать его объект Chart для фактического изменения диаграммы. ChartObject ведет себя больше как Shape чтобы расположить диаграмму на листе.
Код для создания пустой диаграммы
Sub CreateEmptyChart()
'get reference to ActiveSheet
Dim sht As Worksheet
Set sht = ActiveSheet
'create a new ChartObject at position (0, 0) with width 400 and height 300
Dim chtObj As ChartObject
Set chtObj = sht.ChartObjects.Add(0, 0, 400, 300)
'get refernce to chart object
Dim cht As Chart
Set cht = chtObj.Chart
'additional code to modify the empty chart
'...
End Sub
Результирующая диаграмма

Создание диаграммы путем изменения формулы SERIES
Для полного контроля над новым объектом Chart и Series (особенно для динамического названия Series ) вы должны прибегнуть к модификации формулы SERIES напрямую. Процесс создания объектов Range является простым, и основным препятствием является просто построение строки для формулы SERIES .
Формула SERIES принимает следующий синтаксис:
=SERIES(Name,XValues,Values,Order)
Это содержимое может быть предоставлено в виде ссылок или значений массива для элементов данных. Order представляет собой серию позиций в диаграмме. Обратите внимание, что ссылки на данные не будут работать, если они не полностью соответствуют имени листа. Для примера рабочей формулы щелкните любую существующую серию и проверьте панель формул.
Код для создания диаграммы и настройки данных с использованием формулы SERIES
Обратите внимание, что построение строки для создания формулы SERIES использует .Address(,,,True) . Это гарантирует, что ссылка внешнего диапазона используется так, чтобы был включен полный адрес с именем листа. Вы получите сообщение об ошибке, если имя листа исключено .
Sub CreateChartUsingSeriesFormula()
Dim xData As Range
Dim yData As Range
Dim serName As Range
'set the ranges to get the data and y value label
Set xData = Range("B3:B12")
Set yData = Range("C3:C12")
Set serName = Range("C2")
'get reference to ActiveSheet
Dim sht As Worksheet
Set sht = ActiveSheet
'create a new ChartObject at position (48, 195) with width 400 and height 300
Dim chtObj As ChartObject
Set chtObj = sht.ChartObjects.Add(48, 195, 400, 300)
'get refernce to chart object
Dim cht As Chart
Set cht = chtObj.Chart
'create the new series
Dim ser As Series
Set ser = cht.SeriesCollection.NewSeries
'set the SERIES formula
'=SERIES(name, xData, yData, plotOrder)
Dim formulaValue As String
formulaValue = "=SERIES(" & _
serName.Address(, , , True) & "," & _
xData.Address(, , , True) & "," & _
yData.Address(, , , True) & ",1)"
ser.Formula = formulaValue
ser.ChartType = xlXYScatterLines
End Sub
Исходные данные и итоговая диаграмма
Обратите внимание, что для этой диаграммы имя серии правильно задано с диапазоном до нужной ячейки. Это означает, что обновления будут распространяться на Chart .

Размещение диаграмм в сетке
Обычная работа с графиками в Excel — это стандартизация размера и компоновки нескольких диаграмм на одном листе. Если сделать это вручную, вы можете удерживать ALT при изменении размера или перемещении диаграммы, чтобы «придерживаться» границ ячеек. Это работает для пары диаграмм, но подход VBA намного проще.
Код для создания сетки
Этот код создаст сетку диаграмм, начинающихся с заданной (верхней, левой) позиции, с определенным количеством столбцов и определенным общим размером диаграммы. Графики будут размещены в том порядке, в котором они были созданы, и обернут вокруг края, чтобы сформировать новую строку.
Sub CreateGridOfCharts()
Dim int_cols As Integer
int_cols = 3
Dim cht_width As Double
cht_width = 250
Dim cht_height As Double
cht_height = 200
Dim offset_vertical As Double
offset_vertical = 195
Dim offset_horz As Double
offset_horz = 40
Dim sht As Worksheet
Set sht = ActiveSheet
Dim count As Integer
count = 0
'iterate through ChartObjects on current sheet
Dim cht_obj As ChartObject
For Each cht_obj In sht.ChartObjects
'use integer division and Mod to get position in grid
cht_obj.Top = (count int_cols) * cht_height + offset_vertical
cht_obj.Left = (count Mod int_cols) * cht_width + offset_horz
cht_obj.Width = cht_width
cht_obj.Height = cht_height
count = count + 1
Next cht_obj
End Sub
Результат с несколькими графиками
Эти снимки показывают исходную случайную компоновку диаграмм и результирующую сетку от запуска кода выше.
До

После

Excel VBA Charts
We can term charts as objects in VBA. Similar to the worksheet, we can also insert charts in VBA. First, we select the data and chart type we want for our data. Now, there are two different types of charts we provide. One is the embed chart, where the chart is in the same sheet of data. Another is known as the chart sheet, where the chart is in a separate data sheet.
In data analysis, visual effects are the key performance indicators of the person who has done the analysis. Visuals are the best way an analyst can convey their message. Since we are all Excel users, we usually spend considerable time analyzing the data and drawing conclusions with numbers and charts. Creating a chart is an art to master. We hope you have good knowledge of creating charts with excelIn Excel, a graph or chart lets us visualize information we’ve gathered from our data. It allows us to visualize data in easy-to-understand pictorial ways. The following components are required to create charts or graphs in Excel: 1 — Numerical Data, 2 — Data Headings, and 3 — Data in Proper Order.read more. This article will show you how to create charts using VBA coding.
Table of contents
- Excel VBA Charts
- How to Add Charts using VBA Code in Excel?
- #1 – Create Chart using VBA Coding
- #2 – Create a Chart with the Same Excel Sheet as Shape
- #3 – Code to Loop through the Charts
- #4 – Alternative Method to Create Chart
- Recommended Articles
- How to Add Charts using VBA Code in Excel?
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc, Please provide us with an attribution linkArticle Link to be Hyperlinked
For eg:
Source: VBA Charts (wallstreetmojo.com)
How to Add Charts using VBA Code in Excel?
You can download this VBA Charts Excel Template here – VBA Charts Excel Template
#1 – Create Chart using VBA Coding
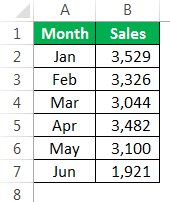
To create any chart, we should have some numerical data. For this example, we are going to use the below sample data.
First, let us jump to the VBA editorThe Visual Basic for Applications Editor is a scripting interface. These scripts are primarily responsible for the creation and execution of macros in Microsoft software.read more.
Step 1: Start Sub Procedure.
Code:
Sub Charts_Example1() End Sub
Step 2: Define the variable as Chart.
Code:
Sub Charts_Example1() Dim MyChart As Chart End Sub
Step 3: Since the chart is an object variable, we need to Set it.
Code:
Sub Charts_Example1() Dim MyChart As Chart Set MyChart = Charts.Add End Sub
The above code will add a new sheet as a chart sheet, not a worksheet.
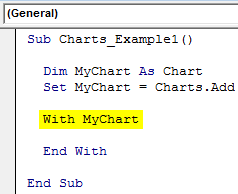
Step 4: Now, we need to design the chart. Open With Statement.
Code:
Sub Charts_Example1() Dim MyChart As Chart Set MyChart = Charts.Add With MyChart End With End Sub
Step 5: The first thing we need to do with the chart is to Set the source range by selecting the “Set Source Data” method.
Code:
Sub Charts_Example1() Dim MyChart As Chart Set MyChart = Charts.Add With MyChart .SetSourceData End With End Sub
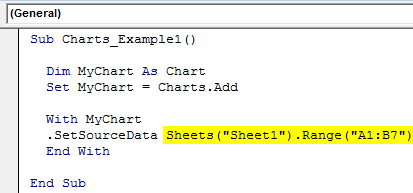
Step 6: We need to mention the source range. In this case, my source range is in the sheet named “Sheet1,” and the range is “A1 to B7”.
Code:
Sub Charts_Example1() Dim MyChart As Chart Set MyChart = Charts.Add With MyChart .SetSourceData Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A1:B7") End With End Sub
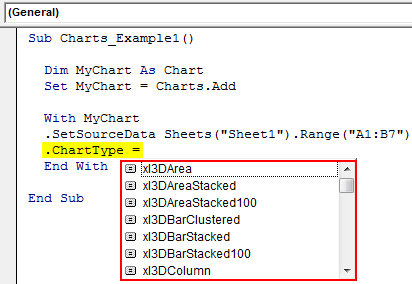
Step 7: Next up, we need to select the kind of chart we are going to create. For this, we need to select the Chart Type property.
Code:
Sub Charts_Example1() Dim MyChart As Chart Set MyChart = Charts.Add With MyChart .SetSourceData Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A1:B7") .ChartType = End With End Sub
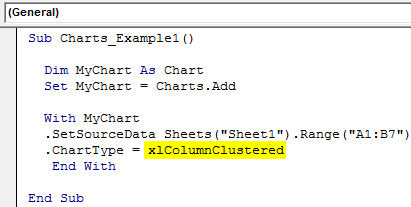
Step 8: Here, we have a variety of charts. I am going to select the “xlColumnClustered” chart.
Code:
Sub Charts_Example1() Dim MyChart As Chart Set MyChart = Charts.Add With MyChart .SetSourceData Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A1:B7") .ChartType = xlColumnClustered End With End Sub
Now let’s run the code using the F5 key or manually and see how the chart looks.
Step 9: Now, change other properties of the chart. To change the chart title, below is the code.
Like this, we have many properties and methods with charts. Use each one of them to see the impact and learn.
Sub Charts_Example1() Dim MyChart As Chart Set MyChart = Charts.Add With MyChart .SetSourceData Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A1:B7") .ChartType = xlColumnClustered .ChartTitle.Text = "Sales Performance" End With End Sub
#2 – Create a Chart with the Same Excel Sheet as Shape
We need to use a different technique to create the chart with the same worksheet (datasheet) as the shape.
Step 1: First, declare three object variables.
Code:
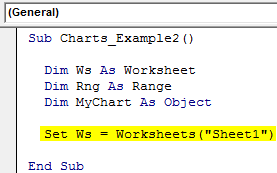
Sub Charts_Example2() Dim Ws As Worksheet Dim Rng As Range Dim MyChart As Object End Sub
Step 2: Then, set the worksheet reference.
Code:
Sub Charts_Example2() Dim Ws As Worksheet Dim Rng As Range Dim MyChart As Object Set Ws = Worksheets("Sheet1") End Sub
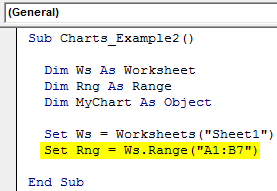
Step 3: Now, set the range object in VBARange is a property in VBA that helps specify a particular cell, a range of cells, a row, a column, or a three-dimensional range. In the context of the Excel worksheet, the VBA range object includes a single cell or multiple cells spread across various rows and columns.read more
Code:
Sub Charts_Example2() Dim Ws As Worksheet Dim Rng As Range Dim MyChart As Object Set Ws = Worksheets("Sheet1") Set Rng = Ws.Range("A1:B7") End Sub
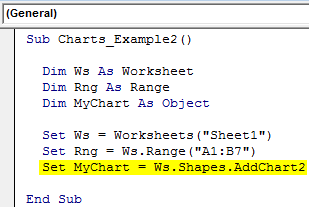
Step 4: Now, set the chart object.
Code:
Sub Charts_Example2() Dim Ws As Worksheet Dim Rng As Range Dim MyChart As Object Set Ws = Worksheets("Sheet1") Set Rng = Ws.Range("A1:B7") Set MyChart = Ws.Shapes.AddChart2 End Sub
Step 5: Now, as usual, we can design the chart using the “With” statement.
Code:
Sub Charts_Example2() Dim Ws As Worksheet 'To Hold Worksheet Reference Dim Rng As Range 'To Hold Range Reference in the Worksheet Dim MyChart As Object Set Ws = Worksheets("Sheet1") 'Now variable "Ws" is equal to the sheet "Sheet1" Set Rng = Ws.Range("A1:B7") 'Now variable "Rng" holds the range A1 to B7 in the sheet "Sheet1" Set MyChart = Ws.Shapes.AddChart2 'Chart will be added as Shape in the same worksheet With MyChart.Chart .SetSourceData Rng 'Since we already set the range of cells to be used for chart we have use RNG object here .ChartType = xlColumnClustered .ChartTitle.Text = "Sales Performance" End With End Sub
It will add the chart below.
#3 – Code to Loop through the Charts
Like how we look through sheets to change the name, insert values, and hide and unhide them. Similarly, we need to use the ChartObject property to loop through the charts.
The below code will loop through all the charts in the worksheet.
Code:
Sub Chart_Loop() Dim MyChart As ChartObject For Each MyChart In ActiveSheet.ChartObjects 'Enter the code here Next MyChart End Sub
#4 – Alternative Method to Create Chart
We can use the below alternative method to create charts. We can use the ChartObject. Add method to create the chart below is the example code.
It will also create a chart like the previous method.
Code:
Sub Charts_Example3() Dim Ws As Worksheet Dim Rng As Range Dim MyChart As ChartObject Set Ws = Worksheets("Sheet1") Set Rng = Ws.Range("A1:B7") Set MyChart = Ws.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=ActiveCell.Left, Width:=400, Top:=ActiveCell.Top, Height:=200) MyChart.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Rng MyChart.Chart.ChartType = xlColumnStacked MyChart.Chart.ChartTitle.Text = "Sales Performance" End Sub
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA Charts. Here, we learn how to create a chart using VBA code, practical examples, and a downloadable template. Below you can find some useful Excel VBA articles: –
- Excel VBA Pivot Table
- What are Control Charts in Excel?
- Top 8 Types of Charts in Excel
- Graphs vs. Charts – Compare
Charts and graphs are one of the best features of Excel; they are very flexible and can be used to make some very advanced visualization. However, this flexibility means there are hundreds of different options. We can create exactly the visualization we want but it can be time-consuming to apply. When we want to apply those hundreds of settings to lots of charts, it can take hours and hours of frustrating clicking. This post is a guide to using VBA for Charts and Graphs in Excel.
The code examples below demonstrate some of the most common chart options with VBA. Hopefully you can put these to good use and automate your chart creation and modifications.
While it might be tempting to skip straight to the section you need, I recommend you read the first section in full. Understanding the Document Object Model (DOM) is essential to understand how VBA can be used with charts and graphs in Excel.
In Excel 2013, many changes were introduced to the charting engine and Document Object Model. For example, the AddChart2 method replaced the AddChart method. As a result, some of the code presented in this post may not work with versions before Excel 2013.
Adapting the code to your requirements
It is not feasible to provide code for every scenario you might come across; there are just too many. But, by applying the principles and methods in this post, you will be able to do almost anything you want with charts in Excel using VBA.
Understanding the Document Object Model
The Document Object Model (DOM) is a term that describes how things are structured in Excel. For example:
- A Workbook contains Sheets
- A Sheet contains Ranges
- A Range contains an Interior
- An Interior contains a color setting
Therefore, to change a cell color to red, we would reference this as follows:
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A1").Interior.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0)Charts are also part of the DOM and follow similar hierarchical principles. To change the height of Chart 1, on Sheet1, we could use the following.
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").ChartObjects("Chart 1").Height = 300Each item in the object hierarchy must be listed and separated by a period ( . ).
Knowing the document object model is the key to success with VBA charts. Therefore, we need to know the correct order inside the object model. While the following code may look acceptable, it will not work.
ActiveWorkbook.ChartObjects("Chart 1").Height = 300In the DOM, the ActiveWorkbook does not contain ChartObjects, so Excel cannot find Chart 1. The parent of a ChartObject is a Sheet, and the Parent of a Sheet is a Workbook. We must include the Sheet in the hierarchy for Excel to know what you want to do.
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").ChartObjects("Chart 1").Height = 300With this knowledge, we can refer to any element of any chart using Excel’s DOM.
Chart Objects vs. Charts vs. Chart Sheets
One of the things which makes the DOM for charts complicated is that many things exist in many places. For example, a chart can be an embedded chart on the face of a worksheet, or as a separate chart sheet.
- On the worksheet itself, we find ChartObjects. Within each ChartObject is a Chart. Effectively a ChartObject is a container that holds a Chart.
- A Chart is also a stand-alone sheet that does not have a ChartObject around it.
This may seem confusing initially, but there are good reasons for this.
To change the chart title text, we would reference the two types of chart differently:
- Chart on a worksheet:
Sheets(“Sheet1”).ChartObjects(“Chart 1”).Chart.ChartTitle.Text = “My Chart Title” - Chart sheet:
Sheets(“Chart 1”).ChartTitle.Text = “My Chart Title”
The sections in bold are exactly the same. This shows that once we have got inside the Chart, the DOM is the same.
Writing code to work on either chart type
We want to write code that will work on any chart; we do this by creating a variable that holds the reference to a Chart.
Create a variable to refer to a Chart inside a ChartObject:
Dim cht As Chart
Set cht = Sheets("Sheet1").ChartObjects("Chart 1").ChartCreate a variable to refer to a Chart which is a sheet:
Dim cht As Chart
Set cht = Sheets("Chart 1")Now we can write VBA code for a Chart sheet or a chart inside a ChartObject by referring to the Chart using cht:
cht.ChartTitle.Text = "My Chart Title"OK, so now we’ve established how to reference charts and briefly covered how the DOM works. It is time to look at lots of code examples.
Inserting charts
In this first section, we create charts. Please note that some of the individual lines of code are included below in their relevant sections.
Create a chart from a blank chart
Sub CreateChart()
'Declare variables
Dim rng As Range
Dim cht As Object
'Create a blank chart
Set cht = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddChart2
'Declare the data range for the chart
Set rng = ActiveSheet.Range("A2:B9")
'Add the data to the chart
cht.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=rng
'Set the chart type
cht.Chart.ChartType = xlColumnClustered
End SubReference charts on a worksheet
In this section, we look at the methods used to reference a chart contained on a worksheet.
Active Chart
Create a Chart variable to hold the ActiveChart:
Dim cht As Chart
Set cht = ActiveChartChart Object by name
Create a Chart variable to hold a specific chart by name.
Dim cht As Chart
Set cht = Sheets("Sheet1").ChartObjects("Chart 1").ChartChart object by number
If there are multiple charts on a worksheet, they can be referenced by their number:
- 1 = the first chart created
- 2 = the second chart created
- etc, etc.
Dim cht As Chart
Set cht = Sheets("Sheet1").ChartObjects(1).ChartLoop through all Chart Objects
If there are multiple ChartObjects on a worksheet, we can loop through each:
Dim chtObj As ChartObject
For Each chtObj In Sheets("Sheet1").ChartObjects
'Include the code to be applied to each ChartObjects
'refer to the Chart using chtObj.cht.
Next chtObjLoop through all selected Chart Objects
If we only want to loop through the selected ChartObjects we can use the following code.
This code is tricky to apply as Excel operates differently when one chart is selected, compared to multiple charts. Therefore, as a way to apply the Chart settings, without the need to repeat a lot of code, I recommend calling another macro and passing the Chart as an argument to that macro.
Dim obj As Object
'Check if any charts have been selected
If Not ActiveChart Is Nothing Then
Call AnotherMacro(ActiveChart)
Else
For Each obj In Selection
'If more than one chart selected
If TypeName(obj) = "ChartObject" Then
Call AnotherMacro(obj.Chart)
End If
Next
End IfReference chart sheets
Now let’s move on to look at the methods used to reference a separate chart sheet.
Active Chart
Set up a Chart variable to hold the ActiveChart:
Dim cht As Chart
Set cht = ActiveChartNote: this is the same code as when referencing the active chart on the worksheet.
Chart sheet by name
Set up a Chart variable to hold a specific chart sheet
Dim cht As Chart
Set cht = Sheets("Chart 1")Loop through all chart sheets in a workbook
The following code will loop through all the chart sheets in the active workbook.
Dim cht As Chart
For Each cht In ActiveWorkbook.Charts
Call AnotherMacro(cht)
Next chtBasic chart settings
This section contains basic chart settings.
All codes start with cht., as they assume a chart has been referenced using the codes above.
Change chart type
'Change chart type - these are common examples, others do exist.
cht.ChartType = xlArea
cht.ChartType = xlLine
cht.ChartType = xlPie
cht.ChartType = xlColumnClustered
cht.ChartType = xlColumnStacked
cht.ChartType = xlColumnStacked100
cht.ChartType = xlArea
cht.ChartType = xlAreaStacked
cht.ChartType = xlBarClustered
cht.ChartType = xlBarStacked
cht.ChartType = xlBarStacked100Create an empty ChartObject on a worksheet
'Create an empty chart embedded on a worksheet.
Set cht = Sheets("Sheet1").Shapes.AddChart2.ChartSelect the source for a chart
'Select source for a chart
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Sheets("Sheet1").Range("A1:B4")
cht.SetSourceData Source:=rngDelete a chart object or chart sheet
'Delete a ChartObject or Chart sheet
If TypeName(cht.Parent) = "ChartObject" Then
cht.Parent.Delete
ElseIf TypeName(cht.Parent) = "Workbook" Then
cht.Delete
End IfChange the size or position of a chart
'Set the size/position of a ChartObject - method 1
cht.Parent.Height = 200
cht.Parent.Width = 300
cht.Parent.Left = 20
cht.Parent.Top = 20
'Set the size/position of a ChartObject - method 2
chtObj.Height = 200
chtObj.Width = 300
chtObj.Left = 20
chtObj.Top = 20Change the visible cells setting
'Change the setting to show only visible cells
cht.PlotVisibleOnly = FalseChange the space between columns/bars (gap width)
'Change the gap space between bars
cht.ChartGroups(1).GapWidth = 50Change the overlap of columns/bars
'Change the overlap setting of bars
cht.ChartGroups(1).Overlap = 75Remove outside border from chart object
'Remove the outside border from a chart
cht.ChartArea.Format.Line.Visible = msoFalse
Change color of chart background
'Set the fill color of the chart area
cht.ChartArea.Format.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(255, 0, 0)
'Set chart with no background color
cht.ChartArea.Format.Fill.Visible = msoFalseChart Axis
Charts have four axis:
- xlValue
- xlValue, xlSecondary
- xlCategory
- xlCategory, xlSecondary
These are used interchangeably in the examples below. To adapt the code to your specific requirements, you need to change the chart axis which is referenced in the brackets.
All codes start with cht., as they assume a chart has been referenced using the codes earlier in this post.
Set min and max of chart axis
'Set chart axis min and max
cht.Axes(xlValue).MaximumScale = 25
cht.Axes(xlValue).MinimumScale = 10
cht.Axes(xlValue).MaximumScaleIsAuto = True
cht.Axes(xlValue).MinimumScaleIsAuto = TrueDisplay or hide chart axis
'Display axis
cht.HasAxis(xlCategory) = True
'Hide axis
cht.HasAxis(xlValue, xlSecondary) = FalseDisplay or hide chart title
'Display axis title
cht.Axes(xlCategory, xlSecondary).HasTitle = True
'Hide axis title
cht.Axes(xlValue).HasTitle = FalseChange chart axis title text
'Change axis title text
cht.Axes(xlCategory).AxisTitle.Text = "My Axis Title"Reverse the order of a category axis
'Reverse the order of a catetory axis
cht.Axes(xlCategory).ReversePlotOrder = True
'Set category axis to default order
cht.Axes(xlCategory).ReversePlotOrder = FalseGridlines
Gridlines help a user to see the relative position of an item compared to the axis.
Add or delete gridlines
'Add gridlines
cht.SetElement (msoElementPrimaryValueGridLinesMajor)
cht.SetElement (msoElementPrimaryCategoryGridLinesMajor)
cht.SetElement (msoElementPrimaryValueGridLinesMinorMajor)
cht.SetElement (msoElementPrimaryCategoryGridLinesMinorMajor)
'Delete gridlines
cht.Axes(xlValue).MajorGridlines.Delete
cht.Axes(xlValue).MinorGridlines.Delete
cht.Axes(xlCategory).MajorGridlines.Delete
cht.Axes(xlCategory).MinorGridlines.DeleteChange color of gridlines
'Change colour of gridlines
cht.Axes(xlValue).MajorGridlines.Format.Line.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(255, 0, 0)Change transparency of gridlines
'Change transparency of gridlines
cht.Axes(xlValue).MajorGridlines.Format.Line.Transparency = 0.5Chart Title
The chart title is the text at the top of the chart.
All codes start with cht., as they assume a chart has been referenced using the codes earlier in this post.
Display or hide chart title
'Display chart title
cht.HasTitle = True
'Hide chart title
cht.HasTitle = FalseChange chart title text
'Change chart title text
cht.ChartTitle.Text = "My Chart Title"Position the chart title
'Position the chart title
cht.ChartTitle.Left = 10
cht.ChartTitle.Top = 10Format the chart title
'Format the chart title
cht.ChartTitle.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Name = "Calibri"
cht.ChartTitle.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Size = 16
cht.ChartTitle.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Bold = msoTrue
cht.ChartTitle.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Bold = msoFalse
cht.ChartTitle.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Italic = msoTrue
cht.ChartTitle.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Italic = msoFalseChart Legend
The chart legend provides a color key to identify each series in the chart.
Display or hide the chart legend
'Display the legend
cht.HasLegend = True
'Hide the legend
cht.HasLegend = FalsePosition the legend
'Position the legend
cht.Legend.Position = xlLegendPositionTop
cht.Legend.Position = xlLegendPositionRight
cht.Legend.Position = xlLegendPositionLeft
cht.Legend.Position = xlLegendPositionCorner
cht.Legend.Position = xlLegendPositionBottom
'Allow legend to overlap the chart.
'False = allow overlap, True = due not overlap
cht.Legend.IncludeInLayout = False
cht.Legend.IncludeInLayout = True
'Move legend to a specific point
cht.Legend.Left = 20
cht.Legend.Top = 200
cht.Legend.Width = 100
cht.Legend.Height = 25Plot Area
The Plot Area is the main body of the chart which contains the lines, bars, areas, bubbles, etc.
All codes start with cht., as they assume a chart has been referenced using the codes earlier in this post.
Background color of Plot Area
'Set background color of the plot area
cht.PlotArea.Format.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(255, 0, 0)
'Set plot area to no background color
cht.PlotArea.Format.Fill.Visible = msoFalse
Set position of Plot Area
'Set the size and position of the PlotArea. Top and Left are relative to the Chart Area.
cht.PlotArea.Left = 20
cht.PlotArea.Top = 20
cht.PlotArea.Width = 200
cht.PlotArea.Height = 150Chart series
Chart series are the individual lines, bars, areas for each category.
All codes starting with srs. assume a chart’s series has been assigned to a variable.
Add a new chart series
'Add a new chart series
Set srs = cht.SeriesCollection.NewSeries
srs.Values = "=Sheet1!$C$2:$C$6"
srs.Name = "=""New Series"""
'Set the values for the X axis when using XY Scatter
srs.XValues = "=Sheet1!$D$2:$D$6"Reference a chart series
Set up a Series variable to hold a chart series:
- 1 = First chart series
- 2 = Second chart series
- etc, etc.
Dim srs As Series
Set srs = cht.SeriesCollection(1)Referencing a chart series by name
Dim srs As Series
Set srs = cht.SeriesCollection("Series Name")Delete a chart series
'Delete chart series
srs.DeleteLoop through each chart series
Dim srs As Series
For Each srs In cht.SeriesCollection
'Do something to each series
'See the codes below starting with "srs."
Next srsChange series data
'Change series source data and name
srs.Values = "=Sheet1!$C$2:$C$6"
srs.Name = "=""Change Series Name"""Changing fill or line colors
'Change fill colour
srs.Format.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(255, 0, 0)
'Change line colour
srs.Format.Line.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(255, 0, 0)Changing visibility
'Change visibility of line
srs.Format.Line.Visible = msoTrue
Changing line weight
'Change line weight
srs.Format.Line.Weight = 10Changing line style
'Change line style
srs.Format.Line.DashStyle = msoLineDash
srs.Format.Line.DashStyle = msoLineSolid
srs.Format.Line.DashStyle = msoLineSysDot
srs.Format.Line.DashStyle = msoLineSysDash
srs.Format.Line.DashStyle = msoLineDashDot
srs.Format.Line.DashStyle = msoLineLongDash
srs.Format.Line.DashStyle = msoLineLongDashDot
srs.Format.Line.DashStyle = msoLineLongDashDotDotFormatting markers
'Changer marker type
srs.MarkerStyle = xlMarkerStyleAutomatic
srs.MarkerStyle = xlMarkerStyleCircle
srs.MarkerStyle = xlMarkerStyleDash
srs.MarkerStyle = xlMarkerStyleDiamond
srs.MarkerStyle = xlMarkerStyleDot
srs.MarkerStyle = xlMarkerStyleNone
'Change marker border color
srs.MarkerForegroundColor = RGB(255, 0, 0)
'Change marker fill color
srs.MarkerBackgroundColor = RGB(255, 0, 0)
'Change marker size
srs.MarkerSize = 8Data labels
Data labels display additional information (such as the value, or series name) to a data point in a chart series.
All codes starting with srs. assume a chart’s series has been assigned to a variable.
Display or hide data labels
'Display data labels on all points in the series
srs.HasDataLabels = True
'Hide data labels on all points in the series
srs.HasDataLabels = FalseChange the position of data labels
'Position data labels
'The label position must be a valid option for the chart type.
srs.DataLabels.Position = xlLabelPositionAbove
srs.DataLabels.Position = xlLabelPositionBelow
srs.DataLabels.Position = xlLabelPositionLeft
srs.DataLabels.Position = xlLabelPositionRight
srs.DataLabels.Position = xlLabelPositionCenter
srs.DataLabels.Position = xlLabelPositionInsideEnd
srs.DataLabels.Position = xlLabelPositionInsideBase
srs.DataLabels.Position = xlLabelPositionOutsideEndError Bars
Error bars were originally intended to show variation (e.g. min/max values) in a value. However, they also commonly used in advanced chart techniques to create additional visual elements.
All codes starting with srs. assume a chart’s series has been assigned to a variable.
Turn error bars on/off
'Turn error bars on/off
srs.HasErrorBars = True
srs.HasErrorBars = FalseError bar end cap style
'Change end style of error bar
srs.ErrorBars.EndStyle = xlNoCap
srs.ErrorBars.EndStyle = xlCapError bar color
'Change color of error bars
srs.ErrorBars.Format.Line.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(255, 0, 0)Error bar thickness
'Change thickness of error bars
srs.ErrorBars.Format.Line.Weight = 5Error bar direction settings
'Error bar settings
srs.ErrorBar Direction:=xlY, _
Include:=xlPlusValues, _
Type:=xlFixedValue, _
Amount:=100
'Alternatives options for the error bar settings are
'Direction:=xlX
'Include:=xlMinusValues
'Include:=xlPlusValues
'Include:=xlBoth
'Type:=xlFixedValue
'Type:=xlPercent
'Type:=xlStDev
'Type:=xlStError
'Type:=xlCustom
'Applying custom values to error bars
srs.ErrorBar Direction:=xlY, _
Include:=xlPlusValues, _
Type:=xlCustom, _
Amount:="=Sheet1!$A$2:$A$7", _
MinusValues:="=Sheet1!$A$2:$A$7"Data points
Each data point on a chart series is known as a Point.
Reference a specific point
The following code will reference the first Point.
1 = First chart series
2 = Second chart series
etc, etc.
Dim srs As Series
Dim pnt As Point
Set srs = cht.SeriesCollection(1)
Set pnt = srs.Points(1)Loop through all points
Dim srs As Series
Dim pnt As Point
Set srs = cht.SeriesCollection(1)
For Each pnt In srs.Points
'Do something to each point, using "pnt."
Next pntPoint example VBA codes
Points have similar properties to Series, but the properties are applied to a single data point in the series rather than the whole series. See a few examples below, just to give you the idea.
Turn on data label for a point
'Turn on data label
pnt.HasDataLabel = TrueSet the data label position for a point
'Set the position of a data label
pnt.DataLabel.Position = xlLabelPositionCenterOther useful chart macros
In this section, I’ve included other useful chart macros which are not covered by the example codes above.
Make chart cover cell range
The following code changes the location and size of the active chart to fit directly over the range G4:N20
Sub FitChartToRange()
'Declare variables
Dim cht As Chart
Dim rng As Range
'Assign objects to variables
Set cht = ActiveChart
Set rng = ActiveSheet.Range("G4:N20")
'Move and resize chart
cht.Parent.Left = rng.Left
cht.Parent.Top = rng.Top
cht.Parent.Width = rng.Width
cht.Parent.Height = rng.Height
End SubExport the chart as an image
The following code saves the active chart to an image in the predefined location
Sub ExportSingleChartAsImage()
'Create a variable to hold the path and name of image
Dim imagePath As String
Dim cht As Chart
imagePath = "C:UsersmarksDocumentsmyImage.png"
Set cht = ActiveChart
'Export the chart
cht.Export (imagePath)
End SubResize all charts to the same size as the active chart
The following code resizes all charts on the Active Sheet to be the same size as the active chart.
Sub ResizeAllCharts()
'Create variables to hold chart dimensions
Dim chtHeight As Long
Dim chtWidth As Long
'Create variable to loop through chart objects
Dim chtObj As ChartObject
'Get the size of the first selected chart
chtHeight = ActiveChart.Parent.Height
chtWidth = ActiveChart.Parent.Width
For Each chtObj In ActiveSheet.ChartObjects
chtObj.Height = chtHeight
chtObj.Width = chtWidth
Next chtObj
End SubBringing it all together
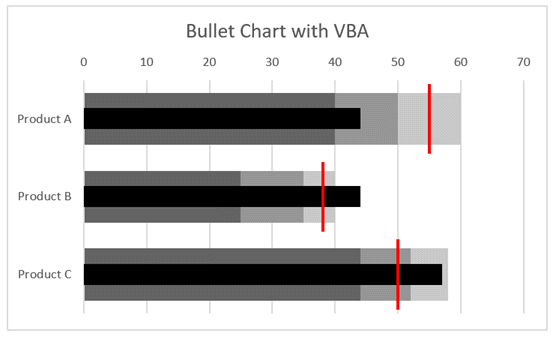
Just to prove how we can use these code snippets, I have created a macro to build bullet charts.
This isn’t necessarily the most efficient way to write the code, but it is to demonstrate that by understanding the code above we can create a lot of charts.
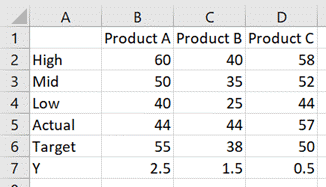
The data looks like this:
The chart looks like this:
The code which achieves this is as follows:
Sub CreateBulletChart()
Dim cht As Chart
Dim srs As Series
Dim rng As Range
'Create an empty chart
Set cht = Sheets("Sheet3").Shapes.AddChart2.Chart
'Change chart title text
cht.ChartTitle.Text = "Bullet Chart with VBA"
'Hide the legend
cht.HasLegend = False
'Change chart type
cht.ChartType = xlBarClustered
'Select source for a chart
Set rng = Sheets("Sheet3").Range("A1:D4")
cht.SetSourceData Source:=rng
'Reverse the order of a catetory axis
cht.Axes(xlCategory).ReversePlotOrder = True
'Change the overlap setting of bars
cht.ChartGroups(1).Overlap = 100
'Change the gap space between bars
cht.ChartGroups(1).GapWidth = 50
'Change fill colour
Set srs = cht.SeriesCollection(1)
srs.Format.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(200, 200, 200)
Set srs = cht.SeriesCollection(2)
srs.Format.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(150, 150, 150)
Set srs = cht.SeriesCollection(3)
srs.Format.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(100, 100, 100)
'Add a new chart series
Set srs = cht.SeriesCollection.NewSeries
srs.Values = "=Sheet3!$B$7:$D$7"
srs.XValues = "=Sheet3!$B$5:$D$5"
srs.Name = "=""Actual"""
'Change chart type
srs.ChartType = xlXYScatter
'Turn error bars on/off
srs.HasErrorBars = True
'Change end style of error bar
srs.ErrorBars.EndStyle = xlNoCap
'Set the error bars
srs.ErrorBar Direction:=xlY, _
Include:=xlNone, _
Type:=xlErrorBarTypeCustom
srs.ErrorBar Direction:=xlX, _
Include:=xlMinusValues, _
Type:=xlPercent, _
Amount:=100
'Change color of error bars
srs.ErrorBars.Format.Line.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(0, 0, 0)
'Change thickness of error bars
srs.ErrorBars.Format.Line.Weight = 14
'Change marker type
srs.MarkerStyle = xlMarkerStyleNone
'Add a new chart series
Set srs = cht.SeriesCollection.NewSeries
srs.Values = "=Sheet3!$B$7:$D$7"
srs.XValues = "=Sheet3!$B$6:$D$6"
srs.Name = "=""Target"""
'Change chart type
srs.ChartType = xlXYScatter
'Turn error bars on/off
srs.HasErrorBars = True
'Change end style of error bar
srs.ErrorBars.EndStyle = xlNoCap
srs.ErrorBar Direction:=xlX, _
Include:=xlNone, _
Type:=xlErrorBarTypeCustom
srs.ErrorBar Direction:=xlY, _
Include:=xlBoth, _
Type:=xlFixedValue, _
Amount:=0.45
'Change color of error bars
srs.ErrorBars.Format.Line.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(255, 0, 0)
'Change thickness of error bars
srs.ErrorBars.Format.Line.Weight = 2
'Changer marker type
srs.MarkerStyle = xlMarkerStyleNone
'Set chart axis min and max
cht.Axes(xlValue, xlSecondary).MaximumScale = cht.SeriesCollection(1).Points.Count
cht.Axes(xlValue, xlSecondary).MinimumScale = 0
'Hide axis
cht.HasAxis(xlValue, xlSecondary) = False
End SubUsing the Macro Recorder for VBA for charts and graphs
The Macro Recorder is one of the most useful tools for writing VBA for Excel charts. The DOM is so vast that it can be challenging to know how to refer to a specific object, property or method. Studying the code produced by the Macro Recorder will provide the parts of the DOM which you don’t know.
As a note, the Macro Recorder creates poorly constructed code; it selects each object before manipulating it (this is what you did with the mouse after all). But this is OK for us. Once we understand the DOM, we can take just the parts of the code we need and ensure we put them into the right part of the hierarchy.
Conclusion
As you’ve seen in this post, the Document Object Model for charts and graphs in Excel is vast (and we’ve only scratched the surface.
I hope that through all the examples in this post you have a better understanding of VBA for charts and graphs in Excel. With this knowledge, I’m sure you will be able to automate your chart creation and modification.
Have I missed any useful codes? If so, put them in the comments.
Looking for other detailed VBA guides? Check out these posts:
- VBA for Tables & List Objects
- VBA for PivotTables
- VBA to insert, move, delete and control pictures
About the author
Hey, I’m Mark, and I run Excel Off The Grid.
My parents tell me that at the age of 7 I declared I was going to become a qualified accountant. I was either psychic or had no imagination, as that is exactly what happened. However, it wasn’t until I was 35 that my journey really began.
In 2015, I started a new job, for which I was regularly working after 10pm. As a result, I rarely saw my children during the week. So, I started searching for the secrets to automating Excel. I discovered that by building a small number of simple tools, I could combine them together in different ways to automate nearly all my regular tasks. This meant I could work less hours (and I got pay raises!). Today, I teach these techniques to other professionals in our training program so they too can spend less time at work (and more time with their children and doing the things they love).
Do you need help adapting this post to your needs?
I’m guessing the examples in this post don’t exactly match your situation. We all use Excel differently, so it’s impossible to write a post that will meet everybody’s needs. By taking the time to understand the techniques and principles in this post (and elsewhere on this site), you should be able to adapt it to your needs.
But, if you’re still struggling you should:
- Read other blogs, or watch YouTube videos on the same topic. You will benefit much more by discovering your own solutions.
- Ask the ‘Excel Ninja’ in your office. It’s amazing what things other people know.
- Ask a question in a forum like Mr Excel, or the Microsoft Answers Community. Remember, the people on these forums are generally giving their time for free. So take care to craft your question, make sure it’s clear and concise. List all the things you’ve tried, and provide screenshots, code segments and example workbooks.
- Use Excel Rescue, who are my consultancy partner. They help by providing solutions to smaller Excel problems.
What next?
Don’t go yet, there is plenty more to learn on Excel Off The Grid. Check out the latest posts:
Charts, Charts, & More Charts!
Graphical visualizations are arguably the pinnacle of how an analyst shares his/her results and possessing the ability to manipulate them is key to the field. Since we as data analysts spend some much time creating graphs, it is more valuable than ever to understand how to automate them.
What if you have 20 graphs on a spreadsheet and they all need to have their legends in the exact same spot? What if you create a bunch of charts and your manager needs the series colors changed at the last minute? Do you want to do this all manually?
Below will be your cheat sheet for manipulating Excel charts & graphs with VBA code. Please let me know via the comments section if there are areas missing from this guide so I can expand on them. Enjoy!
VBA Chart Guide Contents
-
Create/Insert Chart
-
Looping Through Charts/Series
-
Chart Title (Adding/Modifying)
-
Chart Legend (Adding/Modifying)
-
Adding Various Chart Attributes
-
Modifying Various Chart Attributes
-
Removing Various Chart Attributes
-
Change Chart Colors
-
Chart Excel Add-ins
Inserting A Chart
Method 1:
Sub CreateChart()
‘PURPOSE: Create a chart (chart dimensions are not required)
Dim rng As Range
Dim cht As Object
‘Your data range for the chart
Set rng = ActiveSheet.Range(«A24:M27»)
‘Create a chart
Set cht = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddChart2
‘Give chart some data
cht.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=rng
‘Determine the chart type
cht.Chart.ChartType = xlXYScatterLines
End Sub
Sub CreateChart()
‘PURPOSE: Create a chart (chart dimensions are required)
Dim rng As Range
Dim cht As ChartObject
‘Your data range for the chart
Set rng = ActiveSheet.Range(«A24:M27»)
‘Create a chart
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add( _
Left:=ActiveCell.Left, _
Width:=450, _
Top:=ActiveCell.Top, _
Height:=250)
‘Give chart some data
cht.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=rng
‘Determine the chart type
cht.Chart.ChartType = xlXYScatterLines
End Sub
Looping Through Charts & Series
Sub LoopThroughCharts()
‘PURPOSE: How to cycle through charts and chart series
Dim cht As ChartObject
Dim ser As Series
‘Loop Through all charts on ActiveSheet
For Each cht In ActiveSheet.ChartObjects
Next cht
‘Loop through all series in a chart
For Each ser In grph.Chart.SeriesCollection
Next ser
‘Loop Through all series on Activesheet
For Each cht In ActiveSheet.ChartObjects
For Each ser In grph.Chart.SeriesCollection
Next ser
Next cht
End Sub
Adding & Modifying A Chart Title
Add Chart Title
Sub AddChartTitle()
‘PURPOSE: Add a title to a specific chart
Dim cht As ChartObject
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(«Chart 1»)
‘Ensure chart has a title
cht.Chart.HasTitle = True
‘Change chart’s title
cht.Chart.ChartTitle.Text = «My Graph»
End Sub
Move/Reposition Chart Title
Sub RepositionChartTitle()
‘PURPOSE: Reposition a chart’s title
Dim cht As ChartObject
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(«Chart 1»)
‘Reposition title
With cht.Chart.ChartTitle
.Left = 100
.Top = 50
End With
End Sub
Adding & Modifying A Graph Legend
Insert/Create Chart Legend
Sub InsertChartLegend()
Dim cht As Chart
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(«Chart 1»).Chart
‘Add Legend to the Right
cht.SetElement (msoElementLegendRight)
‘Add Legend to the Left
cht.SetElement (msoElementLegendLeft)
‘Add Legend to the Bottom
cht.SetElement (msoElementLegendBottom)
‘Add Legend to the Top
cht.SetElement (msoElementLegendTop)
‘Add Overlaying Legend to the Left
cht.SetElement (msoElementLegendLeftOverlay)
‘Add Overlaying Legend to the Right
cht.SetElement (msoElementLegendRightOverlay)
End Sub
Resize/Move Chart Legend
Sub DimensionChartLegend()
Dim lgd As Legend
Set lgd = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(«Chart 1»).Chart.Legend
lgd.Left = 240.23
lgd.Top = 6.962
lgd.Width = 103.769
lgd.Height = 25.165
End Sub
Adding Various Chart Attributes
Sub AddStuffToChart()
Dim cht As Chart
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(«Chart 1»).Chart
‘Add X-axis
cht.HasAxis(xlCategory, xlPrimary) = True ‘[Method #1]
cht.SetElement (msoElementPrimaryCategoryAxisShow) ‘[Method #2]
‘Add X-axis title
cht.Axes(xlCategory, xlPrimary).HasTitle = True ‘[Method #1]
cht.SetElement (msoElementPrimaryCategoryAxisTitleAdjacentToAxis) ‘[Method #2]
‘Add y-axis
cht.HasAxis(xlValue, xlPrimary) = True ‘[Method #1]
cht.SetElement (msoElementPrimaryValueAxisShow) ‘[Method #2]
‘Add y-axis title
cht.Axes(xlValue, xlPrimary).HasTitle = True ‘[Method #1]
cht.SetElement (msoElementPrimaryValueAxisTitleAdjacentToAxis) ‘[Method #2]
‘Add Data Labels (Centered)
cht.SetElement (msoElementDataLabelCenter)
‘Add Major Gridlines
cht.SetElement (msoElementPrimaryValueGridLinesMajor)
‘Add Linear Trend Line
cht.SeriesCollection(1).Trendlines.Add Type:=xlLinear
End Sub
Modifying Various Chart Attributes
Sub ChangeChartFormatting()
Dim cht As Chart
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(«Chart 1»).Chart
‘Adjust y-axis Scale
cht.Axes(xlValue).MinimumScale = 40
cht.Axes(xlValue).MaximumScale = 100
‘Adjust x-axis Scale
cht.Axes(xlCategory).MinimumScale = 1
cht.Axes(xlCategory).MaximumScale = 10
‘Adjust Bar Gap
cht.ChartGroups(1).GapWidth = 60
‘Format Font Size
cht.ChartArea.Format.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Size = 12
‘Format Font Type
cht.ChartArea.Format.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Name = «Arial»
‘Make Font Bold
cht.ChartArea.Format.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Bold = msoTrue
‘Make Font Italicized
cht.ChartArea.Format.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Italic = msoTrue
End Sub
Removing Various Chart Attributes
Sub RemoveChartFormatting()
Dim cht As Chart
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(«Chart 1»).Chart
‘Remove Chart Series
cht.SeriesCollection(2).Delete
‘Remove Gridlines
cht.Axes(xlValue).MajorGridlines.Delete
cht.Axes(xlValue).MinorGridlines.Delete
‘Remove X-axis
cht.Axes(xlCategory).Delete
‘Remove Y-axis
cht.Axes(xlValue).Delete
‘Remove Legend
cht.Legend.Delete
‘Remove Title
cht.ChartTitle.Delete
‘Remove ChartArea border
cht.ChartArea.Border.LineStyle = xlNone
‘No background color fill
cht.ChartArea.Format.Fill.Visible = msoFalse
cht.PlotArea.Format.Fill.Visible = msoFalse
End Sub
Change Chart Colors
Sub ChangeChartColors()
Dim cht As Chart
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(«Chart 1»).Chart
‘Change first bar chart series fill color
cht.SeriesCollection(1).Format.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(91, 155, 213)
‘Change X-axis label color
cht.Axes(xlCategory).TickLabels.Font.Color = RGB(91, 155, 213)
‘Change Y-axis label color
cht.Axes(xlValue).TickLabels.Font.Color = RGB(91, 155, 213)
‘Change Plot Area border color
cht.PlotArea.Format.Line.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(91, 155, 213)
‘Change Major gridline color
cht.Axes(xlValue).MajorGridlines.Format.Line.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(91, 155, 213)
‘Change Chart Title font color
cht.ChartTitle.Format.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(91, 155, 213)
‘No background color fill
cht.ChartArea.Format.Fill.Visible = msoFalse
cht.PlotArea.Format.Fill.Visible = msoFalse
End Sub
Chart Excel Add-ins
-
Waterfall Chart Excel Add-in — Automatically create editable Waterfall Charts directly in your spreadsheet.
-
AutoChart Excel Add-in — This add-in will allow you to create, manipulate series ranges, and format all your charts at once. Making adjustments has never been easier!
-
myBrand Excel Add-in — Stores your favorite colors to the Excel Ribbon and allows you to color cells, shapes, and charts.
-
Peltier Tech Charts for Excel — A chart-building toolkit with the automated creation of difficult chart builds such as Histograms, Pareto, Marimekko, and many more.
Anything You Would Like To See?
There are a ton of things you can do with VBA and Excel charts. I attempted through this guide to tackle the most general ones, but please don’t hesitate to leave a comment if there is something that you would like to see added to the code in this VBA guide. Hopefully, you were able to find what you were looking for!
About The Author
Hey there! I’m Chris and I run TheSpreadsheetGuru website in my spare time. By day, I’m actually a finance professional who relies on Microsoft Excel quite heavily in the corporate world. I love taking the things I learn in the “real world” and sharing them with everyone here on this site so that you too can become a spreadsheet guru at your company.
Through my years in the corporate world, I’ve been able to pick up on opportunities to make working with Excel better and have built a variety of Excel add-ins, from inserting tickmark symbols to automating copy/pasting from Excel to PowerPoint. If you’d like to keep up to date with the latest Excel news and directly get emailed the most meaningful Excel tips I’ve learned over the years, you can sign up for my free newsletters. I hope I was able to provide you with some value today and I hope to see you back here soon!
— Chris
Founder, TheSpreadsheetGuru.com
Excel Chart VBA Examples and Tutorials
Excel charts are one of the awesome tools available to represent the data in rich visualized graphs. Here are the most frequently used Excel Chart VBA Examples and Tutorials. You can access chart objects, properties and dealing with the methods.
Here are the top most Excel Chart VBA Examples and Tutorials, show you how to deal with chart axis, chart titles, background colors,chart data source, chart types, series and many other chart objects.
Excel Chart VBA Examples and Tutorials – Learning Path
- Example tutorials on Creating Charts using Excel VBA:
- Example tutorials on Chart Type using Excel VBA:
- Example Tutorials on Formatting Chart Objects using Excel VBA:
- Example Tutorials on Chart Collection in Excel VBA:
- Other useful Examples and tutorials on Excel VBA Charting:
- Excel VBA Charting Constants and Enumerations:
- Example File for Free Download:
Creating Charts using Excel VBA
We can create the chart using different methods in Excel VBA, following are the various Excel Chart VBA Examples and Tutorials to show you creating charts in Excel using VBA.
1. Adding New Chart for Selected Data using Sapes.AddChart Method in Excel VBA
The following Excel Chart VBA Examples works similarly when we select some data and click on charts from Insert Menu and to create a new chart. This will create basic chart in an existing worksheet.
Sub ExAddingNewChartforSelectedData_Sapes_AddChart_Method()
Range("C5:D7").Select
ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddChart.Select
End Sub
2. Adding New Chart for Selected Data using Charts.Add Method : Creating Chart Sheet in Excel VBA
The following Excel Chart VBA Examples method will add new chart into new worksheet by default. You can specify a location to embedded in a particular worksheet.
'Here is the other method to add charts using Chart Object. It will add a new chart for the selected data as new chart sheet.
Sub ExAddingNewChartforSelectedData_Charts_Add_Method_SheetChart()
Range("C5:D7").Select
Charts.Add
End Sub
3. Adding New Chart for Selected Data using Charts.Add Method : In Existing Sheet using Excel VBA
We can use the Charts.Add method to create a chart in existing worksheet. We can specify the position and location as shown below. This will create a new chart in a specific worksheet.
Sub ExAddingNewChartforSelectedData_Charts_Add_Method_InSheet()
Range("C5:D7").Select
Charts.Add
ActiveChart.Location Where:=xlLocationAsObject, Name:="Sheet1"
End Sub
4. Difference between embedded Chart and Chart Sheet in Excel:
Both are similar except event handlers, Chart Sheets will have the event handlers,we can write event programming for Chart Sheets. And the other type embedded charts can not support the event handlers. We can write classes to handle the events for the embedded chart, but not recommended.
We have seen multiple methods to create charts, but we cant set the chart at particular position using the above codes. You can use the ChartObjects.Add method to specify the position of the chart.
5. Adding New Chart for Selected Data using ChartObjects.Add Method in Excel VBA
ChartObjects.Add method is the best method as it is very easy to play with the chart objects to change the settings.
Sub ExAddingNewChartforSelectedData_ChartObjects_Add_Method()
With ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
End With
End Sub
6. Assigning Charts to an Object in Excel VBA
Here is another Excel Chart VBA Examples with ChartObjects, here we will assign to an Object and play with that.
Sub ExAddingNewChartforSelectedData_ChartObjects_Object()
Dim cht As Object
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
cht.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
End Sub
7. Changing the Chart Position in Excel VBA
The following VBA example will show you how to change the chart position.
Sub ExAddingNewChartforSelectedData_Object_Position()
Dim cht As Object
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
cht.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
cht.Left = 350
cht.Width = 400
cht.Top = 30
cht.Height = 200
End Sub
8. Align Chart Object at a Particular Range or Cell in Excel VBA
You can set the top,left, height and width properties of a chart object to align in a particular position.
Sub AlignChartAtParticularRange()
' Chart Align
With ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(1)
.Left = Range("A6").Left
.Top = Range("A7").Top
.Width = Range("D6").Left
.Height = Range("D16").Top - Range("D6").Top
End With
End Sub
9. Use with statement while dealing with Charts and avoid the accessing the same object repeatedly in Excel VBA
If you are dealing with the same object, it is better to use with statement. It will make the program more clear to understand and executes faster.
Sub ExChartPostion_Object_Position()
Dim cht As Object
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
With cht
.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
.Left = 350
.Width = 400
.Top = 30
.Height = 200
End With
End Sub
10. You can use ActiveChart Object to access the active chart in Excel VBA
Active chart is the chart which is currently selected or activated in your active sheet.
Sub ExChartPostion_ActiveChart()
ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300).Activate
With ActiveChart
.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
.Parent.Left = 350
.Parent.Width = 400
.Parent.Top = 30
.Parent.Height = 200
End With
End Sub
Top
Setting Chart Types using Excel VBA
We have verity of chart in Excel, we can use VBA to change and set the suitable chart type based on the data which we want to present. Below are the Excel Chart VBA Examples and Tutorials to change the chart type.
We can use Chart.Type property to set the chart type, here we can pass Excel chart constants or chart enumerations to set the chart type. Please refer the following table to understand the excel constants and enumerations.
11. Example to Change Chart type using Excel Chart Enumerations in Excel VBA
This Excel Chart VBA Example will use 1 as excel enumeration to plot the Aria Chart. Please check here list of enumerations available for Excel VBA Charting
Sub Ex_ChartType_Enumeration()
Dim cht As Object
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
With cht
.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
.Chart.Type = 1 ' for aria chart
End With
End Sub
12. Example to Change Chart type using Excel Chart Constants in VBA
This Excel Chart VBA Example will use xlArea as excel constant to plot the Aria Chart. Please check here for list of enumerations available in Excel VBA Charting
Sub Ex_ChartType_xlConstant()
Dim cht As Object
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
With cht
.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
.Chart.Type = xlArea
End With
End Sub
xlConstants is recommended than Excel Enumeration, as it is easy to understand and remember. Following are frequently used chart type examples:
13. Example to set the type as a Pie Chart in Excel VBA
The following VBA code using xlPie constant to plot the Pie chart. Please check here for list of enumerations available in Excel VBA Charting
Sub Ex_ChartType_Pie_Chart()
Dim cht As Object
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
With cht
.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
.Chart.Type = xlPie
End With
End Sub
14. Example to set the chart type as a Line Chart in Excel VBA
The following VBA code using xlLine constant to plot the Pie chart. Please check here for list of enumerations available in Excel VBA Charting
Sub Ex_ChartType_Line_Chart()
Dim cht As Object
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
With cht
.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
.Chart.Type = xlLine
End With
End Sub
15. Example to set the chart type as a Bar Chart in Excel VBA
The following VBA code using xlBar constant to plot the Pie chart. Please check here for list of enumerations available in Excel VBA Charting
Sub Ex_ChartType_Bar_Chart()
Dim cht As Object
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
With cht
.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
.Chart.Type = xlBar
End With
End Sub
16. Example to set the chart type as a XYScatter Chart in Excel VBA
The following code using xlXYScatter constant to plot the Pie chart. Please check here for list of enumerations available in Excel VBA Charting
Sub Ex_ChartType_XYScatter_Chart()
Dim cht As Object
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
With cht
.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
.Chart.Type = xlXYScatter
End With
End Sub
Here is the complete list of Excel Chart Types, Chart Enumerations and Chart Constants:
Top
Formatting Chart Objects using Excel VBA
Below are Excel Chart VBA Examples to show you how to change background colors of charts, series and changing the different properties of charts like Chart Legends, Line Styles, Number Formatting. You can also find the examples on Chart Axis and Chart Axes Setting and Number Formats.
17. Changing Chart Background Color – Chart Aria Interior Color in Excel VBA
The following VBA code will change the background color of the Excel Chart.
Sub Ex_ChartAriaInteriorColor()
Dim cht As Object
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
With cht
.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
.Chart.ChartArea.Interior.ColorIndex = 3
End With
End Sub
18. Changing PlotAria Background Color – PlotAria Interior Color in Excel VBA
The following code will change the background color of Plot Area in Excel VBA.
Sub Ex_PlotAriaInteriorColor()
Dim cht As Object
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
With cht
.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
.Chart.PlotArea.Interior.ColorIndex = 5
End With
End Sub
19.Changing Chart Series Background Color – Series Interior Color in Excel VBA
The following code is for changing the background color of a series using Excel VBA.
Sub Ex_SeriesInteriorColor()
Dim cht As Object
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
With cht
.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
.Chart.SeriesCollection(1).Format.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = rgbRed
.Chart.SeriesCollection(2).Interior.ColorIndex = 5
End With
End Sub
20. Changing Chart Series Marker Style in Excel VBA
Here is the code to change the series marker style using Excel VBA, you can change to circle, diamond, square,etc. Check the excel constants and enumerations for more options available in excel vba.
Sub Ex_ChangingMarkerStyle()
Dim cht As Object
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
With cht
.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
.Chart.Type = xlLine
.Chart.SeriesCollection(1).MarkerStyle = 7
End With
End Sub
21. Changing Chart Series Line Style in Excel VBA
Here is the code to change the line color using Excel VBA, it will change the line style from solid to dash. Check the excel constants for more options.
Sub Ex_ChangingLineStyle()
Dim cht As Object
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
With cht
.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
.Chart.Type = xlLine
.Chart.SeriesCollection(1).Border.LineStyle = xlDash
End With
End Sub
22. Changing Chart Series Border Color in Excel VBA
Here is the code for changing series borders in Excel VBA.
Sub Ex_ChangingBorderColor()
Dim cht As Object
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
With cht
.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
.Chart.Type = xlBar
.Chart.SeriesCollection(1).Border.ColorIndex = 3
End With
End Sub
23. Change Chart Axis NumberFormat in Excel VBA
This code will change the chart axis number format using excel vba.
Sub Ex_ChangeAxisNumberFormat()
Dim cht As Object
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
With cht
.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
.Chart.Type = xlLine
.Chart.Axes(xlValue).TickLabels.NumberFormat = "0.00"
End With
End Sub
24. Formatting Axis Labels: Changing Axis Font to Bold using Excel VBA
The following example is for formating Axis labels using Excel VBA.
Sub Ex_ChangeAxisFormatFontBold()
Dim cht As Object
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
With cht
.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
.Chart.Type = xlLine
.Chart.Axes(xlCategory).TickLabels.Font.FontStyle = "Bold"
End With
End Sub
25. Two Y-axes Left and Right of Charts(Primary Axis and Secondary Axis) using Excel VBA
This code will set the series 2 into secondary Axis using Excel VBA.
Sub Ex_ChangeAxistoSecondary()
Dim cht As Object
Set cht = ActiveSheet.ChartObjects.Add(Left:=300, Width:=300, Top:=10, Height:=300)
With cht
.Chart.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7")
.Chart.Type = xlLine
.Chart.SeriesCollection(2).AxisGroup = 2
End With
End Sub
Top
Chart Collection in Excel VBA
You can use ChartObject Collection to loop through the all charts in worksheet or workbook using Excel VBA. And do whatever you want to do with that particular chart. Here are Excel Chart VBA Examples to deal with Charts using VBA.
26. Set equal widths and heights for all charts available in a Worksheet using Excel VBA
Following is the Excel VBA code to change the chart width and height.
Sub Ex_ChartCollections_Change_widths_heights() Dim cht As Object For Each cht In ActiveSheet.ChartObjects cht.Width = 400 cht.Height = 200 Next End Sub
27. Delete All Charts in a Worksheet using Excel VBA
Following is the Excel VBA example to delete all charts in worksheet.
Sub Ex_DeleteAllCharts() Dim cht As Object For Each cht In ActiveSheet.ChartObjects cht.Delete Next End Sub
Top
Other useful Examples and tutorials on Excel VBA Charting
28. Set Chart Data Source using Excel VBA
Below is the Excel Chart VBA Example to set the chart data source. You can set it by using .SetSourceData Source property of a chart
Sub Ex_ChartDataSource()
Dim cht As Chart
'Add new chart
ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddChart.Select
With ActiveChart
'Specify source data and orientation
.SetSourceData Source:=Sheet1.Range("A1:C5")
End With
End Sub
29. Swap or Switch Rows and Columns in Excel Charts using VBA
Here is the excel VBA code to swap the Rows to Columns.
Sub Ex_SwitchRowsColumns()
Dim cht As Chart
'Add new chart
ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddChart.Select
With ActiveChart
'Specify source data and orientation
.SetSourceData Source:=Sheets("Temp").Range("C5:D7"), PlotBy:=xlRows ' you can use xlColumns to swith it
End With
End Sub
30. Set Chart Data Labels and Legends using Excel VBA
You can set Chart Data Labels and Legends by using SetElement property in Excl VBA
Sub Ex_AddDataLabels()
Dim cht As Chart
'Add new chart
ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddChart.Select
With ActiveChart
'Specify source data and orientation
.SetSourceData Source:=Sheet1.Range("A1:B5"), PlotBy:=xlColumns
'Set Chart type
.ChartType = xlPie
'set data label at center
.SetElement (msoElementDataLabelCenter)
'set legend at bottom
.SetElement (msoElementLegendBottom)
End With
End Sub
31. Changing Axis Titles of a Chart in Excel VBA
Following is the code to change the chart Axis titles using Excel VBA..
Sub Ex_ChangeAxisTitles() activechart.chartobjects(1).activate ActiveChart.Axes(xlCategory).HasTitle = True ActiveChart.Axes(xlCategory).AxisTitle.Text = "Quarter" ActiveChart.Axes(xlValue).HasTitle = True ActiveChart.Axes(xlValue).AxisTitle.Text = "Sales" End Sub
32. Change Titles of a Chart using Excel VBA
Following is the code to change the chart titles using Excel VBA..
Sub Ex_ChangeChartTitles() ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(1).Activate ActiveChart.HasTitle = True ActiveChart.ChartTitle.Text = "Overal Summary" End Sub
33. Send an Excel Chart to an Outlook email using VBA
Download Example File:
ANALYSIS TABS – SendExcelChartToOutLook.xlsm
Following is the code to Send an Excel Chart to an Outlook email using VBA.
Sub SendChartThroughMail()
'Add refernce to Microsoft Outlook object Library
Dim olMail As MailItem
Dim objOL As Object
Dim sImgPath As String
Dim sHi As String
Dim sBody As String
Dim sThanks As String
' Saving chart as image
sImgPath = ThisWorkbook.Path & "Temp_" & Format(Now(), "DD_MM_YY_HH_MM_SS") & ".bmp"
Sheets("Sheet1").ChartObjects(1).Chart.Export sImgPath
'creating html body with image
sHi = "<font size='3' color='black'>" & "Hi," & "<br> <br>" & "Here is the required solution: " & "<br> <br> </font>"
sBody = "<p align='Left'><img src=""cid:" & Mid(sImgPath, InStrRev(sImgPath, "") + 1) & """ width=400 height=300 > <br> <br>"
sThanks = "<font size='3'>" & "Many thanks - ANALYSISTABS.COM <br>The Complete Reference For Analyst <br> website:<A HREF=""https://www.analysistabs.com""> analysistabs.com</A>" & "<br> <br> </font>"
'sending the email
Set objOL = CreateObject("Outlook.Application")
Set olMail = objOL.CreateItem(olMailItem)
With olMail
.To = "youremail@orgdomain.com"
.Subject = "ANALYSISTABS.COM: Test Mail with chart"
.Attachments.Add sImgPath
.HTMLBody = sHi & sBody & sThanks
.Display
End With
'Delete the saved chart
Kill sImgPath
'Free-up the objects
Set olMail = Nothing
Set olApp = Nothing
End Sub
Top
Excel VBA Chart Constants and Enumerations
Chart Types, Constants and Enumerations
| CHART TYPE | VBA CONSTANT | VALUE |
|
AREA Charts |
||
| AREA | xlArea | 1 |
| STACKED AREA | xlAreaStacked | 76 |
| 100% STACKED AREA | xlAreaStacked100 | 77 |
| 3D AREA | xl3DArea | -4098 |
| 3D STACKED AREA | xl3DAreaStacked | 78 |
| 3D 100% STACKED AREA | xl3DAreaStacked100 | 79 |
|
BAR Charts |
||
| 3D CLUSTERED BAR | xl3DBarClustered | 60 |
| 3D STACKED BAR | xl3DBarStacked | 61 |
| 3D 100% STACKED BAR | xl3DBarStacked100 | 62 |
| CLUSTERED BAR | xlBarClustered | 57 |
| STACKED BAR | xlBarStacked | 58 |
| 100% STACKED BAR | xlBarStacked100 | 59 |
| CLUSTERED CONE BAR | xlConeBarClustered | 102 |
| STACKED CONE BAR | xlConeBarStacked | 103 |
| 100% STACKED CONE BAR | xlConeBarStacked100 | 104 |
| CLUSTERED CYLINDER BAR | xlCylinderBarClustered | 95 |
| STACKED CYLINDER BAR | xlCylinderBarStacked | 96 |
| 100% STACKED CYLINDER BAR | xlCylinderBarStacked100 | 97 |
| CLUSTERED PYRAMID BAR | xlPyramidBarClustered | 109 |
| STACKED PYRAMID BAR | xlPyramidBarStacked | 110 |
| 100% STACKED PYRAMID BAR | xlPyramidBarStacked100 | 111 |
| BUBBLE Charts | ||
| 3D BUBBLE, BUBBLE WITH 3D EFFECTS | xlBubble3DEffect | 87 |
| BUBBLE | xlBubble | 15 |
|
COLUMN Charts |
||
| 3D CLUSTERED COLUMN | xl3DColumnClustered | 54 |
| 3D COLUMN | xl3DColumn | -4100 |
| 3D CONE COLUMN | xlConeCol | 105 |
| 3D CYLINDER COLUMN | xlCylinderCol | 98 |
| 3D PYRAMID COLUMN | xlPyramidCol | 112 |
| 3D STACKED COLUMN | xl3DColumnStacked | 55 |
| 3D 100% STACKED COLUMN | xl3DColumnStacked100 | 56 |
| CLUSTERED COLUMN | xlColumnClustered | 51 |
| STACKED COLUMN | xlColumnStacked | 52 |
| 100% STACKED COLUMN | xlColumnStacked100 | 53 |
| CLUSTERED CONE COLUMN | xlConeColClustered | 99 |
| STACKED CONE COLUMN | xlConeColStacked | 100 |
| 100% STACKED CONE COLUMN | xlConeColStacked100 | 101 |
| CLUSTERED CYLINDER COLUMN | xlCylinderColClustered | 92 |
| STACKED CYLINDER COLUMN | xlCylinderColStacked | 93 |
| 100% STACKED CYLINDER COLUMN | xlCylinderColStacked100 | 94 |
| CLUSTERED PYRAMID COLUMN | xlPyramidColClustered | 106 |
| STACKED PYRAMID COLUMN | xlPyramidColStacked | 107 |
| 100% STACKED PYRAMID COLUMN | xlPyramidColStacked100 | 108 |
|
DOUGHNUT Charts |
||
| DOUGHNUT | xlDoughnut | -4120 |
| EXPLODED DOUGHNUT | xlDoughnutExploded | 80 |
|
LINE Charts |
||
| 3D LINE | xl3DLine | -4101 |
| LINE | xlLine | 4 |
| LINE WITH MARKERS | xlLineMarkers | 65 |
| STACKED LINE | xlLineStacked | 63 |
| 100% STACKED LINE | xlLineStacked100 | 64 |
| STACKED LINE WITH MARKERS | xlLineMarkersStacked | 66 |
| 100% STACKED LINE WITH MARKERS | xlLineMarkersStacked100 | 67 |
|
PIE Charts |
||
| 3D PIE | xl3DPie | -4102 |
| 3D EXPLODED PIE | xl3DPieExploded | 70 |
| BAR OF PIE | xlBarOfPie | 71 |
| EXPLODED PIE | xlPieExploded | 69 |
| PIE | xlPie | 5 |
| PIE OF PIE | xlPieOfPie | 68 |
|
RADAR Charts |
||
| RADAR | xlRadar | -4151 |
| FILLED RADAR | xlRadarFilled | 82 |
| RADAR WITH DATA MARKERS | xlRadarMarkers | 81 |
|
SCATTER Charts |
||
| SCATTER | xlXYScatter | -4169 |
| SCATTER WITH LINES | xlXYScatterLines | 74 |
| SCATTER WITH LINES AND NO DATA MARKERS | xlXYScatterLinesNoMarkers | 75 |
| SCATTER WITH SMOOTH LINES | xlXYScatterSmooth | 72 |
| SCATTER WITH SMOOTH LINES AND NO DATA MARKERS | xlXYScatterSmoothNoMarkers | 73 |
|
STOCK Charts |
||
| STOCK HLC (HIGH-LOW-CLOSE) | xlStockHLC | 88 |
| STOCK OHLC (OPEN-HIGH-LOW-CLOSE) | xlStockOHLC | 89 |
| STOCK VHLC (VOLUME-HIGH-LOW-CLOSE) | xlStockVHLC | 90 |
| STOCK VOHLC (VOLUME-OPEN-HIGH-LOW-CLOSE) | xlStockVOHLC | 91 |
|
SURFACE Charts |
||
| 3D SURFACE | xlSurface | 83 |
| 3D SURFACE WIREFRAME | xlSurfaceWireframe | 84 |
| SURFACE TOP VIEW | xlSurfaceTopView | 85 |
| SURFACE TOP VIEW WIREFRAME | xlSurfaceTopViewWireframe | 86 |
Marker Styles, Constants and Enumerations
| Marker Styles | Name | Value |
| Automatic markers | xlMarkerStyleAutomatic | -4105 |
| Circular markers | xlMarkerStyleCircle | 8 |
| Long bar markers | xlMarkerStyleDash | -4115 |
| Diamond-shaped markers | xlMarkerStyleDiamond | 2 |
| Short bar markers | xlMarkerStyleDot | -4118 |
| No markers | xlMarkerStyleNone | -4142 |
| Picture markers | xlMarkerStylePicture | -4147 |
| Square markers with a plus sign | xlMarkerStylePlus | 9 |
| Square markers | xlMarkerStyleSquare | 1 |
| Square markers with an asterisk | xlMarkerStyleStar | 5 |
| Triangular markers | xlMarkerStyleTriangle | 3 |
| Square markers with an X | xlMarkerStyleX | -4168 |
Line Styles, Constants and Enumerations
| Line Style | Value |
| xlContinuous | 1 |
| xlDash | -4115 |
| xlDashDot | 4 |
| xlDashDotDot | 5 |
| xlDot | -4118 |
| xlDouble | -4119 |
| xlLineStyleNone | -4142 |
| xlSlantDashDot | 13 |
Example file to Download
You can download the example file and have a look into the working codes.
ANALYSISTABS- Chart VBA Examples
Reference:
MSDN
A Powerful & Multi-purpose Templates for project management. Now seamlessly manage your projects, tasks, meetings, presentations, teams, customers, stakeholders and time. This page describes all the amazing new features and options that come with our premium templates.
Save Up to 85% LIMITED TIME OFFER

All-in-One Pack
120+ Project Management Templates
Essential Pack
50+ Project Management Templates
Excel Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
PowerPoint Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
MS Word Pack
25+ Word PM Templates
Ultimate Project Management Template
Ultimate Resource Management Template
Project Portfolio Management Templates
Related Posts
-
- Excel Chart VBA Examples and Tutorials – Learning Path
- Creating Charts using Excel VBA
- 1. Adding New Chart for Selected Data using Sapes.AddChart Method in Excel VBA
- 2. Adding New Chart for Selected Data using Charts.Add Method : Creating Chart Sheet in Excel VBA
- 3. Adding New Chart for Selected Data using Charts.Add Method : In Existing Sheet using Excel VBA
- 4. Difference between embedded Chart and Chart Sheet in Excel:
- 5. Adding New Chart for Selected Data using ChartObjects.Add Method in Excel VBA
- 6. Assigning Charts to an Object in Excel VBA
- 7. Changing the Chart Position in Excel VBA
- 8. Align Chart Object at a Particular Range or Cell in Excel VBA
- 9. Use with statement while dealing with Charts and avoid the accessing the same object repeatedly in Excel VBA
- 10. You can use ActiveChart Object to access the active chart in Excel VBA
- Setting Chart Types using Excel VBA
- 11. Example to Change Chart type using Excel Chart Enumerations in Excel VBA
- 12. Example to Change Chart type using Excel Chart Constants in VBA
- 13. Example to set the type as a Pie Chart in Excel VBA
- 14. Example to set the chart type as a Line Chart in Excel VBA
- 15. Example to set the chart type as a Bar Chart in Excel VBA
- 16. Example to set the chart type as a XYScatter Chart in Excel VBA
- Formatting Chart Objects using Excel VBA
- 17. Changing Chart Background Color – Chart Aria Interior Color in Excel VBA
- 18. Changing PlotAria Background Color – PlotAria Interior Color in Excel VBA
- 19.Changing Chart Series Background Color – Series Interior Color in Excel VBA
- 20. Changing Chart Series Marker Style in Excel VBA
- 21. Changing Chart Series Line Style in Excel VBA
- 22. Changing Chart Series Border Color in Excel VBA
- 23. Change Chart Axis NumberFormat in Excel VBA
- 24. Formatting Axis Labels: Changing Axis Font to Bold using Excel VBA
- 25. Two Y-axes Left and Right of Charts(Primary Axis and Secondary Axis) using Excel VBA
- Chart Collection in Excel VBA
- 26. Set equal widths and heights for all charts available in a Worksheet using Excel VBA
- 27. Delete All Charts in a Worksheet using Excel VBA
- Other useful Examples and tutorials on Excel VBA Charting
- 28. Set Chart Data Source using Excel VBA
- 29. Swap or Switch Rows and Columns in Excel Charts using VBA
- 30. Set Chart Data Labels and Legends using Excel VBA
- 31. Changing Axis Titles of a Chart in Excel VBA
- 32. Change Titles of a Chart using Excel VBA
- 33. Send an Excel Chart to an Outlook email using VBA
- Excel VBA Chart Constants and Enumerations
- Chart Types, Constants and Enumerations
- Marker Styles, Constants and Enumerations
- Line Styles, Constants and Enumerations
- Example file to Download
VBA Reference
Effortlessly
Manage Your Projects
120+ Project Management Templates
Seamlessly manage your projects with our powerful & multi-purpose templates for project management.
120+ PM Templates Includes:
30 Comments
-
Tim
December 18, 2013 at 11:33 PM — ReplyHI there PNRao,
This is a really great reference – in the past, I’ve beat around the object browser as well. I use MS Graph in an MS Access application (currently A2007 in process of being upgraded from A2003). I have numerous controls to do some of the tasks you’ve identified here and others as well. I also have a button for the very few advanced users UI have to be able to actually open MS Graph in a separate window and do formatting there. What I’m trying to figure out how to do is enumerate through ALL properties of a chart and save them as an array or tab delimited string in a database (Oracle in this case) field.
Is there anyway to do this? I’ve done lots of the sorts of enumeration that you show show excellently here. What I would very much like to do is to be able to enumerate all formatting properties of a chart to be able to store it (above) and retrieve.
Do you have any ideas? Thanks in advance,
—
Tim -
PNRao
December 19, 2013 at 11:30 AM — ReplyHi Tim,
It is good idea to store all properties as enumerations in a field and draw the charts based on the requirement. You can consider the following things to save in the data base.
1. Chart Type
2. Data Source
3. Axes (Primary/Secondary)
4. Border
5. Number Format
6. Legend Alignment
7. Data Labels
8. Chart titleYou can make all the above properties as dynamic and the other things like Colors and minimum and maximum axis should be automatic.
And you can provide UI to format the charts using drop-down lists and Text boxes. For example, you can show different chart types in drop-down and chart type can be changed based on the user selection. You can provide text box to enter the chart title, it should save in your database for chart titles enumeration to reflect on your chart.
Hope this helps, let me know if you need any help on this.
Thanks
PNRao! -
kamran
February 28, 2014 at 3:44 PM — ReplyOne of the best Tutorial for VBA macro.
-
Antoni
April 23, 2014 at 9:02 PM — ReplyHi,
My boss has asked me to do many graphics chars, i love the example and explanations that have left at this web, I would like to do what our friend says PNRao, please have you any example of how to do it?
Thank you very much.
Antoni. -
PNRao
April 24, 2014 at 8:48 PM — ReplyHi Antoni,
We can automate charting using VBA. We have provided some examples in download page. You can download and see the examples, let us know if you need any help.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Antoni
April 25, 2014 at 8:15 PM — ReplyHi PNRao,
I can’t found examples in the Download section, can you help me please?, or can you send me a links?
Thank you.
-
PNRao
April 26, 2014 at 12:08 AM — ReplyHi Antoni,
I have added the example file at end of the post. Please download and see the code.Thanks-PNRao!
-
Sam
May 4, 2014 at 9:32 AM — ReplyHi,
I am having a task, in which i need to copy chart from one excel sheet to another excel sheet.
So can you please help me in this.
Thanks,
Sam -
PNRao
May 4, 2014 at 11:40 AM — ReplyHi Sam,
You can use the Copy method as shown below:
[vb]
Sub sbVBA_Chart_Copy()
Sheet1.ChartObjects(«Chart 1»).Copy ‘Sheet name and Chart Object name to be copied
Sheet2.Activate ‘Activate your destination Sheet
Range(«G1»).Select ‘Select your destination cell
ActiveSheet.Paste ‘Now Paste
End Sub
[/vb]Thanks-PNRao!
-
Ross
December 29, 2014 at 9:02 PM — ReplyHi PNRao,
Thanks for the above it’s really helpful, although I’m still stuck!
Is there a way to so that when making a graph it has a certain destination within the sheet so it’s not pasted over my data?
Thank you!!
-
เสื้อคู่
May 25, 2015 at 3:43 PM — ReplyHi, this weekend is pleasant in favor of me, since this moment i am reading
this great informative post here at my residence. -
Nkhoma Kenneth
October 4, 2015 at 1:27 PM — ReplyThanks very much for the tutorial, it is a great one indeed and very helpful.
Thanks to you, i have learn’t something.
-
Richard
December 1, 2015 at 4:59 PM — ReplyHi Guys
Great info – ThanksI’m trying to automate some graph formatting, and whilst I’ve worked out how to change the range for a xlTimeScale based graph, I want an easy way for the user to define which graphs need to be scaled to current month rather than all year.
I thought of putting a text string into the Alt Text Description box (found under / but how do I read that field from a macro?
If it were a shape I could use something like shapeDesc = sheet(1).Shapes(1).AlternativeText but that doesn’t work for ChartObjects.
Any ideas?
Thanks
RichardAlways learning …
-
Richard
December 1, 2015 at 7:44 PM — ReplyHah! Got it guys.
I’ve decided to scroll through each sheet. In each sheet scroll through each Shape. If the Shape.Type = msoChart Then I can pick up the Alternative Text and act accordingly.Code extract:
For lShtCtr = 1 To ThisWorkbook.Sheets.Count
Debug.Print “Checking worksheet ” & lShtCtr & ” ” & Sheets(lShtCtr).Name & “. Detected ” & ThisWorkbook.Sheets(lShtCtr).Shapes.Count & ” shapes.”
For lShapeCtr = 1 To ThisWorkbook.Sheets(lShtCtr).Shapes.Count
If ThisWorkbook.Sheets(lShtCtr).Shapes(lShapeCtr).Type = msoChart Then
myText = ThisWorkbook.Sheets(lShtCtr).Shapes(lShapeCtr).AlternativeText
Debug.Print “Alt Text in ” & ThisWorkbook.Sheets(lShtCtr).Shapes(lShapeCtr).Name & ” =:” & myText
If InStr(1, myText, “#AutoScale”, vbTextCompare) > 0 Then
Debug.Print “Scaling axes on ” & ThisWorkbook.Sheets(lShtCtr).Shapes(lShapeCtr).Name
Call ScaleAxes(ThisWorkbook.Sheets(lShtCtr), ThisWorkbook.Sheets(lShtCtr).Shapes(lShapeCtr).Name)
End If ‘myText contains #AutoScale
End If ‘Shape.Type = msoChart
Next lShapeCtr
Next lShtCtrThe debug.print allow you to see what is going on. I’ve used the magic key phrase ‘#AutoScale’ as my command
Thanks
RichardAlways learning
-
Krishnaprasad Menon
January 2, 2016 at 10:45 AM — ReplyVery nice tutorial.. Chart creating example file is not available on download… Kindly make it available
-
PNRao
January 2, 2016 at 11:38 PM — ReplyThanks for your valuable feedback and reporting an issue, we have fixed it.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
HS
March 19, 2016 at 5:12 PM — ReplyVery quickly this site will be famous amid all blogging and site-building
users, due to it’s good posts -
chris
May 9, 2016 at 1:05 AM — Replyi want to explode on a pie chart the piece with the max value. How can i do this? Also what if I have on a pie two pieces with the same max value? Thank you.
-
Nagaraju
July 1, 2016 at 12:17 PM — ReplyHi All,
I’m trying to open website through Vba code….It was done…I need small information that if need code how to search search any information in google and display.
Regards,
Nagu -
Salty
August 25, 2016 at 11:12 PM — ReplyHi
This comment relates to your Example 13, above, but may apply to all of the Chart.Type examples.
Using Excel 2016 on Windows 8, I had to change one line as follows:
From > Chart.Type = xlPie
To > Chart.Chart.Type = xlPie -
Salty
August 29, 2016 at 9:01 AM — ReplyHi
Sorry, I sent you a typo in my August 25 2016 comment. It should have said:
It should have said
To > Chart.ChartType = xlPie -
Raspreet Singh Jaggi
October 21, 2016 at 3:22 PM — ReplyYour codes are very much helpful Mr.PNRao.
-
Dwayne
November 29, 2016 at 10:01 AM — ReplyHi all,
That was quite a read! I’ve come away with many ideas for future spreadsheets..I do have one quick query, I’m using the following script to change the data range for a chart I’m using;
Sub RECPLINE()
ActiveSheet.ChartObjects(“Chart 1”).Activate
ActiveChart.SeriesCollection(1).Select
ActiveChart.SetSourceData Source:=Range(“=Data!$AR$3:$AW$31”)
End SubInstead of having 6 charts crammed into one screen, I aim to have one chart and 6 buttons to change the data range in the chart.
Everything works fine, but I have formatted the visual aspects of the chart to be more appealing. After saving and re-opening the spreadsheet, the first chart has kept the formatting, but all the other charts adopt the standard formatting when the data range is changed..Is there any way I can force the existing visual changes, or will I have to code the changes into the VBA script each time I change the data range?
Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Cheers,
Dwayne. -
Rommel Pastidio
January 29, 2018 at 1:47 PM — ReplyHi PNrao,
The codes here is very useful, for now I am creating excel with VBA for charting. can you help me with below inquiry?
1. if I plot a chart using VBA how can I add comment on the point (if out of specs)? -
anil reddy
March 28, 2019 at 5:47 PM — Replyhi PNrao
how to do data validation using vba
-
paulus
May 20, 2019 at 12:21 PM — Replyhow can i specify range for x-axis and for y-axis when coding for a line graph, and all my data in rows. for example row 1 is my x-axis and row 2 is my y-axis?
-
amol
June 3, 2019 at 4:29 PM — ReplysBody = ” ”
Can you please explain above code…
-
amol
June 3, 2019 at 4:30 PM — ReplyMid(sImgPath, InStrRev(sImgPath, “) + 1)
kindly explain the above code…
-
PNRao
July 4, 2019 at 6:10 PM — Reply
Sub ttt()'Let us say, you have the file path and name asigned to the variable
sImgPath = "C:MainFolderSubFolderYourFileName.xlsm"'You can extract the filename using the given code
Filename = Mid(sImgPath, InStrRev(sImgPath, ") + 1)'Explaination
'InStrRev function checks find the fist finding posing of the given string (") in the sImgPath from the right
'i.e; InStrRev(sImgPath, ") expression results the value 24 in the above code
'And the mid function will return the substing from the given starting positions
'.ie;Mid(sImgPath,24+1) returns the substing of sImgPath from the 25th position
'="YourFileName.xlsm"End Sub
-
PNRao
July 4, 2019 at 6:12 PM — ReplyThis will assign blank space to the sBody variable.
Effectively Manage Your
Projects and Resources
ANALYSISTABS.COM provides free and premium project management tools, templates and dashboards for effectively managing the projects and analyzing the data.
We’re a crew of professionals expertise in Excel VBA, Business Analysis, Project Management. We’re Sharing our map to Project success with innovative tools, templates, tutorials and tips.
Project Management
Excel VBA
Download Free Excel 2007, 2010, 2013 Add-in for Creating Innovative Dashboards, Tools for Data Mining, Analysis, Visualization. Learn VBA for MS Excel, Word, PowerPoint, Access, Outlook to develop applications for retail, insurance, banking, finance, telecom, healthcare domains.
Page load link

3 Realtime VBA Projects
with Source Code!
Go to Top