In VBA, we can delete any file present in the computer using VBA codes. The code used to delete files is known as the “Kill” command. The method to delete any file is that first, we must provide the file’s path, which means the file’s location on the computer. Then, we use the “Kill” command to delete the file.
Table of contents
- How to Delete Files using VBA Code?
- Kill Method to Delete Files in a Folder using VBA Code
- Delete Particular File Name
- Delete All Excel Files
- Delete Entire Folder Only
- Delete All the Text Files in the Folder
- Delete Read-Only Files
- Recommended Articles
How to Delete Files using VBA Code?
VBA is a tough thing initially, but as you spend more time with VBA, you will start loving it just like me. We can open files from another computer folder and work with them. Now, we can delete files as well by using VBA coding. This article will show you how to delete files using VBA code in a specific folder.
When working with large projects, we usually create many intermediate files to support our process. we need to delete those files to avoid future confusion after completing the work.
And one scenario is when we usually receive an email. For example, we save attachments for our regular work, or we want to see the report for that point in time, and later we may need to delete those files.
Deleting those files manually may take time, or we may forget to save them. In addition, it will occupy the space on our computer. Therefore, we will show you how to delete those files with simple VBA codesVBA code refers to a set of instructions written by the user in the Visual Basic Applications programming language on a Visual Basic Editor (VBE) to perform a specific task.read more.
Kill Method to Delete Files in a Folder using VBA Code
A simple Kill function will delete the folder, specific file, all Excel files, etc. Take a look at the syntax of the Kill method in VBA. The Kill method cannot delete read-only files.
Path Name: Pathname is nothing but the folder path in the computer to delete the files.
Note: Path Name can include wildcard characters as well. We can use an asterisk (*) and question marks (?) as wildcard characters in excelIn Excel, wildcards are the three special characters asterisk, question mark, and tilde. Asterisk denotes multiple characters, a question mark denotes a single character, and a tilde denotes the identification of a wild card character.read more.
Asterisk (*) is useful to match any length string. In addition, it also considers zero.
Question mark (?) is useful to match only a single character.
Delete Particular File Name
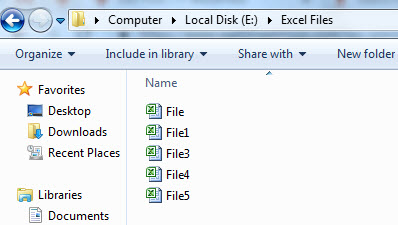
For example, we have a folder like the one below.
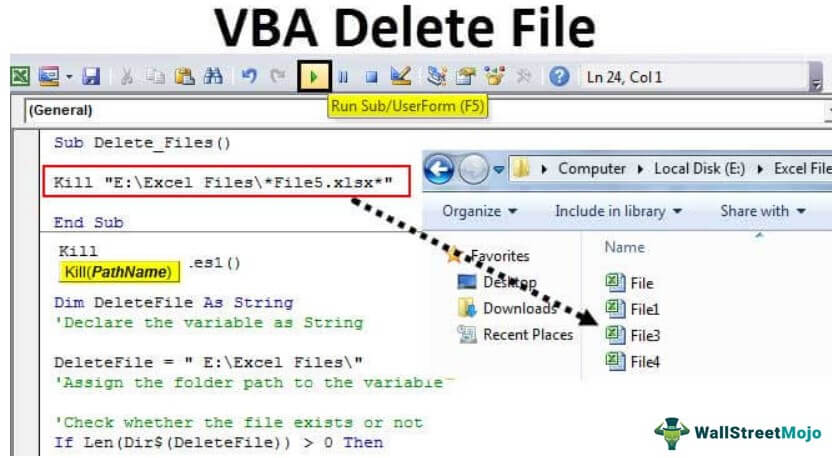
We want to delete the file named “File 5” in this folder. But, first, start the code with the Kill function.
Code:
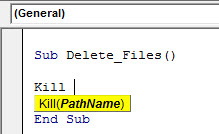
Sub Delete_Files() Kill(PathName) End Sub
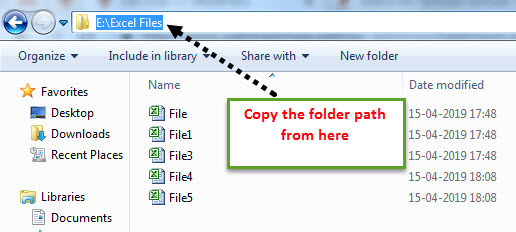
Copy and paste the folder path.
And Paste in double-quotes.
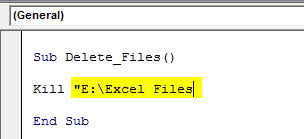
Kill "E:Excel Files"
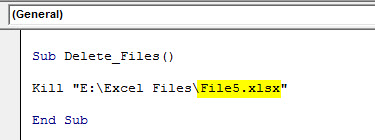
Now put one more backward slash () and enter the file name with extension.
Kill "E:Excel FilesFile5.xlsx"
When you run this code, it will delete the file named “File 5.xlsx” in the mentioned folder path.
Delete All Excel Files
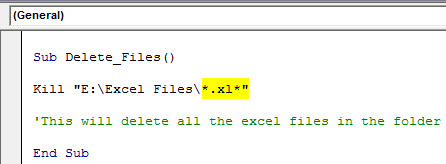
Using VBA, we need to use wildcard characters with the Kill function to delete all the Excel files in the folder. After mentioning the folder path, we need to mention the file as “*.xl*.”
Code:
Kill "E:Excel Files*.xl*"
When you run this code, it will delete all the Excel files in the folder.
We have seen how we can delete a single Excel file and all the Excel files. But if we want to delete all the files in the folder, how can we delete them? Also, since we are using Excel VBA, can it delete other files?
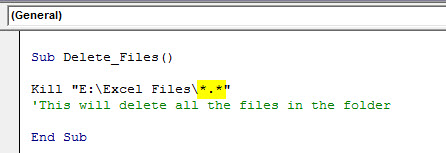
The answer is Yes! Use the below code to delete all the files in the folder.
Code:
Kill "E:Excel Files*.*"
Delete Entire Folder Only
Is it possible to delete the entire folder itself?
Yes, it is possible.
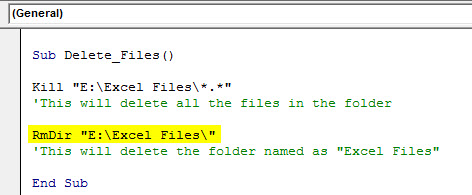
We need to delete all the files in the folder using the Kill function. Then to delete the folder, we need to use one more function called RmDir.
Code:
RmDir "E:Excel Files"
Here RmDir will delete only the empty folder if any subfolder is where it cannot delete them.
Delete All the Text Files in the Folder
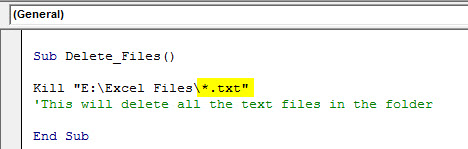
To delete all the text files in the folder, use the below code.
Code:
Kill "E:Excel Files*.txt"
Delete Read-Only Files
As we said, the Kill function cannot delete “Read Only” files in the folder. In such a scenario, we need to use the other two functions: “Dir$” and “SetAttr.” Below is the example code to delete the read-only files as well.
Code:
Sub Delete_Files1() Dim DeleteFile As String DeleteFile = " E:Excel Files" If Len(Dir$(DeleteFile)) > 0 Then SetAttr DeleteFile, vbNormal Kill DeleteFile End If End Sub
You can download this VBA Delete File Excel Template from here – VBA Delete File Excel Template.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA Delete Files. Here, we discuss the VBA code to delete 1. Particular File Name, 2. All files, 3. Entire folder, and 4. Read-only Files with downloadable Excel template. Below are some useful articles related to VBA: –
- VBA InStr
- VBA Join
- New Line in Excel VBA
- Split Function in Excel VBA
Удаление любых файлов из кода VBA Excel с помощью оператора Kill и метода DeleteFile объекта FileSystemObject. Знаки подстановки, синтаксис, примеры.
Оператор Kill
Описание
Kill – это оператор, предназначенный для удаления файлов с диска.
Синтаксис
- PathName – это строковое выражение, задающее одно или несколько имен файлов (по шаблону), которые требуется удалить.
Строка PathName может содержать каталоги (папки) и букву диска. Если файл с именем PathName не существует, будет сгенерирована ошибка.
Оператор Kill поддерживает использование знаков подстановки в последнем компоненте параметра PathName (собственное имя файла без пути к нему):
- Звездочка (*) – заменяет любое количество символов или ни одного.
- Вопросительный знак (?) – заменяет один символ или ни одного.
Знаки подстановки позволяют создать шаблон, по которому можно удалить сразу несколько файлов.
Примеры
Пример 1
Удаление одного файла без проверки его существования (в примере — удаление книги Excel):
|
Sub Primer1() On Error Resume Next Kill ThisWorkbook.Path & «Книга1.xlsx» End Sub |
Инструкция On Error Resume Next нужна для того, чтобы корректно завершить программу в том случае, если файла с именем PathName не существует.
Пример 2
Удаление одного файла с проверкой его существования:
|
Sub Primer2() Dim myPathName As String myPathName = «C:Новая папкаФайл1.docx» If Dir(myPathName) <> «» Then Kill myPathName End Sub |
Пример 3
Удаление нескольких файлов по шаблону:
|
Sub Primer3() On Error Resume Next Kill «C:Новая папкаСправка*» End Sub |
В результате работы этого кода VBA Excel будут удалены все файлы с любыми расширениями, которые начинаются со слова «Справка». Если строку Kill "C:Новая папкаСправка*" заменить строкой Kill "C:Новая папка*2020*", она удалит все файлы, в имени которых есть подстрока «2020».
Как удалить объект ThisWorkbook с помощью оператора Kill из кода VBA Excel, размещенного в нем же, смотрите в статье: Удаление книги из собственного кода.
Метод DeleteFile
Описание
DeleteFile – это метод объекта FileSystemObject, предназначенный для удаления файлов с диска из кода VBA Excel.
Синтаксис
|
Object.DeleteFile PathName, [force] |
- Object – переменная, возвращающая объект FileSystemObject (обязательный параметр);
- PathName – строковое выражение, задающее одно или несколько имен файлов (по шаблону), которые требуется удалить (обязательный параметр);
- force – значение типа Boolean: True – удаляются все файлы, False (по умолчанию) – не удаляются файлы с атрибутом «только для чтения» (необязательный параметр).
В последнем компоненте параметра PathName (собственное имя файла без пути к нему) можно использовать знаки подстановки, также, как и для оператора Kill. Если указанный файл не существует, будет сгенерирована ошибка.
Примеры
Пример 4
Удаление одного файла с проверкой его существования:
|
Sub Primer4() Dim fso As Object ‘Присваиваем переменной fso ссылку на новый экземпляр FileSystemObject Set fso = CreateObject(«Scripting.FileSystemObject») ‘Проверяем существование удаляемого файла If Dir(ThisWorkbook.Path & «Изображение.png») <> «» Then ‘Удаляем файл, если он существует fso.DeleteFile ThisWorkbook.Path & «Изображение.png» End If End Sub |
Пример 5
Удаление нескольких или всех файлов по шаблону:
|
Sub Primer5() Dim fso As Object ‘Присваиваем переменной fso ссылку на новый экземпляр FileSystemObject Set fso = CreateObject(«Scripting.FileSystemObject») ‘Завершаем программу, если не существует ни одного файла, подходящего под указанный шаблон On Error Resume Next ‘Удаляем указанный файл (файлы) fso.DeleteFile «C:Новая папка*.docx» End Sub |
В результате работы этого кода VBA Excel из папки «Новая папка» будут удалены все файлы с расширением .docx.
Фразы для контекстного поиска: удаление файла, удаление всех файлов, удаление нескольких книг, удаление всех книг, удаление по шаблону.
Using VBA, how can I:
- test whether a file exists, and if so,
- delete it?
1.) Check here. Basically do this:
Function FileExists(ByVal FileToTest As String) As Boolean
FileExists = (Dir(FileToTest) <> "")
End Function
I’ll leave it to you to figure out the various error handling needed but these are among the error handling things I’d be considering:
- Check for an empty string being passed.
- Check for a string containing characters illegal in a file name/path
2.) How To Delete a File. Look at this. Basically use the Kill command but you need to allow for the possibility of a file being read-only. Here’s a function for you:
Sub DeleteFile(ByVal FileToDelete As String)
If FileExists(FileToDelete) Then 'See above
' First remove readonly attribute, if set
SetAttr FileToDelete, vbNormal
' Then delete the file
Kill FileToDelete
End If
End Sub
Again, I’ll leave the error handling to you and again these are the things I’d consider:
-
Should this behave differently for a directory vs. a file? Should a user have to explicitly have to indicate they want to delete a directory?
-
Do you want the code to automatically reset the read-only attribute or should the user be given some sort of indication that the read-only attribute is set?
EDIT: Marking this answer as community wiki so anyone can modify it if need be.
2
An alternative way to code Brettski’s answer, with which I otherwise agree entirely, might be
With New FileSystemObject
If .FileExists(yourFilePath) Then
.DeleteFile yourFilepath
End If
End With
Same effect but fewer (well, none at all) variable declarations.
The FileSystemObject is a really useful tool and well worth getting friendly with. Apart from anything else, for text file writing it can actually sometimes be faster than the legacy alternative, which may surprise a few people. (In my experience at least, YMMV).
answered Sep 16, 2008 at 11:03
Mike WoodhouseMike Woodhouse
51.5k12 gold badges88 silver badges127 bronze badges
4
I’ll probably get flamed for this, but what is the point of testing for existence if you are just going to delete it? One of my major pet peeves is an app throwing an error dialog with something like «Could not delete file, it does not exist!»
On Error Resume Next
aFile = "c:file_to_delete.txt"
Kill aFile
On Error Goto 0
return Len(Dir$(aFile)) > 0 ' Make sure it actually got deleted.
If the file doesn’t exist in the first place, mission accomplished!
answered Sep 15, 2008 at 23:34
4
The following can be used to test for the existence of a file, and then to delete it.
Dim aFile As String
aFile = "c:file_to_delete.txt"
If Len(Dir$(aFile)) > 0 Then
Kill aFile
End If
answered Sep 15, 2008 at 23:12
Rich AdamsRich Adams
25.9k4 gold badges39 silver badges62 bronze badges
2
In VB its normally Dir to find the directory of the file. If it’s not blank then it exists and then use Kill to get rid of the file.
test = Dir(Filename)
If Not test = "" Then
Kill (Filename)
End If
ZygD
21k39 gold badges77 silver badges98 bronze badges
answered Sep 15, 2008 at 23:11
Leo MooreLeo Moore
2,0982 gold badges19 silver badges21 bronze badges
set a reference to the Scripting.Runtime library and then use the FileSystemObject:
Dim fso as New FileSystemObject, aFile as File
if (fso.FileExists("PathToFile")) then
aFile = fso.GetFile("PathToFile")
aFile.Delete
End if
answered Sep 15, 2008 at 23:40
BrettskiBrettski
19.1k15 gold badges75 silver badges95 bronze badges
2
Here’s a tip: are you re-using the file name, or planning to do something that requires the deletion immediately?
No?
You can get VBA to fire the command DEL «C:TEMPscratchpad.txt» /F from the command prompt asynchronously using VBA.Shell:
Shell «DEL » & chr(34) & strPath & chr(34) & » /F «, vbHide
Note the double-quotes (ASCII character 34) around the filename: I’m assuming that you’ve got a network path, or a long file name containing spaces.
If it’s a big file, or it’s on a slow network connection, fire-and-forget is the way to go.
Of course, you never get to see if this worked or not; but you resume your VBA immediately, and there are times when this is better than waiting for the network.
1
You can set a reference to the Scripting.Runtime library and then use the FileSystemObject. It has a DeleteFile method and a FileExists method.
See the MSDN article here.
answered Sep 15, 2008 at 23:12
Darrel MillerDarrel Miller
138k31 gold badges193 silver badges242 bronze badges
0
A shorter version of the first solution that worked for me:
Sub DeleteFile(ByVal FileToDelete As String)
If (Dir(FileToDelete) <> "") Then
' First remove readonly attribute, if set
SetAttr FileToDelete, vbNormal
' Then delete the file
Kill FileToDelete
End If
End Sub
Introduction to VBA Delete File
Sometimes when we work in VBA we create some unwanted files, or we have some unwanted files on our computer. How do we get rid of them? We can simply go and delete each file manually by locating the file and right click on it then, we click on the delete button to delete the file. Or we can press the delete button from the keyboard to delete the file. But how do we do this in VBA is what we will learn in this article.
So now we have understood the concept of this topic that we need to delete a file by using VBA macros. In VBA, we have a kill command which is used to delete a file from its location. When we simply delete the file by going through the process of locating the file and right-clicking on it to delete or press the delete button even, the file goes to the recycle bin. But when we use the Kill command in VBA to delete a file the file is permanently deleted from the computer. It doesn’t go to the recycle bin. Now let us look at the syntax which we will be using to delete a file using VBA. It is as follows:
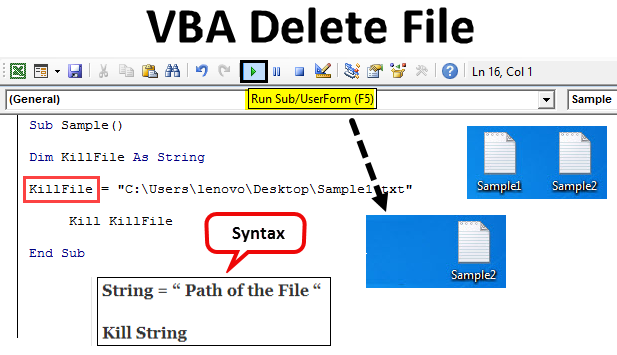
Syntax of Delete File in Excel VBA
String = “ Path of the File “ Kill String
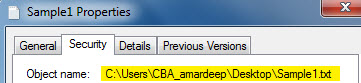
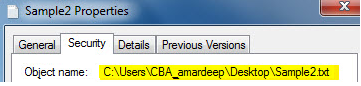
Always remember that the path of the file should be in the inverted commas. Now to delete a file in VBA we must have its path. How do we get a path of the file? We need to right-click on the file and click on properties which give us different options for the properties of the file once we click on the security tab which is the second number in the tabs we can find the path location under the object name. Have a look at the screenshot below for reference.
The path written after the object name is the argument we need to feed for the killfile function in order to delete any file. Now let us start deleting files by looking at a few examples below.
Before we move to examples always ensure that we have the developer’s tab enabled in order to use macros. It is done by moving to the files section and then to the options section. We will find a checkbox that should be checked to enable the developer’s tab. Now let us move ahead to examples. For example, I have two files named sample 1 and sample 2. Both are text files and are on desktop. Have a look at them below.
How to Delete a File Using VBA?
Let’s see the examples of Delete File in Excel VBA.
You can download this VBA Delete File Excel Templates here – VBA Delete File Excel Templates
Example #1 – VBA Delete File
Let us first delete the sample 1 file in this example. Both the examples will have one minute difference which I will explain at the end of the topic. First, we need to get a path for the sample 1 file. In order to do that right click on the file and from the properties option go to security and we will find the path to beside the object name as follows.
Step 1: Now let us enter into VBA from the visual basic option. It can be found under the developer’s tab.
Step 2: Once we are in VBA we need to insert a module. To enter the code window double click on the module which will take us to the code window.
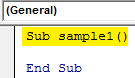
Step 3: Now the first step for writing a VBA code is to name the macro as follows.
Code:
Sub Sample() End Sub
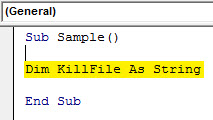
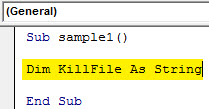
Step 4: Declare a variable as a string which will store the path for the file.
Code:
Sub Sample() Dim KillFile As String End Sub
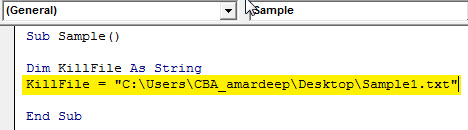
Step 5: Now let us assign the path to this string of the file we want to delete which is sample1.
Code:
Sub Sample() Dim KillFile As String KillFile = "C:UsersCBA_amardeepDesktopSample1.txt" End Sub
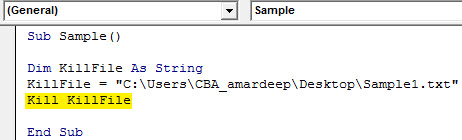
Step 6: Now let us delete the file using the Kill Function as follows.
Code:
Sub Sample() Dim KillFile As String KillFile = "C:UsersCBA_amardeepDesktopSample1.txt" Kill KillFile End Sub
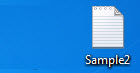
Step 7: When we run the above code and look at the desktop we can no longer find the first text file we created.
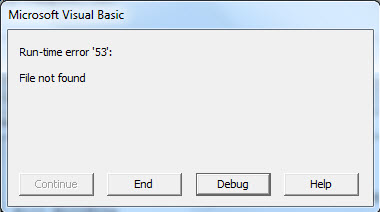
Only the second file is present and the first file is moved. Now, what happens if the file path was wrong or the file didn’t even exist. Now we have deleted the first file and it didn’t even exist so we can run the code again to check what result we will get. Run the above code again.
VBA gives us a runtime error that the file is not found. This is important which we need to keep in mind.
Example #2 – VBA Delete File
Now let us delete the second file using the kill function. Again we need to have the path for the second file for which we need to right click on the file and from the properties option go to security and we will find the path to in beside the object name as follows.
Now we have the path for the second file so let us delete this file.
Step 1: Enter into VBA through the developer’s tab.
Step 2: Once we are in VBA we need to insert a module. To enter the code window double click on the module which will take us to the code window.
Step 3: Name the macro first in order to proceed further as follows.
Code:
Sub sample1() End Sub
Step 4: Similar to above, declare a variable as a string to store the file’s path.
Code:
Sub sample1() Dim KillFile As String End Sub
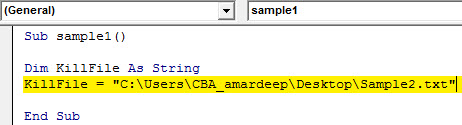
Step 5: In the string store the path of the file as follows.
Code:
Sub sample1() Dim KillFile As String KillFile = "C:UsersCBA_amardeepDesktopSample2.txt" End Sub
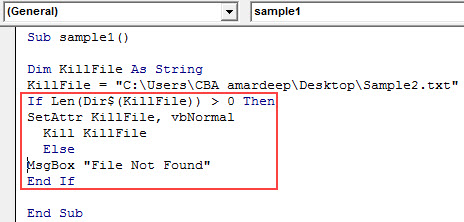
Step 6: Now we will check that the file even exists using the If function as follows.
Code:
Sub sample1() Dim KillFile As String KillFile = "C:UsersCBA_amardeepDesktopSample2.txt" If Len(Dir$(KillFile)) > 0 Then SetAttr KillFile, vbNormal Kill KillFile Else MsgBox "File Not Found" End If End Sub
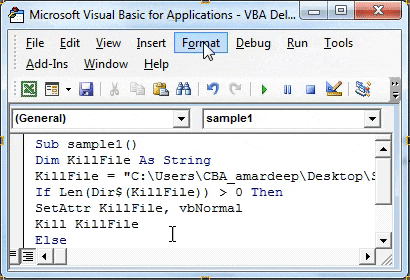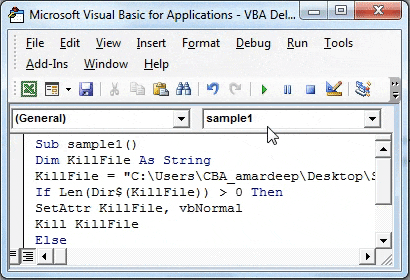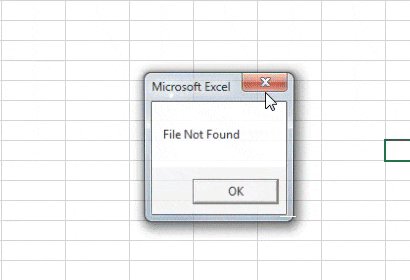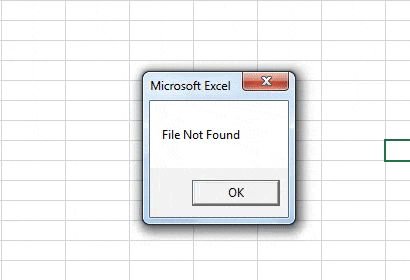
Step 7: Now if we run the above code we can see that the file has been deleted and it is no longer in the desktop.
Step 8: In above example, we have seen that if the file doesn’t exist VBA gives us an error also in this case as the file has been deleted we can run the code again and we can see that instead of the error we get a personalized message as follows.
Things to Remember
There are few things which we need to remember about deleting a file in VBA:
- We use the Kill function to delete a file.
- We need to have the path of the specific file which is to be deleted.
- If the file is not found we encounter an error.
- The files deleted by the Kill function do not go in the recycle bin.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to VBA Delete File. Here we discuss how to use Excel VBA Delete File along with few practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- VBA While Loop
- VBA Remove Duplicates
- VBA Data Types
- VBA Sleep
VBA Delete File in Excel from a folder or directory. You can delete any file like Excel, Word, PowerPoint, CSV, Notepad etc. Let us see different examples in the following tutorial. We are using Kill statement to delete a file.
Table of Contents:
- Objective
- Example on Deleting different type of File using Kill Statement
- Deleting Excel file using VBA FileSystemObject Object
- Instructions to Run VBA Macro Code
- Other Useful Resources
Example on VBA Delete File
Let us see an example how to delete a file in Excel using VBA. The following example helps to delete an Excel file.
'VBA Delete Excel File
Sub VBAF1_Delete_File()
'Variable declaration
Dim sFolderPath As String
Dim sFileName As String
'Define Folder Path and file name
sFolderPath = "C:VBAF1Test"
sFileName = "sample.xlsx"
'Delete Excel file
Kill sFolderPath & sFileName
End Sub
Note:You can check your output by creating sample file in specified folder before and after running macro.
The following macro helps to delete Word document file.
'VBA Delete Word File
Sub VBAF1_Delete_File()
'Variable declaration
Dim sFolderPath As String
Dim sFileName As String
'Define Folder Path and file name
sFolderPath = "C:VBAF1Test"
sFileName = "Documentation.docx"
'Delete Word file
Kill sFolderPath & sFileName
End Sub
The following VBA code helps to delete CSV file.
'VBA Delete CSV File
Sub VBAF1_Delete_File()
'Variable declaration
Dim sFolderPath As String
Dim sFileName As String
'Define Folder Path and file name
sFolderPath = "C:VBAF1Test"
sFileName = "Documentation.csv"
'Delete CSV file
Kill sFolderPath & sFileName
End Sub
Example on Deleting a file using VBA FSO Object
Let us an example VBA macro code to delete Excel file using VBA FileSystemObject (FSO) in Excel.
'VBA Delete Excel File using VBA FileSystemObject object in Excel.
Sub VBAF1_Delete_File_Using_FSO()
'Variable declaration
Dim sFolderPath As String
Dim sFileName As String, oFSO As FileSystemObject
'Define Folder Path and file name
sFolderPath = "C:VBAF1Test"
sFileName = "sample.xlsx"
'Create FSO Object
Set oFSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
'Delete file
oFSO.DeleteFile sFolderPath & sFileName, True
End Sub
Instructions to Run VBA Macro Code or Procedure:
You can refer the following link for the step by step instructions.
Instructions to run VBA Macro Code
Other Useful Resources:
Click on the following links of the useful resources. These helps to learn and gain more knowledge.
VBA Tutorial VBA Functions List VBA Arrays VBA Text Files VBA Tables
VBA Editor Keyboard Shortcut Keys List VBA Interview Questions & Answers Blog
Return to VBA Code Examples
VBA allows you to delete an existing file, using the Kill command. In this tutorial, you will learn how to delete a specific file or multiple files.
If you want to learn how to copy and rename a file, you can click on this link: VBA Copy File
Delete a Single File (or Workbook) in VBA
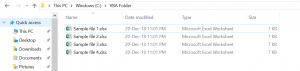
We will show how to delete the file Sample file 1.xlsx in the folder VBA Folder. The folder with the file now looks like in Image 1:
Image 1. Delete a single file
Here is the code which will delete the file:
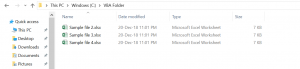
Kill "C:VBA FolderSample File 1.xlsx"After running the code, the file Sample file 1.xlsx is now deleted from the VBA Folder. The output is in Image 2:
Image 2. File deleted from the C:VBA Folder
Delete All Excel Files From the Folder
The same command enables you to delete all Excel files from the folder. You just need to put an asterisk (*) instead of the file name. An asterisk replaces any string. Here is the code:
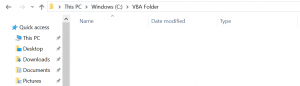
Kill "C:VBA Folder*.xlsx"As you can see in Image 3, all Excel files from Folder VBA are deleted:
Image 3. Delete all Excel files from the C:VBA Folder
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
Home / VBA / VBA Delete Workbook (Excel File)
To delete an Excel file from a folder you can use two different methods. The first method is the “Kill” statement which takes the file path to refer to the file that you wish to delete. The second method is the FileSystemObject object which has a method associated with it to delete a file.
To use these codes, go to the VBE (Code Editor) from the developer tab.
Delete a File using VBA (Kill Function)
Kill function helps you to delete a single file or multiple files, and use wildcard characters to delete more than one file. Below is the one-line code that deletes the file from the folder that I have on the desktop.
Kill "C:UsersDellDesktopSample Datafile-one.xlsx"
This code will show you an error if the workbook that you specified to delete doesn’t exist.
Helpful Links: Run a Macro – Macro Recorder – Visual Basic Editor – Personal Macro Workbook
Delete All the Files from a Folder using VBA
And if you want to delete all the files that you have in a folder, you can use a wildcard character.
Kill "C:UsersDellDesktopSample Data*.xl*"
Delete a File using the FileSystemObject (Object)
The file system object provides you with access to the computer’s file system. You can learn about it from here, but now, let’s write a code to remove a file.
Full Code
Sub vba_delete_file()
Dim FSO
Dim myFile As String
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
myFile = "C:UsersDellDesktopSample Datafile1.xlsx"
FSO.DeleteFile myFile, True
End SubLet’s say you need to write a code that can check for a file, (exists or not) and then delete it. Here’s the code that you need.
Sub vba_delete_file()
Dim FSO
Dim myFile As String
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
myFile = "C:UsersDellDesktopSample Datafile1.xlsx"
If FSO.FileExists(myFile) Then
FSO.DeleteFile myFile, True
MsgBox "Deleted"
Else
MsgBox "There's no workbook with this name."
End If
End SubMore on VBA Workbooks
VBA Save Workbook | VBA Close Workbook | VBA ThisWorkbook | VBA Rename Workbook | VBA Activate Workbook | VBA Combine Workbook | VBA Protect Workbook (Unprotect) | VBA Check IF a Workbook is Open | VBA Open Workbook | VBA Check IF an Excel Workbook Exists in a Folder| VBA Create New Workbook (Excel File)
- VBA Workbook
Delete Files Using VBA
VBA Delete Files Macro helps to Delete Files using VBA from a folder. Generally while dealing with the file operations we create or delete files using VBA in the process. For example when we are automating a specific task, we create lot of intermediate files and finally we produce one final output.At end we clean or delete all the intermediate files using VBA.
Sometimes we may regularly monitor outlook and when we receive a new mail with required input files. We will save these files in a specific folder to process these files and produce the final output.And we will check before saving the input files in the folder and delete if there are any existing files are already available in the directory.
- Solution
- Example Cases
- Delete a specific file from a folder
- Delete all files from a folder or directory
- Delete a selected file from a directory using Open File Dialog
- Delete a specific type of files from a directory – Delete all Excel files from a folder
- Delete all files from a directory if file name contains specific string
- Delete a specific file from a folder and Sub folders
- Output
- Instructions
- Example File
Solution(s):
We can use DeleteFile method of FileSystemObject to delete files using VBA.Follwing are the examples to delete a specific file or files from a location.
VBA Delete Files Macro – Example Cases:
Delete a specific file from a folder
Following is the example to delete a specific file from a folder or a directory.You can use DeleteFile method of FileSystemObject to Delete a specific file from a folder.
First it will check whether the file exists in the sourse location or not. If it exists it will delete from the directory ot it will display message.
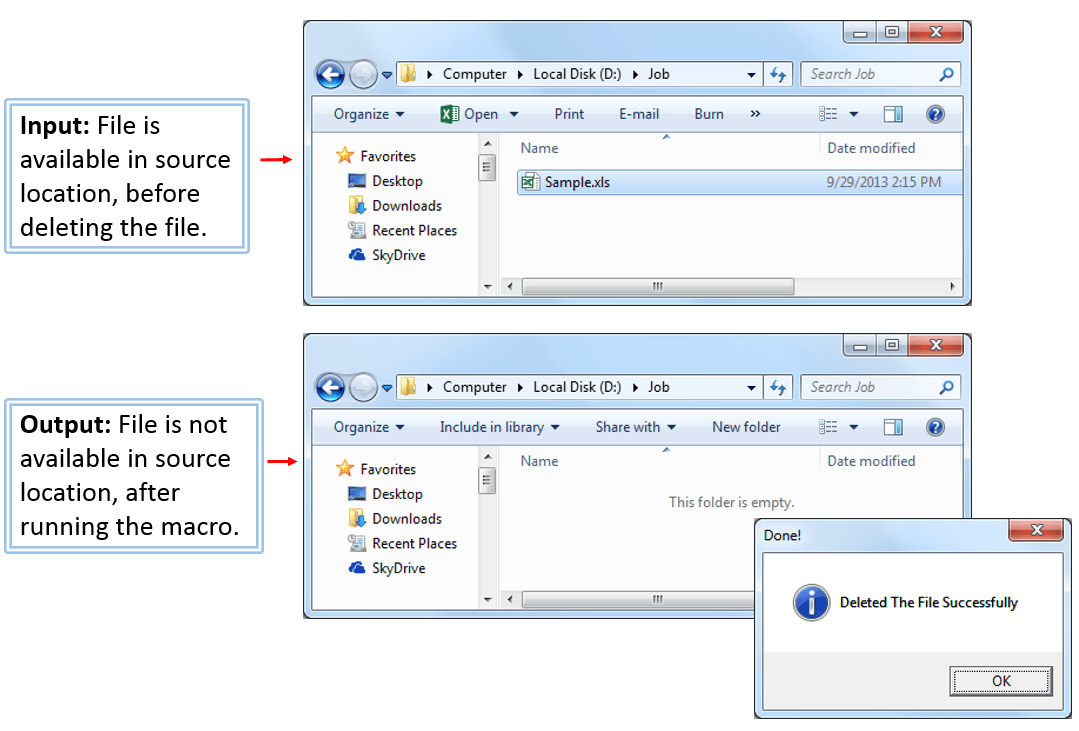
Code:
'In this Example I am deleting a File 'Sample.xls' which exists in the same location of the macro file
Sub sbDeletetingAFile()
Dim FSO
Dim sFile As String
'Source File Location
sFile = "D:Job" & "Sample.xls" 'You can change this Loaction
'Set Object
Set FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
'Check File Exists or Not
If FSO.FileExists(sFile) Then
'If file exists, It will delete the file from source location
FSO.DeleteFile sFile, True
MsgBox "Deleted The File Successfully", vbInformation, "Done!"
Else
'If file does not exists, It will display following message
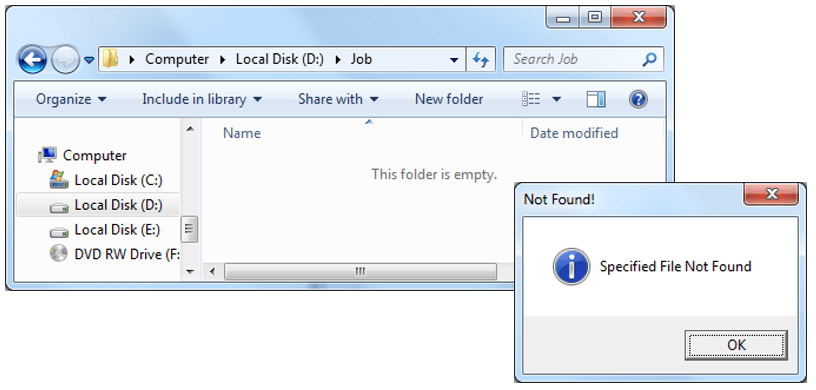
MsgBox "Specified File Not Found", vbInformation, "Not Found!"
End If
End Sub
Output:
Case 1: If file does not exists in the source location to delete, It will display following message.
Case 2: If file is exists in the source location, It will delete the file from source location. And it will display following message.
A Powerful & Multi-purpose Templates for project management. Now seamlessly manage your projects, tasks, meetings, presentations, teams, customers, stakeholders and time. This page describes all the amazing new features and options that come with our premium templates.
Save Up to 85% LIMITED TIME OFFER

All-in-One Pack
120+ Project Management Templates
Essential Pack
50+ Project Management Templates
Excel Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
PowerPoint Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
MS Word Pack
25+ Word PM Templates
Ultimate Project Management Template
Ultimate Resource Management Template
Project Portfolio Management Templates
Related Posts
VBA Reference
Effortlessly
Manage Your Projects
120+ Project Management Templates
Seamlessly manage your projects with our powerful & multi-purpose templates for project management.
120+ PM Templates Includes:
8 Comments
-
Fermin Bas
November 30, 2014 at 9:42 PM — ReplyI’m trying to delete a previous version of a file that my vba program is creating, but when the code that you describe in this page (I’m using it right as yours, only changing the name and location of file, of course) I get an error: “Run-time error ’70’: Permission denied”. I have to clarify something: I did use your code with another program that I wrote in vba excel 2010 where I used to save a file in Desktop because it was a temporary file, then it worked fine, this time I’m deleting a file in a certain address, not in Desktop and then is when I get the error message mentioned before.
Thanks in advance for your assistance
Fermin Bas
-
PNRao
December 4, 2014 at 6:38 PM — ReplyHi Fermin,
We can not delete the files from the web servers using this method. If you want to to delete the the file from your shared drives, make sure you entered correct server path and you have delete permissions.Thanks-PNRao!
-
Atle Olsen
May 7, 2015 at 1:49 PM — ReplyHi, what if I want to delete all files in a folder older then 30days, how is this possible?
-
Mahindra
June 30, 2015 at 4:08 AM — ReplyIs it possible to have a vba procedure/func to close any text based “.dat” type files if they are open from a given directory path.
I have another excel program that runs based on bunch of these dat files as input files from an input folder.
Before running excel program I want to make sure all my text based dat files are closed if they are open in a notepad for example.
There is no need to save these dat files if they are open in notepad before closing them programmatically. -
anjas
April 20, 2016 at 4:27 PM — ReplyThanks for your info, this success in my work… thansk very much
-
chethan
May 25, 2016 at 5:39 PM — ReplyI have created a macro which has scan and delete particular drive(ie D: drive). But i need to add one more drive for the below macro (ie P: drive). and i need to add IF CONDITION for checking if P or D drive is not available in system still i need to get the macro run and log should be saved. Kindly help me
Below is my macro for scanning only one drive
‘Force the explicit delcaration of variables
Option ExplicitSub ListFiles()
‘Set a reference to Microsoft Scripting Runtime by using
‘Tools > References in the Visual Basic Editor (Alt+F11)‘Declare the variables
Dim objFSO As Scripting.FileSystemObject
Dim objTopFolder As Scripting.Folder
Dim strTopFolderName As String‘Insert the headers for Columns A through F
Range(“A1”).Value = “File Name”
Range(“B1”).Value = “File Size”
Range(“C1”).Value = “File Type”
Range(“D1”).Value = “Date Created”
Range(“E1”).Value = “Date Last Accessed”
Range(“F1”).Value = “Date Last Modified”
Range(“G1”).Value = “File Deleted”
Range(“H1”).Value = “File Deletion/Scan Time”
Range(“I1”).Value = “File Path”‘Assign the top folder to a variable
strTopFolderName = “D:”‘Create an instance of the FileSystemObject
Set objFSO = CreateObject(“Scripting.FileSystemObject”)‘Get the top folder
Set objTopFolder = objFSO.GetFolder(strTopFolderName)‘Call the RecursiveFolder routine
Call RecursiveFolder(objTopFolder, True)‘Change the width of the columns to achieve the best fit
Columns.AutoFitEnd Sub
Sub RecursiveFolder(objFolder As Scripting.Folder, _
IncludeSubFolders As Boolean)‘Declare the variables
Dim objFile As Scripting.File
Dim objSubFolder As Scripting.Folder
Dim NextRow As Long‘Find the next available row
NextRow = Cells(Rows.Count, “A”).End(xlUp).Row + 1On Error GoTo Handler
‘Loop through each file in the folder
For Each objFile In objFolder.Files
Cells(NextRow, “A”).Value = objFile.Name
Cells(NextRow, “B”).Value = objFile.Size
Cells(NextRow, “C”).Value = objFile.Type
Cells(NextRow, “D”).Value = objFile.DateCreated
Cells(NextRow, “E”).Value = objFile.DateLastAccessed
Cells(NextRow, “F”).Value = objFile.DateLastModified
Cells(NextRow, “I”).Value = objFile.Path
‘If (DateDiff(“d”, objFile.DateLastModified, Now) > 1) And objFile.Type “Data Base File” And Left(objFile.Name, 2) “~$” ThenIf (DateDiff(“d”, objFile.DateLastModified, Now) > 7) And (objFile.Type = “Microsoft Word Document” Or _
objFile.Type = “Microsoft Word 97 – 2003 Document”) And _
Left(objFile.Name, 2) “~$” Then
‘Set FileSys = Nothing
‘Set objFolder = Nothing
‘Set objSubFolder = Nothing
‘Set objFile = Nothing
Kill (objFile.Path)
Cells(NextRow, “G”).Value = “Yes”
Cells(NextRow, “H”).Value = Format(Now, “yyyy-dd-mm hh:nn”)
Else
Cells(NextRow, “G”).Value = “No”
Cells(NextRow, “H”).Value = Format(Now, “yyyy-dd-mm hh:nn”)
End IfNextRow = NextRow + 1
Next objFile‘Loop through files in the subfolders
If IncludeSubFolders Then
For Each objSubFolder In objFolder.SubFolders
Call RecursiveFolder(objSubFolder, True)
Next objSubFolder
End IfExit Sub
Handler:
Resume Next
End Sub
‘In this Example I am Copying the File From “C:Temp” Folder to “D:Job” Folder
Sub sbCopyingAFile()‘Declare Variables
Dim FSO
Dim sFile As String
Dim sSFolder As String
Dim sDFolder As String‘This is Your File Name which you want to Copy
sFile = “Files_Deletion Macro.xlsm”‘Change to match the source folder path
sSFolder = “D:Desktop Scan and Deletion”‘Change to match the destination folder path
sDFolder = “Z:PMOSDMS Control RoomChethanA5901”‘Create Object
Set FSO = CreateObject(“Scripting.FileSystemObject”)‘Checking If File Is Located in the Source Folder
If Not FSO.FileExists(sSFolder & sFile) Then
MsgBox “Specified File Not Found”, vbInformation, “Not Found”
Else
FSO.CopyFile (sSFolder & sFile), sDFolder, True
End IfEnd Sub
Sub ClearSheet()
Sheet1.Cells.Clear
End Sub
-
Kamila
June 11, 2016 at 12:08 AM — ReplyI am getting this same issue and its very difficult to solve this problem without any third party app, i guess the best thing to do is to use a third party app like Long Path Tool. Just download it and use it to solve this issue. I hope this would help.Give it a try..
-
bobet
October 7, 2016 at 11:59 AM — Replyhow about running a .cmd file from execl macro.
Effectively Manage Your
Projects and Resources
ANALYSISTABS.COM provides free and premium project management tools, templates and dashboards for effectively managing the projects and analyzing the data.
We’re a crew of professionals expertise in Excel VBA, Business Analysis, Project Management. We’re Sharing our map to Project success with innovative tools, templates, tutorials and tips.
Project Management
Excel VBA
Download Free Excel 2007, 2010, 2013 Add-in for Creating Innovative Dashboards, Tools for Data Mining, Analysis, Visualization. Learn VBA for MS Excel, Word, PowerPoint, Access, Outlook to develop applications for retail, insurance, banking, finance, telecom, healthcare domains.
Page load link
Go to Top
The FileSystemObject VBA DeleteFile function deletes a specified file or files. The functions allows you to use wildcards (*) to delete multiple files matching a specific file path pattern which saves a lot of time for easy deletion scenarios.
VBA FileSystemObject Methods
- BuildPath
- CopyFile
- CopyFolder
- CreateFolder
- CreateTextFile
- DeleteFile
- DeleteFolder
- DriveExists
- FileExists
- FolderExists
- GetAbsolutePathName
- GetBaseName
- GetDrive
- GetDriveName
- GetExtensionName
- GetFile
- GetFileName
- GetFolder
- GetParentFolderName
- GetSpecialFolder
- GetTempName
- MoveFile
- MoveFolder
- OpenTextFile
VBA DeleteFile Syntax
fso.DeleteFile( filename, [ force ] )
- filename – The location names of file(s) to delete. You can use wildcards such as *.* to specify more than a single file matching the pattern.
- force – Optional. If True only read-only files are deleted. If False any files are deleted. False is default.
Examples
Set fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
'Delete file Hello.xlsx
fso.DeleteFile "c:SrcHello.xlsx"
'Delete all files with XLSX extension in C:Src folder
fso.DeleteFile "c:Src*.xlsx"
'Delete all files in specified folder
fso.DeleteFile "c:Src*.*"
'Delete all files in subfolders of C:Src
fso.DeleteFile "C:Src**.*"