Recent Examples on the Web
An average of four chargers will be installed per store, Reuters reports.
—
Emergency Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program benefits introduced during the pandemic expired at the end of February, leaving roughly 600,000 to 700,000 Marylanders who receive food assistance short an average of $82 per month.
—
The Hawks score an average of 118.4 points per game, 8.6 more points than the 109.8 the Heat allow to opponents.
—
Each battery can hold more than 3 MWh of energy—or about enough juice to power an average of 3,600 homes for one hour.
—
From 2009 to 2018, such labs reported an average of 98 incidents annually, ranging from minor problems with protective gear to exposures from accidental jabs with contaminated needles, according to CDC records.
—
Last week, the volcano registered an unprecedented average of 6,000 earthquakes per day, likely caused by magma moving through the main fault system, says Colombia’s Geological Service (CGS).
—
Esaad closed on eight units Oct. 27 and another eight on Nov. 11, paying nearly $7.7 million for the 16 units — or an average of nearly $480,000 each, a bankruptcy document show.
—
Separate research Nagata has worked on indicates gay youths use screens an average of nearly four hours a day more than straight kids.
—
Residents of Nantucket county were found to have a life expectancy of 83 years, almost 6 years longer than residents of Hampden County, which includes Springfield and Holyoke, who lived on average to 77.4, researchers found.
—
Senator Tina Smith, a Democrat from Minnesota, pointed out that, in her state, those sessions have lasted, on average, less than six minutes.
—
But women also earn less than men, on average—and women of color earn even less—and live longer.
—
In fact, the vast majority of results — 96%, on average — were eventually submitted to the database.
—
Black male offenders on average receive sentences 19.1% longer than white male offenders in similar cases, according to a 2017 study from the U.S. Sentencing Commission.
—
Since December, carwash workers have lost, on average, half of their usual pay due to the rains, Gonzalez said.
—
Another could force communities to allow at least 50 homes per acre on average to be built within a half-mile of many Long Island Railroad and Metro-North stations.
—
According to an analysis of fiscal year 2021, the attrition rate for entry-level federal employees under 30 was close to 12 percent on average, according to data from Fed Scope.
—
Senior Veronica Puckett is batting .609 (14-for-23) with 15 runs scored and sophomore Jaylene Mieres averages .667 (12-for-18) with 13 RBI for the Wolves.
—
The work hour regulations went into effect July 2011, noting residents could only work a maximum of 80 hours per week averaged over a four-week period, per ACGME.
—
The high-scoring Red Stockings averaged 42 runs a game.
—
The series became a global sensation, averaging 24 million viewers in the U.S., spawning several international spin-offs (and arguably the whole Real Housewives franchise), and returning the likes of Teri Hatcher and Felicity Huffman to the limelight.
—
On the year, Cryer averaged 15 points per game and two assists while shooting 41.5% from deep.
—
The 34-year-old has averaged 26.7 points and 7.3 rebounds (69.0% shooting) in three games with the Suns.
—
Last year, regular-season games averaged 3:03.
—
In 29 games this season, Winslow has averaged 6.8 points, 5.0 rebounds and 3.4 assists.
—
See More
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word ‘average.’ Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In ordinary language, an average is a single number taken as representative of a list of numbers, usually the sum of the numbers divided by how many numbers are in the list (the arithmetic mean). For example, the average of the numbers 2, 3, 4, 7, and 9 (summing to 25) is 5. Depending on the context, an average might be another statistic such as the median, or mode. For example, the average personal income is often given as the median—the number below which are 50% of personal incomes and above which are 50% of personal incomes—because the mean would be higher by including personal incomes from a few billionaires. For this reason, it is recommended to avoid using the word «average» when discussing measures of central tendency.
General properties[edit]
If all numbers in a list are the same number, then their average is also equal to this number. This property is shared by each of the many types of average.
Another universal property is monotonicity: if two lists of numbers A and B have the same length, and each entry of list A is at least as large as the corresponding entry on list B, then the average of list A is at least that of list B. Also, all averages satisfy linear homogeneity: if all numbers of a list are multiplied by the same positive number, then its average changes by the same factor.
In some types of average, the items in the list are assigned different weights before the average is determined. These include the weighted arithmetic mean, the weighted geometric mean and the weighted median. Also, for some types of moving average, the weight of an item depends on its position in the list. Most types of average, however, satisfy permutation-insensitivity: all items count equally in determining their average value and their positions in the list are irrelevant; the average of (1, 2, 3, 4, 6) is the same as that of (3, 2, 6, 4, 1).
Pythagorean means[edit]
The arithmetic mean, the geometric mean and the harmonic mean are known collectively as the Pythagorean means.
Statistical location[edit]
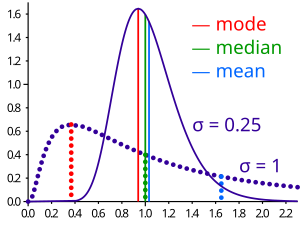
The mode, the median, and the mid-range are often used in addition to the mean as estimates of central tendency in descriptive statistics. These can all be seen as minimizing variation by some measure; see Central tendency § Solutions to variational problems.
| Type | Description | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arithmetic mean | Sum of values of a data set divided by number of values: 
|
(1+2+2+3+4+7+9) / 7 | 4 |
| Median | Middle value separating the greater and lesser halves of a data set | 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 7, 9 | 3 |
| Mode | Most frequent value in a data set | 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 7, 9 | 2 |
| Mid-range | The arithmetic mean of the highest and lowest values of a set | (1+9) / 2 | 5 |
Mode[edit]
The most frequently occurring number in a list is called the mode. For example, the mode of the list (1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4) is 3. It may happen that there are two or more numbers which occur equally often and more often than any other number. In this case there is no agreed definition of mode. Some authors say they are all modes and some say there is no mode.
Median[edit]
The median is the middle number of the group when they are ranked in order. (If there are an even number of numbers, the mean of the middle two is taken.)
Thus to find the median, order the list according to its elements’ magnitude and then repeatedly remove the pair consisting of the highest and lowest values until either one or two values are left. If exactly one value is left, it is the median; if two values, the median is the arithmetic mean of these two. This method takes the list 1, 7, 3, 13 and orders it to read 1, 3, 7, 13. Then the 1 and 13 are removed to obtain the list 3, 7. Since there are two elements in this remaining list, the median is their arithmetic mean, (3 + 7)/2 = 5.
Mid-range[edit]
The mid-range is the arithmetic mean of the highest and lowest values of a set.
Summary of types[edit]
| Name | Equation or description | As solution to optimization problem |
|---|---|---|
| Arithmetic mean |  |

|
| Median | The middle value that separates the higher half from the lower half of the data set | 
|
| Geometric median | A rotation invariant extension of the median for points in  |

|
| Tukey median | Another rotation invariant extension of the median for points in  —a point that maximizes the Tukey depth —a point that maximizes the Tukey depth |

|
| Mode | The most frequent value in the data set | 
|
| Geometric mean | ![{displaystyle {sqrt[{n}]{prod _{i=1}^{n}x_{i}}}={sqrt[{n}]{x_{1}cdot x_{2}dotsb x_{n}}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a3740b9924a63fcde06a3fd26d9691c082910d78) |

|
| Harmonic mean |  |

|
| Lehmer mean |  |
|
| Quadratic mean (or RMS) |
 |

|
| Cubic mean | ![{sqrt[ {3}]{{frac {1}{n}}sum _{{i=1}}^{{n}}x_{i}^{3}}}={sqrt[ {3}]{{frac {1}{n}}left(x_{1}^{3}+x_{2}^{3}+cdots +x_{n}^{3}right)}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/87ea526bc6b48f6abb52bc522d57c9fedacbaf90) |

|
| Generalized mean | ![sqrt[p]{frac{1}{n} cdot sum_{i=1}^n x_{i}^p}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b914d893b094e9e15a5681ef60069e9e5fac54ab) |

|
| Quasi-arithmetic mean |  |
 is monotonic is monotonic
|
| Weighted mean |  |

|
| Truncated mean | The arithmetic mean of data values after a certain number or proportion of the highest and lowest data values have been discarded | |
| Interquartile mean | A special case of the truncated mean, using the interquartile range. A special case of the inter-quantile truncated mean, which operates on quantiles (often deciles or percentiles) that are equidistant but on opposite sides of the median. | |
| Midrange |  |

|
| Winsorized mean | Similar to the truncated mean, but, rather than deleting the extreme values, they are set equal to the largest and smallest values that remain |
The table of mathematical symbols explains the symbols used below.
Miscellaneous types[edit]
Other more sophisticated averages are: trimean, trimedian, and normalized mean, with their generalizations.[1]
One can create one’s own average metric using the generalized f-mean:
where f is any invertible function. The harmonic mean is an example of this using f(x) = 1/x, and the geometric mean is another, using f(x) = log x.
However, this method for generating means is not general enough to capture all averages. A more general method[2][failed verification] for defining an average takes any function g(x1, x2, …, xn) of a list of arguments that is continuous, strictly increasing in each argument, and symmetric (invariant under permutation of the arguments). The average y is then the value that, when replacing each member of the list, results in the same function value: g(y, y, …, y) = g(x1, x2, …, xn). This most general definition still captures the important property of all averages that the average of a list of identical elements is that element itself. The function g(x1, x2, …, xn) = x1+x2+ ··· + xn provides the arithmetic mean. The function g(x1, x2, …, xn) = x1x2···xn (where the list elements are positive numbers) provides the geometric mean. The function g(x1, x2, …, xn) = (x1−1+x2−1+ ··· + xn−1)−1) (where the list elements are positive numbers) provides the harmonic mean.[2]
Average percentage return and CAGR[edit]
A type of average used in finance is the average percentage return. It is an example of a geometric mean. When the returns are annual, it is called the Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR). For example, if we are considering a period of two years, and the investment return in the first year is −10% and the return in the second year is +60%, then the average percentage return or CAGR, R, can be obtained by solving the equation: (1 − 10%) × (1 + 60%) = (1 − 0.1) × (1 + 0.6) = (1 + R) × (1 + R). The value of R that makes this equation true is 0.2, or 20%. This means that the total return over the 2-year period is the same as if there had been 20% growth each year. The order of the years makes no difference – the average percentage returns of +60% and −10% is the same result as that for −10% and +60%.
This method can be generalized to examples in which the periods are not equal. For example, consider a period of a half of a year for which the return is −23% and a period of two and a half years for which the return is +13%. The average percentage return for the combined period is the single year return, R, that is the solution of the following equation: (1 − 0.23)0.5 × (1 + 0.13)2.5 = (1 + R)0.5+2.5, giving an average return R of 0.0600 or 6.00%.
Moving average[edit]
Given a time series, such as daily stock market prices or yearly temperatures, people often want to create a smoother series.[3] This helps to show underlying trends or perhaps periodic behavior. An easy way to do this is the moving average: one chooses a number n and creates a new series by taking the arithmetic mean of the first n values, then moving forward one place by dropping the oldest value and introducing a new value at the other end of the list, and so on. This is the simplest form of moving average. More complicated forms involve using a weighted average. The weighting can be used to enhance or suppress various periodic behavior and there is very extensive analysis of what weightings to use in the literature on filtering. In digital signal processing the term «moving average» is used even when the sum of the weights is not 1.0 (so the output series is a scaled version of the averages).[4] The reason for this is that the analyst is usually interested only in the trend or the periodic behavior.
History[edit]
Origin[edit]
The first recorded time that the arithmetic mean was extended from 2 to n cases for the use of estimation was in the sixteenth century. From the late sixteenth century onwards, it gradually became a common method to use for reducing errors of measurement in various areas.[5][6] At the time, astronomers wanted to know a real value from noisy measurement, such as the position of a planet or the diameter of the moon. Using the mean of several measured values, scientists assumed that the errors add up to a relatively small number when compared to the total of all measured values. The method of taking the mean for reducing observation errors was indeed mainly developed in astronomy.[5][7] A possible precursor to the arithmetic mean is the mid-range (the mean of the two extreme values), used for example in Arabian astronomy of the ninth to eleventh centuries, but also in metallurgy and navigation.[6]
However, there are various older vague references to the use of the arithmetic mean (which are not as clear, but might reasonably have to do with our modern definition of the mean). In a text from the 4th century, it was written that (text in square brackets is a possible missing text that might clarify the meaning):[8]
- In the first place, we must set out in a row the sequence of numbers from the monad up to nine: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9. Then we must add up the amount of all of them together, and since the row contains nine terms, we must look for the ninth part of the total to see if it is already naturally present among the numbers in the row; and we will find that the property of being [one] ninth [of the sum] only belongs to the [arithmetic] mean itself…
Even older potential references exist. There are records that from about 700 BC, merchants and shippers agreed that damage to the cargo and ship (their «contribution» in case of damage by the sea) should be shared equally among themselves.[7] This might have been calculated using the average, although there seem to be no direct record of the calculation.
Etymology[edit]
The root is found in Arabic as عوار ʿawār, a defect, or anything defective or damaged, including partially spoiled merchandise; and عواري ʿawārī (also عوارة ʿawāra) = «of or relating to ʿawār, a state of partial damage».[9] Within the Western languages the word’s history begins in medieval sea-commerce on the Mediterranean. 12th and 13th century Genoa Latin avaria meant «damage, loss and non-normal expenses arising in connection with a merchant sea voyage»; and the same meaning for avaria is in Marseille in 1210, Barcelona in 1258 and Florence in the late 13th.[10] 15th-century French avarie had the same meaning, and it begot English «averay» (1491) and English «average» (1502) with the same meaning. Today, Italian avaria, Catalan avaria and French avarie still have the primary meaning of «damage». The huge transformation of the meaning in English began with the practice in later medieval and early modern Western merchant-marine law contracts under which if the ship met a bad storm and some of the goods had to be thrown overboard to make the ship lighter and safer, then all merchants whose goods were on the ship were to suffer proportionately (and not whoever’s goods were thrown overboard); and more generally there was to be proportionate distribution of any avaria. From there the word was adopted by British insurers, creditors, and merchants for talking about their losses as being spread across their whole portfolio of assets and having a mean proportion. Today’s meaning developed out of that, and started in the mid-18th century, and started in English.[10] [1].
Marine damage is either particular average, which is borne only by the owner of the damaged property, or general average, where the owner can claim a proportional contribution from all the parties to the marine venture. The type of calculations used in adjusting general average gave rise to the use of «average» to mean «arithmetic mean».
A second English usage, documented as early as 1674 and sometimes spelled «averish», is as the residue and second growth of field crops, which were considered suited to consumption by draught animals («avers»).[11]
There is earlier (from at least the 11th century), unrelated use of the word. It appears to be an old legal term for a tenant’s day labour obligation to a sheriff, probably anglicised from «avera» found in the English Domesday Book (1085).
The Oxford English Dictionary, however, says that derivations from German hafen haven, and Arabic ʿawâr loss, damage, have been «quite disposed of» and the word has a Romance origin.[12]
Averages as a rhetorical tool[edit]
Due to the aforementioned colloquial nature of the term «average», the term can be used to obfuscate the true meaning of data and suggest varying answers to questions based on the averaging method (most frequently arithmetic mean, median, or mode) used. In his article «Framed for Lying: Statistics as In/Artistic Proof», University of Pittsburgh faculty member Daniel Libertz comments that statistical information is frequently dismissed from rhetorical arguments for this reason.[13] However, due to their persuasive power, averages and other statistical values should not be discarded completely, but instead used and interpreted with caution. Libertz invites us to engage critically not only with statistical information such as averages, but also with the language used to describe the data and its uses, saying: «If statistics rely on interpretation, rhetors should invite their audience to interpret rather than insist on an interpretation.»[13] In many cases, data and specific calculations are provided to help facilitate this audience-based interpretation.
See also[edit]
- Average absolute deviation
- Law of averages
- Expected value
- Central limit theorem
- Population mean
- Sample mean
References[edit]
- ^ Merigo, Jose M.; Cananovas, Montserrat (2009). «The Generalized Hybrid Averaging Operator and its Application in Decision Making». Journal of Quantitative Methods for Economics and Business Administration. 9: 69–84. ISSN 1886-516X.[permanent dead link]
- ^ a b Bibby, John (1974). «Axiomatisations of the average and a further generalisation of monotonic sequences». Glasgow Mathematical Journal. 15: 63–65. doi:10.1017/s0017089500002135.
- ^ Box, George E.P.; Jenkins, Gwilym M. (1976). Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control (revised ed.). Holden-Day. ISBN 0816211043.
- ^ Haykin, Simon (1986). Adaptive Filter Theory. Prentice-Hall. ISBN 0130040525.
- ^ a b Plackett, R. L. (1958). «Studies in the History of Probability and Statistics: VII. The Principle of the Arithmetic Mean». Biometrika. 45 (1/2): 130–135. doi:10.2307/2333051. JSTOR 2333051.
- ^ a b Eisenhart, Churchill. «The development of the concept of the best mean of a set of measurements from antiquity to the present day.» Unpublished presidential address, American Statistical Association, 131st Annual Meeting, Fort Collins, Colorado. 1971.
- ^ a b Bakker, Arthur. «The early history of average values and implications for education.» Journal of Statistics Education 11.1 (2003): 17-26.
- ^ «Waterfield, Robin. «The theology of arithmetic.» On the Mystical, mathematical and Cosmological Symbolism of the First Ten Number (1988). page 70″ (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2018-11-27.
- ^ Medieval Arabic had عور ʿawr meaning «blind in one eye» and عوار ʿawār meant «any defect, or anything defective or damaged». Some medieval Arabic dictionaries are at Baheth.info Archived 2013-10-29 at the Wayback Machine, and some translation to English of what’s in the medieval Arabic dictionaries is in Lane’s Arabic-English Lexicon, pages 2193 and 2195. The medieval dictionaries do not list the word-form عوارية ʿawārīa. ʿAwārīa can be naturally formed in Arabic grammar to refer to things that have ʿawār, but in practice in medieval Arabic texts ʿawārīa is a rarity or non-existent, while the forms عواري ʿawārī and عوارة ʿawāra are frequently used when referring to things that have ʿawār or damage – this can be seen in the searchable collection of medieval texts at AlWaraq.net (book links are clickable on righthand side).
- ^ a b The Arabic origin of avaria was first reported by Reinhart Dozy in the 19th century. Dozy’s original summary is in his 1869 book Glossaire. Summary information about the word’s early records in Italian-Latin, Italian, Catalan, and French is at avarie @ CNRTL.fr Archived 2019-01-06 at the Wayback Machine. The seaport of Genoa is the location of the earliest-known record in European languages, year 1157. A set of medieval Latin records of avaria at Genoa is in the downloadable lexicon Vocabolario Ligure, by Sergio Aprosio, year 2001, avaria in Volume 1 pages 115-116. Many more records in medieval Latin at Genoa are at StoriaPatriaGenova.it, usually in the plurals avariis and avarias. At the port of Marseille in the 1st half of the 13th century notarized commercial contracts have dozens of instances of Latin avariis (ablative plural of avaria), as published in Blancard year 1884. Some information about the English word over the centuries is at NED (year 1888). See also the definition of English «average» in English dictionaries published in the early 18th century, i.e., in the time period just before the big transformation of the meaning: Kersey-Phillips’ dictionary (1706), Blount’s dictionary (1707 edition), Hatton’s dictionary (1712), Bailey’s dictionary (1726), Martin’s dictionary (1749). Some complexities surrounding the English word’s history are discussed in Hensleigh Wedgwood year 1882 page 11 and Walter Skeat year 1888 page 781. Today there is consensus that: (#1) today’s English «average» descends from medieval Italian avaria, Catalan avaria, and (#2) among the Latins the word avaria started in the 12th century and it started as a term of Mediterranean sea-commerce, and (#3) there is no root for avaria to be found in Latin, and (#4) a substantial number of Arabic words entered Italian, Catalan and Provençal in the 12th and 13th centuries starting as terms of Mediterranean sea-commerce, and (#5) the Arabic ʿawār | ʿawārī is phonetically a good match for avaria, as conversion of w to v was regular in Latin and Italian, and -ia is a suffix in Italian, and the Western word’s earliest records are in Italian-speaking locales (writing in Latin). And most commentators agree that (#6) the Arabic ʿawār | ʿawārī = «damage | relating to damage» is semantically a good match for avaria = «damage or damage expenses». A minority of commentators have been dubious about this on the grounds that the early records of Italian-Latin avaria have, in some cases, a meaning of «an expense» in a more general sense – see TLIO (in Italian). The majority view is that the meaning of «an expense» was an expansion from «damage and damage expense», and the chronological order of the meanings in the records supports this view, and the broad meaning «an expense» was never the most commonly used meaning. On the basis of the above points, the inferential step is made that the Latinate word came or probably came from the Arabic word.
- ^ Ray, John (1674). A Collection of English Words Not Generally Used. London: H. Bruges. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- ^ «average, n.2». OED Online. September 2019. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/13681 (accessed September 05, 2019).
- ^ a b Libertz, Daniel (2018-12-31). «Framed for Lying: Statistics as In/Artistic Proof». Res Rhetorica. 5 (4). doi:10.29107/rr2018.4.1. ISSN 2392-3113.
External links[edit]
Look up average in Wiktionary, the free dictionary.
- Median as a weighted arithmetic mean of all Sample Observations
- Calculations and comparison between arithmetic and geometric mean of two values
- Top Definitions
- Quiz
- Related Content
- Average Vs. Mean Vs. Median Vs. Mode
- Examples
- British
- Scientific
- Cultural
This shows grade level based on the word’s complexity.
[ av-er-ij, av-rij ]
/ ˈæv ər ɪdʒ, ˈæv rɪdʒ /
This shows grade level based on the word’s complexity.
noun
a quantity, rating, or the like that represents or approximates an arithmetic mean: Her golf average is in the 90s. My average in science has gone from B to C this semester.
a typical amount, rate, degree, etc.; norm.
Mathematics. a quantity intermediate to a set of quantities.
Commerce.
- a charge paid by the master of a ship for such services as pilotage or towage.
- an expense, partial loss, or damage to a ship or cargo.
- the incidence of such an expense or loss to the owners or their insurers.
- an equitable apportionment among all the interested parties of such an expense or loss.Compare general average, particular average.
adjective
of or relating to an average; estimated by average; forming an average: The average rainfall there is 180 inches.
typical; common; ordinary: The average secretary couldn’t handle such a workload. His grades were nothing special, only average.
verb (used with object), av·er·aged, av·er·ag·ing.
to find an average value for (a variable quantity); reduce to a mean: We averaged the price of milk in five neighborhood stores.
(of a variable quantity) to have as its arithmetic mean: Wheat averages 56 pounds to a bushel.
to do or have on the average: He averages seven hours of sleep a night.
verb (used without object), av·er·aged, av·er·ag·ing.
to have or show an average: to average as expected.
Verb Phrases
average down, to purchase more of a security or commodity at a lower price to reduce the average cost of one’s holdings.
average out,
- to come out of a security or commodity transaction with a profit or without a loss.
- to reach an average or other figure: His taxes should average out to about a fifth of his income.
average up, to purchase more of a security or commodity at a higher price to take advantage of a contemplated further rise in prices.
QUIZ
CAN YOU ANSWER THESE COMMON GRAMMAR DEBATES?
There are grammar debates that never die; and the ones highlighted in the questions in this quiz are sure to rile everyone up once again. Do you know how to answer the questions that cause some of the greatest grammar debates?
Which sentence is correct?
Idioms about average
on the / an average, usually; typically: She can read 50 pages an hour, on the average.
Origin of average
1485–95; earlier averay charge on goods shipped, originally duty (<Middle French avarie<Old Italian avaria<Arabic ʿawārīyah damaged merchandise), with -age replacing -ay
OTHER WORDS FROM average
av·er·age·a·ble, adjectiveav·er·age·ly, adverbav·er·age·ness, nounsub·av·er·age, adjective
sub·av·er·age·ly, adverbsu·per·av·er·age, adjectivesu·per·av·er·age·ness, nounun·av·er·aged, adjectiveun·der·av·er·age, adjectivewell-av·er·aged, adjective
Words nearby average
Aventine, aventurine, avenue, Avenzoar, aver, average, average adjuster, average deviation, average joe, average life, average revenue
Dictionary.com Unabridged
Based on the Random House Unabridged Dictionary, © Random House, Inc. 2023
AVERAGE VS. MEAN VS. MEDIAN VS. MODE
What’s the difference between average, mean, median, and mode?
In the context of mathematics and statistics, the word average refers to what’s more formally called the mean, which is the sum of a set of values divided by the number of values. In contrast, the median is the middle number in a set of values when those values are arranged from smallest to largest, while the mode of a set of values is the most frequently repeated value in the set.
The word average is of course also very commonly used in more general ways. In math, though, it’s helpful to use more specific terms when determining the most representative or common value in a set of numbers.
To illustrate the difference, let’s look at an example set of seven values: 2, 3, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9.
To get the mean of this set, you’d add up all the values (2+3+3+4+6+8+9=35) and then divide that total by the number of values (7), resulting in a mean of 5. This is what most people are referring to when they refer to the average of some set of numbers.
To find the median, you have to find the one that’s sequentially in the middle. In a set of seven numbers arranged in increasing value, the median is the fourth number (since there are three before and three after). In this set (2, 3, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9), the median is 4. When a set has an even number of values, the median is the mean of the two middle values.
The mode is simply the value that shows up the most. In the example set, the mode is 3, since it occurs twice and all the other values occur only once.
Want to learn more? Read the full breakdown of the difference between average, mean, median, and mode.
Quiz yourself on average vs. mean vs. median vs. mode!
Should average, mean, median, or mode be used in the following sentence?
The most frequently repeated test score is 80, so it’s the _____ of the set.
Words related to average
mediocre, moderate, ordinary, regular, median, standard, boilerplate, common, commonplace, fair, familiar, garden, general, humdrum, intermediate, mainstream, medium, middling, nowhere, plastic
How to use average in a sentence
-
That is roughly in line with a Post average of recent polls from the state that put Biden’s advantage at seven points.
-
FiveThirtyEight’s average of state polls at the end of the 2016 race gave Clinton a five-point lead in Wisconsin and an eight-point lead in Minnesota.
-
Since the lockout of 2004-05, five cup winners have averaged fewer goals per game.
-
The Wisconsin poll is consistent with other recent polls in the state, with The Post’s average showing Biden’s margin at seven points, narrower than in midsummer but not much different from what it was immediately after the GOP convention.
-
That is a somewhat larger margin than a Washington Post average of recent polls in the state, which shows Biden’s lead to be seven percentage points.
-
Well over a thousand holes in, I average less than four strokes per hole.
-
On average, the vaccine has an efficacy of about 60 percent.
-
Average age ranges from 45 to 65, with her youngest client at 18 and the oldest in her 80s.
-
Ramos was 38—nearly two decades older than the average recruit.
-
All because Murthy believes that gun violence, which kills an average of 86 Americans every day, is a public health issue.
-
I do not think the average number of passengers on a corresponding route in our country could be so few as twenty.
-
Though the average speaker is generally limited by one type of voice, which he varies somewhat, it is not often disguised.
-
I should judge that a peck of corn is about the average product of a day’s work through all this region.
-
The average citizen of three generations ago was probably not aware that he was an extreme individualist.
-
He was a pretty bright sort, that same Goodell, quick-witted, nimble of tongue above the average Englishman.
British Dictionary definitions for average
noun
the typical or normal amount, quality, degree, etcabove average in intelligence
Also called: arithmetic mean the result obtained by adding the numbers or quantities in a set and dividing the total by the number of members in the setthe average of 3, 4, and 8 is 5
(of a continuously variable ratio, such as speed) the quotient of the differences between the initial and final values of the two quantities that make up the ratiohis average over the journey was 30 miles per hour
maritime law
- a loss incurred or damage suffered by a ship or its cargo at sea
- the equitable apportionment of such loss among the interested parties
(often plural) stock exchange a simple or weighted average of the prices of a selected group of securities computed in order to facilitate market comparisons
on average, on the average or on an average usually; typicallyon average, he goes twice a week
adjective
usual or typical
mediocre or inferiorhis performance was only average
constituting a numerical averagethe average age; an average speed
approximately typical of a range of valuesthe average contents of a matchbox
verb
(tr) to obtain or estimate a numerical average of
(tr) to assess the general quality of
(tr) to perform or receive a typical number ofto average eight hours’ work a day
(tr) to divide up proportionatelythey averaged the profits among the staff
(tr) to amount to or be on averagethe children averaged 15 years of age
(intr) stock exchange to purchase additional securities in a holding whose price has fallen (average down) or risen (average up) in anticipation of a speculative profit after further increases in price
Derived forms of average
averagely, adverbaverageness, noun
Word Origin for average
C15 averay loss arising from damage to ships or cargoes (shared equitably among all concerned, hence the modern sense), from Old Italian avaria, ultimately from Arabic awār damage, blemish
Collins English Dictionary — Complete & Unabridged 2012 Digital Edition
© William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1979, 1986 © HarperCollins
Publishers 1998, 2000, 2003, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2012
Scientific definitions for average
A number, especially the arithmetic mean, that is derived from and considered typical or representative of a set of numbers. Compare arithmetic mean median mode.
The American Heritage® Science Dictionary
Copyright © 2011. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Cultural definitions for average
A single number that represents a set of numbers. Means, medians, and modes are kinds of averages; usually, however, the term average refers to a mean.
The New Dictionary of Cultural Literacy, Third Edition
Copyright © 2005 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
средний, обычный, среднее число, составлять
прилагательное ↓
- средний
average temperature — средняя температура
average rainfall — средняя норма выпадения осадков
average life — средняя продолжительность жизни
- обычный, нормальный, средний
average man [ability] — средний человек [-ие способности]
average reader — рядовой /широкий/ читатель
a man of average height — человек среднего роста
- посредственный
there was nothing special about his performance, it was only average — в его исполнении не было ничего особенного, оно было весьма средним
boys of average intelligence — ребята, не хватающие звёзд с неба /средних способностей/
существительное ↓
- среднее (число)
above [below] the average — выше [ниже] среднего
his work is about /up to/ the average — его работа не хуже и не лучше, чем у других
on an /the/ average — в среднем
to translate on an average five pages a day — переводить в среднем пять страниц в день
to ascertain /to determine, to obtain/ the average — выводить среднее
- мат. среднее арифметическое
- авария (убытки, причинённые судну, грузу и фрахту)
general [particular, petty] average — общая [частная, малая] авария
- распределение убытков от аварии между владельцами груза, судна
average adjuster — диспашер
average statement — диспаша
глагол ↓
- составлять, достигать, равняться в среднем
his wages average 60 pounds — его заработок составляет в среднем 60 фунтов
they averaged 100 miles a day — они делали в среднем 100 миль в день
- мат. выводить среднее значение, усреднять
- бирж. последовательно скупать или продавать акции по мере изменения их курса
to average down [up] — скупать акции по мере снижения [повышения] их курса
- страх. распределять убыток между акционерами
Мои примеры
Словосочетания
of average height for his age — среднего роста для своего возраста 
a man of average build — человек среднего телосложения 
below the average — ниже среднего 
daily average — среднесуточный 
average earnings — средняя прибыль 
to adjust the average — составлять диспашу 
average output — средняя производительность 
at the average close rate — по среднему заключительному курсу 
above average stature — выше среднего роста 
average attendance — средняя посещаемость 
average woman — обычная женщина 
average cost — средняя стоимость 
Примеры с переводом
She was an average student. 
Она была обычной студенткой.
He is about average in height. 
Роста он примерно среднего.
Last winter was colder than average. 
Прошлая зима была холоднее обычной.
On average, women live longer than men. 
В среднем, женщины живут дольше, чем мужчины.
Smart children talk earlier than the average. 
Одарённые дети начинают разговаривать раньше, чем среднестатистические.
They view on average for thirteen hours a week. 
Они смотрят телевизор в среднем тринадцать часов в неделю.
In an average week I drive about 250 miles. 
В среднем за неделю я проезжаю около двухсот пятидесяти миль.
ещё 23 примера свернуть
Примеры, ожидающие перевода
Shares had a bumpy ride yesterday, falling by an average of 15%. 
The December figures brought the annual average for 2001 up to 10.6 per cent. 
Для того чтобы добавить вариант перевода, кликните по иконке ☰, напротив примера.
Фразовые глаголы
average out — вычислять среднюю величину, составить среднюю величину
Возможные однокоренные слова
averaged — составлять, равняться в среднем, выводить среднее число
Формы слова
verb
I/you/we/they: average
he/she/it: averages
ing ф. (present participle): averaging
2-я ф. (past tense): averaged
3-я ф. (past participle): averaged
noun
ед. ч.(singular): average
мн. ч.(plural): averages
av·er·age
(ăv′ər-ĭj, ăv′rĭj)
n.
1. Mathematics
a. A number that typifies a set of numbers of which it is a function.
2.
a. An intermediate level or degree: near the average in size.
b. The usual or ordinary kind or quality: Although the wines vary, the average is quite good.
3. Sports The ratio of a team’s or player’s successful performances such as wins, hits, or goals, divided by total opportunities for successful performance, such as games, times at bat, or shots: finished the season with a .500 average; a batting average of .274.
4. Law
a. The loss of a ship or cargo, caused by damage at sea.
b. The incurrence of damage or loss of a ship or cargo at sea.
c. The equitable distribution of such a loss among concerned parties.
d. A charge incurred through such a loss.
5. Nautical Small expenses or charges that are usually paid by the master of a ship.
adj.
1. Mathematics Of, relating to, or constituting an average.
2. Being intermediate between extremes, as on a scale: a movie of average length; a player of average ability.
3. Usual or ordinary in kind or character: a poll of average people; average eyesight.
4. Assessed in accordance with the law of averages.
v. av·er·aged, av·er·ag·ing, av·er·ag·es
v.tr.
1. Mathematics To calculate the average of: average a set of numbers.
2. To do or have an average of: averaged three hours of work a day.
3. To distribute proportionately: average one’s income over four years so as to minimize the tax rate.
v.intr.
To be or amount to an average: Some sparrows are six inches long, but they average smaller. Our expenses averaged out to 45 dollars per day.
Phrasal Verbs:
average down
To purchase shares of the same security at successively lower prices in order to reduce the average price of one’s position.
average up
To purchase shares of the same security at successively higher prices in order to achieve a larger position at an average price that is lower than the current market value.
[Early Modern English, damage to a ship or its cargo, equitable distribution of the expenses from such damage, average, from Middle English, charge above the cost of freight, from Old French avarie, from Old Italian avaria, duty, from Arabic ‘awārīya, damaged goods, from ‘awār, blemish, from ‘awira, to be damaged; see ʕwr in Semitic roots.]
av′er·age·ly adv.
av′er·age·ness n.
Synonyms: average, medium, mediocre, middling, fair1, acceptable, indifferent, tolerable
These adjectives indicate a middle position on a scale of evaluation. Average and medium apply to what is midway between extremes and imply both sufficiency and lack of distinction: a novel of average merit; a digital recording of medium quality.
Mediocre and middling stress the undistinguished aspect of what is average: «The caliber of the students … has gone from mediocre to above average» (Judy Pasternak).«Every writer creates weak, middling and strong work» (Frank Conroy).
What is fair or acceptable is satisfactory or moderately good but has room for improvement: a fair chance of winning; an acceptable grade on the test.
Indifferent means neither good nor bad and suggests a detached or resigned acceptance of such a status: «Burningham was an indifferent student at every school he attended … and he preferred to be out of doors» (Andrea Cleghorn).
Something tolerable is good enough under the circumstances, but barely: «Tennyson … suffered … from illness fears, particularly of going blind, though he lived into his eighties with tolerable eyesight» (Carla Cantor).
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
average
(ˈævərɪdʒ; ˈævrɪdʒ)
n
1. the typical or normal amount, quality, degree, etc: above average in intelligence.
2. (Mathematics) Also called: arithmetic mean the result obtained by adding the numbers or quantities in a set and dividing the total by the number of members in the set: the average of 3, 4, and 8 is 5.
3. (Mathematics) (of a continuously variable ratio, such as speed) the quotient of the differences between the initial and final values of the two quantities that make up the ratio: his average over the journey was 30 miles per hour.
4. (Law) maritime law
a. a loss incurred or damage suffered by a ship or its cargo at sea
b. the equitable apportionment of such loss among the interested parties
5. (Stock Exchange) (often plural) stock exchange a simple or weighted average of the prices of a selected group of securities computed in order to facilitate market comparisons
6. on average on the average on an average usually; typically: on average, he goes twice a week.
adj
7. usual or typical
8. mediocre or inferior: his performance was only average.
9. constituting a numerical average: the average age; an average speed.
10. approximately typical of a range of values: the average contents of a matchbox.
vb
11. (tr) to obtain or estimate a numerical average of
12. (tr) to assess the general quality of
13. (tr) to perform or receive a typical number of: to average eight hours’ work a day.
14. (tr) to divide up proportionately: they averaged the profits among the staff.
15. (tr) to amount to or be on average: the children averaged 15 years of age.
16. (Stock Exchange) (intr) stock exchange to purchase additional securities in a holding whose price has fallen (average down) or risen (average up) in anticipation of a speculative profit after further increases in price
[C15 averay loss arising from damage to ships or cargoes (shared equitably among all concerned, hence the modern sense), from Old Italian avaria, ultimately from Arabic awār damage, blemish]
ˈaveragely adv
ˈaverageness n
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
av•er•age
(ˈæv ər ɪdʒ, ˈæv rɪdʒ)
n., adj., v. -aged, -ag•ing. n.
1.
a. a quantity, rating, or the like that represents or approximates an arithmetic mean: a golf average in the 90’s. Compare grade point average.
c. a number or value intermediate to a set of numbers or values.
2. a typical or usual amount, rate, degree, level, etc.; norm.
adj.
3. of, pertaining to, or forming an average; estimated by average: the average rainfall.
4. typical; common; ordinary: the average person.
v.t.
5. to find an average value for (a variable quantity); reduce to a mean.
6. (of a variable quantity) to have as an arithmetic mean: Wheat averages 56 pounds to a bushel.
7. to do or have on the average: to average seven hours of sleep a night.
v.i.
8. to have or show an average.
Idioms:
on the or an average, usually; typically.
[1485–95; late Middle English averay charge on goods shipped, orig. duty (< Middle French avarie < early Italian avaria < Arabic ‘awārīyah damaged merchandise), with -age replacing -ay]
av′er•age•a•ble, adj.
av′er•age•ly, adv.
av′er•age•ness, n.
Random House Kernerman Webster’s College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
av·er·age
(ăv′ər-ĭj)
A number, especially the arithmetic mean, that is derived from and considered typical or representative of a set of numbers. Compare arithmetic mean, median, mode.
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
average
Past participle: averaged
Gerund: averaging
| Imperative |
|---|
| average |
| average |
| Present |
|---|
| I average |
| you average |
| he/she/it averages |
| we average |
| you average |
| they average |
| Preterite |
|---|
| I averaged |
| you averaged |
| he/she/it averaged |
| we averaged |
| you averaged |
| they averaged |
| Present Continuous |
|---|
| I am averaging |
| you are averaging |
| he/she/it is averaging |
| we are averaging |
| you are averaging |
| they are averaging |
| Present Perfect |
|---|
| I have averaged |
| you have averaged |
| he/she/it has averaged |
| we have averaged |
| you have averaged |
| they have averaged |
| Past Continuous |
|---|
| I was averaging |
| you were averaging |
| he/she/it was averaging |
| we were averaging |
| you were averaging |
| they were averaging |
| Past Perfect |
|---|
| I had averaged |
| you had averaged |
| he/she/it had averaged |
| we had averaged |
| you had averaged |
| they had averaged |
| Future |
|---|
| I will average |
| you will average |
| he/she/it will average |
| we will average |
| you will average |
| they will average |
| Future Perfect |
|---|
| I will have averaged |
| you will have averaged |
| he/she/it will have averaged |
| we will have averaged |
| you will have averaged |
| they will have averaged |
| Future Continuous |
|---|
| I will be averaging |
| you will be averaging |
| he/she/it will be averaging |
| we will be averaging |
| you will be averaging |
| they will be averaging |
| Present Perfect Continuous |
|---|
| I have been averaging |
| you have been averaging |
| he/she/it has been averaging |
| we have been averaging |
| you have been averaging |
| they have been averaging |
| Future Perfect Continuous |
|---|
| I will have been averaging |
| you will have been averaging |
| he/she/it will have been averaging |
| we will have been averaging |
| you will have been averaging |
| they will have been averaging |
| Past Perfect Continuous |
|---|
| I had been averaging |
| you had been averaging |
| he/she/it had been averaging |
| we had been averaging |
| you had been averaging |
| they had been averaging |
| Conditional |
|---|
| I would average |
| you would average |
| he/she/it would average |
| we would average |
| you would average |
| they would average |
| Past Conditional |
|---|
| I would have averaged |
| you would have averaged |
| he/she/it would have averaged |
| we would have averaged |
| you would have averaged |
| they would have averaged |
Collins English Verb Tables © HarperCollins Publishers 2011
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
| Noun | 1. | average — a statistic describing the location of a distribution; «it set the norm for American homes»
norm statistics — a branch of applied mathematics concerned with the collection and interpretation of quantitative data and the use of probability theory to estimate population parameters statistic — a datum that can be represented numerically age norm — the average age at which particular performances are expected to appear modal value, mode — the most frequent value of a random variable median, median value — the value below which 50% of the cases fall mean, mean value — an average of n numbers computed by adding some function of the numbers and dividing by some function of n |
| 2. | average — (sports) the ratio of successful performances to opportunities
athletics, sport — an active diversion requiring physical exertion and competition batting average, hitting average — (baseball) a measure of a batter’s performance; the number of base hits divided by the number of official times at bat; «Ted Williams once had a batting average above .400» fielding average — (baseball) a measure of a fielder’s performance; the number of assists and putouts divided by the number of chances ratio — the relative magnitudes of two quantities (usually expressed as a quotient) |
|
| 3. | average — an intermediate scale value regarded as normal or usual; «he is about average in height»; «the snowfall this month is below average»
scale value — a value on some scale of measurement |
|
| Verb | 1. | average — amount to or come to an average, without loss or gain; «The number of hours I work per work averages out to 40»
average out number, total, amount, add up, come — add up in number or quantity; «The bills amounted to $2,000»; «The bill came to $2,000» |
| 2. | average — achieve or reach on average; «He averaged a C»
achieve, attain, accomplish, reach — to gain with effort; «she achieved her goal despite setbacks» |
|
| 3. |  average — compute the average of average — compute the average of
average out arithmetic — the branch of pure mathematics dealing with the theory of numerical calculations compute, calculate, cipher, cypher, figure, reckon, work out — make a mathematical calculation or computation |
|
| Adj. | 1. |  average — approximating the statistical norm or average or expected value; «the average income in New England is below that of the nation»; «of average height for his age»; «the mean annual rainfall» average — approximating the statistical norm or average or expected value; «the average income in New England is below that of the nation»; «of average height for his age»; «the mean annual rainfall»
mean statistics — a branch of applied mathematics concerned with the collection and interpretation of quantitative data and the use of probability theory to estimate population parameters normal — conforming with or constituting a norm or standard or level or type or social norm; not abnormal; «serve wine at normal room temperature»; «normal diplomatic relations»; «normal working hours»; «normal word order»; «normal curiosity»; «the normal course of events» |
| 2. | average — lacking special distinction, rank, or status; commonly encountered; «average people»; «the ordinary (or common) man in the street»
ordinary common — having no special distinction or quality; widely known or commonly encountered; average or ordinary or usual; «the common man»; «a common sailor»; «the common cold»; «a common nuisance»; «followed common procedure»; «it is common knowledge that she lives alone»; «the common housefly»; «a common brand of soap» |
|
| 3. | average — lacking exceptional quality or ability; «a novel of average merit»; «only a fair performance of the sonata»; «in fair health»; «the caliber of the students has gone from mediocre to above average»; «the performance was middling at best»
middling, mediocre, fair ordinary — not exceptional in any way especially in quality or ability or size or degree; «ordinary everyday objects»; «ordinary decency»; «an ordinary day»; «an ordinary wine» |
|
| 4. | average — around the middle of a scale of evaluation; «an orange of average size»; «intermediate capacity»; «medium bombers»
medium, intermediate moderate — being within reasonable or average limits; not excessive or extreme; «moderate prices»; «a moderate income»; «a moderate fine»; «moderate demands»; «a moderate estimate»; «a moderate eater»; «moderate success»; «a kitchen of moderate size»; «the X-ray showed moderate enlargement of the heart» |
|
| 5. | average — relating to or constituting the most frequent value in a distribution; «the modal age at which American novelists reach their peak is 30»
modal statistics — a branch of applied mathematics concerned with the collection and interpretation of quantitative data and the use of probability theory to estimate population parameters normal — conforming with or constituting a norm or standard or level or type or social norm; not abnormal; «serve wine at normal room temperature»; «normal diplomatic relations»; «normal working hours»; «normal word order»; «normal curiosity»; «the normal course of events» |
|
| 6. | average — relating to or constituting the middle value of an ordered set of values (or the average of the middle two in a set with an even number of values); «the median value of 17, 20, and 36 is 20»; «the median income for the year was $15,000»
median statistics — a branch of applied mathematics concerned with the collection and interpretation of quantitative data and the use of probability theory to estimate population parameters normal — conforming with or constituting a norm or standard or level or type or social norm; not abnormal; «serve wine at normal room temperature»; «normal diplomatic relations»; «normal working hours»; «normal word order»; «normal curiosity»; «the normal course of events» |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.
average
noun
1. standard, normal, usual, par, mode, mean, rule, medium, norm, run of the mill, midpoint The pay is about the average for a service industry.
adjective
1. usual, common, standard, general, normal, regular, ordinary, typical, commonplace, unexceptional The average man burns 2000 calories a day.
usual great, bad, different, special, terrible, unusual, outstanding, remarkable, awful, exceptional, memorable, notable, abnormal
3. mediocre, fair, ordinary, moderate, pedestrian, indifferent, not bad, middling, insignificant, so-so (informal), banal, second-rate, middle-of-the-road, tolerable, run-of-the-mill, passable, undistinguished, uninspired, unexceptional, bog-standard (Brit. & Irish slang), no great shakes (informal), fair to middling (informal) I was only average academically.
verb
1. make on average, be on average, even out to, do on average, balance out to pay increases averaging 9.75%
Collins Thesaurus of the English Language – Complete and Unabridged 2nd Edition. 2002 © HarperCollins Publishers 1995, 2002
average
noun
Something, as a type, number, quantity, or degree, that represents a midpoint between extremes on a scale of valuation:
adjective
1. Of moderately good quality but less than excellent:
acceptable, adequate, all right, common, decent, fair, fairish, goodish, moderate, passable, respectable, satisfactory, sufficient, tolerable.
3. Being of no special quality or type:
common, commonplace, cut-and-dried, formulaic, garden, garden-variety, indifferent, mediocre, ordinary, plain, routine, run-of-the-mill, standard, stock, undistinguished, unexceptional, unremarkable.
The American Heritage® Roget’s Thesaurus. Copyright © 2013, 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Translations
عاديمُعَدَّلمُعَدَّل، مُتَوَسِّطيَجِد المُعَدَّل
průměrprůměrnýčinit v průměru
gennemsnitgennemsnitliggennemsnits-middel
keskiarvokeskimääräinenkeskinkertainentavallinentyypillinen
prosječanprosjek
átlagátlag-átlagban kitesz
meîal-, meîaltals-meîaltalná aî meîaltalivenjulegur, meîal-
平均平均の
평균평균의
vidurkisvidutinisvidutiniškai sudarytividutiniškas
caurmēracaurmērsdot /sasniegt caurmērāparastsvidējais
priemerne dosahovať
povprečenpovprečjepovprečno
genomsnittgenomsnittligmedeltal
โดยเฉลี่ยค่าเฉลี่ย
mức trung bìnhtrung bình
average
[ˈævərɪdʒ]
A. ADJ
1. (Math, Statistics) [age, wage, price, speed] → medio, promedio inv
average out
average up VT + ADV to average sth up → sacar el promedio or la media de algo tirando hacia arriba
AVERAGE, HALF
Position of «medio»
You should generally put medio after the noun when you mean «average» and before the noun when you mean «half»: …the average citizen… …el ciudadano medio… …the average salary… …el salario medio… …half a kilo of tomatoes… …medio kilo de tomates…
Collins Spanish Dictionary — Complete and Unabridged 8th Edition 2005 © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1971, 1988 © HarperCollins Publishers 1992, 1993, 1996, 1997, 2000, 2003, 2005
average
[ˈævərɪdʒ]
adj [price, age, wage, person, film] → moyen(ne)
the average price → le prix moyen
vt [+ figure]
We averaged 42 km/h → Nous avons fait 42 km/h en moyenne.
average out
vt sep
We averaged it out to £10 a month each → Nous avons arrondi cela à 10 livres par mois et par personne.
Collins English/French Electronic Resource. © HarperCollins Publishers 2005
average
adj → durchschnittlich; (= ordinary) → Durchschnitts-; (= not good or bad) → mittelmäßig; above/below average → über-/unterdurchschnittlich; the average man, Mr Average → der Durchschnittsbürger; the average Scot → der Durchschnittsschotte; he’s a man of average height → er ist von mittlerer Größe
Collins German Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged 7th Edition 2005. © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1980 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1997, 1999, 2004, 2005, 2007
average
[ˈævərɪdʒ]
1. adj → medio/a (pej) → qualsiasi inv, ordinario/a
2. n → media
on average → in media
above/below (the) average → sopra/sotto la media
Collins Italian Dictionary 1st Edition © HarperCollins Publishers 1995
average
(ˈӕvəridʒ) noun
the result of adding several amounts together and dividing the total by the number of amounts. The average of 3, 7, 9 and 13 is 8 (= 32:4).
adjective
1. obtained by finding the average of amounts etc. average price; the average temperature for the week.
2. ordinary; not exceptional. The average person is not wealthy; His work is average.
verb
to form an average. His expenses averaged (out at) 15 dollars a day.
Kernerman English Multilingual Dictionary © 2006-2013 K Dictionaries Ltd.
average
→ مُعَدَّل průměr, průměrný gennemsnit, gennemsnitlig Durchschnitt, durchschnittlich μέσος, μέσος όρος medio, promedio keskiarvo, keskimääräinen moyen, moyenne prosječan, prosjek media, medio 平均, 平均の 평균, 평균의 gemiddeld, gemiddelde gjennomsnitt, gjennomsnittlig przeciętny, średnia média, médio среднее арифметическое, средний genomsnitt, genomsnittlig โดยเฉลี่ย, ค่าเฉลี่ย ortalama mức trung bình, trung bình 平均数, 平均的
Multilingual Translator © HarperCollins Publishers 2009
av·er·age
n. promedio, término medio; de mediana proporción.
English-Spanish Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
average
adj medio, promedio (inv); the — height la estatura media or promedio; n media, promedio; above (the) — superior a la media or al promedio, por encima de la media or del promedio; below (the) — inferior a la media or al promedio, por debajo de la media or del promedio; on — en promedio
English-Spanish/Spanish-English Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.

![y = f^{-1}left(frac{1}{n}left[f(x_1) + f(x_2) + cdots + f(x_n)right]right)](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5fea48be50f3fe5836ae433848e3e4ca0c9827a5)