From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
WordPerfect, a word processor first released for minicomputers in 1979 and later ported to microcomputers, running on Windows XP
A word processor (WP)[1][2] is a device or computer program that provides for input, editing, formatting, and output of text, often with some additional features.
Early word processors were stand-alone devices dedicated to the function, but current word processors are word processor programs running on general purpose computers.
The functions of a word processor program fall somewhere between those of a simple text editor and a fully functioned desktop publishing program. However, the distinctions between these three have changed over time and were unclear after 2010.[3][4]
Background[edit]
Word processors did not develop out of computer technology. Rather, they evolved from mechanical machines and only later did they merge with the computer field.[5] The history of word processing is the story of the gradual automation of the physical aspects of writing and editing, and then to the refinement of the technology to make it available to corporations and Individuals.
The term word processing appeared in American offices in early 1970s centered on the idea of streamlining the work to typists, but the meaning soon shifted toward the automation of the whole editing cycle.
At first, the designers of word processing systems combined existing technologies with emerging ones to develop stand-alone equipment, creating a new business distinct from the emerging world of the personal computer. The concept of word processing arose from the more general data processing, which since the 1950s had been the application of computers to business administration.[6]
Through history, there have been three types of word processors: mechanical, electronic and software.
Mechanical word processing[edit]
The first word processing device (a «Machine for Transcribing Letters» that appears to have been similar to a typewriter) was patented by Henry Mill for a machine that was capable of «writing so clearly and accurately you could not distinguish it from a printing press».[7] More than a century later, another patent appeared in the name of William Austin Burt for the typographer. In the late 19th century, Christopher Latham Sholes[8] created the first recognizable typewriter although it was a large size, which was described as a «literary piano».[9]
The only «word processing» these mechanical systems could perform was to change where letters appeared on the page, to fill in spaces that were previously left on the page, or to skip over lines. It was not until decades later that the introduction of electricity and electronics into typewriters began to help the writer with the mechanical part. The term “word processing” (translated from the German word Textverarbeitung) itself was created in the 1950s by Ulrich Steinhilper, a German IBM typewriter sales executive. However, it did not make its appearance in 1960s office management or computing literature (an example of grey literature), though many of the ideas, products, and technologies to which it would later be applied were already well known. Nonetheless, by 1971 the term was recognized by the New York Times[10] as a business «buzz word». Word processing paralleled the more general «data processing», or the application of computers to business administration.
Thus by 1972 discussion of word processing was common in publications devoted to business office management and technology, and by the mid-1970s the term would have been familiar to any office manager who consulted business periodicals.
Electromechanical and electronic word processing[edit]
By the late 1960s, IBM had developed the IBM MT/ST (Magnetic Tape/Selectric Typewriter). This was a model of the IBM Selectric typewriter from the earlier part of this decade, but it came built into its own desk, integrated with magnetic tape recording and playback facilities along with controls and a bank of electrical relays. The MT/ST automated word wrap, but it had no screen. This device allowed a user to rewrite text that had been written on another tape, and it also allowed limited collaboration in the sense that a user could send the tape to another person to let them edit the document or make a copy. It was a revolution for the word processing industry. In 1969, the tapes were replaced by magnetic cards. These memory cards were inserted into an extra device that accompanied the MT/ST, able to read and record users’ work.
In the early 1970s, word processing began to slowly shift from glorified typewriters augmented with electronic features to become fully computer-based (although only with single-purpose hardware) with the development of several innovations. Just before the arrival of the personal computer (PC), IBM developed the floppy disk. In the early 1970s, the first word-processing systems appeared which allowed display and editing of documents on CRT screens.
During this era, these early stand-alone word processing systems were designed, built, and marketed by several pioneering companies. Linolex Systems was founded in 1970 by James Lincoln and Robert Oleksiak. Linolex based its technology on microprocessors, floppy drives and software. It was a computer-based system for application in the word processing businesses and it sold systems through its own sales force. With a base of installed systems in over 500 sites, Linolex Systems sold 3 million units in 1975 — a year before the Apple computer was released.[11]
At that time, the Lexitron Corporation also produced a series of dedicated word-processing microcomputers. Lexitron was the first to use a full-sized video display screen (CRT) in its models by 1978. Lexitron also used 51⁄4 inch floppy diskettes, which became the standard in the personal computer field. The program disk was inserted in one drive, and the system booted up. The data diskette was then put in the second drive. The operating system and the word processing program were combined in one file.[12]
Another of the early word processing adopters was Vydec, which created in 1973 the first modern text processor, the «Vydec Word Processing System». It had built-in multiple functions like the ability to share content by diskette and print it.[further explanation needed] The Vydec Word Processing System sold for $12,000 at the time, (about $60,000 adjusted for inflation).[13]
The Redactron Corporation (organized by Evelyn Berezin in 1969) designed and manufactured editing systems, including correcting/editing typewriters, cassette and card units, and eventually a word processor called the Data Secretary. The Burroughs Corporation acquired Redactron in 1976.[14]
A CRT-based system by Wang Laboratories became one of the most popular systems of the 1970s and early 1980s. The Wang system displayed text on a CRT screen, and incorporated virtually every fundamental characteristic of word processors as they are known today. While early computerized word processor system were often expensive and hard to use (that is, like the computer mainframes of the 1960s), the Wang system was a true office machine, affordable to organizations such as medium-sized law firms, and easily mastered and operated by secretarial staff.
The phrase «word processor» rapidly came to refer to CRT-based machines similar to Wang’s. Numerous machines of this kind emerged, typically marketed by traditional office-equipment companies such as IBM, Lanier (AES Data machines — re-badged), CPT, and NBI. All were specialized, dedicated, proprietary systems, with prices in the $10,000 range. Cheap general-purpose personal computers were still the domain of hobbyists.
Japanese word processor devices[edit]
In Japan, even though typewriters with Japanese writing system had widely been used for businesses and governments, they were limited to specialists who required special skills due to the wide variety of letters, until computer-based devices came onto the market. In 1977, Sharp showcased a prototype of a computer-based word processing dedicated device with Japanese writing system in Business Show in Tokyo.[15][16]
Toshiba released the first Japanese word processor JW-10 in February 1979.[17] The price was 6,300,000 JPY, equivalent to US$45,000. This is selected as one of the milestones of IEEE.[18]
Toshiba Rupo JW-P22(K)(March 1986) and an optional micro floppy disk drive unit JW-F201
The Japanese writing system uses a large number of kanji (logographic Chinese characters) which require 2 bytes to store, so having one key per each symbol is infeasible. Japanese word processing became possible with the development of the Japanese input method (a sequence of keypresses, with visual feedback, which selects a character) — now widely used in personal computers. Oki launched OKI WORD EDITOR-200 in March 1979 with this kana-based keyboard input system. In 1980 several electronics and office equipment brands entered this rapidly growing market with more compact and affordable devices. While the average unit price in 1980 was 2,000,000 JPY (US$14,300), it was dropped to 164,000 JPY (US$1,200) in 1985.[19] Even after personal computers became widely available, Japanese word processors remained popular as they tended to be more portable (an «office computer» was initially too large to carry around), and become necessities in business and academics, even for private individuals in the second half of the 1980s.[20] The phrase «word processor» has been abbreviated as «Wa-pro» or «wapuro» in Japanese.
Word processing software[edit]
The final step in word processing came with the advent of the personal computer in the late 1970s and 1980s and with the subsequent creation of word processing software. Word processing software that would create much more complex and capable output was developed and prices began to fall, making them more accessible to the public. By the late 1970s, computerized word processors were still primarily used by employees composing documents for large and midsized businesses (e.g., law firms and newspapers). Within a few years, the falling prices of PCs made word processing available for the first time to all writers in the convenience of their homes.
The first word processing program for personal computers (microcomputers) was Electric Pencil, from Michael Shrayer Software, which went on sale in December 1976. In 1978 WordStar appeared and because of its many new features soon dominated the market. However, WordStar was written for the early CP/M (Control Program–Micro) operating system, and by the time it was rewritten for the newer MS-DOS (Microsoft Disk Operating System), it was obsolete. Suddenly, WordPerfect dominated the word processing programs during the DOS era, while there was a large variety of less successful programs.
Early word processing software was not as intuitive as word processor devices. Most early word processing software required users to memorize semi-mnemonic key combinations rather than pressing keys such as «copy» or «bold». Moreover, CP/M lacked cursor keys; for example WordStar used the E-S-D-X-centered «diamond» for cursor navigation. However, the price differences between dedicated word processors and general-purpose PCs, and the value added to the latter by software such as “killer app” spreadsheet applications, e.g. VisiCalc and Lotus 1-2-3, were so compelling that personal computers and word processing software became serious competition for the dedicated machines and soon dominated the market.
Then in the late 1980s innovations such as the advent of laser printers, a «typographic» approach to word processing (WYSIWYG — What You See Is What You Get), using bitmap displays with multiple fonts (pioneered by the Xerox Alto computer and Bravo word processing program), and graphical user interfaces such as “copy and paste” (another Xerox PARC innovation, with the Gypsy word processor). These were popularized by MacWrite on the Apple Macintosh in 1983, and Microsoft Word on the IBM PC in 1984. These were probably the first true WYSIWYG word processors to become known to many people.
Of particular interest also is the standardization of TrueType fonts used in both Macintosh and Windows PCs. While the publishers of the operating systems provide TrueType typefaces, they are largely gathered from traditional typefaces converted by smaller font publishing houses to replicate standard fonts. Demand for new and interesting fonts, which can be found free of copyright restrictions, or commissioned from font designers, occurred.
The growing popularity of the Windows operating system in the 1990s later took Microsoft Word along with it. Originally called «Microsoft Multi-Tool Word», this program quickly became a synonym for “word processor”.
From early in the 21st century Google Docs popularized the transition to online or offline web browser based word processing, this was enabled by the widespread adoption of suitable internet connectivity in businesses and domestic households and later the popularity of smartphones. Google Docs enabled word processing from within any vendor’s web browser, which could run on any vendor’s operating system on any physical device type including tablets and smartphones, although offline editing is limited to a few Chromium based web browsers. Google Docs also enabled the significant growth of use of information technology such as remote access to files and collaborative real-time editing, both becoming simple to do with little or no need for costly software and specialist IT support.
See also[edit]
- List of word processors
- Formatted text
References[edit]
- ^ Enterprise, I. D. G. (1 January 1981). «Computerworld». IDG Enterprise. Archived from the original on 2 January 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019 – via Google Books.
- ^ Waterhouse, Shirley A. (1 January 1979). Word processing fundamentals. Canfield Press. ISBN 9780064537223. Archived from the original on 2 January 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019 – via Google Books.
- ^ Amanda Presley (28 January 2010). «What Distinguishes Desktop Publishing From Word Processing?». Brighthub.com. Archived from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
- ^ «How to Use Microsoft Word as a Desktop Publishing Tool». PCWorld. 28 May 2012. Archived from the original on 19 August 2017. Retrieved 3 May 2018.
- ^ Price, Jonathan, and Urban, Linda Pin. The Definitive Word-Processing Book. New York: Viking Penguin Inc., 1984, page xxiii.
- ^ W.A. Kleinschrod, «The ‘Gal Friday’ is a Typing Specialist Now,» Administrative Management vol. 32, no. 6, 1971, pp. 20-27
- ^ Hinojosa, Santiago (June 2016). «The History of Word Processors». The Tech Ninja’s Dojo. The Tech Ninja. Archived from the original on 6 May 2018. Retrieved 6 May 2018.
- ^ See also Samuel W. Soule and Carlos Glidden.
- ^ The Scientific American, The Type Writer, New York (August 10, 1872)
- ^ W.D. Smith, “Lag Persists for Business Equipment,” New York Times, 26 Oct. 1971, pp. 59-60.
- ^ Linolex Systems, Internal Communications & Disclosure in 3M acquisition, The Petritz Collection, 1975.
- ^ «Lexitron VT1200 — RICM». Ricomputermuseum.org. Archived from the original on 3 January 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
- ^ Hinojosa, Santiago (1 June 2016). «The History of Word Processors». The Tech Ninja’s Dojo. Archived from the original on 24 December 2018. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
- ^ «Redactron Corporation. @ SNAC». Snaccooperative.org. Archived from the original on 15 December 2018. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
- ^ «日本語ワードプロセッサ». IPSJコンピュータ博物館. Retrieved 2017-07-05.
- ^ «【シャープ】 日本語ワープロの試作機». IPSJコンピュータ博物館. Retrieved 2017-07-05.
- ^ 原忠正 (1997). «日本人による日本人のためのワープロ». The Journal of the Institute of Electrical Engineers of Japan. 117 (3): 175–178. Bibcode:1997JIEEJ.117..175.. doi:10.1541/ieejjournal.117.175.
- ^ «プレスリリース;当社の日本語ワードプロセッサが「IEEEマイルストーン」に認定». 東芝. 2008-11-04. Retrieved 2017-07-05.
- ^
«【富士通】 OASYS 100G». IPSJコンピュータ博物館. Retrieved 2017-07-05. - ^ 情報処理学会 歴史特別委員会『日本のコンピュータ史』ISBN 4274209334 p135-136
Updated: 07/06/2021 by
Sometimes abbreviated as WP, a word processor is a software program capable of creating, storing, and printing typed documents. Today, the word processor is one of the most frequently used software programs on a computer, with Microsoft Word being a popular choice.
Word processors can create multiple types of files, including text files (.txt), rich text files (.rtf), HTML files (.htm & .html), and Word files (.doc & .docx). Some word processors can also be used to create XML files (.xml).
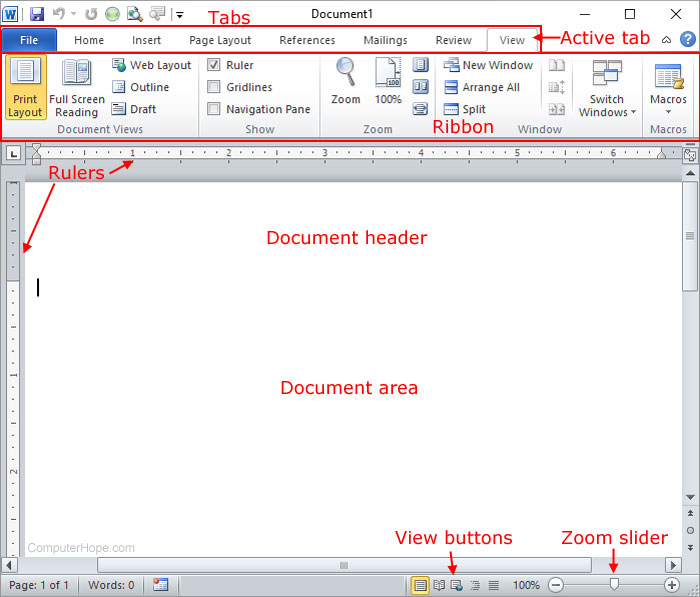
Overview of Word
In a word processor, you are presented with a blank white sheet as shown below. The text is added to the document area and after it has been inserted formatted or adjusted to your preference. Below is an example of a blank Microsoft Word window with areas of the window highlighted.
Features of a word processor
Unlike a basic plaintext editor, a word processor offers several additional features that can give your document or other text a more professional appearance. Below is a listing of popular features of a word processor.
Note
Some more advanced text editors can perform some of these functions.
- Text formatting — Changing the font, font size, font color, bold, italicizing, underline, etc.
- Copying, cutting, and pasting — Once text is entered into a document, it can be copied or cut and pasted in the current document or another document.
- Multimedia — Insert clip art, charts, images, pictures, and video into a document.
- Spelling and Grammar — Checks for spelling and grammar errors in a document.
- Adjust the layout — Capable of modifying the margins, size, and layout of a document.
- Find — Word processors give you the ability to quickly find any word or text in any size of the document.
- Search and Replace — You can use the Search and Replace feature to replace any text throughout a document.
- Indentation and lists — Set and format tabs, bullet lists, and number lists.
- Insert tables — Add tables to a document.
- Word wrap — Word processors can detect the edges of a page or container and automatically wrap the text using word wrap.
- Header and footer — Being able to adjust and change text in the header and footer of a document.
- Thesaurus — Look up alternatives to a word without leaving the program.
- Multiple windows — While working on a document, you can have additional windows with other documents for comparison or move text between documents.
- AutoCorrect — Automatically correct common errors (e.g., typing «teh» and having it autocorrected to «the»).
- Mailers and labels — Create mailers or print labels.
- Import data — Import and format data from CSV, database, or another source.
- Headers and footers — The headers and footers of a document can be customized to contain page numbers, dates, footnotes, or text for all pages or specific pages of the document.
- Merge — Word processors allow data from other documents and files to be automatically merged into a new document. For example, you can mail merge names into a letter.
- Macros — Setup macros to perform common tasks.
- Collaboration — More modern word processors help multiple people work on the same document at the same time.
Examples and top uses of a word processor
A word processor is one of the most used computer programs because of its versatility in creating a document. Below is a list of the top examples of how you could use a word processor.
- Book — Write a book.
- Document — Any text document that requires formatting.
- Help documentation — Support documentation for a product or service.
- Journal — Keep a digital version of your daily, weekly, or monthly journal.
- Letter — Write a letter to one or more people. Mail merge could also be used to automatically fill in the name, address, and other fields of the letter.
- Marketing plan — An overview of a plan to help market a new product or service.
- Memo — Create a memo for employees.
- Report — A status report or book report.
- Résumé — Create or maintain your résumé.
Examples of word processor programs
Although Microsoft Word is popular, there are other word processor programs. Below is a list of some popular word processors in alphabetical order.
- Abiword.
- Apple iWork — Pages.
- Apple TextEdit — Apple macOS included word processor.
- Corel WordPerfect.
- Dropbox Paper (online and free).
- Google Docs (online and free).
- LibreOffice -> Writer (free).
- Microsoft Office -> Microsoft Word.
- Microsoft WordPad.
- Microsoft Works (discontinued).
- SoftMaker FreeOffice -> TextMaker (free).
- OpenOffice -> Writer (free).
- SSuite -> WordGraph (free).
- Sun StarOffice (discontinued).
- Textilus (iPad and iPhone).
- Kingsoft WPS Office -> Writer (free).
Word processor advantages over a typewriter
See our typewriter page for a listing of advantages a computer with a word processor has over a typewriter.
Computer acronyms, Doc, Microsoft Word, Software terms, Untitled, Word processing, Word processor terms, WordStar, Write
What Does Word Processor Mean?
A word processor is a type of software application used for composing, editing, formatting and printing documents. Word processors have a variety of uses and applications within the business environment, at home and in educational contexts.
Techopedia Explains Word Processor
Word processors are used to create, edit and print documents, and well as save them electronically.
Word processors have the following main functionalities:
- Insert
- Copy
- Cut and paste
- Delete
- Find and replace
- Word wrap
Advanced word processors, referred to as full-featured word processors, support additional features such as:
- File management
- Graphics
- Font specification
- Footnotes
- Cross reference
- Headers and footers
- Macros
- Layout
- Spell check
- Thesaurus
A
word processor (more formally known as document preparation system)
is a computer application used for the production (including
composition, editing, formatting, and possibly printing) of any sort
of printable material.
Word
processor may also refer to a type of stand-alone office machine,
popular in the 1970s and 1980s, combining the keyboard text-entry and
printing functions of an electric typewriter with a dedicated
processor (like a computer processor) for the editing of text.
Although features and design varied between manufacturers and models,
with new features added as technology advanced, word processors for
several years usually featured a monochrome display and the ability
to save documents on memory cards or diskettes. Later models
introduced innovations such as spell-checking programs, increased
formatting options, and dot-matrix printing. As the more versatile
combination of a personal computer and separate printer became
commonplace, most business-machine companies stopped manufacturing
the word processor as a stand-alone office machine. As of 2009 there
were only two U.S. companies, Classic and AlphaSmart, which still
made stand-alone word processors.[1] Many older machines, however,
remain in use.
Word
processors are descended from early text formatting tools (sometimes
called text justification tools, from their only real capability).
Word processing was one of the earliest applications for the personal
computer in office productivity.
Although
early word processors used tag-based markup for document formatting,
most modern word processors take advantage of a graphical user
interface providing some form of What You See Is What You Get
editing. Most are powerful systems consisting of one or more programs
that can produce any arbitrary combination of images, graphics and
text, the latter handled with type-setting capability.
Microsoft
Word is the most widely used word processing software. Microsoft
estimates that over 500,000,000 people use the Microsoft Office
suite,[2] which includes Word. Many other word processing
applications exist, including WordPerfect (which dominated the market
from the mid-1980s to early-1990s on computers running Microsoft’s
MS-DOS operating system) and open source applications OpenOffice.org
Writer, AbiWord, KWord, and LyX. Web-based word processors, such as
Google Docs, are a relatively new category.
Word processing
Characteristics
Word
processing typically implies the presence of text manipulation
functions that extend beyond a basic ability to enter and change
text, such as automatic generation of:
• batch
mailings using a form letter template and an address database (also
called mail merging);
• indices
of keywords and their page numbers;
• tables
of contents with section titles and their page numbers;
• tables
of figures with caption titles and their page numbers;
• cross-referencing
with section or page numbers;
• footnote
numbering;
• new
versions of a document using variables (e.g. model numbers, product
names, etc.)
Other
word processing functions include «spell checking»
(actually checks against wordlists), «grammar checking»
(checks for what seem to be simple grammar errors), and a «thesaurus»
function (finds words with similar or opposite meanings). Other
common features include collaborative editing, comments and
annotations, support for images and diagrams and internal
cross-referencing.
Word
processors can be distinguished from several other, related forms of
software:
Text
editors (modern examples of which include Notepad, BBEdit, Kate,
Gedit), were the precursors of word processors. While offering
facilities for composing and editing text, they do not format
documents. This can be done by batch document processing systems,
starting with TJ-2 and RUNOFF and still available in such systems as
LaTeX (as well as programs that implement the paged-media extensions
to HTML and CSS). Text editors are now used mainly by programmers,
website designers, computer system administrators, and, in the case
of LaTeX by mathematicians and scientists (for complex formulas and
for citations in rare languages). They are also useful when fast
startup times, small file sizes, editing speed and simplicity of
operation are preferred over formatting.
Later
desktop publishing programs were specifically designed to allow
elaborate layout for publication, but often offered only limited
support for editing. Typically, desktop publishing programs allowed
users to import text that was written using a text editor or word
processor.
Almost
all word processors enable users to employ styles, which are used to
automate consistent formatting of text body, titles, subtitles,
highlighted text, and so on.
Styles
greatly simplify managing the formatting of large documents, since
changing a style automatically changes all text that the style has
been applied to. Even in shorter documents styles can save a lot of
time while formatting. However, most help files refer to styles as an
‘advanced feature’ of the word processor, which often discourages
users from using styles regularly.
Document
statistics
Most
current word processors can calculate various statistics pertaining
to a document. These usually include:
• Character
count, word count, sentence count, line count, paragraph count, page
count.
• Word,
sentence and paragraph length.
• Editing
time.
Errors
are common; for instance, a dash surrounded by spaces — like either
of these — may be counted as a word.
Typical
usage
Word
processors have a variety of uses and applications within the
business world, home, and education.
Business
Within
the business world, word processors are extremely useful tools.
Typical uses include:
• legal
copies
• letters
and letterhead
• memos
• reference
documents
Businesses
tend to have their own format and style for any of these. Thus,
versatile word processors with layout editing and similar
capabilities find widespread use in most businesses.
Education
Many
schools have begun to teach typing and word processing to their
students, starting as early as elementary school. Typically these
skills are developed throughout secondary school in preparation for
the business world. Undergraduate students typically spend many hours
writing essays. Graduate and doctoral students continue this trend,
as well as creating works for research and publication.
Home
While
many homes have word processors on their computers, word processing
in the home tends to be educational, planning or business related,
dealing with assignments or work being completed at home, or
occasionally recreational, e.g. writing short stories. Some use word
processors for letter writing, résumé creation, and card creation.
However, many of these home publishing processes have been taken over
by desktop publishing programs specifically oriented toward home use.
which are better suited to these types of documents.
History
Toshiba
JW-10, the first word processor for the Japanese language (1971-1978
IEEE milestones)
Examples
of standalone word processor typefaces c. 1980-1981
Brother
WP-1400D editing electronic typewriter (1994)
The
term word processing was invented by IBM in the late 1960s. By 1971
it was recognized by the New York Times as a «buzz word».[3]
A 1974 Times article referred to «the brave new world of Word
Processing or W/P. That’s International Business Machines talk…
I.B.M. introduced W/P about five years ago for its Magnetic Tape
Selectric Typewriter and other electronic razzle-dazzle.»
IBM
defined the term in a broad and vague way as «the combination of
people, procedures, and equipment which transforms ideas into printed
communications,» and originally used it to include dictating
machines and ordinary, manually-operated Selectric typewriters. By
the early seventies, however, the term was generally understood to
mean semiautomated typewriters affording at least some form of
electronic editing and correction, and the ability to produce perfect
«originals.» Thus, the Times headlined a 1974 Xerox product
as a «speedier electronic typewriter», but went on to
describe the product, which had no screen, as «a word processor
rather than strictly a typewriter, in that it stores copy on magnetic
tape or magnetic cards for retyping, corrections, and subsequent
printout.»
Electromechanical
paper-tape-based equipment such as the Friden Flexowriter had long
been available; the Flexowriter allowed for operations such as
repetitive typing of form letters (with a pause for the operator to
manually type in the variable information)[8], and when equipped with
an auxiliary reader, could perform an early version of «mail
merge». Circa 1970 it began to be feasible to apply electronic
computers to office automation tasks. IBM’s Mag Tape Selectric
Typewriter (MTST) and later Mag Card Selectric (MCST) were early
devices of this kind, which allowed editing, simple revision, and
repetitive typing, with a one-line display for editing single lines.
The
New York Times, reporting on a 1971 business equipment trade show,
said
The
«buzz word» for this year’s show was «word
processing,» or the use of electronic equipment, such as
typewriters; procedures and trained personnel to maximize office
efficiency. At the IBM exhibition a girl [sic] typed on an electronic
typewriter. The copy was received on a magnetic tape cassette which
accepted corrections, deletions, and additions and then produced a
perfect letter for the boss’s signature….
In
1971, a third of all working women in the United States were
secretaries, and they could see that word processing would have an
impact on their careers. Some manufacturers, according to a Times
article, urged that «the concept of ‘word processing’ could be
the answer to Women’s Lib advocates’ prayers. Word processing will
replace the ‘traditional’ secretary and give women new administrative
roles in business and industry.»
The
1970s word processing concept did not refer merely to equipment, but,
explicitly, to the use of equipment for «breaking down
secretarial labor into distinct components, with some staff members
handling typing exclusively while others supply administrative
support. A typical operation would leave most executives without
private secretaries. Instead one secretary would perform various
administrative tasks for three or more secretaries.» A 1971
article said that «Some [secretaries] see W/P as a career ladder
into management; others see it as a dead-end into the automated
ghetto; others predict it will lead straight to the picket line.»
The National Secretaries Association, which defined secretaries as
people who «can assume responsibility without direct
supervision,» feared that W/P would transform secretaries into
«space-age typing pools.» The article considered only the
organizational changes resulting from secretaries operating word
processors rather than typewriters; the possibility that word
processors might result in managers creating documents without the
intervention of secretaries was not considered—not surprising in an
era when few but secretaries possessed keyboarding skills.
In
the early 1970s, computer scientist Harold Koplow was hired by Wang
Laboratories to program calculators. One of his programs permitted a
Wang calculator to interface with an IBM Selectric typewriter, which
was at the time used to calculate and print the paperwork for auto
sales.
In
1974, Koplow’s interface program was developed into the Wang 1200
Word Processor, an IBM Selectric-based text-storage device. The
operator of this machine typed text on a conventional IBM Selectric;
when the Return key was pressed, the line of text was stored on a
cassette tape. One cassette held roughly 20 pages of text, and could
be «played back» (i.e., the text retrieved) by printing the
contents on continuous-form paper in the 1200 typewriter’s «print»
mode. The stored text could also be edited, using keys on a simple,
six-key array. Basic editing functions included Insert, Delete, Skip
(character, line), and so on.
The
labor and cost savings of this device were immediate, and remarkable:
pages of text no longer had to be retyped to correct simple errors,
and projects could be worked on, stored, and then retrieved for use
later on. The rudimentary Wang 1200 machine was the precursor of the
Wang Office Information System (OIS), introduced in 1976, whose
CRT-based system was a major breakthrough in word processing
technology. It displayed text on a CRT screen, and incorporated
virtually every fundamental characteristic of word processors as we
know them today. It was a true office machine, affordable by
organizations such as medium-sized law firms, and easily learned and
operated by secretarial staff.
The
Wang was not the first CRT-based machine nor were all of its
innovations unique to Wang. In the early 1970s Linolex, Lexitron and
Vydec introduced pioneering word-processing systems with CRT display
editing. A Canadian electronics company, Automatic Electronic
Systems, had introduced a product with similarities to Wang’s product
in 1973, but went into bankruptcy a year later. In 1976, refinanced
by the Canada Development Corporation, it returned to operation as
AES Data, and went on to successfully market its brand of word
processors worldwide until its demise in the mid-1980s. Its first
office product, the AES-90, combined for the first time a CRT-screen,
a floppy-disk and a microprocessor,[citation needed] that is, the
very same winning combination that would be used by IBM for its PC
seven years later. The AES-90 software was able to handle French and
English typing from the start, displaying and printing the texts
side-by-side, a Canadian government requirement. The first eight
units were delivered to the office of the then Prime Minister, Pierre
Elliot Trudeau, in February 1974. Despite these predecessors, Wang’s
product was a standout, and by 1978 it had sold more of these systems
than any other vendor.
In
the early 1980’s, AES Data Inc. introduced a networked word processor
system, called MULTIPLUS, offering multi-tasking and up to 8
workstations all sharing the resources of a centralized computer
system, a precursor to today’s networks. It followed with the
introduction of SuperPlus and SuperPlus IV systems which also offered
the CP/M operating system answering client needs. AES Data word
processors were placed side-by-side with CP/M software, like
Wordstar, to highlight ease of use.
The
phrase «word processor» rapidly came to refer to CRT-based
machines similar to Wang’s. Numerous machines of this kind emerged,
typically marketed by traditional office-equipment companies such as
IBM, Lanier (marketing AES Data machines, re-badged), CPT, and
NBI.[13] All were specialized, dedicated, proprietary systems, with
prices in the $10,000 ballpark. Cheap general-purpose computers were
still the domain of hobbyists.
Some
of the earliest CRT-based machines used cassette tapes for
removable-memory storage until floppy diskettes became available for
this purpose — first the 8-inch floppy, then the 5-1/4-inch (drives
by Shugart Associates and diskettes by Dysan).
Printing
of documents was initially accomplished using IBM Selectric
typewriters modified for ASCII-character input. These were later
replaced by application-specific daisy wheel printers (Diablo, which
became a Xerox company, and Qume — both now defunct.) For quicker
«draft» printing, dot-matrix line printers were optional
alternatives with some word processors.
With
the rise of personal computers, and in particular the IBM PC and PC
compatibles, software-based word processors running on
general-purpose commodity hardware gradually displaced dedicated word
processors, and the term came to refer to software rather than
hardware. Some programs were modeled after particular dedicated WP
hardware. MultiMate, for example, was written for an insurance
company that had hundreds of typists using Wang systems, and spread
from there to other Wang customers. To adapt to the smaller PC
keyboard, MultiMate used stick-on labels and a large plastic clip-on
template to remind users of its dozens of Wang-like functions, using
the shift, alt and ctrl keys with the 10 IBM function keys and many
of the alphabet keys.
Other
early word-processing software required users to memorize
semi-mnemonic key combinations rather than pressing keys labelled
«copy» or «bold.» (In fact, many early PCs lacked
cursor keys; WordStar famously used the E-S-D-X-centered «diamond»
for cursor navigation, and modern vi-like editors encourage use of
hjkl for navigation.) However, the price differences between
dedicated word processors and general-purpose PCs, and the value
added to the latter by software such as VisiCalc, were so compelling
that personal computers and word processing software soon became
serious competition for the dedicated machines. Word Perfect,
XyWrite, Microsoft Word, Wordstar, Workwriter and dozens of other
word processing software brands competed in the 1980s. Development of
higher-resolution monitors allowed them to provide limited WYSIWYG —
What You See Is What You Get, to the extent that typographical
features like bold and italics, indentation, justification and
margins were approximated on screen.
The
mid-to-late 1980s saw the spread of laser printers, a «typographic»
approach to word processing, and of true WYSIWYG bitmap displays with
multiple fonts (pioneered by the Xerox Alto computer and Bravo word
processing program), PostScript, and graphical user interfaces
(another Xerox PARC innovation, with the Gypsy word processor which
was commercialised in the Xerox Star product range). Standalone word
processors adapted by getting smaller and replacing their CRTs with
small character-oriented LCD displays. Some models also had
computer-like features such as floppy disk drives and the ability to
output to an external printer. They also got a name change, now being
called «electronic typewriters» and typically occupying a
lower end of the market, selling for under $200 USD.
MacWrite,
Microsoft Word and other word processing programs for the bit-mapped
Apple Macintosh screen, introduced in 1984, were probably the first
true WYSIWYG word processors to become known to many people until the
introduction of Microsoft Windows. Dedicated
word processors eventually became museum pieces.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Word_processor
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
A word processor, also known as a WP, is a software program people use for writing letters, documents, books, articles, etc. on a computer. A word processor is capable of creating, storing, and printing documents that have been created using a keyboard.
The most popular word processor in the world today is Microsoft Word, which has been around in one form or another since October 25th, 1983.
Word processors are used to create a wide range of different types of files, including .txt (text files), .rtf (rich text files), .htm & .html (HTML files), as well as .doc & .docx (Word files). A number of word processing programs are able to create .xml (XML files).
The term word processor may also refer to a computer used for word processing, i.e. it means either the software or the hardware. In fact, the first typewriter ever created was a (mechanical) word processor.
According to LlearnersDictionary.com, a word processor is:
“1. A computer used for creating, storing, and printing text : a computer used for word processing. 2. Software used on a computer to perform word processing.”
The word processor (hardware) has been around for literally hundreds of years.
Word processor – brief history
In the 1960s, a word processor was a stand-alone office machine with a keyboard, printer, electric typewriter, and a recording unit. It used either a simple dedicated computer processor or a floppy disk.
According to Harry Henderson, in his book titled ‘Encyclopedia of Computer Science and Technology‘, IBM is believed to have coined the term ‘word processor’ in the 1960s. It was used to refer to a system consisting of a Selectric typewriter with a magnetic tape storage.
During the 1960s and 1970s, the features and designs gradually changed as technology advanced. They had a monochrome (black and white) display, and were able to save documents on diskettes or memory cards.
The first ‘modern’ style word processor was brought to the market by Lexitron and Linolex. As well as a magnetic tape, it also had a video display screen, so that the typist could see and correct errors without having to print it first.
By the late-1970s-early-1980s several innovations were introduced, including improved formatting options and spell-checkers.
In the late 1970s, word-processing systems developed by Wang, Data General, Digital Equipment Corporation, and others were essentially microcomputers with tiny monitors (screens), keyboards, printers and specialized software.
At $8,000 to $20,000 each, and requiring specially-trained operators, very few companies had word-processing systems. With $20,000, an employer could pay the wages of 2.5 secretaries for a whole year in 1979.
When personal computers, printers, and computer applications for word processing came onto the scene, sales of dedicated word processor machines plummeted. In 2009, there were just two American companies – AlphaSmart and Classic – which continued making them.
Today, typical word processing software comprises more than one program and can produce a combination of graphics, images and text – with the text having type-setting capability.
Most programs on the market today have:
- Multiple font sets
- Grammar checking
- Thesaurus
- Spell checking
- Automatic text corrector.
- HTML conversion.
- Web integration.
- Pre-formatted layouts for newsletters, to-do lists, etc.
The image contains the logos of some of the most popular word processors. The term may refer to either software or hardware.
Where are word processors used?
In the world of business, word processors are extremely common. They are used for creating legal documents such contracts, company reports, literature for customers and clients, internal memos, and letters.
Most companies have their own format and style, and either have the company letterhead programmed into the word processor software, pre-printed on paper, or both.
In people’s households, word processors are used for business, educational, and planning purposes.
Some people use the software to write poems, short stories, personal correspondence, greeting cars, or to create résumés (CVs).
Since the advent of social networks and email, the role of the word processor in the home has declined considerably. What used to be done in printed form (on physical paper), is now done almost entirely online.
According to Top Ten Reviews, the top word processors (software) in the world are:
- Microsoft Word (Microsoft Corporation – United States)
- Word Perfect (Corel Corporation – Canada)
- TextMaker (SoftMaker Software GmbH – Germany)
- Google Docs (Google Inc. – United States))
- Kingsoft Writer (Kingsoft 金山软件有限公司 – China))
- Ability Write (Ability Software International – United Kingdom)
- RagTime ((RagTime.de Development GmbH – Germany)
Video – Word processor tutorial
In this video, Chris gives a tutorial for beginners on how to use the world’s most popular word processor – Microsoft Word (2016). Even if you have been using Microsoft Word for many years, the tutorial may serve as a useful reminder.