Business is the practice of making one’s living or making money by producing or buying and selling products (such as goods and services).[1][2][3][4] It is also «any activity or enterprise entered into for profit.»[5]
Having a business name does not separate the business entity from the owner, which means that the owner of the business is responsible and liable for debts incurred by the business. If the business acquires debts, the creditors can go after the owner’s personal possessions.[6] A business structure does not allow for corporate tax rates. The proprietor is personally taxed on all income from the business.
The term is also often used colloquially (but not by lawyers or by public officials) to refer to a company, such as a corporation or cooperative.
Corporations, in contrast with sole proprietors and partnerships, are a separate legal entity and provide limited liability for their owners/members, as well as being subject to corporate tax rates. A corporation is more complicated and expensive to set up, but offers more protection and benefits for the owners/members.
Forms
Forms of business ownership vary by jurisdiction, but several common entities exist:
- A sole proprietorship, also known as a sole trader, is owned by one person and operates for their benefit. The owner operates the business alone and may hire employees. A sole proprietor has unlimited liability for all obligations incurred by the business, whether from operating costs or judgments against the business. All assets of the business belong to a sole proprietor, including, for example, a computer infrastructure, any inventory, manufacturing equipment, or retail fixtures, as well as any real property owned by the sole proprietor.
- A partnership is a business owned by two or more people. In most forms of partnerships, each partner has unlimited liability for the debts incurred by the business. The three most prevalent types of for-profit partnerships are general partnerships, limited partnerships, and limited liability partnerships.[7]
- Corporations’ owners have limited liability and the business has a separate legal personality from its owners. Corporations can be either government-owned or privately owned, and they can organize either for profit or as nonprofit organizations. A privately owned, for-profit corporation is owned by its shareholders, who elect a board of directors to direct the corporation and hire its managerial staff. A privately owned, for-profit corporation can be either privately held by a small group of individuals, or publicly held, with publicly traded shares listed on a stock exchange.
- A cooperative or co-op is a limited-liability business that can organize as for-profit or not-for-profit. A cooperative differs from a corporation in that it has members, not shareholders, and they share decision-making authority. Cooperatives are typically classified as either consumer cooperatives or worker cooperatives. Cooperatives are fundamental to the ideology of economic democracy.
- Limited liability companies (LLC) and other specific types of business organization protect their owners or shareholders from business failure by doing business under a separate legal entity with certain legal protections. In contrast, a general partnership or persons working on their own are usually not as protected.[8]
- A franchise is a system in which entrepreneurs purchase the rights to open and run a business from a larger corporation.[9] Franchising in the United States is widespread and is a major economic powerhouse. One out of twelve retail businesses in the United States are franchised and 8 million people are employed in a franchised business.[10]
- Company limited by guarantee is commonly used where companies are formed for non-commercial purposes, such as clubs or charities. The members guarantee the payment of certain (usually nominal) amounts if the company goes into insolvent liquidation, but otherwise, they have no economic rights in relation to the company. This type of company is common in England. A company limited by guarantee may be with or without having share capital.
- A company limited by shares is the most common form of the company used for business ventures. Specifically, a limited company is a «company in which the liability of each shareholder is limited to the amount individually invested» with corporations being «the most common example of a limited company.»[11] This type of company is common in England and many English-speaking countries. A company limited by shares may be a
- publicly traded company or a
- privately held company.
- A company limited by guarantee with a share capital is a hybrid entity, usually used where the company is formed for non-commercial purposes, but the activities of the company are partly funded by investors who expect a return. This type of company may no longer be formed in the UK, although provisions still exist in law for them to exist.[12]
- An unlimited company with or without a share capital is a hybrid entity, a company where the liability of members or shareholders for the debts (if any) of the company are not limited. In this case, the doctrine of a veil of incorporation does not apply.
Less common types of companies are:
- Most corporations by letters patent are corporations sole and not companies as the term is commonly understood today.
- Charter corporations were the only types of companies before the passing of modern companies legislation. Now they are relatively rare, except for very old companies that still survive (of which there are still many, particularly many British banks), or modern societies that fulfill a quasi-regulatory function (for example, the Bank of England is a corporation formed by a modern charter).
- Statutory companies are certain companies that have been formed by a private statute passed in the relevant jurisdiction, and are relatively rare today.
«Ltd after the company’s name signifies limited company, and PLC (public limited company) indicates that its shares are widely held.»[13]
In legal parlance, the owners of a company are normally referred to as the «members». In a company limited or unlimited by shares (formed or incorporated with a share capital), this will be the shareholders. In a company limited by guarantee, this will be the guarantors. Some offshore jurisdictions have created special forms of offshore company in a bid to attract business for their jurisdictions. Examples include «segregated portfolio companies» and restricted purpose companies.
There are, however, many, many sub-categories of types of company that can be formed in various jurisdictions in the world.
Companies are also sometimes distinguished into public companies and private companies for legal and regulatory purposes. Public companies are companies whose shares can be publicly traded, often (although not always) on a stock exchange which imposes listing requirements/Listing Rules as to the issued shares, the trading of shares and a future issue of shares to help bolster the reputation of the exchange or particular market of exchange. Private companies do not have publicly traded shares, and often contain restrictions on transfers of shares. In some jurisdictions, private companies have maximum numbers of shareholders.
A parent company is a company that owns enough voting stock in another firm to control management and operations by influencing or electing its board of directors; the second company being deemed as a subsidiary of the parent company. The definition of a parent company differs by jurisdiction, with the definition normally being defined by way of laws dealing with companies in that jurisdiction.
Classifications
- Agriculture, such as the domestication of fish, animals, and livestock, as well as lumber, oil, vegetables, fruits, etc.
- Mining businesses that extract natural resources and raw materials, such as wood, petroleum, natural gas, ores, metals or minerals.
- Service businesses offer intangible goods or services and typically charge for labor or other services provided to government, to consumers, or to other businesses. Interior decorators, beauticians, hair stylists, make-up artists, tanning salons, laundromats, dry cleaners, and pest controllers are service businesses.
- Financial services businesses include banks, brokerage firms, credit unions, credit cards, insurance companies, asset and investment companies such as private-equity firms, private-equity funds, real estate investment trusts, sovereign wealth funds, pension funds, mutual funds, index funds, hedge funds, stock exchanges, and other companies that generate profits through investment and management of capital.
- Transportation businesses such as railways, airlines, and shipping companies deliver goods and individuals to their destinations for a fee.
- Utilities produce public services such as water, electricity, waste management or sewage treatment. These industries are usually operated under the charge of a public government.
- Entertainment companies and mass media agencies generate profits primarily from the sale of intellectual property. They include film studios and production houses, mass media companies such as cable television networks, online digital media agencies, talent agencies, mobile media outlets, newspapers, book and magazine publishing houses.
- Sports organizations are involved in producing, facilitating, promoting, or organizing any activity, experience, or business enterprise focused on sports. They make their profits by selling goods and services that are sports related.
- Industrial manufacturers produce products, either from raw materials or from component parts, then export the finished products at a profit. They include tangible goods such as cars, buses, medical devices, glass, or aircraft.
- Real estate businesses sell, invest, construct and develop properties, including land, residential homes, and other buildings.
- Retailers, wholesalers, and distributors act as middlemen and get goods produced by manufacturers to the intended consumers; they make their profits by marking up their prices. Most stores and catalog companies are distributors or retailers.
Activities
Accounting
Accounting is the measurement, processing, and communication of financial information about economic entities[14][15] such as businesses and corporations. The modern field was established by the Italian mathematician Luca Pacioli in 1494.[16] Accounting, which has been called the «language of business»,[17] measures the results of an organization’s economic activities and conveys this information to a variety of users, including investors, creditors, management, and regulators.[18] Practitioners of accounting are known as accountants. The terms «accounting» and «financial reporting» are often used as synonyms.
Commerce
The process of exchanging goods and services.[19]
Finance
Finance is a field that deals with the study of money and investments. It includes the dynamics of assets and liabilities over time under conditions of different degrees of uncertainty and risk.[20]
In the context of business and management, finance deals with the problems of ensuring that the firm can safely and profitably carry out its operational and financial objectives; i.e. that it: (1) has sufficient cash flow for ongoing and upcoming operational expenses, and (2) can service both maturing short-term debt repayments, and scheduled long-term debt payments.
Finance also deals with the long term objective of maximizing the value of the business, while also balancing risk and profitability; this includes the interrelated questions of (1) capital investment, which businesses and projects to invest in; (2) capital structure, deciding on the mix of funding to be used; and (3) dividend policy, what to do with «excess» capital.
Human Resources
Human Resources can be defined as division of business that involves finding, screening, recruiting, and training job applicants.[21] Human Resources, or HR, is crucial for all businesses to succeed as it helps companies adjust to a fast-moving business environment and the increasing demand for jobs.[21]
The term «human resource» was first coined by John R. Commons in his novel The Distribution of Wealth. HR departments are relatively new as they began developing in the late 20th century. HR departments main goal is to maximize employee productivity and protecting the company from any issues that may arise in the future. Some of the most common activities conducted by those working in HR include increasing innovation and creativity within a company, applying new approaches to work projects, and efficient training and communication with employees.
Two of the most popular subdivisions of HR are Human Resource Management,[22] HRM, and Human Resource Information Systems, [23]or HRIS. The HRM route is for those who prefer an administrative role as it involves oversight of the entirety of the company. HRIS involves the storage and organization of employee data including full names, addresses, means of contact, and anything else required by that certain company.
Some careers of those involved in the Human Resource field include enrollment specialists, HR analyst, recruiter, employment relations manager, etc.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the production of merchandise for use or sale using labour and machines, tools, chemical and biological processing, or formulation. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale.
Marketing
Marketing is defined by the American Marketing Association as «the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.»[24] The term developed from the original meaning which referred literally to going to a market to buy or sell goods or services. Marketing tactics include advertising as well as determining product pricing.
With the rise in technology, marketing is further divided into a class called digital marketing. It is marketing products and services using digital technologies.
Research and development
Research and development refer to activities in connection with corporate or government innovation.[25] Research and development constitute the first stage of development of a potential new service or product.[26] Research and development are very difficult to manage since the defining feature of the research is that the researchers do not know in advance exactly how to accomplish the desired result.[26]
Safety
Injuries cost businesses billions of dollars annually.[27] Studies have shown how company acceptance and implementation of comprehensive safety and health management systems reduce incidents, insurance costs, and workers’ compensation claims.[28] New technologies, like wearable safety devices[29] and available online safety training, continue to be developed to encourage employers to invest in protection beyond the «canary in the coal mine» and reduce the cost to businesses of protecting their employees.
Sales
Sales are activity related to selling or the number of goods or services sold in a given time period. Sales are often integrated with all lines of business and are key to a companies’ success.[30]
Management
The efficient and effective operation of a business, and study of this subject, is called management. The major branches of management are financial management, marketing management, human resource management, strategic management, production management, operations management, service management, and information technology management. [31]
Owners may manage their businesses themselves, or employ managers to do so for them. Whether they are owners or employees, managers administer three primary components of the business’s value: financial resources, capital (tangible resources), and human resources. These resources are administered in at least six functional areas: legal contracting, manufacturing or service production, marketing, accounting, financing, and human resources.[citation needed]
Restructuring state enterprises
In recent decades, states modeled some of their assets and enterprises after business enterprises. In 2003, for example, China modeled 80% of its state-owned enterprises on a company-type management system.[32] Many state institutions and enterprises in China and Russia have transformed into joint-stock companies, with part of their shares being listed on public stock markets.
Business process management
Business process management (BPM) is a holistic management approach focused on aligning all aspects of an organization with the wants and needs of clients. BPM attempts to improve processes continuously. It can, therefore, be described as a «process optimization process». It is argued that BPM enables organizations to be more efficient, effective and capable of change than a functionally focused, traditional hierarchical management approach.[who?]
Organization and regulation
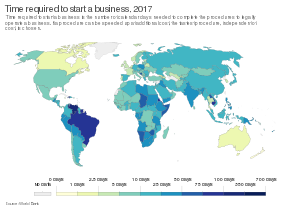
Time required to start a business in 2017[33]
Most legal jurisdictions specify the forms of ownership that a business can take, creating a body of commercial law for each type.
The major factors affecting how a business is organized are usually:
- The size and scope of the business firm and its structure, management, and ownership, broadly analyzed in the theory of the firm. Generally, a smaller business is more flexible, while larger businesses, or those with wider ownership or more formal structures, will usually tend to be organized as corporations or (less often) partnerships. In addition, a business that wishes to raise money on a stock market or to be owned by a wide range of people will often be required to adopt a specific legal form to do so.
- The sector and country. Private profit-making businesses are different from government-owned bodies. In some countries, certain businesses are legally obliged to be organized in certain ways.
- Tax advantages. Different structures are treated differently in tax law and may have advantages for this reason.
- Disclosure and compliance requirements. Different business structures may be required to make less or more information public (or report it to relevant authorities) and may be bound to comply with different rules and regulations.
- Control and coordination requirements. In function of the risk and complexity of the tasks to organize, a business is organized through a set of formal and informal mechanisms.[34][35] In particular, contractual and relational governance can help mitigate opportunism as well as support communication and information sharing.[35]
Many businesses are operated through a separate entity such as a corporation or a partnership (either formed with or without limited liability). Most legal jurisdictions allow people to organize such an entity by filing certain charter documents with the relevant Secretary of State or equivalent and complying with certain other ongoing obligations. The relationships and legal rights of shareholders, limited partners, or members are governed partly by the charter documents and partly by the law of the jurisdiction where the entity is organized. Generally speaking, shareholders in a corporation, limited partners in a limited partnership, and members in a limited liability company are shielded from personal liability for the debts and obligations of the entity, which is legally treated as a separate «person». This means that unless there is misconduct, the owner’s own possessions are strongly protected in law if the business does not succeed.
Where two or more individuals own a business together but have failed to organize a more specialized form of vehicle, they will be treated as a general partnership. The terms of a partnership are partly governed by a partnership agreement if one is created, and partly by the law of the jurisdiction where the partnership is located. No paperwork or filing is necessary to create a partnership, and without an agreement, the relationships and legal rights of the partners will be entirely governed by the law of the jurisdiction where the partnership is located. A single person who owns and runs a business is commonly known as a sole proprietor, whether that person owns it directly or through a formally organized entity. Depending on the business needs, an adviser can decide what kind is proprietorship will be most suitable.
A few relevant factors to consider in deciding how to operate a business include:
- General partners in a partnership (other than a limited liability partnership), plus anyone who personally owns and operates a business without creating a separate legal entity, are personally liable for the debts and obligations of the business.
- Generally, corporations are required to pay tax just like «real» people. In some tax systems, this can give rise to so-called double taxation, because first the corporation pays tax on the profit, and then when the corporation distributes its profits to its owners, individuals have to include dividends in their income when they complete their personal tax returns, at which point a second layer of income tax is imposed.
- In most countries, there are laws that treat small corporations differently from large ones. They may be exempt from certain legal filing requirements or labor laws, have simplified procedures in specialized areas, and have simplified, advantageous, or slightly different tax treatment.
- «Going public» through a process known as an initial public offering (IPO) means that part of the business will be owned by members of the public. This requires the organization as a distinct entity, to disclose information to the public, and adhering to a tighter set of laws and procedures. Most public entities are corporations that have sold shares, but increasingly there are also public LLC’s that sell units (sometimes also called shares), and other more exotic entities as well, such as, for example, real estate investment trusts in the US, and unit trusts in the UK. A general partnership cannot «go public».
Commercial law
A very detailed and well-established body of rules that evolved over a very long period of time applies to commercial transactions. The need to regulate trade and commerce and resolve business disputes helped shape the creation of law and courts. The Code of Hammurabi dates back to about 1772 BC for example and contains provisions that relate, among other matters, to shipping costs and dealings between merchants and brokers.[36] The word «corporation» derives from the Latin corpus, meaning body, and the Maurya Empire in Iron-Age India accorded legal rights to business entities.[37]
In many countries, it is difficult to compile all the laws that can affect a business into a single reference source. Laws can govern the treatment of labour and employee relations, worker protection and safety, discrimination on the basis of age, gender, disability, race, and in some jurisdictions, sexual orientation, and the minimum wage, as well as unions, worker compensation, and working hours and leave.
Some specialized businesses may also require licenses, either due to laws governing entry into certain trades, occupations or professions, that require special education or to raise revenue for local governments. Professions that require special licenses include law, medicine, piloting aircraft, selling liquor, radio broadcasting, selling investment securities, selling used cars, and roofing. Local jurisdictions may also require special licenses and taxes just to operate a business.
Some businesses are subject to ongoing special regulation, for example, public utilities, investment securities, banking, insurance, broadcasting, aviation, and health care providers. Environmental regulations are also very complex and can affect many businesses.
Capital
When businesses need to raise money (called capital), they sometimes offer securities for sale.[38]
Capital may be raised through private means, by an initial public offering or IPO on a stock exchange,[39] or in other ways.[38]
Major stock exchanges include the Shanghai Stock Exchange, Singapore Exchange, Hong Kong Stock Exchange, New York Stock Exchange and NASDAQ (the USA), the London Stock Exchange (UK), the Tokyo Stock Exchange (Japan), and Bombay Stock Exchange (India). Most countries with capital markets have at least one.
Businesses that have gone public are subject to regulations concerning their internal governance, such as how executive officers’ compensation is determined, and when and how information is disclosed to shareholders and to the public. In the United States, these regulations are primarily implemented and enforced by the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Other western nations have comparable regulatory bodies. The regulations are implemented and enforced by the China Securities Regulation Commission (CSRC) in China. In Singapore, the regulatory authority is the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS), and in Hong Kong, it is the Securities and Futures Commission (SFC).
The proliferation and increasing complexity of the laws governing business have forced increasing specialization in corporate law. It is not unheard of for certain kinds of corporate transactions to require a team of five to ten attorneys due to sprawling regulation. Commercial law spans general corporate law, employment and labor law, health-care law, securities law, mergers and acquisitions, tax law, employee benefit plans, food and drug regulation, intellectual property law on copyrights, patents, trademarks, telecommunications law, and financing.
Other types of capital sourcing include crowdsourcing on the Internet, venture capital, bank loans, and debentures.
Intellectual property
Businesses often have important «intellectual property» that needs protection from competitors for the company to stay profitable. This could require patents, copyrights, trademarks, or preservation of trade secrets.[40] Most businesses have names, logos, and similar branding techniques that could benefit from trademarking. Patents and copyrights in the United States are largely governed by federal law, while trade secrets and trademarking are mostly a matter of state law. Because of the nature of intellectual property, a business needs protection in every jurisdiction in which they are concerned about competitors. Many countries are signatories to international treaties concerning intellectual property, and thus companies registered in these countries are subject to national laws bound by these treaties. In order to protect trade secrets, companies may require employees to sign noncompete clauses which will impose limitations on an employee’s interactions with stakeholders, and competitors.
Trade union
A trade union (or labor union) is an organization of workers who have come together to achieve common goals such as protecting the integrity of its trade, improving safety standards, achieving higher pay and benefits such as health care and retirement, increasing the number of employees an employer assigns to complete the work, and better working conditions.[41] The trade union, through its leadership, bargains with the employer on behalf of union members (rank and file members) and negotiates labor contracts (collective bargaining) with employers.[41] The most common purpose of these associations or unions is «maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment».[42] This may include the negotiation of wages, work rules, complaint procedures, rules governing hiring, firing, and promotion of workers, benefits, workplace safety and policies.
See also
- Accounting
- List of accounting topics
- Advertising
- Bank
- Big business
- Business acumen
- Business broker
- Business ethics
- Social responsibility
- Business hours
- Business law topics
- Business mathematics
- Business mediator
- Business school
- Business tourism
- Business valuation
- Businessperson
- Capitalism
- Change management analyst
- Commerce
- Company
- Corporate personhood
- Cost overrun
- E-commerce
- Electronic business
- Economics
- Economic democracy
- Financial economics
- List of economics topics
- Entrepreneurship
- Finance
- List of finance topics
- Franchising
- Government ownership
- Human resources
- Industry categories
- Innovation
- Insurance
- Intellectual property
- Interim management
- International trade
- List of international trade topics
- Investment
- Job creation program
- Labour economics
- Limited liability
- List of company registers
- List of largest employers
- List of oldest companies
- Lists of companies
- Management information system
- Manufacturing
- List of production topics
- Marketing
- List of marketing topics
- Money
- Organizational studies
- Profit
- Real estate
- List of real estate topics
- Revenue shortfall
- Shareholder value
- Small business
- Strategic management
- Strategic planning
- Tax
- Trade
- Types of business entity
References
- ^ American Heritage Dictionary. Archived from the original on March 31, 2019.
business [:] 1. The activity of buying and selling commodities, products, or services.
- ^ Longman Business English Dictionary (2nd ed.). Pearson Longman. 2007. ISBN 9781405852593. OCLC 954137383.
- ^ Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English. Archived from the original on July 9, 2019.
business [:] 1 […] the activity of making money by producing or buying and selling goods, or providing services.
- ^ Oxford Living Dictionaries. Archived from the original on May 1, 2019.
business [:] 2 The practice of making one’s living by engaging in commerce.
- ^ Burton, William (2007). Burton’s Legal Thesaurus (4th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education. p. 68. ISBN 9780071472623. OCLC 70864526.
- ^ «Definition of POSSESSION». www.merriam-webster.com. Retrieved 2022-11-20.
- ^ Holloway, S. S.; Parmigiani, A. (2014). «Friends and Profits Don’t Mix: The Performance Implications of Repeated Partnerships». Academy of Management Journal. 59 (2): 460. doi:10.5465/amj.2013.0581. S2CID 168091169.
- ^ «Choose a business structure». Small Business Administration. Archived from the original on 2020-10-30. Retrieved 2021-05-13.
- ^ Gleeson, Patrick. «Definition of a Franchise Business». Small Business — Chron.com. Archived from the original on 2016-11-26. Retrieved 2016-11-25.
- ^ Welsh, Dianne H. B.; Desplaces, David E.; Davis, fAmy E. (2011). «A Comparison of Retail Franchises, Independent Businesses, and Purchased Existing Independent Business Startups: Lessons from the Kauffman Firm Survey». Journal of Marketing Channels. 18: 3. doi:10.1080/1046669X.2011.533109. S2CID 154304180.
- ^ Black’s Law and lee Dictionary. Second Pocket Edition. Bryan A. Garner, editor. West. 2001.
- ^ Companies Act 2006
- ^ Hargrave, Marshall. «What Public Limited Company (PLC) Means in the U.K.» Investopedia. Archived from the original on 2018-07-06. Retrieved 2018-07-06.
- ^ Needles, Belverd E.; Powers, Marian (2013). Principles of Financial Accounting. Financial Accounting Series (12 ed.). Cengage Learning.
- ^ Accounting Research Bulletins No. 7 Reports of Committee on Terminology (Report). Committee on Accounting Procedure, American Institute of Accountants. November 1940. Archived from the original on 7 January 2014. Retrieved 31 December 2013.
- ^ DIWAN, Jaswith. ACCOUNTING CONCEPTS & THEORIES. LONDON: MORRE. pp. 001–002. id# 94452.
- ^ Peggy Bishop Lane on Why Accounting Is the Language of Business, Knowledge @ Wharton High School, September 23, 2013, archived from the original on 13 June 2018, retrieved 25 December 2013
- ^ «Department of Accounting». Foster School of Business. Foster School of Business. 2013. Archived from the original on 19 March 2015. Retrieved 31 December 2013.
- ^ «Commerce». Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- ^ CFI. «What is Finance?». Archived from the original on 7 April 2020. Retrieved 7 April 2020.
- ^ a b «Human Resources (HR) Meaning and Responsibilities». Investopedia. Retrieved 2022-11-29.
- ^ «What is HR (Human Resource Management)?». TheBalance. Retrieved 2022-11-29.
- ^ «What is an HRIS (Human Resource Information System)?». SearchHRSoftware. Retrieved 2022-11-29.
- ^ Marketing definition approved in October 2007 by the American Marketing Association: [1] Archived 2010-12-27 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Kenton, Will. «Why Research and Development (R&D) Matters». Investopedia. Archived from the original on 2018-07-10. Retrieved 2020-06-12.
- ^ a b «Research and development». Encyclopedia Britannica. Archived from the original on 2020-10-03. Retrieved 2020-06-12.
- ^ Leigh, J. (2011). Economic Burden of Occupational Injury and Illness in the United States. Milbank Quarterly, 89(4), 728-772. doi:10.1111/j.1468-0009.2011.00648.x
- ^ Rowe, Kelly P. (2007). OSHA and small businesses: A winning combination: When small businesses tap into OSHA’s many resources, everyone benefits. Occupational Hazards, 69(3), 33.
- ^ Goldberg, S. (2016). Business Technical: Wearable Devices at Work. Business Insurance, 50(2), 1.
- ^ «How To Organize Your Marketing Department In The Digital Age». Archived from the original on April 26, 2018. Retrieved October 15, 2018.
- ^ «What Are the Branches of Business Management?». business.com. Retrieved 2022-11-26.
- ^ Major Industries Archived 2008-06-11 at the Wayback Machine. People.com
- ^ «Time required to start a business». Our World in Data. Archived from the original on 23 November 2020. Retrieved 7 March 2020.
- ^ Poppo, Laura; Zenger, Todd (2002). «Do formal contracts and relational governance function as substitutes or complements?». Strategic Management Journal. 23 (8): 707–725. doi:10.1002/smj.249. ISSN 1097-0266. Archived from the original on 2021-03-08. Retrieved 2020-09-05.
- ^ a b Long, Chris P.; Sitkin, Sim B. (2018). «Control–Trust Dynamics in Organizations: Identifying Shared Perspectives and Charting Conceptual Fault Lines». Academy of Management Annals. 12 (2): 725–751. doi:10.5465/annals.2016.0055. ISSN 1941-6520. S2CID 150017645. Archived from the original on 2022-03-03. Retrieved 2020-09-05.
- ^ «Law Code of Hammurabi». Archived from the original on 2013-10-19. Retrieved 2013-10-18.
- ^ Vikramaditya S. Khanna. «The Economic History of the Corporate Form in Ancient India» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-10-19.
- ^ a b Hargrave, Marshall. «What Is Capital?». Investopedia. Archived from the original on 11 August 2021. Retrieved 21 January 2021.
- ^ «What is Ipo? Definition of Ipo, Ipo Meaning». The Economic Times. Archived from the original on 10 August 2021. Retrieved 21 January 2021.
- ^ «What is Intellectual Property (IP)?». www.wipo.int. Archived from the original on 22 January 2021. Retrieved 21 January 2021.
- ^ a b «What is Trade Union? Definition of Trade Union, Trade Union Meaning». The Economic Times. Archived from the original on 1 February 2021. Retrieved 21 January 2021.
- ^ Webb, Sidney; Webb, Beatrice (1920). History of Trade Unionism. Longmans and Co. London. ch. I
External links
often attributive
1
a
: a usually commercial or mercantile activity engaged in as a means of livelihood : trade, line
in the restaurant business
b
: a commercial or sometimes an industrial enterprise
c
: dealings or transactions especially of an economic nature : patronage
took their business elsewhere
2
a
: role, function
how the human mind went about its business of learning—
c
: a particular field of endeavor
4
b
: right
you have no business speaking to me that way
5
a
: serious activity requiring time and effort and usually the avoidance of distractions
7
: movement or action (such as lighting a cigarette) by an actor intended especially to establish atmosphere, reveal character, or explain a situation
called also
stage business
9
: a bowel movement
—used especially of pets
10
archaic
: purposeful activity : busyness
Synonyms
Choose the Right Synonym for business
business, commerce, trade, industry, traffic mean activity concerned with the supplying and distribution of commodities.
business may be an inclusive term but specifically designates the activities of those engaged in the purchase or sale of commodities or in related financial transactions.
commerce and trade imply the exchange and transportation of commodities.
industry applies to the producing of commodities, especially by manufacturing or processing, usually on a large scale.
traffic applies to the operation and functioning of public carriers of goods and persons.
synonyms see in addition
work
Example Sentences
Forever Odd is a direct sequel to 2003’s Odd Thomas, the book in which we were introduced to the title character, a young man who can see the dead. They can’t talk to him, but they can nudge him in the direction they want, which is usually to help them tidy up some unfinished business from when they were alive.
—
The Sun may never set, but air temperatures can plummet to -4 degrees Fahrenheit, and blinding snowstorms appear without warning. Sunbathing here can be risky business: even huddled in our parkas and boots, the members of our expedition live under the constant threat of frostbite and hypothermia.
—
Such high attrition means that most of the dot-coms here today will be gone tomorrow. The business environment is already harsh, and competition is growing.
—
Lancaster and Columbia have plenty of history apart from the Civil War, of course. For example, Lancaster was home to F. W. Woolworth’s first successful 5&10 and Milton S. Hershey’s first successful candy business.
—
The store has lost a significant amount of business since the factory closed.
She works in the publishing business.
David has decided to go into business with his brother.
Their publishing company is the best in the business.
I have to go to New York City on business next week.
They advertised to increase business.
He has the skills necessary to run a business.
The town is trying to attract new businesses.
Do we have any other business we need to discuss?
No, I didn’t ask him what he wanted the car for. That’s his business.
See More
Recent Examples on the Web
Sandeep Arora, 48, of Naperville, picked up the woman and a friend at a Naperville business in July 2017, according to a DuPage County State’s Attorney’s Office account of the evidence.
—
Enter Email Sign Up On March 1, Atwood’s owners Patrick and Ryan Magee posted a notice on their website explaining that the final day of the month would be their last in business.
—
Corner Charcuterie chef, Atlas bartender team up Bernard Dehaene was retired from the restaurant business and living on a boat in Canton with his rescue dog Lou when Octavio Vazquez approached him with an enticing new opportunity to return to the chef’s life.
—
The memory business has long been one of volatile swings, but Micron hasn’t seen a sustained sales downturn of the same degree since the industry was reeling from the dot-com crash in 2001, according to data from S&P Global Market Intelligence.
—
Vigil’s ancestors arrived in this valley 12 generations ago, and in 1939 his grandfather bought two acres and turned an old dance hall into a funeral business.
—
Then, the television landscape was dominated by the big four national networks, Netflix was a mail-order DVD rental business, and Apple’s hot product was the iPod Mini.
—
Growing up with a family in the restaurant business, Stefani was able to combine her nutrition expertise with culinary skills taught to her by her mother and grandmother.
—
Got a tip about the healthcare business?
—
See More
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word ‘business.’ Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
Etymology
Middle English bisynesse, from bisy busy + -nesse -ness
First Known Use
14th century, in the meaning defined at sense 10
Time Traveler
The first known use of business was
in the 14th century
Dictionary Entries Near business
Cite this Entry
“Business.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary, Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/business. Accessed 13 Apr. 2023.
Share
More from Merriam-Webster on business
Last Updated:
1 Apr 2023
— Updated example sentences
Subscribe to America’s largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!
Merriam-Webster unabridged
Britannica Dictionary definition of BUSINESS
1
[noncount]
a
:
the activity of making, buying, or selling goods or providing services in exchange for money
-
The store will be open for business next week. [=the store will be ready for customers next week]
-
The store has lost a significant amount of business since the factory closed.
-
Allowing customers to leave your store unsatisfied is bad (for) business.
-
The new Web site has been good for (attracting) business.
-
What line of business [=work] are you in?
-
She works in the publishing business.
-
the fashion/music/restaurant business
-
We do business with [=sell to or buy from] companies overseas.
-
David has decided to go into business with his brother.
-
Remember that your customers can take their business elsewhere. [=your customers can go to another place to do business]
-
Their publishing company is the best in the business.
-
a place of business [=a place, such as a store, bank, etc., where business is done]
— often used before another noun
-
business opportunities/contacts/interests
-
The business world is responding to changes in technology. [=businesses are responding to changes in technology]
-
Someone will be available to answer your call during regular business hours. [=the hours that the office is open to do business]
-
a business meeting [=a meeting at which matters of business are discussed]
—
see also agribusiness, big business, in business (below), out of business (below), show business
b
:
work that is part of a job
-
Is your trip to Miami (for) business or pleasure?
-
I have to go to New York City on/for business next week.
— sometimes used before another noun
-
a business trip [=a trip that is made in order to do business]
-
I am flying business class [=in a seating section of an airplane that is more expensive than the main section but less expensive than first class] from Tokyo to New York.
c
:
the amount of activity that is done by a store, company, factory, etc.
-
Business has been slow/bad lately. [=there have been few customers, sales, etc., lately]
-
Business was good/booming.
-
They advertised to increase business.
-
How is business?
2
[count]
:
an organization (such as a store, company, or factory) that makes, buys, or sells goods or provides services in exchange for money
-
He has the skills necessary to run/operate/start a business.
-
The town is trying to attract new businesses.
-
local businesses
-
She joined the family business [=the business owned or operated by her family] after graduating from college.
— sometimes used before another noun
-
I had lunch with some business associates.
-
In addition to being married, the two are also business partners.
-
The restaurant is in the business district. [=the part of a city or town where there are many businesses]
-
the business community [=people involved in the upper levels of businesses]
3
[singular]
:
something that concerns a particular person, group, etc.
:
something that needs to be considered or dealt with
-
Do we have any other business we need to discuss?
-
Air quality is a serious business. [=air quality is something people should think about seriously]
-
What’s this business [=news] I hear about you moving away?
-
Educating students is the business [=responsibility] of schools.
-
No, I didn’t ask him what he wanted the car for. That’s his business.
-
I won’t answer that question. Who I choose to vote for is my business.
-
He’s decided to make it his business [=make it his goal] to bring more affordable housing to the city.
-
“Who did you vote for?” “That’s none of your business.” [=that’s private information that you should not be asking about]
-
It’s no business of yours who I voted for.
◊ The phrase mind your own business is used as an informal and often somewhat impolite way to tell someone to stop watching or asking about something that is private.
-
Mind your own business and let them talk alone.
◊ To say that you were minding your own business when something happened means that you were doing what you normally do and were not bothering anyone.
-
I was walking down the street, minding my own business, when all of a sudden some man started yelling at me.
◊ If you say something is nobody’s business, you mean that it is private and other people do not need to know about it.
-
It’s nobody’s business what we were talking about.
◊ Someone who has no business doing something has no right to do it.
-
You have no business telling me what I can and cannot wear! I’ll wear whatever I like!
4
[noncount]
:
something that must be done
-
I have some business in town Friday afternoon. [=I have to do something in town Friday afternoon]
-
He had to leave the meeting early because he had to attend to some unfinished business. [=something not done that needs to be done]
-
Now that we’ve all introduced ourselves, let’s get down to business. [=start doing what needs to be done, start working]
-
I was just going about my business [=doing what I usually do], when I heard a big crash.
-
Sarah is good at taking care of business [=doing what needs to be done], so she’s been put in charge of organizing the event.
-
The church has hired someone to take care of the bills and all that business. [=everything else that needs to be done]
-
A public library is in the business of providing information to the public. [=the job/purpose of a public library is to provide information]
-
I’m not in the business of lending money to people I hardly know. [=I don’t lend money to people I hardly know]
5
[singular]
:
a matter, event, or situation
— usually used after an adjective
-
Divorce can be such a messy business. [=affair]
-
The earthquake was a terrible business.
-
Predicting how people will react to something is a tricky business.
-
Investing all your money in one stock is (a) very risky business.
-
“How long did the ceremony take?” “Oh, the whole business was over in less than an hour.”
-
Let’s just forget about that business of me being unhappy with my job.
—
see also monkey business
business as usual
— used to say that something is working or continuing in the normal or usual way
-
Much of the town lost electricity in the storm, but for people with generators it was business as usual.
-
As the election nears, both political parties continue to blame each other for all the city’s problems. In other words, it’s business as usual.
business is business
— used to say that in order for a business to be successful it is necessary to do things that may hurt or upset people
-
I’m sorry I have to let you go, but understand that business is business.
in business
1
:
operating as a business
-
The hotel has been in business for over 150 years.
-
Customer satisfaction is important if you want to stay in business.
2
informal
:
ready to begin doing or using something
-
Just plug in the computer and you’re in business! [=you will be able to use the computer]
-
All the musicians have finally arrived, so we’re in business!
-
He quickly changed the tire, and was back in business [=ready to drive again] in 10 minutes.
like nobody’s business
informal
:
very well or quickly or in very large amounts
-
She can design computer programs like nobody’s business.
-
It’s been raining like nobody’s business.
mean business
:
to be serious about doing something
-
We thought he was joking at first, but then we saw that he really meant business.
out of business
:
closed down
:
no longer in business
-
My favorite flower shop is out of business.
-
Small grocery stores are being driven/forced/put out of business by large stores. [=small grocery stores cannot compete with large stores and so are closing permanently]
-
The store has gone out of business. [=has closed]
the business
British slang
:
a very good or impressive person or thing
-
Since he’s won the tournament, he thinks he’s the business. [=the best]
-
You should see their new flat. It’s the business.
Business is a
word which is commonly used in many different languages. But exactly
what does it mean? The concepts and activities of business have
increased in modern times. Traditionally, business simply meant
exchange or trade for things people wanted or needed. Today it has a
more technical definition.
One
definition of business is the production, distribution, and sale of
goods and services for a profit. To examine this definition, we will
look at its various parts.
First,
production is the creation of services or the changing of materials
into products. One example is the conversion of iron ore into metal
car parts. Next these products need to be moved from the factory to
the marketplace. This is known as distribution. A car might be moved
from a factory in Detroit to а
car dealership in Miami.
Third is the
sale of goods and services. Sale is the exchange of a product or
service for money. A car is sold to someone in exchange for money.
Goods are products which people either need or want; for example,
cars can be classified as goods. Services, on the other hand, are
activities which a person or group performs for another person or
organisation. For instance, an auto-mechanic performs a service when
he repairs a car. A doctor also performs a service by taking care of
people when they are sick.
Business then,
is a combination of all these activities: production, distribution,
and sale. However, there is one other important factor. This factor
is the creation of profit or economic surplus. A major goal in the
functioning of an American business company is making a profit.
Profit is the money that remains after all the expenses are paid.
Creating an economic surplus or profit is, therefore, a primary goal
of business activity.
Translation
Что такое бизнес?
Бизнес
— слово, которое обычно используется на
многих различных языках. Но что это
точно означает? Понятия и действия
бизнеса увеличились в современные
времена. Традиционно, бизнес просто
означал обмен или торговлю вещами,
которые были желанны или необходимы
людям. Сегодня для этого есть более
техническое определение.
Одно
определение бизнеса — производство,
распределение и продажа товаров и услуг
для прибыли. Чтобы исследовать это
определение, мы будем смотреть на его
различные части.
Во-первых,
производство — создание услуг или
изменение материалов в продуктах. Один
пример — преобразование железной руды
в металлические автозапчасти. Затем
эти продукты должны быть перемещены с
фабрики на рынок. Это известно как
распределение. Автомобиль должен быть
перемещен из фабрики в Детройте в
автомобильное представительство в
Майами.
Третье
— продажа товаров и услуг. Продажа — обмен
продуктов или обслуживания на деньги.
Автомобиль продан кому-то в обмен на
деньги. Товары — продукты, в которых люди
или нуждаются или хотят; например,
автомобили могут быть классифицированы
как товары. Услуги, с другой стороны,
являются действиями, которые человек
или группа выполняют для другого человека
или организации. Например, автомеханик
выполняет обслуживание, когда он
ремонтирует автомобиль. Доктор также
выполняет обслуживание, заботясь о
людях, когда они больны.
Бизнес
тогда, это комбинация всех этих действий:
производство, распределение, и продажа.
Однако есть один другой важный фактор.
Этот фактор — создание прибыли или
экономического излишка. Главная цель
в функционировании американской деловой
компании получать прибыль. Прибыль —
деньги, которые остаются после того,
как все расходы заплачены. Создание
экономических излишков или прибыли
является, следовательно, основной целью
коммерческой деятельности
COMPREHENSION
A.
Answer the following questions about the meaning of business. The
questions which are starred (*) cannot be answered directly from the
text. Space is provided at the end for you to add your own questions.
-
What is one
modern definition of business?
Business
is the production, distribution, and sale of goods and services for a
profit.
2.
*How does this modern meaning of business differ from the traditional
one? *What factors have brought about these changes?
Traditionally,
business simply meant exchange or trade for things people wanted or
needed. In modern definition profit reception is target of business.
Development manufactory, industrial production, development of trade
relations, change of principles of economic policy are factors which
brought about these changes.
3.
What does production involve?
Production
involves creation of services or the changing of materials into
products
4. What
example of distribution is given in the reading? Can you think of
another example from real life?
A
car might be moved from a factory in Detroit to a car dealership in
Miami. Sugar might be moved from a plant in Skidel to a shop in
Minsk.
5.
How do goods differ from services?
Goods
are products which people either need or want; for example, cars can
be classified as goods. Services, on the other hand, are activities
which a person or group performs for another person or organization.
6.
In addition to production, distribution, and sale, what other factor
is important in defining business?
This
factor is the creation of profit or economic surplus
7.
What is profit? *In general, what do companies do with their profits?
Profit
is the money that remains after all the expenses are paid
8.
Compare your definition of business with the one given in the
reading. *How are they similar? *In what ways does your definition
differ from the one presented in the text?
9.
Additional questions____________________
B.
Determine which of the following statements true and which are false.
Then put T or F in the blanks. Correct those statements which are
false by rewriting them.
-
Additional
questions
-
Bring
examples of the goods and examples of services. -
What
is the distribution? -
What
is the largest manufactures in your city? -
Distribution
is included in definition of business, isn’t it? -
What
is meant services?
-
Determine
which of the following statements true and which are false. Then put
T or F in the blanks. Correct those statements which are false by
rewriting them.
-
(
T )
Business is not just one activity but a combination of different
operations such as production, distribution and sale. -
(
F )
From ancient to modern times the definition of business has remained
the same.
-
(
F )
Moving a truckload of oranges from the orchard to the supermarket is
an example of production.
-
(
T )
A sales clerk provides a service by answering customers’ questions.
VOCABULARY
EXERCISES
-
Look
at the terms in the left-hand column and find the correct synonyms
in the right-hand column. Copy the corresponding letters in the
blanks.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
Fill
in the blanks with noun or verb forms. Use your dictionary if
necessary.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
Use
the correct noun or verb form in the sentences. Change the
grammatical form of the words if necessary.
-
sell
a.
An annual report includes the sale’s
figures of the company for the current year.
b.
An auto dealership sells
cars, trucks, vans, and something recreational vehicles.
-
distribute
a.
Some companies hold exclusive distributive
rights for specific products.
b.
Factory representatives distribute
products to wholesalers and retailers.
-
produce
a.
How efficiently a company produce
its products will in large measure determine its success.
b.
The production
of high-technology instruments is one of the most rapidly growing
industries in the 1980s.
-
classify
a.
Items classify
in order to show the relationship between them.
b.
Classification means the grouping of items to show the difference
between them.
-
convert
a.
When travelling from country to country on either business or
leisure, people convert one currency to another.
b.
The production process often involves the convert raw materials into
finished products.
CLASSIFICATION
Classification
means the grouping of items to show the relationship between them.
Items that are classified together have something in common: that in,
something must apply to all the items in that group or class. Look at
the items below. They may be classified as either goods or services.
Review the definitions and examples given in the reading (lines
17-20). Classify the following items as either goods, or services.
|
1. |
машина |
goods |
|
2. |
медицинский |
services |
|
3. |
туристическое |
services |
|
4. |
портфель |
goods |
|
5. |
ремонт |
services |
|
6. |
финансовое |
services |
|
7. |
компьютер |
goods |
|
8. |
видеомагнитофон |
goods |
|
9. |
консультант |
services |
|
10. |
бухгалтерская |
goods |
|
11. |
калькулятор |
goods |
|
12. |
работа |
services |
|
13. |
костюм |
goods |
|
14. |
грузоподъемник |
goods |
|
15. |
ремонт |
services |
|
16. |
доставка |
services |
|
17. |
компьютерное |
services |
|
18. |
табельные |
goods |
|
19. |
кодекс |
goods |
|
20. |
подготовка |
services |
APPLICATION
-
Match
these parts of the business definition to the following real-life
situations.
production
of goods distribution of goods
sale
of goods sale of services
Examples:
Iron
ore is made into metal car parts production of goods
A
salesman sells a car sale of goods
An
auto mechanic repairs a car sale of services
|
1. |
distribution |
|
. |
|
|
2. |
production |
|
3. |
sale |
|
4. |
distribution |
|
5. |
production |
CAREERS
IN BUSINESS
PREREADING
ACTIVITY
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
the occupation and skills of a confectioner
the occupation of athletes who compete for pay
agriculture considered as an occupation or way of life
your occupation or line of work
the particular occupation for which you are trained
the occupation for which you are paid
the job to which you are (or hope to be) appointed
a job in an organization
a job involving drudgery and confinement
the skilled practice of a practical occupation
an occupation requiring special education (especially in the liberal arts or sciences)
an occupation for which you are especially well suited
the occupation of maintaining and auditing records and preparing financial reports for a business
the occupation of taking and printing photographs or making movies
providing food and services
a job, especially a temporary job
the job of a professional coach
employment for performers or performing groups that lasts for a limited period of time
the work of a minister of religion
the work of a sailor
boxing for money
wrestling for money
a Japanese form of wrestling; you lose if you are forced out of a small ring or if any part of your body (other than your feet) touches the ground
playing golf for money
football played for pay
playing baseball for money
playing basketball for money
playing tennis for money
work that a person is expected to do in a specified time
work paid for according to the quantity produced
the special line of work you have adopted as your career
the principal work of your career
careers in general
employment in or work for another
employment at home while communicating with the workplace by phone or fax or modem
performance of duties or provision of space and equipment helpful to others
employment within a government system (especially in the civil service)
the position of member of an honorary academy
the position of accountant
the office of admiral
the post of ambassador
the position of apostle
the position of apprentice
the position of associate (as in an office or academy)
the position of attorney
the office of bailiff
the state of a baronet
the office and dignity of a bishop
the position of cadet
the office of a caliph
the post of captain
the office of cardinal
the position of chairman
the office of chancellor
the position of chaplain
the position of chieftain
the job of clerk
the position or office of commander
the position of comptroller
the post of consul
the position of controller
the position of council member
the position of counselor
the position of a curate
the position of curator
the position of custodian
the position or office of a dean
the position of a director of a business concern
the position of disciple
the position of editor
the office of elder
the office of an emir
the status of a father
the status of a religious leader
the position of foreman
the office and authority of a general
the office of governor
the position of head
the position of headmaster or headmistress
a difficult position where you are subjected to stress and criticism
the office of an incumbent
the office of inspector
the position of instructor
the position of a medical intern
the position of judge
the position of a khan
the post of lecturer
the post or office of legate
the office of legislator
the position of librarian
the position of a lieutenant
the position of magistrate
the position of manager
the status of being a man
the post of marshall
the position of master
the position of mayor
the position of messiah
the position of moderator
the position of overlord
the position of pastor
the state of being a peasant
a highly desirable position or assignment
the office of praetor
the position of precentor
the position of preceptor
the office of prefect
the office or station of a prelate
the office of premier
the office and function of president
the office of primate
the post of principal
the office of prior
the position of proconsul
the position of proctor
the position of professor
the position of protector
a position concerning the people as a whole
the office or function of a rabbi
the office of a receiver
the office or station of a rector
the office of a regent
the position of physician who is receiving special training in a hospital (usually after completing an internship)
the position of ruler
the status and dignity of a saint
the position of secretary
the position and authority of a feudal lord
the office of senator
an office that involves minimal duties
the position of solicitor
the position of Speaker
the position of steward
the position of student
the position of teacher
the position of thane
the position and power of an exalted person (a sovereign or bishop) who is entitled to sit in a chair of state on ceremonial occasions
the position of treasurer
the position of tribune
the position of trustee
the office and function of a vice president
the position of viceroy
the position of vizier
the position of warden
the position of warder
the status of a woman
a career in industrial or commercial or professional activities
the craft of building and repairing airplanes
the craft of building and repairing automobiles
the craft of basket making
the craft of a carpenter: making things out of wood
the craft of drawing blueprints
the craft of making dresses
the craft of an electrician
the trade of planning the layout and furnishings of an architectural interior
the trade of cutting or preparing or selling timber
the craft of a mason
the craft of an oculist
the occupation of a house painter
the craft of making paper
the occupation of a pilot
the occupation of a plumber (installing and repairing pipes and fixtures for water or gas or sewage in a building)
the craft of making earthenware
one of the three professions traditionally believed to require advanced learning and high principles
the profession or art of a writer
the profession of designing buildings and environments with consideration for their esthetic effect
the profession of teaching (especially at a school or college or university)
the profession of reporting or photographing or editing news stories for one of the media
the profession devoted to governing and to political affairs
the craft of making fireworks
the shoemaker’s trade
the craft of a roofer
the craft of doing sheet metal work (as in ventilation systems)
the laying on of shingles
the occupation of a tailor
the craft of making special tools and dies
keeping account of the costs of items in production
the activity of recording business transactions
accounting that controls and evaluates inventory
a craft that requires skillful hands
the job of delivering newspapers regularly
act or process of minting coins
making leather from rawhide
the practical application of science to commerce or industry
the craft of composing type and printing from it
the trade of a funeral director
the craft of upholstering
the craft and science of growing grapes and making wine