From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Network, networking and networked may refer to:
Science and technology[edit]
- Network theory, the study of graphs as a representation of relations between discrete objects
- Network science, an academic field that studies complex networks
Mathematics[edit]
- Networks, a graph with attributes studied in network theory
- Scale-free network, a network whose degree distribution follows a power law
- Small-world network, a mathematical graph in which most nodes are not neighbors, but have neighbors in common
- Flow network, a directed graph where each edge has a capacity and each edge receives a flow
Biology[edit]
- Biological network, any network that applies to biological systems
- Ecological network, a representation of interacting species in an ecosystem
- Neural network, a network or circuit of neurons
Technology and communication[edit]
- Artificial neural network, a computing system inspired by animal brains
- Broadcast network, radio stations, television stations, or other electronic media outlets that broadcast content from a centralized source
- News network
- Radio network, including both broadcast and two-way communications
- Television network, used to distribute television program content
- Electrical network, an interconnection of electrical components
- Social networking service, an online platform that people use to build social networks
- Telecommunications network, allowing communication between separated nodes
- Computer network or data network, a digital telecommunications network
- Network hardware: Network switch, Ethernet cables
- Wireless network, a computer network using wireless data connections
- Computer network or data network, a digital telecommunications network
- Network (typeface), used on the transport network in the West Midlands, UK
Sociology and business[edit]
- Social network, in social science research
- Scientific collaboration network, a social network wherein nodes are scientists and links are co-authorships
- Social group, a network of people
- Network of practice, a social science concept
- Business networking, the sharing of information or services between people, companies or groups
- Personal networking, the practice of developing and maintaining a personal network
- Supply network, a pattern of temporal and spatial processes carried out at facility nodes and over distribution links
- Transport network, a network in geographic space
Arts, entertainment and media[edit]
- Network (1976 film), a 1976 American film
- Network (2019 film), an Indian film
- Network (album), a 2004 album by Saga
- Network (comics), a series of Marvel Comics characters
- Network (play), a 2017 play based on the 1976 film
- Network (TV series), a Canadian variety television series
- Network (video game), a 1980 business simulation game for the Apple II
- Network, aka Taryn Haldane, a fictional character and member of the Sovereign Seven comic book series
- Network, the members’ newsletter of the British Sociological Association
- The Network, an American new wave band
- «The Network», a 1987 Matlock episode
- The Network, a fictional organization in the comic strip Modesty Blaise
- «Networking», a song by We Are the Physics from We Are the Physics Are OK at Music
Organizations[edit]
- NETWORK (Slovak party), a political party in Slovakia
- Network (lobby group), an American social justice group
- The Network (political party), an Italian political party (1991–1999)
- The Network (professional wrestling), a professional wrestling stable
- The Network 2018, an Italian political party (2011–present)
- Network (Russia), allegedly an anti-government anarchist organization active in Russia in 2015–2017
See also[edit]
- List of university networks
- Nettwerk, Nettwerk Music Group, a record label
- Netzwerk (disambiguation)
- Networked: The New Social Operating System, a 2012 book
When you buy a new computer, the first thing you’ll probably try to do is connect to the Internet. To do this, you establish a connection to your router, which receives the data from the Internet and then forwards it to the computer.
Of course that’s not all: Next, you could also connect your printer, smartphone or TV to the router so that these devices are also connected to the Internet. Now you have connected different devices to each other via a central access point and created your own network.
But what exactly does that mean?
Contents
- What is a network?
- Network example: your home Wi-Fi
- What are the tasks and advantages of a network?
- How does a network work?
- Client-server architecture
- Network protocols
- Network addresses
- What types of networks are there?
- Wireless vs. wired
- Network range
$1 Domain Names
Register great TLDs for less than $1 for the first year.
Why wait? Grab your favorite domain name today!
Matching email
SSL certificate
24/7/365 support
In information technology, a network is defined as the connection of at least two computer systems, either by a cable or a wireless connection. The simplest network is a combination of two computers connected by a cable. This type of network is called a peer-to-peer network. There is no hierarchy in this network; both participants have equal privileges. Each computer has access to the data of the other device and can share resources such as disk space, applications or peripheral devices (printers, etc.).
Today’s networks tend to be a bit more complex and don’t just consist of two computers. Systems with more than ten participants usually use client-server networks. In these networks, a central computer (server) provides resources to the other participants in the network (clients).
Definition: Network
A network is a group of two or more computers or other electronic devices that are interconnected for the purpose of exchanging data and sharing resources.
Network example: your home Wi-Fi
The Wireless LAN (Wireless Local Area Network, i.e. the Wi-Fi network) in your home is a good example of a small client-server network. The various devices in your home are wirelessly connected to the router, which acts as a central node (server) for the household. The router itself is connected to a much larger network: the Internet.
Since the devices are connected to the router as clients, they are part of the network and can use the same resource as the server, namely the Internet. The devices can also communicate with each other without having to establish a direct connection to each device. For example, you can send a print job to a Wi-Fi-enabled printer without first connecting the printer to the computer using a cable.
Before the advent of modern networks, communication between different computers and devices was very complicated. Computers were connected using a LAN cable. Mechanical switches were used so that peripheral devices could also be shared. Due to physical limitations (cable length), the devices and computers always had to be very close to each other.
Note
If you need an extremely stable connection you should consider the possibility of a wired connection to the router or device, despite the advantages of Wi-Fi.
What are the tasks and advantages of a network?
The main task of a network is to provide participants with a single platform for exchanging data and sharing resources. This task is so important that many aspects of everyday life and the modern world would be unimaginable without networks.
Here’s a real-life example: In a typical office, every workstation has its own computer. Without a network of computers, it would be very difficult for a team to work on a project since there would be no common place to share or store digital documents and information, and team members would not be able to share certain applications.
In addition, many offices only have one printer or a few printers that are shared by everyone. Without a network, the IT department would have to connect every single computer to the printer, which is difficult to implement from a technical standpoint. A network elegantly solves this problem because all computers are connected to the printer via one central node.
The main advantages of networks are:
- Shared use of data
- Shared use of resources
- Central control of programs and data
- Central storage and backup of data
- Shared processing power and storage capacity
- Easy management of authorizations and responsibilities
How does a network work?
In a typical client-server network there is a central node called the server. The server is connected to the other devices, which are called clients. This connection is either wireless (Wireless LAN) or wired (LAN).
In a typical home network, the router assumes the role of the server. It is connected to the Internet and provides the “Internet” resource for the other devices (computers, smartphones, etc.).
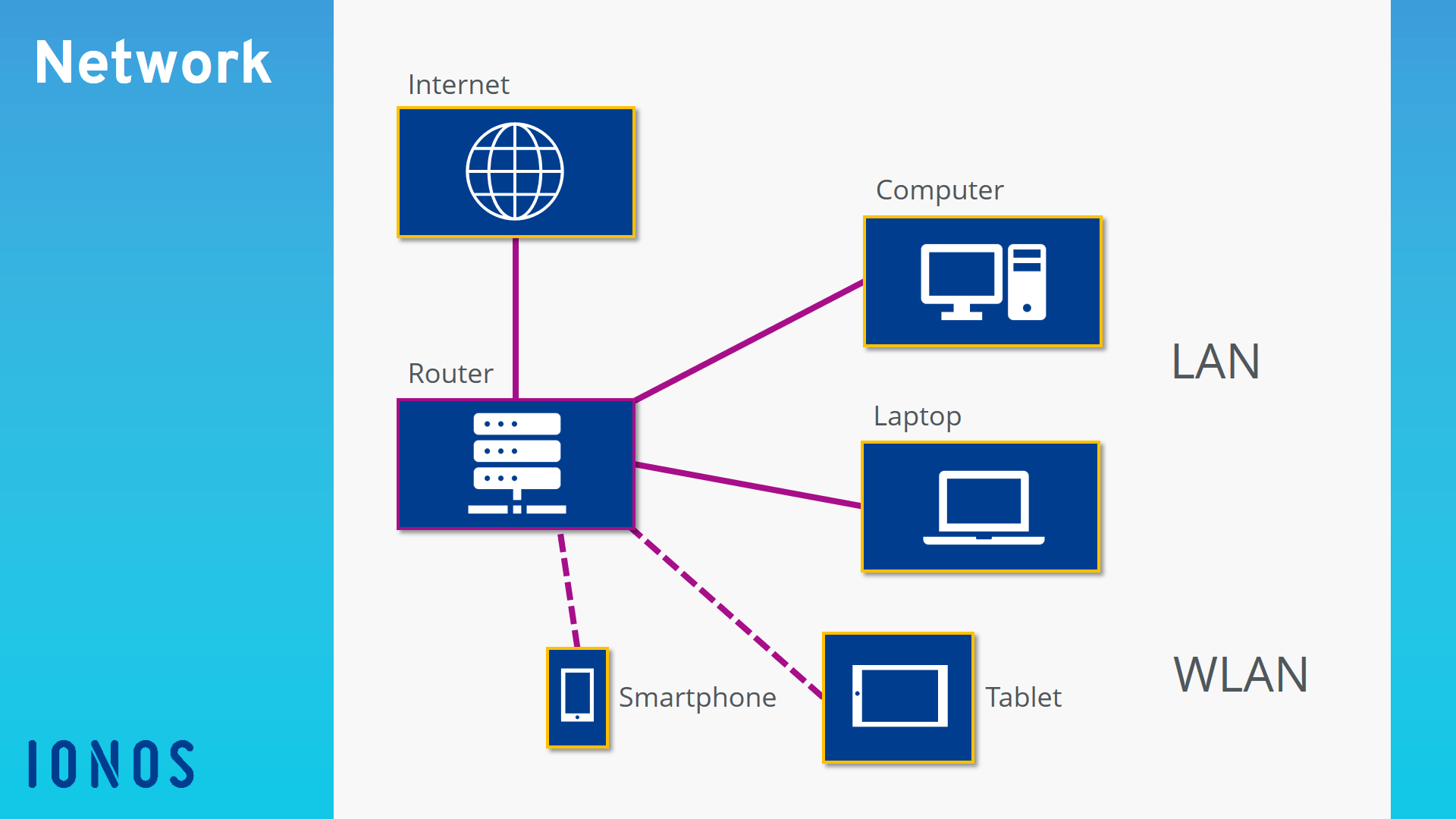
Client-server architecture
In larger networks, such as corporate networks, the server is usually a central computer. This computer is used exclusively for running special server software and services, not regular applications and programs. The server must operate continuously, whereas the other computers (clients) can be switched off.
The server and the client communicate as follows in this server-based network: The client first sends a request to the server. The server evaluates the request and then transmits the response. In this model, the client always connects to the server, never the other way around.
Network protocols
Network protocols ensure smooth communication between the different components in a network. They control data exchange and determine how communication is established and terminated as well as which data is transmitted. There are usually multiple network protocols that each perform a specific subtask and are hierarchically organized into layers.
Network addresses
In addition, it is necessary to ensure that the transmitter and receiver can be correctly identified. Network addresses are used for this purpose. In computer networks, each computer typically has an IP address, similar to a telephone number, that uniquely identifies the computer. This internal IP address is used only for communication between the participants in the local network. For communication on the Internet, external IP addresses are used that are automatically assigned by the Internet provider.
A distinction is also made between IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. IPv4 addresses used to be standard, but only a total of around 4.3 billion of these addresses could be assigned before they were exhausted. Due to the massive expansion of the Internet, additional IP addresses were urgently needed. Therefore, the new IPv6 standard was developed, allowing up to 3.4 x 1038 (340 sextillion) addresses. This should be sufficient for the future.
You can find detailed information on the IP protocol and its important role in computer networks in our article “What is the Internet Protocol ?”.
What types of networks are there?
Networks are usually divided into different network types according to transmission type and range, that is, depending on how or how far the data is transmitted.
Wireless vs. wired
Networks are classified by transmission type as either wireless or wired. Examples of wireless networks include Wi-Fi networks based on the IEEE 802.11 standard, or the LTE networks used for mobile devices and smartphones. Wired networks such as DSL are also known as broadband Internet.
Network range
Networks are typically classified by range as follows:
- Personal Area Network (PAN): A PAN is used for interconnecting devices within a short range of approximately 10 meters. Examples include Bluetooth technology or Apple’s Airdrop ad hoc Wi-Fi service.
- Local Area Network (LAN): Local area networks are among the most widespread networks and are used in households or small and medium-sized companies.
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): These types of networks cover cities or single geographic regions.
- Wide Area Network (WAN): The nationwide broadband or cellular network in the US is an example of a Wide Area Network.
- GAN (Global Area Network): The best known example of a global network is the Internet.
Note that there is some overlap between the different network types: As a Wi-Fi user, you are simultaneously part of a WAN and a GAN when you’re connected to the Internet.
WLAN security: how to make your wireless network into a fortress
When you’re traveling with portable devices, you’ll find public WLAN everywhere, giving you access to the world wide web. Even in residential and work spaces, practical wireless networking is widespread. It’s easy to forget that there’s a risk involved when transferring data using one of these access points. In the following article, we explain the biggest security risks and show you how to make…
WLAN security: how to make your wireless network into a fortress

How to do a Penetration test
The more complex a network is, the more vulnerable it is to attacks. In times when customers and partners have access to internal network structures via the internet, and can control various applications via web interfaces, IT employees are encountering more and more problems. Large companies, in particular, prefer to use penetration testing to check how well their security concept works. This…
How to do a Penetration test

Use subnetting to get the most out of your network
Dividing a corporate network into smaller subnets has some advantages in terms of speed, security, and logical organization. However, many people find it difficult to set up. Binary computational operations and long series of numbers are frightening, but the principle itself is not so complicated. We explain what subnetting is, how to calculate a subnetmask, and what you need subnets for, so that…
Use subnetting to get the most out of your network

Hubs: what are they and how do they work?
Hubs are becoming less common in the construction of networks. For various reasons, these network devices are being replaced by the more modern switches. Nevertheless, it pays to know about them. In this article, you can learn what a hub is, how it works, and what advantages and disadvantages the technology has compared to its successor.
Hubs: what are they and how do they work?
Смотреть что такое NETWORK в других словарях:
NETWORK
[`netwɜːk]сеть, сетка; плетенкасетьрешетчатая системарадиотрансляционная сеть; вещательная компания; радиовещание, телевидениесхема, цепьвзаимосвязанна… смотреть
NETWORK
network: translation•Roman•I.•/Roman• noun
1 connectionsADJECTIVE
▪ extensive, large, vast, wide, widespread
▪ an extensive network of underground … смотреть
NETWORK
network: translation
▪ I. network net‧work 1 [ˈnetwɜːk ǁ -wɜːrk] noun [countable]
1. a group of people or organizations that are con… смотреть
NETWORK
1) сеть 2) схема • — ac network — active network — adjustment network — all-pass network — analog cellular network — asynchronous network — automatic secure voice communication network — automatic voice network — average-capacity radio-relay network — backbone network — banyan network — baseband network — baseband-switched network — baseline network — branched network — bridged-T network — broadband integrated-service digital network — building-out network — bus network — butterfly network — cable telephone network — cable-news network — cable-television network — carrier recovery network — CATV network — cellular paging network — cellular radio network — circuit-switched network — circuit-switching network — circular radiocommunication network — closed cellular network — combined distribution network — commercial communcation network — common-telegraph network — common-telephone network — common-user network — communication network — compromise network — computer network — computerized transport communication network — conferencing network — coordinate network — copy network — core network — corporate network — corporative network — corrective network — coupling network — cross-connect network — customer network — damaged network — data-communication network — data-computing network — data-transmission network — decoding network — decoupling network — deemphasis network — Deep-Space network — degraded network — delay-line network — democratic network — democratically-synchronized network — departmental communication network — departmental data-transmission network — departmental engineering communication network — departmental facsimile network — departmental radio network — departmental telegraph network — departmental telephone network — derived-services network — despotic network — despotically-synchronized network — dial network — dial-up network — differentiating network — digital cellular network — discrete communication network — dispersed network — district center telephone network — district telephone network — dual network — electric communication networks — electric switched network — electrically switched network — engineering subscribers network — enhanced other networks — equivalent network — expansion network — facsimile-communication network — federal paging network — fiber-hubbed network — fiber-optical network — flip network — four-pole network — four-wire distribution network — full-service network — gas-pipeline servicing relay network — go-around radio network — group channels network — group network — half-open cellular network — hierarchic computer network — hierarchical computer network — hierarchically-synchronized network — high-capacity radio relay network — highly hierarchical network — highly pipelined network — H-network — homogeneous network — hybrid communication network — hybrid fiber-and-coaxial network — inductance network — inductance-capacitance network — inductance-resisitance network — inductive cable network — information network — in-house network — integrated digital communication network — integrated digital network — integrated transport network — integrated-services backbone network — integrated-services digital network — intelligent network — interactive network — interbuilding network — intercity network — intercom network — international communication network — interoffice transit network — interorganization network — intraairport communication network — intraareal network — intrabuilding communication network — intraindustrial communication network — intraindustrial telephone network — intraobject communication network — intraoffice network — joint-academic network — landing radio network — lead network — leased-line network — line communication network — line radio communication network — linear network — line-building-out network — local communication network — local paging network — local telephone network — local transport network — long distance communication network — loop network — loudspeaker dividing network — main network — managed-data network — mesh network — message switching network — meteorological radio network — metropolitan-area network — microwave network — mid-split network — mine telephone network — Ministry of Communication network — mixed network — modem-based network — monochannel network — multiaccess network — multifrequency network — multilayer network — multipath network — multiple-domain network — multiple-switching network — multiring network — multistation network — multisystem network — mutually-synchronized network — narrowband digital integrated-service network — nation-wide network — n-layer network — NMT network — nodeless network — nonhomogeneous network — nonintegrated network — nonswitched network — nonsynchronous network — oil-pipeline servicing relay network — oligarchically-synchronized network — open cellular network — optoelectronic network — originating-switching network — packet wireless communication network — packet-radio network — packet-switching network — parallel-T network — passenger train-chief radio network — passenger train-master radio network — passive network — personal radio network — phase-correcting network — planetext network — polled network — port-annunciation network — preemphasis network — press-teletype network — primary-trunk communication network — private intercompany network — private voice-band network — private-business network — proliferated network — protected network — provincial center telephone network — public-data network — public-switched telephone network — public-telegraph network — public-transport network — pulse-delay network — pulse-forming network — queueing network — radial paging network — radio network — radiotransmitters network — railway center radio network — railway communication network — railway telephone network — random-access network — Raynet network — RC network — reconfigured network — regional communication network — regional paging network — reserved radio network — resistance-capacitance network — ring network — ring-radial network — ring-star network — road communication network — routing network — rural telephone network — salvation radio network — satellite network — secondary computerized communication network — selective network — separate crossover network — shaping network — ship telephone network — short-haul network — shuffle-exchange network — silent network — simplex zonal radio network — simulcast network — single-frequency network — slotted-envelope network — slotted-ring network — small-capacity radio relay network — software-defined network — space network — space-time-space network — special communication network — spread of work radio communication network — stage-controlled network — star network — star-shape network — station communication network — submarine cable network — subscriber’s telegraph network — switched-message network — switching network — synchronous-data network — take-off radio network — talk-TV network — taxi radio network — telecode communication network — telecommunication network — telecommunication-management network — telegraph communication network — telephone network — teleprocessing network — teletex network — teletype network — teletypewriter network — television network — telex-communication network — temporary line dispatch radio network — terminating switching network — token passing network — token-bus network — token-ring network — token-sharing network — toll-telephone network — transit network — transmission network — trunk telephone network — trunking channels network — underground antenna network — united automatized state communication network — urban telephone network — video area network — virtual network — voice network — water-communication network — waterside communication network — wire-hanger network — wireless network — word processor network… смотреть
NETWORK
1. сущ.1) сеть
а) общ. (совокупность взаимосвязанных объектов или лиц)
communications network — сеть коммуникаций, сеть связи, система связиroad networ… смотреть
NETWORK
1) сеть2) многополюсник3) сетевой график4) электросеть5) схема6) цепь7) многоплюсник8) плетение9) сетка10) сеточный11) сетчатый12) схемный13) каркас– a… смотреть
NETWORK
сеть- backbone network
— backup communication network
— bulk encryption network
— cable-based network
— campus network
— ciphony communication network
… смотреть
NETWORK
1. сеть, сетка
2. сетка размещения скважин
3. сеть электрических линий или проводов
4. решетчатая система, ре детчатое устройство
5. расчётная или… смотреть
NETWORK
1) схема; цепь 2) многополюсник 3) плетение 4) сетевой график 5) сетка || сеточный 6) сеть 7) электросеть • anastomotic modular network — анастомотическая модульная сеть arbitrarily reliable network — произвольно надежная сеть capacitated transport network — упорядоченная по пропускной способности транспортная сеть correcting [corrective] network — корректирующая схема direction finding network — радиопеленгаторная сеть frequency selective network — частотноизбирательная схема gated resistance network — управляемое цифровое сопротивление integrated digital network — интегральная цифровая сеть связи interpenetrating network of samples — взаимопроникающая группа выборок iterative switching network — итеративная структура local telephone network — местная телефонная сеть loosely coupled network — сеть слабосвязанная mainline communications network — связь сеть магистральных связей network with gains — т. граф. сеть с усилениями radio telephone network — радиотелефонная сеть rural area network — сельская связь shortest connection network — кратчайшая связывающая сеть shunt-peaking compensation network — тех. схема коррекции верхних частот параллельная signal shaping network — электр. контур исправления сигнала synchronous optical network — стандарт на сеть синхронной оптической связи triangular recursive network — треугольная рекурсивная сеть — abstract network — assignment network — augmented network — basis network — bilateral network — bounded network — branching network — building-out network — combinatorial network — communication network — compensating network — compromise network — connected network — cut in network — directed network — distributing network — dual network — dynamic network — eight-terminal network — equalizer network — equalizing network — event network — four-pole network — four-terminal network — functional network — fuzzy network — generalized network — hierarchical network — indecomposable network — industrial network — information network — integrating network — intercity network — iterated network — ladder network — lattice network — learning network — linear network — local-area network — logical network — long-distance network — loop network — matching network — meshed network — meteorological network — monotone network — multiterminal network — network of coordinates — network of graph — network of samples — nonplanar network — non-planar network — optimum network — packet network — passive network — peaking network — PERT network — phase-shifting network — pi network — private network — pseudosymmetric network — public network — radio network — rearrangeable network — reciprocal network — reduced network — redundant network — resistance network — ringed network — self-organizing network — sequential network — sink of network — stochastic network — susbscriber network — switching network — symmetrical network — telephone network — television network — transport network — transportation network — tree network — two-terminal network — two-terminal pair network — undirected network — unilateral network — universal network — unoriented network… смотреть
NETWORK
1. [ʹnetwɜ:k] n1. 1) сеть, сетка2) плетёнка2. 1) сеточка, филе (в рукоделии)2) текст. ажурное полотно3. 1) плетение, вязание2) переплетение, хитросплет… смотреть
NETWORK
1) сеть; сетка 2) информационная сеть; вычислительная сеть 3) схема; цепь; контур 4) охватывать информационной сетью, объединять информационной сетью 5) встраивать в (информационную) сеть, вводить в (информационную) сеть 6) объединять в систему с внутренними связями (напр. станки) • — activation network — adaptive control network — adjustment network — AGV network — artificial mains network — artificial neural network — baseband network — bridge network — broadband network — CAN network — capacitor networks — carrierband network — CIM network — citation network — coaxial network — communications network for manufacturing applications — communications network — compensating network — competitive-learning network — complementary network — computer local area network — continuous network — controlled network — controller area network — corrective network — data management network — data-shearing network — delivery cart network — delta network — dependency network — development information network — discrimination network — distributed interactive data networks — distributed network of control — DNC network — EDS network — enterprise networks — equivalent network — ESD network — fiber-optic DNC network — fiber-optic MAP network — fiber-optic network — gaging network — grid network — information network — integrated communication network — integrated intracell network — integrated services digital network — interconnected network — isolated network — lead network — local area network — local bus/multidrop network — local data-processing network — local network — localized network — MAP network — MAP OSI network — MAP-backbone network — MAP-broadband network — matched network — material-handling network — microcomputer network — national information network — network of queues — neural network — nodal network — PC network — phase-advance network — plane separation network — plant-wide network — PLC network — predictor network — proprietory network — public data network — queueing network — regional information network — responsive network — SDS network — self-test network — separation network — shaping network — shopfloor network — stabilizing network — tandem compensation network — teletypewriter exchange network — teletypewriter network — thermistor network — threshold logic network — trunk network — unidirectional network — V-network — wide network — wide-area network — wire network… смотреть
NETWORK
1) сеть; сетка
2) информационная сеть; вычислительная сеть
3) схема; цепь; контур
4) охватывать информационной сетью, объединять информационной сетью
5) встраивать в (информационную) сеть, вводить в (информационную) сеть
6) объединять в систему с внутренними связями (напр. станки)
•
— network of queues- activation network- adaptive control network- adjustment network- AGV network- artificial mains network- artificial neural network- baseband network- bridge network- broadband network- CAN network- capacitor networks- carrierband network- CIM network- citation network- coaxial network- communications network- communications network for manufacturing applications- compensating network- competitive-learning network- complementary network- computer local area network- continuous network- controlled network- controller area network- corrective network- data management network- data-shearing network- delivery cart network- delta network- dependency network- development information network- discrimination network- distributed network of control- distributed interactive data networks- DNC network- EDS network- enterprise networks- equivalent network- ESD network- fiber-optic network- fiber-optic DNC network- fiber-optic MAP network- gaging network- grid network- information network- integrated communication network- integrated intracell network- integrated services digital network- interconnected network- isolated network- lead network- local network- local area network- local bus/multidrop network- local data-processing network- localized network- MAP network- MAP-backbone network- MAP-broadband network- MAP OSI network- matched network- material-handling network- microcomputer network- national information network- neural network- nodal network- PC network- phase-advance network- plane separation network- plant-wide network- PLC network- predictor network- proprietory network- public data network- queueing network- regional information network- responsive network- SDS network- self-test network- separation network- shaping network- shopfloor network- stabilizing network- tandem compensation network- teletypewriter network- teletypewriter exchange network- thermistor network- threshold logic network- trunk network- unidirectional network- V-network- wide network- wide-area network- wire network… смотреть
NETWORK
ком., марк., тк., комп. n мережа; a мережний
1. сукупність осіб, підприємств, організацій і т. ін., пов’язаних певною метою; 2. сукупність телевізійних або радіомовних станцій, об’єднаних системою ліній зв’язку з метою одночасної трансляції різних програм; ♦ існує чотири основні форми мереж: національна (national network), яка транслює по всій території країни; регіональна (regional network), яка транслює на місцеву територію; кабельна (cable network), яка транслює через супутник, охоплюючи частину світу теле- чи радіосигналами; на замовлення (tailor-made network) для разової трансляції оперативних актуальних подій, які мають загальнонаціональне чи міжнародне значення; 3. система ліній зв’язку, які об’єднують комп’ютери, різні прилади у формі модемів, друкарських пристроїв тощо з метою спільного користування даними (data²), програмними засобами (software) тощо
advertising ~ мережа рекламних агентств; agency ~ мережа агентств • агентська мережа; backbone ~ базова мережа; basic ~ базова основа мережі • основна мережа; Blue ~ компанія Ей-Бі-Сі; branch ~ мережа філіалів; broadcasting ~ трансляційна мережа; cable network; Cable News ~ Сі-Ен-Ен; cable television ~ мережа кабельного телебачення; commercial ~ торговельна мережа; commercial television ~ комерційна телемережа • мережа комерційного телебачення; communications-control ~ інформаційно-керуюча мережа комунікацій; computer ~ комп’ютерна мережа; data bank ~ мережа банку даних; data-exchange ~ мережа обміну інформацією; dealer ~ ділерська мережа; dir
~ cabling укладання мережного кабелю; ~ externality мережний взаємовплив; ~ marketing мережний маркетинг; ~ of agents мережа агентів; ~ of trade outlets торговельна мережа; ~ stations мережні станції; ~ structure мережна структура; ~ terminals мережні термінали; to be connected to a ~ бути пов’язаним з мережею; to be linked to a ~ бути пов’язаним з мережею; to construct a ~ будувати/збудувати мережу; to create a ~ створювати/створити мережу; to develop a ~ розвивати/розвинути мережу • створювати/створити мережу; to form a ~ утворювати/утворити мережу • формувати/сформувати мережу; to install a ~ проводити/провести мережу; to set up a ~ засновувати/заснуват… смотреть
NETWORK
1. {ʹnetwɜ:k} n 1. 1) сеть, сетка 2) плетёнка 2. 1) сеточка, филе (в рукоделии) 2) текст. ажурное полотно 3. 1) плетение, вязание 2) переплетение… смотреть
NETWORK
• ABC or UPN, e.g. • AFI’s #66 (1976) • Broadcasting company • Communications system • Computer-user’s hookup • Do some strategic schmoozing • Dunaway… смотреть
NETWORK
nсеть; системаto break a network smuggling hi-tech equipment into a country — ликвидировать сеть контрабандистов, ввозивших в какую-л. страну высокотех… смотреть
NETWORK
network [ˊnetwɜ:k]
1. n
1) сеть, се́тка; плетёнка
2) сеть (железных дорог, каналов и т.п.)
3) соо́бщество
4) тех. решётчатая систе́ма
5) радиотрансля… смотреть
NETWORK
Network: übersetzung
Net|work [‘nɛtwə:k ], das; -[s], -s [engl. network, eigtl. = Netzwerk, aus: net = Netz u. work = Arbeit, Werk]:
1. Vernetzung mehr… смотреть
NETWORK
1. сущ. 1) сеть, сетка; плетенка 2) сеть а) (совокупность железных дорог, каналов и т. п.) communications network — сеть коммуникаций, сеть связи, система связи road network — сеть дорог network of rails — сеть железных дорог community health network — амер. местная сеть здравоохранения б) взаимосвязанная цепочка или система нематериальных объектов; схематическое представление событий и действий при изучении эффективности производственного процесса Network, a schematic representation of events and activities which shows their inter-relationships. — Сеть — схематическое изображение событий и действий в их взаимосвязи. activity network — эк. сетевой график; временная последовательность операций 3) тех. решетчатая система 4) радиотрансляционная сеть; вещательная компания; радиовещание, телевидение 5) эл. схема, цепь 6) взаимосвязанная группа людей, организация, сообщество I was paid about L500 for infiltrating the IRA network in London. — Мне заплатили около 500 фунтов стерлингов за то, чтобы я проник в ряды ИРА в Лондоне. — old-boy network 2. гл. 1) информ. подключать к системе Each computer is networked to a file server. — Каждый компьютер подключен к файловому серверу. 2) брит. передавать по радиосети, телесети a show which was networked across the UK — шоу, которое транслировалась по всей Британии 3) амер.покрывать сетью densely networked with roads — покрытый густой сетью дорог… смотреть
NETWORK
aeronautical fixed telecommunication network — (наземная) сеть авиационной фиксированной электросвязиaviation meteorological facsimile network — сеть а… смотреть
NETWORK
network 1. [ʹnetwɜ:k] n 1. 1) сеть, сетка 2) плетёнка 2. 1) сеточка, филе (в рукоделии) 2) текст. ажурное полотно 3. 1) плетение, вязание 2) переп… смотреть
NETWORK
1. сеть (трубопроводная, дорожная и т. п.)
2. сетевой график- network of motorroads- activity network- aerial network- air termination network- ba… смотреть
NETWORK
n1) мережа2) теле- чи радіомовлення•- aeronautical fixed telecommunication network- air route network- basic network- climatological station network- c… смотреть
NETWORK
Сеть- network of queues- activity network- algorithmic network- automated wire network- branch network- distributive network- equipment replacement net… смотреть
NETWORK
сеть, сеткаresistance analogue network for seepage — сетка сопротивлений для моделирования просачивания— drainage network
— flow network
— gauge networ… смотреть
NETWORK
network: translationSynonyms and related words:arabesque, arrangement, basketry, basketwork, cancellation, circuit, coast-to-coast hookup, complex, cro… смотреть
NETWORK
1. опорная сеть 2. сетка, сеть 3. штокверк (рудная залежь в виде прожилков в породе); месторождение с сетчатой или камерной структурой network of crack… смотреть
NETWORK
совокупность рабочих станций, соединённых между собой с помощью сетевого оборудования и среды передачи данных, в качестве которой может использоваться кабель, телефонные линии или беспроводная связь. Предназначена для совместного использования вычислительных ресурсов, периферийных устройств, приложений и данных. Сети классифицируются по географическому признаку (локальные, кампусные, городские, региональные, глобальные), по топологии, по передающей среде, способу коммутации и т.д. см. тж. backbone, CAN 2), LAN, MAN, segment 1), subnetwork, transport netwotk, WAN… смотреть
NETWORK
network: translation points (vertices) joined by links. The links allow transfers between the points. Examples might include roads, railways, sewage p… смотреть
NETWORK
1) сеть; сетка
2) бот. гудайера пушистая (Goodyera pubescens)
•- capillary network- cellular network- chromatin network- social network- wonderful netw… смотреть
NETWORK
1) сеть; система (связей); схема 2) присоединяться к сети 3) создавать или поддерживать горизонтальные (деловые или информационные) связи 4) распространять, транслировать (информацию) • — activity network — computer network — library network — local network — national patent information network — network of patents — office network… смотреть
NETWORK
1. n 1) сітка, сіть; 2) плетінка; 3) плетіння, в’язання; 4) переплетення, хитросплетення; 5) мережа (залізнична тощо); radio ~ радіомережа; communication ~ система зв’язку; 6) тех. ґратчаста (решітчаста) система; 7) розрахункова схема; ♦ ~ announcer амер. диктор; 2. v амер. створювати мережу залізниць…. смотреть
NETWORK
nounсеть f
planar network планар-ная сеть queueing network сеть обслуживания
NETWORK
Network: traducción Grupo de estaciones de radio o televisión que están afiliadas a la misma compañía de transmisión, y ofrecen cobertura para anunci… смотреть
NETWORK
n1) сітка, мережа (залізниць, каналів і т. ін.)2) рад. сітка радіотрансляційних установокradio network — радіосіткаcommunication network — система зв’я… смотреть
NETWORK
1. сшивка
2. образование поперечных связей
3. поперечно сшитая структура
NETWORK
1) сеть; сетка
2) схема; цепь
•- highway network- road network* * *• решетка
• сеть
NETWORK
1) сеть; сетка2) схема; цепь; контур- satellite network- telecommunications network
NETWORK
n 1. перен. сітка, переплетіння; хитросплетіння
2. мережа (залізнична, радіотрансляційна, телевізійна тощо)
— ~ of espionage шпигунська мере-
— ~ of intrigue тенета інтриг… смотреть
NETWORK
Сіткаплетіннясхемамережаланцюг
NETWORK
n. сеть, сетка, плетенка, плетение; цепь, схема; радиотрансляционная сеть, телевизионная сеть; многополюсник, четырехполюсник
NETWORK
m англ.
1) сеть взаимосвязанных телевизионных станций
2) вчт. (коммуникационная) сеть
Итальяно-русский словарь.2003.
NETWORK
Сеть; сетка;
Схема; цепь; контур;
Сеть (компьютерная, сбытовая).
Краткий толковый словарь по полиграфии.2010.
NETWORK
ˈnetwə:kсеть,рамка,сеть(жд,радиотрансляционная)
NETWORK
мед.сущ. сеть; ячеистая структура сетевой
Англо-русский медицинский словарь.2012.
NETWORK
передавать (информацию) через (компьютерную) сеть
NETWORK
v. создавать сеть, передавать по радиосети, передавать по телевизионной сети
NETWORK
мережа (1. мережа ЕОМ; мережа передачі даних 2. зв’язний орієнтований граф)
NETWORK
сеть, сетка; плетенка сеть (железных дорог, каналов и т. п.) сообщество
NETWORK
1) (вычислительная) сеть ( net ) 2) схема 3) сетевой график
NETWORK
співтовариство, плетінка, сітка, мережу, мережа
NETWORK
• распределительная сеть
• расчётная схема
NETWORK
(n) переплетение; сетевой график; сеть
NETWORK
сіткаплетіння
схема
мережа
ланцюг
Updated: 07/06/2021 by
A network is a collection of computers, servers, mainframes, network devices, peripherals, or other devices connected to allow data sharing. An example of a network is the Internet, which connects millions of people all over the world. To the right is an example image of a home network with multiple computers and other network devices all connected.
Examples of network devices
- Desktop computers, laptops, mainframes, and servers.
- Consoles and thin clients.
- Firewalls
- Bridges
- Repeaters
- Network Interface cards
- Switches, hubs, modems, and routers.
- Smartphones and tablets.
- Webcams
Network topologies and types of networks
The term network topology describes the relationship of connected devices in terms of a geometric graph. Devices are represented as vertices, and their connections are represented as edges on the graph. It describes how many connections each device has, in what order, and what sort of hierarchy.
Typical network configurations include bus topology, mesh topology, ring topology, star topology, tree topology, and hybrid topology.
Most home networks are configured in a tree topology that connects to the Internet. Corporate networks often use tree topologies, but they also often incorporate star topologies and an Intranet.
What is the difference between public and private networks?
Often offered by nearby businesses and other publicly accessible areas, public networks are a convenient way to connect to the Internet.
- Some public Wi-Fi networks require a password before a connection is made. If the network displays a lock icon in your list of available Wi-Fi networks, it requires a password.
- Some networks do not require a password to connect, but require you to log in using your web browser before accessing the Internet.
- Other public networks do not require a password at all. Any compatible device may connect to these Wi-Fi networks without authentication.
Note
All public networks are less secure than your home network. Even if the websites you visit use encryption, the URLs you visit can be eavesdropped. For this reason, you should not transmit private or sensitive information on a public Wi-Fi network if you can do it elsewhere. If a public network does not require a password, we strongly recommend you do not connect any of your devices to it.
Private networks have security measures in place to prevent unwanted or unauthorized connections. Private networks are often used for home, business, school Wi-Fi networks, or mobile hotspots for security and to preserve bandwidth.
Advantages of a network
There are more advantages to a network than disadvantages. In fact, many companies today wouldn’t exist without accessing some form of network. Below are the advantages of a network.
- Share data and information — One of the biggest advantages of a network is sharing data and information between each of the devices on it. In addition, networks allow access to databases and help with collaboration on more complex work.
- Communication — A network gives all users the ability to quickly communicate with each other using chat, instant messaging, e-mail, and videoconferencing.
- Share hardware — Hardware devices connected to a network can be shared with all users. Below are a few examples of network hardware that can be shared.
- NAS (network-attached storage) can store and access vast amounts of information.
- A network printer allows all network users to print to one printer.
- More powerful computers, supercomputers, and render farms can perform complex tasks that would take a normal, single computer longer to complete.
- Share software — With the proper software license, software can also be shared.
- Transferring money — Being connected to a secure network allows a person or business to digitally transfer money between banks and users. For example, a network could allow a company to not only manage employees’ payroll, but also transfer their pay to the employee’s bank account.
Disadvantages of a network
Although there are many advantages to a network (mentioned above), there are some disadvantages. Below are the disadvantages of a network.
- Virus and malware — Networks make sharing information between network users easy. Unfortunately, this also means that viruses and malware have an easier time spreading between computers on a network.
- Vulnerabilities — When a network is created, it introduces new methods of accessing the computers remotely, especially if they’re connected to the Internet. With these potential new methods of accessing the computer, it can introduce new vulnerabilities to computers, users, and data on a network.
- Complexity — Networks are complex, and setting up and managing a network for a business or corporation requires someone with a lot of experience or certification.
What was the first computer network?
One of the first computer networks to use packet switching, ARPANET, was developed in the mid-1960s and is the direct predecessor of the modern Internet. The first ARPANET message was sent on October 29, 1969.
Internet, LAN, Network terms
Recent Examples on the Web
Walmart plans to build an electric vehicle charging network with fast charging stations at thousands of its stores by 2030.
—
Canada is a member of the Five Eyes intelligence-sharing network, which also includes the United States, United Kingdom, Australia and New Zealand.
—
Three months after the 2023 Golden Globes ceremony marked the show’s return to network TV for the first time since 2021, the Hollywood Foreign Press Association announced Monday that 215 new members joined the group’s voting ranks, bringing the HFPA’s total membership to 310.
—
Production interruptions added to the pressures already facing broadcast networks — ABC, CBS, NBC and Fox.
—
By 2030, Walmart plans to build an EV fast-charging network at thousands of its locations across the U.S.
—
Now there’s also a documentary, This is Gwar, paid for by horror network Shudder, also available for a few bucks streaming on Amazon Prime.
—
The latter is derivative of the cryptocurrency ether that is locked up until the Ethereum network transitions to a less energy-intensive model.
—
Pickleball professional leagues sprung up along with a pickleball draft—last year CBS televised the game for the first time on a major broadcast network, which featured a match with Waters and her mom.
—
Trade groups, professional associations, and informal online communities are easy sources of high-quality networking contacts.
—
Divided into three poles, the new lab will help immersive projects across development, production, and distribution, offering residencies and networking assistance at each phase.
—
That means cracking jokes with perfect timing, flirting with just enough coyness, or networking with perfect execution.
—
Young Black & ‘N Business, a networking organization that works to empower young entrepreneurs in San Diego’s underserved communities, is hosting its second annual BIZCON on April 5 and 6 at the San Diego Convention Center.
—
More and more professionals came to realize that networking technology would generate important benefits.
—
Amplifying her profile through speaking opportunities, awards, networking at events, interviews, blog posts and social media builds our brand through her name and expertise.
—
The news comes after the social-networking platform laid off 11,000 people in November.
—
Participants will begin by networking, enjoying snacks like fresh fruit and cheeses, and grabbing a cocktail or mocktail while listening to music by female artists.
—
See More
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word ‘network.’ Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.


