Watch video – Convert Date to Text in Excel
Date and Time in Excel are stored as numbers. This enables a user to use these dates and time in calculations. For example, you can add a specific number of days or hours to a given date.
However, sometimes you may want these dates to behave like text. In such cases, you need to know how to convert the date to text.
Below is an example where dates are combined with text. You can see that the dates don’t retain their format and show up as numbers in the combined text.
In such situations, it’s required to convert a date into text.
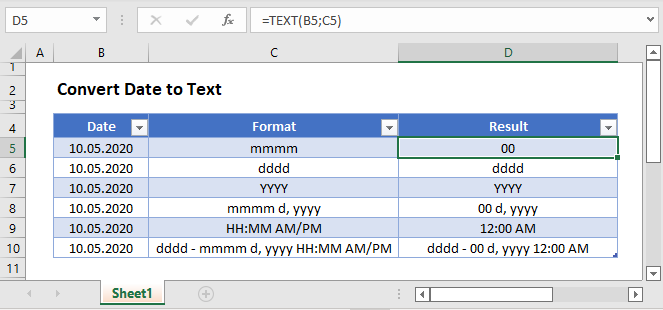
Convert Date to Text in Excel
In this tutorial, you’ll learn three ways to convert the date to text in Excel:
- Using the Text Function
- Using the Text to Column feature
- Using the Copy-Paste method
Convert Date to Text using Text Function
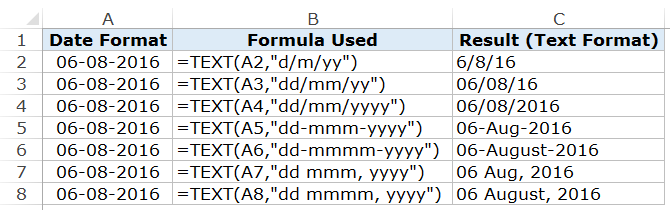
TEXT function is best used when you want to display a value in a specific format. In this case, it would be to display the date (which is a number) in the date format.
Let’s first see how the text function works.
Here is the syntax:
=TEXT(value, format_text)
It takes two arguments:
- value – the number that you want to convert into text. This can be a number, a cell reference that contains a number, or a formula result that returns a number.
- format_text – the format in which you want to display the number. The format needs to be specified within double quotes.
Using the Text function requires a basic understanding of the formats that you can use in it.
In the case of dates, there are four parts to the format:
- day format
- month format
- year format
- separator
Here are the formats you can use for each part:
- Day Format:
- d – it shows the day number without a leading zero. So 2 will be shown as 2 and 12 will be shown as 12.
- dd – it shows the day number with a leading zero. So 2 will be shown as 02, and 12 will be shown as 12
- ddd – it shows the day name as a three letter abbreviation of the day. For example, if the day is a Monday, it will show Mon.
- dddd – it shows the full name of the day. For example, if it’s Monday, it will be shown as Monday.
- Month Format:
- m – it shows the month number without a leading zero. So 2 will be shown as 2 and 12 will be shown as 12.
- mm – it shows the month number with a leading zero. So 2 will be shown as 02, and 12 will be shown as 12
- mmm – it shows the month name as a three letter abbreviation of the day. For example, if the month is August, it will show Aug.
- mmmm – it shows the full name of the month. For example, if the month is August, it will show August.
- Year Format:
- yy – it shows the two digit year number. For example, if it is 2016, it will show 16.
- yyyy – it shows the four digit year number. For example, if it is 2016, it will show 2016.
- Separator:
- / (forward slash): A forward slash can be used to separate the day, month, and year part of a date. For example, if you specify “dd/mmm/yyyy” as the format, it would return a date with the following format: 31/12/2016.
- – (dash): A dash can be used to separate the day, month, and year part of a date. For example, if you specify “dd-mmm-yyyy” as the format, it would return a date with the following format: 31-12-2016.
- Space and comma: You can also combine space and comma to create a format such as “dd mmm, yyyy”. This would show the date in the following format: 31 Mar, 2016.
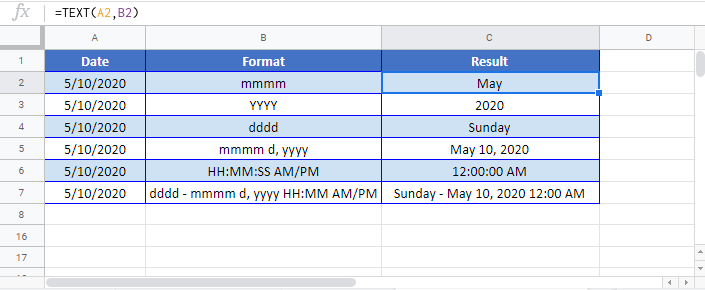
Let’s see a few examples of how to use the TEXT function to convert date to text in Excel.
Example 1: Converting a Specified Date to Text
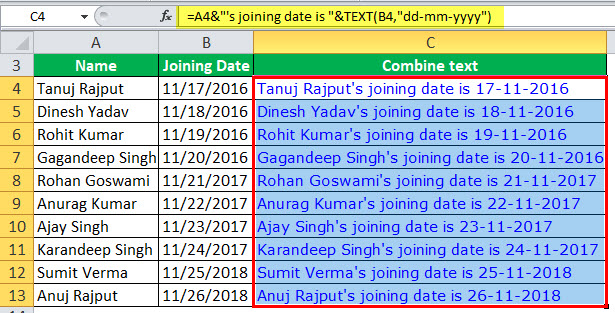
Let’s again take the example of the date of joining:
Here’s the formula that will give you the right result:
=A2&"'s joining date is "&TEXT(B2,"dd-mm-yyyy")
Note that instead of using the cell reference that has the date, we have used the TEXT function to convert it into text using the specified format.
Below are some variations of different formats that you can use:
You can experiment with other formats as well and create your own combinations.
Also read: How to Convert Text to Date in Excel (8 Easy Ways)
Example 2: Converting Current Date to Text
To convert the current date into text, you can use the TODAY function along with the TEXT function.
Here is a formula that will do it:
="Today is "&TEXT(TODAY(),"dd/mm/yyyy")
This could be useful in dashboards/reports, where as soon as the file is opened (or any changes are made), the date refreshes to show the current date.
Convert Date to Text using Text to Column
If you’re not a fan of Excel formulas, there is another cool way to quickly convert date to text in Excel – the Text to Column feature.
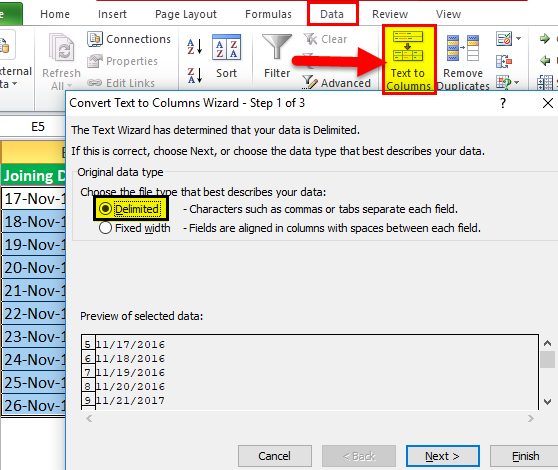
Suppose you have a dataset as shown below and you want to convert these dates into text format:
Here are the steps to do this:
- Select all the cells that contain dates that you want to convert to text.
- Go to Data –> Data Tools –> Text to Column.
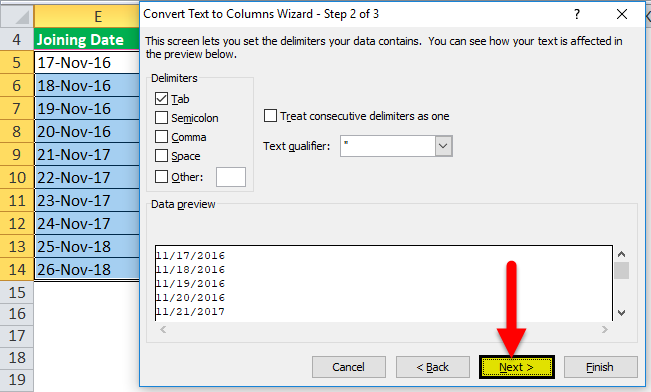
- In the Text to Column Wizard, make the following selections:
This would instantly convert the dates into text format.
Note: There is a difference in the format of the dates in the two columns. While the original format had dd mmm, yyyy format, the result is dd-mm-yyyy. Remember that the Text to Column feature will always convert dates to the default short date format (which is dd-mm-yyyy as per my systems regional settings. It could be different for yours).
Also read: How to Convert Serial Numbers to Dates in Excel (2 Easy Ways)
If you want the date in other formats, use the formula method, or the copy-paste method shown below.
Convert Date to Text using the Copy-Paste Method
This is the fastest way to convert date to text.
Here are the steps:
You May Also Like the Following Excel Tutorials:
- Convert Text to Numbers in Excel – A Step By Step Tutorial.
- How to Convert Formulas to Values in Excel.
- How to Quickly Transpose Data in Excel.
- [Quick Tip] How to Split Cells in Excel.
- Excel Timesheet Calculator Template.
- How to Insert Date and Timestamp in Excel.
- Excel Calendar Template.
- How to Remove Time from Date in Excel
- Convert Time to Decimal Number in Excel (Hours, Minutes, Seconds)
- How To Convert Date To Serial Number In Excel?
How to Convert Date to Text in Excel?
The conversion of the date to text is very easy and simple. There are four simple ways to convert dates to text in Excel:
- Using the TEXT function (most commonly used)
- Using the TEXT to COLUMN option
- Using the copy-paste method
- Using VBA
Use of Date to Text in Worksheet
Excel Text functionTEXT function in excel is a string function used to change a given input to the text provided in a specified number format. It is used when we large data sets from multiple users and the formats are different.read more is commonly used to convert a numeric value to a text string and display it in the format you specify so we can use it to convert date to text in Excel format.
Table of contents
- How to Convert Date to Text in Excel?
- Date to Text Function in Excel
- #1 Using Text Function
- Example #1
- Example #2
- #2 Using Text to Column
- #3 Using Copy Paste Method
- #4 Using VBA
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
Date to Text Function in Excel
The TEXT formula in excelTEXT function in excel is a string function used to change a given input to the text provided in a specified number format. It is used when we large data sets from multiple users and the formats are different.read more is as follows:
- Value: It is a numeric value you want to convert to text. It can be a number, a formula that returns a numeric value, or a reference to a cell containing a number.
- format_text: This is how you want to format the resulting text value, provided as a text string enclosed in quotation marks.
Using the TEXT function to convert dates to text in Excel requires a basic understanding of the formats we can use.
In the case of dates, there are four parts to the format:
- day format
- month format
- year format
- separator
You can download this Convert Date to Text Excel Template here – Convert Date to Text Excel Template
#1 Using Text Function
Example #1
Apply the formula =A4&”‘s joining date is “&TEXT(B4,”dd-mm-yyyy”)
To get the below output.
Example #2
You can also convert the current date to text by the below formula:
=”Today is “&TEXT(TODAY(),”dd/mm/yyyy”)
To get the below output.
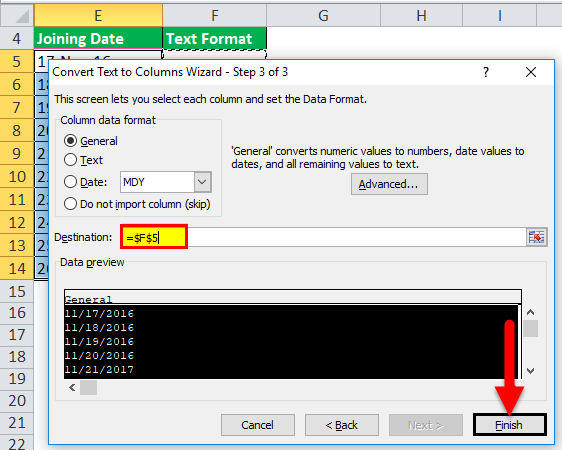
#2 Using Text to Column
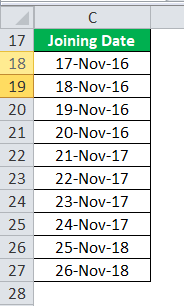
Suppose we have a dataset, as shown below, and we want to convert these dates into textTo convert a date to text in Excel, right-click on the date cell and select the format cells option. A new window will open. You can convert the date to text by selecting the desired format from a list of options.read more format:
Below are the steps to convert the date into text:
- First, we must select the data and go to “Data,” then “Data Tools,” and Text to Column in Excel.
- Press “Next” and uncheck all “Delimiters.”
- Then, we must select the location and click on the “Finish,” as shown below.
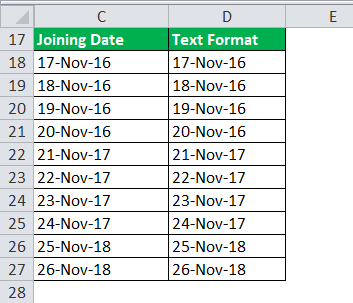
The output will be as follows:
#3 Using Copy Paste Method
Consider the data set of the joining date.
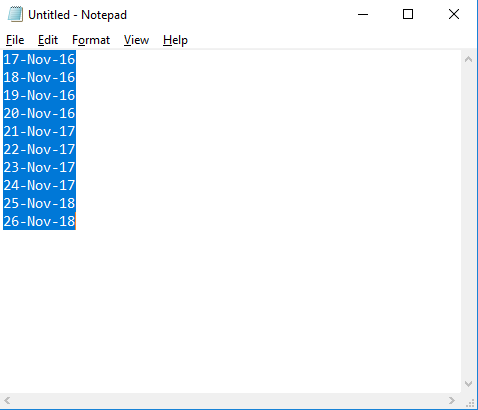
- First, copy the data. Then, open a notepad and paste it there. As soon as you paste the dates into the notepad, it automatically gets converted into text.
- Now switch back to Excel and select the cells where you want to paste these dates.
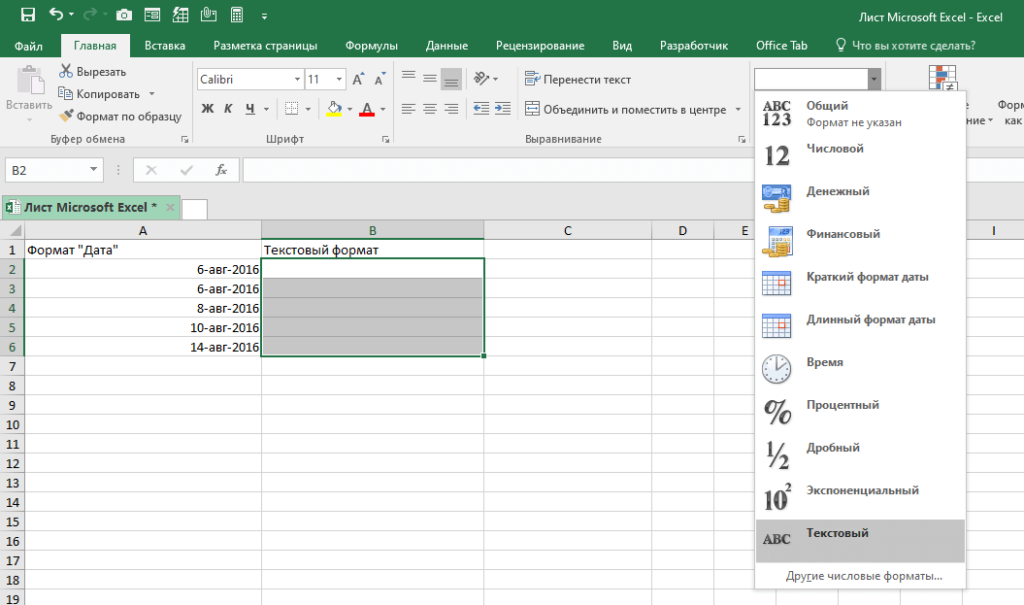
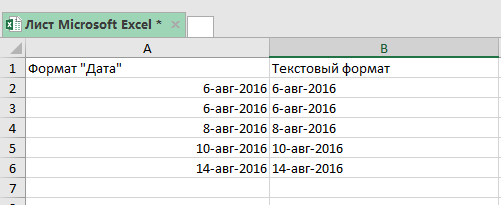
- Then, we must go to “Home” then “Number” with the cells selected and select the “Text” format (from the drop-down).
- Finally, paste the date as text.
#4 Using VBA
Suppose we have the text in sheet1 and the H2 cell, then apply the date to the text using the below VBA codeVBA code refers to a set of instructions written by the user in the Visual Basic Applications programming language on a Visual Basic Editor (VBE) to perform a specific task.read more.
Sub Datetotexts ()
Dim c As Range
For Each c In Selection
c.Value = Format(c.Value, “dd.mm.yyyy”)
Next c
End Sub
Things to Remember
- It must be left-aligned by default.
- If several text dates are selected, the Status BarAs the name implies, the status bar displays the current status in the bottom right corner of Excel; it is a customizable bar that can be customized to meet the needs of the user.read more only shows “Count.”
- There may be a leading apostrophe visible in the formula bar.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide on How To Convert Date to Text in Excel. Here, we discuss the top 3 methods to convert the date to text: 1) Text Formula, 2) Text to Column, and 3) Copy Paste Method, along with examples and a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at these useful functions in Excel: –
- How to add Leading Zeros in Excel?
- Char Function In Excel
- CODE Excel Function
Return to Excel Formulas List
Download Example Workbook
Download the example workbook
This tutorial will teach you how to convert dates to text in Excel & Google Sheets.
Convert Dates to Text
Excel stores dates as serial numbers, where each whole number represents a unique date.
This is extremely useful as it allows you to perform calculations on the dates, but in some cases you may wish to convert that date to text.
Text Function
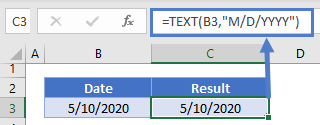
To convert dates to text, you can use the TEXT Function:
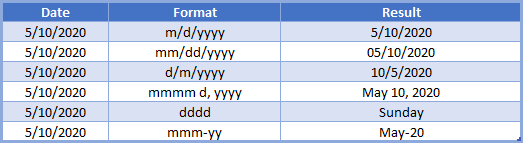
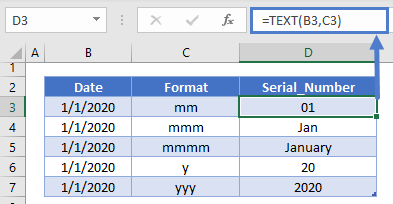
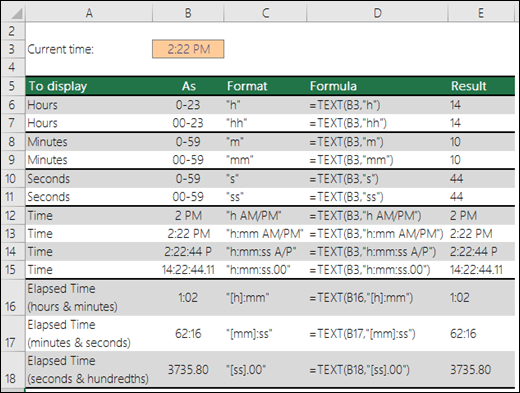
=TEXT(B3,"M/D/YYYY")The most important input in the TEXT Function is the display format. Notice in the previous example we used the “m/d/yyyy” format. Here are other common date display formats:
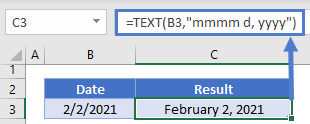
Notice that you can use the TEXT Function to write out a full date
=TEXT(B3,"mmmm d, yyyy")You can also display only the month name or year:
or you can use any of those format types to build your desired date format.
Date Formatting
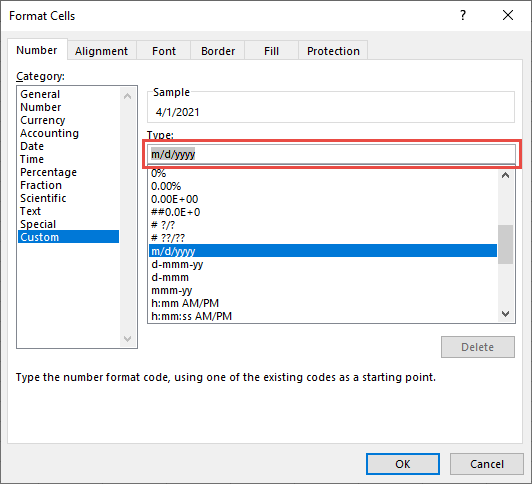
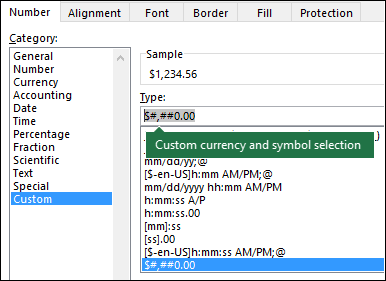
The easiest way to test your date formatting is by opening up the Format Cells Menu and selecting Custom. To open the menu, press CTRL + 1 or click this button:
Navigate to the Custom Form and edit the custom formatting:
Here you can see the result of your formatting in real-time. Once you have the formatting you need, simply copy and paste it into the TEXT Function.
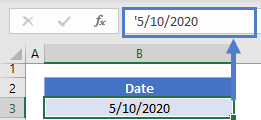
Type Date as Text
If you’re entering a new date into a cell, simply start the date with an apostrophe (‘). By starting a cell with an apostrophe you tell Excel to trade that cell as text.
This keeps the date exactly as entered and prevents it from being converted to a date stored as a serial number.
Convert Date to Text in Google Sheets
All of the above examples work exactly the same in Google Sheets as in Excel.
Dates and times in Excel are stored as serial numbers and converted to human readable values on the fly using number formats. When you enter a date in Excel, you can apply a number format to display that date as you like. In a similar way, the TEXT function allows you to convert a date or time into text in a preferred format. For example, if the date January 9, 2000 is entered in cell A1, you can use TEXT to convert this date into the following text strings as follows:
=TEXT(A1,"mmm") // "Jan"
=TEXT(A1,"dd/mm/yyyy") // "09/01/2012"
=TEXT(A1,"dd-mmm-yy") // "09-Jan-12"
Date format codes
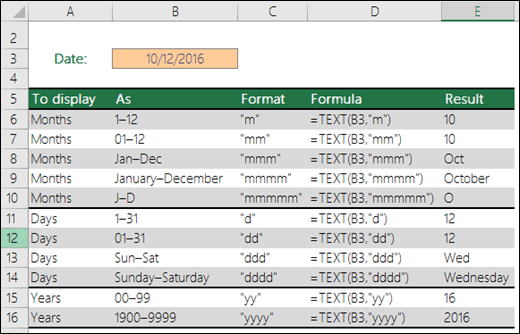
Assuming a date of January 9, 2012, here is a more complete set of formatting codes for date, along with sample output.
| Format code | Output |
| d | 9 |
| dd | 09 |
| ddd | Mon |
| dddd | Monday |
| m | 1 |
| mm | 01 |
| mmm | Jan |
| mmmm | January |
| mmmmm | J |
| yy | 12 |
| yyyy | 2012 |
| mm/dd/yyyy | 01/09/2012 |
| m/d/y | 1/9/12 |
| ddd, mmm d | Mon, Jan 9 |
| mm/dd/yyyy h:mm AM/PM | 01/09/2012 5:15 PM |
| dd/mm/yyyy hh:mm:ss | 09/01/2012 17:15:00 |
You can use the TEXT function to convert dates or any numeric value to a fixed text format. You can explore available formats by navigating to Format Cells (Win: Ctrl + 1, Mac: Cmd + 1) and selecting various format categories in the list to the left. Also see: Excel custom number formats.
На чтение 5 мин Просмотров 4.3к. Опубликовано 19.02.2022
Excel сохраняет даты в виде порядковых номеров. Человеку невозможно их читать и понимать, но, таким образом, можно использовать их в функциях расчета, к примеру добавить к дате или времени какое-то количество времени (день, год и так далее).
Но, довольно часто, вам может быть нужно использовать даты в одних ячейках с текстом, так сказать, объединять.
На картинке пример объединения даты с текстом в одной ячейке. Видите как выглядит наша дата? Это формат порядкового номера Excel.
Именно в таких ситуациях вам может понадобиться привести дату в «читаемый» формат.
Содержание
- Переводим дату в текстовый формат
- Как привести указанную дату в текстовый формат
- Как привести текущую дату в текстовый формат
- Переводим дату в текстовый формат с помощью функции «Текст по столбцам»
- Переводим дату в текстовый формат с помощью копирования и вставки
Переводим дату в текстовый формат
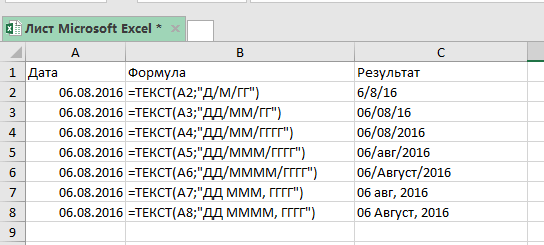
Когда нам нужно привести дату в определенный формат (к примеру, 16-08-2016), мы можем вызвать функцию ТЕКСТ.
Итак, как она работает.
Синтаксис:
=ТЕКСТ(значение; формат_текста)Она принимает два аргумента:
- Значение — в нашем случае это дата, которую вы хотите преобразовать в текст нужного формата. Это может быть просто дата, ссылка на ячейку с датой, или результат формулы.
- Формат_текста — формат, в котором нужно показать нашу дату. Формат должен быть указан в двойных кавычках.
Какие есть форматы и разделители?
Формат дат состоит из 4 составляющих:
- день
- месяц
- год
- разделитель
Ниже приведены форматы, которые можно использовать для каждой части:
Формат дня:
- Д — день будет отображаться без нуля, т.е. 1 будет отображаться как 1, а 12 как 12.
- ДД — день будет отображаться с нулем, т.е. 1 будет 01, а 12 как 12.
- ДДД — будет отображаться день недели(сокращенно), т.е. «Пятница» будет «Пят».
- ДДДД — будет отображаться день недели(полностью), т.е. «Пятница» будет «Пятница».
Формат месяца:
- М — месяц будет отображаться без нуля, т.е. 1 будет отображаться как 1, а 12 как 12.
- ММ — месяц будет отображаться с нулем, т.е. 1 будет 01, а 12 как 12.
- МММ — месяц будет отображаться с сокращенным названием, т.е. «Сентябрь» будет «Сен».
М — месяц будет отображаться без нуля, т.е. 1 будет отображаться как 1, а 12 как 12.
ММ — месяц будет отображаться с нулем, т.е. 1 будет 01, а 12 как 12.
МММ — месяц будет отображаться с сокращенным названием, т.е. «Сентябрь» будет «Сен».
ММММ — месяц будет отображаться с полным названием, т.е. «Сентябрь» будет «Сентябрь».
Формат года:
- ГГ — год будет отображаться как 2 цифры, т.е. 2019 будет 19.
- ГГГГ — год будет отображаться полностью, т.е. 2019 будет 2019.
Разделитель:
- «/» : это просто разделитель между цифрами в дате, т.е. отображаться будет как 01/01/2019.
- «-»: такой же разделитель между цифрами, т.е. отображаться будет как 01-01-2019.
- Пробелы и запятые: тут немного посложней, вы можете комбинировать и создавать свои форматы отображения, например, 01 января, 2019 года.
Итак, разберем примеры.
Как привести указанную дату в текстовый формат
Пример:
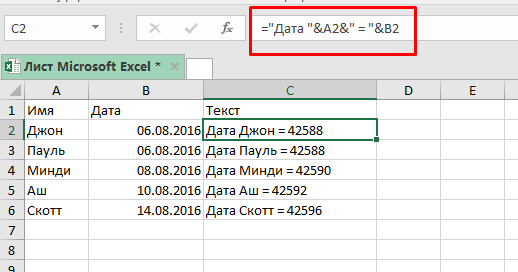
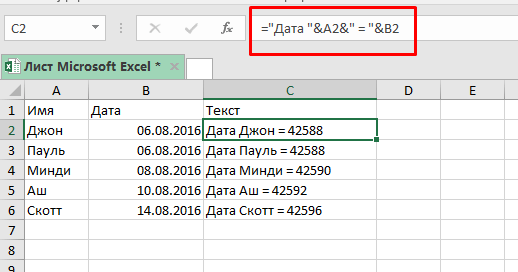
Итак, мы получили дату вместе с текстом, но дата сейчас в формате порядкового номера Excel.
Формула:
="Дата"&A2&"="&B2 Теперь, нам нужно получить дату в «привычном» для нас виде.
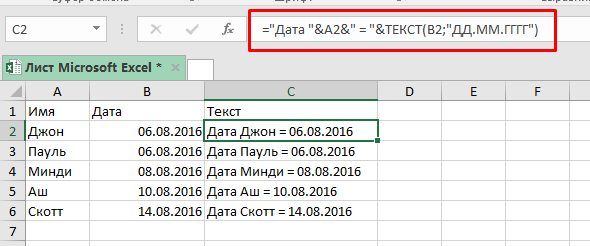
Формула будет:
="Дата "&A2&" = "&ТЕКСТ(B2;"ДД.ММ.ГГГГ")Итак, мы вызвали функцию ТЕКСТ, указали ссылку на ячейку и определили формат, результат вы видите на картинке выше.
Какие еще есть форматы и как они выглядят на «выходе»:
Как привести текущую дату в текстовый формат
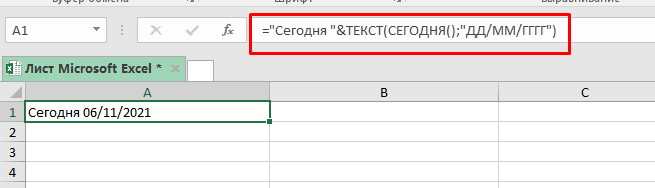
Для того чтобы получить текущую дату мы можем использовать функцию СЕГОДНЯ.
Формула:
="Сегодня "&ТЕКСТ(СЕГОДНЯ();"ДД/ММ/ГГГГ")Эта функция может пригодиться вам в случае, если вы формируете отчеты, где важна, например, дата изменения файла.
Переводим дату в текстовый формат с помощью функции «Текст по столбцам»
Если формулы и вызов функций вам не по душе, есть вариант и для вас.
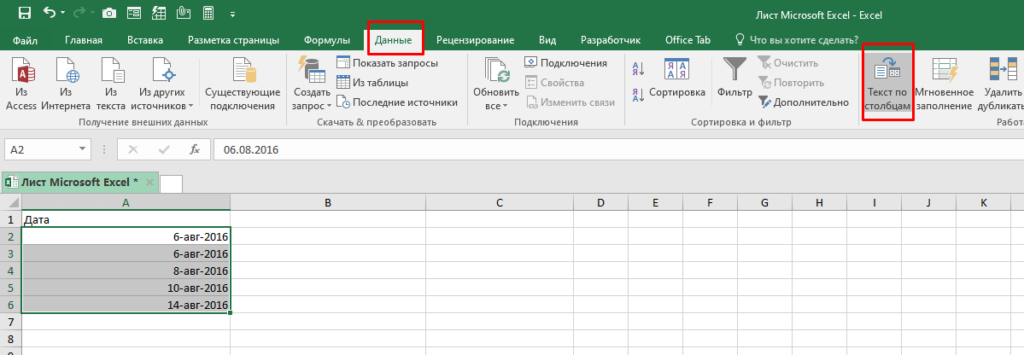
Допустим, у нас есть следующие данные и нам нужно преобразовать их в текстовый формат:
Пошаговая инструкция:
- Выделите ячейки, которые необходимо преобразовать в текст;
- Перейдите в раздел «Данные» -> «Текст по столбцам»;
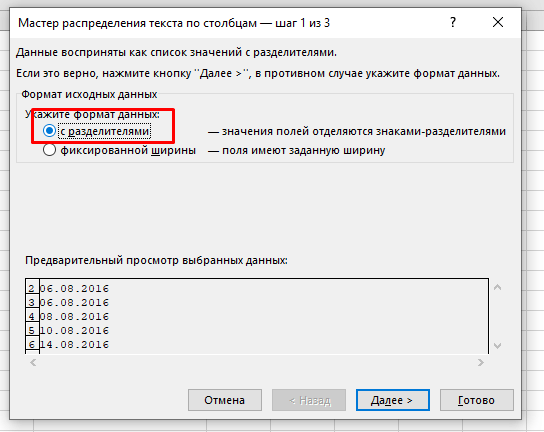
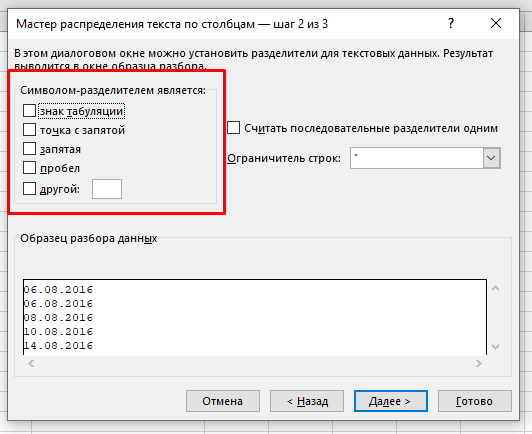
- В открывшемся окне:
- Выберите опцию «с разделителями»;
- Снимите все галочки и нажмите «Далее»;
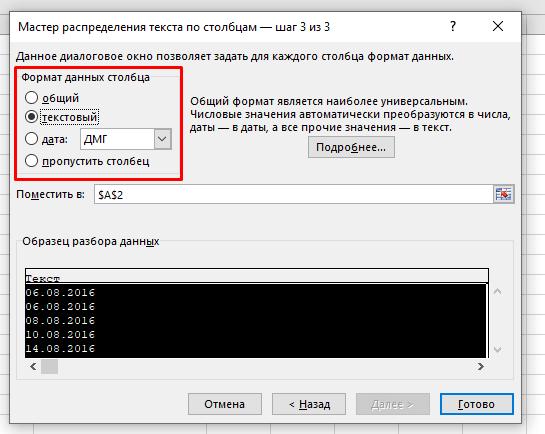
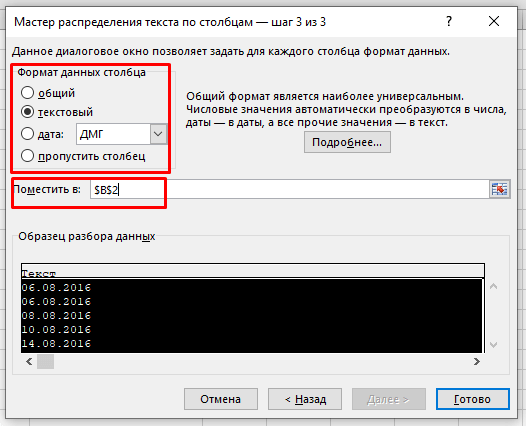
- Выберите формат «текстовый» укажите куда поместить наши, уже текстовые, значения и нажмите «Готово».
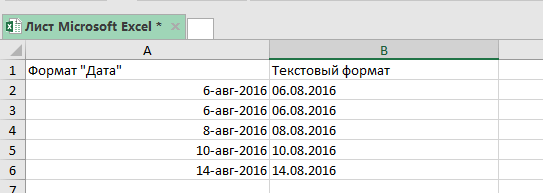
Функция сразу же переводит даты в текстовый формат.
Важная информация: эта функция устанавливает формат для дат по умолчанию для настроек вашей системы. То есть если вы хотите записать даты в определенном формате вам нужно использовать способы рассмотренные ранее, но для начала дочитайте нашу статью, возможно следующий вариант подойдет вам.
Переводим дату в текстовый формат с помощью копирования и вставки
Пошаговая инструкция:
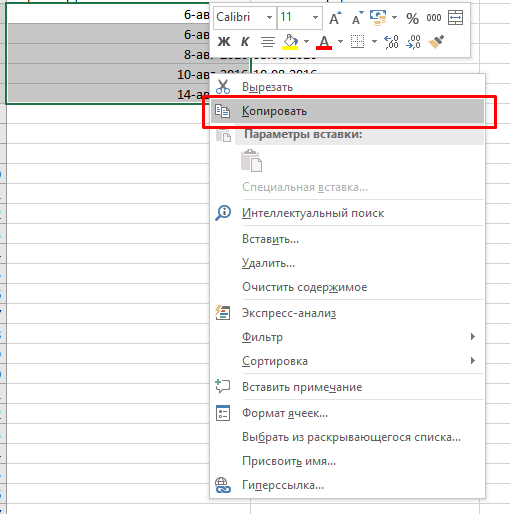
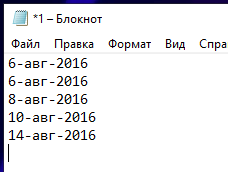
- Выделите ячейки с датами, которые нужно преобразовать, и скопируйте их;
- Откройте обычный блокнот и вставьте наши данные туда, как только вы это сделаете, данные сразу же потеряют формат, т.е. станут обычным текстом (потому что в блокноте нет никаких форматов данных, кроме текста);
- Выделите ячейки, куда вы будете вставлять даты и поменяйте их формат на «Текстовый»;
- А теперь, заново скопируйте даты из блокнота, а затем вставьте их в Excel.
Excel сохраняет даты в виде порядковых номеров. Человеку невозможно их читать и понимать, но, таким образом, можно использовать их в функциях расчета, к примеру добавить к дате или времени какое-то количество времени (день, год и так далее).
Но, довольно часто, вам может быть нужно использовать даты в одних ячейках с текстом, так сказать, объединять.
На картинке пример объединения даты с текстом в одной ячейке. Видите как выглядит наша дата? Это формат порядкового номера Excel.
The TEXT function lets you change the way a number appears by applying formatting to it with format codes. It’s useful in situations where you want to display numbers in a more readable format, or you want to combine numbers with text or symbols.
Note: The TEXT function will convert numbers to text, which may make it difficult to reference in later calculations. It’s best to keep your original value in one cell, then use the TEXT function in another cell. Then, if you need to build other formulas, always reference the original value and not the TEXT function result.
Syntax
TEXT(value, format_text)
The TEXT function syntax has the following arguments:
|
Argument Name |
Description |
|
value |
A numeric value that you want to be converted into text. |
|
format_text |
A text string that defines the formatting that you want to be applied to the supplied value. |
Overview
In its simplest form, the TEXT function says:
-
=TEXT(Value you want to format, «Format code you want to apply»)
Here are some popular examples, which you can copy directly into Excel to experiment with on your own. Notice the format codes within quotation marks.
|
Formula |
Description |
|
=TEXT(1234.567,«$#,##0.00») |
Currency with a thousands separator and 2 decimals, like $1,234.57. Note that Excel rounds the value to 2 decimal places. |
|
=TEXT(TODAY(),«MM/DD/YY») |
Today’s date in MM/DD/YY format, like 03/14/12 |
|
=TEXT(TODAY(),«DDDD») |
Today’s day of the week, like Monday |
|
=TEXT(NOW(),«H:MM AM/PM») |
Current time, like 1:29 PM |
|
=TEXT(0.285,«0.0%») |
Percentage, like 28.5% |
|
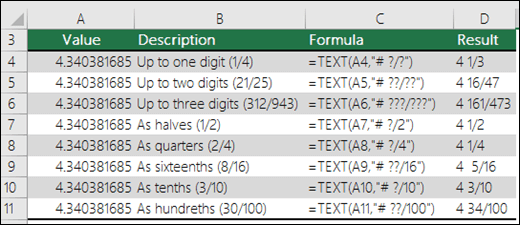
=TEXT(4.34 ,«# ?/?») |
Fraction, like 4 1/3 |
|
=TRIM(TEXT(0.34,«# ?/?»)) |
Fraction, like 1/3. Note this uses the TRIM function to remove the leading space with a decimal value. |
|
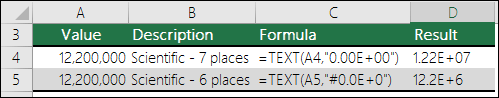
=TEXT(12200000,«0.00E+00») |
Scientific notation, like 1.22E+07 |
|
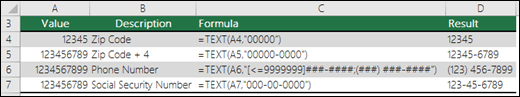
=TEXT(1234567898,«[<=9999999]###-####;(###) ###-####») |
Special (Phone number), like (123) 456-7898 |
|
=TEXT(1234,«0000000») |
Add leading zeros (0), like 0001234 |
|
=TEXT(123456,«##0° 00′ 00»») |
Custom — Latitude/Longitude |
Note: Although you can use the TEXT function to change formatting, it’s not the only way. You can change the format without a formula by pressing CTRL+1 (or 
Download our examples
You can download an example workbook with all of the TEXT function examples you’ll find in this article, plus some extras. You can follow along, or create your own TEXT function format codes.
Download Excel TEXT function examples
Other format codes that are available
You can use the Format Cells dialog to find the other available format codes:
-
Press Ctrl+1 (
+1 on the Mac) to bring up the Format Cells dialog.
-
Select the format you want from the Number tab.
-
Select the Custom option,
-
The format code you want is now shown in the Type box. In this case, select everything from the Type box except the semicolon (;) and @ symbol. In the example below, we selected and copied just mm/dd/yy.
-
Press Ctrl+C to copy the format code, then press Cancel to dismiss the Format Cells dialog.
-
Now, all you need to do is press Ctrl+V to paste the format code into your TEXT formula, like: =TEXT(B2,»mm/dd/yy«). Make sure that you paste the format code within quotes («format code»), otherwise Excel will throw an error message.
Format codes by category
Following are some examples of how you can apply different number formats to your values by using the Format Cells dialog, then use the Custom option to copy those format codes to your TEXT function.
Why does Excel delete my leading 0’s?
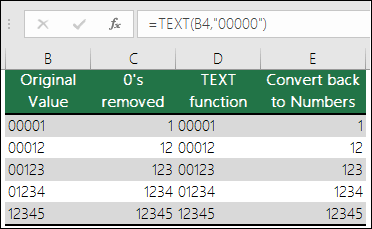
Excel is trained to look for numbers being entered in cells, not numbers that look like text, like part numbers or SKU’s. To retain leading zeros, format the input range as Text before you paste or enter values. Select the column, or range where you’ll be putting the values, then use CTRL+1 to bring up the Format > Cells dialog and on the Number tab select Text. Now Excel will keep your leading 0’s.
If you’ve already entered data and Excel has removed your leading 0’s, you can use the TEXT function to add them back. You can reference the top cell with the values and use =TEXT(value,»00000″), where the number of 0’s in the formula represents the total number of characters you want, then copy and paste to the rest of your range.
If for some reason you need to convert text values back to numbers you can multiply by 1, like =D4*1, or use the double-unary operator (—), like =—D4.
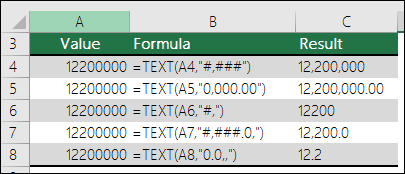
Excel separates thousands by commas if the format contains a comma (,) that is enclosed by number signs (#) or by zeros. For example, if the format string is «#,###», Excel displays the number 12200000 as 12,200,000.
A comma that follows a digit placeholder scales the number by 1,000. For example, if the format string is «#,###.0,», Excel displays the number 12200000 as 12,200.0.
Notes:
-
The thousands separator is dependent on your regional settings. In the US it’s a comma, but in other locales it might be a period (.).
-
The thousands separator is available for the number, currency and accounting formats.
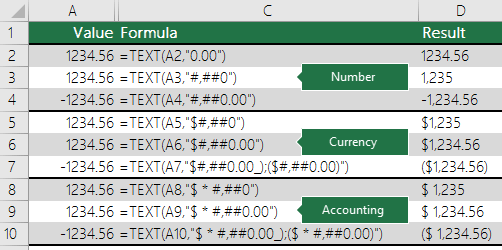
Following are examples of standard number (thousands separator and decimals only), currency and accounting formats. Currency format allows you to insert the currency symbol of your choice and aligns it next to your value, while accounting format will align the currency symbol to the left of the cell and the value to the right. Note the difference between the currency and accounting format codes below, where accounting uses an asterisk (*) to create separation between the symbol and the value.
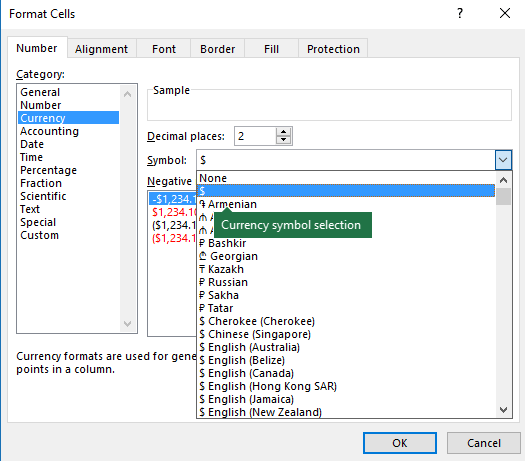
To find the format code for a currency symbol, first press Ctrl+1 (or 
Then click Custom on the left from the Category section, and copy the format code, including the currency symbol.
Note: The TEXT function does not support color formatting, so if you copy a number format code from the Format Cells dialog that includes a color, like this: $#,##0.00_);[Red]($#,##0.00), the TEXT function will accept the format code, but it won’t display the color.
You can alter the way a date displays by using a mix of «M» for month, «D» for days, and «Y» for years.
Format codes in the TEXT function aren’t case sensitive, so you can use either «M» or «m», «D» or «d», «Y» or «y».
You can alter the way time displays by using a mix of «H» for hours, «M» for minutes, or «S» for seconds, and «AM/PM» for a 12-hour clock.
If you leave out the «AM/PM» or «A/P», then time will display based on a 24-hour clock.
Format codes in the TEXT function aren’t case sensitive, so you can use either «H» or «h», «M» or «m», «S» or «s», «AM/PM» or «am/pm».
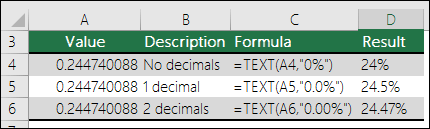
You can alter the way decimal values display with percentage (%) formats.
You can alter the way decimal values display with fraction (?/?) formats.
Scientific notation is a way of displaying numbers in terms of a decimal between 1 and 10, multiplied by a power of 10. It is often used to shorten the way that large numbers display.
Excel provides 4 special formats:
-
Zip Code — «00000»
-
Zip Code + 4 — «00000-0000»
-
Phone Number — «[<=9999999]###-####;(###) ###-####»
-
Social Security Number — «000-00-0000»
Special formats will be different depending on locale, but if there aren’t any special formats for your locale, or if these don’t meet your needs then you can create your own through the Format Cells > Custom dialog.
Common scenario
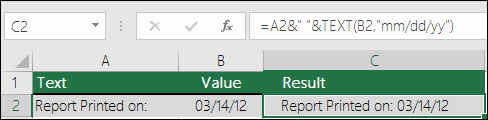
The TEXT function is rarely used by itself, and is most often used in conjunction with something else. Let’s say you want to combine text and a number value, like “Report Printed on: 03/14/12”, or “Weekly Revenue: $66,348.72”. You could type that into Excel manually, but that defeats the purpose of having Excel do it for you. Unfortunately, when you combine text and formatted numbers, like dates, times, currency, etc., Excel doesn’t know how you want to display them, so it drops the number formatting. This is where the TEXT function is invaluable, because it allows you to force Excel to format the values the way you want by using a format code, like «MM/DD/YY» for date format.
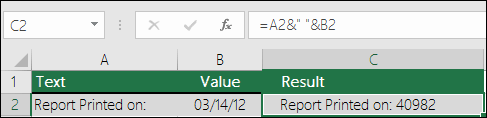
In the following example, you’ll see what happens if you try to join text and a number without using the TEXT function. In this case, we’re using the ampersand (&) to concatenate a text string, a space (» «), and a value with =A2&» «&B2.
As you can see, Excel removed the formatting from the date in cell B2. In the next example, you’ll see how the TEXT function lets you apply the format you want.
Our updated formula is:
-
Cell C2:=A2&» «&TEXT(B2,»mm/dd/yy») — Date format
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, you can use the UPPER, LOWER and PROPER functions. For example, =UPPER(«hello») would return «HELLO».
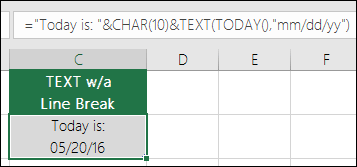
Yes, but it takes a few steps. First, select the cell or cells where you want this to happen and use Ctrl+1 to bring up the Format > Cells dialog, then Alignment > Text control > check the Wrap Text option. Next, adjust your completed TEXT function to include the ASCII function CHAR(10) where you want the line break. You might need to adjust your column width depending on how the final result aligns.
In this case, we used: =»Today is: «&CHAR(10)&TEXT(TODAY(),»mm/dd/yy»)
This is called Scientific Notation, and Excel will automatically convert numbers longer than 12 digits if a cell(s) is formatted as General, and 15 digits if a cell(s) is formatted as a Number. If you need to enter long numeric strings, but don’t want them converted, then format the cells in question as Text before you input or paste your values into Excel.
See Also
Create or delete a custom number format
Convert numbers stored as text to numbers
All Excel functions (by category)
I have an Excel file which has a column formatted as date in the format dd-mm-YYYY.
I need to convert that field to text. If I change the field type excel converts it to a strange value (like 40603).
I tried the text function but it gives me Error 508.
Any help?
Lance Roberts
22.2k32 gold badges112 silver badges129 bronze badges
asked Apr 3, 2012 at 12:04
2
You don’t need to convert the original entry — you can use TEXT function in the concatenation formula, e.g. with date in A1 use a formula like this
="Today is "&TEXT(A1,"dd-mm-yyyy")
You can change the «dd-mm-yyyy» part as required
answered Apr 3, 2012 at 12:20
barry houdinibarry houdini
45.5k8 gold badges63 silver badges80 bronze badges
2
You can use TEXT like this as part of a concatenation
=TEXT(A1,"dd-mmm-yy") & " other string"
answered Apr 3, 2012 at 12:23
brettdjbrettdj
54.6k16 gold badges113 silver badges176 bronze badges
If that is one table and have nothing to do with this — the simplest solution can be copy&paste to notepad then copy&paste back to excel 
answered Apr 3, 2012 at 12:10
AlexHalkinAlexHalkin
1,08814 silver badges33 bronze badges
2
Как-то пришлось создать базу в Excel по дням на весь год. Для дальнейшего управления мне надо было перевести дату в текст.
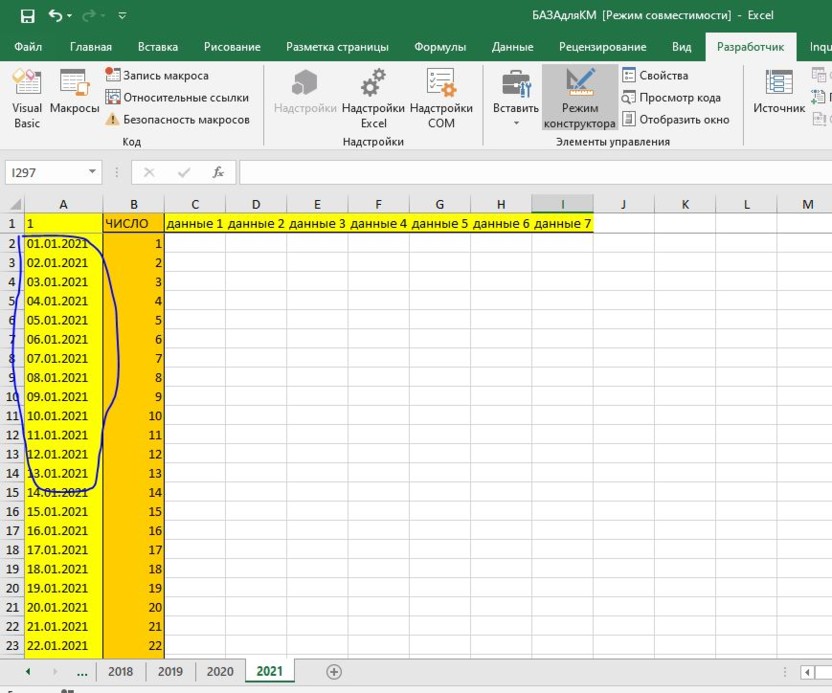
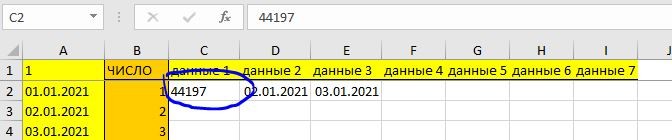
Можно было просто выставить начальную дату и потом протянуть ее, но дело в том, что когда ячейка обладала типом «Дата», появлялись кое-какие глюки. Пришлось перевести ее в текстовый тип. И тут снова проблема – если формат ячейки типа «Дата» переводить в тип «Текст», выходит вот такая штука:
Не знаю, как всем, а мне легче было накидать маленький макрос.
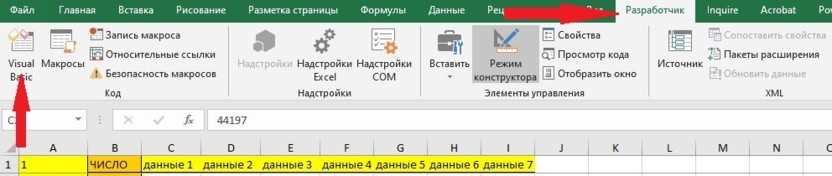
Двойным щелчком по вкладке модулей в открывшемся окне накидал следующее:
Разбор макроса. В нем я использую три переменные:
- newdate – тип «Дата» для перебора даты,
- dateWrite – тип «Текст» для перевода даты в текст,
- а – число для смены ячеек.
а = 2 – первоначальный номер ячейки. Затем переменной newdate присваиваем первоначальную дату «1 января 2021 года» – #1/1/2021#, запускаем цикл, пока год даты не изменится на 2022.
В цикле переменной dateWrite присваивается дата, записываем в ячейку значение dateWrite, затем номер ячейки мы увеличиваем на один, а дату – на один день. И цикл запускается заново.
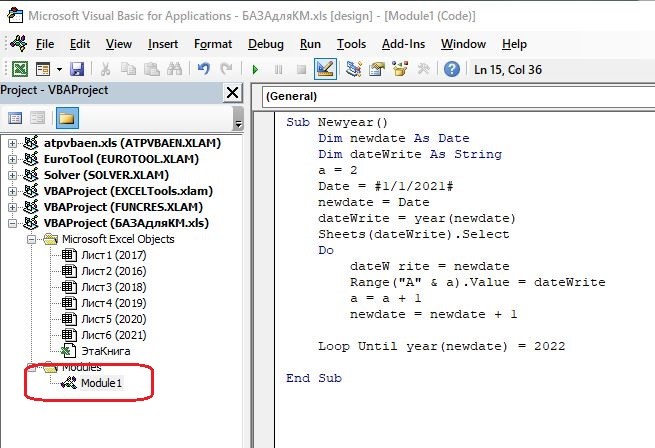
Текс полного макроса:
Sub Newyear()
Dim newdate As Date
Dim dateWrite As String
a = 2
Date = #1/1/2021#
newdate = Date
dateWrite = year(newdate)
Sheets(dateWrite).Select
Do
dateWrite = newdate
Range(«A« & a).Value = dateWrite
a = a + 1
newdate = newdate + 1
Loop Until year(newdate) = 2022
End Sub
Прочел статью про функцию сегодня(), вспомнил про этот метод и решил поделиться им. Это моя первая статья, так что строго не судите. Может, кому и пригодится.