Insert Fields in a Microsoft Word Document to Display Variable Content
by Avantix Learning Team | Updated January 10, 2021
Applies to: Microsoft® Word® 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019 or 365 (Windows)
You can insert built-in or custom fields in Word documents to display variable content that will change when you update the fields. Some fields (like page numbers, merge fields or cross-references) are inserted automatically when you use Microsoft Word features. If you want to insert custom fields, you will need to create custom document properties.
By default, Word displays the result of a field rather than its field codes. You can right-click a field and select Toggle Field Codes to display field codes or field results.
Recommended article: How to Hide Comments in Word (or Display Them)
Do you want to learn more about Microsoft Word? Check out our virtual classroom or live classroom Word courses >
If you are working with fields in Microsoft Word, you will be using quite a few function keys (such as F9). On some laptops, you will need to press the Fn key on your keyboard to enable your function keys. For example, instead of pressing F9 to update a field or fields, you would press Fn + F9.
Inserting built-in fields
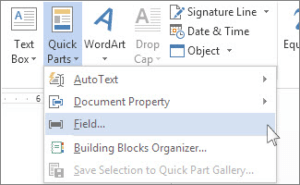
To insert a field, click Quick Parts in the Text group on the Insert tab in the Ribbon. The Field command appears in the Quick Parts drop-down menu as follows:
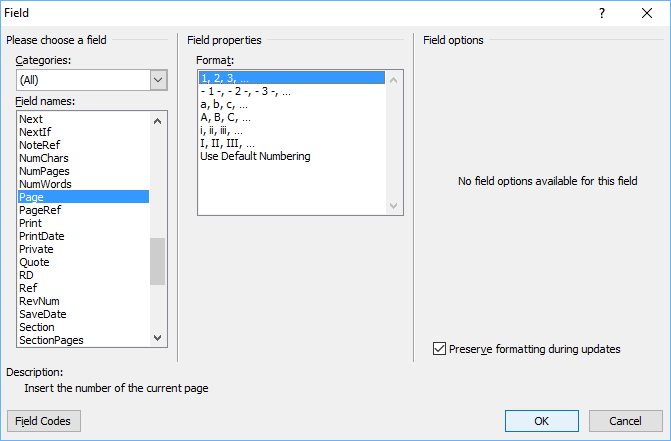
Below is the Field dialog box in Microsoft Word with Page selected:
To insert a built-in field using the Field dialog box:
- Navigate to the location in the Word document where you want to insert a field.
- Click the Insert tab in the Ribbon and then click Quick Parts in the Text group. A drop-down menu appears.
- Select Field. A dialog box appears.
- In the list of Field names, select a field. You can filter the list by clicking the down arrow in the Categories list and selecting a category first. Select All to display all fields.
- Under Field properties, select any properties or options you want.
- To view the codes for a field in the Field box, click Field Codes. For some fields, this button is clicked by default.
- Ensure that Preserve Formatting During Updates is checked so that formatting you apply is not removed when the fields are updated.
- Click OK. The field is inserted into the document.
Format the field results by applying text formatting to the field using the Home tab in the Ribbon.
You can view or hide all field codes in your document by pressing Alt + F9. Field codes appear between braces or curly brackets { } and you cannot type these braces. Be sure to hide the field codes again by pressing Alt + F9.
To edit a built-in field in the Field dialog box:
- Right-click the field and then click Edit Field. A dialog box appears.
- Change the field properties and options.
- Click OK.
Understanding Word document properties
There are 3 different types of document properties in Word:
- Standard document properties (also called built-in document properties)
- Custom document properties
- Document library properties
Word documents contain a set of standard document properties such as Title, Author, Keywords and Comments. These properties are used to store metadata about your document. You cannot change the name of standard properties but you can edit the value of some of them (such as Title). Other standard properties that cannot be edited store data that is updated automatically (such as Size or Last Modified).
Document library properties are related to documents that are stored in a document library on a website or in a public folder (such as files in SharePoint).
In addition to the standard properties, you can create your own custom document properties. These properties can be created to store additional information in a document other than the standard document properties. For example, custom document properties could be created for Product1, Product2, Product3, Sponsor, Project Manager, Cell Phone or Disclaimer. Each custom document property must be assigned a name, a data type and a value. The four data types are Text, Date, Number and Yes or No.
After you create custom document properties for your Word document, you can then insert them as custom fields.
Adding a custom document property
To add a custom document property:
- Open the Word document in which you want to add a custom document property.
- Click the File tab in the Ribbon and then click Info on the left. Info is usually selected by default.
- On the right side of screen, click Properties. A drop-down menu appears.
- Select Advanced Properties. A dialog box appears.
- Click the Custom tab in the dialog box.
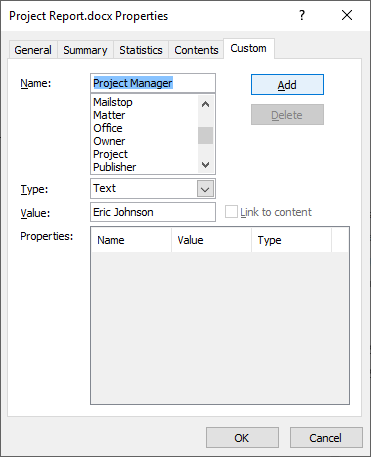
- Type a name for the custom document property in the Name box. You can also choose one of the other properties that appear in the drop-down list.
- Select Text, Date, Number or Yes or No as the data type for the custom property.
- Enter a value for the property in the Value box.
- Click Add. The custom property appears in the list at the bottom of the dialog box.
- Click OK.
After you have added a custom document property, you will be able to insert it into your document as a field.
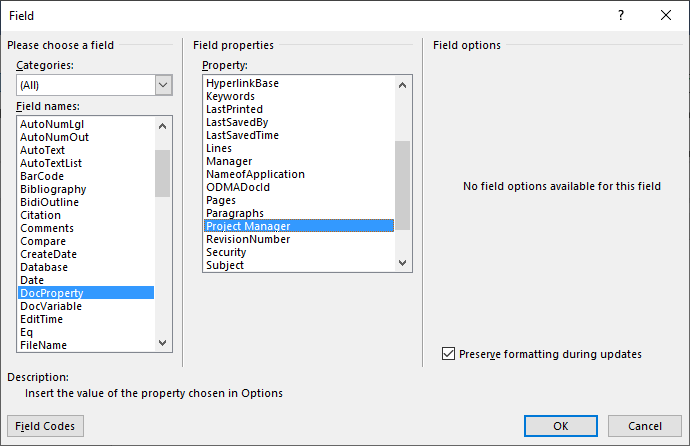
In the example below, we’re adding a field for Project Manager:
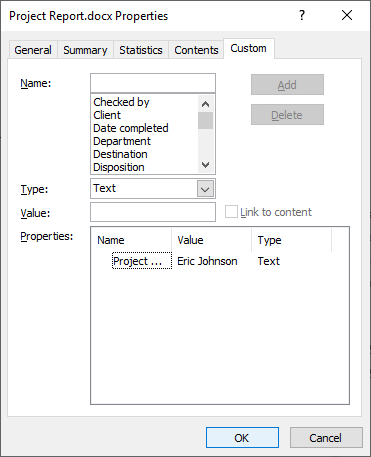
After you click Add, the custom field appears in the Properties list:
Inserting custom document property fields
The value of a custom document property can be inserted in a Word document using DocProperty fields. Custom document properties that have been added to a document are saved with the document whether they are inserted as a DocProperty field or not. You can insert DocProperty fields multiple times in a document.
To insert a custom document property field using the Field dialog box:
Navigate to the location in the Word document where you want to insert a field.
- Click the Insert tab in the Ribbon and then click Quick Parts in the Text group. A drop-down menu appears.
- Select Field. A dialog box appears.
- In the list of Field names on the left, select DocProperty.
- Under Field properties, select a property name.
- To view the codes for a field in the Field box, click Field Codes. For some fields, this button is clicked by default.
- Ensure that Preserve Formatting During Updates is checked so that formatting you apply is not removed when the fields are updated.
- Click OK. The field is inserted into the document.
In the example below, we’re inserting the custom Project Manager field we created in Advanced Properties:
Updating built-in and custom fields
Word should automatically update fields when a document is opened. Many fields are also updated automatically when you go to Print Preview (click the File tab and then click Print). If you prefer, you can update fields manually.
To update a field manually, right-click the field and then click Update Field or press F9.
To update all fields manually in the main body of a document, press Ctrl + A to select all and then press F9.
Some fields in headers, footers or text boxes must be updated separately. Click in the header, footer or text box, press Ctrl + A to select all and then press F9. Page fields do not need to be updated manually because they update when you go the Print Preview.
If you want to edit a custom DocProperty field, you will need to edit it in the Advanced Properties dialog box.
Subscribe to get more articles like this one
Did you find this article helpful? If you would like to receive new articles, join our email list.
More resources
How to Create, Save, Edit and Use Templates in Word
How to Insert, Format and Update Cross-References in Word
5 Ways to Insert the Division Symbol in Word (Type or Insert ÷)
10 Microsoft Word Tips, Tricks and Shortcuts for Selecting in Tables
How to Create a Table of Contents in Word (Insert, Format and Update a TOC)
Related courses
Microsoft Word: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft Excel: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft PowerPoint: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft Word: Long Documents Master Class
Microsoft Word: Styles, Templates and Tables of Contents
Microsoft Word: Designing Dynamic Word Documents Using Fields
VIEW MORE COURSES >
Our instructor-led courses are delivered in virtual classroom format or at our downtown Toronto location at 18 King Street East, Suite 1400, Toronto, Ontario, Canada (some in-person classroom courses may also be delivered at an alternate downtown Toronto location). Contact us at info@avantixlearning.ca if you’d like to arrange custom instructor-led virtual classroom or onsite training on a date that’s convenient for you.
Copyright 2023 Avantix® Learning
Microsoft, the Microsoft logo, Microsoft Office and related Microsoft applications and logos are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in Canada, US and other countries. All other trademarks are the property of the registered owners.
Avantix Learning |18 King Street East, Suite 1400, Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5C 1C4 | Contact us at info@avantixlearning.ca
on
September 8, 2021, 8:17 AM PDT
3 ways to enter fields in Microsoft Word
Microsoft Word fields house instructions that help you create dynamic content; they’re flexible and powerful, if you know how to use them.
We may be compensated by vendors who appear on this page through methods such as affiliate links or sponsored partnerships. This may influence how and where their products appear on our site, but vendors cannot pay to influence the content of our reviews. For more info, visit our Terms of Use page.

Occasionally, a requirement simply can’t be easily met with the built-in features. Microsoft Word fields are similar to little bits of code that have a specific job. They return values that you can’t easily do in Word any other way. Fortunately, they’re easy to use once you get the hang of entering them properly. In this article, I’ll show you three ways to enter a Word field:
- Use the interface
- Ctrl + F9
- Type and convert
I’m using Microsoft 365 on a Windows 10 64-bit system, but you can use earlier versions. Word fields aren’t supported by Word Online; the original values will display, but they won’t update, nor can you enter them.
SEE: 83 Excel tips every user should master (TechRepublic)
About Word fields
You can insert fields to display content that will change when you update those fields. You might not realize it, but you’re already using fields. Page numbers, merge fields and so on are inserted automatically when you use those features.
You’ll notice as you work your way through the quick examples, that the function key, F9, plays a big part when working with fields. Specifically, here’s what this key does:
- Ctrl + F9 enters a blank field.
- Alt + F9 toggles all the fields in the document.
- Shift + F9 toggles the selected field.
In addition to entering and toggling fields, you can modify them using switches. A switch is an additional bit of information; it always starts with a backslash (). Switches add formats and change the field’s behavior a bit. We won’t include switches in this article, but you’ll want to explore them later.
When you enter a field, the underlying field code will use the following syntax:
{ FIELD NAME Properties Optional switches }
See Table A for an explanation of these elements.
Table A
| FIELD TYPE | This is the name of the code and determines what the field does. You’ll often see this part in all uppercase letters, but it isn’t case sensitive. |
| Properties | Optional instructions, but not all fields have them. In the interface dialog that you’ll see in the next section, these are referred to as Field Properties. |
| Switches | These are specific instructions, often to do with formatting that you can enable or disable. The character always denotes a switch. |
When including fields in a document, remember that anyone viewing the document in Word can view the underlying codes, so be careful about including personal or confidential information. I’ve never run into this situation but it’s worth noting.
Now that you have a good feel for what fields are, let’s start inserting them. We’ll begin with the interface method.
How to insert a Word field using the interface
Word’s interface provides the most comprehensive method for inserting fields. Even if you find another method easier, I encourage you to review the interface so you can learn what fields are available and about their switches.
SEE: Windows 10: Lists of vocal commands for speech recognition and dictation (free PDF) (TechRepublic)
To enter a field using the interface, do the following:
- Position the cursor where you want to insert the field, which can be in the document body, or the header or footer.
- Click the Insert tab and then click the Quick Parts dropdown in the Text group.
- From the dropdown, choose Fields (Figure A).
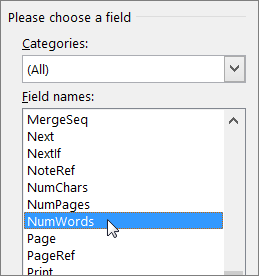
- The resulting dialog lists the Word fields in the Field Names list, which you can filter using the Categories list. For this simple example, select Author and then select First Capital in the Format list as shown in Figure B.
- Click OK, and you’ll see the author’s name in the document (Figure C).
Figure A
Figure B
Figure C
You may have noticed a few other options in the dialog:
- Field Codes will display the underlying field code.
- Options will display formatting options and other specialized options that are specific to the field.
- Preserve Formatting During Updates does just what it says: it preserves formatting.
You’ll want to explore the list of fields and their many options when you have more time.
You can use the interface to nest fields. After choosing one field, move the cursor inside that field and then return to the list and choose the second field. This capability takes a bit of practice. In fact, many users find it easier to enter a nested field manually.
How to insert a Word field by typing and converting
Perhaps the easiest method to enter any field is to simply type it, select it and then press Ctrl + F9. Doing so converts the text to the field(s). Let’s try this with again, the Author field:
- Position the cursor where you want to insert the field.
- Type Author
- Select the text you just typed (Figure D).
- Press Ctrl + F9 to convert the string into a true field. As you can see, Word adds the brackets.
- To display the field value instead of the field, press F9.
Figure D
This is a quick and easy way to enter a single field when you know the field code and any switches you might want to include. You can also use this method to insert a nested field, but you must insert each individually. You can’t type out an entire string and convert all the fields at once.
How to insert a Word field by using Ctrl + F9
The third method is similar to the previous method. Press Ctrl + F9 to insert a pair of empty brackets and then type the field code and any switches. Let’s try this method with the same { Author } field:
- Position the cursor where you want to insert the field.
- Press Ctrl + F9 to enter a blank field, as shown in Figure E.
- Enter the field code Author inside the brackets and press F9 to calculate the result.
Figure E
Word displays a field’s results rather than the field code, by default. Right-clicking serves as a toggle to display the underlying field code instead of its result. Doing so converts only the one field, so this is an easy way to quickly edit only one field.
For a full list of field codes, visit List of field codes in Word.
Also See
-
How to make fewer mistakes and work more efficiently using predictive text in Microsoft 365
(TechRepublic) -
How to use the many text wrapping options in Microsoft Word
(TechRepublic) -
Microsoft 365: A cheat sheet
(TechRepublic) -
Zoom vs. Microsoft Teams, Google Meet, Cisco WebEx and Skype: Choosing the right video-conferencing apps for you (free PDF)
(TechRepublic) -
Checklist: Securing Windows 10 systems
(TechRepublic Premium) -
Must-read coverage: Windows 10
(TechRepublic on Flipboard)
-
Microsoft
-
Software
Inserting fields can give you precise control over dynamic text in your document. Fields are an important part of Word, but it’s good to know that many fields are inserted for you through built-in commands and features. For example, fields are at work when you insert page numbers or create a table of contents. In these cases, it’s probably simpler to let Word automatically add them for you. Fields are most useful when you need placeholders for data that might change in your document and for creating form letters or labels in mail-merge documents.
These steps work for inserting any field code in Word. For a list of all field codes with detailed information about each, see List of field codes in Word.
Insert a field
-
Click where you want to insert a field.
Tip: If you know the field code for the field that you want to insert, you can type it directly in your document. First press CTRL+F9, and then type the code within the brackets.
-
Click Insert > Quick Parts > Field.
-
In the Field names list, select a field name.
Tip: You can filter the list by clicking the down arrow in the Categories list.
-
Under Field properties, select any properties or options you want, and click OK.
Notes:
-
To see the codes for a particular field in the Field box, click Field Codes. For some fields, this button is clicked by default.
-
To nest a field within another field, first insert the outer, or container, field (steps 1-4 above). Then place the insertion point inside the field code where you want to insert the inner field, and repeat steps 2-4 above.
-
If you want to see the codes for a particular field in the Field dialog box, click Field Codes.
-
To nest a field within another field, first insert the outer, or container, field, by using the Field dialog box. In your document, place the insertion point inside the field code where you want to insert the inner field. Then use the Field dialog box to insert the inner field.
If you know the field code for the field that you want to insert, you can also type it directly in your document. First press CTRL+F9, and then type the code within the brackets.
About field codes and syntax
You can insert a field if you want to:
-
Add, subtract, or perform other calculations. To do so, use the = (Formula) field.
-
Work with documents in a mail merge. For example, insert ASK and FILLIN fields to display a prompt as Word merges each data record with the main document.
In other cases, it is simpler to use the commands and options that are provided in Word to add the information that you want. For example, you can insert a hyperlink by using the HYPERLINK field, but it is easier to use the Hyperlink command in the Links group on the Insert tab.
Important: You cannot insert field code brackets by typing the brace characters on the keyboard. To insert field code brackets, press CTRL+F9.
Field code syntax
Field codes appear between curly brackets ( { } ). Fields behave like formulas in Microsoft Office Excel — the field code is like the formula, and the field result is like the value that the formula produces. You can switch between displaying field codes and results in your document by pressing ALT+F9.
When you view a field code in your document, the syntax looks like this:
{ FIELD NAME Properties Optional switches }
-
FIELD NAME This is the name that appears in the list of field names in the Field dialog box.
-
Properties These are any instructions or variables that are used in a particular field. Not all fields have parameters, and in some fields, parameters are optional instead of required.
-
Optional switches These are any optional settings that are available for a particular field. Not all fields have switches available, other than those that govern the formatting of the field results.
For example, you can place the file name and path of your document in the header or footer by inserting the FILENAME field.
The syntax for the FILENAME field code with the path included looks like this:
{ FILENAME p }
Edit a field
-
Right-click in the field, and then click Edit Field.
-
Change the field properties and options. For information about the properties and options available for a particular field, see List of field codes in Word or search on the field name in Help.
Notes:
-
For some fields, you must display the field code to edit the field. To display all the field codes in the document, press ALT+F9.
-
Some fields are edited in their own dialog boxes instead of in the Field dialog box. For example, if you right-click a hyperlink and then click Edit Hyperlink, the Edit Hyperlink dialog box opens
-
Display the field results
By default, Word displays the field results seamlessly with the content of your document so that someone reading the document is unaware that part of the content is in a field. However, fields can also be displayed with a shaded background, to make them more visible in the document.
You can make the field results blend into the content of the document by turning off the option to display fields with a shaded background and by formatting the field results, or you can call attention to fields by displaying them with a shaded background, either all the time or only when the field is selected.
You can format the field results by applying text formatting to the field or by adding formatting switches to the field code.
Change the shaded background of fields
-
Click the File > Options. (In Word 2007, click Microsoft Office Button
, and then click Word Options.)
-
Click Advanced.
-
Under Show document content, in the Field shading list, do one of the following:
-
To make fields stand out from the rest of the document content, select Always.
-
To make fields blend in seamlessly with the document content, select Never.
-
To make users of Word aware that they have clicked in a field, select When selected.
When the field shading option is set to When selected, the field displays a gray background when you click within the field. However, the gray shading does not indicate that the field is selected. When you select the field by double-clicking or dragging the mouse, highlighting that indicates selection is added to the gray shading.
-
Apply text formatting to a field
-
Select the field that you want to format, and then apply the formatting by using the commands in the Font group on the Home tab.
For example, to underline the name that is inserted by an AUTHOR field, select the entire field code, including brackets (or select the entire field result), and then click Underline in the Font group on the Home tab.
If you update a field, any formatting that you applied to the field results may be lost. To retain the formatting, include the * MERGEFORMAT switch in the field code. When you insert fields by using the Field dialog box, the * MERGEFORMAT switch is included by default.
Add a formatting switch to a field code
-
Right-click the field, and then click Edit Field.
-
Do one of the following:
-
If Field properties and Field options are displayed, select the formatting options that you want.
-
If only the field code is displayed, click Options, and then select the formatting options that you want.
If the Options button appears dimmed, additional formatting options may not be available.
-
You can use three formatting switches to format field results:
-
Format switch (*)
-
Numeric format switch (#)
-
Date-Time format switch (@)
Format switch(*)
The Format field switch (*) defines how to display field results. The format instructions determine the following:
-
The use of uppercase and lowercase letters
-
Number formats — for example, whether 9 is displayed as ix (roman numerals) or ninth (ordinal text)
-
character formats
Format switches also retain a field result’s formatting when the field is updated.
Capitalization formats:
The following is a list of switches and the items that they capitalize:
-
* Caps This switch capitalizes the first letter of each word. For example, { FILLIN «Type your name:» * Caps } displays Luis Alverca even if the name is typed in lowercase letters.
To select this option in the Field Options dialog box, click Title case.
-
* FirstCap This switch capitalizes the first letter of the first word. For example, { COMMENTS * FirstCap } displays Weekly report on sales.
To select this option in the Field Options dialog box, click First capital.
-
* Upper This switch capitalizes all letters. For example, { QUOTE «word» * Upper } displays WORD.
To select this option in the Field Options dialog box, click Uppercase.
-
* Lower This switch capitalizes none of the result; all letters are lowercase. For example, { FILENAME * Lower } displays weekly sales report.doc.
This switch has no effect if the entire field that contains the switch is formatted as small capital letters.
To select this option in the Field Options dialog box, click Lowercase.
Number formats:
The following is a list of number switches and their results:
-
*alphabetic This switch displays results as alphabetic characters. The result has the same case as the word «alphabetic» in the field code. For example, { SEQ appendix * ALPHABETIC } displays B (instead of 2), and { SEQ appendix * alphabetic } displays b.
To select this option in the Field Options dialog box, click a, b, c,.
-
*Arabic This switch displays results as Arabic cardinal numerals. For example, { PAGE * Arabic } displays 31.
Notes:
-
If the Number format setting in the Page Number Format dialog box is not Arabic, this switch overrides the Number format setting.
-
For page numbers only, there is also an ArabicDash format, which displays results as Arabic cardinal numbers surrounded by hyphen characters. For example, { PAGE * ArabicDash } displays — 31 —.
To select this option in the Field Options dialog box, click 1, 2, ,3, ….
-
-
*CardText This switch displays results as cardinal text. The result is formatted in lowercase letters unless you add a format switch to specify a different capitalization. For example, { = SUM(A1:B2) * CardText } displays seven hundred ninety, and { = SUM(A1:B2) * CardText * Caps } displays Seven Hundred Ninety.
To select this option in the Field Options dialog box, click One, Two, Three.
-
*DollarText This switch displays results as cardinal text. Word inserts and at the decimal place and displays the first two decimals (rounded) as Arabic numerators over 100. The result is formatted in lowercase letters unless you add a format switch to specify a different capitalization. For example, { = 9.20 + 5.35 * DollarText * Upper } displays FOURTEEN AND 55/100.
To select this option in the Field Options dialog box, click Dollar Text.
-
*Hex This switch displays results as hexadecimal numbers. For example, { QUOTE «458» * Hex } displays 1CA.
To select this option in the Field Options dialog box, click hex ….
-
*OrdText This switch displays results as ordinal text. The result is formatted in lowercase letters unless you add a format switch to specify a different capitalization. For example, { DATE @ «d» * OrdText } displays twenty-first, and { DATE @ «d» * OrdText * FirstCap } displays Twenty-first.
To select this option in the Field Options dialog box, click First, Second, Third, ….
-
*Ordinal This switch displays results as ordinal Arabic numerals. For example, { DATE @ «d» * Ordinal } displays 30th.
To select this option in the Field Options dialog box, click 1st, 2nd, 3rd.
-
*roman This switch displays results as Roman numerals. The result has the same case as the word «roman» in the field code. For example, { SEQ CHAPTER * roman } displays xi, and { SEQ CHAPTER * ROMAN } displays XI.
To select this option in the Field Options dialog box, click I, II, III,.
Character formats and protecting previously applied formats:
The following are character formatting switches and their results:
-
*Charformat This switch applies the formatting of the first letter of the field name to the entire result. The result of the following example has bold formatting because the R in REF is bold.
{ REF chapter2_title * Charformat } displays Whales of the Pacific in bold text.
To add this switch, type it in the field code or in the Field codes box in the Field dialog box.
-
*MERGEFORMAT This switch applies the formatting of the previous result to the new result. For example, if you select the name displayed by the field { AUTHOR * MERGEFORMAT } and apply bold formatting, Word retains the bold formatting when the field is updated to display a new author name.
When you insert fields by using the Field dialog box , the *MERGEFORMAT switch is included by default. You can turn this option off by clearing the Preserve formatting during updates check box in the Field dialog box.
Back to formatting switches
Numeric format switch (#)
The Numeric format switch (#) specifies the display of a numeric result.
For example, the switch # $#,##0.00 in { = SUM(ABOVE) # $#,##0.00 } displays a result such as «$4,455.70.» If the result of a field is not a number, this switch has no effect.
Note: Quotation marks are not required around simple numeric formats that do not include spaces — for example, { MarchSales # $#,##0.00 }. For more complex numeric formats and those that include text or spaces, enclose the numeric format in quotation marks, as shown in the following examples. Word adds quotation marks to numeric format switches if you insert a field by using the Field dialog box or the Formula command in the Data group of the Layout tab (Table Tools contextual tab).
Combine the following format items to build a numeric format switch:
-
0 (zero) This format item specifies the requisite numeric places to display in the result. If the result does not include a digit in that place, Word displays a 0 (zero). For example, { = 4 + 5 # 00.00 } displays 09.00.
-
# This format item specifies the requisite numeric places to display in the result. If the result does not include a digit in that place, Word displays a space. For example, { = 9 + 6 # $### } displays $ 15.
-
x This format item drops digits to the left of the «x» placeholder. If the placeholder is to the right of the decimal point, Word rounds the result to that place. For example:
{ = 111053 + 111439 # x## } displays 492.
{ = 1/8 # 0.00x } displays 0.125.
{ = 3/4 # .x } displays .8. -
. (decimal point) This format item determines the decimal point position. For example, { = SUM(ABOVE) # $###.00 } displays $495.47.
Use the decimal symbol that is specified as part of the regional settings in Control Panel.
-
, (digit grouping symbol) This format item separates a series of three digits. For example, { = NetProfit # $#,###,### } displays $2,456,800.
Use the digit grouping symbol that is specified as part of the regional settings in Control Panel.
-
— (minus sign) This format item adds a minus sign to a negative result or adds a space if the result is positive or 0 (zero). For example, { = 10 — 90 # -## } displays -80.
-
+ (plus sign) This format item adds a plus sign to a positive result, a minus sign to a negative result, or a space if the result is 0 (zero). For example, { = 100 — 90 # +## } displays +10, and { = 90 — 100 # +## } displays -10.
-
%, $, *, and so on This format item includes the specified character in the result. For example, { = netprofit # «##%» } displays 33%.
-
«example formatting for positive; negative» This format item specifies different number formats for positive and negative results, separated by a semicolon. For example, if the bookmark Sales95 is a positive value, the field { Sales95 # «$#,##0.00;-$#,##0.00» } displays the value with regular formatting — for example, «$1,245.65». A negative value is displayed with bold formatting and a minus sign — for example, -$ 345.56.
-
«example formatting for positive; negative; zero» This format item specifies different number formats for a positive result, a negative result, and a 0 (zero) result, separated by semicolons. For example, depending on the value of the Sales95 bookmark, { Sales95 # «$#,##0.00;($#,##0.00);$0» } displays positive, negative, and 0 (zero) values as follows: $1,245.65, ($ 345.56), $0.
-
‘text’ This format item adds text to the result. Enclose the text in single quotation marks. For example, { = { Price } *8.1% # «$##0.00 ‘is sales tax’ » } displays $347.44 is sales tax.
-
`numbereditem` This format item displays the number of the preceding item that you numbered by using the Caption command (References tab, Captions group) or by inserting a SEQ field. Enclose the item identifier, such as «table» or «figure,» in grave accents (`). The sequential number is displayed in Arabic numerals. For example, { = SUM(A1:D4) # «##0.00 ‘is the total of Table’ `table`» } displays 456.34 is the total of Table 2.
Back to formatting switches
Date-Time format switch (@)
The Date-Time format switch (@) specifies the display of a date or time.
For example, the switch @ «dddd, MMMM d, yyyy» in the field { DATE @ «dddd, MMMM d, yyyy» } displays «Friday, November 23, 2007.» Combine the following date and time instructions — day (d), month (M), and year (y); hours (h) and minutes (m) — to build a date-time format. You can also include text, punctuation, and spaces.
Date instructions:
Month (M)
The letter M must be uppercase to distinguish months from minutes.
-
M This format item displays the month as a number without a leading 0 (zero) for single-digit months. For example, July is 7.
-
MM This format item displays the month as a number with a leading 0 (zero) for single-digit months. For example, July is 07.
-
MMM This format item displays the month as a three-letter abbreviation. For example, July is Jul.
-
MMMM This format item displays the month as its full name.
Day (d)
The letter d displays the day of the month or the day of the week. The letter d can be either uppercase or lowercase.
-
d This format item displays the day of the week or month as a number without a leading 0 (zero) for single-digit days. For example, the sixth day of the month is displayed as 6.
-
dd This format item displays the day of the week or month as a number with a leading 0 (zero) for single-digit days. For example, the sixth day of the month is displayed as 06.
-
ddd This format item displays the day of the week or month as a three-letter abbreviation. For example, Tuesday is displayed as Tue.
-
dddd This format item displays the day of the week as its full name.
Year (y)
The letter y displays the year as two or four digits. The letter y can be either uppercase or lowercase.
-
yy This format item displays the year as two digits with a leading 0 (zero) for years 01 through 09. For example, 1999 is displayed as 99, and 2006 is displayed as 06.
-
yyyy This format item displays the year as four digits.
Time instructions:
Hours (h)
A lowercase h bases time on the 12-hour clock. An uppercase H bases time on the 24-hour, or military, clock; for example, 5 P.M. is displayed as 17.
-
h or H This format item displays the hour without a leading 0 (zero) for single-digit hours. For example, the hour of 9 A.M. is displayed as 9.
-
hh or HH This format item displays the hour with a leading 0 (zero) for single-digit hours. For example, the hour of 9 A.M. is displayed as 09.
Minutes (m)
The letter m must be lowercase to distinguish minutes from months.
-
m This format item displays minutes without a leading 0 (zero) for single-digit minutes. For example, { TIME @ «m» } displays 2.
-
mm This format item displays minutes with a leading 0 (zero) for single-digit minutes. For example, { TIME @ «mm» } displays 02.
Seconds (s)
-
s This format item displays seconds without a leading 0 (zero) for single-digit seconds. For example { TIME @ «s» displays 5.
-
ss This format item displays seconds with a leading 0 (zero) for single-digit seconds For example { TIME @ «ss» displays 05.
A.M. and P.M. (AM/PM)
This displays A.M. and P.M. To change the A.M. and P.M. symbols for Microsoft Windows, change the regional settings in Control Panel.
-
am/pm or AM/PM This format item displays A.M. and P.M. as uppercase. For example, { TIME @ «h AM/PM» } and { TIME @ «h am/pm» } display 9 AM or 5 PM.
Other text and punctuation:
-
‘text’ This format item displays any specified text in a date or time. Enclose the text in single quotation marks. For example, { TIME @ «HH:mm ‘Greenwich mean time’ » } displays 12:45 Greenwich mean time.
-
character This format item includes the specified character in a date or time, such as a : (colon), — (hyphen), * (asterisk), or space. For example, { DATE @ «HH:mm MMM-d, ‘yy» } displays 11:15 Nov-6, ’99.
-
`numbereditem` This format item includes in a date or time the number of the preceding item that you numbered by using the Caption command in the Captions group (References tab), or by inserting a SEQ field. Enclose the item identifier, such as table or figure, in grave accents (`). Word displays the sequential number in Arabic numerals. For example, { PRINTDATE @ «‘Table’ `table` ‘was printed on’ M/d/yy» } displays Table 2 was printed on 9/25/02.
Note: Quotation marks are not required around simple date-time formats that do not include spaces or text — for example, { DATE @ MM/yy }. For more complex date-time formats and those that include spaces or text, enclose the entire date-time format in quotation marks, for example, { DATE @ «dddd MMMM d, yyyy’, at’ h:mm» }. Word adds quotation marks to date-time format switches if you insert a field by using the Date and Time command in the Text group of the Insert tab or the Field dialog box.
Back to formatting switches
Control how fields are updated
By default, Word automatically updates fields when a document is opened. That way, information stays up to date. There are situations where you might not want this to happen, however. For example, you may want the date in the header to reflect a particular date rather than automatically updating to the current date every time the document is opened.
Fields can also be updated by right-clicking a field and then clicking Update Field or by clicking in a field and then pressing F9.
To manually update all the fields in the main body of a document, press CTRL+A, and then press F9. Fields in headers, footers, or text boxes must be updated separately. Click within the header, footer, or text box, press CTRL+A, and then press F9.
You can lock fields to prevent automatic or inadvertent updating of the field.
Lock or unlock a particular field
Do one of the following:
-
To lock a field so that field results are not updated, click the field, and then press CTRL+F11.
-
To unlock a field so that field results can be updated, click the field, and then press CTRL+SHIFT+F11.
Lock results of BOOKMARK, INCLUDETEXT, and REF fields
The Lock Result (!) field switch prevents a field that is included in the result of a BOOKMARK, INCLUDETEXT, or REF field from being updated unless the field result in the original location has changed. Without this switch, Word updates fields that are included in a field result whenever the BOOKMARK, INCLUDETEXT, or REF field is updated.
For example, the field { INCLUDETEXT C:\SalesQtr4 Sales.doc ! } inserts the contents of the document «Qtr4 Sales.doc,» which contains a DATE field and an EMBED field. If you update the INCLUDETEXT field, the ! switch prevents Word from updating the DATE and EMBED fields in the included text unless they are first updated in the original document («Qtr4 Sales.doc»). The switch ensures that the text inserted by the INCLUDETEXT field matches the text in the original document.
To update the DATE and EMBED fields in both locations, update fields in the original document (Qtr4 Sales.doc), and then update the INCLUDETEXT field.
There are two simple methods to create fillable fields in Word. One is to create custom fields. The other is to use developer tools and the various data-entry controls that are available there.
Whenever there’s a need for fillable forms, people often turn toward advanced PDF editors with interactive form tools. However, not many people realize that it’s simple to create fillable forms in Word.
There are two methods to do this in Word. One is to use text boxes throughout and then creating custom fields. The other is to use developer tools and the various data-entry controls that are available there.
Which Option Should You Choose?
The method you use depends on what kind of form you’re creating.
You should use the custom field method if the form:
- Has only text fields to fill out
- You don’t mind training your users how to fill out custom fields
- You need forms filled out quickly
You should use developer tools if the form:
- Requires drop-down lists or checkboxes
- You’re sending an individual file to each user
- You don’t want to have to train users on how to use the form
Once you’ve decided which approach you want to take, you can learn how to use each option below.
Create Fillable Forms In Word with Custom Fields
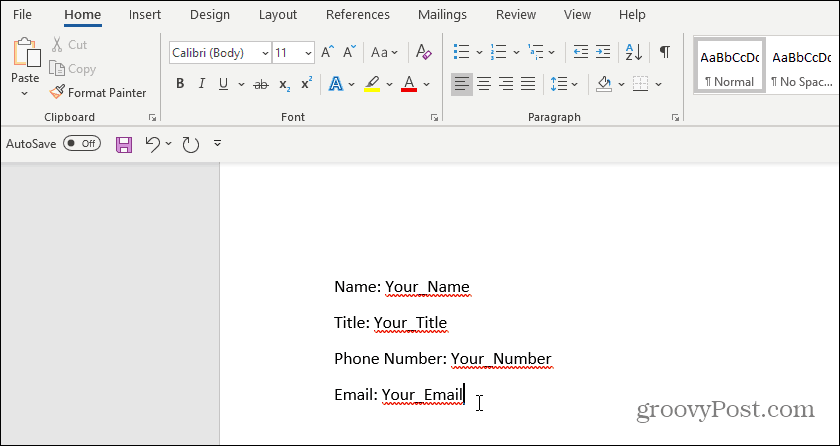
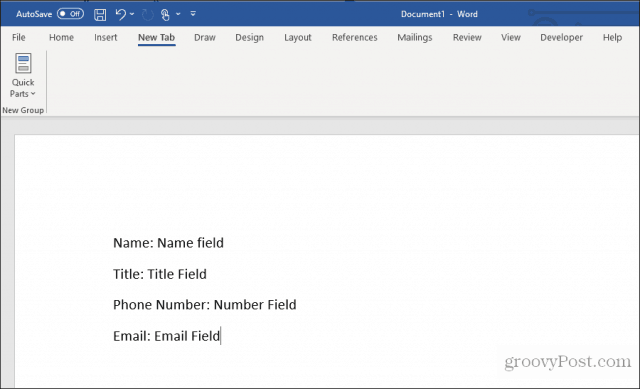
Creating a fillable form with fields is very simple. First, create your form by typing the name for each field and filler text for where the answers should go.
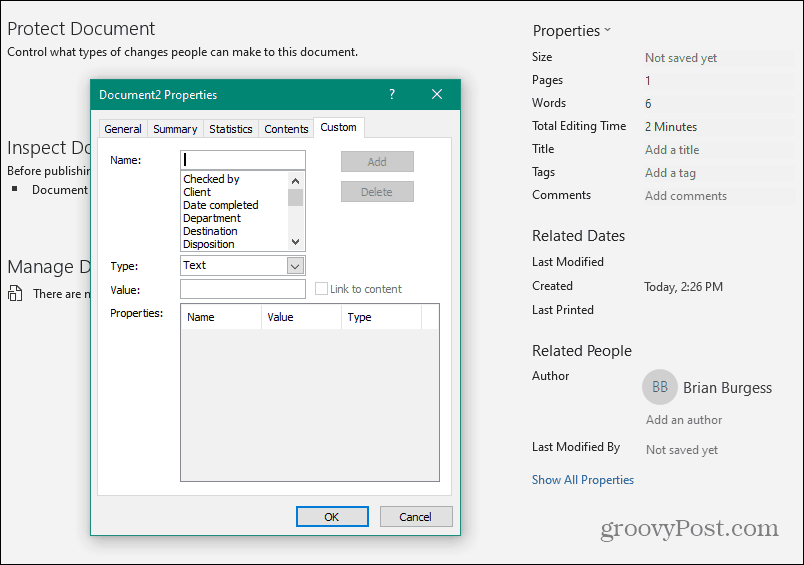
Next, you’ll need to create custom fields for data entry. To do this, select File, Options, and Properties. Then, under Properties, select Advanced Properties.
This will open a Document Properties dialog window. Select the Custom tab.
This window is where you’ll create each custom field that will go into your fillable form. Then, one at a time, name each field and give it an initial value.
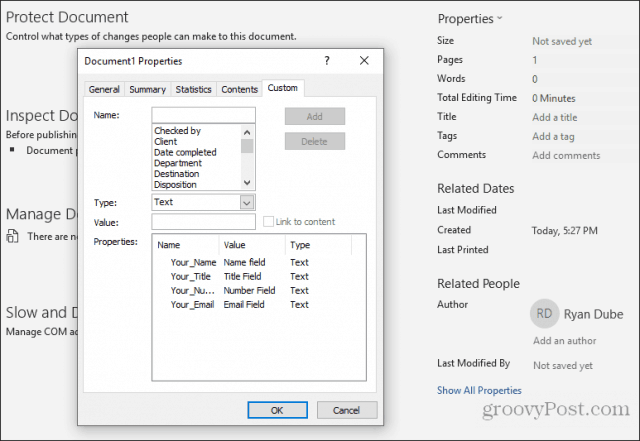
Select Add to add each field, and then continue by entering all of the fields in your form.
Select OK when you’re done.
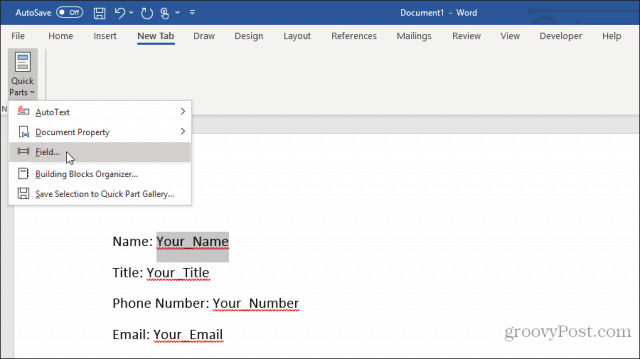
In your document, highlight the first field in your form. Then, in the Word menu, click on the Insert menu, click the Quick Parts dropdown, and select Fields. If Quick Parts doesn’t appear under the Insert menu, you’ll need to add Quick Parts to the ribbon to access the Field item.
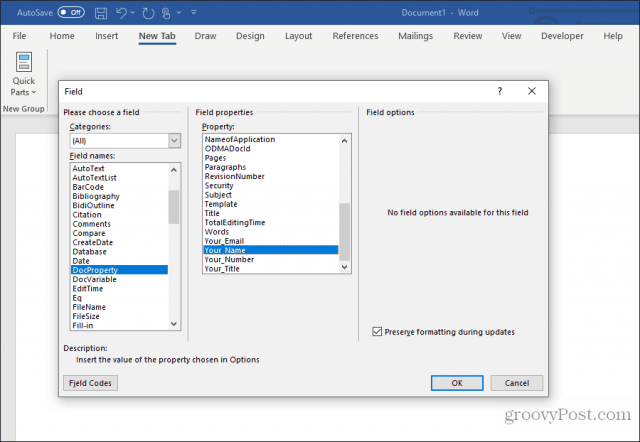
Click on DocProperty under Field names in the pop-up window, and click on Your_Name (or whatever you named the field) under Property.
Continue this process for all remaining fields in your form until they’re all converted to fields.
You can learn more about using custom fields in a variety of ways to automate your documents.
Filling out a Form with Custom Fields
Now, all your users need to fill out the form is to go through all of the custom fields and enter the values.
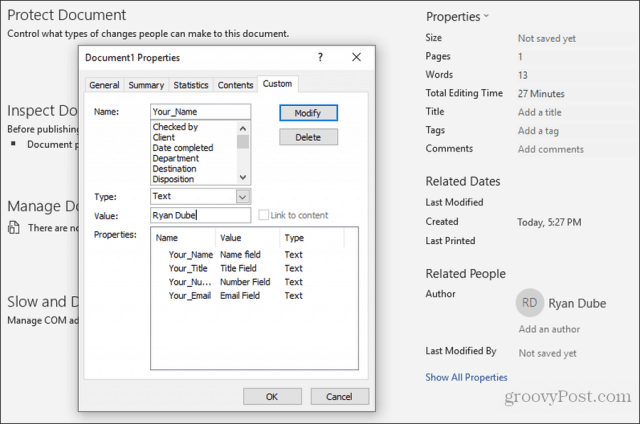
To do this, they’ll need to select File, Options, and Properties. Under Properties, select Advanced Properties. This will open a Document Properties dialog window. Select the Custom tab.
In the Document Properties window, your users need to select each of the properties, enter the correct value for those fields, and select Modify.
After entering the custom fields’ values, clicking OK will add those values to the correct fields in the form.
You can update each form in the field by right-clicking on it and selecting Update Field. Or, you can select all of the fields and press F9.
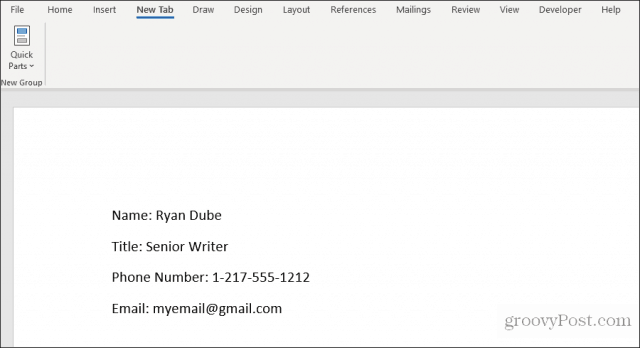
Once they’re all updated, the customized Word form will contain all the answers entered into the custom fields.
Your user can then save the form and send it to you with all the fields properly filled out.
As you can see, this approach saves a lot of time because all of the field values can be entered quickly in one place.
Create Fillable Forms In Word with Developer Tools
If you need a more versatile form, then you’re better off using developer tools in Word to create the required form entry fields. Before you can do this, you’ll need to enable the developer menu in Word.
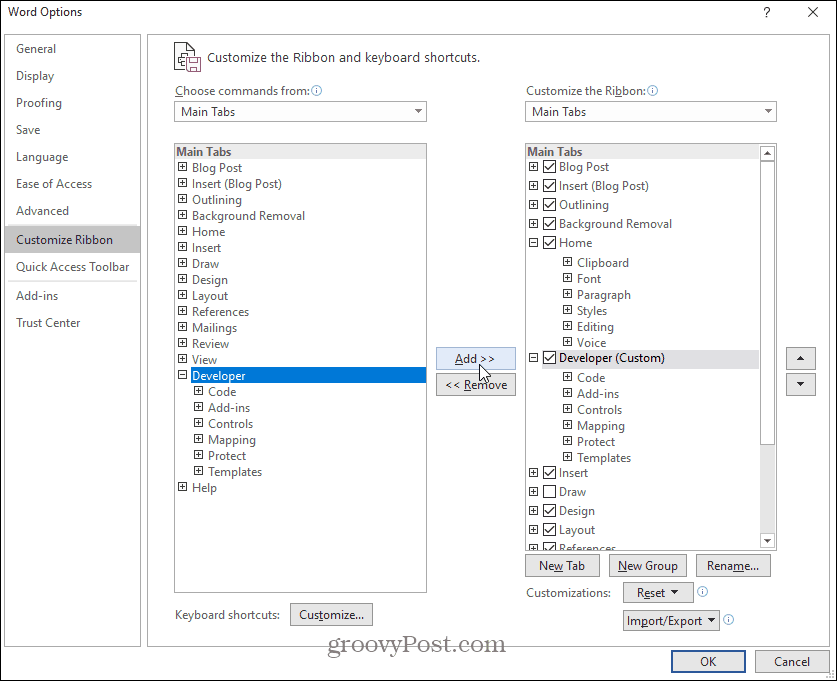
Select the File menu, and select Options. In the Word Options dialog window, select Customize Ribbon from the left navigation pane. Under Choose commands from, select Main tabs. If Developer is already displayed in the right pane, select the checkbox to enable it. If it isn’t, select Developer in the left pane and select the Add>> button to add it to the right pane.
Select OK to finish. Now you should see Developer appear in the Windows menu.
Open a new Word document by selecting File from the menu, select New, and choose Blank document.
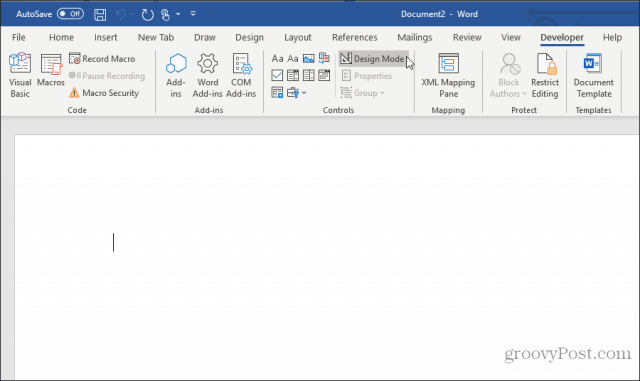
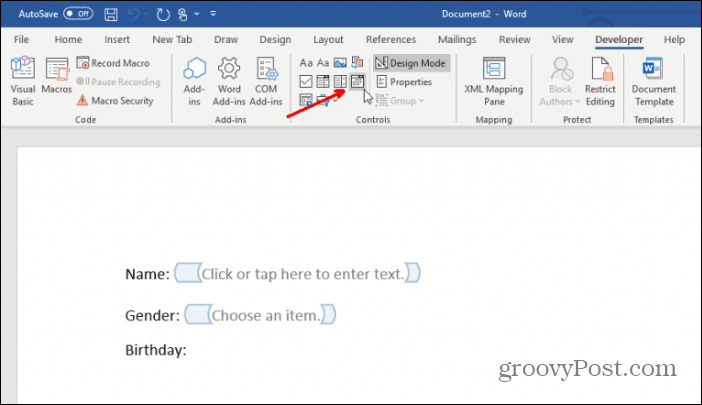
Select Developer in the menu, and select Design Mode.
Insert a Text Field
For a text field entry, choose the Plain Text Content Control.
This will insert a text entry box into the fillable form.
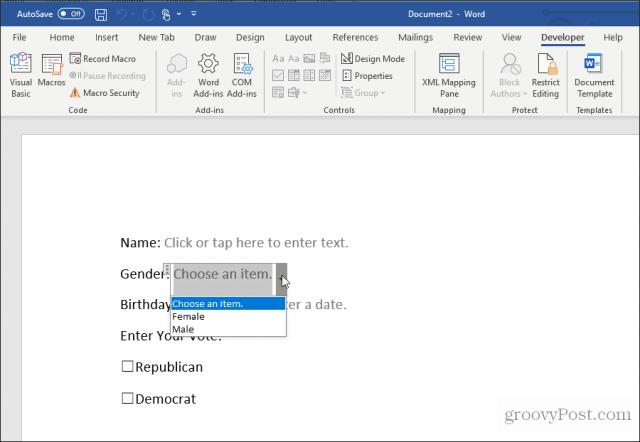
Insert a Drop-Down List
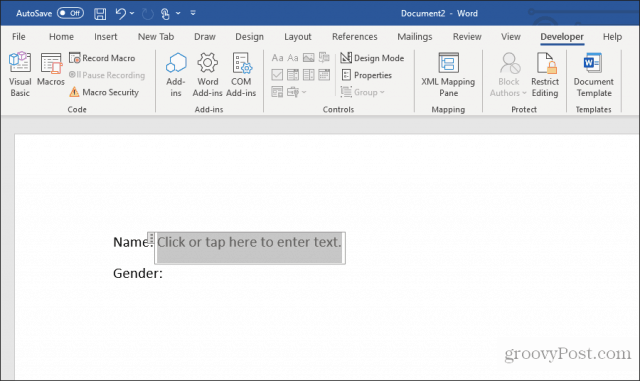
To add a dropdown box entry, select Drop-Down List Content Control.
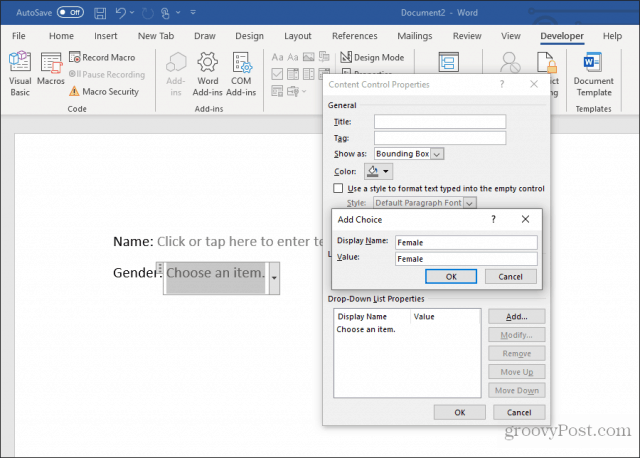
This will insert a drop-down list into the fillable form. However, to fill out the list box, you need to set up the list. To do this, right-click the drop-down list control and select Properties. In the Content Control Properties box, select the Add button to add new items to the list.
When you’re done, select OK. Now you’ll see the drop-down list appear in your fillable form.
You won’t see the dropdown list while you’re creating the form in Design Mode. But you can select Design Mode to turn it off and test what the drop-down list will look like.
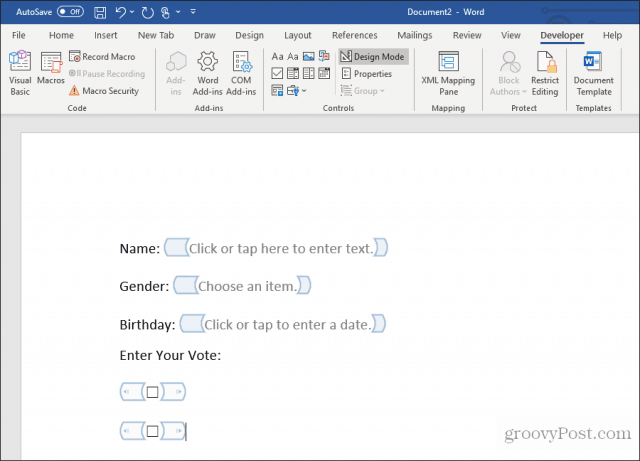
Insert a Date Picker
Another useful tool to use for a fillable form in Word is the Date Picker Content Control. Select this to add a date picker option in your form.
You don’t have to do anything to customize this control. It’ll work as required to let the user choose a date for this field.
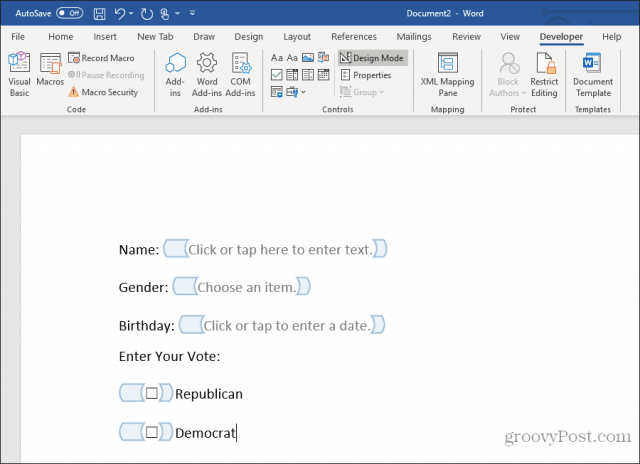
Insert Check Boxes
The next control that’s useful in a fillable form is the Check Box Content Control.
First, insert the number of checkboxes you need in your form after writing the question above it.
Next, type the text for each selection beside each checkbox.
Testing Your Fillable Form in Word
You can add any number of controls throughout your fillable form to suit your needs. When you’re finished, select Design mode from the Controls menu to turn off Design Mode and see your finished fillable form.
Test all of the controls in your form to ensure that they work as you expect.
As you can see, creating a fillable form in Word isn’t as difficult as it may seem. The approach you choose depends on the complexity of the form and the types of responses you’re looking for.
Give it a try and see what kind of form you can create in Word using either of the two methods above.






 , and then click Word Options.)
, and then click Word Options.)