Данный пример демонстрирует работу с файлами Excel через интерфейс доступа к данным ADO (ActiveX Data Objects). Объекты ADO входят в состав Windows, поэтому через данный интерфейс можно получить информацию из xls-файла даже на компьютере без предустановленного пакета Microsoft Office.
Файл данных (xls) содержит таблицу дней рождений знаменитых людей. Программа на языке vbscript (файл с расширением .vbs) ищет совпадающие с сегодняшней датой дни рождения и вывод на экран информационное сообщение. Для запуска просто кликните дважды на vbs-файле. Данные и программа должны быть предварительно сохранены в одной папке.
'''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''
' Пример доступа к файлам Excel через интерфейс ADO
'
' © 2011, ExcelFin.ru
'''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''
const adOpenStatic = 3
const fileXLS = "birthdays_ADO.xls"
const sheetData = "Data"
dim globalPath, filenameXLS, copyfilenameXLS, conn, result
globalPath = Replace(WScript.ScriptFullName, WScript.ScriptName, "")
filenameXLS = globalPath & fileXLS
copyfilenameXLS = globalPath & "_temp_" & fileXLS
OpenConnection_
HandleData_
CloseConnection_
ShowResult_
'''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''
sub ShowResult_
WScript.Echo "Сегодня: " & FormatDateTime(Date(), 2) & vbCrLf & "День рождения: " & vbCrLf & result
end sub
'''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''
sub HandleData_
dim rsData
dim sSQL
result = ""
sSQL = "SELECT * FROM [" & sheetData & "$A1:B]" & _
" WHERE [Дата] is not null"
set rsData = CreateObject("ADODB.Recordset")
rsData.Open sSQL, conn, adOpenStatic
do while not rsData.EOF
if (Month(Date())= Month(rsData.Fields("Дата"))) And _
(Day(Date())= Day(rsData.Fields("Дата"))) then
result = result & FormatDateTime(rsData.Fields("Дата"), 2) & " - " & rsData.Fields("Имя") & vbCrLf
end if
rsData.MoveNext
loop
rsData.Close
set rsData = Nothing
if (result = "") then
result = "нет данных"
end if
end sub
'''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''
sub OpenConnection_
Dim fso
Set fso = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
fso.CopyFile filenameXLS, copyfilenameXLS, true
Set fso = nothing
set conn = CreateObject("ADODB.Connection")
conn.Open "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=" & _
copyfilenameXLS & _
";Extended Properties=""Excel 8.0;HDR=Yes;IMEX=2"";"
end sub
sub CloseConnection_
conn.Close
set conn = Nothing
end sub
В процедуре OpenConnection_ происходит предварительное создание копии файла данных. Это позволяет работать с открытым файлом xls.
В строке SQL таблица данных обозначается именем листа и координатами в формате A1, но последнюю строку диапазона можно не указывать.
»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»’
‘ Пример доступа к файлам Excel через интерфейс ADO
‘
‘ © 2011, ExcelFin.ru
»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»’
const adOpenStatic = 3
const fileXLS = «birthdays_ADO.xls»
const sheetData = «Data»
dim globalPath, filenameXLS, copyfilenameXLS, conn, result
globalPath = Replace(WScript.ScriptFullName, WScript.ScriptName, «»)
filenameXLS = globalPath & fileXLS
copyfilenameXLS = globalPath & «_temp_» & fileXLS
OpenConnection_
HandleData_
CloseConnection_
ShowResult_
»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»’
sub ShowResult_
WScript.Echo «Сегодня: » & FormatDateTime(Date(), 2) & vbCrLf & «День рождения: » & vbCrLf & result
end sub
»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»’
sub HandleData_
dim rsData
dim sSQL
result = «»
sSQL = «SELECT * FROM [» & sheetData & «$A1:B]» & _
» WHERE [Дата] is not null»
set rsData = CreateObject(«ADODB.Recordset»)
rsData.Open sSQL, conn, adOpenStatic
do while not rsData.EOF
if (Month(Date())= Month(rsData.Fields(«Дата»))) And _
(Day(Date())= Day(rsData.Fields(«Дата»))) then
result = result & FormatDateTime(rsData.Fields(«Дата»), 2) & » — » & rsData.Fields(«Имя») & vbCrLf
end if
rsData.MoveNext
loop
rsData.Close
set rsData = Nothing
if (result = «») then
result = «нет данных»
end if
end sub
»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»»’
sub OpenConnection_
Dim fso
Set fso = CreateObject(«Scripting.FileSystemObject»)
fso.CopyFile filenameXLS, copyfilenameXLS, true
Set fso = nothing
set conn = CreateObject(«ADODB.Connection»)
conn.Open «Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=» & _
copyfilenameXLS & _
«;Extended Properties=»»Excel 8.0;HDR=Yes;IMEX=2″»;»
end sub
sub CloseConnection_
conn.Close
set conn = Nothing
end sub
Смотри также
» Пересчет отдельных формул в рабочей книге
Типичная проблема при работе с большими или очень большими файлами Excel — это слишком сильное замедление при выполнении любых расчетов….
» Класс сохранения настроек Excel
В данной статье описывается небольшой, но очень удобный класс для сохранения и автоматического восстановления таких параметров…
» Основные принципы оптимизации работы в электронных таблицах
Знание специальных приемов работы в электронных таблицах Excel позволяет в разы сократить время разработки моделей, повысить…
» Надстройки Excel
Те, кто программирует на VBA для Excel, в определенный момент задумываются над распространением своих приложений в качестве независимых…
» Автоматизация в Excel
Создание программного кода для автоматизации определенных процедур открывает практически безграничные возможности по развитию и…
Здравствуйте, в этой статье я расскажу Вам, как использовать в своем приложении (программе) на Delphi БД в виде MS Excel. Да да именно MS Excel. Тут ничего сложного нету. Для начала давайте заполним наш лист в MS Excel. Первая строка в каждом столбце всегда будет брать наше приложение как название столбцов, то есть оно не берет название столбцов такое — A, B, C и так далее. Так что в первсой строке столбца А и столбца B я написал ФИО и Оценка соответственно для каждого столбца. Это и будут наши заголовки, затем ниже я заполнил данные, которые будут в моей БД, ну это фамилии и оценки сами напиши. Так БД у нас готова. Теперь создадим к ней подключение. создается подключение похоже как и в MS Access, так что тут ничего сложного нету. На форме у нас старые компоненты это
- TDBGrid
- TADOQuery
- TADOConnection
- TDataSource
Как связывать эти компоненты я расскажу быстро, так как это уже было сказано мною.
- TADOQuery c TADOConnection в свойстве — Connection
- TDataSource с TADOQuery в свойстве DataSet
- TDBGrid c TDataSource в свойстве DataSource
В TADOConnection установим свойство LongPromt в False. Вроде бы небольшую настройку сделали. Теперь приходим к непосредственному подключени. В свойстве TADOConnection — ConnectionString нажимаем на кнопку «…«, далее у нас появляется окно вида
Нажимаем на кнопку «Build…» и появляется следующее окно
В данном окне выбираем следующего провайдера: Microsoft OLE DB Provider for ODBC Drivers и нажимаем кнопку «Далее>>» и видем следующее окно
В этом окне сразу ставим указатель на «Использовать строку подключения» и нажимаем на кнопку «Сборка«, после чего появляется окно
В этом окне переходим на вкладку Источник данных компьютера, в появившемся списке выбираем — Файлы Excel, а точнее жмем левой кнопкой мыши по этой сроке двойным щелчком и в появившемся окне указываем путь к нашей Excel-книги, которую мы создавали. После этого нажимаем на пноку «Ok«. Все подключение у нас готово. Хочу добавить еще, если у Вас файл Excel, где ваша таблица находится лежит в одном каталоге с программой, то в свойстве компонента TADOConnection — ConnectionString будет прописан путь к Вашему Excel-файлу, стерите путь, а оставьте просто имя Вашего Excel файла с расширением, а в свойстве DefaultDataBase этого же компонента, напишите имя вашего Excel-файла с расширением. Тогда при запуске вашего приложения, не будет возникать ошибок с неправильно заданым путем к вашей БД. Далее в TDBGrid нажмем по нему двойным щелчком и в появившемся окне создаим 2 строки, это наши столбцы будут. А создаются они путем нжатия в данном окне на кнопку «Add New (Ins)«. Далее выделив кажду строку в свойстве FieldName для первой строки напишем — ФИО, так как в Excel-файле я именно так написал в первую строку название столбца (для ячейки A1 я так написал), а выделив вторую строку, что создали в TDBGrid, в свойстве FieldName напишем — Оценка, так как именно я такое название столбца написал (в ячейке А2 я так написал). Все теперь нам можно активировать наши данные. Для этого на событие главной формы — OnCreate напишем следующее
procedure TForm1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject); begin try ADOQuery1.SQL.Clear; ADOQuery1.SQL.Add('SELECT * FROM [Лист1$]'); ADOQuery1.Active:=True; except on e:Exception do end; end;
Как видите все тот же запрос, только вместо имя таблица, как у нас было в MS Access мы указываем имя листа нашего в Excel, заключив его в квадратные скобки и поставив в конце знак $. Как видите ничего сложного нету. В следующей статье про БД MS Excel я расскажу как вставлять данные, редактировать и так далее.
askit.ru
Подключение к таблице Excel средствами ADO
6-9 минут
Подключение к таблице Excel средствами ADO, создание именованного диапазона, создание источника данных ODBC
Очень часто в практической работе возникает необходимость подключиться к таблице на листе Excel, как к базе данных. Конечно, можно работать и средствами объектной модели Excel (см. раздел 11 «Программирование в Excel»), но использование объектов ADO дает значительные преимущества:
- намного проще и удобнее производить поиск записи, вставку новых записей в таблицу, изменение существующих записей. Объекты ADO изначально проектировались именно для этих целей;
- объектную модель Excel можно использовать только в Excel, а объекты ADO универсальны и могут использоваться для подключения к любым источникам данных. Если вы используете объекты ADO, то вы можете использовать фактически одно и то же приложение как для работы с данными в Excel, так и для работы с информацией в «большой» базе данных — например, SQL Server или Oracle. Ситуация, когда часть информации находится в базе данных, а другая часть — в книге Excel, встречается на практике очень часто.
Подключиться к таблице на листе Excel совсем не сложно, но самостоятельно догадаться до всей последовательности действий бывает трудно. Поэтому ниже приведена пошаговая последовательность действий.
Предположим, что у нас есть книга Excel, которая называется Fact.xls и лежит в корневом каталоге диска C:. На первом листе этой книге есть такая совсем несложная таблица, представленная на рис. 9.7
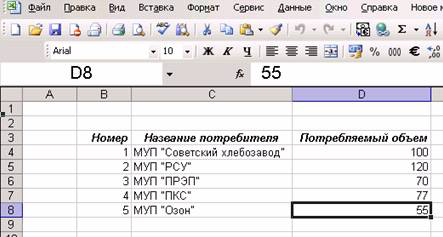
Рис. 9.7 Таблица в Excel, к которой нужно обратиться средствами ADO
Нам необходимо подключиться к этой таблице, как к базе данных. Что нам нужно сделать?
Первый этап — это подготовка. Иногда можно обойтись и без нее (если лист Excel — это одна таблица). На практике же часто бывает так, что на листе у нас несколько таблиц, или таблица с комментариями, или внизу таблицы посчитаны итоги и т.п. Чтобы не смущать Excel, лучше явно указать нашу таблицу. Сделать это очень просто: нужно ее выделить (в нашем случае — выделить диапазон с B3 по D8) и присвоить выделенному диапазону имя. Для этого в Excel в меню Вставка нужно выбрать Имя -> Присвоить и ввести нужное имя. В нашем случае мы присвоим имя Volumes (см. рис. 9.8)
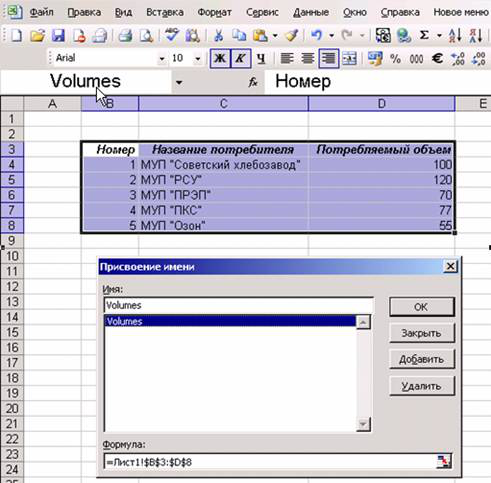
Рис. 9.8 Присваиваем имя диапазону
Обратите внимание, что нужно выбирать диапазон вместе с названиями столбцов.
После того, как имя присвоено, Excel можно закрывать — он больше нам не нужен.
Дальше по плану нужно было бы создать файл *.UDL и настроить в нем подключение к нашему файлу C:Fact.xls. Однако напрямую из файла UDL можно работать только с драйверами OLE DB, а нужного драйвера, к сожалению, нет (Microsoft JET 4.0 OLE DB Provider хочет работать только с файлами MDB). Поэтому делаем еще один подготовительный шаг — создаем источник данных ODBC (поскольку драйвер ODBC для подключения к Excel есть). Первое действие — в Панели управления открываем Administrative Tools (Средства администрирования) и два раза щелкаем по иконке Data Sources (ODBC) (Источники данных ODBC). Откроется окно, аналогичное представленному на рис. 9.9.
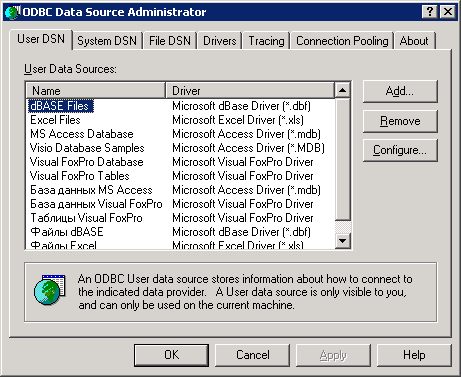
Рис. 9.9 Окно управления источниками данных ODBC
В вашем распоряжении — три типа DSN (Data Source Name, то есть источников данных ODBC):
- User DSN — информация об этих источниках данных хранится в части реестра, специфической для пользователя, поэтому эти источники данных доступны только тому пользователю, который их создал;
- System DSN — информация об этих источниках данных хранится в общей части реестра и доступна для всех пользователей на этом компьютере;
- File DSN — информация об этих источниках данных записывается в файл в файловой системе.
Чаще всего используются System DSN — системные источники данных, поэтому переходим на вкладку System DSN и нажимаем на кнопку Add (Создать).
Первое, о чем нас спросят — это о типе драйвера, который мы хотим использовать. Выбираем, конечно, Microsoft Excel Driver и нажимаем на кнопку Finish. Но создание источника данных на этом далеко не кончилось.
На следующем экране нам потребуется:
- в поле Data Source Name ввести имя источника данных. Можно ввести любое имя — главное, чтобы вы его не забыли. Мы введем имя ExcelVolumes;
- нажать на кнопку Select Workbook и выбрать нужную нам рабочую книгу (в нашем случае — C:Fact.xls);
- нажать на кнопку Options и подумать, будем ли изменять из программы нашу таблицу. Если да, то флажок Read Only нужно снять.
В итоге окно может выглядеть так, как представлено на рис. 9.10.
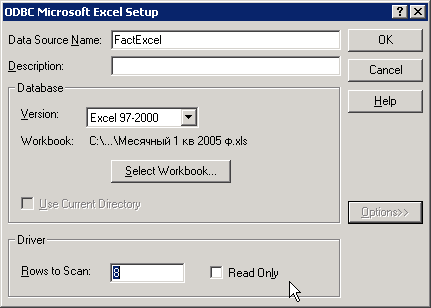
Рис. 9.10 Настраиваем источник ODBC для подключения к файлу Excel
Осталось нажать два раза на кнопку OK, чтобы закрыть окно создания источника данных ODBC.
В принципе, в коде программы можно написать значение свойства ConnectionString вручную, воспользовавшись документацией по ADO. Выглядеть соответствующая строка, к примеру, может так:
cn.ConnectionString = «Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN = FactExcel;DBQ=C:Fact.xls ;»
Но зачем что-то писать руками, когда можно сгенерировать нужное значение автоматически? А сгенерировать можно очень просто:
- так, как описано в предыдущем разделе, создаем файл UDL (можно воспользоваться уже готовым);
- щелкаем по нему два раза мышью, переходим на вкладку Provider и выбираем Microsoft OLE DB Provider for ODBC Drivers;
- переходим на вкладку Connection и в списке Use Data Source Name выбираем созданный нами источник данных ExcelVolumes. Остальные поля можно не заполнять (см. рис. 9.11). Для проверки можно нажать на кнопку Test Connection, а затем — OK.
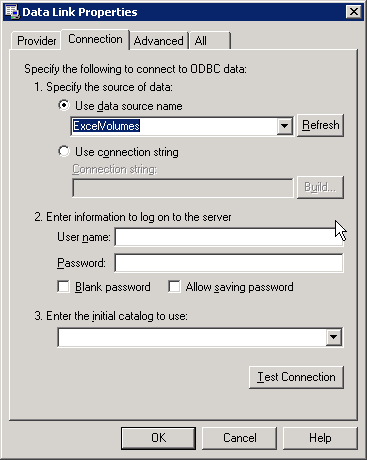
Рис. 9.11 Настраиваем параметры подключения к созданному источнику ODBC
- последнее действие — открываем созданный нами файл UDL в блокноте, копируем из него строку подключения и используем в нашей программе.
Итоговый код процедуры для подключения к Excel может выглядеть так:
Public Sub ConnectToExcel()
Dim cn As New ADODB.Connection
cn.ConnectionString = «Provider=MSDASQL.1;Data Source=ExcelVolumes»
cn.Open
‘Про Recordset мы будем говорить в следующем разделе
‘Этот код помещен для наглядной проверки
Dim rs As New ADODB.Recordset
rs.Open «Volumes», cn
MsgBox rs.GetString
End Sub
Чтобы подключиться к файлу Excel, нам потребовалось:
- Создать именованный диапазон в книге Excel;
- Создать источник данных ODBC с именем ExcelVolumes;
- Написать три строки кода начиная с создания объекта Connection до вызова его метода Open.


Еще по теме:
1. Тема: Выгрузка с форматированием: задать диапазон выгружаемых данных
2. Тема: Пример записи / чтения с Microsoft Excel в VB
Способы передачи данных с Visual Basic в Excel
Источник: MSDN
В данной статье рассматриваются способы передачи данных в Microsoft Excel из приложения Microsoft Visual Basic. В статье также представлены преимущества и недостатки каждого из способов, что позволяет пользователю выбрать наиболее подходящий способ для конкретной ситуации.
Дополнительная информация
Чаще всего для передачи данных в книгу Excel используется программирование объектов (автоматизация). Этот способ обладает наибольшим спектром возможностей для указания местоположения данных в книге Excel, а также обеспечивает возможность форматирования книги и настройки различных параметров во время выполнения. Программирование объектов позволяет использовать для передачи данных несколько подходов:
- Передача данных по одной ячейке
- Передача массива данных в диапазон ячеек
- Передача набора записей ADO в диапазон ячеек с помощью способа CopyFromRecordset
- Создание в листе Excel объекта QueryTable, содержащего результаты запроса по источнику данных ODBC или OLEDB
- Передача данных в буфер обмена с последующей вставкой содержимого буфера обмена в лист Excel
Также существуют способы передачи данных в Excel, не требующие программирования объектов. При работе с серверным приложением рекомендуется освободить клиентов от большого объема обрабатываемых данных. Ниже приведены способы передачи данных, не использующие программирование объектов.
- Передача данных в текстовый файл, использующий запятые или знаки табуляции в качестве разделителей, который Excel впоследствии может разобрать на ячейки листа
- Передача данных на лист Excel с помощью ADO
- Передача данных в Excel с помощью динамического обмена данными (DDE)
В следующих разделах приведены дополнительные сведения о каждом решении.
Примечание. При использовании Microsoft Office Excel 2007 для сохранения книги Excel 2007 можно использовать новый формат файла (XSLX). Для этого найдите следующую строку кода в приведенных ниже примерах:
Visual Basic
oBook.SaveAs "C:Book1.xls"
Замените этот код следующей строкой кода:
Visual Basic
oBook.SaveAs "C:Book1.xlsx"
Кроме того, база данных «Борей» не входит в состав Office 2007 по умолчанию. Тем не менее базу данных «Борей» можно загрузить с веб-узла русской версии Microsoft Office Online.
Перенос данных по одной ячейке с помощью автоматизации
Автоматизация позволяет передавать данные на лист Excel по одной ячейке:
| Visual Basic | ||
|
Передача данных по одной ячейке является оптимальным способом передачи небольших объемов данных. Этот способ позволяет помещать данные в любом месте рабочей книги и форматировать ячейки во время выполнения. Однако этот способ не рекомендуется применять при передаче больших объемов данных в книгу Excel. Каждый объект Range, получаемый во время выполнения, вызывает запрос к интерфейсу, поэтому такой способ передачи данных может оказаться очень медленным. Кроме того, в Microsoft Windows 95 и Windows 98 существует ограничение на запросы к интерфейсу, составляющее 64 КБ. При превышении лимита в 64 КБ сервер автоматизации (Excel) может перестать отвечать на запросы или может отображаться сообщение о нехватке памяти. Это ограничение для Windows 95 и Windows 98 рассматривается в следующей статье базы знаний Майкрософт:
216400 Автоматизация COM может привести к зависанию клиентского приложения в Win 95/98 (Эта ссылка может указывать на содержимое полностью или частично на английском языке).
Таким образом, передача данных по одной ячейке допустима только для небольших объемов данных. Для передачи больших объемов данных в Excel следует использовать один из способов, описанных ниже.
Примеры сценариев для автоматизации Excel см. в следующей статье базы знаний Майкрософт:
219151 Использование Visual Basic для автоматизации Microsoft Excel
Передача массива данных в диапазон ячеек листа с помощью программирования объектов
Массив данных можно одновременно передать в диапазон ячеек листа:
| Visual Basic | ||
|
Передача большого объема данных с помощью массива происходит значительно быстрее, чем передача данных по одной ячейке. Обратите внимание на строку из приведенного выше сценария, которая одновременно передает данные в 300 ячеек листа:
Visual Basic
oSheet.Range("A2").Resize(100, 3).Value = DataArray
Эта строка представляет всего два запроса к интерфейсу (один для объекта Range, возвращаемого методом Range, и один для объекта Range, возвращаемого методом Resize). При этом при передаче данных по одной ячейке потребовалось бы 300 запросов к интерфейсу для объектов Range. Поэтому по возможности рекомендуется выполнять массовый перенос данных, чтобы сократить число запросов к интерфейсу.
Перенос набора записей ADO в диапазон листа с помощью автоматизации
В Excel 2000 появился метод CopyFromRecordset, позволяющий переносить наборы данных ADO (или DAO) в диапазон ячеек листа. Приведенный ниже сценарий является примером автоматизации Excel 2000, Excel 2002 или Office Excel 2003 для переноса содержимого таблицы Orders образца базы данных «Борей» с помощью метода CopyFromRecordset.
| Visual Basic | ||
|
Примечание. При использовании версии базы данных «Борей» для Office 2007 необходимо заменить в примере следующую строку кода:
| Visual Basic | ||
|
Замените эту строку кода следующей строкой:
| Visual Basic | ||
|
В Excel 97 также имеется метод CopyFromRecordset, однако его можно использовать только для набора записей DAO. CopyFromRecordset в Excel 97 не поддерживает ADO.
Дополнительные сведения об использовании ADO и метода CopyFromRecordset см. в следующей статье базы знаний Майкрософт:
246335 Использование программирования объектов для передачи данных из набора записей в Excel
(Эта ссылка может указывать на содержимое полностью или частично на английском языке)
Создание объекта QueryTable с помощью программирования объектов
Объект QueryTable представляет собой таблицу, содержащую данные, возвращенные из внешнего источника. При автоматизации Microsoft Excel для создания объекта QueryTable следует просто указать строку подключения к источнику данных OLEDB или ODBC в строке SQL. Далее Excel генерирует набор записей и вставляет его в указанное местоположение на листе. Использование объекта QueryTables обладает несколькими преимуществами по сравнению с использованием метода CopyFromRecordset:
- Созданием набора записей и его размещением на листе управляет Excel.
- Запрос можно сохранить в объекте QueryTable таким образом, чтобы в дальнейшем его можно было обновить и получить обновленный набор записей.
- При добавлении нового объекта QueryTable к листу можно переместить данные, уже находящиеся в ячейках листа, чтобы свободно разместить новые данные (см. свойство RefreshStyle).
Ниже приводится пример сценария, позволяющего автоматизировать Excel 2000, Excel 2002 или Office Excel 2003 для создания нового объекта QueryTable на листе Excel с данными из базы Northwind:
| Visual Basic | ||
|
Использование буфера обмена
Буфер обмена Windows также может использоваться как механизм передачи данных на лист Excel. Чтобы вставить данные в несколько ячеек листа, можно скопировать строку, в которой столбцы разделены знаками табуляции, а строки – символами возврата каретки. В приведенном ниже сценарии показано, как Visual Basic может использовать буфер обмена для передачи данных в Excel:
| Visual Basic | ||
|
Создание текстового файла с разделителями, который Excel может разобрать на строки и столбцы
Excel может открывать файлы с разделителями-запятыми и знаками табуляции и разбирать данные по ячейкам. Этим можно воспользоваться при необходимости передачи большого объема данных в лист Excel с минимальным использованием автоматизации. Этот подход рекомендуется для приложений типа клиент-сервер, поскольку текстовый файл может генерироваться серверным приложением. Затем текстовый файл можно открыть с помощью клиентского приложения, при необходимости используя автоматизацию.
Ниже приведен сценарий, иллюстрирующий создание текстового файла с разделителями-запятыми из набора записей ADO:
| Visual Basic | ||
|
Примечание. При использовании версии базы данных «Борей» для Office 2007 необходимо заменить в примере следующую строку кода:
| Visual Basic | ||
|
Замените эту строку кода следующей строкой:
| Visual Basic | ||
|
Если файл имеет расширение CSV, Excel открывает его без отображения мастера импорта текста и по умолчанию принимает, что в файле используются разделители-запятые. Если же файл имеет расширение TXT, Excel автоматически разбирает его, используя в качестве разделителей знаки табуляции.
В приведенном выше примере запуск Excel осуществлялся с помощью оператора Shell, а имя файла использовалось как аргумент командной строки. А в этом примере автоматизация не использовалась. Однако при желании можно применить минимум автоматизации, чтобы открыть текстовый файл и сохранить его в формате книги Excel:
| Visual Basic | ||
|
Дополнительные сведения об операциях ввода-вывода файлов из приложения Visual Basic см. в следующей статье базы знаний Майкрософт:
172267 RECEDIT.VBP демонстрирует ввод-вывод файлов в Visual Basic recedit.rar
(Эта ссылка может указывать на содержимое полностью или частично на английском языке)
Передача данных на лист Excel с помощью ADO
С помощью Microsoft Jet OLE DB Provider можно добавлять записи в таблицу существующей книги Excel. «Таблицей» в Excel считается диапазон с заданным именем. Первая строка диапазона содержит заголовки (или имена полей), а все последующие строки – записи. Ниже приведен пример создания книги с пустой таблицей MyTable.
Excel 97, Excel 2000 и Excel 2003
1. Откройте новую книгу Excel.
2. Добавьте следующие заголовки в ячейки A1:B1 листа Sheet1:
A1: FirstName B1: LastName
3. Выровняйте ячейку B1 по правому краю.
4. Выделите A1:B1.
5. В меню Вставка выберите Имя, а затем Присвоить. Введите имя MyTable и нажмите кнопку OK.
6. Сохраните новую книгу как C:Book1.xls и закройте Excel.
Чтобы добавить записи в таблицу MyTable с помощью ADO, понадобится сценарий приблизительно следующего вида:
| Visual Basic | ||
|
Excel 2007
1. В Excel 2007 создайте книгу.
2. Добавьте следующие заголовки в ячейки A1:B1 листа «Лист1»:
A1: FirstName B1: LastName
3. Выровняйте ячейку B1 по правому краю.
4. Выделите диапазон A1:B1.
5. На ленте откройте вкладку Формулы и выберите пункт Определить имя. Введите имя MyTable и нажмите кнопку ОК.
6. Сохраните новую книгу как C:Book1.xlsx и закройте Excel.
Чтобы добавить записи в таблицу MyTable с помощью ADO, используйте код, подобный приведенному ниже.
| Visual Basic | ||
|
При подобном добавлении записей в таблицу производится форматирование книги. В приведенном выше примере новые поля, добавляемые в столбец B, выравниваются по правому краю. Каждая запись, добавляемая в строку, форматируется так же, как предыдущая.
Обратите внимание на то, что при добавлении в ячейку или ячейки листа запись заменяет любые данные, находившиеся в этих ячейках ранее; другими словами, строки листа не сдвигаются вниз при добавлении новых записей. Это следует иметь в виду при планировании размещения данных на листе.
Примечание. Обновление данных на листе Excel с помощью ADO или DAO невозможно в среде Visual Basic для приложений в Access после установки пакета обновления 2 (SP2) для Office 2003 или обновления для Access 2002, описанного в статье 904018 базы знаний Майкрософт. Однако этот способ можно использовать в среде Visual Basic для приложений в других приложениях Office, например в Word, Excel и Outlook. Дополнительные сведения см. в следующих статьях базы знаний Майкрософт:
904953 Запрещается вносить изменения, добавлять или удалять данные, источником которых являются книги Excel в Office Access 2003 или в Access 2002
904018 Описание обновления для Access 2002: от 18 октября 2005 г.
Дополнительные сведения об использовании ADO для доступа к книгам Excel см. в следующих статьях базы знаний Майкрософт:
195951 Создание запросов и обновление данных Excel с помощью ADO со страниц ASP
(Эта ссылка может указывать на содержимое полностью или частично на английском языке)
Передача данных в Excel с помощью DDE
Наряду с программированием объектов DDE является способом связи с Excel и передачи данных; однако, в противоположность автоматизации и COM, DDE больше не является часто используемым способом связи с другими приложениями и должен использоваться только при отсутствии других решений.
Для передачи данных в Excel с помощью DDE можно воспользоваться одним из следующих способов:
- LinkPoke для вставки данных в указанный диапазон ячеек
. - LinkExecute для отправки команд, которые будет выполнять Excel.
В приведенном ниже примере показано, как установить связь DDE с Excel таким образом, чтобы модно было поместить данные в ячейки листа и выполнить команды. В этом примере для успешного установления связи DDE с файлом LinkTopic Excel|MyBook.xls книга с именем MyBook.xls уже должна быть открыта в запущенном экземпляре Excel.
Примечание. При использовании Excel 2007 для сохранения книг можно использовать новый формат файла (XLSX). Обязательно обновите имя файла в приведенном ниже примере кода.
Примечание. В данном примере Text1 представляет элемент управления Text Box формы Visual Basic:
| Visual Basic | ||
|
При использовании метода LinkPoke с Excel необходимо указать диапазон в формате строка-столбец (R1C1) для LinkItem. Если данные вставляются в несколько ячеек, можно использовать строку, в которой столбцы разделены символами табуляции, а строки – символами возврата каретки.
Если метод LinkExecute используется для выполнения команды в Excel, синтаксис команды должен соответствовать языку Excel Macro Language (XLM). Документация по XLM не входит в состав Excel 97 и более поздних версий. Дополнительные сведения о получении документации по XLM см. в следующей статье базы знаний Майкрософт:
143466 Файл Macro97.exe доступен для загрузки. macro97.rar
(Эта ссылка может указывать на содержимое полностью или частично на английском языке)
DDE не является рекомендуемым способом связи с Excel. Программирование объектов предоставляет больше возможностей и обеспечивает лучший доступ к новым функциям Excel.
Все ссылки MSDN по теме:
Автоматизация COM может привести к зависанию клиентского приложения в Win 95/98
Использование Visual Basic для автоматизации Microsoft Excel
Использование программирования объектов для передачи данных из набора записей в Excel
RECEDIT.VBP демонстрирует ввод-вывод файлов в Visual Basic
Запрещается вносить изменения, добавлять или удалять данные, источником которых являются книги Excel в Office Access 2003 или в Access 2002
Описание обновления для Access 2002: от 18 октября 2005 г.
Создание запросов и обновление данных Excel с помощью ADO со страниц ASP (Эта ссылка может указывать на содержимое полностью или частично на английском языке)
Документация по XLM
ADO in Excel VBA – Connecting to database using SQL
ADO Excel VBA – SQL Connecting to Database Example Macros helps to connect the different data sources from Excel VBA. Select, Delete,Update Records set.
In this Section:
- What is ADO?
- What is Database?
- What is SQL?
- adodb.connection VBA Reference
- Practical Learning: Using ADO and SQL with VBA
- Example File
What is ADO?
ADO Stands for ActiveX Data Objects, is Microsoft’s Client-Server technology to access the data between Client and Server. ADO can’t access the data source directly, it will take help of OLE DB Provider to communicate with the data source. Most of the times OLE DB providers are specific to a particular Data Source Type. However, we have an OLE DB provider for ODBC, it is a general purpose provider with help of this ADO can access any Data source which can understand ODBC.
What is Database?
Database (DB) is a collection of information organized in such a way that a computer program can easily understand and read the data. And the Database Management System (DBMS) are designed to understand and interact with other computer applications to perform the different operations on the data. MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Access, Oracle, and IBM DB2 are some of the well know DBMS.
Generally the information stored in the data in the form of tables, and a table is designed with set of records (rows) and fields (columns).
You can use Microsoft Excel to store some data, where an Excel workbook will act as a data source, worksheet will be a table and the rows and the columns of the worksheet will be records and the fields of the table.
What is SQL?
SQL Stands for Structured Query Language, ADO use SQL commands to communicate with the databases. Following are the most commonly used SQL commands to deal with the databases:
| SELECT command used to retrieve the data from a data source |
| INSERT command used to insert the records to a data source |
| UPDATE command used to modify the existing records of the data source |
| DELETE command used to delete the records from a data source |
adodb.connection VBA Reference
adodb.connection VBA Reference helps as to refer ADO in Excel VBA. We can use ADO in Excel VBA to connect the data base and perform data manipulating operations. We need add ‘Microsoft Activex Data Objects Library’ from References to reference the ADO in VBA. Here is the adodb.connection VBA Reference screen-shot.
ADO in Excel VBA – Practical Learning: Using ADO and SQL with VBA
To retrieve the data from any data source into Excel using ADO:
1. We have to Open the connection to the Data Source
2. We need to run the required SQL command
3. We have to copy the resulted record set into our worksheet
4. We have to close the record set and connection
We will consider the Excel workbook as data source and we will connect to the worksheet (table) to retrieve the data. In this example we will get the data from Sheet1 to Sheet2 using ADO.
Assuming you have an excel workbook with the following data in Sheet1, as shown below.
| EmpID | EmpName | EmpSalary |
|
1 |
Jo |
22000 |
|
2 |
Kelly |
28000 |
|
3 |
Ravi |
30000 |
Step 1:Add reference for Microsoft Activex Data Objects Library
1. Go to VBE (Alt+F11) and Select References.. from Tools Menu.
2. Then select ” Microsoft Activex Data Objects Library” from the list.
3. And Create sub procedure to write the code:
Sub sbADOExample() 'We will write the code here End Sub
Step 2: Create the Connection String with Provider and Data Source options
Dim sSQLQry As String
Dim ReturnArray
Dim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.Recordset
Dim DBPath As String, sconnect As String
DBPath = ThisWorkbook.FullName 'Refering the sameworkbook as Data Source
'You can provide the full path of your external file as shown below
'DBPath ="C:InputData.xlsx"
sconnect = "Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=" & DBPath & ";HDR=Yes';"
'If any issue with MSDASQL Provider, Try the Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB:
'sconnect = "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=" & DBPath _
& ";Extended Properties=""Excel 8.0;HDR=Yes;IMEX=1"";"
Step 3: Open the Connection to data source
Conn.Open sconnect
Step 4: Create SQL Command String
sSQLSting = "SELECT * From [Sheet1$]" ' Your SQL Statement (Table Name= Sheet Name=[Sheet1$])
Step 5: Get the records by Opening this Query with in the Connected data source
mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn
Step 6: Copy the reords into our worksheet
Sheet2.Range("A2").CopyFromRecordset mrs
Step 7: Close the Record Set and Connection
'Close Recordset
mrs.Close
'Close Connection
Conn.Close
So, the final program should look like this:
Sub sbADOExample()
Dim sSQLQry As String
Dim ReturnArray
Dim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.Recordset
Dim DBPath As String, sconnect As String
DBPath = ThisWorkbook.FullName
'You can provide the full path of your external file as shown below
'DBPath ="C:InputData.xlsx"
sconnect = "Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=" & DBPath & ";HDR=Yes';"
'If any issue with MSDASQL Provider, Try the Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB:
'sconnect = "Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=" & DBPath _
& ";Extended Properties=""Excel 8.0;HDR=Yes;IMEX=1"";"
Conn.Open sconnect
sSQLSting = "SELECT * From [Sheet1$]" ' Your SQL Statement (Table Name= Sheet Name=[Sheet1$])
mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn
'=>Load the Data into an array
'ReturnArray = mrs.GetRows
''OR''
'=>Paste the data into a sheet
Sheet2.Range("A2").CopyFromRecordset mrs
'Close Recordset
mrs.Close
'Close Connection
Conn.Close
End Sub
Example File
You can download the example files here and explore it. Getting Data Using ADO (Using MSDASQL Provider)
Getting Data Using ADO (Using MSDASQL Provider)
Download the Example File: ANALYSIS TABS – Getting Data Using ADO (Using Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB Provider)
Getting Data Using ADO (Using Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB Provider)
A Powerful & Multi-purpose Templates for project management. Now seamlessly manage your projects, tasks, meetings, presentations, teams, customers, stakeholders and time. This page describes all the amazing new features and options that come with our premium templates.
Save Up to 85% LIMITED TIME OFFER

All-in-One Pack
120+ Project Management Templates
Essential Pack
50+ Project Management Templates
Excel Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
PowerPoint Pack
50+ Excel PM Templates
MS Word Pack
25+ Word PM Templates
Ultimate Project Management Template
Ultimate Resource Management Template
Project Portfolio Management Templates
Related Posts
-
- What is ADO?
- What is Database?
- What is SQL?
- adodb.connection VBA Reference
- ADO in Excel VBA – Practical Learning: Using ADO and SQL with VBA
- Example File
VBA Reference
Effortlessly
Manage Your Projects
120+ Project Management Templates
Seamlessly manage your projects with our powerful & multi-purpose templates for project management.
120+ PM Templates Includes:
134 Comments
-
Vandana
August 7, 2013 at 4:49 PM — Reply -
lisa Pereira
February 12, 2014 at 7:33 AM — ReplyHI,
Nice one.. I am trying to pull multiple values from one parameter in excel, for example. I need to pull the parameter from Range(“a2”) separated by commas,
how can I do this? -
PNRao
February 25, 2014 at 11:58 PM — ReplyHi Lisa,
Assuming you have data at A1 as “1st,2nd,3rd,4th” and you want to separate it.
You can use Split function to separate the values. Please see the following code.
fullText=Range(“A1″).Value ‘i.e; fullText=”1,2,3,4″
arraySplitValues=Split(fullText,”,”)Now your array contains the comma delimited values:
arraySplitValues(0) contains 1st
arraySplitValues(1) contains 2nd
arraySplitValues(2) contains 3rd
arraySplitValues(3) contains 4thYou can print the values at any Range like:
Range(“B1”)=arraySplitValues(3)or you can loop the entire array to print all values:
For iCntr=0 to ubound(arraySplitValues,1)
Cells(iCntr+1,2)=arraySplitValues(iCntr) ‘ this will print all the values in the B Column
NextPlease explain your question in more detailed,so that I can help you in better way.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Hi – great article! 2 questions:
1. Do you have to install the ActiveX Object library 2.8 on every machine that uses this Excel file? I ask because I need to set up multiple files for multiple users who could benefit from this functinality (ADODB + SQL queries vs. Linked spreadsheets).
2. Do you know how to create an auto-install program for these MS library features? I ask because I don’t prefer to guide every user through the installation procedure.Thanks again!
Stephen -
PNRao
March 24, 2014 at 11:13 PM — ReplyHi Stephen,
Thanks for your comments! Please see my answers below:
1.You do not required to install ActiveX Object library in every machine, by default it is installed when user have installed in MS Office.
2.I think the above information answers this question too…To help you in understanding clearly: ActiveX Object Library is .DLL file which is installed with your office installation. You need to this reference this in your code, to use the ADO functionality in Excel VBA.
When you successfully write any code using ADO by referring ActiveX Object Library in your workbook. You can send the file to any one, it should work automatically in any system.
Hope this helps.
Thanks-PNRao! -
Lisa Pereira
June 18, 2014 at 5:00 AM — ReplyHi PN,
You are awesome , i love this site.have used your ideas and has helped me a lot. love it..
What i needed to know was that having pulled the record set into sheet :-
1) I want to use the values listed in rows in column A
2) transpose them into a cell and use these values to pull another query record-set with the IN statement.
is there a way to do this in one connection only or open another connection.?
let me know if this is possible.
Regards..
lisa -
PNRao
June 19, 2014 at 12:11 AM — ReplyHi Lisa,
How are you doing! Thanks for your feedback!
Yes, this can be done. Here is an example case:
To explain this, I have entered some data in ADO sheet of the example file (available at end of the article)
Step1: Entered 1 at Range A2, 2 at Range A3
The I concatenate these values at C1 using the below formul
-> =A2&”,”&A3
i.e; Now you can see ‘1,2’ at C1, I want to pass this in my SQL IN Operator, So – I changed the SQL Query string as follows:Step2: sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [DataSheet$] where Quarter IN (” & Range(“C1”) & “);”
i.e; it will form the query as ‘SELECT * From [DataSheet$] where Quarter IN (1,2);’Step3: Now executed and got the required values in the ADO sheet.
Hope this helps!
Thanks-PNRao! -
Jon McNeil
July 1, 2014 at 9:58 PM — ReplyThanks PN,
This is working nicely. The only thing that I cannot appear to fix is that when one user has the source file open (from which the data comes from) the other user, who is using the destination file (where the data is pulled to), opens a read-only source file when they run the macro. Is there a way round this?
The source file is only supposed to be viewed by one person whereas the destination file is for multiple usersThanks in advance,
Jon
-
Shubhangi
July 1, 2014 at 11:24 PM — ReplyI used this code to connect to MS Access 2007 database but am getting a runtime error and an application error when I try to open the same. I used DSN as MS Access Database and Provider as Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0.
Please help. -
PNRao
July 2, 2014 at 3:35 PM — Reply -
Noz
July 3, 2014 at 3:24 PM — ReplyThis is very well explained, if this had been available when I was first learning it would have save me loads of time. Do you have something similar on how to insert into SQL tables from excel?
-
PNRao
July 4, 2014 at 12:48 AM — ReplyHi Noz, Thanks for your comments!
Yes, you can write insert query, you can download the example file and change the query string as follows:
sSQLSting = “INSERT INTO [DataSheet$](Quarter, Sales) Values(2,5000)”and comment the below line, as insert query will not return any values.
‘ActiveSheet.Range(“A2”).CopyFromRecordset mrsNow your ADO procedure should look like this:
Sub sbADO()
Dim sSQLQry As String
Dim ReturnArrayDim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.RecordsetDim DBPath As String, sconnect As String
DBPath = ThisWorkbook.FullName
'You can provide the full path of your external file as shown below
'DBPath ="C:InputData.xlsx"sconnect = "Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=" & DBPath & ";HDR=Yes';"
Conn.Open sconnect
'sSQLSting = "SELECT * From [DataSheet$]" ' Your SQL Statemnt (Table Name= Sheet Name=[DataSheet$])
sSQLSting = "INSERT INTO [DataSheet$](Quarter, Sales) Values(2,5000)"
mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn
'=>Load the Data into an array
'ReturnArray = mrs.GetRows
''OR''
'=>Paste the data into a sheet
'ActiveSheet.Range("A2").CopyFromRecordset mrs
'Close Recordset
mrs.Close'Close Connection
Conn.CloseEnd Sub
-
Jaishree Ramani
July 10, 2014 at 8:08 PM — Replyhello, this really helps when you have a simple query.. would you be kind enough to provide an example for a parameter query (multiple) i.e for dates say selct* from table data between fromDate and toDate?
-
PNRao
July 11, 2014 at 1:29 AM — ReplyHi,
Sure, you change the query to suits your requirement.
For example:
I have changed the query sting from sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [DataSheet$]” to sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [DataSheet$] Where Quarter Between 2 And 4” in the example file. And now it will pull the data if the quarter is between 2 and 4.For your requirement, sSQLSting will be something like below:
sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [DataSheet$] Where YOUR_Date_Varibale Between ‘LowerDate’ And ‘UpperDate’”
If Dates creates any problems, try to use date values.
Hope this helps-Thanks-PNRao!
-
Jaishree Ramani
July 11, 2014 at 6:57 PM — ReplyHi Sir,
that works but I am having issue with the parameters dates as my query below
“O.DELIVERY_DATE BETWEEN :”From date” AND :”To Date” ) . how do i setup the parameters in vba to ensure that the record-set only pulls data in ‘DD-MMM-YYYY’ format. right now i have the dates converted to text(“dd-mmm-yyyy”) but when the data is returned its shows up in ‘mm/ddd/yyyy’ .note :i have the user to input the dates..
-
PNRao
July 12, 2014 at 1:05 PM — ReplyHi,
You can create the query string use as shown below:FromDate = 1 / 1 / 2010
ToDate = 12 / 30 / 2012
sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [DataSheet$] Where O.DELIVERY_DATE Between ” & FromDate & ” And ” & ToDateAnd your excel, default date format is ‘mm/ddd/yyyy’, you can format the dates using either sql or VBA.
In VBA it is like this: Format(YourDate,”mm-dd-yyyy”)
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Jaishree Ramani
July 14, 2014 at 8:21 PM — ReplyHi Sir,
my code is
userInput (“Pls type FromDate”) ,FromDate
userInput (“Pls type ToDate”) ,ToDate
FromDate = format(FromDate,”dd-mmm-yyyy”)
ToDate = format(ToDate,”dd-mmm-yyyy”)“select…
…..”AND O276054.DELIVERY_DATE BETWEEN ” & FromDate & ” And ” & ToDate & _ ”i tried that but i keep getting error ‘saying missing expression..’
what am i doing wrong?? -
PNRao
July 15, 2014 at 10:56 AM — ReplyHi,
I could not find any issue in the code. As per the Error message, something wrong with the query string. Could you please provide me the complete query string.Or you can try this: You can use Debug.Print YourstrQery, now look into the Immediate Window to see the resulted query.
You can send me the file with some dummy data to our email id: info@analysistabs.com
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Nigel
July 18, 2014 at 7:29 PM — ReplyHello, very good site .. quick question do you have an example for record-sets and Pivot tables or cross-tabs.?
i have an issue which I am trying to merge two query’s into one record-set and Pivot them into a cross report?
something similar to what Discoverer does. but I am trying to combine aggregate data points with Detail data points into one sheet without errors..(that’s why the two query s)please direct in a right direction if this is doable???
-
PNRao
July 20, 2014 at 12:31 AM — ReplyHi Nigel,
Please look into the example below:
'Add reference for Microsoft Activex Data Objects LibrarySub sbADO()
Dim sSQLQry As String
Dim ReturnArrayDim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.RecordsetDim DBPath As String, sconnect As String
DBPath = ThisWorkbook.FullName
'You can provide the full path of your external file as shown below
'DBPath ="C:InputData.xlsx"sconnect = "Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=" & DBPath & ";HDR=Yes';"
Conn.Open sconnect
sSQLSting = "SELECT * From [DataSheet$]"'***********> You can change this query as per your requirement (Join / Union)
mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn
'Set record set as a pivot table data source
Set objPivotCache = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Add( _
SourceType:=xlExternal)
Set objPivotCache.Recordset = mrs
With objPivotCache
.CreatePivotTable TableDestination:=Range("G20"), _
TableName:="MyPivotTable1"
End With'Close Recordset
mrs.Close'Close Connection
Conn.CloseEnd Sub
Hope this helps! Thanks-PNRao!
-
Gavrav
July 24, 2014 at 1:59 PM — ReplyHi,
I would like to automate my daily process by using VBA and macro actually my doubt is there any solution for instead of copying and pasting the query statement to SSMS 2005 which is stored in excel.So by making that statements as link or by clicking some command buttons to pass that query to SSMS and thus the statement should be executed automatically by using ODBC conn or OLEDB data sources. Is it Possible ??? -
PNRao
July 24, 2014 at 2:53 PM — ReplyHi Gavrav,
Yes – we can do this. You can simply record a macro and fetch the data using tools in Data menu tab.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Ricky Dobriyal
July 26, 2014 at 9:39 PM — ReplyHi All,
I am very glad that I visited this website and would like thank you for giving such valuable info.
I have one question in VBA while using ADO and database as excel how we can use where condition and other query on excel sheet like below example of this website.sconnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=Yes’;”
Conn.Open sconnect
sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [DataSheet$] WHERE ” ‘ Your SQL Statemnt (Table Name= Sheet Name=[DataSheet$])mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn
‘=>Load the Data into an array
‘ReturnArray = mrs.GetRows
”OR”
‘=>Paste the data into a sheet
ActiveSheet.Range(“A2”).CopyFromRecordset mrs
‘Close Recordset
mrs.CloseHere is only select condition used. Please help me how we can use different SQL condition.
Another question how we can connect to MYsql database using VBA?
Please help me in the above questions and thanks a ton in advannce.
Regards,
Ricky -
PNRao
July 26, 2014 at 9:49 PM — ReplyHi Ricky,
Thanks for your comments.
Please check the codes provided in the comments section, I have given the example queries which you have mentioned.
And regarding MySQL, you can use the following connection string:
sconnect = “DRIVER={MySQL ODBC 5.1 Driver};” & _ “SERVER=[Server];” & _ “DATABASE=[Database];” & _ “USER=[UserName];” & _ “PASSWORD=[Password];” & _ “Option=3”And replace [Server], [Database], [UserName] and [Password] with the respective original server name, database, User and Password.
If your system is not insstalled MySQL, then you have to download and install MYSQL ODBC Driver: http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/odbc/5.1.html
Hope this helps!
Thanks-PNRao! -
Nigel
July 29, 2014 at 8:32 PM — ReplyHi Pn,
Thanks your previous example works perfectly. would you be able to help with multiple record sets. I need to add the second query record-set in between the data of the first record set after exporting to sheet. -
Nigel
July 30, 2014 at 5:30 AM — ReplyHi PN, sorry hope if didn’t confuse you with my inquiry.. I will provide an example
I need to combine two record sets as I cannot put them in one query due to the data constraints.
query1= “select Total_DLV , AVAIL_DLV between date1 and date2 from Table1″ into Sheet1
query2=”select Sch_DLV , between date1 and date2 from Table2” into Sheet1
combine data from the two querys into sheet1 like
DLV_date—>aug1, Aug 2 ,aug3 (horizontal)
Total_DLV , ..
AVAIL_DLV
Sch_DLV
please let me know if this is possible.. -
Amir
August 1, 2014 at 4:08 PM — ReplyHi
Nice explanation!
Question: how can i get the data from different ‘sourcerange’ from within one sheet i.e multiple columns?code:
SourceRange = “C1:C6500 ,D1:D6500 ,AB1:AB6500,AG1:AG6500”
szSQL = “SELECT * FROM [” & SourceSheet$ & “$” & SourceRange$ & “];” -
Nigel
August 7, 2014 at 12:00 AM — ReplyHi PN ,
i fixed the issue.,, this was more to do with my query itself. i managed to fix this within the first query itself. no need for multiple queries.
however please provide an example for multiple record-sets if possible.. -
Ricky Dobriyal
August 17, 2014 at 12:54 AM — ReplyHello Team,
I have a sheet with thousand records and I want filter recordes based on Activsheet name
Query is working fine when I am putting directly the value in condition like below
sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [Data$] where Country =’India’; ”
But I want to filter it based on Acrive sheet name.
I tried two methods but it is prompting same Run time error.
s = ActiveSheet.Name
sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [Data$] where Country =s ”
sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [Data$] where Country =Activeshet.name ”
sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [Data$] where Country =’Activeshet.name’ ”Please cound you advise me how I can do this..
-
PNRao
August 17, 2014 at 11:15 AM — ReplyHi Amir,
You can mention the column names, instead of specifying multiple ranges, for example:
szSQL = “SELECT Column1, Column2 FROM [Sheet1$]”Thanks-PNRao!
-
PNRao
August 17, 2014 at 11:44 AM — ReplyHi Ricky,
Please change your code like this:s = ActiveSheet.Name
sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [Data$] where Country = ‘” & s & “‘”Thanks-PNRao!
-
Graig
September 1, 2014 at 4:10 AM — ReplyI see you share interesting content here, you can earn some additional
cash, your blog has huge potential, for the
monetizing method, just search in google – K2 advices
how to monetize a website -
Yogesh
September 10, 2014 at 10:55 PM — Replyis there a way to send parameters(through InputBox/MsgBox) using Select statement and extracting user specific data into excel using ADO.
Thanks for all your help and support.
Yogesh -
Mandeep
September 11, 2014 at 9:56 AM — ReplyDear Pn rao,
Please let me know if you are pulling data from excel , is this code using sql while retrieving data ? because this is not connecting to server. waiting for your response. thanks in advance.
MAndeep -
Mandeep
September 11, 2014 at 9:59 AM — ReplyExplain me this line of code please ” sconnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=Yes’;”
-
PNRao
September 11, 2014 at 8:19 PM — ReplyHi Mandeep,
We need to create a connection string to connect any data base using VBA.
sconnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=Yes’;”Provider=MSDASQL.1 : This is OLEDB Provider, this helps excel to understand the data base query syntax.
DSN=Excel Files : Data Source Name, Excel Files is data source in the given example.
DBQ= &DBPath : Data base file path, this is the full path of Excel File to connect.
HDR=Yes’: Headers, Yes – if the first line of your data (in sheet or range) having headers, other wise No.Hope this helps!
Thanks-PNRao! -
PNRao
September 11, 2014 at 8:22 PM — ReplyHi Mandeep,
Yes, we are pulling the data from Excel using ADO. You need to change the connection string if you are connecting any other DB.Thanks-PNRao!
-
PNRao
September 11, 2014 at 8:28 PM — ReplyHi Yogesh,
Yes, you can use Inputbox to enter some parameters and change the query accordingly.
Example:
x = InputBox(“Please enter field to select”, “Please Enter”)
‘You cna change the below query
‘sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [Sheet1$]
‘As shown below:
sSQLSting = “SELECT ” & x & ” From [Sheet1$]”
‘Your remaing code here, similarly you can keep a WHERE Condition—Thanks-PNRao!
-
Navneet Rao Ingle
September 15, 2014 at 2:35 PM — ReplyHi PN,
I am trying to copy the data from one workbook to another. Everything goes fine till the fetching of data from the source workbook but when I tried to paste the data in the destination workbook I am getting the following error:Run-time error ‘-2147467259 (80004005)’:
You cannont move a part of a PivotTable report, or insert worksheet
cells, rows, or columns inside a PivotTable report. To insert worksheet
cells, rows, or columns, first move the PivotTable report (with the
PivotTable report selected, on the Options tab, in the Actions group,
click Move PivotTable). To add, move, or remove cells within the
report, do one of the following:Code used is:
Dim DNameRecvd
Dim query As String
Dim ReturnArrayDNameRecvd = DName
Dim conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.RecordsetDim DBPath As String, sconnect As String
DBPath = ThisWorkbook.FullNamesconnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=Yes’;”
conn.Open sconnect
query = “SELECT * from [Data$]”
mrs.Open query, connWorkbooks(“DestinationFile”).Activate
Sheets(“Sheet4”).ActivateSheet4.Range(“A2”).CopyFromRecordset mrs ‘—-Receiving error message at this line
mrs.Close
ActiveWorkbook.Save
MsgBox (“Done”)Please help. Thanks in Advance.
-
gayathiri
September 22, 2014 at 3:47 PM — ReplyDear Pn Rao
i have to go through entire spreadsheet/workbook to find current status of articles by adding received date to 20 and if it matches today’s date. change the color of that row. can i do it without ADO connection -
PNRao
September 22, 2014 at 7:56 PM — ReplyHi Gayathri,
Yes, we can open the workbook and do whatever we want without using VBA. Your code will be some thing like this:
You can open the required file:
set Wb=Workbooks.Open(“C:tempworkbook.xlsx”)
Assuming you have recieved date in Column A
iCntr=1
Do while Wb.Sheets(“SheetName”).Cells(iCntr,1)<>”
If Format(Wb.Sheets(“SheetName”).Cells(iCntr,1),”DD-MM-YYYY”)=Format(Now(),”DD-MM-YYYY”) then
‘Here you can change the cell/range color
End If
LoopHope this helps!
Thanks-PNRao! -
gayathiri
September 23, 2014 at 11:14 AM — Replythanks a lot.. :)but where to put this code. either by keeping a button or create a macro module for this workbook. My requirement is Say if the article is received on september 10 i have to get that row say in green color on september 30
-
gayathiri
September 24, 2014 at 1:37 PM — ReplyMr.Rao thanks for your timely help:)
Customized ur code and it works well..
-
PNRao
September 26, 2014 at 9:31 PM — ReplyYou are most welcome!
Thanks-PNRao! -
Est228
October 10, 2014 at 9:45 PM — ReplyDear PnRao
I am using this code to connect to MS Access 2013 and used your previous comment to Shubhangi to structure the code. Everything seems to be working fine until I get to this part of the code:
sSQLSting = “SELECT * FROM [BD_X]” where BD_X is the name of my Access table
Here I keep getting an Error. I all ready have the required OLEDB and also tried using this code instead:
sSQLSting = “SELECT * FROM [BD_X$]”
I would appreciate some help. -
PNRao
October 12, 2014 at 10:06 AM — ReplyHi,
You can use the table name directly: sSQLSting = “SELECT * FROM BD_X”.If you want to refer Excel sheet as table then it will be like [BD_X$], if you connect any data base like MS Access, MS SQL Server, Oracle or Teradata you can use the table name.
Hope this helps!
Thanks-PNRao! -
Philip
October 26, 2014 at 8:48 PM — ReplyGreetings PNRao,
I am in between developing a small project for the place I work at.
Currently I am helping out the call center gang with automating their reports.
There is a huge report that they spool off a web site at the end of each month…
They obtain it in the form of an excel file with 97 format, which means each sheet is limited to 65535 rows only.
So therefore the report spans to 4 sheets and could be more…
I have completely automated this report into various pivot format for them per their requirement using Excel VBA.
However the code is slow to about 10 seconds.
There are many data analysis involved like filtering out the blanks off 2 columns, unwanted rows from another and pivoting them to obtain 4 reports using different criteria each.
I am talking about 260000+ records analyzed to about 72000+ actual meaningful data for the report.Now, I thought maybe ADO could work out the trick more efficiently and faster.
I have worked with ADO before in access/excel and know how to on the basics of connection etc.Currently, I need to know 2 things at this point:
1) Is the ADO method faster than using excel automation via variant and/or range methods combined with loops?
2) How do I append data from 4 sheets into 1 recordset to later analyze it with various select statements? Do I have to use an append query to obtain data from each sheets? If so, let me know how the query would look.Note: What I am thinking of doing is to completely do the required data manipulations within ADODB recordset and insert the manipulated data into a new sheet in Excel 8 format. Also, to run queries and to obtain the reports required from these manipulated data and again insert sheets into excel form query object.
Could you kindly guide me into the various steps I need to be looking at to achieve these goals.
Thanks in advance,
Philip -
Suruchi
October 27, 2014 at 10:47 PM — ReplyHi PN ,
This is really helpful .
One thing that is not working at my end is changing HDR=No’; … this code is not giving me the header which is required.
I tried with for loop which is working in that case , just wanted to know if how would HDR would work.Thank you
-
Suruchi
October 28, 2014 at 11:55 AM — ReplyHi PN,
This code is working fine , but I am not able to get the header eve after making HDR =No .
Could you please help me on this .Thanks ,
Suruchi -
PNRao
October 29, 2014 at 10:34 PM — ReplyHi Philip,
PivotTable is better than ADO, if your customers use Excel 2010 or higher. And to combine the Data into one record set, you query all data into one record set using UNIONs.Hope this helps.
Thanks-PNRao! -
PNRao
October 29, 2014 at 10:38 PM — ReplyHi Suruchi,
The usage of HDR is to tell the ADO whether your data has headers or not.
HDR= Yes means: You have the data and the first row is having headers and data starts from the next row.
HDR= No means: Your data has no header row and and data the data starts from the first row.Hope this clarifies your query.
Thanks-PNRao! -
Mani
November 6, 2014 at 2:29 PM — ReplyHi PNRao,
This is a great & Nice Information!
Would you be kind enough to answer the following question too,Question: how can i get the data from Oracle Database, currently I use SQL Developer to query and store the result in excel and process it later, but since the number of individual sqls increased i’m looking for something like this and if you can help me in this regard, it would be great.
Thanks in advance
Mani -
Amjed
November 14, 2014 at 4:34 PM — ReplyHi,
i would like to connect to PL/SQL developer from MS Excel and fetch the records from it and copy to the excel sheet. The query i want to execute is ‘SELECT * FROM TABLE_NAME’. Please let me know the connection string to use.
Thanks in Advance. -
Satyarth Rao
November 19, 2014 at 11:54 PM — ReplyHi PN,
I am trying to pull data from SQL Server 2012 using excel VBA Code but it is showing that SQL Sever is not exit or access is denied. Please let me know how to do so. It will be a great help.
Thanks in Advance. -
Scott
November 28, 2014 at 4:08 AM — ReplyIs it possible to join 2 tables from separate databases in an SQL query within Excel VBA?
I am currently extracting data from a table in a Firebird database but need to access data from records form a table in another Firebird database. The results of the query are used as input to a case statement that totals and dumps data into a worksheet.
I can do this in Access since I link to the tables as required, can I have 2 connections open at once in Excel? -
Prasad Sakpal
December 2, 2014 at 12:40 PM — ReplyAmazing Website…………..Thank you for giving me proper information.
-
Prasad Sakpal
December 2, 2014 at 12:44 PM — ReplyWith help of this website, i have entered the insert query & it is properly working but on this “mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn” statement getting errors ‘Run-Time Error 3704’. Please help on this..I appreciated.
-
Prasad Sakpal
December 2, 2014 at 12:45 PM — ReplyRecord is properly inserted into SQL database but getting above error message. please check…
-
Sub sbADO()
Dim sSQLQry As String
Dim ReturnArray
Dim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.Recordset
Dim DBPath As String, sconnect As String
sconnect = “Provider=SQLOLEDB.1;Data Source=******;Initial Catalog=******;User ID=*******;Password=*****;”
Conn.Open sconnect
sSQLSting = “INSERT INTO [tablename](code, fname,lname,process) Values(‘20202020′,’Prasad’,’Sakpal’,’PC001′)”
mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn ‘ Getting error message on this line, but record is properly inserted in to SQL database.
mrs.Close
Conn.Close
End SubError is = ‘Run-Time Error 3704′
Application Defined or Object Defined Error -
sandeep
December 5, 2014 at 4:49 PM — ReplyHi,
I have a query. While uploading data to SQL, if i try to download data from SQL using excal vba it is failing and throwing error.Do we have any wayt to handle mulitple calls in SQL using VBA….
An really confused shud it be done at vba end or SQL end? -
This thread has been very helpful in getting going. However, there is one problem. I am using an ODBC driver talking to Google big query but I imagine this problem I have could be relevant to any DBMS connection that has it’s own SQL variant. The key requirement for me is to be able to pass the NATIVE SQL code that the DBMS supports rather than being forced into submitting ANSI SQL which very limiting. I’m using a driver that is meant to supports both.
The following works as intended:
Dim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.Recordset
Conn.Open “DSN=bq”
SQLString = “SELECT count(*) as a from EVENTS.Game_20141205 ”
mrs.Open SQLString, Conn
Sheet2.Range(“A2”).CopyFromRecordset mrs
mrs.Close
Conn.CloseBut if I try and submit any non-ANSI SQL statement for example:
SQLString = “select a from (SELECT count(*) as a from EVENTS.Game_20141205) ”
(and this SQL runs perfectly well if you send it directly to Google bigquery directly from the google webconsole)The driver pops an error:
Run-time error ‘-2147217911 (80040e09)’:
[Simba][SQLEngine] (31480) syntax error near ‘select a from (SELECT count(*) as a from EVENTS.Game_20141205) <<>>
which I assume is because it’s not ANSI form SQL. Does anyone know how to submit the native SQL through vba (which should directly be passed through to the DBMS without any checking) -
Henning
December 15, 2014 at 8:06 PM — ReplyIn the file “remedy-export” there are no header and 5 rows of data
When I run the code, it only assigns data from row 2 to row 5 to the array. What am I doing wrong?
[code]
Sub Connect_to_Sheet()
Dim SQLString As String
Dim ReturnArray
Dim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim rsRecordset As New ADODB.Recordset
Dim DBPath As String, sConnect As StringDim Col_Idx, Row_Idx As Long
DBPath = ThisWorkbook.Path & “remedy-export.xlsx”
sConnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=NO’;”
Conn.Open sConnectSQLString = “SELECT * From [Ark2$]”
rsRecordset.Open SQLString, Conn, adOpenStatic, adLockReadOnly
Row_Idx = rsRecordset.RecordCount
ReturnArray = rsRecordset.GetRows
rsRecordset.CloseConn.Close
End Sub
[end code] -
saibabu
December 19, 2014 at 12:14 AM — ReplyHi All,
i want to copy only specific cells range.
KINDLY HELP ME.
-
kesav
December 30, 2014 at 1:12 PM — Replyhi pn
i am trying to connect ms access 2010 data base but its showing erroe
provider not recognized can to help me for over comming from this problem
thanks
kesav -
baha
January 6, 2015 at 11:14 PM — ReplyHo to delete table in existing access database? by using
-
PNRao
January 12, 2015 at 9:25 PM — ReplyHi Baha,
You can delete the table using TRUNCATE or Drop statement if have full permissions.
To delete only the data: TRUNCATE TABLE table_name;Warning: If you use the below statement, you will loss the entire table and you can not roll back.
To delete entire data: DROP TABLE table_name;Thanks-PNRao!
-
Haridas
January 25, 2015 at 12:37 AM — ReplyHi,
I need VBA & SQL learning material because i don’t have knowledge in VBA but i have knowledge in MS Office(Advance excel..).
Any one please send to my email. -
sachin
January 27, 2015 at 6:10 PM — ReplyI was creating a macro to remove exact row duplicate in excel using sql query,but it it giving me “Runtime error -2147217865(80040e37)”. Below isthe VBA code
Sub sbADOExample()
Dim sSQLQry As String
Dim ReturnArrayDim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.RecordsetDim DBPath As String, sconnect As String
DBPath = ThisWorkbook.FullName
‘You can provide the full path of your external file as shown below
‘DBPath =”E:tempInputData.xlsx”sconnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=Yes’;”
Conn.Open sconnect
sSQLSting = “select distinct column1, count(*) From [Sheet1$] group by column1 having count(*) >1″
‘ Your SQL Statement (Table Name= Sheet Name=[Sheet1$])
mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn
‘=>Load the Data into an array
‘ReturnArray = mrs.GetRows
”OR”
‘=>Paste the data into a sheet
Sheet2.Range(“A2”).CopyFromRecordset mrs
‘Close Recordset
mrs.Close‘Close Connection
Conn.CloseEnd Sub
Note : Above code working perfectly fine for 2 column
-
PNRao
February 3, 2015 at 9:53 PM — ReplyHi Sachin,
I found no issues in your code. Please send your file with some dummy data. So that we can help you to solve your issue.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Manoj
February 23, 2015 at 5:40 PM — ReplyHi PN Rao – Thanks for the post really helpful
I am trying to use Sum( Case when ( condition) then 1 else 0 end ) in this concept and it keeps saying automation error
The same code is working perfectly in SQL server
Please adviseThanks
Manoj -
Hi Rao
I am also getting the same kind of error as Sachin is geeting
I am getting the error in this line “mrs.Open sSQLsting,conn”
error is “Runtime error -2147217865(80040e37)”
-
PNRao
March 2, 2015 at 7:05 PM — ReplyHi Richard and Sachin,
Please make sure that the field names are correct. I could not find any issue in the Sachin’s query.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Enrico
March 19, 2015 at 9:13 PM — ReplyDear analists
the code is working but I am retrieving in Sheets(1) just 54’816 lines on 575’000 present in Sheets(2).
do you know why?
I am using Excel 2010Thanks
Enrico -
Aswin
March 23, 2015 at 11:41 PM — ReplyHi PN ,
Read through the post great information you are sharing indeed.. I have a scenario where i would need to pull the values in a column in sheet say Sheet1 whose range may be dynamically changing into IN clause in SQL server query with values like ‘A’,’B’,’C’ etc
-
guys77
March 29, 2015 at 10:36 AM — ReplyHi experts..
How about Dbf files?what string/connection code?
Thanks -
KUMAR
May 4, 2015 at 1:07 PM — ReplyReally great. I could get what I could not even in Microsoft site
-
HONEY
May 8, 2015 at 12:23 PM — ReplyHi,
I want to access the info of memory usage of production database in my excel sheet.
can anyone help me with vba.
-
sheriff
May 14, 2015 at 9:54 PM — ReplyHi,
I want to get a notification automatically when a file is copied in a folder. Can this be done by VBA macro ?
Please help me.
Thanks,
Sheriff -
sheriff
May 14, 2015 at 9:58 PM — Reply -
Sam
May 22, 2015 at 8:04 AM — ReplyHi,
Thanks for sharing this info…
Very usefulregards
sam -
Anand Jo
May 29, 2015 at 9:19 PM — ReplyThanks for the code. It works with the user input when input command is used. But, it does not work when the user enters a value in the textfield in the userform created in excel VBA. Why does this happen? It just does not work with the userform text field input. Any help is appreciated. Here is the code:
Sub UForm()
Dim sSQLSting As String
Dim ReturnArrayDim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.Recordset
Dim DBPath As String, sconnect As StringDBPath = ThisWorkbook.FullName
sconnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=Yes’;”
Conn.Open sconnect
sSQLSting = “SELECT * From [Sheet1$] where Order_Number = ” & ordernotext1 ‘ Your SQL Statement (Table Name= Sheet Name=[Sheet1$])
mrs.Open sSQLSting, ConnSheets(“ReportsO”).Range(“A8”).CopyFromRecordset mrs
mrs.Close
Conn.Close
End Sub -
kishan Sanghani
June 5, 2015 at 4:18 AM — ReplyHi ,
I am able to execute query from VBA on my DB2. But sometime I need to abort query because of DB conjunction. Please suggest me way to abort query , if executed through VBA.
Thanks in advance.
Regards,
Kishan Sanghani -
Krishna
June 10, 2015 at 9:00 PM — ReplyHi,
Am able to connect to excel data source using ADO connection. But my excel has 265000 rows and 118 columns. When I try to open record set, it struck and it taking more time.. Is that any way to use Ado connection and open record set in quick turnaround? Pls suggest.. Tnx
-
UDAY PRATAP
June 17, 2015 at 5:09 PM — ReplyNice Explanation…..Thanks.
If I want to save picture of employees in (the respective rows) a column. for example Emp_Photo
and if I run Select * from [Sheet1$] it is bringing all information but not the pictures
How to achieve it? -
UDAY PRATAP
June 17, 2015 at 5:12 PM — ReplyTry to connect in a blank New workbook and after connection is established then copy the original sheet into this new workseets.
-
Vic
June 30, 2015 at 7:37 PM — ReplyHi,
The code you gave worked! I am really kinda new to this old VBA stuff. My problem is it opens on a new sheet in a new workbook. How can I have the data displayed on an existing sheet with existing columns?
Thank you in advance for your help PN.
– V
-
Sameer
July 9, 2015 at 5:56 PM — ReplyHi PN – Your site has awesome content and I am hoping you can resolve my query.
I have a MySQL database and I have connect it to excel using VBA on the local machine. Now I want to give the same excel file as an input/output mechanism to all the users to interact with the database installed on my computer. All the users are in a network. Any help would be greatly appreciated.
-
PNRao
July 9, 2015 at 7:51 PM — ReplyHi Sameer,
Thanks for your feedback!
Here are the possible solutions and my preference order:
Solution 1: You can create new database in any server and export the local database into server and change the connection string. All your user need to have MySQL OLEDB Provider in their PCs.
Solution 2. You can export to MS Access database and change the connection string. For this your user do not required to install any additional Provider.
Hope this helps!
Thanks-PNRao! -
Mahantesh
September 9, 2015 at 5:18 PM — ReplyStrSQL=”SELECT * FROM [Shee1$] MINUS SELECT * FROM [Sheet2$] is not getting executed.
Help required.
-
Dung Nguyen
September 14, 2015 at 8:58 PM — ReplyHi PNRao,
I would query to the first worksheet of selected workbook through navigate to the workbook location and user select it( I used worksheets(1) but can not successful), can you show me a sample how to assign this parameter of worksheets(1) to the vba query?
Regards/Dung
-
This paragraph ցives ϲlear idea in support οf the new users.
-
Sriram
October 7, 2015 at 12:48 PM — ReplyHi
Am trying to run sql Analysis query in excel macro . Can you please help me .Thanks in advance
-
Dan
October 21, 2015 at 7:20 AM — ReplyHi,
Very helpful page, thank you.
I have managed to use a select query to retreive data from a second sheet however I am wanting to update data in a sheet using this method. I have changed the sSQLSting to an update query which appears to run but the data does not update.
Could I please trouble you for a simple example of how to update a cell value?
Column A (Dealer) is unique and Column B (Value) is the cell that I am trying to update
Sheet name = DATA
Column A = Dealer
Column B = ValueThank you,
Dan
-
Dan
October 21, 2015 at 10:19 AM — ReplySorry for wasting your time with my first message, was a pretty simple mistake in the end.
I have it working however I am wanting to source the value that I am updating from a cell on the sheet. I have done this with:
Dim NewVal As String
NewVal = Sheets(“ADO”).Range(“N2”).Value
When I try to put this into the sSQLSting it errors. Can you please help me out.Thanks again.
Code:
‘Add reference for Microsoft Activex Data Objects Library
Sub sbADOUPDATE()
Dim sSQLQry As String
Dim sSQLQry2 As String
Dim NewVal As StringDim ReturnArray
Dim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.RecordsetDim DBPath As String, sconnect As String
DBPath = “P:DocumentsSALESOrderwrite2015TestingBook2.xlsx”
NewVal = Sheets(“ADO”).Range(“N2″).Value‘You can provide the full path of your external file as shown below
‘DBPath =”C:InputData.xlsx”sconnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=Yes’;”
Conn.Open sconnect
sSQLSting = “UPDATE [Data$] SET Content = ‘testing2’ WHERE Dealer = ‘Q325′”mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn
sSQLSting2 = “UPDATE [Data$] SET Content = 1000 WHERE Dealer = ‘Q375′”mrs.Open sSQLSting2, Conn
‘Close Connection
Conn.CloseEnd Sub
-
Masaru
November 1, 2015 at 11:58 PM — ReplyQuestion: I have a header where it has been merge with under a 3 column, is it possible to call the sub column? Thanks!
-
Michael
November 10, 2015 at 8:37 PM — ReplyHi All
I have a spreadsheet with an Excel Table named Table1 with two Columns named Quarter and Sales.
The Table has say 4 rows of data beneath the header. Then there is more data in the rows below the table which is not part of the table.How do I copy only the data in the Table rows?
Using SqlQry = “SELECT [Quarter], [Sales] FROM [Sheet2$][Table1$]”
Copied all the data in the two columns including the data outside the Table.
Thanks. -
loes
November 25, 2015 at 7:52 PM — ReplyHello,
I am trying to set up a connection to MySQL and came across this example. I applied the code to my own file. But what i can not seem to figure out is why the file does not take the values you write in A1, A2 etc. where in the code do you tell the code to skip the first line?
-
Ray
November 26, 2015 at 10:35 AM — ReplyThis is precisely what i was searching for..Thanks a Ton.
One question please….Here we saw fetching data from a spreadsheet using ADO.
Can we write data from a User interface,like a form (in Spreadsheet A) to a Database (Spreadsheet B) using ADO ?
Please can you point me to where can I get more info on this.
All the best with your efforts. God bless !
-
mike
January 15, 2016 at 1:22 PM — ReplyHello,
I have made a connection with a dbf file with VBA this works great, but is it also possible to open multiple dbf files en join them in the SQL? Iám trying hard but can’t figure it out.
-
Shwetanjali Das
February 11, 2016 at 12:10 PM — ReplyHi,
I want to fetch records from a database. How to do that? I have read only access to that database.
-
srimeenakshi
March 22, 2016 at 6:01 PM — Replyhi friends,
i want a code to update a table in a database. when we click command button in vba?
anyone can help me -
Iris
March 29, 2016 at 3:21 PM — Replyhi, i couldn’t download the example file, seems the linkage was corrupted.
-
Akit
May 3, 2016 at 10:09 AM — ReplyHI ,
Really helpful blog, I am encountering an error when I tried to use Like operator in my sql statement.
exs
Dim sSQLQry As String
Dim ReturnArray
Dim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim mrs As New ADODB.Recordset
Dim DBPath As String, sconnect As String
DBPath = ThisWorkbook.FullName
‘You can provide the full path of your external file as shown below
‘DBPath =”C:InputData.xlsx”
sconnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=Yes’;”
Conn.Open sconnect
Debug.Print YourstrQery,1. SQLSting = “SELECT * From [Sheet1$] WHERE [URL] like ‘%POST /login.form HTTP/1.1%’ ”
2. SQLSting = “SELECT * From [Sheet1$] WHERE session in(Select Distinct session from [Sheet1$]) and [URL] like ‘%POST /login.form HTTP/1.1%’ ”
mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn
-
ram
May 10, 2016 at 12:34 PM — ReplyThere are records in the sheet titled ‘Table2’, which have Cust_ID not present in column Cust_ID in the sheet titled ‘Table1’ (e.g. 110, 117). Can you write an Excel VBA program that transfers the data in these sheets to 2 separate tables in Access DB, runs the appropriate query and provides the list of unmatched records from ‘Table2’? Please use ADO method for database connectivity. The program should execute on clicking a button in Excel and output should comprise of unmatched records displayed in a new Excel sheet.
-
Guilherme
June 4, 2016 at 12:08 AM — ReplyI did’nt find the example file =(
Can you send me the link? -
PNRao
June 4, 2016 at 9:43 PM — ReplyThanks- We have fixed the download link.
Thanks-PNRao!
-
Kamal Kroor
June 21, 2016 at 1:08 PM — ReplyDear All,
Any one can help me with using variables in update command? in the above example, update is used only with exact number which will not be the case for real time situation. We need a variable that takes values from the user form.
Thanks,Kamal Kroor
-
Célio Ávila
June 21, 2016 at 7:56 PM — ReplyDamn… I’ve been trying so hard to learn this, but nothing ever seems to work.
I finally downloaded the example file and not even that is working. I get the message, “System error &H8000FFFF (-2147418113). Catastrophic Failure.”
I activated the 2.8 library something, so I dont know what could be going wrong.Also, every source I look for to study gives me a completely different macro example, so I can’t even compare them to better understand the coding.
When I do find good content to learn SQL from, it doesnt seem to be related to excel vba, so it doesnt help me all that much.
I’m trying to learn how to filter data with ADO insteand of using autofilter. At first I saw someone posting this example:
Sub testConnection()
Dim wb As Workbook
Dim c As WorkbookConnection
Dim sql As StringSet wb = ActiveWorkbook
Set c = wb.Connections.Item(1)
sql = c.ODBCConnection.CommandText
sql = Replace(sql, “WHERE (`’Sheet1$’`.k=10)”, _
“WHERE (`’Sheet1$’`.k=9) AND (`’Sheet1$’`.l=11) AND (`’Sheet1$’`.m=12) AND (`’Sheet1$’`.n=13) “)
c.ODBCConnection.CommandText = sql
c.RefreshEnd Sub
can anyone make sense of this?
-
Ankush
June 28, 2016 at 3:31 PM — ReplyHi
Could you let me know if we can connect a macro to the server and get the information from the log files.
And if yes , then could you let me know how we could connect to the server.
-
Stanley
July 1, 2016 at 1:25 PM — ReplyHi PNRao,
Your website is awesome!
Do you have experience to use RANK() OVER(PARTITION BY) function by ADODB connection?
I need to rank first and output them.
Any help would be greatly appreciated.Stanley
-
Stewart
July 15, 2016 at 2:27 PM — ReplyHI PNRao,
New to using VBA & ADO , I wish to use a similar code that uses an input-box to pull through the relevant input from a closed workbook to my current active workbook, is this possible?
Kind Regards,
Stewart
-
Sanjeev Sharma
August 6, 2016 at 12:54 AM — ReplyThanks!! for the valuable information!!
-
Pawan
August 30, 2016 at 10:49 AM — ReplyVery nice Article. I have one query in this that I have one column which has number as well as text and I found one thing that vb query that declare the fields type as Number and it will not show Text values. So is it possible to import all the fields with data type as a string because string can capture both number as well as text.
-
Tomi
August 30, 2016 at 11:58 PM — ReplyHi, I am new to VBA and application development. Please how can someone start with learning VBA and Database Application development? Thank you
-
Durgam Sasidhar
January 4, 2017 at 7:36 PM — ReplyWOW, This is what am searching for entire day, and this post Cleared My doubts and issues. Thx a lot
-
Sunil Sehgal
April 5, 2017 at 11:05 AM — ReplyHello sir,
While I run my code it is showing automation error. Can you please etell me why is it so occuring.. tell me the solutio n for the same. -
Hasan
May 4, 2017 at 9:05 PM — ReplyHi,
when the Excel file is opened read-only, the sql query (with both providers MSDASQL and Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB) does not return any results.
Any ideas how to overcome this, maybe using additional parameters?
-
Rakesh
May 17, 2017 at 2:43 PM — ReplyHi PNRao,
Information provided by you in your website is excellent.
I customised this code to postgresql,but getting an Run-Time error object required: 424.Can you please help me with this error.Thanks
Rakesh -
AK
July 19, 2017 at 7:57 PM — ReplyDear PN,
Really, this webpage is very useful, thanks for your efforts.
I have one question here:
Instead of figures (2 & 5000) at ‘Values(2,500)’ how can use variables or cells from active sheet?Thanks in advance & regards,
AK -
PNRao
July 19, 2017 at 8:51 PM — ReplyYou need to form the string as per your requirement. Replace the below statement: sSQLSting = “INSERT INTO [DataSheet$](Quarter, Sales) Values(2,5000)”. With: sSQLSting = “INSERT INTO [DataSheet$](Quarter, Sales) Values(" &Range("A1") &"," &Range("A2") &")”.The second statement will read the values from Range A1 and A2 of ActiveSheet. You can also specify the sheet name if it is not a active sheet, Sheets(“SheetName”).Range(“A1”)
Thanks!
-
YasserKhalil
July 20, 2017 at 10:59 PM — ReplyThat’s really awesome. Thank you very much
How to update closed workbook using ADO? -
Andi permana
November 30, 2017 at 4:36 PM — ReplyHow do I use where statement and group by??
-
Mayur raj
March 4, 2018 at 12:50 PM — ReplyHi recordset stores the result in array form, when using select a view/output is getting stored.but using insert there is no output, it will process the query and store data in mentioned table.
Add one more line, select * from [inserted_table]
Before msr.
Hope you get the logic.
Thanks -
Anil
April 19, 2018 at 6:10 PM — ReplyHi Sir,
I have insert code but show the error.
Option Explicit
Dim BlnVal As BooleanPrivate Sub Done_Click()
Dim sSQLQry As String
Dim ReturnArray
Dim con As ADODB.Connection
Dim sqlstr As String, datasource As String
Set con = New ADODB.Connection
datasource = “D:TEST.xlsx” ‘change to suitDim sconnect As String
sconnect = “Provider=Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0;” & _
“Data Source=” & datasource & “;” & _
“Extended Properties=”Excel 12.0;HDR=YES”;”
With con
.Open sconnect
‘
sqlstr = “Insert Into [Sheet2$](Sno, Name, Amt) Values (GP.ComboBox1.Value, GP.TextBox1, GP.TextBox2)”
‘
.Execute sqlstr
.Close
End WithSet con = Nothing
End Sub
-
Anil
April 19, 2018 at 6:14 PM — ReplyI have insert data in offline Excel File & Same Update Data Combobox1 and TextBox1 only Number accept. not Text.
-
nalini raju
May 14, 2018 at 6:47 PM — Reply‘Iam not able to insert
‘Iam getting error–Automation error in runtime
‘Using MSDASQL Provider
‘sconnect = “Provider=MSDASQL.1;DSN=Excel Files;DBQ=” & DBPath & “;HDR=Yes’;”‘Using Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB Provider – If you get an issue with Jet OLEDN Provider try MSDASQL Provider (above statement)
sconnect = “Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=” & DBPath _
& “;Extended Properties=”Excel 8.0;HDR=Yes;IMEX=1″;”Conn.Open sconnect
‘DeleteId = InputBox(“Name”)
” sSQLSting = “SELECT DISTINCT Date,SalesRep,Product,Discount,Units,Region,Net_Sales From [DataSheet$]”
‘ Your SQL Statemnt (Table Name= Sheet Name=[DataSheet$])
‘ sSQLSting = “UPDATE [DataSheet$] SET SalesRep=10,Product=10,Discount=10,Units=10,Region=10 WHERE Units=1”
sSQLSting = “INSERT INTO [RAMA$](Quarter, Sales) Values(” & Sheets(“RAMA”).Range(“A1”) & “,” & Sheets(“RAMA”).Range(“A2”) & “)”
‘ sSQLSting = “Select * from [DataSheet$]” ‘ where Date is not null”
mrs.Open sSQLSting, Conn‘ Sheets(“RAMA”).Range(“A1”).CopyFromRecordset mrs
mrs.Close
‘Close Connection
Conn.Close
End Sub -
Taesoo
June 14, 2018 at 4:51 PM — ReplyHi,
I read date from db file but can not read full data.
Below is the data in db file
Date
4/16/2016 16:39
4/19/2016 12:50
4/22/2016 16:12
4/25/2016 10:28
4/27/2016 10:51This is what I read
Date
4/16/2016
4/19/2016
4/22/2016
4/25/2016
4/27/2016Sub db_query()
Dim conn As Object, rst As Object
Worksheets(“results”).Range(“A2:AI5001”).ClearContentsSet conn = CreateObject(“ADODB.Connection”)
Set rst = CreateObject(“ADODB.Recordset”)conn.Open “DRIVER=SQLite3 ODBC Driver;Database=D:backup.db;”
strSQL = “SELECT Date from Tb_Result_Summary”
rst.Open strSQL, conn, 1, 1Worksheets(“results”).Range(“A2”).CopyFromRecordset rst
rst.CloseSet rst = Nothing: Set conn = Nothing
End Sub
-
Baze
July 9, 2018 at 3:50 PM — ReplyHi PN, thank you for this material. it is very educative especially for a person who is beginner in VBA like me.
I am trying to make a connection from my excel file to a database and i tried your code but it resulted in a mistake :‘Sheet1$’ is not a valid name. Make sure that it does not include invalid characters or punctuation and that it is not too long
I am apologizing in advance, cause this question might seem very beginner for you, but I am in my first steps with VBA.
-
Deepak Bisht
October 2, 2018 at 6:45 PM — ReplyEach time i pull data the file opened in read only mode.. Please advise
-
Prabhu Murugan
December 20, 2018 at 9:42 AM — ReplyHi,
A column in an excel file consist of values only. But still select query for the field throws data type mismatch in criteria even after I changed all the cells to values.
select * from table where field < 0
It works only for
select * from table where field < ‘0’
-
Amber
July 18, 2019 at 5:58 AM — ReplyI want to get into an array all records brought by getRows but I can’t. When I try like this, the array stay empty anyway. I only get success by using getString but my goal is insert each record into a cell of a listbox. I hope you can understend my english!
-
anil
November 17, 2019 at 12:50 PM — Replythanks for efforts sir as a beginer easyly understand whole concept
-
Mon
February 9, 2020 at 1:15 PM — ReplyHi,
please advise how can I use the SQL command to delete the record
thank you
-
Dinesh
May 2, 2020 at 10:37 PM — Reply
Effectively Manage Your
Projects and Resources
ANALYSISTABS.COM provides free and premium project management tools, templates and dashboards for effectively managing the projects and analyzing the data.
We’re a crew of professionals expertise in Excel VBA, Business Analysis, Project Management. We’re Sharing our map to Project success with innovative tools, templates, tutorials and tips.
Project Management
Excel VBA
Download Free Excel 2007, 2010, 2013 Add-in for Creating Innovative Dashboards, Tools for Data Mining, Analysis, Visualization. Learn VBA for MS Excel, Word, PowerPoint, Access, Outlook to develop applications for retail, insurance, banking, finance, telecom, healthcare domains.
Page load link

3 Realtime VBA Projects
with Source Code!
Go to Top






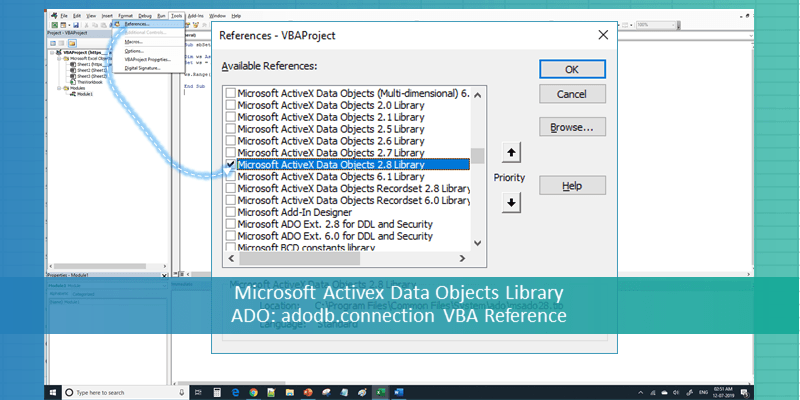
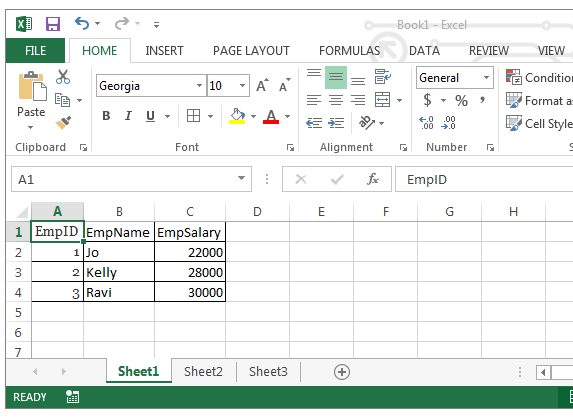
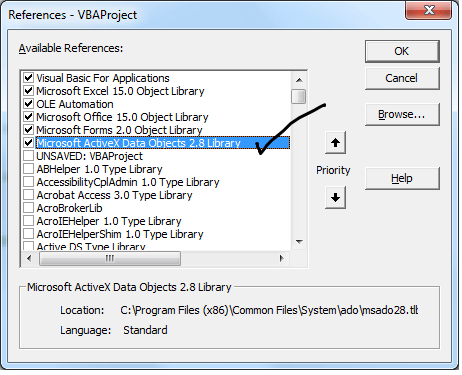
 Customized ur code and it works well..
Customized ur code and it works well..