Word for Microsoft 365 Word 2021 Word 2019 Word 2016 Word 2013 Word 2010 Word 2007 More…Less
Inserting a document
You can insert the content of previously-created Word documents into a new or different Word document.
-
Click or tap where you want to insert the content of the existing document.
-
Go to Insert and select the arrow next to Object
.
-
Select Text from File.
-
Locate the file that you want and then double-click it.
-
To add in the contents of additional Word documents, repeat the above steps as needed.
Important: If you want to insert the header and footer also, be sure to insert the text from the file in a new section so that the header and footer are applied to only those pages. For more info on sections, see Insert a section break.
Need more help?
Word 2016 is designed to help you create professional-quality documents. Word can also help you organize and write documents more efficiently.
When you create a document in Word, you can choose to start from a blank document or let a template do much of the work for you. From then on, the basic steps in creating and sharing documents are the same. And Word’s powerful editing and reviewing tools can help you work with others to make your document great.
Start a document
It’s often easier to create a new document using a template instead of starting with a blank page. Word templates come ready-to-use with pre-set themes and styles. All you need to do is add your content.
Each time you start Word, you can choose a template from the gallery, click a category to see more templates, or search for more templates online.
For a closer look at any template, click it to open a large preview.
If you’d rather not use a template, click Blank document.
Open a document
Every time you start Word, you’ll see a list of your most recently used documents in the left column. If the document you’re looking for isn’t there, click Open Other Documents.

If you’re already in Word, click File > Open and then browse to the file’s location.
When you open a document that was created in earlier versions of Word, you see Compatibility Mode in the title bar of the document window. You can work in compatibility more or you can upgrade the document to use Word 2016.
Save a document
To save a document for the first time, do the following:
-
On the File tab, click Save As.
-
Browse to the location where you’d like to save your document.
Note: To save the document on your computer, choose a folder under This PC or click Browse. To save your document online, choose an online location under Save As or click Add a Place. When your files are online, you can share, give feedback and work together on them in real time.
-
Click Save.
Note: Word automatically saves files in the .docx file format. To save your document in a format other than .docx, click the Save as type list, and then select the file format that you want.
To save your document as you continue to work on it, click Save in the Quick Access Toolbar.
Read documents
Open your document in Read Mode to hide most of the buttons and tools so you can get absorbed in your reading without distractions.

-
Open the document you want to read.
Note: Some documents open in Read Mode automatically, such as protected documents or attachments.
-
Click View > Read Mode.
-
To move from page to page in a document, do one of the following:
-
Click the arrows on the left and right sides of the pages.
-
Press page down and page up or the spacebar and backspace on the keyboard. You can also use the arrow keys or the scroll wheel on your mouse.
-
If you’re on a touch device, swipe left or right with your finger.
Tip: Click View > Edit Document to edit the document again.
-
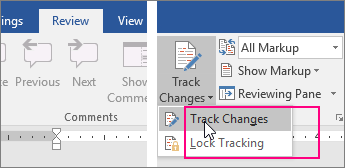
Track changes
When you’re working on a document with other people or editing a document yourself, turn on Track Changes to see every change. Word marks all additions, deletions, moves, and formatting changes.
-
Open the document to be reviewed.
-
Click Review and then on the Track Changes button, select Track Changes.
Read Track changes to learn more.
Print your document
All in one place, you can see how your document will look when printed, set your print options, and print the file.
-
On the File tab, click Print.
-
Do the following:
-
Under Print, in the Copies box, enter the number of copies you want.
-
Under Printer, make sure the printer you want is selected.
-
Under Settings, the default print settings for your printer are selected for you. If you want to change a setting, just click the setting you want to change and then select a new setting.
-
-
When you’re satisfied with the settings, click Print.
For details, see Print a document.
Beyond the basics
For more on the fundamentals of using Word, see What’s new in Word 2016.
Top of Page
With Word for the web, you use your web browser to create, view, and edit the personal documents that you store on OneDrive. If your organization or college has a Microsoft 365 plan or SharePoint site, start using Word for the web by creating or storing documents in libraries on your site.Save changes
Word saves your changes automatically. Look on the status bar at the bottom left corner of Word for the web. It will either show Saved or Saving.

Share documents online
Because your document is online, you can share it by sending a link instead of an email attachment. People can read it in their web browser or mobile device.
Click File > Share > Share with People.
Comment in the browser
A comment balloon shows where comments have been made in the doc.
Reply to comments, and check off items you’ve addressed.
Edit in the browser
If you try to type in the document and nothing happens, you’re probably in Reading view. Switch to Editing view: click Edit Document > Edit in Word for the web.
Type and format text, add pictures, adjust the layout of the page, and more. For more advanced editing, click Open in Word.
Work together on the same doc
To work together in Word for the web, you edit a document as you normally would. If others are also editing it, Word for the web alerts you to their presence. You can see everyone who is currently working in the document by clicking in the ribbon.
Clicking on an author’s name jumps you to where they’re working in the doc. And you’ll see the changes they make as they’re happening. They can be working in Word for the web, Word 2010 or later, or Word for Mac 2011.
Add a header or footer
Go to Insert > Header & Footer to add headers and footers to your document.
Click Options to choose how you’d like them to appear.

Add page numbers
Click Insert > Page Numbers and then choose from the gallery where you’d like the page numbers to appear.
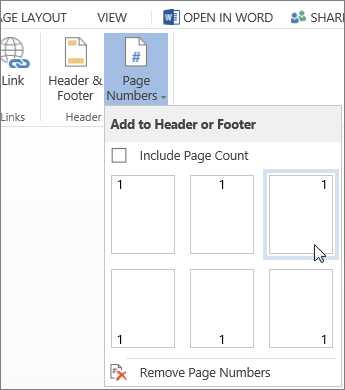
Select Include Page Count to show the current page number along with the total number of pages (page X of Y).
Find and replace text
Quickly search for every occurrence of a specific word or phrase in your document by clicking Home > Find (or type Ctrl+F). Results appear next to your document so you can see the term in context. Clicking on a search result jumps you to that occurrence.
Click Replace (or type Ctrl+H) to find and replace text.
Print in Word for the web
Go to File > Print. Word for the web creates a PDF preview of your document that keeps all the layout and formatting of your document. Send the PDF to your printer and it will print the way you expect.
Microsoft Word 2013 is a word-processing program designed to help you create professional-quality documents. Word helps you organize and write your documents more efficiently.
Your first step in creating a document in Word 2013 is to choose whether to start from a blank document or to let a template do much of the work for you. From then on, the basic steps in creating and sharing documents are the same. Powerful editing and reviewing tools help you work with others to make your document perfect.
Choose a template
It’s often easier to create a new document using a template instead of starting with a blank page. Word templates are ready to use with themes and styles. All you need to do is add your content.
Each time you start Word 2013, you can choose a template from the gallery, click a category to see the templates it contains, or search for more templates online. (If you’d rather not use a template, just click the Blank document.)

For a closer look at any template, just click it to open a large preview.
Top of Page
Open a document
Every time you start Word, you’ll see a list of your most recently used documents in the left column. If the document you’re looking for isn’t there, click Open Other Documents.
If you’re already in Word, click File > Open and then browse to the file’s location.
When you open a document that was created in earlier versions of Word, you see Compatibility Mode in the title bar of the document window. You can work in compatibility more or you can upgrade the document to use features that are new or enhanced in Word 2013.
Top of Page
Save a document
To save a document for the first time, do the following:
-
Click the File tab.
-
Click Save As.
-
Browse to the location where you’d like to save your document.
Note: To save the document on your computer, choose a folder under Computer or click Browse. To save your document online, choose a location under Places or Add a Location. When your files are online, you can share, give feedback and work together on them in real time.
-
Click Save.
Note: Word automatically saves files in the .docx file format. To save your document in a format other than .docx, click the Save as type list, and then select the file format that you want.
To save your document as you continue to work on it, click Save in the Quick Access Toolbar.
Top of Page
Read documents
Open your document in Read Mode to hide most of the buttons and tools so you can get absorbed in your reading without distractions.

-
Open the document you want to read.
Note: Some documents open in Read Mode automatically, such as protected documents or attachments.
-
Click View > Read Mode.
-
To move from page to page in a document, do one of the following:
-
Click the arrows on the left and right sides of the pages.
-
Press page down and page up or the spacebar and backspace on the keyboard. You can also use the arrow keys or the scroll wheel on your mouse.
-
If you’re on a touch device, swipe left or right with your finger.
Tip: Click View > Edit Document to edit the document again.
-
Top of Page
Track changes
When you’re working on a document with other people or editing a document yourself, turn on Track Changes to see every change. Word marks all additions, deletions, moves, and formatting changes.
-
Open the document to be reviewed.
-
Click Review and then on the Track Changes button, select Track Changes.

Read Track changes to learn more.
Top of Page
Print your document
All in one place, you can see how your document will look when printed, set your print options, and print the file.
-
Click the File tab and then click Print.
-
Do the following:
-
Under Print, in the Copies box, enter the number of copies you want.
-
Under Printer, make sure the printer you want is selected.
-
Under Settings, the default print settings for your printer are selected for you. If you want to change a setting, just click the setting you want to change and then select a new setting.
-
-
When you’re satisfied with the settings, click Print.
For details, see Print and preview documents.
Beyond the basics
Go beyond the basics with your documents by creating a table of contents or saving a document as a template.
Top of Page
Important:
Office 2010 is no longer supported. Upgrade to Microsoft 365 to work anywhere from any device and continue to receive support.
Upgrade now
In this article
-
What is Word?
-
Find and apply a template
-
Create a new document
-
Open a document
-
Save a document
-
Read documents
-
Track changes and insert comments
-
Print your document
What is Word?
Microsoft Word 2010 is a word-processing program, designed to help you create professional-quality documents. With the finest document-formatting tools, Word helps you organize and write your documents more efficiently. Word also includes powerful editing and revising tools so that you can collaborate with others easily.
Top of Page
Find and apply a template
Word 2010 allows you to apply built-in templates, to apply your own custom templates, and to search from a variety of templates available on the web.
To find and apply a template in Word, do the following:
-
On the File tab, click New.
-
Under Available Templates, do one of the following:
-
To use one of the built-in templates, click Sample Templates, click the template that you want, and then click Create.
-
To reuse a template that you’ve recently used, click Recent Templates, click the template that you want, and then click Create.
-
To use your own template that you previously created, click My Templates, click the template that you want, and then click OK.
-
To find a template on Office.com, under Office.com Templates, click the template category that you want, click the template that you want, and click Download to download the template from Office.com to your computer.
-
Note: You can also search for templates on Office.com from within Word. In the Search Office.com for templates box, type one or more search terms, and then click the arrow button to search.
Top of Page
Create a new document
-
Click the File tab and then click New.
-
Under Available Templates, click Blank Document.
-
Click Create.
For more information about how to create a new document, see Create a document.
Top of Page
Open a document
-
Click the File tab, and then click Open.
-
In the left pane of the Open dialog box, click the drive or folder that contains the document.
-
In the right pane of the Open dialog box, open the folder that contains the drawing that you want.
-
Click the document and then click Open.
Top of Page
Save a document
To save a document in the format used by Word 2010 and Word 2007, do the following:
-
Click the File tab.
-
Click Save As.
-
In the File name box, enter a name for your document.
-
Click Save.
To save a document so that it is compatible with Word 2003 or earlier, do the following:
-
Open the document that you want to be used in Word 2003 or earlier.
-
Click the File tab.
-
Click Save As.
-
In the Save as type list, click Word 97-2003 Document. This changes the file format to .doc.
-
In the File name box, type a name for the document.
-
Click Save.
For more information about how to create a document that is compatible with Word 2003 or earlier versions, see Create a document to be used by previous versions of Word.
Top of Page
Read documents
-
Open the document that you want to read.
-
On the View tab, in the Document Views group, click Full Screen Reading
-
To move from page to page in a document, do one of the following:
-
Click the arrows in the lower corners of the pages.
-
Press PAGE DOWN and PAGE UP or SPACEBAR and BACKSPACE on the keyboard.
-
Click the navigation arrows at the top center of the screen.
Tip: Click View Options, and then click Show Two Pages
to view two pages, or screens, at a time.
-
For more information about how to view documents, see Read documents in Word.
Top of Page
Track changes and insert comments
-
To turn on change tracking, on the Review tab, in the Tracking group, click Track Changes.
-
To insert a comment, on the Review tab, in the Comments group, click New Comment.
For more information about how to track changes made while revising, see Track changes and insert comments.
Top of Page
Print your document
-
Click the File tab and then click Print.
-
Do the following:
-
Under Print, in the Copies box, enter the number of copies that you want to print.
-
Under Printer, make sure that the printer that you want is selected.
-
Under Settings, the default print settings for your printer are selected for you. If you want to change a setting, click the setting you want to change and then select the setting that you want.
-
-
When you are satisfied with the settings, click Print.
For more information about how to print a file, see Preview and print a file.
Top of Page
Download Article
Download Article
This wikiHow teaches you how to insert the contents of and/or a link to another document into a Microsoft Word document on Windows or Mac.[1]
Steps
-
1
Open a Microsoft Word document. To do so, double-click the blue app that contains or is shaped like a W. Then click File at the top of the screen and Open….
- To create a new document, click New in the file menu.
-
2
Click the place in the document where you want to insert the file.
Advertisement
-
3
Click the Insert tab. It’s at the top of the window.
-
4
Click the
next to Object. It’s in the Text group on the right side of the tool bar at the top of the window.
- On Mac, click Text to expand the group.
-
5
Choose the type of file to insert.
- Click Object… to insert a PDF, image, or another type of non-text file into your Word document. Then click From File… on the left side of the dialog box that opens.
- If you prefer to insert a link to and/or icon of the file, rather than the entire document, click Options on the left side of the dialog box and check Link to File and/or Display as Icon.
- Click Text from File… to insert the text of another Word or text document into the current Word document.
- Click Object… to insert a PDF, image, or another type of non-text file into your Word document. Then click From File… on the left side of the dialog box that opens.
-
6
Select the file to insert.
-
7
Click OK. The file contents, a linked icon, or the text of the file will be inserted into your Word document.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
I like that I can copy the file and paste to a blank page within another Word file. Is there a way to paste a document that’s more than one page?
Open Microsoft Word. On the top left menu choose Insert. Choose File. Browse through your file system to the file you want. Click on the file name. Choose Insert. For an existing document, place the cursor at the point you want to insert the document, then follow the above instructions. You can also choose a range of pages substituting the final Insert with Range.
-
Question
How do I insert a file into a Word document?
Read and follow the instructions listed in the article above.
-
Question
I need to email a document that is not already in a file. What do I do?
Okay, where is the document? All documents are files. If you don’t like the current format, save it to another format, or copy the material into another file in a standard format. If desperate, take a screenshot by pressing the PrintScreen key and pasting it into a Word document. Save it and you’ll have a file. If you mean the document is a physical piece of paper and not on your computer, you can either scan it or just take a picture of it with your phone.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Open a Word document.
2. Click a place in the document.
3. Click Insert.
4. Click the Object drop-down.
5. Choose the type of file to insert.
6. Select a file to insert.
7. Click OK.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 455,641 times.
Is this article up to date?
How to embed files, including other Word files, into a Word document
Updated on September 6, 2022
What to Know
- Open Word doc > place curser where you want to insert file > select Insert tab.
- Next, select Object drop-down arrow > choose Text from File > select document > Insert.
This article explains how to insert one Word document into another — even when the copied document includes headers and footers. Instructions apply to Word 2019, Word 2016, Word 2013, Word 2010, and Word for Microsoft 365.
How to Insert a Word Document Into Another Word Document
If you have an existing Microsoft Word document that would augment a document you’re working on, you have a few options. If you want to add an entire document to a second Word doc, your best bet is knowing how to insert a document into Word.
Word inserts the document into the current document without changing the formatting applied to either document. Images, tables, shapes, and other objects in the existing document carry over into the new Word file as well.
-
Start Word and open the document into which you want to insert another Word document.
Alternatively, select New > Blank Document to open a new, blank Word document to insert an existing document into.
-
Place the cursor on the spot in the document where you want to insert an existing Word file.
-
Select the Insert tab.
-
Select the drop-down arrow next to Object in the Text group.
-
Choose Text from File in the drop-down list that appears. The Insert from File dialog box will open.
If you select Object from the Object drop-down menu, you can embed an existing Word document as a clickable file from the Create from File tab of the Object dialog box that appears. Alternatively, you can create a new, blank document that becomes a clickable object when saved using the Create New tab in that dialog box. This is a useful way to reference a document without importing the text into your existing document.
-
Navigate to the Word file you want to insert into the current Word document and select it.
-
Select Insert. Word will insert the document into the current document.
-
Save the changes to the combined file, if desired.
-
You can repeat the steps to insert additional Word docs into the Word file you are currently working on.
Any changes made to the contents of the inserted document does not affect the original Word document.
How to Insert a Word Document With Headers or Footers Into Word
If the file you want to insert has headers and footers you want to carry over into the new file, add a section break before selecting the insertion point in the new document.
-
Place the cursor on the spot in the document where you want to insert an existing Word file.
-
Select the Layout tab.
-
Select the Breaks drop-down arrow in the Page Setup group.
-
Either select Next Page to add a section break and insert the Word document starting on the next page, or select Continuous to add a section break and insert the Word document starting on the same page.
-
Insert the Word document using the same steps listed above. The header and footer will only be applied to the pages of the newly inserted document.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe
The goal is to get the full path to the document opened in an instance of Microsoft Word that I have a process reference for.
Pseudocode Example:
Process myWordProcess = something; // This is my process reference
DocumentInformation docInfo = SomeNamespace.GetDocumentInformation(myWordProcess);
string documentPath = docInfo.FullName; // "C:UserFooDocumentsTest.docx"
The starting point is a Process object which is executed by WINWORD.exe.
I am not looking for a way that includes parsing process.MainWindowTitle, but rather a more, let’s say, «proper» solution.
Having done a fair bit of initial research, I believe what’s required is the Windows Accessibility API.
Pinvoke mentiones the AccessibleObjectFromWindow signature. That being said, the resulting accessible object does not provide me with much more information than the process already does.
Here’s what I tried from Pinvoke:
internal enum OBJID : uint
{
WINDOW = 0x00000000,
SYSMENU = 0xFFFFFFFF,
TITLEBAR = 0xFFFFFFFE,
MENU = 0xFFFFFFFD,
CLIENT = 0xFFFFFFFC,
VSCROLL = 0xFFFFFFFB,
HSCROLL = 0xFFFFFFFA,
SIZEGRIP = 0xFFFFFFF9,
CARET = 0xFFFFFFF8,
CURSOR = 0xFFFFFFF7,
ALERT = 0xFFFFFFF6,
SOUND = 0xFFFFFFF5,
}
public class DocumentLocator
{
[DllImport("oleacc.dll")]
internal static extern int AccessibleObjectFromWindow(IntPtr hwnd, uint id, ref Guid iid, [In] [Out] [MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.IUnknown)] ref object ppvObject);
public static void GetWordInfo(Process process)
{
var mainWindowHandle = process.MainWindowHandle;
var guid = new Guid("{618736E0-3C3D-11CF-810C-00AA00389B71}");
object obj = null;
var retVal = AccessibleObjectFromWindow(mainWindowHandle, (uint)OBJID.WINDOW, ref guid, ref obj);
var accessible = (IAccessible) obj; // Not much information is contained in this object
}
}
Perhaps the solution is to somehow get a Document interface (Office COM Interop, see here for the interface) from the process or window handle? Or, perhaps, first getting a Window and then the Document?
Then, equipped with that information from Office Interop, one could read the Path property.
I am open to any solutions for this.
If you know how to perform this regarding Excel or PowerPoint — then that would be fine, too, as I assume the same process can be applied for Word (after changing a couple of interfaces and GUIDs).
Welcome to our guide to the menus in Microsoft Word.
We cover all of the menus individually, with explanations of what the various commands do. We include the File, Edit, View, Insert, Format, Tools and Table menus.
Note: These menus disappeared in Word versions 2007 and 2010.
The File Menu
The file menu is one you will find yourself using extensively. It is used to create new documents, open existing documents and saving your new/updated documents. It also includes the page setup, print preview, and other important functions relating to your document and its properties.
New: This creates a new Microsoft Word document. The page setup of the new document, ie, the size, margins, etc, will depend on your page settings.
Open: This opens an existing Microsoft Word document, it will open a file explorer window allowing you to navigate to the file you want to open.
Close: This will close the current word document. Microsoft Word may prompt you to save the file, if you have made changes to the document since the last save.
Save: Saves the current document, replacing the existing file (if previously saved).
Save As: This allows you to save the document as a different file. This is very useful, imagine you open your letterhead template and write a letter that you want to save, if you just saved it (using the option above), it would replace your letterhead template. When you click on Save As you will be able to choose the new filename and location for your document.
Save As Web Page: This option will save the current document with the HTM(L) extension, allowing it to be viewed by a web browser.
Search: Clicking Search will open the basic search window, allowing you to search your computer for documents containing certain text.
Versions: This feature allows you to save different versions of the current Microsoft Word document. For example, if you changed your letterhead and wanted to keep the older version too.
Web Page Preview: Clicking on this option will display your current document as it would look in a web browser. When you click, Microsoft Word will open the document in your default web browser.
Page Setup: This opens the page setup options dialogue box. It allows you to set the properties (dimensions, margins, etc) of the current document and change the default for new Microsoft Word documents.
Print Preview: Selecting this option opens the print preview window, allowing you to preview how your document will look when printed.
Print: Opens the print dialogue box allowing you to print the current document.
Send To: Hovering your mouse over this option will allow you to send your document via email, or export it to Microsoft Powerpoint (if installed).
Properties: This will open the Microsoft Word document properties dialogue box, allowing you to view/edit various properties of the document. Including author information, statistics, type, location and filesize of the document.
The A symbol in fig 1.1 above shows where a list of recently opened documents are listed. This is a very handy feature of Microsoft Word, it saves using the normal opening procedure.
Exit: Clicking this will exit Microsoft Word, it may prompt you to save any unsaved documents.
The Edit Menu
The edit menu, as its name suggests, includes commands relating to the editing of your document. It includes important editing features such as undo, repeat, cut, copy, paste, select all, find, replace and more.
Undo (last task): This option allows you to undo the last thing you did in your Microsoft Word document, in our example (fig 1.1) you can see our last action was to type some text. This is a handy command, especially if you delete something by accident.
Repeat (last task): This repeats your last action. In our example clicking on the Repeat Typing will repeatedly insert the same piece of text into the document.
Cut: This command will cut (delete) the currently selected element. For example if you highlight (select) some text and then click on cut, it will be deleted.
Copy: The Copy command will copy the curently selected element (text, image, etc) into the office clipboard. It can then be inserted (pasted) into a document using the Paste command (see below), which will appear in the edit menu once you have copied something to the office clipboard.
Office Clipboard: This command will display the current contents of the office clipboard, allowing you to click on the stored elements to insert (paste) them directly into the current document. Elements (text, images, etc) can be added to the clipboard using the Copy command (see above), this clipboard will also show any elements stored in the Windows Clipboard.
Paste: This will paste (insert) into the current document the last element to be stored in the Office Clipboard.
Paste Special: Clicking on this command will bring up the Microsoft Word Paste Special dialogue box, it allows you to control the format of the text that will be inserted (pasted) from the Office/Windows clipboard.
Paste as Hyperlink: This command allows you to link (create a hyperlink) to a certain place in another Microsoft Word document, Excel worksheet, PowerPoint slide, or Access database. To achieve this, first copy the element that you want to link to into the clipboard, and then select the Paste as Hyperlink command.
note: The target file must have been saved previously, likewise if you are linking to an element in the current document, it must be saved first.
Clear: This command allows you to remove any formatting from the currently selected (highlighted) element (text/image). It also allows you to delete the selected element.
Select All: This will select (highlight) every element in the current document.
Find: Find allows you to search the current document for a certain word or phrase.
Replace: Replace allows you to replace a given text with a substitute of your choice.
Goto: Goto allows you to go directly to a certain page, section, line, bookmark, comment, footnote, endnote, field, table, graphic, equation, object, or heading.
Links: This allows you to manage any linked objects in the current document. A linked object is information (data) that is stored in another file, for example a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet, Microsoft Access database, or other compatible source. We will be covering linked objects in a future Microsoft Word tutorial.
Objects: This command allows you to manage any embedded objects within the current document.
The View Menu
This menu is used to control not only the visual layout of your Word document but also the printing configuration. It is also used to select which toolbars are visible in the Word environment. Commands include web layout, print layout, outline, task pane, toolbars, ruler, header and footer, footnotes, full screen view and zoom.
Normal: Selecting this will show your current document in a layout without the document margins.
Web Layout: The Web Layout view will show you how the current document will look on a web browser, a full-screen layout.
Print Layout: This view will show the document in a layout including all margins and page breaks.
Outline: The Outline view allows you to change the structure of your document, when selected it will open the Outline Toolbar. The Outline Toolbar allows you to, amongst other things, move headings up or down and/or change the heading types.
Task Pane: This command toggles (shows/hides) the Task Pane. The task pane is designed to give you quick access to frequently used commands, including Document Commands, The Office Clipboard, Basic Search, Style and Formatting and more.
Toolbars: When you hover your mouse pointer over Toolbars you will be presented with a submenu, this includes all of the different toolbars that are available. You can toggle (hide/show) the different toolbars by simply clicking on them within the submenu.
Ruler: Clicking on this will toggle (hide/show) the document ruler which appears across the top and down the side of the Microsoft Word document.
Document Map: The document map is a handy feature which allows you to navigate the current document, it will list the headings (heading 1, heading 2, etc) in the current document. To go directly to a certain paragraph heading, simply click on it in the left hand pane that opens.
Header and Footer: This allows you to edit the header and footer of the current document. We show you how to edit the header and footer in our letterhead tutorial here.
Footnotes: This command will show all footnotes and endnotes (you will be promoted for which) within the current document. Footnotes and Endnotes will be covered in a future Microsoft Word tutorial.
Markup: This will toggle (hide/show) any Markup (comments and tracked alterations/additions) in the current document.
Full Screen: This will show the current Microsoft Word document in full screen mode.
Zoom: This will open the zoom dialogue box, enabling you to change the percentage of zoom for the current view.
The Insert Menu
The insert menu is used to place various objects into your document, such as page numbers, pictures, symbols, comments and other objects. Commands include break, date and time, field, symbol, reference, web component, text box, file and hyperlink.
Break: This command opens the Break dialogue box, allowing you to insert page breaks and section breaks into the current document.
Page Numbers: Clicking on Page Numbers will open a dialogue box, which allows you to insert page numbers into the document using various options.
Date and Time: This command will open the Date and Time dialogue box. You can choose from many different date and time formats, you may also have different languages to choose from.
Autotext: Choosing this option will open the Microsoft Word Autotext dialogue box. We will cover Autotext in a future tutorial.
Field: This command allows you to enter specified fields into your document. The available fields include Date & Time, Document Automation, Document Information, Equations and Formulas, Index and Tables, Links and References, Mail Merge, Numbering and User Information.
Symbol: This allows you to insert symbols and special characters into your document. For example, if you wanted to include a copyright symbol or a trademark symbol, then you would use this feature. Other symbols (special characters) include currency symbols, mathematical symbols and foreign language alphabet characters.
Comment: This command will place a comment into the document at the location of the cursor. You will be able to type your comment into the comment box, once done, simply click anywhere outside of the comment box.
Reference: The Reference command will allow you to insert a footnote, caption, cross-reference, index, and tables.
Web Component: This command is used to insert any web components into your Microsoft Word document.
Picture: Allows you to insert a picture into your document. You will be offered various locations to locate the image, including clip art, the file system on your computer, and a digital camera or scanner.
Diagram: The Diagram command will open the diagram gallery dialogue box. You can choose from a selection of diagrams to insert into your document, including an organization chart, cycle diagram, radial diagram, pyramid diagram, venn diagram and a target diagram. You may have less or more diagrams available to insert, depending on your Microsoft Word installation.
Text Box: This allows you to insert text boxes, we will be covering text boxes in a future tutorial.
File: Enables you to insert part or all of a file into the current document.
Object: This command will insert an object of your choice, including media clips, Microsoft Excel charts and worksheets, Microsoft Powerpoint slides and presentations.
Bookmark: This handy feature allows you to bookmark a certain element (text, image, etc). You can name the bookmark and then return to it at any time by using the goto command in the edit menu.
Hyperlink: The Insert Hyperlink dialogue box allows you to add a hyperlink to an existing file, web page, certain place in the current document, a new document, or an email address.
The Format Menu
A guide to the format menu which controls your font’s properties along with the borders and shading options. Commands include paragraph, bullets and numbering, columns, tabs, text direction, background, autoformat, reveal formatting and more.
Font: This will change the font attributes of either the currently selected text, or any subsequent text, using the font dialogue box.
Paragraph: This command will open the Paragraph dialogue box, allowing you to make changes to either existing text or subsequent text. To change an existing paragraph, select the text you wish to change and then use this command to make the alterations, such as alignment, indentation, and spacing.
Bullets and Numbering: This is a handy command, it creates indented lists with various formats. You can either click the command and then start typing your list (pressing enter for the next line), or you can select some existing text to convert to a list. The listing format options include bulleted, numbered, outline numbered, and other styles.
Borders and Shading: This command allows you to create borders and shading on elements within your Microsoft Word document. The borders and shading can be applied to text, paragraphs, pictures, and more.
Columns: The Columns command will split the current document into the number of columns you specify. You can either split the whole page, or just from that point onwards.
Tabs: This command allows you to manage tabs, including the alignment, spacing, and whether the tab has a leader or not.
Drop Cap: A drop cap is a letter at the start of a paragraph of text that spans 2 or more rows of text, you will often see a drop cap in a book at the start of a chapter. This tool allows you to either add a drop cap character to your document or change an existing letter (at the start of a sentence) to a drop cap.
Text Direction: This allows you to change the text direction of a text object, for example a text box.
Change Case: The Change case tool allows you to alter the case of existing text. Options include sentence case, lowercase, uppercase, title case, and toggle case.
Background: This changes the background colour (color) of your Microsoft Word document. It also allows you to add watermarks and use different gradient effects.
Theme: The themes command will open the theme dialogue box, allowing you to change the theme of your document, including heading style, hyperlinks and background colour (color).
Frames: This command opens the Frames dialogue box.
AutoFormat: The AutoFormat feature will format a whole document with preset attributes.
Styles and Formatting: This will open the Styles and Formatting toolbar, allowing you create headings, lists and more.
Reveal Formatting: Clicking on this will show a dialogue box detailing the format attributes of the selected element.
Object: Allows you to make changes to any existing objects within the current document.
The Tools Menu
The tools menu will also be one you may use regularly, it includes the options command which controls spelling and grammar, security and more. Commands include language, word count, speech, letters and mailing, macro, customize and more.
Spelling and Grammar: This command will check the spelling and grammar of the current Microsoft Word document. It also allows you to add words to the dictionary, as well as changing the dictionary language (if available).
Language: The language tool has various options, including setting the language of the document, translating text, open the thesaurus and manage hyphenation.
Word Count: This will open the Word Count dialogue box, enabling you to count the amount of words in the whole document, or the currently selected text.
AutoSummarize: This can be a handy feature of Microsoft Word, depending on the type and format of your document. It will summarize a document using the attributes you give it, for example, you can choose the percentage of the document to be used for the summary, as well as the format of the summary.
Speech: This will open the Speech Recognition feature of Microsoft Word (if installed/available).
Track Changes: Clicking on this command will cause Microsoft Word to track any subsequent changes to the document. These changes can then be viewed by turning on the Markup option on the Edit menu.
Compare and Merge Documents: This feature enables you to easily compare and/or merge 2 documents.
Protect Document: This command allows you to control the protection of the document, including tracked changes, comments and forms.
Online Collaboration: Enables NetMeeting allowing you to communicate with others in real time via the internet or local network.
Letters and Mailing: Gives you access to various features, including the Mail Merge Wizard, the Letter Wizard, the Envelopes and Labels tool, and the Mail Merge Toolbar.
Macro: This opens the Macro Dialogue box, allowing you to manage subsequent and existing macros. We will be covering Microsoft Word macros in a future tutorial.
Templates and Add-Ins: Opens the Templates and Add-Ins Dialogue box, allowing you to add, remove or update styles and template.
AutoCorrect Options: Opens the AutoCorrect dialogue box, enabling you to manage capitalisation, and also the replace text as you type settings.
Customize: Allows you to customize the Microsoft Word toolbars, commands, and other options.
Options: This opens the main options dialogue box in Microsoft Word. It allows you to change many aspects of the current document and Microsoft Word environment.
The Table Menu
Tables are a great way of laying out content within your document. The table menu provides all you need to manage your tables and cells. Includes draw table, insert, delete, merge cells, split cells, split table, autoformat, convert, sort and more.
Draw Table: This command opens the Tables and Borders dialogue box with the draw table tool active. First you draw the outline of your table, then using the same tool, you can create cells by vertical or horizontal movements within the table.
Insert: Allows you to insert a whole table or just columns, rows and cells into the current document.
Delete: Delete complete tables, columns, rows and selected cells.
Select: This command allows you to select the current table, column, row or cell.
Merge Cells: This tool will merge the currently selected cells into one.
Split Cells: This will split the selected cell/s into your chosen amount of columns and rows, it will also offer (if more than one cell selected) to merge the selected cells before the split.
Split Table: This command will split the current table, making the split at the currently selected cells.
Table AutoFormat: This command will open the Microsoft Word Table AutoFormat dialogue box, where you can choose from a number of different table templates, including preset fonts and cell background colours (colors).
AutoFit: This tools gives you several options for resizing the selected table in relation with the contents or window. It also allows you to automate the distribution between columns and rows.
Heading Rows Repeat: This handy tool will repeat the currently selected row at the top of every page for the length of the table.
Convert: This command will convert existing text into a table format. The text will have to have a common separator to indicate the different columns, it will also needs new paragraphs where you would like each row.
Sort: This opens the Sort Table dialogue box. You can choose which column you would like to sort and by what order.
Formula: This tool allows you to apply a formula to the selected cell. For example, if you wanted to add up the contents of several rows in a specific column, you could use the SUM formula in the Formla dialogue box.
Hide Gridlines: This simply hides the gridlines of the selected table.
Table Properties: This will display the various properties of the selected table.

 .
. 
 to view two pages, or screens, at a time.
to view two pages, or screens, at a time.