I feel silly for not being able to figure this out, but how do I turn off wordwrap? the css word-wrap property can be forced on with break-word, but cannot be forced off (only can be left alone with normal value).
How do I force word wrap off?
Jon
425k79 gold badges733 silver badges803 bronze badges
asked Jan 10, 2011 at 23:19
Alexander BirdAlexander Bird
38k42 gold badges124 silver badges159 bronze badges
2
You need to use the CSS white-space attribute.
In particular, white-space: nowrap and white-space: pre are the most commonly used values. The first one seems to be what you ‘re after.
answered Jan 10, 2011 at 23:21
0
Added webkit specific values missing from above
white-space: -moz-pre-wrap; /* Firefox */
white-space: -o-pre-wrap; /* Opera */
white-space: pre-wrap; /* Chrome */
word-wrap: break-word; /* IE */
answered Jul 7, 2015 at 15:07
I wonder why you find as solution the «white-space» with «nowrap» or «pre», it is not doing the correct behaviour: you force your text in a single line!
The text should break lines, but not break words as default. This is caused by some css attributes: word-wrap, overflow-wrap, word-break, and hyphens. So you can have either:
word-break: break-all;
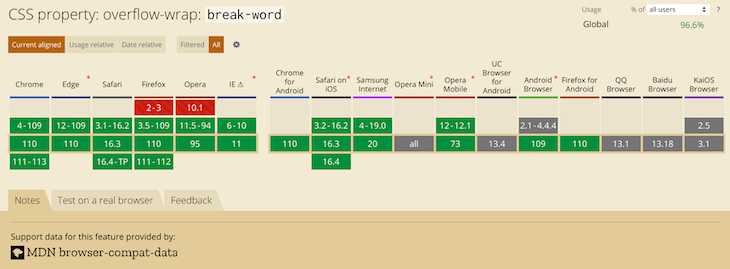
word-wrap: break-word;
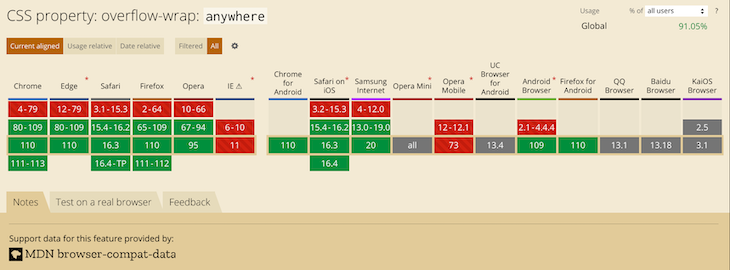
overflow-wrap: break-word;
-webkit-hyphens: auto;
-moz-hyphens: auto;
-ms-hyphens: auto;
hyphens: auto;
So the solution is remove them, or override them with «unset» or «normal»:
word-break: unset;
word-wrap: unset;
overflow-wrap: unset;
-webkit-hyphens: unset;
-moz-hyphens: unset;
-ms-hyphens: unset;
hyphens: unset;
UPDATE: i provide also proof with JSfiddle: https://jsfiddle.net/azozp8rr/
answered May 12, 2018 at 9:55
zodzod
3773 silver badges4 bronze badges
2
white-space: nowrap;: Will never break text, will keep other defaults
white-space: pre;: Will never break text, will keep multiple spaces after one another as multiple spaces, will break if explicitly written to break(pressing enter in html etc)
answered Nov 13, 2020 at 20:28
1
This worked for me to stop silly work breaks from happening within Chrome textareas
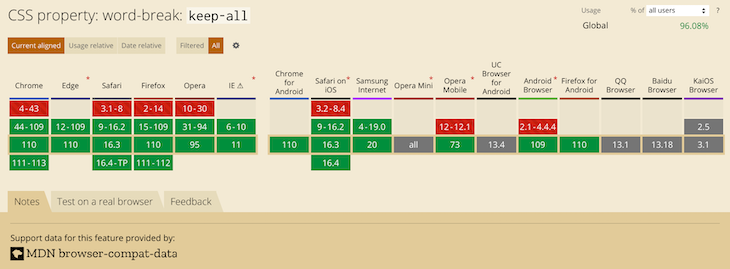
word-break: keep-all;
answered Oct 2, 2019 at 21:54
If you want a HTML only solution, we can just use the pre tag. It defines «preformatted text» which means that it does not format word-wrapping. Here is a quick example to explain:
div {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
padding: 20px;
background: #adf;
}
pre {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
padding: 20px;
font: inherit;
background: #fda;
}<div>Look at this, this text is very neat, isn't it? But it's not quite what we want, though, is it? This text shouldn't be here! It should be all the way over there! What can we do?</div>
<pre>The pre tag has come to the rescue! Yay! However, we apologise in advance for any horizontal scrollbars that may be caused. If you need support, please raise a support ticket.</pre>answered Nov 4, 2020 at 19:41
corn on the cobcorn on the cob
1,8043 gold badges19 silver badges26 bronze badges
Свойство white-space управляет тем, как обрабатываются пробельные символы внутри элемента.
Интерактивный пример
Сводка
/* Ключевые значения */
white-space: normal;
white-space: nowrap;
white-space: pre;
white-space: pre-wrap;
white-space: pre-line;
white-space: break-spaces;
/* Глобальные значения */
white-space: inherit;
white-space: initial;
white-space: unset;
| Начальное значение | normal |
|---|---|
| Применяется к | все элементы |
| Наследуется | да |
| Обработка значения | как указано |
| Animation type | discrete |
Синтаксис
Свойство white-space определяется, как одно ключевое слово, выбранное из списка значений, указанных ниже.
Значения
normal-
Последовательности пробелов объединяются в один пробел. Символы новой строки в источнике обрабатываются, как отдельный пробел. Применение данного значения при необходимости разбивает строки для того, чтобы заполнить строчные боксы.
nowrap-
Объединяет последовательности пробелов в один пробел, как значение
normal, но не переносит строки (оборачивание текста) внутри текста. pre-
Последовательности пробелов сохраняются так, как они указаны в источнике. Строки переносятся только там, где в источнике указаны символы новой строки и там, где в источнике указаны элементы
<br>. pre-wrap-
Последовательности пробелов сохраняются так, как они указаны в источнике. Строки переносятся только там, где в источнике указаны символы новой строки и там, где в источнике указаны элементы
<br>, и при необходимости для заполнения строчных боксов. pre-line-
Последовательности пробелов объединяются в один пробел. Строки разбиваются по символам новой строки, по элементам
<br>, и при необходимости для заполнения строчных боксов.. break-spaces-
Поведение идентично
pre-wrapсо следующими отличиями:- Последовательности пробелов сохраняются так, как они указаны в источнике, включая пробелы на концах строк.
- Строки переносятся по любым пробелам, в том числе в середине последовательности пробелов.
- Пробелы занимают место и не висят на концах строк, а значит влияют на внутренние размеры (min-content и max-content).
В приведённой ниже таблице указано поведение различных значений свойства white-space:
| Новые строки | Пробелы и табуляция | Перенос текста по словам | Пробелы в конце строки | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
normal |
Объединяются в одну | Объединяются в один пробел | Переносится | Удаляются |
nowrap |
Объединяются в одну | Объединяются в один пробел | Не переносится | Удаляются |
pre |
Сохраняются как в источнике | Сохраняются как в источнике | Не переносится | Сохраняются как в источнике |
pre-wrap |
Сохраняются как в источнике | Сохраняются как в источнике | Переносится | Висят |
pre-line |
Сохраняются как в источнике | Объединяются в один пробел | Переносится | Удаляются |
break-spaces |
Сохраняются как в источнике | Сохраняются как в источнике | Переносится | Переносятся |
Формальный синтаксис
white-space =
normal | (en-US)
pre | (en-US)
nowrap | (en-US)
pre-wrap | (en-US)
break-spaces | (en-US)
pre-line
Примеры
Основной пример
code {
white-space: pre;
}
Перенос строк внутри элементов <pre>
pre {
word-wrap: break-word; /* IE 5.5-7 */
white-space: pre-wrap; /* текущие браузеры */
}
Спецификации
| Specification |
|---|
| CSS Text Module Level 3 # white-space-property |
Браузерная совместимость
BCD tables only load in the browser
Труднопереносимыми бывают не только люди, но и слова. К примеру, химическое соединение метилпропенилендигидроксициннаменилакрилическая кислота очень похожа на некоторых людей с «подвывертом»! Не знаем, как справляться с такими трудными личностями, но реализовать перенос текста CSS точно поможет.
- Зачем переносить «непереносимое»
- Решаем проблему переноса слов с помощью HTML
- Как реализовать CSS перенос слов
- Как реализовать запрет переноса слов CSS
В большинстве случаев при отображении текстового содержимого веб-страниц в браузере перенос слов не применяется. Если слово не вмещается целиком в область экрана, то по умолчанию оно полностью «переезжает» на следующую строчку.
Частичный перенос применяется лишь к длинным и сложным словам, состоящим из нескольких терминов и разделенных дефисом. Вот тут и возникают проблемы отображения этих слов на разных по диагонали экранах и в разных браузерах. При этом точно предугадать, как длинное слово будет «выглядеть» на клиентской стороне трудно, поэтому задавать переносы «вручную» бессмысленно:
Перед тем, как рассмотреть CSS перенос слов , изучим возможности решения этой проблемы с помощью языка гипертекста.
Для этого в HTML имеется несколько вариантов:
- Использование символа мягкого разрыва — позволяет задать место разрыва сложного слова. При изменении размеров окна браузера на следующую строку переносится только часть длинного слова, стоящая после ­, а после первой половины выводится знак переноса, похожий на дефис:
<body> <p>Пример сложного химического соединения и текста - метилпропенилендигидрок­сициннаменилакрилическая кислота</p> </body>
- Использование тега — элемент появился в HTML 5. Он также служит для указания браузеру места для разрыва сложного или длинного слова. Но в отличие от предыдущего спецсимвола этот тег не выводит в месте «разлома» знак переноса, что может негативно сказаться на читаемости всего текста:
<style>
wbr { display: inline-block; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>метилпропенилен<wbr>дигидроксицинна<wbr>менилакрилическая кислота</p>
</body>
В некоторых браузерах поддержка тега <wbr> реализована некорректно. В них он будет работать, если для него в коде CSS прописано свойство display со значением inline-block.
Перед тем, как реализовать CSS перенос слов, давайте рассмотрим несколько свойств, способных разрешить основную проблему:
- word-wrap – описывает, как производить перенос слов, которые по длине не помещаются в установленные размеры контейнера. Сразу стоит предупредить, что с валидацией этого свойства возникают проблемы, и с реализацией его поддержки в CSS консорциум W3C еще не определился. Поэтому специализированные валидаторы при наличии word-wrap в коде будут выдавать ошибку:
Тем не менее, это свойство «воспринимается» всеми современными браузерами и является эффективным решением проблемы переноса длинных слов. word-wrap принимает следующие значения:
- normal – слова не переносятся;
- break-word – автоматический перенос слов;
- inherit – наследование значения родителя.
Пример, иллюстрирующий применение этого свойства:
<style>
.container{
background-color: rgb(204,204,204);
padding:10px;
width:200px;
}
.content{
word-wrap: break-word;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<p class="content">метилпропенилендигидроксициннаменилакрилическая кислота</p>
</div>
</body>
В новой спецификации CSS свойство word-wrap было переименовано в overflow-wrap. Оба свойства принимают одинаковые значения. Но поддержка overflow-wrap пока реализована слабо, поэтому лучше использовать старую версию свойства:
Как видно на расположенном выше скриншоте, новое свойство поддерживается Google Chrome, но не поддерживается в IE. Поэтому overflow-wrap лучше не использовать того чтобы реализовать CSS перенос слов.
- word-break – устанавливает правила переноса строк внутри контейнера, если они не помещаются в него по ширине. Это новое свойство, и его поддержка была реализована в CSS3. Оно является валидным, но предназначено для работы со строками, поэтому перенос слов может производиться грамматически неправильно.
Свойство принимает три значения:
- normal – используются правила переноса, установленные по умолчанию;
- word-break – перенос строк осуществляется автоматически, чтобы слово поместилось в установленные по ширине размеры контейнера;
- keep-all – отключает автоматический перенос слов в китайском, японском и корейском. Для остальных языков действие значения аналогично normal.
Пример:
<style>
.content {
font-size: 30px;
background: rgb(51,204,153);
width: 170px;
padding: 10px;
word-break:break-all;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="content">
<p>Синхрофазотрон</p>
<p>Обеспокоенное состояние</p>
<p>Одиннадцатиклассница</p>
<p>метоксихлордиэтиламинометилбутиламин</p>
</div>
</body>
hyphens – новое свойство, которое появилось с выходом CSS3. Оно устанавливает, как браузер будет осуществлять перенос слов в выводимом тексте. Свойство принимает несколько значений:
- none – отключает CSS перенос слов;
- manual (значение по умолчанию) – слова переносятся в тех участках текстового блока, где это задано с помощью тега <wbr> или мягкого переноса ();
- auto – браузер автоматически переносит слова на основе своих настроек.
Для корректной работы свойства в теге <html> или <p> должен присутствовать атрибут lang со значением «ru» (lang=»ru»).
Свойство поддерживается последними версиями IE, Opera и Firefox. Для каждого из них прописывается своя строчка CSS. Hyphens не поддерживается Google Chrome. Пример:
<style>
.container{
background-color: rgb(153,255,204);
padding:10px;
width:200px;
}
.content{
-webkit-hyphens: auto;
-moz-hyphens: auto;
-ms-hyphens: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<p class="content" lang="ru">метилпропенилендигидроксициннаменилакрилическая кислота</p>
</div>
</body>
Иногда нужно сделать так, чтобы строка отображалась полностью без разрыва. Запрет использовать CSS перенос слов можно реализовать несколькими способами:
- С помощью неразрывного пробела  , который устанавливается в местах переноса строки или слов;
- Задав свойству white-space значение «nowrap» (white-space: nowrap).
Пример реализации:
<style>
.container{
background-color: rgb(153,255,204);
padding:10px;
width:200px;
}
.content{
-webkit-hyphens: auto;
-moz-hyphens: auto;
-ms-hyphens: auto;
}
.nowrap
{
white-space: nowrap;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<p>метилпропенилендигидроксициннаменилакрилическая кислота раз</p>
<p class="content" lang="ru">метилпропенилендигидроксициннаменилакрилическая два</p>
<p class="nowrap">метилпропенилендигидроксициннаменилакрилическая кислота три</p>
<p>метилпропенилендигидроксициннаменилакрилическая кислота четыри</p>
</div>
</body>
Теперь вы сможете переносить с помощью CSS даже самые длинные слова. Но вот с проблемой труднопереносимых людей вам придется разбираться самостоятельно. Попробуйте воздействовать на них методами CSS – может и получиться, хотя мы сами не проверяли.
1. Introduction
This module describes the typesetting controls of CSS;
that is, the features of CSS that control the translation of
source text to formatted, line-wrapped text.
Various CSS properties provide control over case transformation, white space collapsing, text wrapping, line breaking rules and hyphenation, alignment and justification, spacing,
and indentation.
See Additions Since Level 3 for additions since Level 3.
Further information about the typesetting requirements
of various languages and writing systems around the world
can be found in the Internationalization Working Group’s Language Enablement Index. [TYPOGRAPHY]
1.1. Module Interactions
This module, together with the CSS Text Decoration Module,
replaces and extends the text-level features defined in Cascading Style Sheets Level 2 chapter 16. [CSS-TEXT-DECOR-3] [CSS2]
In addition to the terms defined below,
other terminology and concepts used in this specification are defined
in Cascading Style Sheets Level 2 and the CSS Writing Modes Module. [CSS2] and [CSS-WRITING-MODES-4].
1.2. Value Definitions
This specification follows the CSS property definition conventions from [CSS2] using the value definition syntax from [CSS-VALUES-3].
Value types not defined in this specification are defined in CSS Values & Units [CSS-VALUES-3].
Combination with other CSS modules may expand the definitions of these value types.
In addition to the property-specific values listed in their definitions,
all properties defined in this specification
also accept the CSS-wide keywords as their property value.
For readability they have not been repeated explicitly.
1.3. Languages and Typesetting
Authors should accurately language-tag their content
for the best typographic behavior.
Many typographic effects vary by linguistic context.
Language and writing system conventions can affect
line breaking, hyphenation, justification, glyph selection,
and many other typographic effects. In CSS, language-specific typographic tailorings
are only applied when the content language is known (declared). Therefore,
higher quality typography requires authors to communicate to the UA
the correct linguistic context of the text in the document.
The content language of an element is the (human) language
the element is declared to be in, according to the rules of the document language.
Note that it is possible for the content language of an element
to be unknown—e.g. untagged content,
or content in a document language that does not have a language-tagging facility,
is considered to have an unknown content language.
Note: Authors can declare the content language using the global lang attribute in HTML
or the universal xml:lang attribute in XML.
See the rules for determining the content language of an HTML element in HTML,
and the rules for determining the content language of an XML element in XML 1.0. [HTML] [XML10]
The content language an element is declared to be in
also identifies the specific written form of that language used in that element,
known as the content writing system.
Depending on the document language’s facilities for identifying the content language,
this information can be explicit or implied.
See the normative Appendix F:
Identifying the Content Writing System.
Note: Some languages have more than one writing system tradition;
in other cases a language can be transliterated into a foreign writing system.
Authors should subtag such cases
so that the UA can adapt appropriately.
For example, Korean (ko) can be written in
Hangul (-Hang),
Hanja (-Hani),
or a combination (-Kore).
Historical documents written solely in Hanja
do not use word spaces and
are formatted more like modern Chinese than modern Korean.
In other words, for typographic purposes ko-Hani behaves more like zh-Hant than ko (ko-Kore).
As another example Japanese (ja) is typically written
in a combination (-Japn) of Hiragana (-Hira),
Katakana (-Kana), and Kanji (-Hani).
However, it can also be ”romanized” into Latin (-Latn)
for special purposes like language-learning textbooks,
in which case it should be formatted more like English than Japanese.
As a third example contemporary Mongolian is written in two scripts:
Cyrillic (-Cyrl, officially used in Mongolia)
and Mongolian (-Mong, more common in Inner Mongolia, part of China).
These have very different formatting requirements,
with Cyrillic behaving similar to Latin and Greek,
and Mongolian deriving from both Arabic and Chinese writing conventions.
1.4. Characters and Letters
The basic unit of typesetting is the character.
However, because writing systems are not always as simple as the basic English alphabet,
what a character actually is depends on the context in which the term is used.
For example, in Hangul (the Korean writing system),
each square representation of a syllable
(e.g. 한=Han)
can be considered a character.
However, the square symbol is really composed of multiple letters each representing a phoneme
(e.g. ㅎ=h, ㅏ=a, ㄴ=n)
and these also could each be considered a character.
A basic unit of computer text encoding, for any given encoding,
is also called a character,
and depending on the encoding,
a single encoding character might correspond
to the entire pre-composed syllabic character (e.g. 한),
to the individual phonemic character (e.g. ㅎ),
or to smaller units such as
a base letterform (e.g. ㅇ)
and any combining marks that vary it (e.g. extra strokes that represent aspiration).
In turn, a single encoding character can be represented in the data stream as one or more bytes;
and in programming environments one byte is sometimes also called a character.
Therefore the term character is fairly ambiguous where technical precision is required.
For text layout, we will refer to the typographic character unit as the basic unit of text.
Even within the realm of text layout,
the relevant character unit depends on the operation.
For example, line-breaking and letter-spacing will segment
a sequence of Thai characters that include U+0E33 ำ THAI CHARACTER SARA AM differently;
or the behavior of a conjunct consonant in a script such as Devanagari
may depend on the font in use.
So the typographic character represents a unit of the writing system—such as a Latin alphabetic letter (including its diacritics),
Hangul syllable,
Chinese ideographic character,
Myanmar syllable cluster—that is indivisible with respect to a particular typographic operation
(line-breaking, first-letter effects, tracking, justification, vertical arrangement, etc.).
Unicode Standard Annex #29: Text Segmentation defines a unit called the grapheme cluster which approximates the typographic character. [UAX29] A UA must use the extended grapheme cluster (not legacy grapheme cluster), as defined in UAX29,
as the basis for its typographic character unit.
However, the UA should tailor the definitions
as required by typographic tradition
since the default rules are not always appropriate or ideal—and is expected to tailor them differently
depending on the operation as needed.
Note: The rules for such tailorings are out of scope for CSS.
The following are some examples of typographic character unit tailorings
required by standard typesetting practice:
- In some scripts such as Myanmar or Devanagari,
the typographic character unit for both justification and line-breaking
is an entire syllable,
which can include more than one Unicode grapheme cluster. [UAX29] -
In other scripts such as Thai or Lao,
even though for line-breaking the typographic character matches Unicode’s default grapheme clusters,
for letter-spacing the relevant unit
is less than a Unicode grapheme cluster,
and may require decomposition or other substitutions
before spacing can be inserted. [UAX29]For instance,
to properly letter-space the Thai word คำ (U+0E04 + U+0E33),
the U+0E33 needs to be decomposed into U+0E4D + U+0E32,
and then the extra letter-space inserted before the U+0E32: คํ า.A slightly more complex example is น้ำ (U+0E19 + U+0E49 + U+0E33).
In this case, normal Thai shaping will first decompose the U+0E33 into U+0E4D + U+0E32
and then swap the U+0E4D with the U+0E49, giving U+0E19 + U+0E4D + U+0E49 + U+0E32.
As before the extra letter-space is then inserted before the U+0E32: นํ้ า. - Vertical typesetting can also require tailoring.
For example, when typesetting upright text,
Tibetan tsek and shad marks are kept with the preceding grapheme cluster,
rather than treated as an independent typographic character unit. [CSS-WRITING-MODES-4]
A typographic letter unit (or letter for the purpose of this specification)
is a typographic character unit belonging to one of the Letter or Number general categories.
See Appendix E:
Characters and Properties for how to determine the Unicode properties of a typographic character unit.
The rendering characteristics of a typographic character unit divided
by an element boundary is undefined.
Ideally each component should be rendered
according to the formatting requirements of its respective element’s properties
while maintaining correct shaping and positioning
of the typographic character unit as a whole.
However, depending on the nature of the formatting differences between its parts
and the capabilities of the font technology in use,
this is not always possible.
Therefore such a typographic character unit may be rendered as belonging to either side of the boundary,
or as some approximation of belonging to both.
Authors are forewarned that dividing grapheme clusters or ligatures
by element boundaries may give inconsistent or undesired results.
1.5. Text Processing
CSS is built on Unicode. [UNICODE] UAs that support Unicode must adhere to all normative requirements
of the Unicode Core Standard,
except where explicitly overridden by CSS.
UAs implemented on the basis of a non-Unicode text encoding model are still
expected to fulfill the same text handling requirements
by assuming an appropriate mapping and analogous behavior.
For the purpose of determining adjacency for text processing
(such as white space processing, text transformation, line-breaking, etc.),
and thus in general within this specification,
intervening inline box boundaries and out-of-flow elements
must be ignored.
With respect to text shaping, however, see § 8.7 Shaping Across Element Boundaries.
2. Transforming Text
2.1. Case Transforms: the text-transform property
| Name: | text-transform |
|---|---|
| Value: | none | [capitalize | uppercase | lowercase ] || full-width || full-size-kana |
| Initial: | none |
| Applies to: | text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | specified keyword |
| Canonical order: | n/a |
| Animation type: | discrete |
This property transforms text for styling purposes.
It has no effect on the underlying content,
and must not affect the content of a plain text copy & paste operation.
Authors must not rely on text-transform for semantic purposes;
rather the correct casing and semantics should be encoded
in the source document text and markup.
Values have the following meanings:
- none
- No effects.
- capitalize
- Puts the first typographic letter unit of each word, if lowercase, in titlecase;
other characters are unaffected. - uppercase
- Puts all letters in uppercase.
- lowercase
- Puts all letters in lowercase.
- full-width
- Puts all typographic character units in full-width form.
If a character does not have a corresponding full-width form,
it is left as is.
This value is typically used to typeset Latin letters and digits
as if they were ideographic characters. - full-size-kana
- Converts all small Kana characters to the equivalent full-size Kana.
This value is typically used for ruby annotation text,
where authors may want all small Kana to be drawn as large Kana
to compensate for legibility issues at the small font sizes typically used in ruby.
The following example converts the ASCII characters
used in abbreviations in Japanese text to their full-width variants
so that they lay out and line break like ideographs:
abbr:lang(ja) { text-transform: full-width; }
Note: The purpose of text-transform is
to allow for presentational casing transformations
without affecting the semantics of the document.
Note in particular that text-transform casing operations are lossy,
and can distort the meaning of a text.
While accessibility interfaces may wish to convey
the apparent casing of the rendered text to the user,
the transformed text cannot be relied on to accurately represent
the underlying meaning of the document.
In this example,
the first line of text is capitalized as a visual effect.
section > p:first-of-type::first-line {
text-transform: uppercase;
}
This effect cannot be written into the source document
because the position of the line break depends on layout.
But also, the capitalization is not reflecting a semantic distinction
and is not intended to affect the paragraph’s reading;
therefore it belongs in the presentation layer.
In this example,
the ruby annotations,
which are half the size of the main paragraph text,
are transformed to use regular-size kana
in place of small kana.
rt { font-size: 50%; text-transform: full-size-kana; }
:is(h1, h2, h3, h4) rt { text-transform: none; /* unset for large text*/ }
Note that while this makes such letters easier to see at small type sizes,
the transformation distorts the text:
the reader needs to mentally substitute small kana in the appropriate places—not unlike reading a Latin inscription
where all “U”s look like “V”s.
For example, if text-transform: full-size-kana were applied to the following source,
the annotation would read “じゆう” (jiyū), which means “liberty”,
instead of “じゅう” (jū), which means “ten”,
the correct reading and meaning for the annotated “十”.
<ruby>十<rt>じゅう</ruby>
2.1.1. Mapping Rules
For capitalize, what constitutes a “word“ is UA-dependent; [UAX29] is suggested (but not required)
for determining such word boundaries.
Out-of-flow elements and inline element boundaries
must not introduce a text-transform word boundary
and must be ignored when determining such word boundaries.
Note: Authors cannot depend on capitalize to follow
language-specific titlecasing conventions
(such as skipping articles in English).
The UA must use the full case mappings for Unicode characters,
including any conditional casing rules,
as defined in the Default Case Algorithms section of The Unicode Standard. [UNICODE] If (and only if) the content language of the element is,
according to the rules of the document language,
known,
then any appropriate language-specific rules must be applied as well.
These minimally include,
but are not limited to,
the language-specific rules in Unicode’s SpecialCasing.txt.
For example, in Turkish there are two “i”s,
one with a dot—“İ” and “i”—and one without—“I” and “ı”.
Thus the usual case mappings between “I” and “i”
are replaced with a different set of mappings
to their respective dotless/dotted counterparts,
which do not exist in English.
This mapping must only take effect
if the content language is Turkish
written in its modern Latin-based writing system (or another Turkic language that uses Turkish casing rules);
in other languages,
the usual mapping of “I” and “i” is required.
This rule is thus conditionally defined in Unicode’s SpecialCasing.txt file.
The definition of full-width and half-width forms
can be found in Unicode Standard Annex #11: East Asian Width. [UAX11] The mapping to full-width form is defined
by taking code points with the <wide> or the <narrow> tag
in their Decomposition_Mapping in Unicode Standard Annex #44: Unicode Character Database. [UAX44] For the <narrow> tag,
the mapping is from the code point to the decomposition
(minus <narrow> tag),
and for the <wide> tag,
the mapping is from the decomposition
(minus the <wide> tag)
back to the original code point.
The mappings for small Kana to full-size Kana are defined in Appendix G:
Small Kana Mappings.
2.1.2. Order of Operations
When multiple values are specified
and therefore multiple transformations need to be applied,
they are applied in the following order:
- capitalize, uppercase, and lowercase
- full-width
- full-size-kana
Text transformation happens after § 4.3.1 Phase I: Collapsing and Transformation but before § 4.3.2 Phase II: Trimming and Positioning.
This means that full-width only transforms
spaces (U+0020) to U+3000 IDEOGRAPHIC SPACE within preserved white space.
Note: As defined in Appendix A:
Text Processing Order of Operations,
transforming text affects line-breaking and other formatting operations.
2.2. Word Boundaries
In a number of languages and writing system,
such as Japanese or Thai,
words are not deliminated by spaces (or any other character)
as is the case in English
(See Approaches to line breaking for a discussion the approach various languages take to word separation and line breaking).
However, even if text without spaces is the dominant style in such languages,
there are cases where making word boundaries (or phrase boundaries) visible
through the use of spaces
is desired.
This is a purely stylistic effect,
with no implication on the semantics of the text.
In Japan for instance, this is commonly done in books for people learning the language—young children or foreign students.
People with dyslexia also tend to find this style easier to read.
The mechanism described in this specification builds upon the existing use
of the wbr element
or of U+200B ZERO WIDTH SPACE
(See [UNICODE])
in the document markup as a word (or phrase) delimiter.
Should we have a shorthand
for the following two properties?
2.2.1. Detecting Word Boundaries: the word-boundary-detection property
| Name: | word-boundary-detection |
|---|---|
| Value: | normal | manual | auto(<lang>) |
| Initial: | normal |
| Applies to: | text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | N/A |
| Computed value: | as specified (However, see special provision for unsupported <lang>) |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
| Animation type: | discrete |
The design of this property is still being worked out.
Don’t implement it just yet!
You can ask the editors about status if this is blocking you.
This property allows the author to decide
whether and how
the user agent must analyse the content
to determine where word boundaries are,
and to insert virtual word boundaries accordingly.
A virtual word boundary is similar to the presence
of the ZERO WIDTH SPACE (U+200B) character:
it introduces a soft wrap opportunity and is affected by the word-boundary-expansion property.
However, its presence alone has no effect on text shaping, spacing, or justification.
Inserting virtual word boundaries must have no effect on the underlying content,
and must not affect the content of a plain text copy & paste operation.
- manual
-
Linguistic analysis is not used
in any language or writing system
to determine line wrapping opportunities not indicated by the markup or characters of the element.The user agent must not insert virtual word boundaries.
Typographic character units with class SA in [UAX14] must be treated as if they had class AL
(i.e. assuming word-break: normal and a value of line-break other than anywhere,
there is no soft wrap opportunity between pairs of such characters).Authors using this value for Southeast Asian languages
are expected to manually indicate word boundaries,
for instance usingwbror U+200B.
Otherwise, there will be no soft wrap opportunity and the text may overflow. - normal
-
The user agent must not insert virtual word boundaries,
except within runs of characters belonging to Southeast Asian languages,
where content analysis must be performed
to determine where to insert virtual word boundaries.As with manual, typographic character units with class SA in [UAX14] must be treated as if they had class AL;
however, the user agent must additionally
analyse the content of a run of such characters
and insert virtual word boundaries where appropriate.
Within the constraints set by this specification,
the specific algorithm used is UA-dependent.As various languages can be written in scripts
which use the characters with class SA,
if the content language is known,
the user agent should use this information
to tailor its analysis.In order to avoid unexpected overflow,
if the user agent is unable to perform this analysis
for any subset of the characters with class SA—for example due to lacking a dictionary for certain languages—there must be a soft wrap opportunity between pairs of typographic letter units in that subset.Note: This soft wrap opportunity is not
a virtual word boundary,
and is ignored by word-boundary-expansion.Note: This provision is not triggered merely when
the UA fails to find a word boundary in a particular text run;
the text run may well be a single unbreakable word.
It applies for example
when a text run is composed of Khmer characters (U+1780 to U+17FF)
if the user agent does not know how to determine
word boundaries in Khmer. - auto(<lang>)
-
This value directs the user agent to perform language-specific content analysis
to determine where to insert virtual word boundaries.<lang> must be a valid CSS <ident> or <string>.
It represents an IETF BCP 47 language range
(see [BCP47]).
If the UA does not support word-boundary detection
for all languages represented by the specified range,
that specified value is invalid
(and will cause the declaration to be ignored).Note: Wildcards in the language subtag would imply
support for detecting word boundaries in an undefined and effectively unlimited set of languages.
As this is not possible,
wildcards in the language subtag always result in the declaration
being treated as invalid.Note: Whether a word boundary detection system designed for one language
is suitable for some or all dialects of that language is somewhat subjective,
and this specifications leaves it at the discretion of the user agent.
Even if a detection system is not able to cope with all nuances of a particular dialect,
it may be reasonable to claim support
if the detection correctly recognizes word boundaries most of the time.
However, the user agent would do a disservice to authors and users
if it claimed support for languages
where it fails to detect most word boundaries
or has a high error rate.If the element’s content language,
as represented in BCP 47 syntax [BCP47],
does not match the language range described by the computed value’s <lang> in an extended filtering operation
per [RFC4647] Matching of Language Tags (section 3.3.2)
with both the content language and <lang> then the used value is normal,
and this property has no effect on this element.
Otherwise,
the user agent must insert a virtual word boundary at each detected word boundary
within the text sequence children of this element.
Within the constraints set by this specification,
the specific algorithm used is UA-dependent.Note: This is the same matching logic as the one used for the :lang() selector.
If a user agent has a word-boundary detection system for Cantonese
that is not suitable for the broader set of Chinese languages,
it is expected to accept auto(yue), auto(zh-yue), or auto(zh-HK),
but not auto(zh) or auto(zh-Hant).
However, if the user agent supports a generic word-boundary detection system
that is suitable for Chinese in general,
it is expected to accept the broad auto(zh) characterization,
as well as any more specific ones,
such as auto(zh-yue), auto(zh-Hant-HK), auto(zh-Hans-SG), or auto(zh-hak).
Specifying the language for which the word boundary detection is to be performed
and making unsupported language ranges invalid
is required in order to make this feature meaningfully testable with @supports.
For example, Japanese text normally allows line breaking between letters of a word
(see word-break: normal).
The following code disables that in h1 elements,
and only allows line breaking at autodetected word boundaries instead,
without requiring the author to manually indicate word boundaries in the markup.
However, if word boundary detection is not supported for Japanese,
this change is not applied,
as word-break: keep-all could remove all soft wrap opportunities from the element,
and risk causing overflow.
@supports (word-boundary-detection: auto(ja)) {
h1:lang(ja) {
word-boundary-detection: auto(ja);
word-break: keep-all;
}
}
User agents may activate
language-specific content analysis
in response to user preferences.
User agents with this behavior must do this
by setting the declared value of word-boundary-detection to »word-boundary-detection/auto(<lang>)»
in the User Origin.
User agents that do not support the User Origin may use the User-Agent Origin instead.
Manual analysis of the content can be more reliable than UA heuristics.
For best results, authors who can perform this analysis are encouraged to markup their documents
using wbr or U+200B
to exhaustively indicate word boundaries.
Authors who prepare their content in this manner
should not rely on the initial value, and
should explicitly specify word-boundary-detection: manual on the relevant parts of the content,
in order to override a potential »word-boundary-detection: auto(<lang>)»
in the User Origin or User-Agent Origin.
Virtual word boundary insertion happens before CSS Text 3 § 4.1.1 Phase I: Collapsing and Transformation and before § 2.2.2 Making Word Boundaries Visible: the word-boundary-expansion property.
Later operations
(including CSS Text 3 § 4.1 The White Space Processing Rules, line breaking, and intrinsic sizing)
must take the presence of the virtual word boundary into account. Selectors are not affected.
Inline box boundaries
and out-of-flow elements must be ignored
when determining word boundaries.
If a word boundary is found at the same position as
one or more inline box boundaries,
the virtual word boundary must be inserted
in the outermost element that participates in this inline box boundary.
In the following example,
the red “|” indicates
reasonable positions for a user agent to insert virtual word boundaries:
กรุงเทพ|คือ|สวยงามIf that sentence had contained some inline markup,
the following example shows the correct position to insert the virtual word boundaries:
กรุงเทพ|คือ|<em>สวยงาม</em>The following example shows incorrect positions:
กรุงเทพ|คือ<em>|สวยงาม</em>The following shows the correct positions in a more contrived situation:
กรุงเทพ|<b><u>คือ</u>|<em>สวยงาม</em></b>The user agent may tailor its word boundary detection algorithm
depending on whether line-break is loose/normal/strict.
The user agent must not insert a virtual word boundary:
- at the beginning or end of any box
(including inline boxes)
whose parent box has a used value of manual. -
immediately adjacent to a word-separator character,
or an other space separator,
or a ZERO WIDTH SPACE (U+200B) character.Note: This implies that for languages such as English
where words are separated by spaces or other separating characters, auto() has no effect. - between characters that compose a single typographic character unit.
- between a typographic letter unit and a subsequent typographic character unit from the [UAX14] CL, CP, IS, or EX line break classes,
- between a typographic letter unit and a preceding typographic character unit from the [UAX14] OP line break class,
- between a typographic letter unit and an adjacent typographic character unit from the [UAX14] GL, WJ, or ZWJ line break classes.
The user agent should not insert a virtual word boundary:
- between a typographic letter unit and a subsequent typographic character unit from the [UAX14] PO, NS line break classes,
- between a typographic letter unit and a preceding typographic character unit from the [UAX14] PR line break class,
2.2.2. Making Word Boundaries Visible: the word-boundary-expansion property
| Name: | word-boundary-expansion |
|---|---|
| Value: | none | space | ideographic-space |
| Initial: | none |
| Applies to: | text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | N/A |
| Computed value: | as specified |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
| Animation type: | discrete |
The design of this property is still being worked out.
Don’t implement it just yet!
You can ask the editors about status if this is blocking you.
This name is quite long, we may want to find a better one.
We should also consider how we may want to add values to this property,
so that the name is compatible with them.
For example,
it has been suggested that we may want to use this
to turn visible “spaces” such as the ETHIOPIC WORD SPACE (U+1361)
into an ordinary SPACE (U+0020).
This property allows transforming certain word-separating characters
into other word-separating characters,
to accommodate variant typesetting styles.
- none
- This property has no effect.
- space
- Instances of U+200B ZERO WIDTH SPACE
within the child text of this element
are replaced by U+0020 SPACE. - ideographic-space
- Instances of U+200B ZERO WIDTH SPACE
within the child text of this element
are replaced by U+3000 IDEOGRAPHIC SPACE.
The user agent must not replace
instances of U+200B immediately preceding or following
a forced line break (ignoring any intervening inline box boundaries,
and associated margin/border/padding).
Instances of wbr are considered equivalent to U+200B,
and are also replaced,
as are virtual word boundaries inserted by word-boundary-detection.
Unlike text-transform,
this substitution happens before CSS Text 3 § 4.1.1 Phase I: Collapsing and Transformation so that later operations that depend on the characters in the content
(including CSS Text 3 § 4.1 The White Space Processing Rules, line breaking, and intrinsic sizing)
use that character instead of the original U+200B.
Like text-transform, this property transforms text for styling purposes.
It has no effect on the underlying content,
and must not affect the content of a plain text copy & paste operation.
Note: The effects of this property are similar
to those of the text-transform property.
However, it is defined as a separate property
rather than additional values to text-transform because:
-
This property needs to take effect before CSS Text 3 § 4.1 The White Space Processing Rules,
but text-transform happens after that.
This is needed so that the spaces inserted by this property
behave as normal spaces for text layout purposes,
and can collapse with other collapsible spaces
or participate in Trimming and Positioning. -
The uses cases for this property and text-transform,
and the author’s decision to apply either or both,
are independent,
making it desirable for these two properties to cascade separately.
Unlike books for adults, Japanese books for young children often feature spaces between sentence segments,
to facilitate reading.
Absent any particular styling, the following sentence would be rendered as depicted below.
<p>むかしむかし、<wbr>あるところに、<wbr>おじいさんと<wbr>おばあさんが<wbr>すんでいました。
むかしむかし、あるところに、おじいさんとおばあさんがすんでいました。
Phrase-based spacing can be achieved with the following css:
p {
word-boundary-expansion: ideographic-space;
}
むかしむかし、 あるところに、 おじいさんと おばあさんが すんでいました。
Another common variant additionally restricts the allowable line breaks to these phrase boundaries.
Using the same markup, this is easily achieved with the following css:
p {
word-break: keep-all;
word-boundary-expansion: ideographic-space;
}
むかしむかし、 あるところに、 おじいさんと おばあさんが すんでいました。
In addition to making the source code more readable,
using wbr rather than U+200B in the markup
also allow authors to classify the delimiters into different groups.
In the following example, wbr elements are either
unmarked when they delimit a word,
or marked with class p when they also delimit a phrase.
<p>らいしゅう<wbr>の<wbr>じゅぎょう<wbr>に<wbr class=p
>たいこ<wbr>と<wbr>ばち<wbr>を<wbr class=p
>もって<wbr>きて<wbr>ください。
Using this, it is possible not only to enable the rather common phrase-based spacing,
but also word-by-word spacing
that is likely to be preferred
by people with dyslexia to reduce ambiguities,
or other variants
such as a combination of phrase-based spacing and of word-based wrapping.
らいしゅうのじゅぎょうにたいことばちをもってきてください。
p wbr.p {
word-boundary-expansion: ideographic-space;
}
らいしゅうのじゅぎょうに たいことばちを もってきてください。
p wbr {
word-boundary-expansion: ideographic-space;
}
らいしゅう の じゅぎょう に たいこ と ばち を もって きて ください。
p {
word-break: keep-all;
}
p wbr.p {
word-boundary-expansion: ideographic-space;
}
らいしゅうのじゅぎょうに たいことばちを もってきてください。
p {
word-break: keep-all;
}
p wbr {
word-boundary-expansion: ideographic-space;
}
らいしゅう の じゅぎょう に たいこ と ばち を もって きて ください。
3. White Space and Wrapping: the white-space property
| Name: | white-space |
|---|---|
| Value: | normal | pre | nowrap | pre-wrap | pre-line | <‘white-space-collapse’> || <‘text-wrap’> || <‘white-space-trim’> |
| Initial: | normal |
| Applies to: | text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | specified keyword |
| Canonical order: | n/a |
| Animation type: | discrete |
This property is a shorthand for white-space-collapse, text-wrap, and white-space-trim.
It specifies two things:
- whether and how white space is collapsed;
see White Space Processing - whether lines may wrap at unforced soft wrap opportunities;
see Line Breaking
Note: This shorthand combines both inheritable and non-inheritable properties.
If this is a problem, please inform the CSSWG.
Unless otherwise specified, any omitted longhand is set to its initial value.
The following table gives the normative mapping
of the values of the shorthand’s special keywords
to their equivalent longhand values.
| white-space | white-space-collapse | text-wrap | white-space-trim |
|---|---|---|---|
| normal | collapse | wrap | none |
| pre | preserve | nowrap | none |
| pre-wrap | preserve | wrap | none |
| pre-line | preserve-breaks | wrap | none |
These keywords have the following informative definitions:
Remove these definitions once the tests annotations have been redistributed.
- normal
- This value directs user agents to collapse sequences of white space into a single character
(or in some cases, no character).
Lines may wrap at allowed soft wrap opportunities,
as determined by the line-breaking rules in effect,
in order to minimize inline-axis overflow. - pre
- This value prevents user agents from collapsing sequences of white space. Segment breaks such as line feeds
are preserved as forced line breaks.
Lines only break at forced line breaks;
content that does not fit within the block container overflows it. - nowrap
- Like normal,
this value collapses white space;
but like pre, it does not allow wrapping. - pre-wrap
- Like pre,
this value preserves white space;
but like normal,
it allows wrapping. - pre-line
- Like normal,
this value collapses consecutive white space characters and allows wrapping,
but it preserves segment breaks in the source as forced line breaks.
Note: In some cases, preserved white space and other space separators can hang when at the end of the line;
this can affect whether they are measured for intrinsic sizing.
The following informative table summarizes the behavior
of various white-space values:
| New Lines | Spaces and Tabs | Text Wrapping | End-of-line spaces | End-of-line other space separators | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| normal | Collapse | Collapse | Wrap | Remove | Hang |
| pre | Preserve | Preserve | No wrap | Preserve | No wrap |
| nowrap | Collapse | Collapse | No wrap | Remove | Hang |
| pre-wrap | Preserve | Preserve | Wrap | Hang | Hang |
| break-spaces | Preserve | Preserve | Wrap | Wrap | Wrap |
| pre-line | Preserve | Collapse | Wrap | Remove | Hang |
4. White Space Processing & Control Characters
The source text of a document often contains formatting
that is not relevant to the final rendering:
for example, breaking the source into segments (lines) for ease of editing
or adding white space characters such as tabs and spaces to indent the source code.
CSS white space processing allows the author
to control interpretation of such formatting:
to preserve or collapse it away when rendering the document.
White space processing in CSS
(which is controlled with the white-space-collapse and white-space-trim properties)
interprets white space characters only for rendering:
it has no effect on the underlying document data.
Note: Depending on the document language,
segments can be separated by a particular newline sequence
(such as a line feed or CRLF pair),
or delimited by some other mechanism,
such as the SGML RECORD-START and RECORD-END tokens.
For CSS processing,
each document language–defined “segment break” or “newline sequence”—or if none are defined, each line feed (U+000A)—in the text is treated as a segment break,
which is then interpreted for rendering as specified by the white-space property.
In the case of HTML,
each newline sequence is normalized to a single line feed (U+000A)
for representation in the DOM,
so when an HTML document is represented as a DOM tree
each line feed (U+000A)
is treated as a segment break. [HTML] [DOM]
Note: In most common CSS implementations,
HTML does not get styled directly.
Instead, it is processed into a DOM tree,
which is then styled.
Unlike HTML,
the DOM does not give any particular meaning to carriage returns (U+000D),
so they are not treated as segment breaks.
If carriage returns (U+000D) are inserted into the DOM
by means other than HTML parsing,
they then get treated as defined below.
Note: A document parser might
not only normalize any segment breaks,
but also collapse other space characters or
otherwise process white space according to markup rules.
Because CSS processing occurs after the parsing stage,
it is not possible to restore these characters for styling.
Therefore, some of the behavior specified below
can be affected by these limitations and
may be user agent dependent.
Note: Anonymous blocks consisting entirely of collapsible white space are removed from the rendering tree.
Thus any such white space surrounding a block-level element is collapsed away.
See CSS 2.1 § 9.2.2.1 Anonymous inline boxes. [CSS2]
Control characters (Unicode category Cc)—other than tabs (U+0009),
line feeds (U+000A),
carriage returns (U+000D)
and sequences that form a segment break—must be rendered as a visible glyph
which the UA must synthesize if the glyphs found in the font are not visible,
and must be otherwise treated as any other character
of the Other Symbols (So) general category and Common script.
The UA may use a glyph provided by a font specifically for the control character,
substitute the glyphs provided for the corresponding symbol in the Control Pictures block,
generate a visual representation of its code point value,
or use some other method to provide an appropriate visible glyph.
As required by Unicode,
unsupported Default_ignorable characters
must be ignored for text rendering. [UNICODE]
Carriage returns (U+000D) are treated identically to spaces (U+0020) in all respects.
Note: For HTML documents,
carriage returns present in the source code
are converted to line feeds at the parsing stage
(see HTML § 13.2.3.5 Preprocessing the input stream and the definition of normalize newlines in Infra and therefore do no appear as U+000D CARRIAGE RETURN to CSS. [HTML] [INFRA])
However, the character is preserved—and the above rule observable—when encoded using an escape sequence (
).
4.1. White Space Collapsing: the white-space-collapse property
This section is still under discussion and may change in future drafts.
| Name: | white-space-collapse |
|---|---|
| Value: | collapse | discard | preserve | preserve-breaks | preserve-spaces | break-spaces |
| Initial: | collapse |
| Applies to: | text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | specified keyword |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
| Animation type: | discrete |
This property specifies whether and how white space is collapsed.
Values have the following meanings,
which must be interpreted according to
the White Space Processing Rules:
- collapse
- This value directs user agents to collapse sequences of white space into a single character
(or in some cases, no character). - preserve
- This value prevents user agents from collapsing sequences of white space. Segment breaks such as line feeds
are preserved as forced line breaks. - preserve-breaks
- Like collapse,
this value collapses consecutive white space characters,
but preserves segment breaks in the source as forced line breaks. - preserve-spaces
- This value prevents user agents
from collapsing sequences of white space,
and converts tabs and segment breaks to spaces.
(This value is intended to represent the behavior
ofxml:space="preserve"in SVG.) - break-spaces
-
The behavior is identical to that of preserve,
except that:- Any sequence of preserved white space or other space separators always takes up space,
including at the end of the line. - A soft wrap opportunity exists
after every preserved white space character
and after every other space separator (including between adjacent spaces).
Note: This value does not guarantee
that there will never be any overflow due to white space:
for example, if the line length is so short
that even a single white space character does not fit,
overflow is unavoidable. - Any sequence of preserved white space or other space separators always takes up space,
- discard
-
This value directs user agents to “discard”
all white space in the element.Does this preserve line break opportunities or no? Do we need a distinct «hide» value?
If it preserves line break opportunities,
maybe it should be replaced with a word-boundary-expansion value?
White space that was not removed or collapsed due to white space processing
is called preserved white space.
The following style rules implement MathML’s white space processing:
@namespace m "http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML";
m|* {
white-space-collapse: discard;
}
m|mi, m|mn, m|mo, m|ms, m|mtext {
white-space-trim: discard-inner;
}
4.2. White Space Trimming: the white-space-trim property
| Name: | white-space-trim |
|---|---|
| Value: | none | discard-before || discard-after || discard-inner |
| Initial: | none |
| Applies to: | inline boxes and block containers |
| Inherited: | no |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | specified keyword(s) |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
| Animation type: | discrete |
This property allows authors to specify trimming behavior
at the beginning and end of a box.
Values have the following meanings:
- discard-before
- This value directs the UA to collapse all collapsible whitespace
immediately before the start of the element. - discard-after
- This value directs the UA to collapse all collapsible whitespace
immediately after the end of the element. - discard-inner
- For block containers this value directs UAs to discard
all whitespace at the beginning of the element up to and including
the last segment break before the first non-white-space character in the element
as well as to discard all white space at the end of the element
starting with the first segment break after the last non-white-space character in the element.
For other elements this value directs UAs to discard
all whitespace at the beginning and end of the element.
Note: Discarding document white space using white-space-trim can change where soft wrap opportunities occur in the text.
The following style rules render DT elements as a comma-separated list,
even if they are coded on separate lines of the source document:
dt { display: inline; }
dt + dt:before { content: ", "; white-space-trim: discard-before; }
The following style rule removes source-formatting white space
adjacent to the opening/closing tags of a preformatted block,
but not any indentation or interleaved white space
applied to the actual contents of the element:
pre { white-space: pre; white-space-trim: discard-inner; }
This results in the following two source-code snippets:
<pre> some preformatted text </pre>
<pre> some preformatted text</pre>
rendering identically as:
some preformatted text
If instead we apply it to an inline element:
span { white-space: normal; white-space-trim: discard-inner; }
start[<span> some inline text </span>]end
start[<span> some inline text</span>]end
this directs the UA to discard all of the leading/trailing white space
before the actual contents of the element:
start[some inline text]end
White space processing for white-space-trim takes place before § 4.3.1 Phase I: Collapsing and Transformation.
4.3. The White Space Processing Rules
Except where specified otherwise,
white space processing in CSS affects only
the document white space characters: spaces (U+0020), tabs (U+0009), and segment breaks.
Note: The set of characters considered document white space (part of the document content)
and those considered syntactic white space
(part of the CSS syntax)
are not necessarily identical.
However, since both include spaces (U+0020), tabs (U+0009), and line feeds (U+000A)
most authors won’t notice any differences.
Besides space (U+0020)
and no-break space (U+00A0),
Unicode defines a number of additional space separator characters. [UNICODE] In this specification
all characters in the Unicode general category Zs
except space (U+0020)
and no-break space (U+00A0)
are collectively referred to as other space separators.
4.3.1. Phase I: Collapsing and Transformation
Note: white-space-trim is taken into account prior to this phase.
For each inline
(including anonymous inlines;
see CSS 2.1 § 9.2.2.1 Anonymous inline boxes [CSS2])
within an inline formatting context, white space characters are processed as follows
prior to line breaking and bidi reordering,
ignoring bidi formatting characters (characters with the Bidi_Control property [UAX9])
as if they were not there:
-
If white-space-collapse is set to collapse or preserve-breaks, white space characters are considered collapsible and are processed by performing the following steps:
- Any sequence of collapsible spaces and tabs immediately preceding or following a segment break is removed.
- Collapsible segment breaks are transformed for rendering
according to the segment break transformation rules. - Every collapsible tab is converted to a collapsible space (U+0020).
- Any collapsible space immediately following another collapsible space—even one outside the boundary of the inline containing that space,
provided both spaces are within the same inline formatting context—is collapsed to have zero advance width.
(It is invisible,
but retains its soft wrap opportunity,
if any.)
- If white-space-collapse is set to preserve-spaces,
each tab and segment break is converted to a space. - If white-space-collapse is set to preserve or preserve-spaces,
any sequence of spaces is treated as a sequence of non-breaking spaces
except that
a soft wrap opportunity exists at the end of each maximal sequence of spaces and/or tabs.
For break-spaces,
a soft wrap opportunity exists after every space and every tab.
The following example illustrates
the interaction of white-space collapsing and bidirectionality.
Consider the following markup fragment, taking special note of spaces (with varied backgrounds and borders for emphasis and identification):
<ltr>A <rtl> B </rtl> C</ltr>where the <ltr> element represents a left-to-right embedding
and the <rtl> element represents a right-to-left embedding.
If the white-space property is set to normal,
the white-space processing model will result in the following:
- The space before the B ( )
will collapse with the space after the A ( ). - The space before the C ( )
will collapse with the space after the B ( ).
This will leave two spaces,
one after the A in the left-to-right embedding level,
and one after the B in the right-to-left embedding level.
The text will then be ordered according to the Unicode bidirectional algorithm,
with the end result being:
A BC
Note that there will be two spaces between A and B,
and none between B and C.
This is best avoided by putting spaces outside the element
instead of just inside the opening and closing tags
and, where practical,
by relying on implicit bidirectionality instead of explicit embedding levels.
4.3.2. Phase II: Trimming and Positioning
Then, the entire block is rendered.
Inlines are laid out,
taking bidi reordering into account,
and wrapping as specified by the text-wrap property.
As each line is laid out,
- A sequence of collapsible spaces at the beginning of a line
is removed. -
If the tab size is zero, preserved tabs are not rendered.
Otherwise, each preserved tab is rendered
as a horizontal shift that lines up
the start edge of the next glyph with the next tab stop.
If this distance is less than 0.5ch,
then the subsequent tab stop is used instead. Tab stops occur at points
that are multiples of the tab size from the starting content edge
of the preserved tab’s nearest block container ancestor.
The tab size is given by the tab-size property.Note: See the Unicode rules on how tabulation (U+0009) interacts with bidi. [UAX9]
-
A sequence of collapsible spaces at the end of a line is removed,
as well as any trailing U+1680 OGHAM SPACE MARK
whose white-space-collapse property is collapse or preserve-breaks.Note: Due to Unicode Bidirectional Algorithm rule L1,
a sequence of collapsible spaces located at the end of the line
prior to bidi reordering will also be at the end of the line after reordering. [UAX9] [CSS-WRITING-MODES-4] -
If there remains any sequence of white space, other space separators,
and/or preserved tabs at the end of a line
(after bidi reordering [CSS-WRITING-MODES-4]):- If white-space-collapse is collapse or preserve-breaks,
the UA must hang this sequence (unconditionally). -
If white-space-collapse is preserve and text-wrap is not nowrap,
the UA must (unconditionally) hang this sequence,
unless the sequence is followed by a forced line break,
in which case it must conditionally hang the sequence instead.
It may also visually collapse the character advance widths
of any that would otherwise overflow.Note: Hanging the white space rather than collapsing it
allows users to see the space when selecting or editing text. -
If white-space-collapse is set to break-spaces, spaces, tabs, and other space separators are treated the same as other visible characters:
they cannot hang nor have their advance width collapsed.Note: Such characters therefore take up space,
and depending on the available space
and applicable line breaking controls
will either overflow or cause the line to wrap.
What should happen here for white-space-collapse: preserve-spaces?
- If white-space-collapse is collapse or preserve-breaks,
This example shows that conditionally hanging white space
at the end of lines with forced breaks
provides symmetry with the start of the line.
An underline is added to help visualize the spaces.
p {
white-space: pre-wrap;
width: 5ch;
border: solid 1px;
font-family: monospace;
text-align: center;
}
<p> 0 </p>
The sample above would be rendered as follows:
0
Since the final space is before a forced line break
and does not overflow,
it does not hang,
and centering works as expected.
This example illustrates the difference
between hanging spaces at the end of lines without forced breaks,
and conditionally hanging them at the end of lines with forced breaks.
An underline is added to help visualize the spaces.
p {
white-space: pre-wrap;
width: 3ch;
border: solid 1px;
font-family: monospace;
}
<p> 0 0 0 0 </p>
The sample above would be rendered as follows:
0
0 0
0
If p { text-align: right; } was added,
the result would be as follows:
0
0 0
0
As the preserved spaces at the end of lines without a forced break must hang,
they are not considered when placing the rest of the line during text alignment.
When aligning towards the end,
this means any such spaces will overflow,
and will not prevent the rest of the line’s content from being flush with the edge of the line.
On the other hand,
preserved spaces at the end of a line with a forced break conditionally hang.
Since the space at the end of the last line would not overflow in this example,
it does not hang and therefore is considered during text alignment.
In the following example,
there is not enough room on any line to fit the end-of-line spaces,
so they hang on all lines:
the one on the line without a forced break because it must,
as well as the one on the line with a forced break,
because it conditionally hangs and overflows.
An underline is added to help visualize the spaces.
p {
white-space: pre-wrap;
width: 3ch;
border: solid 1px;
font-family: monospace;
}
<p>0 0 0 0 </p>
0 0
0 0
The last line is not wrapped before the last 0 because characters that conditionally hang are not considered
when measuring the line’s contents for fit.
4.3.3. Segment Break Transformation Rules
When white-space-collapse is not collapse, segment breaks are not collapsible.
For values other than collapse or preserve-spaces (which transforms them into spaces), segment breaks are instead transformed into a preserved line feed (U+000A).
When white-space-collapse is collapse, segment breaks are collapsible,
and are collapsed as follows:
- First, any collapsible segment break immediately following another collapsible segment break is removed.
-
Then any remaining segment break is either transformed into a space (U+0020)
or removed
depending on the context before and after the break.
The rules for this operation are UA-defined in this level.Should we define this for Level 4?
Note: The white space processing rules have already
removed any tabs and spaces around the segment break before this context is evaluated.
The purpose of the segment break transformation rules
(and white space collapsing in general)
is to “unbreak” text that has been broken into segments to make the document source code easier to work with.
In languages that use word separators, such as English and Korean,
“unbreaking” a line requires joining the two lines with a space.
Here is an English paragraph that is broken into multiple lines in the source code so that it can be more easily read and edited in a text editor.
Here is an English paragraph that is broken into multiple lines in the source code so that it can be more easily read and edited in a text editor.
requires maintaining a space in its place.
In languages that have no word separators, such as Chinese,
“unbreaking” a line requires joining the two lines with no intervening space.
這個段落是那麼長, 在一行寫不行。最好 用三行寫。
這個段落是那麼長,在一行寫不行。最好用三行寫。
requires eliminating any intervening white space.
The segment break transformation rules can use adjacent context
to either transform the segment break into a space
or eliminate it entirely.
Note: Historically, HTML and CSS have unconditionally converted segment breaks to spaces,
which has prevented content authored in languages such as Chinese
from being able to break lines within the source.
Thus UA heuristics need to be conservative about where they discard segment breaks even as they strive to improve support for such languages.
4.4. Tab Character Size: the tab-size property
| Name: | tab-size |
|---|---|
| Value: | <number> | <length> |
| Initial: | 8 |
| Applies to: | text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | the specified number or absolute length |
| Canonical order: | n/a |
| Animation type: | by computed value type |
This property determines the tab size used to render preserved tab characters (U+0009).
A <number> represents the measure
as a multiple of the advance width of the space character (U+0020)
of the nearest block container ancestor of the preserved tab,
including its associated letter-spacing and word-spacing.
Negative values are not allowed.
5. Line Breaking and Word Boundaries
When inline-level content is laid out into lines, it is broken across line boxes.
Such a break is called a line break.
When a line is broken due to explicit line-breaking controls
(such as a preserved newline character),
or due to the start or end of a block,
it is a forced line break.
When a line is broken due to content wrapping (i.e. when the UA creates unforced line breaks
in order to fit the content within the measure),
it is a soft wrap break.
The process of breaking inline-level content into lines is called line breaking.
Wrapping is only performed at an allowed break point,
called a soft wrap opportunity.
When wrapping is enabled (see white-space),
the UA must minimize the amount of content overflowing a line
by wrapping the line at a soft wrap opportunity,
if one exists.
In most writing systems,
in the absence of hyphenation a soft wrap opportunity occurs only at word boundaries.
Many such systems use spaces or punctuation to explicitly separate words,
and soft wrap opportunities can be identified by these characters.
Scripts such as Thai, Lao, and Khmer, however,
do not use spaces or punctuation to separate words.
Although the zero width space (U+200B) can be used as an explicit word delimiter
in these scripts,
this practice is not common.
As a result, a lexical resource is needed
to correctly identify soft wrap opportunities in such texts.
In some other writing systems, soft wrap opportunities are based on orthographic syllable boundaries,
not word boundaries.
Some of these systems, such as Javanese and Balinese,
are similar to Thai and Lao in that they
require analysis of the text to find breaking opportunities.
In others such as Chinese (as well as Japanese, Yi, and sometimes also Korean),
each syllable tends to correspond to a single typographic letter unit,
and thus line breaking conventions allow the line to break
anywhere except between certain character combinations.
Additionally the level of strictness in these restrictions
varies with the typesetting style.
While CSS does not fully define where soft wrap opportunities occur,
some controls are provided to distinguish common variations:
- The line-break property allows choosing various levels of “strictness”
for line breaking restrictions. - The word-break property controls what types of letters
are glommed together to form unbreakable “words”,
causing CJK characters to behave like non-CJK text or vice versa. - The hyphens property controls whether automatic hyphenation
is allowed to break words in scripts that hyphenate. - The overflow-wrap property allows the UA to take a break anywhere
in otherwise-unbreakable strings that would otherwise overflow.
Note: Unicode Standard Annex #14: Unicode Line Breaking Algorithm defines a baseline behavior
for line breaking for all scripts in Unicode,
which is expected to be further tailored. [UAX14] More information on line breaking conventions
can be found in Requirements for Japanese Text Layout [JLREQ] and Formatting Rules for Japanese Documents [JIS4051] for Japanese, Requirements for Chinese Text Layout [CLREQ] and General Rules for Punctuation [ZHMARK] for Chinese.
See also the Internationalization Working Group’s Language Enablement Index which includes more information on additional languages. [TYPOGRAPHY] Any guidance on additional appropriate references
would be much appreciated.
5.1. Line Breaking Details
When determining line breaks:
- The interaction of line breaking and bidirectional text is defined by CSS Writing Modes 4 § 2.4 Applying the Bidirectional Reordering Algorithm and the Unicode Bidirectional Algorithm (UAX9§3.4 Reordering Resolved Levels in particular). [CSS-WRITING-MODES-4] [UAX9]
-
Preserved segment breaks, and—regardless of the white-space value—any Unicode character with the
BKandNLline breaking class,
must be treated as forced line breaks. [UAX14]Note: The bidi implications of such forced line breaks are defined by the Unicode Bidirectional Algorithm. [UAX9]
- Except where explicitly defined otherwise
(e.g. for line-break: anywhere or overflow-wrap: anywhere)
line breaking behavior defined for
theWJ,ZW,GL,
andZWJUnicode line breaking classes
must be honored. [UAX14] - UAs that allow wrapping at punctuation
other than word separators in writing systems that use them should prioritize breakpoints.
(For example, if breaks after slashes are given a lower priority than spaces,
the sequence “check /etc” will never break between the «/» and the «e».)
As long as care is taken to avoid such awkward breaks,
allowing breaks at appropriate punctuation other than word separators is recommended,
as it results in more even-looking margins, particularly in narrow measures.
The UA may use the width of the containing block, the text’s language,
the line-break value,
and other factors in assigning priorities:
CSS does not define prioritization of soft wrap opportunities.
Prioritization of word separators is not expected,
however,
if word-break: break-all is specified
(since this value explicitly requests line breaking behavior
not based on breaking at word separators)—and is forbidden under line-break: anywhere. - Out-of-flow elements
and inline element boundaries
do not introduce a forced line break or soft wrap opportunity in the flow. - For Web-compatibility
there is a soft wrap opportunity before and after each replaced element or other atomic inline,
even when adjacent to a character that would normally suppress them,
such as U+00A0 NO-BREAK SPACE. - For soft wrap opportunities created by characters
that disappear at the line break (e.g. U+0020 SPACE),
properties on the box directly containing that character
control the line breaking at that opportunity.
For soft wrap opportunities defined by the boundary between two characters,
the white-space property
on the nearest common ancestor of the two characters
controls breaking;
which elements’ line-break, word-break, and overflow-wrap properties
control the determination of soft wrap opportunities at such boundaries
is undefined in Level 3. - For soft wrap opportunities before the first
or after the last character of a box,
the break occurs immediately before/after the box
(at its margin edge)
rather than breaking the box
between its content edge and the content. - Line breaking in/around Ruby is defined
in CSS Ruby Annotation Layout 1 § 3.4 Breaking Across Lines. [CSS-RUBY-1] -
In order to avoid unexpected overflow,
if the user agent is unable to perform the requisite lexical
or orthographic analysis
for line breaking any content language that requires it—for example due to lacking a dictionary for certain languages—it must assume a soft wrap opportunity between pairs of typographic letter units in that writing system.Note: This provision is not triggered merely when
the UA fails to find a word boundary in a particular text run;
the text run may well be a single unbreakable word.
It applies for example
when a text run is composed of Khmer characters (U+1780 to U+17FF)
if the user agent does not know how to determine
word boundaries in Khmer.
5.2. Breaking Rules for Letters: the word-break property
| Name: | word-break |
|---|---|
| Value: | normal | keep-all | break-all | break-word |
| Initial: | normal |
| Applies to: | text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | specified keyword |
| Canonical order: | n/a |
| Animation type: | discrete |
This property specifies soft wrap opportunities between letters,
i.e. where it is “normal” and permissible to break lines of text.
Specifically it controls whether a soft wrap opportunity generally exists
between adjacent typographic letter units,
treating non-letter typographic character units belonging to the NU, AL, AI,
or ID Unicode line breaking classes
as typographic letter units for this purpose (only). [UAX14] It does not affect rules governing the soft wrap opportunities created by white space (as well as by other space separators)
and around punctuation.
(See line-break for controls affecting punctuation and small kana.)
For example,
in some styles of CJK typesetting,
English words are allowed to break between any two letters,
rather than only at spaces or hyphenation points;
this can be enabled with word-break:break-all.
being broken at an arbitrary point in the word.
As another example, Korean has two styles of line-breaking:
between any two Korean syllables (word-break: normal)
or, like English, mainly at spaces (word-break: keep-all).
각 줄의 마지막에 한글이 올 때 줄 나눔 기 준을 “글자” 또는 “어절” 단위로 한다.
각 줄의 마지막에 한글이 올 때 줄 나눔 기준을 “글자” 또는 “어절” 단위로 한다.
Ethiopic similarly has two styles of line-breaking,
either only breaking at word separators (word-break: normal),
or also allowing breaks between letters within a word (word-break: break-all).
ተወልዱ፡ኵሉ፡ሰብእ፡ግዑዛን፡ወዕሩያን፡ በማዕረግ፡ወብሕግ።ቦሙ፡ኅሊና፡ወዐቅል፡ ወይትጌበሩ፡አሐዱ፡ምስለ፡አሀዱ፡ በመንፈሰ፡እኍና።
ተወልዱ፡ኵሉ፡ሰብእ፡ግዑዛን፡ወዕሩያን፡በማ ዕረግ፡ወብሕግ።ቦሙ፡ኅሊና፡ወዐቅል፡ወይትጌ በሩ፡አሐዱ፡ምስለ፡አሀዱ፡በመንፈሰ፡እኍና።
Note: To enable additional break opportunities only in the case of overflow,
see overflow-wrap.
Values have the following meanings:
- normal
- Words break according to their customary rules,
as described above.
Korean, which commonly exhibits two different behaviors,
allows breaks between any two consecutive Hangul/Hanja.
For Ethiopic, which also exhibits two different behaviors,
such breaks within words are not allowed. - break-all
-
Breaking is allowed within “words”:
specifically,
in addition to soft wrap opportunities allowed for normal,
any typographic letter units (and any typographic character units resolving to theNU(“numeric”),AL(“alphabetic”),
orSA(“Southeast Asian”)
line breaking classes [UAX14])
are instead treated asID(“ideographic characters”)
for the purpose of line-breaking.
Hyphenation is not applied.Note: This value does not affect
whether there are soft wrap opportunities around punctuation characters.
To allow breaks anywhere, see line-break: anywhere.Note: This option enables the other common behavior for Ethiopic.
It is also often used in a context where
the text consists predominantly of CJK characters
with only short non-CJK excerpts,
and it is desired that the text be better distributed on each line. - keep-all
-
Breaking is forbidden within “words”:
implicit soft wrap opportunities between typographic letter units (or other typographic character units belonging to theNU,AL,AI,
orIDUnicode line breaking classes [UAX14])
are suppressed,
i.e. breaks are prohibited between pairs of such characters
(regardless of line-break settings other than anywhere)
except where opportunities exist due to dictionary-based breaking.
Otherwise this option is equivalent to normal.
In this style, sequences of CJK characters do not break.Note: This is the other common behavior for Korean
(which uses spaces between words),
and is also useful for mixed-script text where CJK snippets are mixed
into another language that uses spaces for separation.
Symbols that line-break the same way as letters of a particular category
are affected the same way as those letters.
Here’s a mixed-script sample text:
这是一些汉字 and some Latin و کمی خط عربی และตัวอย่างการเขียนภาษาไทย በጽሑፍ፡ማራዘሙን፡አንዳንድ፡
The break-points are determined as follows (indicated by ‘·’):
- word-break: normal
-
这·是·一·些·汉·字·and·some·Latin·و·کمی·خط·عربی·และ·ตัวอย่าง·การเขียน·ภาษาไทย·በጽሑፍ፡·ማራዘሙን፡·አንዳንድ፡
- word-break: break-all
-
这·是·一·些·汉·字·a·n·d·s·o·m·e·L·a·t·i·n·و·ﮐ·ﻤ·ﻰ·ﺧ·ﻁ·ﻋ·ﺮ·ﺑ·ﻰ·แ·ล·ะ·ตั·ว·อ·ย่·า·ง·ก·า·ร·เ·ขี·ย·น·ภ·า·ษ·า·ไ·ท·ย·በ·ጽ·ሑ·ፍ፡·ማ·ራ·ዘ·ሙ·ን፡·አ·ን·ዳ·ን·ድ፡
- word-break: keep-all
-
这是一些汉字·and·some·Latin·و·کمی·خط·عربی·และ·ตัวอย่าง·การเขียน·ภาษาไทย·በጽሑፍ፡·ማራዘሙን፡·አንዳንድ፡
Japanese is usually typeset allowing line breaks within words.
However, it is sometimes preferred to suppress these wrapping opportunities
and to only allow wrapping at the end of certain sentence fragments.
This is most commonly done in very short pieces of text,
such as headings and table or figure captions.
This can be achieved by marking the allowed wrapping points
with wbr or U+200B ZERO WIDTH SPACE,
and suppressing the other ones using word-break: keep-all.
For instance, the following markup can produce either of the renderings below,
depending on the value of the word-break property:
<h1>窓ぎわの<wbr>トットちゃん</h1>
h1 { word-break: normal }
|
h1 { word-break: keep-all }
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Expected rendering |
窓ぎわのトットちゃ ん |
窓ぎわの トットちゃん |
| Result in your browser | 窓ぎわのトットちゃん | 窓ぎわのトットちゃん |
When shaping scripts such as Arabic
are allowed to break within words due to break-all the characters must still be shaped
as if the word were not broken (see § 6.4 Shaping Across Intra-word Breaks).
For compatibility with legacy content,
the word-break property also supports
a deprecated break-word keyword.
When specified, this has the same effect as word-break: normal and overflow-wrap: anywhere,
regardless of the actual value of the overflow-wrap property.
5.3. Line Breaking Strictness: the line-break property
| Name: | line-break |
|---|---|
| Value: | auto | loose | normal | strict | anywhere |
| Initial: | auto |
| Applies to: | text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | specified keyword |
| Canonical order: | n/a |
| Animation type: | discrete |
This property specifies the strictness of line-breaking rules applied
within an element:
especially how wrapping interacts with punctuation and symbols.
Values have the following meanings:
- auto
- The UA determines the set of line-breaking restrictions to use,
and it may vary the restrictions based on the length of the line;
e.g., use a less restrictive set of line-break rules for short lines. - loose
- Breaks text using the least restrictive set of line-breaking
rules. Typically used for short lines, such as in newspapers. - normal
- Breaks text using the most common set of line-breaking rules.
- strict
- Breaks text using the most stringent set of line-breaking rules.
- anywhere
-
There is a soft wrap opportunity around every typographic character unit,
including around any punctuation character
or preserved white spaces,
or in the middle of words,
disregarding any prohibition against line breaks,
even those introduced by characters with theGL,WJ, orZWJline breaking classes
or mandated by the word-break property. [UAX14] The different wrapping opportunities must not be prioritized.
Hyphenation is not applied.Note: This value triggers the line breaking rules typically seen in terminals.
Note: anywhere only allows preserved white spaces at the end of the line
to be wrapped to the next line
when white-space is set to break-spaces,
because in other cases:- preserved white space at the end/start of the line is discarded
(normal, pre-line) - wrapping is forbidden altogether (nowrap, pre)
- the preserved white space hang (pre-wrap).
When it does have an effect on preserved white space,
with white-space: break-spaces,
it allows breaking before the first space of a sequence,
which break-spaces on its own does not. - preserved white space at the end/start of the line is discarded
CSS distinguishes between four levels of strictness
in the rules for text wrapping.
The precise set of rules in effect for each of loose, normal,
and strict is up to the UA
and should follow language conventions.
However, this specification does require that:
-
The following breaks are forbidden in strict line breaking
and allowed in normal and loose:- breaks before Japanese small kana
or the Katakana-Hiragana prolonged sound mark,
i.e. characters
from the Unicode line breaking classCJ. [UAX14]
- breaks before Japanese small kana
-
The following breaks are allowed for normal and loose line breaking
if the writing system is Chinese or Japanese,
and are otherwise forbidden:- breaks before certain CJK hyphen-like characters:
〜 U+301C,
゠ U+30A0
- breaks before certain CJK hyphen-like characters:
-
The following breaks are allowed for loose line breaking
if the preceding character
belongs to the Unicode line breaking classID[UAX14] (including when the preceding character
is treated asIDdue to word-break: break-all),
and are otherwise forbidden:- breaks before hyphens:
‐ U+2010, – U+2013
- breaks before hyphens:
-
The following breaks are forbidden for normal and strict line breaking
and allowed in loose:- breaks before iteration marks:
々 U+3005, 〻 U+303B, ゝ U+309D,
ゞ U+309E, ヽ U+30FD, ヾ U+30FE - breaks between inseparable characters
(such as ‥ U+2025, … U+2026)
i.e. characters from the Unicode line breaking classIN. [UAX14]
- breaks before iteration marks:
-
The following breaks are allowed for loose if the writing system is Chinese or Japanese and are otherwise forbidden:
- breaks before certain centered punctuation marks:
・ U+30FB,
: U+FF1A, ; U+FF1B, ・ U+FF65,
‼ U+203C,
⁇ U+2047, ⁈ U+2048, ⁉ U+2049,
! U+FF01, ? U+FF1F - breaks before suffixes:
Characters with the Unicode line breaking classPO[UAX14] and the East Asian Width property [UAX11]Ambiguous,Fullwidth,
orWide. - breaks after prefixes:
Characters with the Unicode line breaking classPR[UAX14] and the East Asian Width property [UAX11]Ambiguous,Fullwidth,
orWide.
- breaks before certain centered punctuation marks:
Note: The requirements listed above
only create distinctions in CJK text.
In an implementation that matches only the rules above,
and no additional rules, line-break would only affect CJK code points
unless the writing system is tagged as Chinese or Japanese.
Future levels may add additional specific rules
for other writing systems and languages
as their requirements become known.
As UAs can add additional distinctions
between strict/normal/loose modes,
these values can exhibit differences in other writing systems as well.
For example, a UA with sufficiently-advanced Thai language processing ability
could choose to map different levels of strictness in Thai line-breaking
to these keywords,
e.g. disallowing breaks within compound words in strict mode
(e.g. breaking ตัวอย่างการเขียนภาษาไทย as ตัวอย่าง·การเขียน·ภาษาไทย)
while allowing more breaks in loose (ตัวอย่าง·การ·เขียน·ภาษา·ไทย).
Note: The CSSWG recognizes that in a future edition of the specification
finer control over line breaking may be necessary
to satisfy high-end publishing requirements.
5.4. Hyphenation: Morphological Breaking Within Words
5.4.1. Hyphenation Control: the hyphens property
Hyphenation is the controlled splitting of words
where they usually would not be allowed to break
to improve the layout of paragraphs,
typically splitting words at syllabic or morphemic boundaries
and visually indicating the split
(usually by inserting a hyphen, U+2010).
In some cases, hyphenation may also alter the spelling of a word.
Regardless, hyphenation is a rendering effect only:
it must have no effect on the underlying document content
or on text selection or searching.
Hyphenation Across Languages
Hyphenation practices vary across languages,
and can involve not just inserting a hyphen before the line break,
but inserting a hyphen after the break (or both),
inserting a different character than U+2010,
or changing the spelling of the word.
| Language | Unbroken | Before | After |
|---|---|---|---|
| English | Unbroken | Un‐ | broken |
| Dutch | cafeetje | café‐ | tje |
| Hungarian | Összeg | Ösz‐ | szeg |
| Mandarin | tú’àn | tú‐ | àn |
| àizēng‐fēnmíng | àizēng‐ | ‐fēnmíng | |
| Uyghur | داميدى | داميـ | دى |
Hyphenation occurs
when the line breaks at a valid hyphenation opportunity,
which is a type of soft wrap opportunity that exists within a word where hyphenation is allowed.
In CSS hyphenation opportunities are controlled
with the hyphens property.
CSS Text Level 3 does not define the exact rules for hyphenation;
however UAs are strongly encouraged
to optimize their choice of break points
and to chose language-appropriate hyphenation points.
Note: The soft wrap opportunity introduced by
the U+002D — HYPHEN-MINUS character
or the U+2010 ‐ HYPHEN character
is not a hyphenation opportunity,
as no visual indication of the split is created when wrapping:
these characters are visible whether the line is wrapped at that point or not.
Hyphenation opportunities are considered when calculating min-content intrinsic sizes.
Note: This allows tables to hyphenate their contents
instead of overflowing their containing block,
which is particularly important in long-word languages like German.
| Name: | hyphens |
|---|---|
| Value: | none | manual | auto |
| Initial: | manual |
| Applies to: | text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | specified keyword |
| Canonical order: | n/a |
| Animation type: | discrete |
This property controls whether hyphenation is allowed to create more soft wrap opportunities within a line of text.
Values have the following meanings:
- none
-
Words are not hyphenated,
even if characters inside the word
explicitly define hyphenation opportunities.Note: This does not suppress the existing soft wrap opportunities introduced by always visible characters such as
U+002D — HYPHEN-MINUS
or U+2010 ‐ HYPHEN. - manual
-
Words are only hyphenated where there are characters inside the word
that explicitly suggest hyphenation opportunities.
The UA must use the appropriate language-specific hyphenation character(s)
and should apply any appropriate spelling changes
just as for automatic hyphenation at the same point.In Unicode, U+00AD is a conditional «soft hyphen»
and U+2010 is an unconditional hyphen. Unicode Standard Annex #14 describes the role of soft hyphens in Unicode line breaking. [UAX14] In HTML,
­ represents the soft hyphen character,
which suggests a hyphenation opportunity.ex­ample
- auto
- Words may be broken at hyphenation opportunities determined automatically by a language-appropriate hyphenation resource
in addition to those indicated explicitly by a conditional hyphen.
Automatic hyphenation opportunities elsewhere within a word must be ignored
if the word contains a conditional hyphen
(­ or U+00AD SOFT HYPHEN),
in favor of the conditional hyphen(s).
However, if, even after breaking at such opportunities,
a portion of that word is still too long to fit on one line,
an automatic hyphenation opportunity may be used.
Correct automatic hyphenation requires a hyphenation resource
appropriate to the language of the text being broken.
The UA must therefore only automatically hyphenate text
for which the content language is known
and for which it has an appropriate hyphenation resource.
Authors should correctly tag their content’s language (e.g. using the HTML lang attribute
or XML xml:lang attribute)
in order to obtain correct automatic hyphenation.
The UA may use language-tailored heuristics
to exclude certain words
from automatic hyphenation.
For example, a UA might try to avoid hyphenation in proper nouns
by excluding words matching certain capitalization and punctuation patterns.
Such heuristics are not defined by this specification.
(Note that such heuristics will need to vary by language:
English and German, for example, have very different capitalization conventions.)
For the purpose of the hyphens property,
what constitutes a “word” is UA-dependent.
However, inline element boundaries
and out-of-flow elements
must be ignored when determining word boundaries.
Any glyphs shown due to hyphenation
at a hyphenation opportunity created by a conditional hyphen character
(such as U+00AD SOFT HYPHEN)
are represented by that character
and are styled according to the properties applied to it.
When shaping scripts such as Arabic are allowed to break within words
due to hyphenation,
the characters must still be shaped
as if the word were not broken (see § 6.4 Shaping Across Intra-word Breaks).
For example, if the Uyghur word “داميدى”
were hyphenated, it would appear as ![[isolated DAL + isolated ALEF + initial MEEM +
medial YEH + hyphen + line-break + final DAL +
isolated ALEF MAKSURA]](https://www.w3.org/TR/css-text-4/images/uyghur-hyphenate-joined.png)
![[isolated DAL + isolated ALEF + initial MEEM +
final YEH + hyphen + line-break + isolated DAL +
isolated ALEF MAKSURA]](https://www.w3.org/TR/css-text-4/images/uyghur-hyphenate-unjoined.png)
5.4.2. Hyphens: the hyphenate-character property
| Name: | hyphenate-character |
|---|---|
| Value: | auto | <string> |
| Initial: | auto |
| Applies to: | text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | specified keyword |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
| Animation type: | discrete |
This property specifies the string that is shown
between parts of hyphenated words.
Values have the following meanings:
- auto
- Specifies that the user agent should find an appropriate string
based on the content language’s typographic conventions,
possibly from the same source as the hyphenation dictionary. - <string>
-
Specifies the string that appears
at the hyphenation break when hyphenating.
(The position of this string is not affected:
the UA must insert the string
according to the typographic conventions of the content language,
defaulting to immediately before the hyphenation break.)
The UA may truncate the used value to a limited number of typographic character units;
it must not truncate only part of a typographic character unit.Note: Specifying the empty string «» is valid,
and causes the UA to break at hyphenation opportunities without inserting a visible hyphenation character.
The hyphen character (U+2010) is most typically used
to indicate that a word has been split.
However, hyphenate-character can be used
to specify a different type of hyphen when necessary.
[lang]:lang(ojs) { hyphenate-character: "᐀" /* CANADIAN SYLLABICS HYPHEN (U+1400) */ }
Note: Both hyphens triggered by automatic hyphenation
and hyphens triggered by soft hyphens
are rendered according to hyphenate-character.
5.4.3. Hyphenation Size Limit: the hyphenate-limit-zone property
| Name: | hyphenate-limit-zone |
|---|---|
| Value: | <length-percentage> |
| Initial: | 0 |
| Applies to: | block containers |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | refers to length of the line box |
| Computed value: | computed <length-percentage> value |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
| Animation type: | by computed value type |
Is hyphenate-limit-zone a good name? Comments/suggestions?
This property specifies the maximum amount of unfilled space
(before justification)
that may be left in the line box before hyphenation is triggered
to pull part of a word from the next line back up into the current line.
5.4.4. Hyphenation Character Limits: the hyphenate-limit-chars property
| Name: | hyphenate-limit-chars |
|---|---|
| Value: | [ auto | <integer> ]{1,3} |
| Initial: | auto |
| Applies to: | text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | three values, each either the auto keyword or an integer |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
| Animation type: | by computed value type |
This property specifies the minimum number of characters
in a hyphenated word.
If the word does not meet the required minimum number of characters
in the word / before the hyphen / after the hyphen,
then the word must not be hyphenated.
Nonspacing combining marks (Unicode General Category Mn)
and intra-word punctuation (Unicode General Category P*)
do not count towards the minimum.
If three values are specified,
the first value is the required minimum for the total characters in a word,
the second value is the minimum for characters before the hyphenation point,
and the third value is the minimum for characters after the hyphenation point.
If the third value is missing, it is the same as the second.
If the second value is missing, then it is auto.
The auto value means that
the UA chooses a value that adapts to the current layout.
Note: Unless the UA is able to calculate a better value,
it is suggested that auto means
2 for before and after, and 5 for the word total.
In the example below,
the minimum size of a hyphenated word is left to the UA
(which means it may vary depending on the language,
the length of the line, or other factors),
but the minimum number of characters
before and after the hyphenation point
is set to 3.
p { hyphenate-limit-chars: auto 3; }
5.4.5. Hyphenation Line Limits: the hyphenate-limit-lines and hyphenate-limit-last properties
| Name: | hyphenate-limit-lines |
|---|---|
| Value: | no-limit | <integer> |
| Initial: | no-limit |
| Applies to: | block containers |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | specified keyword or integer |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
| Animation type: | by computed value type |
This property indicates the maximum number of
successive hyphenated lines in an element.
The no-limit value means that there is no limit.
In some cases, user agents may not be able to honor the specified value.
(See overflow-wrap.)
It is not defined whether hyphenation introduced by such emergency breaking
influences nearby hyphenation points.
| Name: | hyphenate-limit-last |
|---|---|
| Value: | none | always | column | page | spread |
| Initial: | none |
| Applies to: | block containers |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | specified keyword |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
| Animation type: | discrete |
This property indicates hyphenation behavior at the end
of elements, column, pages, and spreads.
A spread is a set of two pages
that are visible to the reader at the same time.
Values have the following meanings:
- none
- No restrictions imposed.
- always
- The last full line of the element,
or the last line before any column, page, or spread break inside the element
should not be hyphenated. - column
- The last line before any column, page, or spread break inside the element
should not be hyphenated. - page
- The last line before page or spread break inside the element
should not be hyphenated. - spread
- The last line before any spread break inside the element
should not be hyphenated.
p { hyphenate-limit-last: always }
div.chapter { hyphenate-limit-last: spread }
A paragraph may be formatted like this
when hyphenate-limit-last: none is set:
This is just a simple example to show Antarc- tica.
With ‘hyphenate-limit-last: always’ one would get:
This is just a simple example to show Antarctica.
5.5. Overflow Wrapping: the overflow-wrap/word-wrap property
| Name: | overflow-wrap, word-wrap |
|---|---|
| Value: | normal | break-word | anywhere |
| Initial: | normal |
| Applies to: | text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | specified keyword |
| Canonical order: | n/a |
| Animation type: | discrete |
This property specifies whether the UA may break
at otherwise disallowed points within a line
to prevent overflow,
when an otherwise-unbreakable string is too long to fit within the line box.
It only has an effect when white-space allows wrapping. Possible values:
- normal
- Lines may break only at allowed break points.
However,
the restrictions introduced by word-break: keep-all may be relaxed
to match word-break: normal if there are no otherwise-acceptable break points in the line. - anywhere
- An otherwise unbreakable sequence of characters may be broken at an arbitrary point
if there are no otherwise-acceptable break points in the line.
Shaping characters are still shaped
as if the word were not broken,
and grapheme clusters must stay together as one unit.
No hyphenation character is inserted at the break point. Soft wrap opportunities introduced by anywhere are considered when calculating min-content intrinsic sizes. - break-word
- As for anywhere except that soft wrap opportunities introduced by break-word are not considered
when calculating min-content intrinsic sizes.
For legacy reasons, UAs must treat word-wrap as a legacy name alias of the overflow-wrap property.
6. Text Wrapping
Where text is allowed to wrap is controlled
by the line-breaking rules and controls above; whether it is allowed to wrap
and how multiple soft wrap opportunities within a line are prioritized
is controlled
by the text-wrap, wrap-before, wrap-after,
and wrap-inside properties:
6.1. Text Wrap Settings: the text-wrap property
| Name: | text-wrap |
|---|---|
| Value: | wrap | nowrap | balance | stable | pretty |
| Initial: | wrap |
| Applies to: | text and block containers |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | specified keyword |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
| Animation type: | discrete |
This property specifies the mode for text wrapping.
Possible values:
- wrap
-
Inline-level content may break across lines
at allowed soft wrap opportunities,
as determined by the line-breaking rules in effect
in order to minimize inline-axis overflow.The exact algorithm is UA-defined.
The algorithm may consider multiple lines
when making break decisions.
The UA may bias for speed over best layout.
The UA must not attempt to even out all lines
(including the last) as for balance.
This value selects the UA’s preferred (or most Web-compatible)
wrapping algorithm. - nowrap
- Inline-level content does not break across lines;
content that does not fit within the block container overflows it. - balance
-
Same as wrap for inline boxes.
For block containers that
establish an inline formatting context,
line breaks are chosen to balance
the remaining (empty) space in each line box,
if better balance than wrap is possible.
This must not change the number of line boxes
the block would contain
if text-wrap were set to wrap.The remaining space to consider
is that which remains after placing floats and inline content,
but before any adjustments due to text justification.
Line boxes are balanced when the standard deviation
from the average inline-size of the remaining space in each line box
is reduced over the block
(including lines that end in a forced break).The exact algorithm is UA-defined.
UAs may treat this value as wrap if there are more than ten lines to balance.
- stable
- When applied to a block container that establishes an inline formatting context,
specifies that content on subsequent lines should not be considered when making break decisions
so that when editing text any content before the cursor
remains stable;
otherwise equivalent to wrap, - pretty
- When applied to a block container that establishes an inline formatting context,
specifies the UA should bias for better layout over speed,
and is expected to consider multiple lines,
when making break decisions.
Otherwise equivalent to wrap,
Regardless of the text-wrap value,
lines always break at forced breaks:
for all values,
line-breaking behavior defined
for the BK, CR, LF, CM, NL, and SG line breaking classes
in [UAX14] must be honored.
Additionally, if wrapping is allowed (i.e. text-wrap is not nowrap),
line breaking behavior defined
for the WJ, ZW, and GL line-breaking classes
in [UAX14] must be honored.
UAs that allow breaks at punctuation other than spaces
should prioritize breakpoints.
For example,
if breaks after slashes have a lower priority than spaces,
the sequence “check /etc”
will never break between the ‘/’ and the ‘e’.
The UA may use the width of the containing block,
the text’s language,
and other factors in assigning priorities.
As long as care is taken to avoid such awkward breaks,
allowing breaks at appropriate punctuation other than spaces
is recommended,
as it results in more even-looking margins,
particularly in narrow measures.
Note: The wrap value will typically map
to Web browsers’ speedy legacy line breaking,
which has so far used first-fit/greedy algorithms
that can often give sub-optimal results.
UAs can experiment with better line breaking algorithms
with this default value,
but as optimal results often take more time, pretty is offered as an opt-in
to take more time for better results.
The pretty value is intended for body text,
where the last line is expected to be a bit shorter than the average line;
the balance value is intended for titles and captions,
where equal-length lines of text tend to be preferred;
and the stable is intended for sections that are,
or are likely become toggled as,
editable.
6.2. Controlling Breaks Between Boxes: the wrap-before/wrap-after properties
| Name: | wrap-before, wrap-after |
|---|---|
| Value: | auto | avoid | avoid-line | avoid-flex | line | flex |
| Initial: | auto |
| Applies to: | inline-level boxes and flex items |
| Inherited: | no |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | specified keyword |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
| Animation type: | discrete |
These properties specify modifications to break opportunities
in line breaking (and flex line breaking [CSS3-FLEXBOX]).
Possible values:
- auto
- Lines may break at allowed break points
before and after the box,
as determined by the line-breaking rules in effect. - avoid
- Line breaking is suppressed immediately before/after the box:
the UA may only break there
if there are no other valid break points
in the line.
If the text breaks,
line-breaking restrictions are honored as for auto. - avoid-line
- Same as avoid,
but only for line breaks. - avoid-flex
- Same as avoid,
but only for flex line breaks. - line
- Force a line break immediately before/after the box
if the box is an inline-level box. - flex
- Force a flex line break immediately before/after the box
if the box is a flex item in a multi-line flex container.
Forced line breaks on inline-level boxes propagate upward
through any parent inline boxes the same way forced breaks on block-level boxes propagate upward
through any parent block boxes in the same fragmentation context. [CSS3-BREAK]
6.3. Controlling Breaks Within Boxes: the wrap-inside property
| Name: | wrap-inside |
|---|---|
| Value: | auto | avoid |
| Initial: | auto |
| Applies to: | inline boxes |
| Inherited: | no |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | specified keyword |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
| Animation type: | discrete |
- auto
- Lines may break at allowed break points
within the box,
as determined by the line-breaking rules in effect. - avoid
-
Line breaking is suppressed within the box:
the UA may only break within the box
if there are no other valid break points in the line.
If the text breaks,
line-breaking restrictions are honored as for auto.If boxes with avoid are nested
and the UA must break within these boxes,
a break in an outer box must be used
before a break within an inner box may be used.
6.3.1. Example of using ‘wrap-inside: avoid’ in presenting a footer
The priority of breakpoints can be set
to reflect the intended grouping of text.
Given the rules
footer { wrap-inside: avoid; }
venue { wrap-inside: avoid; }
date { wrap-inside: avoid; }
place { wrap-inside: avoid; }
and the following markup:
<footer> <venue>27th Internationalization and Unicode Conference</venue> • <date>April 7, 2005</date> • <place>Berlin, Germany</place> </footer>
In a narrow window the footer could be broken as
27th Internationalization and Unicode Conference • April 7, 2005 • Berlin, Germany
or in a narrower window as
27th Internationalization and Unicode Conference • April 7, 2005 • Berlin, Germany
but not as
27th Internationalization and Unicode Conference • April 7, 2005 • Berlin, Germany
6.4. Shaping Across Intra-word Breaks
When shaping scripts such as Arabic wrap at unforced soft wrap opportunities within words
(such as when breaking due to word-break: break-all, line-break: anywhere, overflow-wrap: break-word, overflow-wrap: anywhere,
or when hyphenating)
the characters must still be shaped
(their joining forms chosen)
as if the word were still whole.
For example,
if the word “نوشتن” is broken between the “ش” and “ت”,
the “ش” still takes its initial form (“ﺷ”),
and the “ت” its medial form (“ﺘ”)—forming as in “ﻧﻮﺷ | ﺘﻦ”, not as in “نوش | تن”.
6.5. Last Line Minimum Length
See thread.
Issue is about requiring a minimum length for lines.
Common measures seem to be
- At least as long as the text-indent.
- At least X characters.
- Percentage-based.
Suggestion for value space is »match-indent | <length> | <percentage>»
(with Xch given as an example to make that use case clear).
Alternately <integer> could actually count the characters.
It’s unclear how this would interact with text balancing (above);
one earlier proposal had them be the same property
(with 100% meaning full balancing).
People have requested word-based limits, but since this is really
dependent on the length of the word, character-based is better.
7. Alignment and Justification
Alignment and justification controls
how inline content is distributed within a line box.
7.1. Text Alignment: the text-align shorthand
| Name: | text-align |
|---|---|
| Value: | start | end | left | right | center | <string> | justify | match-parent | justify-all |
| Initial: | start |
| Applies to: | block containers |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | see individual properties |
| Computed value: | see individual properties |
| Animation type: | discrete |
| Canonical order: | n/a |
This shorthand property sets the text-align-all and text-align-last properties
and describes how the inline-level content of a block
is aligned along the inline axis
if the content does not completely fill the line box.
Values other than justify-all or match-parent are assigned to text-align-all and reset text-align-last to auto.
Values have the following meanings:
- start
- Inline-level content is aligned
to the start edge of the line box. - end
- Inline-level content is aligned
to the end edge of the line box. - left
- Inline-level content is aligned
to the line-left edge of the line box.
(In vertical writing modes,
this can be either the physical top or bottom,
depending on writing-mode.) [CSS-WRITING-MODES-4] - right
- Inline-level content is aligned
to the line-right edge of the line box.
(In vertical writing modes,
this can be either the physical top or bottom,
depending on writing-mode.) [CSS-WRITING-MODES-4] - center
- Inline-level content is centered within the line box.
- <string>
- The string must be a single character;
otherwise the declaration is invalid and must be ignored.
When applied to a table cell, specifies the alignment character around which the cell’s contents will align.
See below for further details
and how this value combines with keywords. - justify
- Text is justified
according to the method specified by the text-justify property,
in order to exactly fill the line box.
Unless otherwise specified by text-align-last,
the last line before a forced break
or the end of the block
is start-aligned. - justify-all
- Sets both text-align-all and text-align-last to justify,
forcing the last line to justify as well. - match-parent
-
This value behaves the same as inherit (computes to its parent’s computed value)
except that an inherited value of start or end is interpreted against the parent’s direction value
and results in a computed value of either left or right.
Computes to start when specified on the root element.When specified on the text-align shorthand,
sets both text-align-all and text-align-last to match-parent.
A block of text
is a stack of line boxes.
This property specifies how the inline-level boxes within each line box
align with respect to the start and end sides of the line box.
Alignment is not with respect to the viewport or containing block.
In the case of justify,
the UA may stretch or shrink any inline boxes
by adjusting their text.
(See text-justify.)
If an element’s white space is not collapsible,
then the UA is not required to adjust its text
for the purpose of justification
and may instead treat the text
as having no justification opportunities.
If the UA chooses to adjust the text,
then it must ensure
that tab stops continue to line up as required by the white space processing rules.
If (after justification, if any)
the inline contents of a line box are too long to fit within it,
then the contents are start-aligned:
any content that doesn’t fit
overflows the line box’s end edge.
See § 9.3 Bidirectionality and Line Boxes for details on how to determine
the start and end edges
of a line box.
7.2. Character-based Alignment in a Table Column
When multiple cells in a column have an alignment character specified,
the alignment character of each such cell in the column
is centered along a single column-parallel axis
and the rest of the text in the column shifted accordingly.
(Note that the strings do not have to be the same for each cell,
although they usually are.)
Is this intended to say that it’s the centers
of the alignment characters that should be aligned?
It’s not clear that’s what it says,
but that (or a different behavior) needs to be specified,
to describe what happens
when different occurrences of the alignment character
are in different fonts.
(Further, is that the intended behavior? Probably the most
significant use case to consider is bold vs. non-bold text,
which only varies slightly in width.)
[feedback]
[minutes face-to-face 2016-02-02 10:00 AM]
The following style sheet:
TD { text-align: "." center }
will cause the column of dollar figures in the following HTML table:
<TABLE> <COL width="40"> <TR> <TH>Long distance calls <TR> <TD> $1.30 <TR> <TD> $2.50 <TR> <TD> $10.80 <TR> <TD> $111.01 <TR> <TD> $85. <TR> <TD> N/A <TR> <TD> $.05 <TR> <TD> $.06 </TABLE>
to align along the decimal point. The table might be rendered as
follows:
+---------------------+ | Long distance calls | +---------------------+ | $1.30 | | $2.50 | | $10.80 | | $111.01 | | $85. | | N/A | | $.05 | | $.06 | +---------------------+
A keyword value may be specified in conjunction with the <string> value;
if it is not given, it defaults to right.
This value is used:
- when character-based alignment is applied
to boxes that are not table cells. - when the text wraps to multiple lines (at unforced break points).
- when a character-aligned cell spans more than one column.
In this case the keyword alignment value is used
to determine which column’s axis to align with:
the leftmost column for left,
the rightmost column for right and center,
the startmost column for start,
the endmost column for end. - when the column is wide enough that the character alignment alone
does not determine the positions of its character-aligned contents.
In this case the keyword alignment of the first cell in the column
with a specified alignment character
is used to slide the position of the character-aligned contents
to match the keyword alignment
insofar as possible without changing the width of the column.
For center,
the UA may center the aligned contents using its extremes,
center the alignment axis itself (insofar as possible),
or optically center the aligned contents some other way
(such as by taking a weighted average
of the extent of the cells’ contents to either side of the axis).
Note: Right alignment is used by default for character-based alignment
because numbering systems are almost all left-to-right
even in right-to-left writing systems,
and the primary use case of character-based alignment
is for numerical alignment.
If the alignment character appears more than once in the text,
the first instance is used for alignment.
If the alignment character does not appear in a cell at all,
the string is aligned as if
the alignment character had been inserted at the end of its contents.
This needs to specify what text is searched
for the alignment character.
Is it only in-flow text whose containing block is the cell?
Or is text within any in-flow descendants
in the block formatting context established by the cell considered?
If so, is it considered only as long as its text-align property
is consistent with the cell’s?
(Consistent in the alignment character, or fully consistent?)
This behavior of aligning as though he alignment character
had been inserted at the end of the contents of the cell,
combined with center-of-character alignment,
will produce gaps on the end-side of lines
that are alone on a line with <string> text-alignment,
when none of the lines of the column has the alignment character,
or, more importantly, when some of the lines
do have the alignment character,
but the column is not laid out at its max-content width.
This is probably undesirable.
When the alignment character is inserted
at the end of the contents,
which font is used?
(In particular, if the alignment character might be within a descendant block,
is it the font of the block or the font of the table cell?
Or if the insertion is at a forced break within an inline,
does it use the font of the inline or the font of the block or cell?)
Character-based alignment occurs before table cell width computation
so that auto width computations can leave enough space for alignment.
Whether column-spanning cells participate in the alignment
prior to or after width computation is undefined.
If width constraints on the cell contents prevent
full alignment throughout the column,
the resulting alignment is undefined.
This should have a formal definition
of how character alignment affects
the min-content and max-content intrinsic widths
(of table columns and all content that can be inside table columns).
Max-content intrinsic widths need to be split
into three numbers (assuming that it’s the centers of the
alignment character that are aligned):
one for widths without alignment characters,
one for widths on the inline-start side
of the center of the alignment character,
one for widths on the inline-end side
of the center of the alignment character.
This operates based on all segments of text
between forced breaks for max-content widths.
For min-content widths, segments of text between forced breaks
that contain optional breaks within them should clearly contribute
only to the without-alignment-character width.
However, it’s less clear
whether all min-content widths should work this way,
or whether segments between forced breaks
that do not have optional breaks
(and perhaps only those that actually contain the alignment character)
should contribute to start-side-of-alignment-character
and end-side-of-alignment-character min-content widths instead;
this choice is a tradeoff between the meaning of min-content
sizing of a table meaning the narrowest reasonable size versus
honoring alignment characters in more cases.
Another option might be to use whether line-breaking of optional breaks
is allowed as a control for which behavior to use.
Formally defining the intrinsic width contributions
of column-spanning cells with <string> values of text-align is a complicated (although straightforward) extension
of the decisions made for intrinsic width contributions
of non-column-spanning cells;
this should also be formally defined.
Contributions end up being made to the split intrinsic widths
of the startmost or endmost column (whichever is used for alignment),
and to the without-alignment-character intrinsic widths
of the other spanned columns.
7.3. Default Text Alignment: the text-align-all property
| Name: | text-align-all |
|---|---|
| Value: | start | end | left | right | center | justify | match-parent |
| Initial: | start |
| Applies to: | block containers |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | keyword as specified, except for match-parent which computes as defined above |
| Canonical order: | n/a |
| Animation type: | discrete |
This longhand of the text-align shorthand property specifies the inline alignment of all lines of inline content in the block container,
except for last lines
overridden by a non-auto value of text-align-last.
See text-align for a full description of values.
Authors should use the text-align shorthand instead of this property.
7.4. Last Line Alignment: the text-align-last property
| Name: | text-align-last |
|---|---|
| Value: | auto | start | end | left | right | center | justify | match-parent |
| Initial: | auto |
| Applies to: | block containers |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | specified keyword |
| Canonical order: | n/a |
| Animation type: | discrete |
This property describes how the last line of a block or a line
right before a forced line break is aligned.
If auto is specified,
content on the affected line is aligned per text-align-all unless text-align-all is set to justify,
in which case it is start-aligned.
All other values are interpreted as described for text-align.
7.5. Justification Method: the text-justify property
| Name: | text-justify |
|---|---|
| Value: | [ auto | none | inter-word | inter-character ] || no-compress |
| Initial: | auto |
| Applies to: | text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | specified keyword (except for the distribute legacy value) |
| Canonical order: | n/a |
| Animation type: | discrete |
This property selects the justification method
used when a line’s alignment is set to justify (see text-align).
The property applies to text,
but is inherited from block containers
to the root inline box containing their inline-level contents.
It takes the following values:
- auto
-
The UA determines the justification algorithm to follow,
based on a balance between performance and adequate presentation quality.
Since justification rules vary by writing system and language,
UAs should, where possible,
use a justification algorithm appropriate to the text.For example,
the UA could use by default a justification method
that is a simple universal compromise for all writing systems—such as primarily expanding word separators and between CJK typographic letter units along with secondarily expanding
between Southeast Asian typographic letter units.
Then, in cases where the content language of the paragraph is known,
it could choose a more language-tailored justification behavior
e.g. following the Requirements for Japanese Text Layout for Japanese [JLREQ],
using cursive elongation for Arabic,
using inter-word for German,
etc.An example of cursively-justified Arabic text,
rendered by Tasmeem.
Like English,
Arabic can be justified by adjusting the spacing between words,
but in most styles
it can also be justified by calligraphically elongating
or compressing the letterforms themselves.
In this example,
the upper text is extended to fill the line
by the use of elongated (kashida) forms and swash forms,
while the bottom line is compressed slightly
by using a stacked combination for the characters between ت and م.
By employing traditional calligraphic techniques,
a typesetter can justify the line while preserving flow and color,
providing a very high quality justification effect.
However, this is by its nature a very script-specific effect.Mixed-script text with text-justify: auto:
this interpretation uses a universal-compromise justification method,
expanding at spaces as well as between CJK and Southeast Asian letters.
This effectively uses inter-word + inter-ideograph spacing
for lines that have word-separators and/or CJK characters
and falls back to inter-cluster behavior for lines that don’t
or for which the space stretches too far. - none
-
Justification is disabled:
there are no justification opportunities within the text.Mixed-script text with text-justify: none Note: This value is intended for use in user stylesheets
to improve readability or for accessibility purposes. - inter-word
-
Justification adjusts spacing at word separators only
(effectively varying the used word-spacing on the line).
This behavior is typical for languages that separate words using spaces,
like English or Korean.Mixed-script text with text-justify: inter-word - inter-character
-
Justification adjusts spacing
between each pair of adjacent typographic character units (effectively varying the used letter-spacing on the line).
This value is sometimes used in East Asian systems such as Japanese.Mixed-script text with text-justify: inter-character For legacy reasons,
UAs must also support the alternate keyword distribute which must compute to inter-character,
thus having the exact same meaning and behavior.
UAs may treat this as a legacy value alias. - ruby
-
Justification adjusts spacing as for auto except:
-
Justification opportunities are disabled at word separators.
-
Justification opportunities are disabled between Bopomofo characters
Note: This value is intended for use in ruby annotations,
providing a reasonable default alignment.
See [CSS-RUBY-1]. -
- no-compress
-
Justification must not compress spacing controlled by text-spacing-trim or text-autospace.
(If this value is not specified,
the justification process may reduce such spacing
except when the spacing is at the start or end of the line.)Note: An example of compression rules is given for Japanese
in 3.8 Line Adjustment in [JLREQ].This keyword used to be part of text-spacing;
it might need renaming to be more specific now that it’s here,
as it implies that e.g. U+0020 cannot be compressed. [Issue #7079]
Since optimal justification is language-sensitive,
authors should correctly language-tag their content for the best results.
Note: The guidelines in this level of CSS
do not describe a complete justification algorithm.
They are merely a minimum set of requirements
that a complete algorithm should meet.
Limiting the set of requirements gives UAs some latitude
in choosing a justification algorithm
that meets their needs and desired balance of quality, speed, and complexity.
7.5.1. Expanding and Compressing Text
When justifying text,
the user agent takes the remaining space
between the ends of a line’s contents and the edges of its line box,
and distributes that space throughout its content
so that the contents exactly fill the line box.
The user agent may alternatively distribute negative space,
putting more content on the line
than would otherwise fit under normal spacing conditions.
A justification opportunity is a point
where the justification algorithm may alter spacing within the text.
A justification opportunity can be provided by a single typographic character unit (such as a word separator),
or by the juxtaposition of two typographic character units.
As with controls for soft wrap opportunities,
whether a typographic character unit provides a justification opportunity is controlled by the text-justify value of its parent;
similarly,
whether a justification opportunity exists
between two consecutive typographic character units is determined by the text-justify value of their nearest common ancestor.
Space distributed by justification is in addition to the spacing defined by the letter-spacing or word-spacing properties.
When such additional space is distributed
to a word separator justification opportunity,
it is applied under the same rules as for word-spacing.
Similarly, when space is distributed
to a justification opportunity between two typographic character units,
should be applied under the same rules as for letter-spacing.
A justification algorithm may divide justification opportunities into different priority levels.
All justification opportunities within a given level
are expanded or compressed at the same priority,
regardless of which typographic character units created that opportunity.
For example,
if justification opportunities between two Han characters
and between two Latin letters
are defined to be at the same level
(as they are in the inter-character justification style),
they are not treated differently
because they originate from different typographic character units.
It is not defined in this level
whether or how other factors
(such as font size, letter-spacing, glyph shape, position within the line, etc.)
may influence the distribution of space to justification opportunities within the line.
The UA may enable or break optional ligatures
or use other font features
such as alternate glyphs or glyph compression
to help justify the text under any method.
This behavior is not controlled by this level of CSS.
However,
UAs must not break required ligatures
or otherwise disable features required to correctly shape complex scripts.
If a justification opportunity exists within a line,
and text alignment specifies full justification
(justify)
for that line,
it must be justified.
7.5.2. Handling Symbols and Punctuation
When determining justification opportunities,
a typographic character unit from the Unicode Symbols (S*) and Punctuation (P*) classes
is generally treated the same as a typographic letter unit of the same script
(or, if the character’s script property is Common,
then as a typographic letter unit of the dominant script).
However, by typographic tradition
there may be additional rules controlling the justification of symbols and punctuation.
Therefore, the UA may reassign specific characters
or introduce additional levels of prioritization
to handle justification opportunities involving symbols and punctuation.
For example, there are traditionally no justification opportunities between consecutive
U+2014 — EM DASH,
U+2015 ― HORIZONTAL BAR,
U+2026 … HORIZONTAL ELLIPSIS,
or U+2025 ‥ TWO DOT LEADER
characters [JLREQ];
thus a UA might assign these characters to a “never” prioritization level.
As another example, certain full-width punctuation characters
(such as U+301A [ LEFT WHITE SQUARE BRACKET)
are considered to contain a justification opportunity in Japanese.
The UA might therefore assign these characters to a higher prioritization
level than the opportunities between ideographic characters.
7.5.3. Unexpandable Text
If the inline contents of a line cannot be stretched to the full width of the line box,
then they must be aligned as specified by the text-align-last property.
(If text-align-last is justify,
then they must be aligned as for center.)
7.5.4. Cursive Scripts
Justification must not introduce gaps
between the joined typographic letter units of cursive scripts such as Arabic.
If it is able,
the UA may translate space distributed to justification opportunities within a run of such typographic letter units into some form of cursive elongation for that run.
It otherwise must assume that no justification opportunity exists
between any pair of typographic letter units in cursive script (regardless of whether they join).
The following are examples of unacceptable justification:
Some font designs allow for the use of the tatweel character for justification.
A UA that performs tatweel-based justification
must properly handle the rules for its use.
Note that correct insertion of tatweel characters depends on context,
including the letter-combinations involved,
location within the word,
and location of the word within the line.
7.5.5. Minimum Requirements for auto Justification
For auto justification,
this specification does not define
what all of the justification opportunities are,
how they are prioritized,
or when and how multiple levels of justification opportunities interact.
However, it does require that:
-
Unless contraindicated by the typographic traditions
of the content language or adjacent symbols/punctuation,
each of the following provides a justification opportunity:- Word separators
- The boundary between a typographic character unit of any block scripts and any other typographic character unit
- The boundary between a typographic character unit of any clustered scripts and any other typographic character unit
- All letters belonging to all block scripts are treated the same,
and all letters belonging to all clustered scripts are treated the same.
For example, no distinction is made
between the justification opportunity
between a Han letter followed by another Han letter,
vs. the justification opportunity
between a Han letter followed by a Hangul letter.
Further information on text justification can be found in (or submitted to) “Approaches to Full Justification”,
which indexes by writing system and language,
and is maintained by the W3C Internationalization Working Group. [JUSTIFY]
7.6. Aligning a block of text within its container: the text-group-align property
| Name: | text-group-align |
|---|---|
| Value: | none | start | end | left | right | center |
| Initial: | none |
| Applies to: | block containers |
| Inherited: | no |
| Percentages: | N/A |
| Computed value: | specified keyword |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
| Animation type: | discrete |
This property aligns the contents of the line boxes as a group
while maintaining their text alignment.
Group alignment is performed by finding the line box with the shortest remaining space
and adding that amount of space as padding to one or both sides of the line box,
reducing the amount of space available for its contents; text alignment is then applied
to its contents within the remaining space.
All descendant in-flow line boxes within the same block formatting context are considered
both when searching for the shortest remaining space
and when adding the padding;
the contents of descendants that establish independent formatting contexts are skipped.
A variant of this property is inherited,
and applies on each block container individually,
only affecting the line boxes that are direct children of that block.
This is less useful, but probably easier to implement.
Somehow also moving the floats that originate in the same block container
by the same amount
would make things line up more nicely,
which would be especially valuable in CJK layout.
Exactly how that works, and how it interacts with intruding floats
from ancestor elements is left as an exercise for the reader.
Values have the following meanings:
- none
- Text alignment happens normally: group alignment is not performed.
- start
- Inline-level content is group-aligned to the inline start side,
by padding the inline end side of each line box. - end
- Inline-level content is group-aligned to the inline end side,
by padding the inline start side of each line box. - left
- Inline-level content is group-aligned to the line-left side,
by padding the line-right side of each line box. - right
- Inline-level content is group-aligned to the line-right side,
by padding the line-left side of each line box. - center
- Inline-level content is group-aligned to the center,
by padding both sides of each line box,
half the spacing to each side.
8. Spacing
CSS offers control over regular text spacing
via the word-spacing, letter-spacing, and line-padding properties,
which specify additional space
around word separators between typographic character units,
or at the start/end of the line,
respectively.
It also provides contextual control over spacing
via the text-spacing-trim property,
which allows for contextual fullwidth vs halfwidth setting of CJK punctuation;
and the text-autospace property,
which allows automatic insertion of extra space
at script changes or around punctuation.
8.1. Word Spacing: the word-spacing property
| Name: | word-spacing |
|---|---|
| Value: | normal | <length-percentage> |
| Initial: | normal |
| Applies to: | text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | relative to computed font-size, i.e. 1em |
| Computed value: | an absolute length and/or a percentage |
| Canonical order: | n/a |
| Animation type: | by computed value type |
This property specifies additional spacing
between “words”.
Values are interpreted as defined below:
- normal
- No additional spacing is applied.
Computes to zero. - <length-percentage>
-
Specifies extra spacing in addition to the intrinsic inter-word spacing
defined by the font.Note: Percentages inherit intact,
and are resolved against
the computed font-size of the current element
(and thus represent a size relative to
the size of the text to which they apply),
unlike em units which are resolved against
the computed font-size of the element from which they inherit,
as an absolute length.
Additional spacing is applied to each word separator left in the text
after the white space processing rules have been applied,
and should be applied half on each side of the character
unless otherwise dictated by typographic tradition.
Values may be negative, but there may be implementation-dependent limits.
Word-separator characters are typographic character units whose primary purpose and general usage is to separate words.
In Unicode this includes
(but is not exhaustively defined as)
the space (U+0020),
the no-break space (U+00A0),
the Ethiopic word space (U+1361),
the Aegean word separators (U+10100,U+10101),
the Ugaritic word divider (U+1039F),
and the Phoenician word separator (U+1091F). [UNICODE]
Note: Neither punctuation in general,
nor fixed-width spaces (such as U+3000 and U+2000 through U+200A),
are considered word-separator characters,
because even though they frequently happen to separate words,
their primary purpose is not to separate words.
If there are no word-separator characters,
or if a word-separating character has a zero advance width
(such as U+200B ZERO WIDTH SPACE)
then the user agent must not create an additional spacing between words.
8.2. Tracking: the letter-spacing property
| Name: | letter-spacing |
|---|---|
| Value: | normal | <length-percentage> |
| Initial: | normal |
| Applies to: | inline boxes and text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | relative to computed font-size, i.e. 1em |
| Computed value: | an absolute length and/or a percentage |
| Canonical order: | n/a |
| Animation type: | by computed value type |
This property specifies additional spacing
(commonly called tracking)
between adjacent typographic character units.
Letter-spacing is applied after bidi reordering and is in addition to kerning and word-spacing. [CSS-WRITING-MODES-4] [CSS-FONTS-3] Depending on the justification rules in effect,
user agents may further increase or decrease the space
between typographic character units in order to justify text.
Values have the following meanings:
- normal
- No additional spacing is applied. Computes to zero.
- <length>
-
Specifies additional spacing
between typographic character units.
Values may be negative,
but there may be implementation-dependent limits.Note: Percentages inherit intact,
and are resolved against
the computed font-size of the current element
(and thus represent a size relative to
the size of the text to which they apply),
unlike em units which are resolved against
the computed font-size of the element from which they inherit,
as an absolute length.
For legacy reasons,
a computed letter-spacing of zero
yields a resolved value (getComputedStyle() return value)
of normal.
For the purpose of letter-spacing,
each consecutive run of atomic inlines (such as images and inline blocks)
is treated as a single typographic character unit.
Letter-spacing must not be applied at the beginning of a line.
Whether letter-spacing is applied at the end of a line is undefined in this level.
When letter-spacing is not applied at the beginning or end of a line,
text always fits flush with the edge of the block.
p { letter-spacing: 1em; }
<p>abc</p>
a b c
a b c
UAs therefore really should not [RFC6919] append letter spacing to the right or trailing edge of a line:
a b c
Letter spacing between two typographic character units effectively “belongs” to the innermost element
that contains the two typographic character units:
the total letter spacing between two adjacent typographic character units (after bidi reordering)
is specified by and rendered within the innermost element
that contains the boundary
between the two typographic character units.
However, the UA may instead attach letter-spacing at element boundaries
to one or the other typographic character unit using the letter-spacing value pertaining to its containing element.
Note: This secondary behavior is permitted in this level
due to Web-compat concerns.
An inline box is expected to only include
letter spacing between characters completely contained within that element,
thus excluding letter spacing on the right or trailing edge of the element:
p { letter-spacing: 1em; }
<p>a<span>bb</span>c</p>
a b b c
a b b c
Consequently a given value of letter-spacing is expected
to only affect the spacing between characters
completely contained within the element for which it is specified:
p { letter-spacing: 1em; }
span { letter-spacing: 2em; }
<p>a<span>bb</span>c</p>
a b b c
This further implies that applying letter-spacing to
an element containing only a single character
has no effect on the rendered result:
p { letter-spacing: 1em; }
span { letter-spacing: 2em; }
<p>a<span>b</span>c</p>
a b c
Since letter spacing is inserted after RTL reordering,
the letter spacing applied to the inner span below likewise has no effect,
since after reordering the «c» doesn’t end up next to «א»:
p { letter-spacing: 1em; }
span { letter-spacing: 2em; }
<!-- abc followed by Hebrew letters alef (א), bet (ב) and gimel (ג) --> <!-- Reordering will display these in reverse order. --> <p>ab<span>cא</span>בג</p>
a b c א ב ג
Letter spacing ignores invisible zero-width formatting characters
(such as those from the Unicode Cf category).
Spacing must be added as if those characters did not exist in the document.
For example, letter-spacing applied to AB is identical to AB,
regardless of where any element boundaries might fall.
When the effective spacing between two characters is not zero
(due to either justification or a non-zero value of letter-spacing),
user agents should not apply optional ligatures,
i.e. those that are not defined as required
for fundamentally correct glyph shaping.
However, ligatures and other font features
specified via the low-level font-feature-settings property
take precedence over this rule.
See CSS Fonts Module Level 3 § feature-precedence.
For example, if the word “filial” is letter-spaced,
an “fi” ligature should not be used
as it will prevent even spacing of the text.
filial vs filial
Note: In OpenType, required ligatures are expected
to be associated to the rlig feature.
All other ligatures are therefore considered optional.
In some cases, however, UA or platform heuristics
apply additional ligatures in order to handle broken fonts;
this specification does not define or override such exceptional handling.
8.2.1. Cursive Scripts
If it is able,
the UA may apply letter spacing to cursive scripts by translating the total extra space to be distributed to a run of such letters
into some form of cursive elongation
(or compression, for negative tracking values)
for that run
that results in an equivalent total expansion (or compression) of the run.
Otherwise,
if the UA cannot expand text from a cursive script without breaking its cursive connections,
it must not apply spacing
between any pair of that script’s typographic letter units at all
(effectively treating each word as a single typographic letter unit for the purpose of letter-spacing).
Both cases will result in an effective spacing of zero between such letters;
however the former will preserve the sense of stretching out the text.
Note: Proper cursive elongation or compression of a text
can vary depending on the
script,
typeface,
language,
location within a word,
location within a line,
implementation complexity,
font capabilities,
and calligraphic preferences,
and may not be possible in certain cases at all.
It may involve the use of shortening ligatures,
swash variants,
contextual forms,
elongation glyphs such as U+0640 ـ ARABIC TATWEEL,
or other microtypography.
It is outside the scope of CSS to define rules for these effects.
Authors should avoid applying letter-spacing to cursive scripts
unless they are prepared to accept non-interoperable results.
8.3. Line Start/End Padding: the line-padding property
| Name: | line-padding |
|---|---|
| Value: | <length> |
| Initial: | 0 |
| Applies to: | inline boxes |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | N/A |
| Computed value: | absolute length |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
| Animation type: | by computed value type |
Whereas letter-spacing adjusts spacing
between typographic letter units and does not apply at the start or end of a line,
this property adjusts spacing only at the start/end of a line.
The extra spacing is applied only
by the innermost inline box at the start/end of the line box,
and is inserted between that inline box’s content edge
and the adjacent inline-level content
(text or atomic inline).
This extra space is not a justification opportunity.
Given the following HTML and CSS:
p { line-padding: 0.5em; line-height: 1; text-align: center }
span { background: black; color: white; }
em { background: green; color: white; }
<p><span>Here is <em>some text</em></span>
Line-padding will be inserted such that
an extra 0.5em of inline background will be visible
on each side of each line.
If it renders such that there is a break between “some” and “text”,
the additional padding will be:
on the first line, black on the left and green on the right,
and on the second line, green on both sides.
Here is some
text
8.4. Automatic Contextual Spacing: the text-autospace property
| Name: | text-autospace |
|---|---|
| Value: | normal | <autospace> | auto |
| Initial: | normal |
| Applies to: | text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | N/A |
| Computed value: | specified keyword(s) |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
| Animation type: | discrete |
Controls spacing between adjacent characters
on the same line within the same inline formatting context using a set of character-class-based rules,
allowing for automatic control over inter-script spacing
and for spacing around punctuation.
Values are defined as follows:
<autospace> = no-autospace |
[ ideograph-alpha || ideograph-numeric || punctuation ]
|| [ insert | replace ]
- normal
- Same behavior as ideograph-alpha ideograph-numeric.
- no-autospace
- No automatic space is inserted.
- insert
-
The specified spacing is automatically inserted
if there are no space characters of any kind (Unicode general categoryZ) already there.If neither insert nor replace are specified,
the behavior is the same as insert. - replace
-
The specified spacing is automatically inserted
even if there is already a space (U+0020) at that point;
additionally, the space (U+0020) is removed.
Other types of space characters (Unicode general categoryZ)
suppress automatic spacing, as for insert.Note: This is for correcting text which is using the easy-to-type U+0020
instead of proper spacing. - ideograph-alpha
- Creates extra spacing between runs of ideographs and non-ideographic letters,
see § 8.4.1 Inter-script Spacing. - ideograph-numeric
- Creates extra spacing between runs of ideographs and non-ideographic numerals,
see § 8.4.1 Inter-script Spacing. - punctuation
-
Creates extra non-breaking spacing around punctuation as required by language-specific typographic conventions.
In this level, if the element’s content language is French,
narrow no-break space (U+202F) and no-break space (U+00A0) is inserted
where required by French typographic guidelines.
Otherwise this value has no effect.
However future specifications may add automatic spacing behavior for other languages. - auto
-
The user agent chooses a set of typographically high quality spacing values.
Different user agents running on different platforms may pick different values.Note: These spacing values may or may not match OS platform conventions.
This property is additive with the word-spacing and letter-spacing properties.
That is, the amount of spacing contributed by the letter-spacing setting (if any)
is added to the spacing created by text-autospace.
The same applies to word-spacing.
At element boundaries, the amount of extra spacing introduced between characters
is determined by and rendered within the innermost element that contains the boundary.
8.4.1. Inter-script Spacing
The ideograph-alpha and ideograph-numeric values
introduce spacing at the boundary between particular classes of characters
when they are directly adjoining on a line,
i.e. without any intervening non-zero margin, border, or padding or intervening characters (such as a quotation mark or a space).
The amount of space introduced by these keywords is 1/8 of the CJK advance measure,
i.e 0.125ic.
Note: Spacing conventions vary, but values typically range from 1/4ic to as low as 1/8ic,
with 1/4ic being more common in historical contexts due to metal type limitations
and 1/6ic or thinner being more common in proportional typesetting.
Because these spaces are inserted by default
(through the initial value, normal),
CSS uses 1/8ic in order to be conservative in its interference.
A future level of this module may introduce control
over the amount of spacing.
8.5. CJK Punctuation Spacing: the text-spacing-trim property
| Name: | text-spacing-trim |
|---|---|
| Value: | <spacing-trim> | auto |
| Initial: | space-first |
| Applies to: | text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | N/A |
| Computed value: | specified keyword(s) |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
| Animation type: | discrete |
Controls spacing around CJK punctuation characters
on the same line within the same inline formatting context using a set of character-class-based rules,
allowing them to be set halfwidth or fullwidth
based on their position and neighbors within the line.
Values are defined as follows:
<spacing-trim> = space-all | trim-auto | [ allow-end || space-first ]
- space-all
- All fullwidth punctuation characters are set with full-width glyphs (spaced).
- trim-auto
- Set fullwidth opening punctuation with half-width glyphs (flush)
at the start of each line;
set fullwidth closing punctuation with half-width glyphs (flush)
at the end of each line;
and collapse spacing between punctuation glyphs as described below. - space-first
-
Set fullwidth opening punctuation with full-width glyphs (spaced)
on the first line the block container.
Otherwise as trim-auto (unless allow-end is also specified).This value exists for compat requirements.
This value exists to manage formatting of existing Chinese and Japanese content,
for which trim-auto would have been appropriate typographically,
except that they are already written
to expect the first line to be set as for space-all.Specifically,
due to the lack of reliable hanging-punctuation support across UAs,
existing content (especially ePub content)
uses U+3000 ideographic space in place of text-indent,
but omits it when the paragraph begins with punctuation
that is desired to hang in the indent
in order to create the hanging punctuation effect.
Using trim-auto on the first line
would thus trim away the effective indent in such content
and thus obscure that line’s distinction
as the first line of a new paragraph.Note that this typesetting practice
of using ideographic spaces for indentation
(sometimes and not always)
is contrary to the separation of content and style offered by HTML and CSS.
Using hanging-punctuation and text-indent to control paragraph formatting
rather than tweaking the text content of the document
preserves the text’s true semantics in the document source
and allows the style sheet designer
to freely switch among the various spacing/indentation styles
without needing to alter the content.
See § 8.5.3 Japanese Paragraph-start Conventions in CSS for examples. - allow-end
- Set fullwidth closing punctuation with half-width glyphs (flush)
at the end of each line
if it does not otherwise fit prior to justification,
else set the punctuation with full-width glyphs.
Otherwise as trim-auto (unless space-first is also specified). - auto
-
The user agent chooses a set of typographically high quality spacing values.
Different user agents running on different platforms may pick different values.Note: These spacing values may or may not match OS platform conventions.
Do we need auto? It would be weird for the author to choose platform-dependent behavior at the start of the first line, and it should otherwise use trim-auto.
8.5.1. Fullwidth Punctuation Collapsing
Typically, fullwidth characters have glyphs with the same advance width
as a standard Han character (e.g. 水 U+6C34).
However, many fullwidth punctuation glyphs only take up part of the fullwidth design space.
Thus such punctuation are not always set fullwidth.
Several values of text-spacing-trim allow the author to control
when such characters are set half-width (typically half the width of an ideograph)
and when they are set full-width.
In order to set the text as specified, the UA will need to either
- trim (kern) the blank half of the glyphs,
if they are given full-width and must be set half-width, or - add space to the glyphs,
if they are given half-width and must be set full-width.
The UA may use the OpenType halt and vhal features
if implemented by a font
in order to perform the requisite trimming of a particular glyph.
The UA must not use the hwid feature
or otherwise substitute halfwidth forms
as switching to halfwidth glyphs can change the glyph shape
which is not acceptable here.
Some fonts use proportional glyphs for fullwidth punctuation characters.
If there is no support in the font for distinguishing
fullwidth vs halfwidth glyph shapes
(e.g. through font features),
then for such proportional glyphs,
the given advance width is considered
simultaneously full-width and half-width:
the UA must not add or remove space to these glyphs.
Note: The advance width of a standard Han character
can be determined either from font metrics
such as the OpenType ideo and idtp baselines for the opposite writing mode,
or by taking the advance width of a Han character such as 水 U+6C34.
(The opposite writing mode must be used because some fonts are compressed
so that the characters are not square.)
More information on OpenType metrics can be found in the OpenType spec.
Note that if 水 U+6C34, 卜 U+535C, and 一 U+4E00 do not all have the same advance width,
the font has proportional ideographs
and the fullwidth advance width cannot be reliably determined by measuring glyphs.
Unless text-spacing-trim is set to space-all (or the font has proportional fullwidth punctuation glyphs),
the UA must collapse the space typically associated with such full width glyphs
when placed adjacently on a line
as follows:
-
Set fullwidth opening punctuation half-width if the previous character is any of:
-
a fullwidth opening punctuation
-
a fullwidth middle dot punctuation
-
an ideographic space (U+3000)
-
a fullwidth closing punctuation of an equivalent or larger font-size
-
a character belonging to Unicode general category
Ps
Otherwise set it full-width.
-
-
Set fullwidth closing punctuation half-width if the next character is any of:
-
a fullwidth closing punctuation
-
a fullwidth middle dot punctuation
-
an ideographic space (U+3000)
-
a fullwidth opening punctuation of a larger font-size
-
a character belonging to Unicode general category
Pe
Otherwise set it full-width.
-
The following example table lists the punctuation pairs
affected by adjancent-pairs trimming.
It uses halfwidth equivalents to approximate the trimming effect.
| Combination | Sample Pair | Looks Like |
|---|---|---|
| Opening—Opening | 〔+( | 〔( |
| Middle Dot—Opening | ・+( | ・( |
| Closing—Opening | 〕+( | 〕( |
| Ideographic Space—Opening | +( | ( |
| Closing—Closing | )+〕 | )〕 |
| Closing—Middle Dot | )+・ | )・ |
| Closing—Ideographic Space | )+ | ) |
8.5.2. Text Spacing Character Classes
In the context of this property the following definitions apply:
Classes and Unicode code points need to be reviewed.
- ideographs
-
Includes all typographic character units [CSS-TEXT-3] whose base character is listed below:
- All characters in the range of U+3041 to U+30FF,
except those that belong to Unicode Punctuation [P*] general category. - CJK Strokes (U+31C0 to U+31EF).
- Katakana Phonetic Extensions (U+31F0 to U+31FF).
- All characters that have the Han script property.
- All characters in the range of U+3041 to U+30FF,
- non-ideographic letters
-
Includes all typographic character units that
belong to Unicode Letters [L*] and Mark [M*] general category,
except when any of the following conditions are met:- is defined as ideograph.
- is categorized as East Asian Fullwidth (F) by [UAX11].
- is upright in vertical text flow using the text-orientation property
or the text-combine-upright property.
- non-ideographic numerals
-
Includes all typographic character units that
belong to the Unicode Decimal Digit Number [Nd] general category,
except when any of the following conditions are met:- is categorized as East Asian Fullwidth (F) by [UAX11].
- is upright in vertical text flow using the text-orientation property
or the text-combine-upright property.
- fullwidth opening punctuation
- Includes any opening punctuation character (Unicode category
Ps)
that belongs to the CJK Symbols and Punctuation block (U+3000–U+303F)
or is categorized as East Asian Fullwidth (F) by [UAX11].
Also includes LEFT SINGLE QUOTATION MARK (U+2018) and LEFT DOUBLE QUOTATION MARK (U+201C).
When trimmed, the left (for horizontal text) or top (for vertical text) half is kerned. - fullwidth closing punctuation
- Includes any closing punctuation character (Unicode category
Pe)
that belongs to the CJK Symbols and Punctuation block (U+3000–U+303F)
or is categorized as East Asian Fullwidth (F) by [UAX11].
Also includes RIGHT SINGLE QUOTATION MARK (U+2019) and RIGHT DOUBLE QUOTATION MARK (U+201D).
May also include fullwidth colon punctuation and/or fullwidth dot punctuation (see below).
When trimmed, the right (for horizontal text) or bottom (for vertical text) half is kerned. - fullwidth middle dot punctuation
- Includes MIDDLE DOT (U+00B7), HYPHENATION POINT (U+2027), and KATAKANA MIDDLE DOT (U+30FB).
May also include fullwidth colon punctuation and/or fullwidth dot punctuation (see below). - fullwidth colon punctuation
- Includes FULLWIDTH COLON (U+FF1A) and FULLWIDTH SEMICOLON (U+FF1B).
- fullwidth dot punctuation
- Includes
IDEOGRAPHIC COMMA (U+3001),
IDEOGRAPHIC FULL STOP (U+3002),
FULLWIDTH COMMA (U+FF0C),
FULLWIDTH FULL STOP (U+FF0E).
Whether fullwidth colon punctuation and fullwidth dot punctuation should be considered fullwidth closing punctuation or fullwidth middle dot punctuation depends on where in the glyph’s box the punctuation is drawn.
If the punctuation is centered,
then it should be considered middle dot punctuation.
If the punctuation is drawn to one side (left in horizontal text, top in vertical text)
and the other half is therefore blank
then the punctuation should be considered closing punctuation and trimmed accordingly.
The UA must classify fullwidth colon punctuation and fullwidth dot punctuation under either the fullwidth closing punctuation category or the fullwidth middle dot punctuation category
as appropriate.
The UA may rely on language conventions and the writing mode (horizontal vs. vertical),
and/or font information to determine this categorization.
The UA may also add additional characters to any category as appropriate.
The following informative table summarizes language conventions
for classifying fullwidth colon and dot punctuation:
| colon punctuation | dot punctuation | |
|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese (horizontal) | closing | closing |
| Simplified Chinese (vertical) | closing | closing |
| Traditional Chinese | middle dot | middle dot |
| Korean | middle dot | closing |
| Japanese | middle dot | closing |
Note that for Chinese fonts at least,
the author observes that the standard convention is often not followed.
8.5.3. Japanese Paragraph-start Conventions in CSS
Japanese has three common start-edge typesetting schemes,
which are distinguished by their handling of opening brackets.
Positioning of opening brackets at line head [JLREQ]
Assuming a UA style sheet of p { margin: 1em 0; },
CSS can achieve the Japanese typesetting styles with the following rules:
-
Brackets flush with indent, flush with other lines (first scheme):
p { /* Flush alignment */ margin: 0; text-indent: 1em; text-spacing-trim: trim-auto; } -
Brackets preserve fullwidth spacing on all lines (second scheme):
p { /* Fullwidth alignment */ margin: 0; text-indent: 1em; text-spacing-trim: space-all; } -
Brackets hang in indent, flush with other lines (third scheme):
p { /* Hanging alignment */ margin: 0; text-indent: 1em; text-spacing-trim: trim-auto; hanging-punctuation: first; }
8.6. Character Class Spacing Shorthand: the text-spacing property
| Name: | text-spacing |
|---|---|
| Value: | normal | none | auto | <autospace> || <spacing-trim> |
| Initial: | see individual properties |
| Applies to: | text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | N/A |
| Computed value: | specified keyword(s) |
| Animation type: | discrete |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
This property is a shorthand
for setting text-spacing-trim and text-autospace in a single declaration.
Values are defined as follows:
- normal
- Specifies the baseline behavior,
setting each sub-property to its initial value.
Equivalent to space-first ideograph-alpha ideograph-numeric. - none
- Turns off all text-spacing features:
sets text-spacing-trim to space-all and text-autospace to no-autospace. - auto
- Sets both text-spacing-trim and text-autospace to auto.
- <spacing-trim>
- Sets text-spacing-trim to the specified value.
If no <autospace> value is given, text-autospace is set to its initial value. - <autospace>
- Sets text-autospace to the specified value.
If no <spacing-trim> value is given, text-spacing-trim is set to its initial value.
8.7. Shaping Across Element Boundaries
Text shaping must be broken at inline box boundaries
when any of the following are true
for any box whose boundary separates the two typographic character units:
- Any of margin/border/padding separating the two typographic character units in the inline axis
is non-zero. - vertical-align is not baseline.
- The boundary is a bidi isolation boundary.
Text shaping must not be broken across inline box boundaries
when there is no effective change in formatting,
or if the only formatting changes do not affect the glyphs
(as in applying text decoration).
Text shaping should not be broken across inline box boundaries otherwise,
if it is reasonable and possible for that case given the limitations of the font technology.
An example of reasonable and possible shaping across boundaries
is Arabic shaping:
in many systems this is performed by the font engine,
allowing the font to provide variant glyphs
with potentially very sophisticated contextual shaping.
It’s not generally possible to rely on this system across a font change
unless the font engine has an API to provide context,
but it is straightforward and therefore quite reasonable
for an engine to work around this limitation by, for example,
using the zero-width-joiner (U+200D) or zero-width-non-joiner (U+200C)
as appropriate to solicit the correct choice of
initial/medial/final/isolated glyph.
An example of possible but not reasonable shaping across boundaries
is handling a font that is sensitive to 20 characters of context
on either side to choose its glyphs:
passing all the text before and after the string in question,
even through multiple inline boundaries with formatting changes,
is complicated.
The UA could handle such cases,
but is not required to,
as they are not typical or fundamentally required
by any modern writing system.
An example of impossible shaping across boundaries
is a change in font weight partway through the word “and”
in a font where a ligature would replace
all three letters of the word “and”
with an ampersand glyph (“&”).
9. Edge Effects
Edge effects control
the indentation of lines with respect to other lines in the block (text-indent)
and how content is measured at the start and end edges of a line (hanging-punctuation).
9.1. First Line Indentation: the text-indent property
| Name: | text-indent |
|---|---|
| Value: | [ <length-percentage> ] && hanging? && each-line? |
| Initial: | 0 |
| Applies to: | block containers |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | refers to block container’s own inline-axis inner size |
| Computed value: | computed <length-percentage> value, plus any specified keywords |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
| Animation type: | by computed value type |
This property specifies the indentation
applied to lines of inline content in a block.
The indent is treated as a margin
applied to the start edge of the line box.
Unless otherwise specified
by the each-line and/or hanging keywords,
only lines that are the first formatted line of an element are affected. [CSS-PSEUDO-4] For example, the first line of an anonymous block box is only affected
if it is the first child of its parent element.
Values have the following meanings:
- <length>
- Gives the amount of the indent as an absolute length.
- <percentage>
-
Gives the amount of the indent
as a percentage of the block container’s own logical width.Percentages must be treated as 0 for the purpose of calculating intrinsic size contributions,
but are always resolved normally when performing layout.Note: This can lead to the element overflowing.
It is not recommended to use percentage indents and intrinsic sizing together. - each-line
- Indentation affects the first line of each block container
and each line after a forced line break (but not lines after a soft wrap break). - hanging
- Inverts which lines are affected.
If text-align is start and text-indent is 5em in
left-to-right text with no floats present, then first line of text
will start 5em into the block:
Since CSS1 it has been possible to indent the first line of a block element 5em by setting the 'text-indent' property to '5em'.
If we add the hanging keyword,
then the first line will start flush,
but other lines will be indented 5em:
In CSS3 we can instead indent all other
lines of the block element by 5em
by setting the 'text-indent' property
to 'hanging 5em'.
Since the text-indent property only affects the “first formatted line”,
a line after a forced break will not be indented.
For example, in the middle of
this paragraph is an equation,
which is centered:
x + y = z
The first line after the equation
is flush (else it would look like
we started a new paragraph).
However, sometimes (as in poetry or code),
it is appropriate to indent each line
that happens to be long enough to wrap.
In the following example, text-indent is given a value of 3em hanging each-line,
giving the third line of the poem a hanging indent
where it soft-wraps at the block’s right boundary:
In a short line of text There need be no wrapping, But when we go on and on and on and on, Sometimes a soft break Can help us stay on the page.
Note: Since the text-indent property inherits,
when specified on a block element, it will affect descendant
inline-block elements.
For this reason, it is often wise to specify text-indent: 0 on
elements that are specified display: inline-block.
9.2. Hanging Glyphs
When a glyph at the start or end edge of a line hangs,
it is not considered
when measuring the line’s contents for fit, alignment, or justification.
Depending on the line’s alignment/justification, this can
result in the mark being placed outside the line box.
The hanging glyph is also not taken into account
when computing intrinsic sizes (min-content size and max-content size),
and any sizes derived thereof.
(The interaction of this measurement and kerning is currently UA-defined;
the CSSWG welcomes advice on this point.)
A hanging glyph is still enclosed inside its parent inline box
and still participates in text justification:
its character advance is just not measured when determining
how much content fits on the line,
how much the line’s contents need to be expanded or compressed for justification,
or how to position the content within the line box for text alignment.
Effectively, the hanging glyph character advance
is re-interpreted as an additional negative margin
on the affected edge of its parent inline box;
the line is otherwise laid out as usual.
An overflowing hanging glyph should typically be considered ink overflow so as to avoid creating unnecessary scrollbars,
but the UA may treat it as scrollable overflow when the content is editable
or in other circumstances where treating it as scrollable overflow would be useful to the user. [CSS-OVERFLOW-3]
In some cases, a glyph at the end of a line
can conditionally hang:
it hangs only if it does not otherwise fit in the line prior to justification.
It is not considered when measuring the line’s contents for fit;
however, any part of it that does not fit
is considered to hang.
Glyphs that conditionally hang are not taken into account
when computing min-content sizes and any sizes derived thereof,
but they are taken into account for max-content sizes and any sizes derived thereof.
Non-zero inline-axis borders or padding between
a hangable glyph and the edge of the line prevent the glyph from hanging.
For example, a period at the end of an inline box with end padding
does not hang at the end edge of a line.
Multiple adjacent glyphs can hang together,
however specific limits on how many are allowed to hang may be specified
(e.g. at most one punctuation character may hang at each edge of the line).
9.2.1. Hanging Punctuation: the hanging-punctuation property
| Name: | hanging-punctuation |
|---|---|
| Value: | none | [ first || [ force-end | allow-end ] || last ] |
| Initial: | none |
| Applies to: | text |
| Inherited: | yes |
| Percentages: | n/a |
| Computed value: | specified keyword(s) |
| Canonical order: | per grammar |
| Animation type: | discrete |
This property determines whether a punctuation mark,
if one is present, hangs and may be placed outside the line box (or in the indent)
at the start or at the end of a line of text.
Note: If there is not sufficient padding on the
block container, hanging-punctuation can trigger overflow.
Values have the following meanings:
- none
- No punctuation character is made to hang.
- first
- An opening bracket, quote, or ideographic space at the start
of the first formatted line of an element hangs.
This applies to all characters in the Unicode categories Ps, Pf, Pi
plus the ASCII quote marks U+0027 ‘ APOSTROPHE and U+0022 » QUOTATION MARK
and the IDEOGRAPHIC SPACE U+3000. - last
- A closing bracket or quote at the end
of the last formatted line of an element hangs.
This applies to all characters in the Unicode categories Pe, Pf, Pi
plus the ASCII quote marks U+0027 ‘ APOSTROPHE and U+0022 » QUOTATION MARK. - force-end
- A stop or comma at the end of a line hangs.
- allow-end
- A stop or comma at the end of a line conditionally hangs.
At most one punctuation character may hang at each edge of the line.
Stops and commas allowed to hang include:
| U+002C | , | COMMA |
| U+002E | . | FULL STOP |
| U+060C | ، | ARABIC COMMA |
| U+06D4 | ۔ | ARABIC FULL STOP |
| U+3001 | 、 | IDEOGRAPHIC COMMA |
| U+3002 | 。 | IDEOGRAPHIC FULL STOP |
| U+FF0C | , | FULLWIDTH COMMA |
| U+FF0E | . | FULLWIDTH FULL STOP |
| U+FE50 | ﹐ | SMALL COMMA |
| U+FE51 | ﹑ | SMALL IDEOGRAPHIC COMMA |
| U+FE52 | ﹒ | SMALL FULL STOP |
| U+FF61 | 。 | HALFWIDTH IDEOGRAPHIC FULL STOP |
| U+FF64 | 、 | HALFWIDTH IDEOGRAPHIC COMMA |
The UA may include other characters as appropriate.
Note: The CSS Working Group would appreciate if UAs including
other characters would inform the working group of such additions.
The allow-end and force-end are two variations
of hanging punctuation used in East Asia.
The punctuation at the end of the first line for allow-end does not hang, because it fits without hanging.
However, if force-end is used, it is forced to hang.
The justification measures the line without the hanging punctuation.
Therefore when the line is expanded, the punctuation is pushed outside the line.
9.3. Bidirectionality and Line Boxes
The start and end sides of a line box
are determined by the inline base direction of the line box.
Although they usually match,
the inline base direction of a line box is distinct from the inline base direction of the containing block or the bidi paragraph.
The line box’s inline base direction affects text-align-all, text-align-last, text-indent, and hanging-punctuation—i.e. the position and alignment of its contents with respect to its edges.
It does not affect the formatting or ordering of inline content
(which is controlled by the Unicode Bidirectional Algorithm as applied by CSS Writing Modes [UAX9] [CSS-WRITING-MODES-4]).
In most cases, a line box’s inline base direction is given by its containing block’s computed direction.
However,
if its containing block has unicode-bidi: plaintext [CSS-WRITING-MODES-4]:
- If the bidi paragraph to which the line box belongs
(that is, the bidi paragraph for which the line box holds content)
has strong directionality,
the line box’s inline base direction is that direction. - If the line box is empty
(i.e. contains no atomic inlines or
characters other than the newline character, if any)
or otherwise has no strong directionality
(contains only weak or neutral characters),
its inline base direction is taken
from the preceding line box (if any),
or, if this is the first line box in the containing block,
from the direction property of the containing block.
(This can result in an RTL line box whose contents have an LTR base direction.)
In the following example,
assuming the <block> is a start-aligned preformatted block
(display: block; white-space: pre; text-align: start),
every other line is right-aligned:
<block style="unicode-bidi: plaintext"> français فارسی français فارسی français فارسی </block>
Because neutral characters (such as punctuation)
and isolated runs are skipped
when finding the inline base direction of a plaintext bidi paragraph,
the line box in the following example will be left-to-right
(and thus left-aligned given text-align: start),
as dictated by the first strong character, ‘h’:
<para style="display: block; direction: rtl; unicode-bidi:plaintext"> “<quote style="unicode-bidi:plaintext">שלום!</quote>”, he said. </para>
<textarea style="direction: rtl; unicode-bidi:plaintext"> Hello! </textarea>
Because of unicode-bidi: plaintext,
the “Hello!” is typeset LTR
(i.e. with the exclamation mark on the right side)
and left-aligned,
ignoring the containing block’s RTL direction.
This makes the empty line following it LTR as well,
which means that a caret on that line should appear at its left edge.
The empty first line, however, is right-aligned:
having no preceding line,
it assumes the RTL direction of its containing block.
Appendix A:
Text Processing Order of Operations
This appendix is normative.
The following list defines the order of text operations.
(Implementations are not bound to this order as long as the resulting layout is the same.)
- § 4.2 White Space Trimming: the white-space-trim property and § 2.2.2 Making Word Boundaries Visible: the word-boundary-expansion property
- white space processing part I (pre-wrapping)
- text transformation
- text combination [CSS-WRITING-MODES-4]
- text orientation [CSS-WRITING-MODES-4]
-
text wrapping while applying per line:
-
indentation
-
bidirectional reordering [CSS2] / [CSS-WRITING-MODES-4]
-
white space processing part II
-
font/glyph selection and positioning [CSS-FONTS-3]
-
letter-spacing, word-spacing, text-spacing, and line-padding
-
hanging punctuation
-
- justification (which may affect glyph selection and/or text wrapping, looping back into that step)
- text alignment
- text group alignment
Appendix B:
Conversion to Plaintext
This appendix is normative for the purpose of plaintext copy-paste operations.
When a CSS-rendered document is converted to a plaintext format,
it is expected that:
- The text-transform property has no effect.
- white-space-trim and § 4.3.1 Phase I: Collapsing and Transformation is applied
and any sequence of collapsible white space at the beginning of a block or immediately following a forced line break is removed.
Appendix C:
Default UA Stylesheet
This appendix is informative, and is to help UA developers to implement a default stylesheet for HTML,
but UA developers are free to ignore or modify as appropriate.
/* make option elements align together */
option { text-align: match-parent; }
/* do not allow white space to collapse in textarea */
textarea { white-space-collapse: preserve !important; }
/* preserve character grid in preformatted text */
pre, code, kbd, samp, tt { text-spacing: none; }
Appendix D:
Scripts and Spacing
This appendix is normative.
Typographic behavior varies somewhat by language,
but varies drastically by writing system.
This appendix categorizes some common scripts in Unicode 6.0
according to their justification and spacing behavior.
Category descriptions are descriptive, not prescriptive;
the determining factor is the prioritization of justification opportunities.
- block scripts
- CJK and by extension all Wide characters
(see East Asian Width [UAX11]).
The following Unicode scripts are included:
Bopomofo, Han, Hangul, Hiragana, Katakana, and Yi.
Characters of the East Asian Width propertyWideandFullwidthare also included,
butAmbiguouscharacters are included
only if the writing system is Chinese, Korean,
or Japanese. - clustered scripts
- Clustered scripts have discrete units
and break only at word boundaries,
but do not use visible word separators.
They prioritize stretching spaces,
but comfortably admit inter-character spacing for justification.
The clustered scripts include,
but are not limited to,
the following Unicode scripts:
Khmer,
Lao,
Myanmar,
New Tai Lue,
Tai Le,
Tai Tham,
Tai Viet,
Thai - cursive scripts
-
Cursive scripts do not admit gaps
between their letters for either justification or letter-spacing.
The following Unicode scripts are included:
Arabic,
Mandaic,
Mongolian,
N’Ko,
Phags Pa,
SyriacNote: Indic scripts with baseline connectors
(such as Devanagari and Gujarati) are not considered cursive scripts,
and do admit such gaps
between typographic character units.
See Indic Layout Requirements. [ILREQ]
User agents should update this list
as they update their Unicode support
to handle as-yet-unencoded cursive scripts in future versions of Unicode,
and are encouraged to ask the CSSWG to update this spec accordingly.
Appendix E:
Characters and Properties
This appendix is normative.
Unicode defines four code point-level properties
that are referenced in CSS typesetting:
- East Asian width property
- Defined in Unicode Standard Annex #11 [UAX11] and given as the
East_Asian_Widthproperty
in the Unicode Character Database [UAX44]. - general category
- Defined in Unicode Standard Annex #44 [UAX44] and given as the
General_Categoryproperty
in the Unicode Character Database [UAX44]. - script property
- Defined in Unicode Standard Annex #24 [UAX24] and given as the
Scriptproperty
in the Unicode Character Database [UAX44].
(UAs must include any ScriptExtensions.txt assignments in this mapping.) - Vertical Orientation
- Defined in Unicode Standard Annex #50 [UAX50] as the Vertical_Orientation property
in the Unicode Character Database [UAX44].
Unicode defines properties for individual code points,
but sometimes it is necessary to determine the properties
of a typographic character unit.
For the purposes of CSS Text,
the properties of a typographic character unit are given
by the base character of its first grapheme cluster—except in two cases:
- Grapheme clusters formed with an Enclosing Mark
(Me)
of the Common script
are considered to be Other Symbols
(So)
in the Common script.
They are assumed to have the same Unicode properties
as the replacement character (U+FFFD). - Grapheme clusters formed with a Space Separator
(Zs)
as the base
are considered to be Modifier Symbols
(Sk).
They are assumed to have the same East Asian Width property as the base,
but take their other properties
from the first combining character in the sequence.
Appendix F:
Identifying the Content Writing System
This appendix is normative.
While most languages have a preferred writing system,
some have multiple, and
most can also be transcribed into one or more foreign writing systems.
As a common example, most languages have at least one Latin transcription,
and can thus be written in the Latin writing system.
Transcribed texts typically adopt the typographic conventions of the writing system:
for example Japanese “romaji” and Chinese Pinyin use Latin letters and word spaces,
and follow Latin line-breaking and justification practices accordingly.
As another example, historical ideographic Korean
(ko-Hani)
does not use word spaces,
and should therefore be typeset similar to Chinese
rather than modern Korean.
In HTML or any other document language using BCP47 tags for identifying languages to declare the content language,
authors can disambiguate or indicate the use of an atypical writing system
with script subtags. [BCP47] For example, to indicate use of the Latin writing system
for languages which don’t natively use it,
the -Latn script subtag can be added,
e.g. ja-Latn for Japanese romaji.
Other subtags exist for other writing systems,
see ISO’s Code for the Representation of Names of Scripts and the ISO15924 script tag registry. [ISO15924]
Some common/historical examples of using BCP47 tags with script subtags:
zh-Latn- Chinese, written in Latin transcription.
ko-Hani- Korean, written in Hanja (Chinese ideographic characters).
tr-Arab- Turkish, written in Arabic script.
mn-Cyrl- Mongolian, written in Cyrillic.
mn-Mong- Mongolian, written in traditional Mongolian script.
However, BCP47 script subtags are not typically used
(and are in fact discouraged)
for languages strongly associated with a single writing system:
instead that writing system is expected to be implied
when no other is specified. [BCP47] IANA maintains a database of various languages’ most common writing system
via the Suppress-Script field in its language subtag registry for this purpose.
Note: More advice on language tagging can be found in
the Internationalization Working Group’s “Language tags in HTML and XML” and “Choosing a Language Tag”.
When no writing system is explicitly indicated,
UAs should assume the most common writing system
of the declared content language for language-sensitive typographic behaviors
such as line-breaking or justification.
However, UAs must not assume that writing system
if the author has explicitly declared a different one.
If the UA has no language-specific knowledge
of a particular language and writing system combination,
it must use the typographic conventions of the declared writing system
(assuming the conventions of a different language if necessary),
not the conventions of the declared language in an assumed writing system,
which would be inappropriate to the declared writing system.
The full correspondence between languages and their most common writing systems
is out of scope for this document.
However, user agents must assume at least the following:
- If the content language is Chinese and the writing system is unspecified,
or for any content language if the writing system to specified to be one of the Hant, Hans, Hani, Hanb,
or Bopo ISO script codes,
then the writing system is Chinese. - If the content language is Japanese and the writing system is unspecified,
or for any content language if the writing system to specified to be one of the Jpan, Hrkt, Hira,
or Kana ISO script codes,
then the writing system is Japanese. - If the content language is Korean and the writing system is unspecified,
or for any content language if the writing system to specified to be one of the Kore, Hang,
or Jamo ISO script codes,
then the writing system is Korean. -
The writing system is only considered
to be unknown if the content language itself is unknown,
or if it explicitly indicates an unknown writing system.Note: Mere omission of the writing system information
when the content language is declared
means the that the writing system is implied, not unknown.
Appendix G:
Small Kana Mappings
This appendix is normative.
| Small | Full-size |
|---|---|
| ぁ U+3041 | あ U+3042 |
| ぃ U+3043 | い U+3044 |
| ぅ U+3045 | う U+3046 |
| ぇ U+3047 | え U+3048 |
| ぉ U+3049 | お U+304A |
| ゕ U+3095 | か U+304B |
| ゖ U+3096 | け U+3051 |
| っ U+3063 | つ U+3064 |
| ゃ U+3083 | や U+3084 |
| ゅ U+3085 | ゆ U+3086 |
| ょ U+3087 | よ U+3088 |
| ゎ U+308E | わ U+308F |
| ァ U+30A1 | ア U+30A2 |
| ィ U+30A3 | イ U+30A4 |
| ゥ U+30A5 | ウ U+30A6 |
| ェ U+30A7 | エ U+30A8 |
| ォ U+30A9 | オ U+30AA |
| ヵ U+30F5 | カ U+30AB |
| ㇰ U+31F0 | ク U+30AF |
| ヶ U+30F6 | ケ U+30B1 |
| ㇱ U+31F1 | シ U+30B7 |
| ㇲ U+31F2 | ス U+30B9 |
| ッ U+30C3 | ツ U+30C4 |
| ㇳ U+31F3 | ト U+30C8 |
| ㇴ U+31F4 | ヌ U+30CC |
| ㇵ U+31F5 | ハ U+30CF |
| ㇶ U+31F6 | ヒ U+30D2 |
| ㇷ U+31F7 | フ U+30D5 |
| ㇸ U+31F8 | ヘ U+30D8 |
| ㇹ U+31F9 | ホ U+30DB |
| ㇺ U+31FA | ム U+30E0 |
| ャ U+30E3 | ヤ U+30E4 |
| ュ U+30E5 | ユ U+30E6 |
| ョ U+30E7 | ヨ U+30E8 |
| ㇻ U+31FB | ラ U+30E9 |
| ㇼ U+31FC | リ U+30EA |
| ㇽ U+31FD | ル U+30EB |
| ㇾ U+31FE | レ U+30EC |
| ㇿ U+31FF | ロ U+30ED |
| ヮ U+30EE | ワ U+30EF |
| ァ U+FF67 | ア U+FF71 |
| ィ U+FF68 | イ U+FF72 |
| ゥ U+FF69 | ウ U+FF73 |
| ェ U+FF6A | エ U+FF74 |
| ォ U+FF6B | オ U+FF75 |
| ッ U+FF6F | ツ U+FF82 |
| ャ U+FF6C | ヤ U+FF94 |
| ュ U+FF6D | ユ U+FF95 |
| ョ U+FF6E | ヨ U+FF96 |
Privacy and Security Considerations
This specification introduces no new security considerations.
This specification leaks the user’s installed hyphenation and line-breaking dictionaries.
Acknowledgements
This specification would not have been possible without the help from:
Addison Phillips,
Aharon Lanin,
Alan Stearns,
Ambrose Li,
Arnold Schrijver,
Arye Gittelman,
Ayman Aldahleh,
Ben Errez,
Bert Bos,
Chris Lilley,
Chris Pratley,
Chris Thrasher,
Chris Wilson,
Dave Hyatt,
David Baron,
Emilio Cobos Álvarez,
Eric LeVine,
Etan Wexler,
Frank Tang,
Håkon Wium Lie,
IM Mincheol,
Ian Hickson,
James Clark,
Javier Fernandez,
John Daggett,
Jonathan Kew,
Ken Lunde,
Laurie Anna Edlund,
Marcin Sawicki,
Martin Dürst,
Martin Heijdra,
Masafumi Yabe,
Masayasu Ishikawa,
Michael Jochimsen,
Michel Suignard,
Mike Bemford,
Myles Maxfield,
Nat McCully,
Paul Nelson,
Pierre-Anthony Lemieux,
Rahul Sonnad,
Randy Edmunds,
Richard Ishida,
Shinyu Murakami,
Stephen Deach,
Steve Zilles,
Takao Suzuki,
Tantek Çelik,
Xidorn Quan,
Yaniv Feinberg.
Changes
Significant changes since the 1 March 2022 Working Draft include:
-
Completed the translation of white-space to multiple longhands by
-
adding break-spaces to white-space-collapse so that all shorthand values can be represented in the longhands
(Issue 8256) -
integrating all longhand keywords into the white-space shorthand
-
updating prose accordingly
-
-
Renamed text-space-collapse and text-space-trim to white-space-collapse and white-space-trim.
(Issue 8273)
Significant changes since the 31 December 2022 Working Draft include:
-
Redesigned text-spacing by:
-
Removing non-useful keyword combinations
(Issues 4246, 8288) -
Making space-first the initial value
(Issue 2462) -
Splitting into longhands
(Issues 4246, 7183, 8288) -
Ensuring the ability to turn each feature “off”.
(Issues 6950, 8288) -
Add keywords to allow replacing incorrect space characters in the source.
(Issues 318, 7183, 8263) -
Allow hanging-punctuation to hang leading ideographic spaces
to compensate for plaintext-derived source text practices.
(Issue 2462) -
Move no-compress to text-justify since it controls justification more than spacing.
(Issue 7079)
-
-
Extended contextual characters evaluated in text-spacing to include characters from the
PeandPscategories.
(Issue 6091) -
Renamed text-space-collapse back to white-space-collapse.
(Issue 8273)
Significant changes since the 5 May 2022 Working Draft include:
- Added ruby value to text-justify.
(Issue 771 Issue 779) - Switched text-spacing: normal to use trim-end instead of allow-end.
(Issue 7055) - Switched text-spacing: normal to also apply ideograph-alpha and ideograph-numeric,
updated UA default stylesheet to exclude these from monospace contexts,
specified that non-zero margin/border/padding inhibits space insertion,
and defined the amount of inserted space as 0.125ic.
(Issue 6950) - Defined text-align: match-parent to compute to start on the root element for simplicity of implementation.
(Issue 6542) - Allow distribute keyword to be a legacy value alias or to simply compute to inter-character;
this allows UAs to do whichever is easier, since the distinction does not matter for backwards-compatibility.
(Issue 7322) - Renamed trim-inner value of white-space-trim to discard-inner for consistency with other values.
(Issue 448)
Significant changes since the 2019 Working Draft include:
- Integrating the full text of [CSS-TEXT-3].
- Adding percentages to word-spacing and letter-spacing to represent sizes relative to the current font-size.
(Issue 2165) - Suggesting a UA rule to prevent spaces in
textareafrom collapsing.
(Issue 6309)
Additions Since Level 3
New features in Level 4:
-
word-boundary-detection, for automatically detecting word boundaries (at risk)
-
word-boundary-expansion, for transforming word separators
-
white-space-collapse longhand (of the longstanding white-space property) and its preserve-spaces and discard values
-
white-space-trim, for trimming excess white space at the boundaries of an element
-
text-wrap longhand (of the white-space property) and its balance, stable, and pretty values
-
wrap-before, wrap-after, and wrap-inside, to avoid or force wrapping (similar to the break-* properties for pagination)
-
hyphenate-character, to explicitly control the hyphenation character
-
hyphenate-limit-zone, hyphenate-limit-chars, hyphenate-limit-lines, hyphenate-limit-last, for better control over automatic hyphenation
-
<string> values for text-align for aligning on, e.g., a decimal point
-
text-group-align for group-aligning a set of line boxes whose contents are aligned by text-align
-
line-padding for inserting spaces within the inline box at the start/end of lines
-
text-spacing for automatic spacing around punctuation and script changes
Conformance requirements are expressed with a combination of
descriptive assertions and RFC 2119 terminology. The key words “MUST”,
“MUST NOT”, “REQUIRED”, “SHALL”, “SHALL NOT”, “SHOULD”, “SHOULD NOT”,
“RECOMMENDED”, “MAY”, and “OPTIONAL” in the normative parts of this
document are to be interpreted as described in RFC 2119.
However, for readability, these words do not appear in all uppercase
letters in this specification.
All of the text of this specification is normative except sections
explicitly marked as non-normative, examples, and notes. [RFC2119]
Examples in this specification are introduced with the words “for example”
or are set apart from the normative text with class="example",
like this:
Informative notes begin with the word “Note” and are set apart from the
normative text with class="note", like this:
Note, this is an informative note.
Advisements are normative sections styled to evoke special attention and are
set apart from other normative text with <strong class="advisement">, like
this: UAs MUST provide an accessible alternative.
A style sheet is conformant to this specification
if all of its statements that use syntax defined in this module are valid
according to the generic CSS grammar and the individual grammars of each
feature defined in this module.
A renderer is conformant to this specification
if, in addition to interpreting the style sheet as defined by the
appropriate specifications, it supports all the features defined
by this specification by parsing them correctly
and rendering the document accordingly. However, the inability of a
UA to correctly render a document due to limitations of the device
does not make the UA non-conformant. (For example, a UA is not
required to render color on a monochrome monitor.)
An authoring tool is conformant to this specification
if it writes style sheets that are syntactically correct according to the
generic CSS grammar and the individual grammars of each feature in
this module, and meet all other conformance requirements of style sheets
as described in this module.
So that authors can exploit the forward-compatible parsing rules to
assign fallback values, CSS renderers must treat as invalid (and ignore
as appropriate) any at-rules, properties, property values, keywords,
and other syntactic constructs for which they have no usable level of
support. In particular, user agents must not selectively
ignore unsupported component values and honor supported values in a single
multi-value property declaration: if any value is considered invalid
(as unsupported values must be), CSS requires that the entire declaration
be ignored.
Once a specification reaches the Candidate Recommendation stage,
non-experimental implementations are possible, and implementors should
release an unprefixed implementation of any CR-level feature they
can demonstrate to be correctly implemented according to spec.
To establish and maintain the interoperability of CSS across
implementations, the CSS Working Group requests that non-experimental
CSS renderers submit an implementation report (and, if necessary, the
testcases used for that implementation report) to the W3C before
releasing an unprefixed implementation of any CSS features. Testcases
submitted to W3C are subject to review and correction by the CSS
Working Group.
Editor’s note: This complete guide to word-wrap, overflow-wrap, and word-break in CSS was last updated 24 February 2023 to reflect the reflect the most recent version of CSS, include interactive code examples, and include a section on how to wrap text using CSS. To learn more about the overflow property, check out our guide to CSS overflow.
Making a site responsive so that it displays correctly on all devices is very important in this day and age. Unfortunately, despite your best efforts to do so, you may still end up with broken layouts. Broken layouts can happen when certain words are too long to fit in their container. Content overflow can occur when you are dealing with user-generated content you have no control over, such as the comments section of a post. Therefore, you need to apply styling to prevent content from overflowing their container.
Content overflow is a common problem for frontend developers. On the web, overflow occurs when your content doesn’t fit entirely within its containing element. As a result, it spills outside. In CSS, you can manage content overflow mainly using the overflow, word-wrap, overflow-wrap, and word-break CSS properties. However, our focus in this article will be on the word-wrap, overflow-wrap, and word-break CSS properties.
Jump ahead:
- Using
word-wrap,overflow-wrap, andword-breakCSS properties- How does content wrapping occur in browsers?
- What is the difference between a soft wrap break and a forced line break?
- Understanding the
Word-wrapandoverflow-wrapCSS propertiesNormalAnywhereBreak-word
- Implementing the
Word-breakCSS property- Setting
word-breaktoNormal - The
Break-allvalue - Using the
Keep-allvalue
- Setting
- What is the difference between
overflow-wrapandword-break? - How to wrap text using CSS
- Troubleshooting CSS content overflow with Chrome DevTools
Using word-wrap, overflow-wrap, and word-break CSS properties
You can use the word-wrap, overflow-wrap, or word-break CSS properties to wrap or break words that would otherwise overflow their container. This article is an in-depth tutorial on the word-wrap, overflow-wrap, and word-break CSS properties and how you can use them to prevent content overflow from ruining your nicely styled layout. Before we get started, let us understand how browsers wrap content in the next section.
How does content wrapping occur in browsers?
Browsers and other user agents perform content wrapping at allowed breakpoints, referred to as soft wrap opportunities. A browser will wrap content at a soft wrap opportunity, if one exists, to minimize content overflow. In English and other similar writing systems, soft wrap opportunities occur by default at word boundaries in the absence of hyphenation. Because words are bound by spaces and punctuation, that is where soft wraps occur.
Although soft wraps occur in space characters in English texts, the situation might be different for non-English writing systems. Some languages do not use spaces to separate words, meaning that content wrapping depends on the language or writing system. The value of the lang attribute you specify on the HTML element is mostly used to determine which language system is used.
This article will focus mainly on the English language writing system. The default wrapping at soft wrap opportunities may not be sufficient if you are dealing with long, continuous text, such as URLs or user-generated content, which you have very little or no control over. Before we go into a detailed explanation of these CSS properties, let’s look at the differences between soft wrap break and forced line break in the section below.
What is the difference between a soft wrap break and a forced line break?
Any text wrap that occurs at a soft wrap opportunity is referred to as a soft wrap break. For wrapping to occur at a soft wrap opportunity, you need to make sure you’ve enabled wrapping. For example, setting the value of white-space CSS property to nowrap will disable wrapping. Forced line breaks are caused by explicit line-breaking controls or line breaks marking the end or start of blocks of text.
Understanding the Word-wrap and overflow-wrap CSS properties
The name word-wrap is the legacy name for the overflow-wrap CSS property. Word-wrap was originally a non-prefixed Microsoft extension and was not part of the CSS standard, though most browsers implemented it with the name word-wrap. According to the draft CSS3 specification, browsers should treat word-wrap as a legacy name alias of the overflow-wrap property for compatibility.
Most recent versions of popular web browsers have implemented the overflow-wrap property. The draft CSS3 specification refers to the overflow-wrap property as:
This property specifies whether the browser may break at otherwise disallowed points within a line to prevent overflow when an otherwise-unbreakable string is too long to fit within the line box.
If you have a white-space property on an element, you need to set its value to allow wrapping for overflow-wrap to have an effect. Below are the values of the overflow-wrap property:
overflow-wrap: normal; overflow-wrap: anywhere; overflow-wrap: break-word;
You can also use the global values inherit, initial, revert, and unset with overflow-wrap, but we won’t cover them here. In the subsections below, we will look at the values of the overflow-wrap CSS property outlined above to understand the behavior of this property.
Normal
Applying the value normal will make the browser use the default line-breaking behavior of the system. For English and other related writing systems, line breaks will therefore occur at whitespaces and hyphens, as shown below:
.my-element{
overflow-wrap: normal;
}
In the example below, there is a word in the text that is longer than its container. Because there is no soft wrap opportunity and the value of the overflow-wrap property is normal, the word overflows its container. It describes the default line-breaking behavior of the system:
See the Pen
overflow-wrap-normal by Joseph Mawa (@nibble0101)
on CodePen.
Anywhere
Using the value anywhere will break an otherwise unbreakable string at arbitrary points between two characters. It will not insert a hyphen character even if you apply the hyphens property on the same element.
The browser will break the word only if displaying the word on its line will cause an overflow. If the word still overflows when placed on its line, it will break the word at the point where an overflow would otherwise occur. When you use anywhere, the browser will consider the soft wrap opportunities introduced by the word break when calculating min-content intrinsic sizes:
.my-element{
overflow-wrap: anywhere;
}
Unlike in the previous section, where we used overflow-wrap: normal, in the example below, we are using overflow-wrap: anywhere. The overflowing word that is otherwise unbreakable is broken into chunks of text using overflow-wrap: anywhere so that it fits in its container:
See the Pen
overlow-wrap-anywhere by Joseph Mawa (@nibble0101)
on CodePen.
Most recent versions of desktop browsers support overflow-wrap: anywhere. However, support for some mobile browsers is either lacking or unknown. The image below shows the browser support:
Break-word
The value break-word is like anywhere in terms of functionality. If the browser can wrap the overflowing word to its line without overflowing, that is what it will do. However, if the word still overflows its container even when it is on its line, the browser will break it at the point where the overflow would otherwise occur:
.my-element{
overflow-wrap: break-word;
}
The example below shows how the browser breaks the overflowing text when you apply overflow-wrap: break-word:
See the Pen
overflow-wrap-break-word by Joseph Mawa (@nibble0101)
on CodePen.
Notice that the text appears the same as in the last subsection. The difference between overflow-wrap: anywhere and overflow-wrap: break-word is in the min-content intrinsic sizes.
The difference between anywhere and break-word is apparent when calculating the min-content intrinsic sizes. With break-word, the browser doesn’t consider the soft wrap opportunities introduced by the word break when calculating min-content intrinsic sizes, but it does with anywhere. For more about min-content intrinsic sizes, check out our guide here.
The value break-word has decent coverage among the most recent versions of desktop browsers. Unfortunately, you cannot say the same about their mobile counterpart. It is, therefore, safer to use the legacy word-wrap: break-word instead of the more recent overflow-wrap: break-word.
The image below shows browser support for overflow-wrap: break-word:
The most recent versions of desktop browsers have support, while support for some mobile browsers is unknown.
Implementing the Word-break CSS property
Word-break is another CSS property you can use to specify soft wrap opportunities between characters. You can use this property to break a word at the exact spot where an overflow would occur and wrap it onto the following line.
The draft CSS3 specification refers to the word-break CSS property as:
This property specifies soft wrap opportunities between letters, i.e., where it is “normal” and permissible to break lines of text. It controls what types of letters the browser can glom together to form unbreakable “words” — causing CJK characters to behave like non-CJK text or vice versa.
Below are the possible values of the word-break CSS property. Like overflow-wrap, you can use the global values inherit, initial, revert, and unset with word-break, but we won’t cover them here:
word-break: normal; word-break: break-all; word-break: keep-all;
Break-word is also a value of the word-break CSS property, though it was removed. However, browsers still support it for legacy reasons. Specifying this property has the same effect as word-break: normal and overflow-wrap: anywhere.
Now that we know the break-word CSS property and its corresponding values, let us look at them in the subsections below.
Setting word-break to Normal
Setting the value of the word-break property to normal will apply the default word breaking rules:
.my-element{
word-break: normal;
}
The example below illustrates what happens when you apply the styling word-break: normal to a block of text that contains a word longer than its container:
See the Pen
word-break-normal by Joseph Mawa (@nibble0101)
on CodePen.
What you see is the browser’s usual word-breaking rules in effect.
The Break-all value
The value break-all will insert a line break at the exact point where the text would otherwise overflow for non-Chinese, non-Japanese, and non-Korean writing systems. It will not put the word on its own line, even if doing so will prevent the need to insert a line break:
.my-element{
word-break: break-all;
}
In the example below, I am applying word-break: break-all styling to a p element of width 240px containing an overflowing text. The browser will insert a line break at the point where an overflow would occur and wrap the remaining text to the following line:
See the Pen
word-break-break-all by Joseph Mawa (@nibble0101)
on CodePen.
Using break-all will break a word between two characters at the exact point where an overflow would occur in English and other related language systems. However, it won’t apply the same behavior to Chinese, Japanese, and Korean (CJK) texts.
It doesn’t apply the same behavior for CJK texts because CJK writing systems have their own rules for applying breakpoints. Creating a line break between two characters arbitrarily just for the sake of avoiding overflow might significantly change the overall meaning of the text. For CJK systems, the browser will apply line breaks at the point where such breaks are allowed.
Using the Keep-all value
If you use the value keep-all, the browser will not apply word breaks to CJK texts, even if there is content overflow. The effect of applying keep-all value is the same as that of normal for non-CJK writing systems:
.my-element{
word-break: keep-all;
}
In the example below, applying word-break: keep-all will have the same effect as word-break: normal for a non-CJK writing system such as English:
See the Pen
word-break-keep-all by Joseph Mawa (@nibble0101)
on CodePen.
The image below shows the browser support for word-break: keep-all:
This value has support in most popular desktop browsers. Unfortunately, it is not the case for mobile browsers. Now that we have looked at the overflow-wrap and word-break CSS properties, what is the difference between the two? The section below will shed light on that.
What is the difference between overflow-wrap and word-break?
You can use the CSS properties overflow-wrap and word-break to manage content overflow. However, there are differences in the way the two properties handle it.
Using overflow-wrap will wrap the entire overflowing word to its line if it can fit in a single line without overflowing its container. The browser will break the word only if it cannot place it on a new line without overflowing. In most cases, the overflow-wrap property or its legacy name word-wrap might manage content overflow. Using word-wrap: break-word will wrap the overflowing word onto a new line and goes ahead to break it between two characters if it still overflows its container.
Word-break will ruthlessly break the overflowing word between two characters even if placing it on its line will negate the need for word break. Some writing systems, like the CJK writing systems, have strict word breaking rules the browser takes into consideration when creating line breaks using word-break.
How to wrap text using CSS
As hinted above, if you want to wrap text or break a word overflowing the confines of its box, your best bet is the overflow-wrap CSS property. You can also use its legacy name, word-wrap. Try the word-break CSS property if the overflow-wrap property doesn’t work for you. However, be aware of the differences between overflow-wrap and word-break highlighted above.
Below is an illustration of the overflow-wrap and word-wrap CSS properties. You can play with the CodePen to understand their effects:
See the Pen
how-to-wrap-text by Joseph Mawa (@nibble0101)
on CodePen.
Troubleshooting CSS content overflow with Chrome DevTools
More often than not, you might need to fix broken layouts caused by content overflow, as complex user interfaces are now commonplace in frontend development. Modern web browsers come with tools for troubleshooting such layout issues, such as Chrome DevTools.
It provides the capability to select an element in the DOM tree so that you can view, add, and remove CSS declarations and much more. It will help you track down the offending CSS style in your layout and fix it with ease.
To open the Chrome DevTools, you can use the F12 key. When open, it looks like in the image below. Selecting an element in the DOM tree will display its corresponding CSS styles. You can modify the styles and see the effect on your layout as you track down the source of the bug:
As already mentioned, if you have white-space property on an element, set its value to allow wrapping for overflow-wrap: anywhere or overflow-wrap: break-word to work.
Setting the value of overflow-wrap property to anywhere or break-word on a table content won’t break an overflowing word like in the examples above. The table will overflow its container and create a horizontal scroll if necessary. To get the table to fit within its container and overflow-wrap to work, set the value of the table-layout property to fixed and set the table width to 100% or to some fixed value.
Conclusion
As pointed out in the above sections, overflow-wrap and word-break are similar in so many ways, and you can use both of them for line-breaking controls. The name overflow-wrap is an alias of the legacy word-wrap property. Therefore, you can use the two interchangeably. However, it is worth mentioning that the browser support for the newer overflow-wrap property is still low. You are better off using word-wrap instead of overflow-wrap if you want near-universal browser support.
According to the draft CSS3 specification, browsers and user agents should continue supporting word-wrap for legacy reasons. If you are looking to manage content overflow, overflow-wrap or its legacy name word-wrap might be sufficient. You can also use word-break to break a word between two characters if the word overflows its container. Just like overflow-wrap, you need to tread with caution when using word-break because of limitations in the browser support.
Now that you know the behavior associated with the two properties, you can decide where and when to use them. Did I miss anything? Leave a comment in the comments section. I will be happy to update this article.
Is your frontend hogging your users’ CPU?
As web frontends get increasingly complex, resource-greedy features demand more and more from the browser. If you’re interested in monitoring and tracking client-side CPU usage, memory usage, and more for all of your users in production, try LogRocket.
LogRocket is like a DVR for web and mobile apps, recording everything that happens in your web app, mobile app, or website. Instead of guessing why problems happen, you can aggregate and report on key frontend performance metrics, replay user sessions along with application state, log network requests, and automatically surface all errors.
Modernize how you debug web and mobile apps — Start monitoring for free.