-
Create a table
Video
-
Sort data in a table
Video
-
Filter data in a range or table
Video
-
Add a Total row to a table
Video
-
Use slicers to filter data
Video
Sign in with Microsoft
Sign in or create an account.
Hello,
Select a different account.
You have multiple accounts
Choose the account you want to sign in with.
Thank you for your feedback!
×
-
Select a cell within your data.
-
Select Home > Format as Table.
-
Choose a style for your table.
-
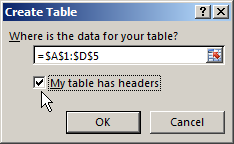
In the Create Table dialog box, set your cell range.
-
Mark if your table has headers.
-
Select OK.
-
Insert a table in your spreadsheet. See Overview of Excel tables for more information.
-
Select a cell within your data.
-
Select Home > Format as Table.
-
Choose a style for your table.
-
In the Create Table dialog box, set your cell range.
-
Mark if your table has headers.
-
Select OK.
To add a blank table, select the cells you want included in the table and click Insert > Table.
To format existing data as a table by using the default table style, do this:
-
Select the cells containing the data.
-
Click Home > Table > Format as Table.
-
If you don’t check the My table has headers box, Excel for the web adds headers with default names like Column1 and Column2 above the data. To rename a default header, double-click it and type a new name.
Note: You can’t change the default table formatting in Excel for the web.
Download Article
Download Article
This wikiHow teaches you how to create a table of information in Microsoft Excel. You can do this on both Windows and Mac versions of Excel.
-
1
Open your Excel document. Double-click the Excel document, or double-click the Excel icon and then select the document’s name from the home page.
- You can also open a new Excel document by clicking Blank Workbook on the Excel home page, but you’ll need to input your data before continuing.
-
2
Select your table’s data. Click the cell in the top-left corner of the data group you want to include in your table, then hold down ⇧ Shift while clicking the bottom-right cell in the data group.
- For example: if you have data in cells A1 down to A5 and over to D5, you would click A1 and then click D5 while holding ⇧ Shift.
Advertisement
-
3
Click the Insert tab. It’s a tab in the green ribbon at the top of the Excel window. Doing so will display the Insert toolbar below the green ribbon.
- If you’re on a Mac, make sure you don’t click the Insert menu item in your Mac’s menu bar.
-
4
Click Table. This option is in the «Tables» section of the toolbar. Clicking it brings up a pop-up window.
-
5
Click OK. It’s at the bottom of the pop-up window. Doing so will create your table.
- If your data group has cells at the top of it that are dedicated to column names (e.g., headers), click the «My table has headers» checkbox before you click OK.
Advertisement
-
1
Click the Design tab. It’s in the green ribbon near the top of the Excel window. This will open a toolbar for your table’s design directly below the green ribbon.
- If you don’t see this tab, click your table to prompt it to appear.
-
2
Select a design scheme. Click one of the colored boxes in the «Table Styles» section of the Design toolbar to apply the color and design to your table.
- You can click the downward-facing arrow to the right of the colored boxes to scroll through different design options.
-
3
Review the other design options. In the «Table Style Options» section of the toolbar, check or uncheck any of the following boxes:
- Header Row — Checking this box places column names in the top cell of the data group. Uncheck this box to remove headers.
- Total Row — When enabled, this option adds a row at the bottom of the table that displays the total value of the right-most column.
- Banded Rows — Check this box to color in alternating rows, or uncheck it to leave all rows in your table the same color.
- First Column and Last Column — When enabled, these options make the headers and data in the first and/or last columns bold.
- Banded Columns — Check this box to color in alternating columns, or uncheck it to leave all columns in your table the same color.
- Filter Button — When checked, this box places a drop-down box next to each header in your table that allows you to change the data displayed in that column.
-
4
Click the Home tab again. This will take you back to the Home toolbar. Your table’s changes will remain.
Advertisement
-
1
Open the filter menu. Click the drop-down arrow to the right of the header for the column whose data you want to filter. A drop-down menu will appear.
- In order to do this, you must have both the «Header Row» and the «Filter» boxes checked in the «Table Style Options» section of the Design tab.
-
2
Select a filter. Click one of the following options in the drop-down menu:
- Sort Smallest to Largest
- Sort Largest to Smallest
- You may also have additional options such as Sort by Color or Number Filters depending on your data. If so, you can select one of these options and then click a filter in the pop-out menu.
-
3
Click OK if prompted. Depending on the filter you choose, you may also have to select a range or a different type of data before you can continue. Your filter will be applied to your table.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
How do I resize the columns?
Place your mouse between the columns until the cursor changes into a double arrow pointing to the left and to the right. Left click and hold. Drag the mouse, while holding the left button, to the left to shrink or to the right to enlarge the column.
-
Question
How do I change the width of a column in Excel?
If you go up to «Format,» and select «Width» you will be able to change the size.
-
Question
How do I make a table in Excel fit the size of a paper?
In Excel 2013, click the «Page Layout» tab, then click the «Size» dropdown menu. Most printers use 8.5 x 11 inch paper.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
-
If you no longer need the table, you can either delete it entirely or turn it back into a range of data on the spreadsheet page. To delete the table entirely, select the table and press your keyboard «Delete» key. To change it back to a range of data, right-click any of its cells, select «Table» from the popup menu that appears, and then select «Convert to Range» from the Table submenu. The sort and filter arrows disappear from the column headers, and any table name references in the cell formulas are removed. The column header names and the table formatting remain, however.
-
If you place your table so that the header for the first column is in the upper left corner of the spreadsheet (Cell A1), the column headers will replace the spreadsheet’s column headers when you scroll up. If you place the table anywhere else, the column headers will scroll out of view when you scroll up, and you’ll need to use Freeze Panes to keep them constantly displayed.
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Open a file with data.
2. Select data for the table.
3. Click Insert.
4. Click Table.
5. Click OK.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 553,245 times.
Is this article up to date?
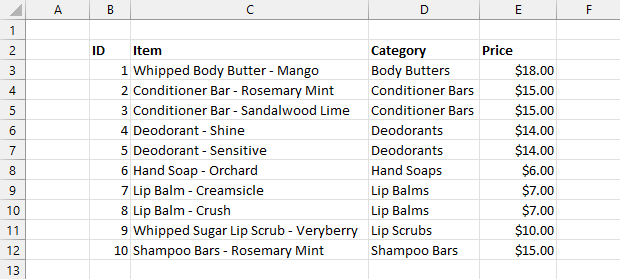
Do you want to make a table in Excel? This post is going to show you how to create a table from your Excel data.
Entering and storing data is a common task in Excel. If this is something you’re doing, then you need to use a table.
Tables are containers for your data! They help you keep all your related data together and organized.
Tables have a lot of great features and work well with other tools inside and outside of Excel, so you should definitely be using them with your data.
This post is going to show you all the ways you can create a table from your data in Excel. Get your copy of the example workbook used in this post and follow along!
Tabular Data Format for Excel Tables
Excel tables are the perfect container for tabular datasets due to their row and column structure. Just make sure your data follows these rules.
- The first row of your dataset should contain a descriptive column heading.
- Your data should have no blank column headings.
- Your data should have no blank columns or blank rows.
- Your data should have no subtotals or grand totals.
- One row in your data should represent exactly one record of data.
- One column should contain exactly one type of data.
If your data is rectangular in shape and adheres to the above rules, then it’s ready to be put into a table.
Create a Table from the Insert Tab
Now that your data is ready to be placed inside a table, how can you do that?
It’s very easy and will only take a few clicks!
You’ll be able to add your data in a table from the Insert tab. Follow these steps to get your data into a table!
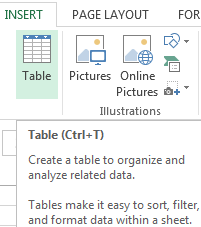
- Select a cell inside your data.
- Go to the Insert tab.
- Select the Table command in the Tables section.
This is going to open the Create Table menu with your data range selected. You should see a green dash line around your selected data and you can adjust the selection if needed.
- Check the My table has headers option. This is needed if the first row of your data contains column name headings.
- Press the OK button.
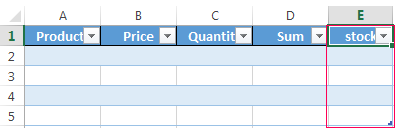
Your data is now inside a table! You’ll easily be able to tell the data is inside an Excel Table now because a default table formatting is automatically applied.
You can go to the Table Design tab and select other style options from the Table Styles section.
💡 Tip: Your table will get a default name such as Table1. You should give your new table a descriptive name as this is how you will refer to it in formulas and other tools.
Create a Table from the Home Tab
Another place you can access the table command is from the Home tab.
You can use the Format as Table command to create a table.
- Select a cell inside your data.
- Go to the Home tab.
- Select the Format as Table command in the Styles section.
- Select a style option for your table.
- Check the option for My table has headers.
- Press the OK button.
This is a great option as you get to choose the table style during the process of making your table.
Create a Table with a Keyboard Shortcut
Creating a table is such a common task that there is a keyboard shortcut for it.
Select your data and press Ctrl + T on your keyboard to turn your dataset into a table.
This is an easy shortcut to remember since T stands for Table.
There is also a legacy shortcut available from when tables were called lists. Select your data and if you press Ctrl + L this will also make a table. In this case, L stands for List.
Create a Table with Quick Analysis
When you select any range Excel will show you the Quick Analysis options in the lower right corner.
This will give you quick access to conditional formatting, pivot tables, charts, totals, and sparklines. The menu also includes the table command to convert the data into a table.
You can follow these steps to create a table from the Quick Analysis tools.
- Select your entire dataset. You can select any cell in the data and press Ctrl + A and this will select the full range.
This should automatically show the Quick Analysis tool in the lower right corner of the selected range.
- Click on the Quick Analysis tools or press Ctrl + Q to open the Quick Analysis menu.
- Go to the Tables tab.
- Click on the Table command. When you hover your cursor over the Table command it will show you a preview of your data inside a table!
📝 Note: This method allows you to skip the Create Table menu and the Quick Analysis will guess if your data has column headings or not. Excel will apply any column headings to your table accordingly.
Quick Analysis can be disabled from the Excel Options menu if the pop-up command is something you find annoying.
- Go to the File tab.
- Select the Options menu.
- Go to the General tab of the Excel Options menu.
- Uncheck the Show Quick Analysis options on selection option.
- Press the OK button.
📝 Note: This will only disable the small pop-up command from showing when you select your data. You can still use the Ctrl + Q keyboard shortcut to access the Quick Analysis tools for any selected range.
Create a Table with Power Query
Power Query is a very useful tool for transforming your data, but you can also create a table during the process of building your queries.
If your data isn’t already inside a table, you can use the From Table/Range query to make a table.
- Select your data.
- Go to the Data tab.
- Press the From Table/Range command in the Get & Transform Data section.
This will open the Create Table menu.
- Check the My table has headers option if the first row in your data contains column headings.
- Press the OK button.
This will add your data to a table and then open the Power Query Editor where you will be able to build your query based on the new table.
When you are finished building your query, you can go to the Home tab of the Power Query editor and press the Close and Load command.
This will give you the option to create another table filled with the transformed data. Select the Table option and press the OK button to load the transformed data into a table.
⚠️ Warning: This method does create a table, but doesn’t give you the opportunity to name the table before you build your queries. This means your queries will reference the generic table name such as Table1, and if you later change the table name you will also have to update the reference in your query.
Create Multiple Tables from a List with VBA
Suppose you need to create multiple tables in your Excel file. Maybe you need to create a table of sales data for each month of the year. Doing this manually could be a time-consuming process.
This is where you could use VBA to create multiple tables with the required columns.
Go to the Developer tab and select the Visual Basic command to open the visual basic editor. Then go to the Insert tab of the visual basic editor and select the Module option to create a new module to add your VBA macro.
Sub AddTables()
Dim myRange As Range
Dim sheetTest As Boolean
Dim myHeadings As Variant
Dim colCount As Integer
Set myRange = Selection
myHeadings = [{"ID","Date","Item","Quantity","Price"}]
colCount = UBound(myHeadings)
For Each c In myRange.Cells
sheetTest = False
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If ws.Name = c.Value Or c.Value = "" Then
sheetTest = True
End If
Next ws
If Not (sheetTest) Then
With Sheets
Sheets.Add.Name = c.Value
Sheets(c.Value).Select
Range("A1").Resize(1, colCount).Value = myHeadings
ActiveSheet.ListObjects.Add(xlSrcRange, Range("A1").Resize(1, colCount), , xlYes).Name = c.Value & "Sales"
End With
End If
Next c
End SubThis code will loop through the selected range and add a new sheet for each cell in the range. The code tests if the sheet name exists and if it doesn’t then it creates a new sheet named from the cell value.
The column headings are added to the new sheet starting at cell A1. This is then turned into a table and the table is named based on the sheet name.
myHeadings = [{"ID","Date","Item","Quantity","Price"}]The above line of code is used to create the column headings in each table. You can adjust this to suit your needs.
You can then run this macro to create multiple tables.
- Select the range of cells that contain the list the names for each table you want to create. For example, you might want a list of month names to create a table for each month.
- Press the Alt + F8 keyboard shortcut to open the Macro menu.
- Select your macro.
- Press the Run button.
This will run and create a new sheet for each item in your selection. Each sheet will contain a table with the same column headings and be named based on the items in the selected list.
Create Multiple Tables from a List with Office Scripts
If you are using Excel online and want to automate the process of creating multiple tables from a list, then you will need to use Office Scripts.
This is a JavaScript based language that can help you automate tasks in Excel online.
Go to the Automate tab and select the New Script command to open the Office Script Editor.
function main(workbook: ExcelScript.Workbook) {
//Create an array with the column headings
let myHeaders = [["ID", "Date", "Item", "Quantity", "Price"]]
let colCount = myHeaders[0].length;
//Create an array with the values from the selected range
let selectedRange = workbook.getSelectedRange();
let selectedValues = selectedRange.getValues();
//Get dimensions of selected range
let rowHeight = selectedRange.getRowCount();
let colWidth = selectedRange.getColumnCount();
//Loop through each item in the selected range
for (let i = 0; i < rowHeight; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < colWidth; j++) {
try {
//Create a new sheet with name from the selected range
let thisSheet = workbook.addWorksheet(selectedValues[i][j]);
//Add column headings to new sheet and convert to table
thisSheet.getRange("A1").getAbsoluteResizedRange(1, colCount).setValues(myHeaders);
let newTable = workbook.addTable(thisSheet.getRange("A1").getAbsoluteResizedRange(1, colCount), true);
newTable.setName(selectedValues[i][j] + "Sales");
}
catch (e) {
//do nothing
};
};
};
};Copy and paste the above code into the Code Editor. Press the Save script button to save the script and then you can use the Run button to execute the script.
This Office Script code will loop through the active range in your workbook and create a new sheet for each cell in the selected range and name it based on the value in the cell.
let myHeaders = [["ID", "Date", "Item", "Quantity", "Price"]]The column headings are added to each new sheet starting in cell A1. You can adjust the above line of code to change the column headings to suit your needs.
These column headings are then turned into a table and the table is named based on the sheet name.
You can then run this script using the following steps.
- Select a range of cells that contain the list of tables you want to create.
- Click on the Run button in the Code Editor.
The code will run and create all the sheets with tables in each sheet.
Conclusions
Tables are a very useful feature for your tabular data in Excel.
Your data can be added to a table in several ways such as from the Insert tab, from the Home tab, with a keyboard shortcut, or using the Quick Analysis tools.
Tables work well with other tools in Excel such as Power Query. Because of this, Excel will even automatically convert your data into a table before using Power Query.
Creating multiple tables in your workbook can also be automated using either VBA or Office Scripts.
How do you make your tables? Do you know any other tips? Let me know in the comments section below!
About the Author
John is a Microsoft MVP and qualified actuary with over 15 years of experience. He has worked in a variety of industries, including insurance, ad tech, and most recently Power Platform consulting. He is a keen problem solver and has a passion for using technology to make businesses more efficient.
Microsoft Excel is convenient for creating tables and doing calculations. Its working area is a set of cells to be filled with data. Consequently, the data can be formatted, used for building graphs, charts, summary reports.
For a beginner, working with tables in Excel may seem complicated at the first glance. It is differs considerably from the principles of table construction in Word. However, let us start from the very basics: creating and formatting tables. By the time you reach the end of this article, you will understand there is no better tool for creating tables than Excel.
Creating a table in Excel: a dummy’s guide
Working with Excel tables for dummies does not tolerate haste. There are different ways to create a table for a specific purpose, and each of them has its advantages. Therefore, let us start with assessing the situation visually.
Look carefully at the work sheet of the table processor:
It is a set of cells in columns and rows. Essentially, it’s a table. The columns are marked with letters. The rows are designated with numbers. There are no borders.
First of all, let’s learn to work with cells, rows and columns.
How to select a column and a row
To select the entire column, left-click on the letter that marks it.
To select a row, click on the number it’s designated with.
To select several columns or rows, left-click on the name, hold down the button and drag the pointer.
To select a column with the help of hot keys, place the cursor in any cell of the column and press Ctrl + Space. The key combination Shift + Space is used to select a row.
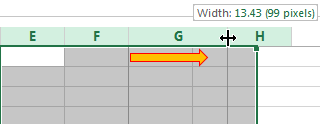
How to resize cells
If your information does not fit in the table, you need to resize the cells.
- You can move them manually by grabbing the cell boundary with the left mouse button.
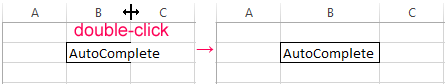
- If the cell contains a long word, you can double-click on the boundary of the column/row. The program will expand its boundary automatically.
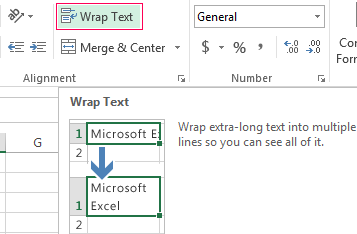
- If you need to increase the height of a row preserving the column width, use the button «Wrap Text» in the tool bar.
To change the column width and the row height in a certain range, resize 1 column/row (by dragging its boundaries manually) – and all the selected columns and rows will be resized automatically.
Important note. To go back to the previous size, you can press the «Undo Typing» button or the hot-key combination CTRL+Z. However, it works only if used immediately. Later on, it will not help.
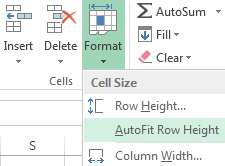
To bring the rows to their initial boundaries, open the tool menu: «HOME»-«Format» and choose «AutoFit Row Height».
This method does not work for columns. Click «Format» — « AutoFit Row Width» Memorize this number. Select any cell in the column that needs to go back to the initial size. Click «Format» — «Column Width» again and enter the value suggested by the program (as a rule, it’s 8.43 – the number of characters in the Calibri font, size 11 pt). OK.
How to insert a column or row
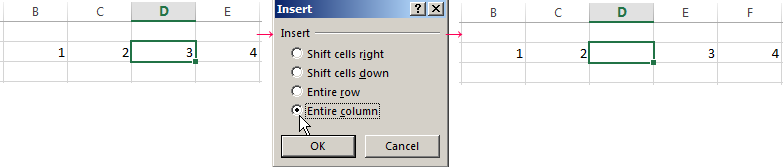
Select the column/row to the right of/below the place where the insertion needs to be made. That is, the new column will appear to the left of the selected cell. The new row will be pasted above it.
Right-click on the cell and select «Insert» in the drop-down menu (or hit the hot-key combination CTRL+SHIFT+»=»).
Select «Entire column» and press OK.
Hint. To insert a new column quickly, select a column in the desired position and hit CTRL+SHIFT+PLUS.
All these skills will come handy when building a table in Excel. You will need to resize the cells and insert rows/columns in the process.
Creating a table with formulas step by step
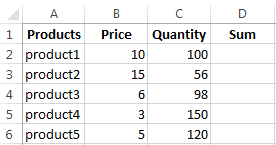
- Fill in the header manually by entering the column headings. Fill in the rows by entering your data. Apply the acquired knowledge in practice: expand the column boundaries, adjust the row height.
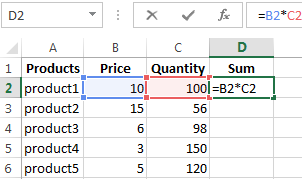
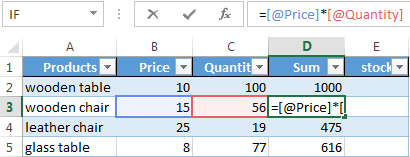
- To fill in the «Sum» column, place the cursor in its first cell. Enter «=». In such a way, we inform Excel: a formula will be here. Select the cell B2 (with the first price). Enter the multiplication symbol (*). Select the cell C2 (with the quantity). Press ENTER.
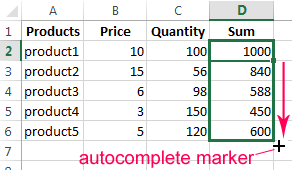
- When you hover the pointer over the cell containing the formula, a small cross will appear in its bottom right corner. It points out the autocomplete marker. Grab it with the left mouse button and drag it to the end of the column. The formula will be copied into every cell.
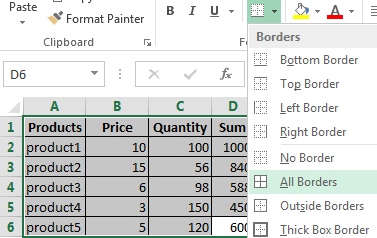
- Designate the boundaries of your table. Select the range containing your data. Click the button «HOME»-«Border» (on the main page in the «Font» menu). And click «All Borders».
Now the column and row borders will be visible when you print the table.
The «Font» menu allows you to format the data in your Excel table the way you would do it in Word.
For example, change the font size and highlight the header in bold. You may also apply center alignment, word wrap, etc.
Creating a table in Excel: a step-by-step instruction
You already know the simplest way to create tables. However, Excel can offer a more convenient variant (in terms of the subsequent formatting and work with the data).
Let us construct a smart (dynamic) table:
- Go to the «INSERT» tab – the «Table» tool (or press the hot-key combination CTRL+T).
- This will open a dialog window, in which you need to enter the data range. Check the box for a table with headings. Click OK. It’s no big deal if you don’t enter the proper range on the first try. The smart table is flexible, dynamic.
Important note. You can also take an alternative route: start with selecting the range of cells, then press the «Table» button.
Now enter your data into the ready framework. If you need an additional column, place the cursor in the heading cell. Make the entry and press ENTER. The range will expand automatically.
If you need additional rows, grab the autocomplete marker in the bottom right corner and drag it downward.
How to work with a table in Excel
With the release of new versions of the program, working with tables in Excel has become more interesting and dynamic. After a smart table has been formed on the spreadsheet, the tool «TABLE TOOLS» — «DESIGN» becomes available.
Here you can name the table or resize it.
Various styles are available to you, as well as the opportunity to transform the table into a regular range or a consolidated sheet.
MS Excel dynamic electronic tables offer immense opportunities. Let us begin with the basic skills of data entry and autocompletion:
- Select a cell by clicking on it with the left mouse button. Enter the text/numeric value. Press ENTER. If you need to change the value, place the cursor in the cell again and enter the new data.
- When you enter a value repetitively, Excel will recognize it. You will only need to enter several symbols and press enter.
- In a smart table, to apply a formula to the entire column, enter it in the first cell. The program will copy the formula in other cells automatically.
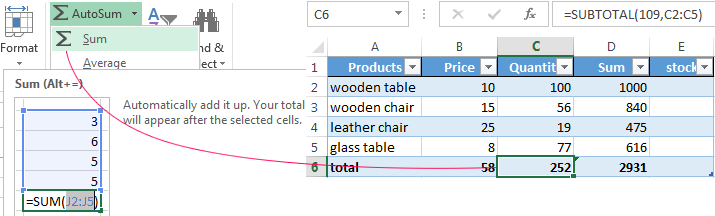
- To calculate the totals, select the column containing the values plus an empty cell for the future total and click the «Sum» button (the «Editing» tool group on the «HOME» tab, or press the hot-key combination ALT+»=»).
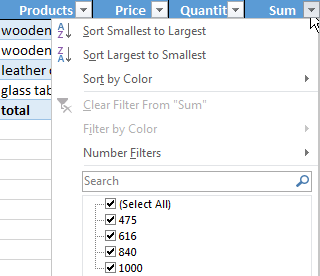
When you click on the little arrow to the right of every subheading in the header, you obtain access to the additional tools for working with the data in the table.
Sometimes the user has to work with huge tables, in which you need to scroll several thousand rows to see the totals. Deleting the rows is not an option (you will still need the data later). However, you can hide them. To this end, use number filters (depicted in the image above). Uncheck the values that need to be hidden.
Surely you all know the Microsoft Excel application. Microsoft Excel is an application or software that is useful for processing numbers. As you already know, this application has a lot of uses and benefits.
The usefulness of this application is that it can create, analyze, edit, Rank, and sort several data because this application can calculate with arithmetic and statistics.
This tutorial will explain how to sort or rank data using Microsoft Excel.
How to Rank in Microsoft Excel
You can rank data in Microsoft Excel. By using the application, you can easily do work in processing data. Ranking data is also very useful for those who work as teachers.
Because this application can rank data in a very easy way and can be done by everyone. Here are ways to rank data in Microsoft Excel:
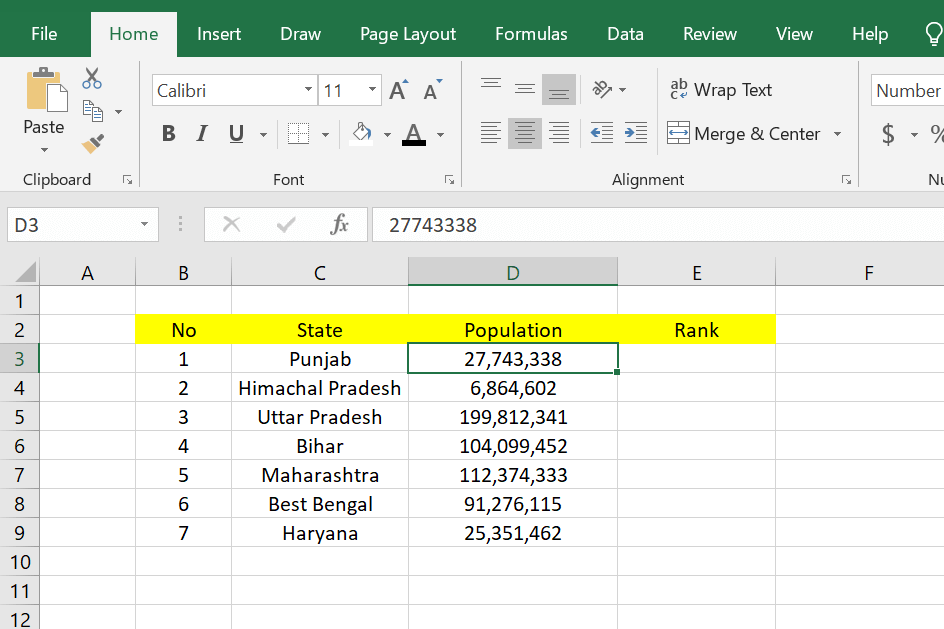
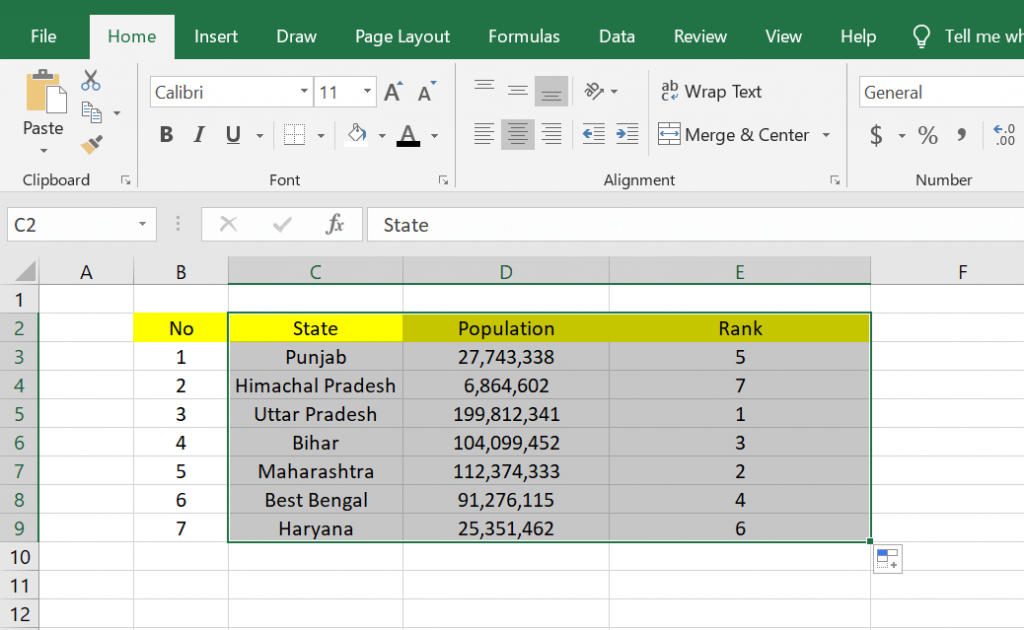
1. The first step you can take is to open a Microsoft Excel worksheet that already has the data you want to rank. In the example below, I want to rank students in a class by sorting them from rank 1 to 7 You can also rank according to the data you have.
2. After that, you can place your cursor in the cell, where you will rank the cells in the first order. You can see an example in the image below.
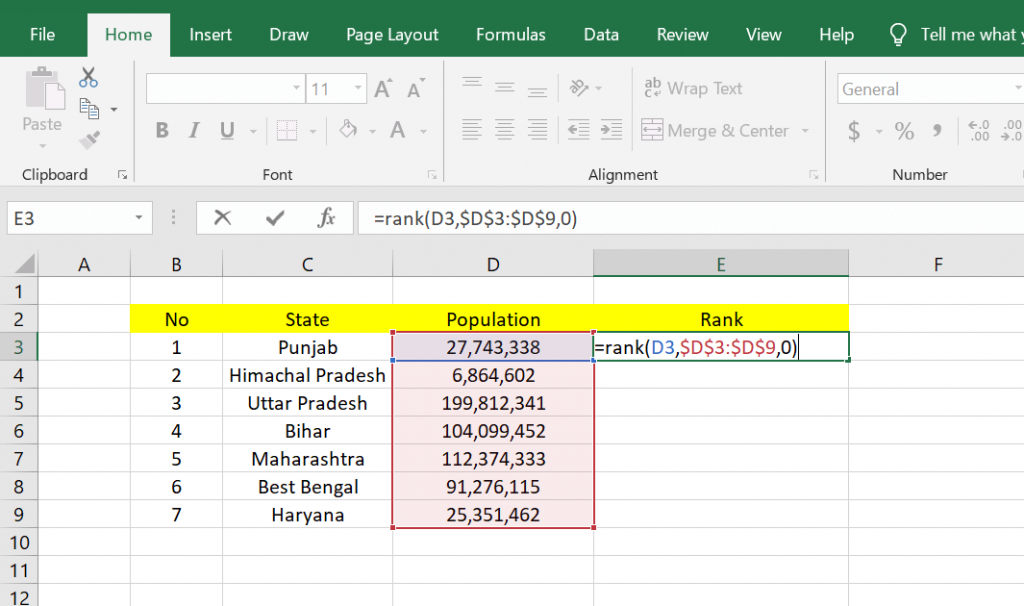
After that, you can write a formula to rank in Microsoft Excel in the fx column. And here’s the formula, =rank(number;ref;order) .
The meaning of the formula is = Rank Rank, which means it is a rank function. And (number; ref; order) means the initial cell number that has a value to be ranked, its reference, and the final cell number that has a value to be ranked, the reference.
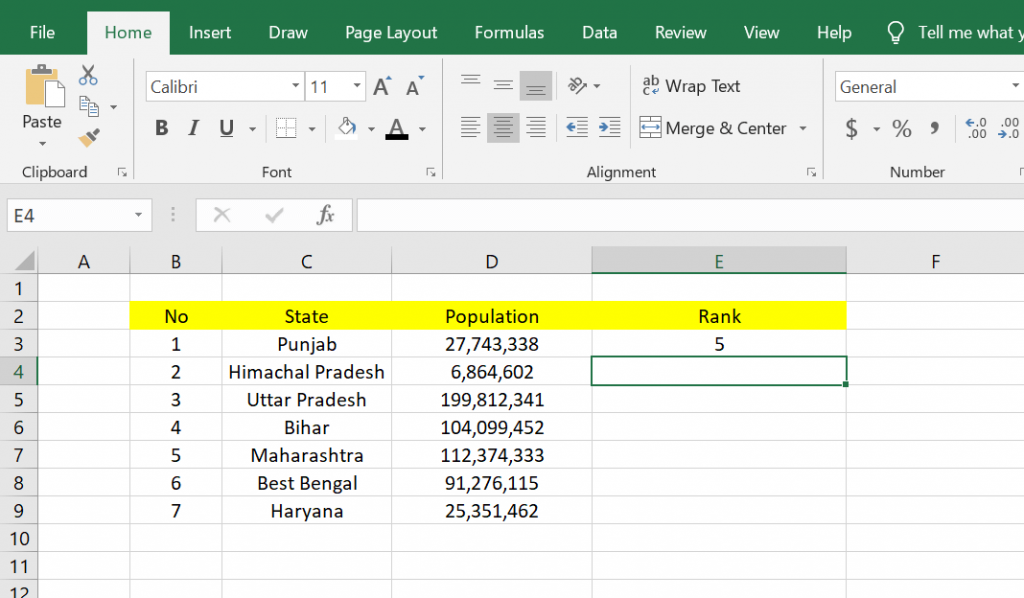
The formula is =Rank(D3;$D$3:$D$9;0) in the example below. After entering the function, you can press the Enter key on your keyboard. And here are the results, namely the ranking on data number 1, which has a ranking of 1.
3. If you want to do the same thing to all data as in data number 1, you have to copy the previous column, and then you can block the column below it and click Paste. Then you can see the results. All the columns in the Rank entity have been ranked in such away.
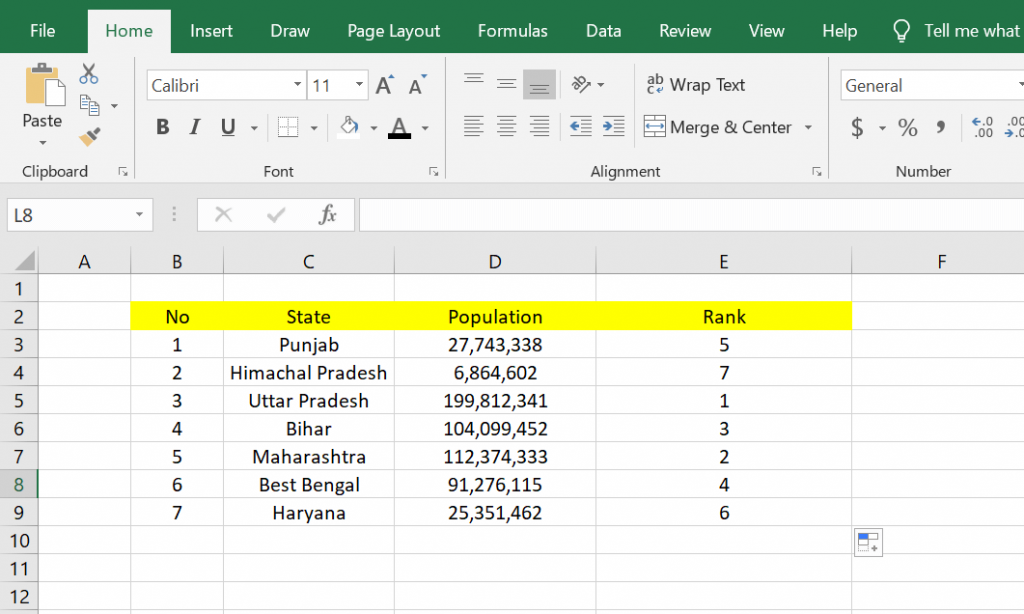
4. The results above are not satisfactory because the data is still not sorted, so it looks messy. We must make it sequentially according to the ranking from the smallest to the largest, and this example must be sorted from rank 1 to rank 9.
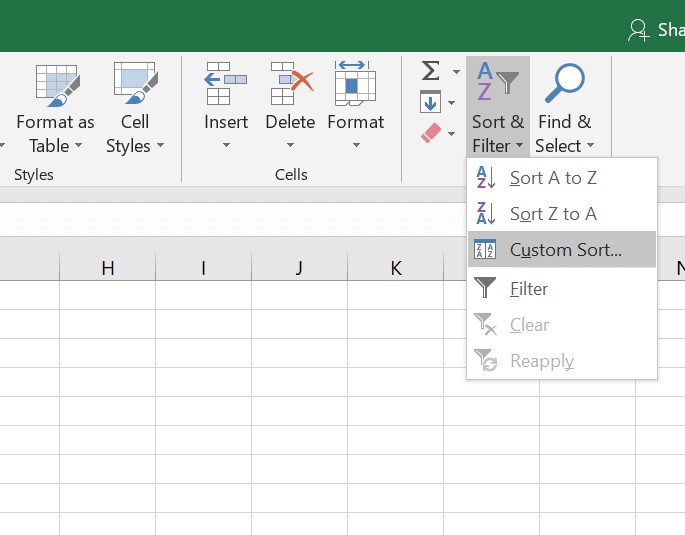
The way to sort it is to block the contents of all tables, but not with the column names and the contents of the column number.
5. After that, you can do the sorting by going to the Editing tool, clicking Sort & Filter, and then clicking the Custom Sort option…
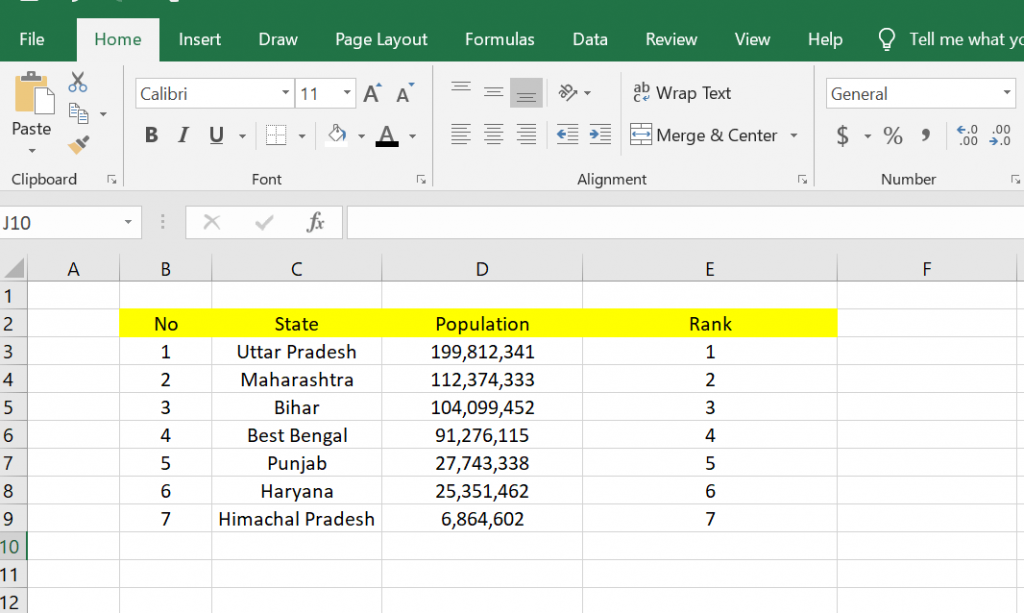
6. Then the Sort box will appear, where you have to choose sort by with the Rank option, some kind on with the Values option, and order with the Smallest to Largest option. After that, you can click OK.
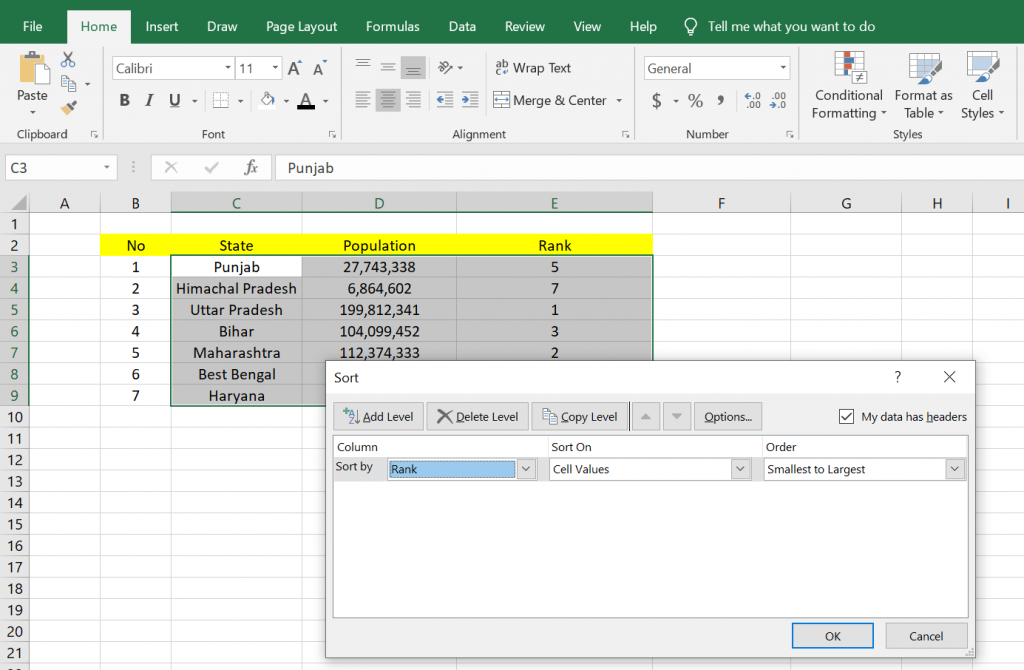
7. Below is the result of the sorting we have done above. In this way, the data that has been ranked will be sorted according to its ranking.
That’s the tutorial on how to rank using Microsoft Excel. Hopefully, this article can be useful for you.
Содержание
- Основы создания таблиц в Excel
- Способ 1: Оформление границ
- Способ 2: Вставка готовой таблицы
- Способ 3: Готовые шаблоны
- Вопросы и ответы
Обработка таблиц – основная задача Microsoft Excel. Умение создавать таблицы является фундаментальной основой работы в этом приложении. Поэтому без овладения данного навыка невозможно дальнейшее продвижение в обучении работе в программе. Давайте выясним, как создать таблицу в Экселе.
Таблица в Microsoft Excel это не что иное, как набор диапазонов данных. Самую большую роль при её создании занимает оформление, результатом которого будет корректное восприятие обработанной информации. Для этого в программе предусмотрены встроенные функции либо же можно выбрать путь ручного оформления, опираясь лишь на собственный опыт подачи. Существует несколько видов таблиц, различающихся по цели их использования.
Способ 1: Оформление границ
Открыв впервые программу, можно увидеть чуть заметные линии, разделяющие потенциальные диапазоны. Это позиции, в которые в будущем можно занести конкретные данные и обвести их в таблицу. Чтобы выделить введённую информацию, можно воспользоваться зарисовкой границ этих самых диапазонов. На выбор представлены самые разные варианты чертежей — отдельные боковые, нижние или верхние линии, толстые и тонкие и другие — всё для того, чтобы отделить приоритетную информацию от обычной.
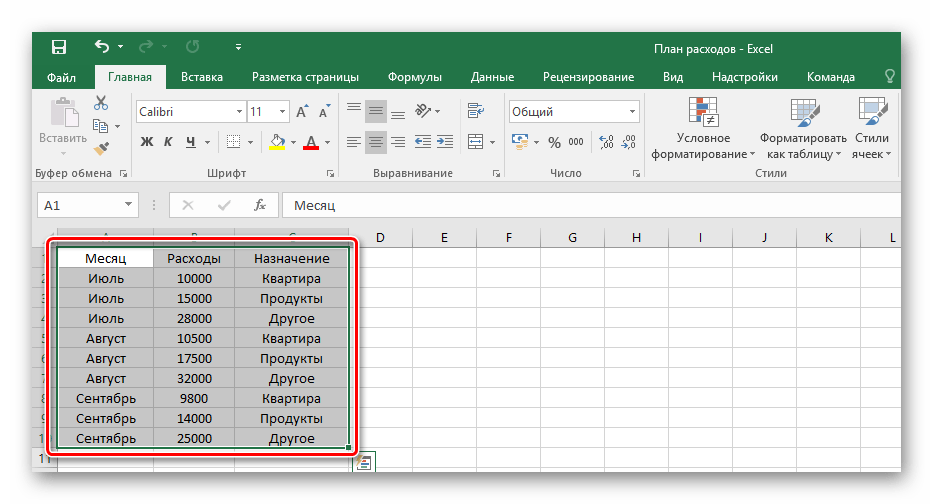
- Для начала создайте документ Excel, откройте его и введите в желаемые клетки данные.
- Произведите выделение ранее вписанной информации, зажав левой кнопкой мыши по всем клеткам диапазона.
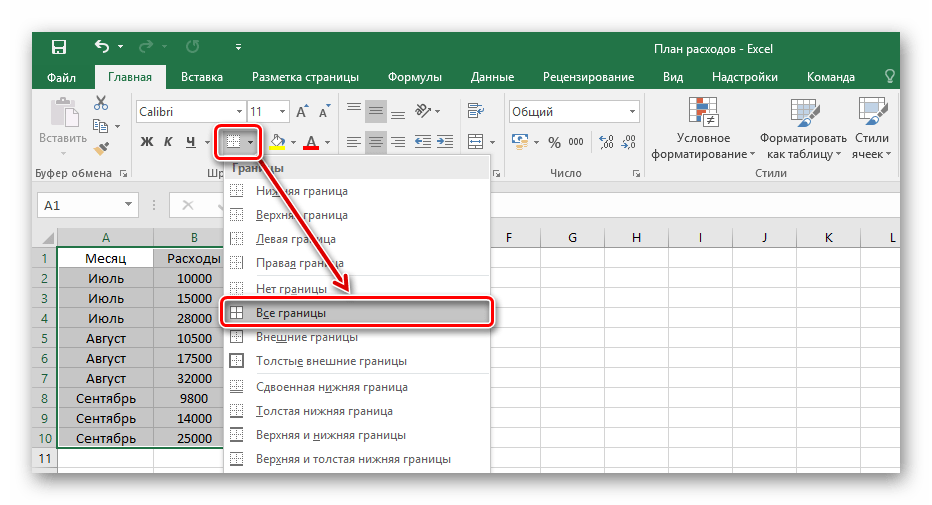
- На вкладке «Главная» в блоке «Шрифт» нажмите на указанную в примере иконку и выберите пункт «Все границы».
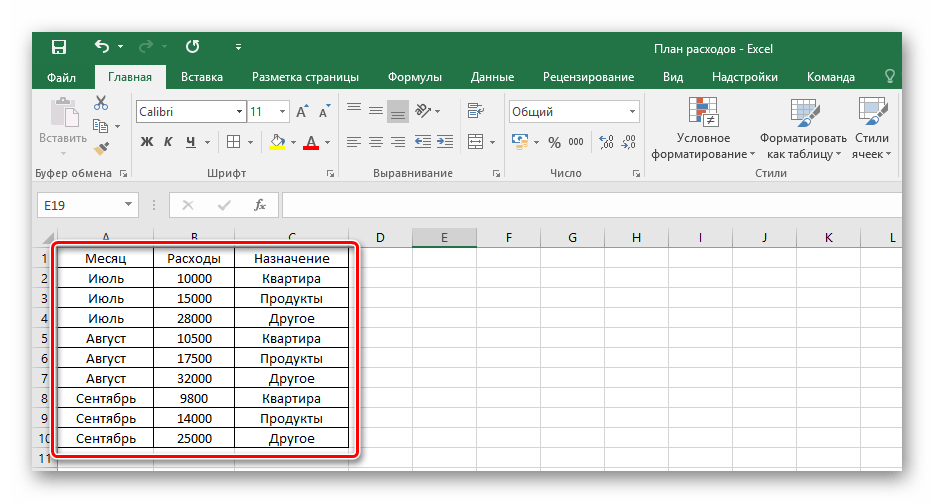
- В результате получится обрамленный со всех сторон одинаковыми линиями диапазон данных. Такую таблицу будет видно при печати.
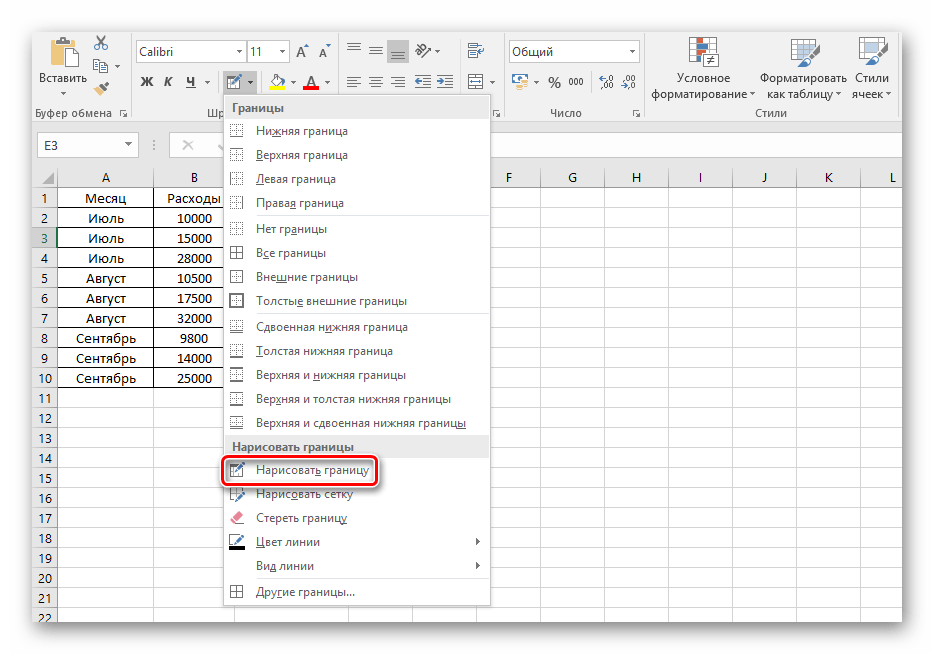
- Для ручного оформления границ каждой из позиций можно воспользоваться специальным инструментом и нарисовать их самостоятельно. Перейдите уже в знакомое меню выбора оформления клеток и выберите пункт «Нарисовать границу».
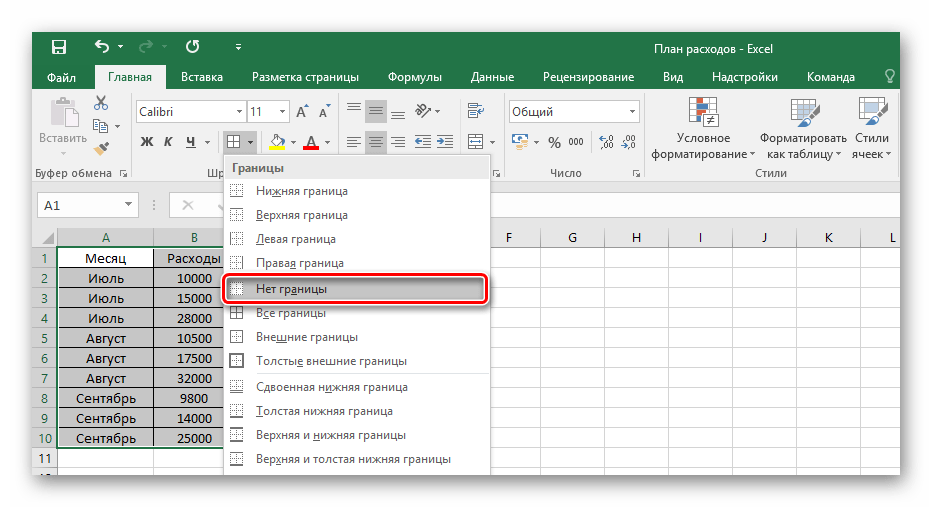
Соответственно, чтобы убрать оформление границ у таблицы, необходимо кликнуть на ту же иконку, но выбрать пункт «Нет границы».
Пользуясь выбранным инструментом, можно в произвольной форме разукрасить границы клеток с данными и не только.
Обратите внимание! Оформление границ клеток работает как с пустыми ячейками, так и с заполненными. Заполнять их после обведения или до — это индивидуальное решение каждого, всё зависит от удобства использования потенциальной таблицей.
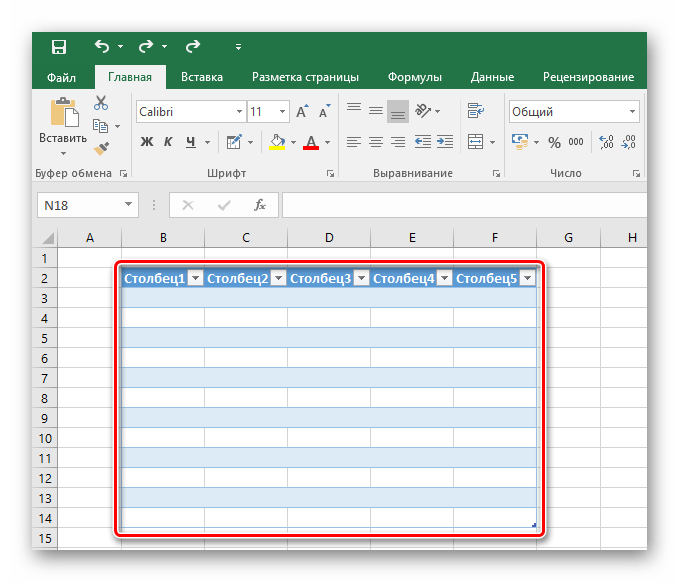
Способ 2: Вставка готовой таблицы
Разработчиками Microsoft Excel предусмотрен инструмент для добавления готовой шаблонной таблицы с заголовками, оформленным фоном, границами и так далее. В базовый комплект входит даже фильтр на каждый столбец, и это очень полезно тем, кто пока не знаком с такими функциями и не знает как их применять на практике.
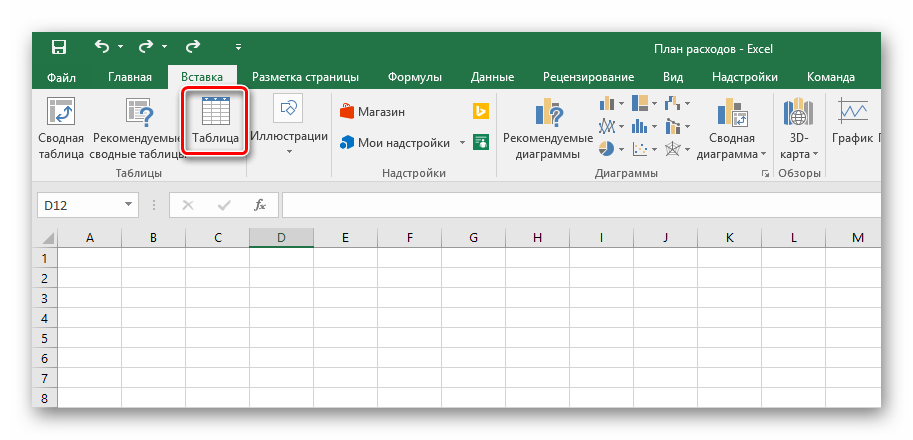
- Переходим во вкладку «Вставить».
- Среди предложенных кнопок выбираем «Таблица».
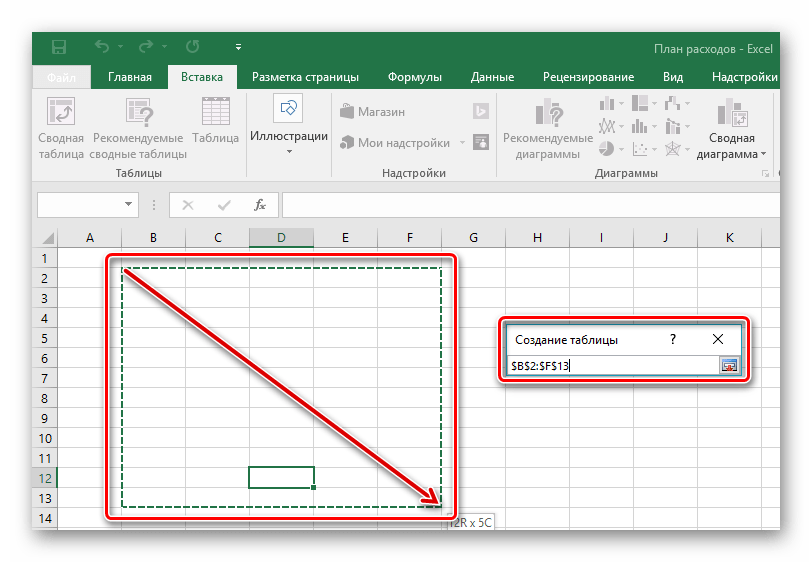
- После появившегося окна с диапазоном значений выбираем на пустом поле место для нашей будущей таблицы, зажав левой кнопкой и протянув по выбранному месту.
- Отпускаем кнопку мыши, подтверждаем выбор соответствующей кнопкой и любуемся совершенно новой таблице от Excel.
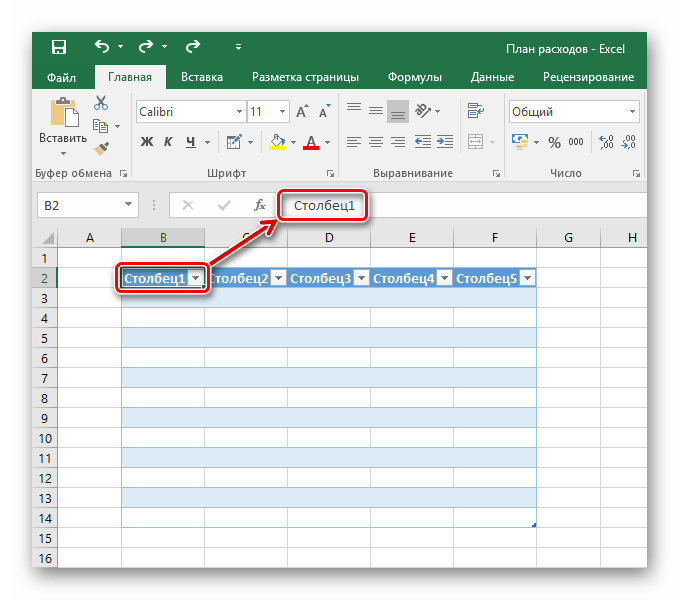
- Редактирование названий заголовков столбцов происходит путём нажатия на них, а после — изменения значения в указанной строке.
- Размер таблицы можно в любой момент поменять, зажав соответствующий ползунок в правом нижнем углу, потянув его по высоте или ширине.
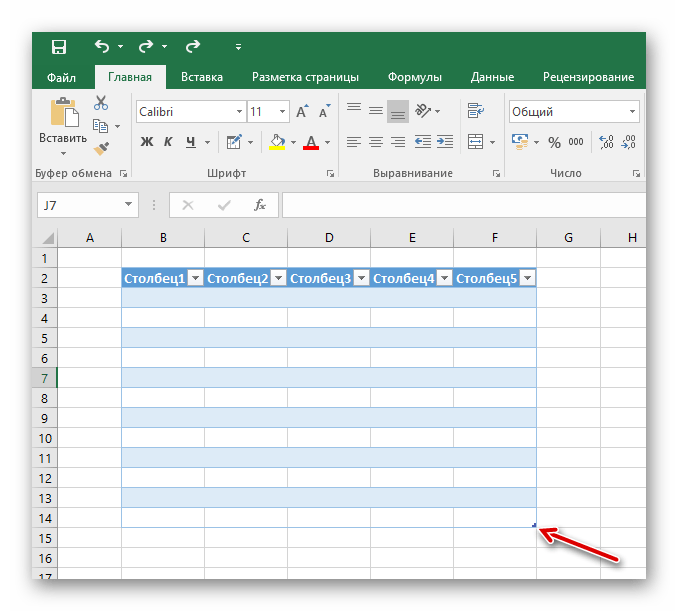
Таким образом, имеется таблица, предназначенная для ввода информации с последующей возможностью её фильтрации и сортировки. Базовое оформление помогает разобрать большое количество данных благодаря разным цветовым контрастам строк. Этим же способом можно оформить уже имеющийся диапазон данных, сделав всё так же, но выделяя при этом не пустое поле для таблицы, а заполненные клетки.
Способ 3: Готовые шаблоны
Большой спектр возможностей для ведения информации открывается в разработанных ранее шаблонах таблиц Excel. В новых версиях программы достаточное количество готовых решений для ваших задач, таких как планирование и ведение семейного бюджета, различных подсчётов и контроля разнообразной информации. В этом методе всё просто — необходимо лишь воспользоваться шаблоном, разобраться в нём и пользоваться в удовольствие.
- Открыв Excel, перейдите в главное меню нажатием кнопки «Файл».
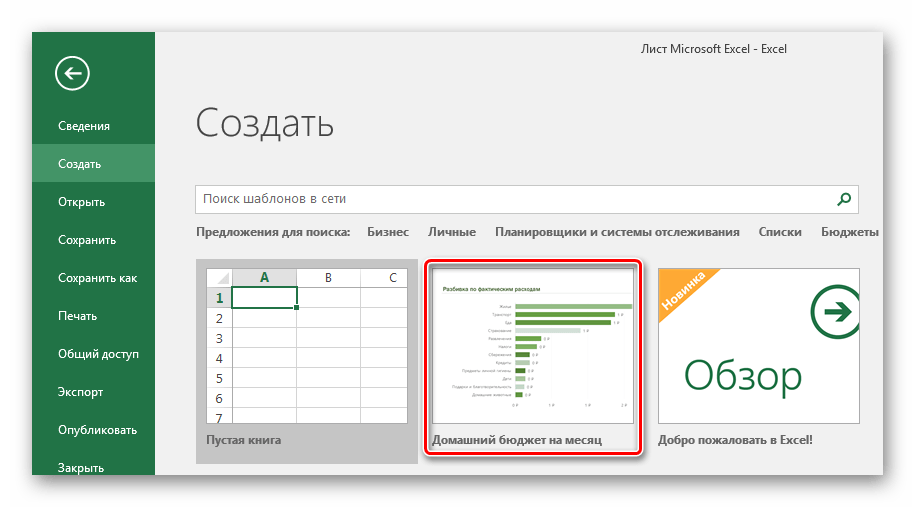
- Нажмите вкладку «Создать».
- Выберите любой понравившийся из представленных шаблон.
- Ознакомьтесь с вкладками готового примера. В зависимости от цели таблицы их может быть разное количество.
- В примере с таблицей по ведению бюджета есть колонки, в которые можно и нужно вводить свои данные — воспользуйтесь этим.
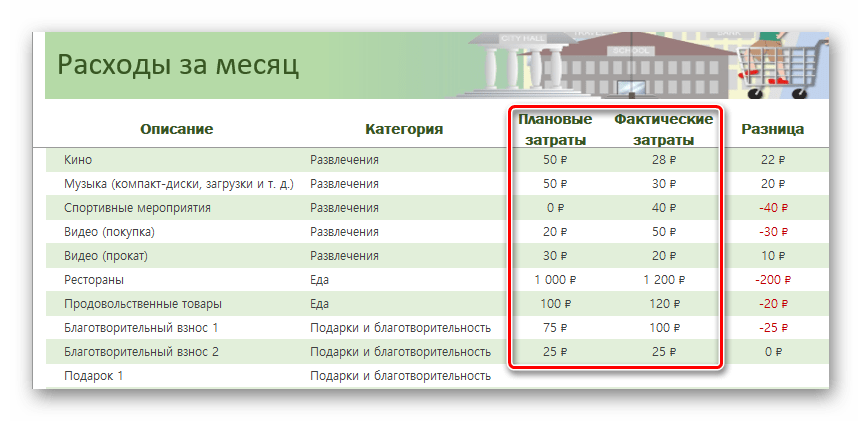
Таблицы в Excel можно создать как вручную, так и в автоматическом режиме с использованием заранее подготовленных шаблонов. Если вы принципиально хотите сделать свою таблицу с нуля, следует глубже изучить функциональность и заниматься реализацией таблицы по маленьким частицам. Тем, у кого нет времени, могут упростить задачу и вбивать данные уже в готовые варианты таблиц, если таковы подойдут по предназначению. В любом случае, с задачей сможет справиться даже рядовой пользователь, имея в запасе лишь желание создать что-то практичное.
Еще статьи по данной теме: