Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 for Mac More…Less
You can create a form in Excel by adding content controls, such as buttons, check boxes, list boxes, and combo boxes to a workbook. Other people can use Excel to fill out the form and then print it if they choose to.
Step 1: Show the Developer tab
-
On the Excel menu, click Preferences.
-
Under Authoring, click View.
-
Under In Ribbon, Show, select Developer tab.
Step 2: Add and format content controls
-
On the Developer tab, click the control that you want to add.
-
In the worksheet, click where you want to insert the control.
-
To set specific properties for the control, hold down CONTROL and click the control, and then click Format Control.
-
In the Format Control box, set the properties that you want, such as font, alignment, and color.
-
Repeat steps 1 through 4 for each control that you want to add.
Step 3: Protect the sheet that contains the form
-
On the Tools menu, point to Protection, and then click Protect Sheet.
-
Select the protection options that you want.
-
Save and close the workbook.
Tip: To continue editing after you have protected the form, on the Tools menu, point to Protect Sheet, and then click Unprotect Sheet.
Step 4: Test the form (optional)
If you want, you can test the form before you distribute it.
-
Protect the form as described in step 3.
-
Reopen the form, fill it out as the user would, and then save a copy.
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
Содержание
- Применение инструментов заполнения
- Способ 1: встроенный объект для ввода данных Excel
- Способ 2: создание пользовательской формы
- Вопросы и ответы
Для облегчения ввода данных в таблицу в Excel можно воспользоваться специальными формами, которые помогут ускорить процесс заполнения табличного диапазона информацией. В Экселе имеется встроенный инструмент позволяющий производить заполнение подобным методом. Также пользователь может создать собственный вариант формы, которая будет максимально адаптирована под его потребности, применив для этого макрос. Давайте рассмотрим различные варианты использования этих полезных инструментов заполнения в Excel.
Применение инструментов заполнения
Форма заполнения представляет собой объект с полями, наименования которых соответствуют названиям колонок столбцов заполняемой таблицы. В эти поля нужно вводить данные и они тут же будут добавляться новой строкой в табличный диапазон. Форма может выступать как в виде отдельного встроенного инструмента Excel, так и располагаться непосредственно на листе в виде его диапазона, если она создана самим пользователем.
Теперь давайте рассмотрим, как пользоваться этими двумя видами инструментов.
Способ 1: встроенный объект для ввода данных Excel
Прежде всего, давайте узнаем, как применять встроенную форму для ввода данных Excel.
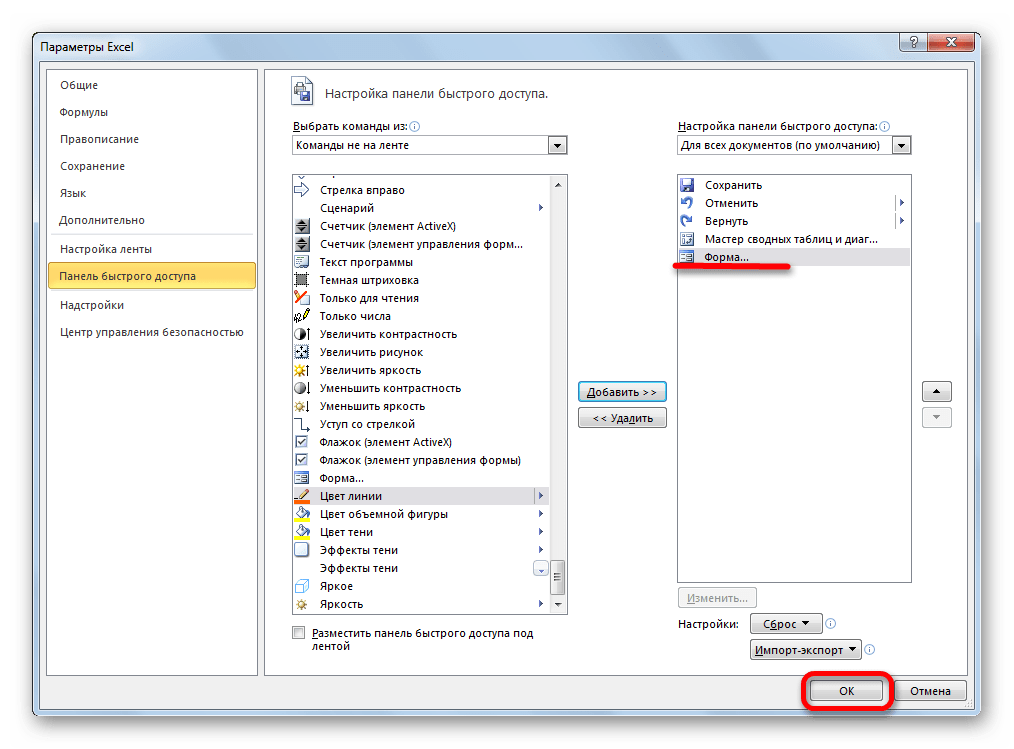
- Нужно отметить, что по умолчанию значок, который её запускает, скрыт и его нужно активировать. Для этого переходим во вкладку «Файл», а затем щелкаем по пункту «Параметры».
- В открывшемся окне параметров Эксель перемещаемся в раздел «Панель быстрого доступа». Большую часть окна занимает обширная область настроек. В левой её части находятся инструменты, которые могут быть добавлены на панель быстрого доступа, а в правой – уже присутствующие.
В поле «Выбрать команды из» устанавливаем значение «Команды не на ленте». Далее из списка команд, расположенного в алфавитном порядке, находим и выделяем позицию «Форма…». Затем жмем на кнопку «Добавить».
- После этого нужный нам инструмент отобразится в правой части окна. Жмем на кнопку «OK».
- Теперь данный инструмент располагается в окне Excel на панели быстрого доступа, и мы им можем воспользоваться. Он будет присутствовать при открытии любой книги данным экземпляром Excel.
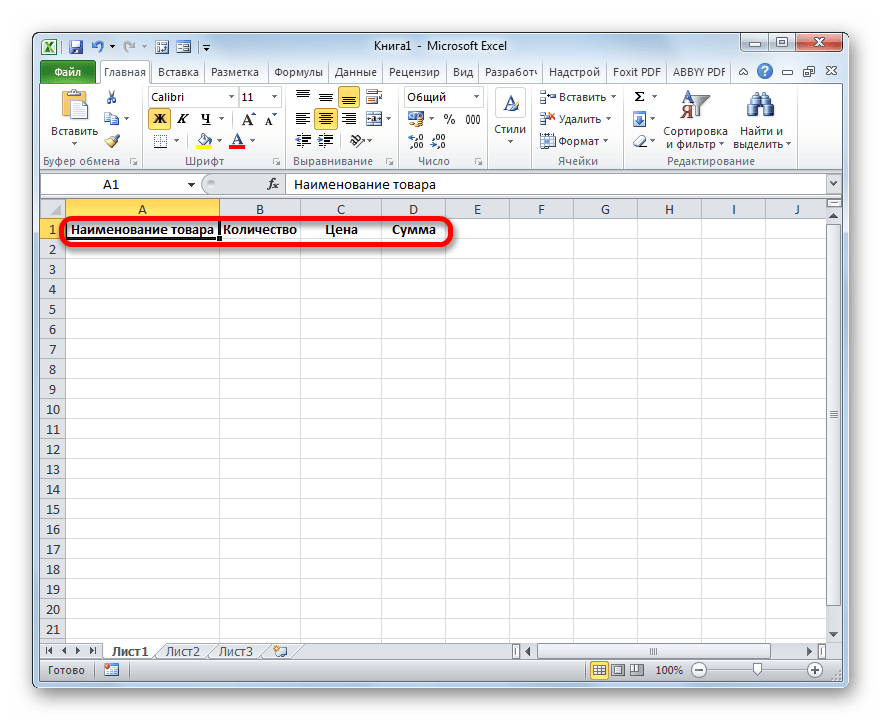
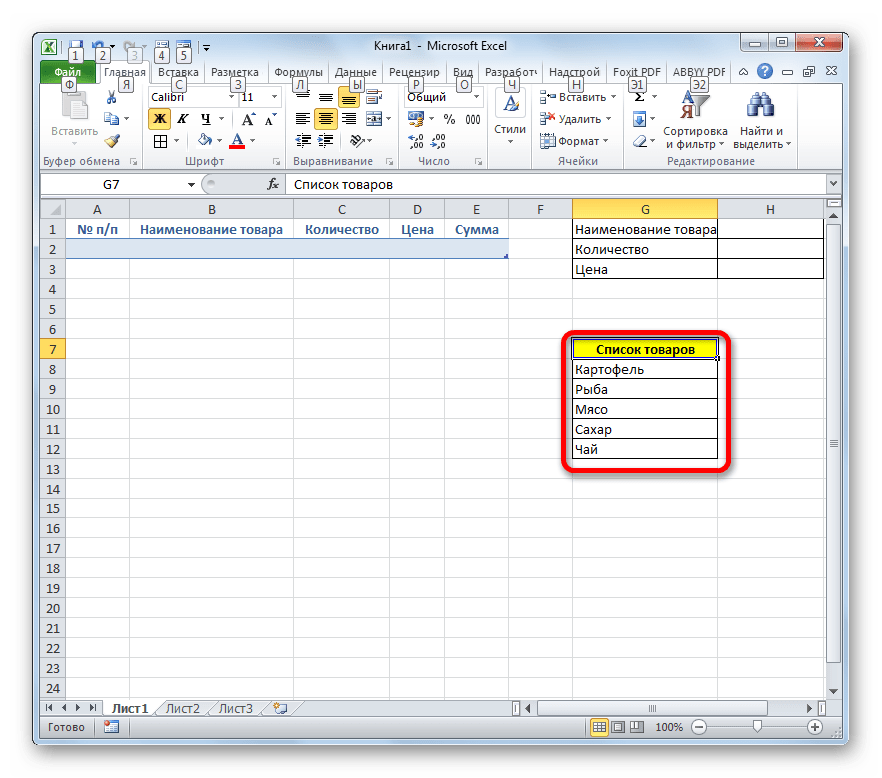
- Теперь, чтобы инструмент понял, что именно ему нужно заполнять, следует оформить шапку таблицы и записать любое значение в ней. Пусть табличный массив у нас будет состоять из четырех столбцов, которые имеют названия «Наименование товара», «Количество», «Цена» и «Сумма». Вводим данные названия в произвольный горизонтальный диапазон листа.
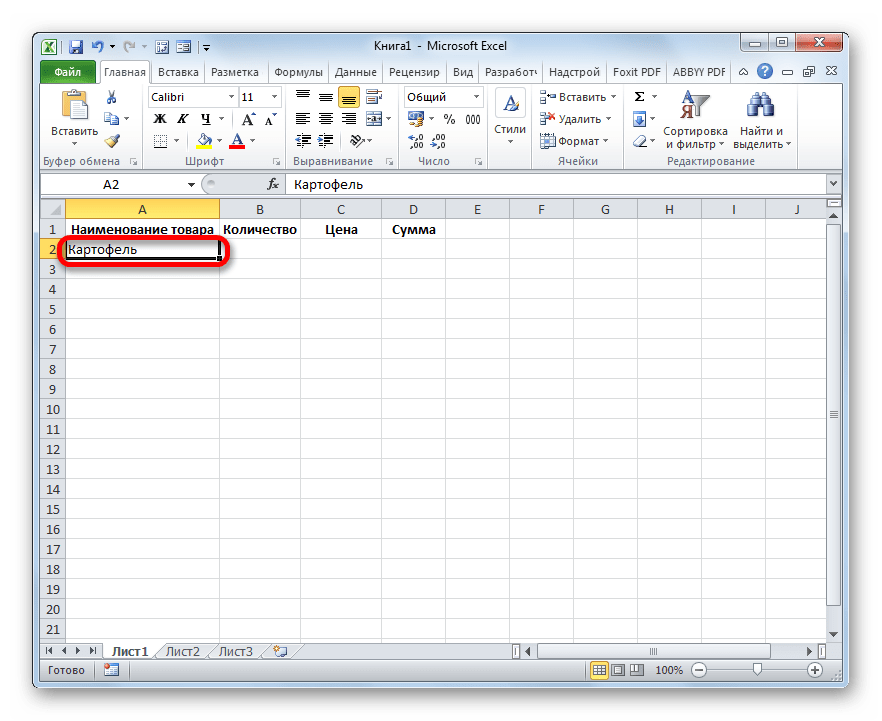
- Также, чтобы программа поняла, с каким именно диапазонам ей нужно будет работать, следует ввести любое значение в первую строку табличного массива.
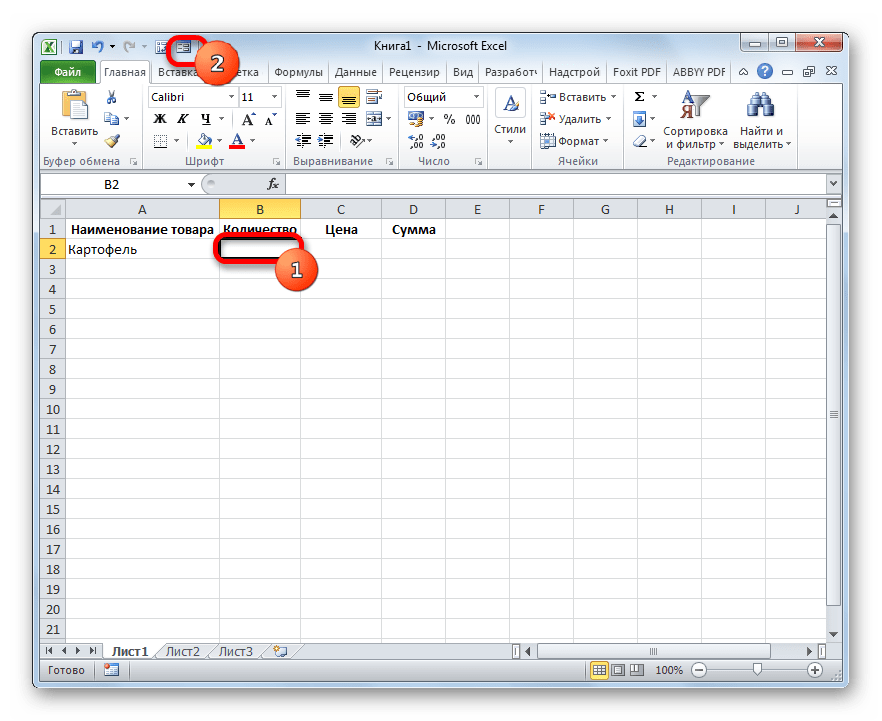
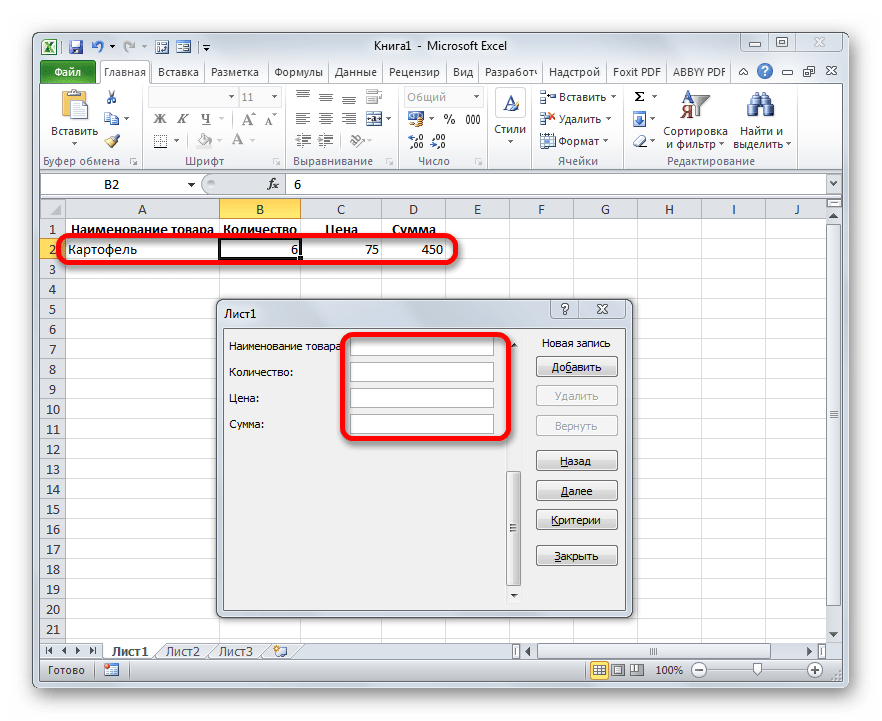
- После этого выделяем любую ячейку заготовки таблицы и щелкаем на панели быстрого доступа по значку «Форма…», который мы ранее активировали.
- Итак, открывается окно указанного инструмента. Как видим, данный объект имеет поля, которые соответствуют названиям столбцов нашего табличного массива. При этом первое поле уже заполнено значением, так как мы его ввели вручную на листе.
- Вводим значения, которые считаем нужными и в остальные поля, после чего жмем на кнопку «Добавить».
- После этого, как видим, в первую строку таблицы были автоматически перенесены введенные значения, а в форме произошел переход к следующему блоку полей, который соответствуют второй строке табличного массива.
- Заполняем окно инструмента теми значениями, которые хотим видеть во второй строке табличной области, и снова щелкаем по кнопке «Добавить».
- Как видим, значения второй строчки тоже были добавлены, причем нам даже не пришлось переставлять курсор в самой таблице.
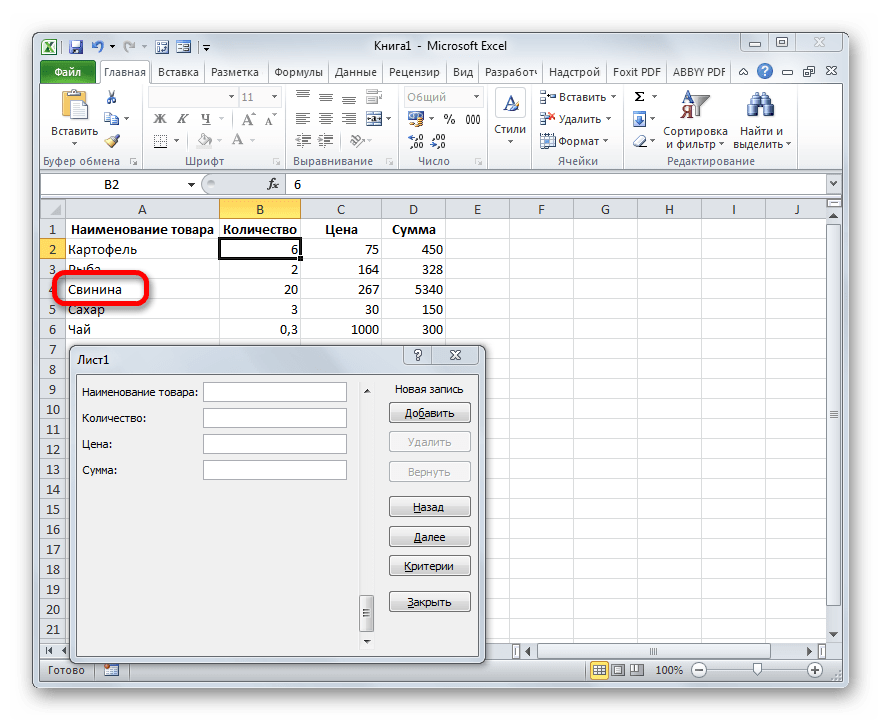
- Таким образом, заполняем табличный массив всеми значениями, которые хотим в неё ввести.
- Кроме того, при желании, можно производить навигацию по ранее введенным значениям с помощью кнопок «Назад» и «Далее» или вертикальной полосы прокрутки.
- При необходимости можно откорректировать любое значение в табличном массиве, изменив его в форме. Чтобы изменения отобразились на листе, после внесения их в соответствующий блок инструмента, жмем на кнопку «Добавить».
- Как видим, изменение сразу произошло и в табличной области.
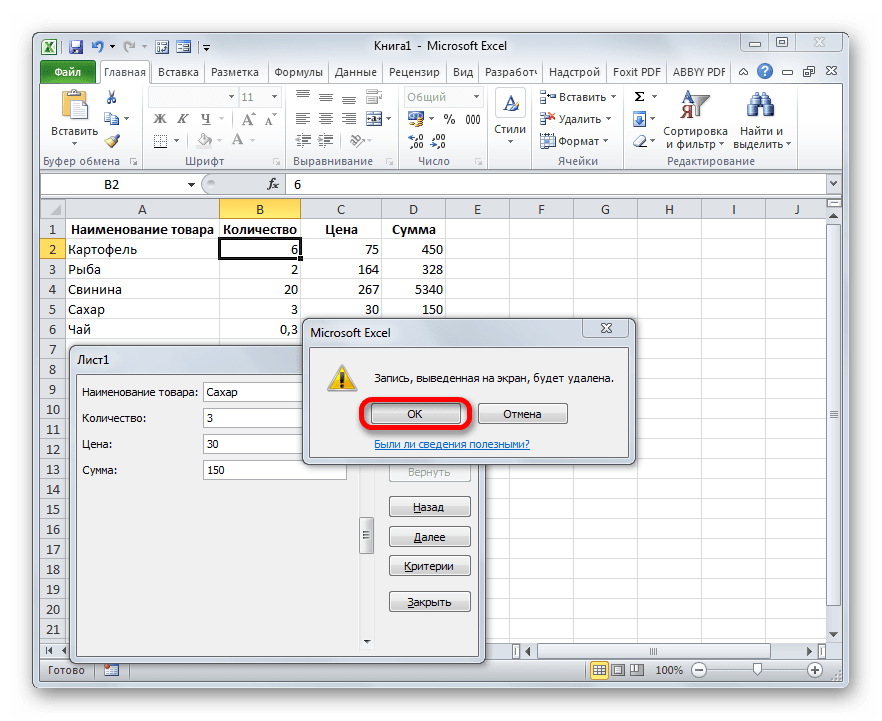
- Если нам нужно удалить, какую-то строчку, то через кнопки навигации или полосу прокрутки переходим к соответствующему ей блоку полей в форме. После этого щелкаем по кнопке «Удалить» в окошке инструмента.
- Открывается диалоговое окно предупреждения, в котором сообщается, что строка будет удалена. Если вы уверены в своих действиях, то жмите на кнопку «OK».
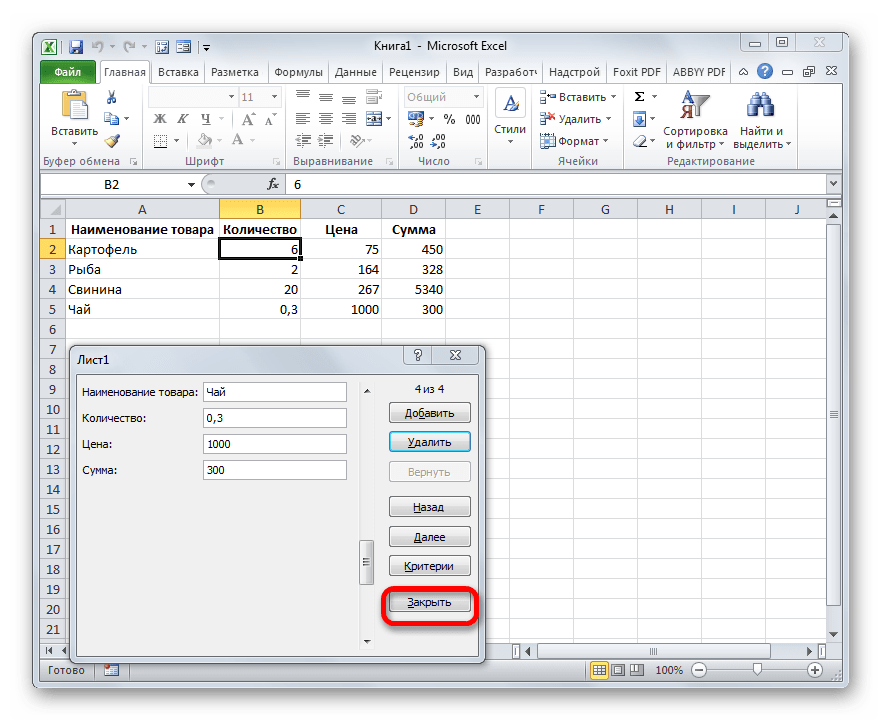
- Как видим, строчка была извлечена из табличного диапазона. После того, как заполнение и редактирование закончено, можно выходить из окна инструмента, нажав на кнопку «Закрыть».
- После этого для предания табличному массиву более наглядного визуального вида можно произвести форматирование.
Способ 2: создание пользовательской формы
Кроме того, с помощью макроса и ряда других инструментов существует возможность создать собственную пользовательскую форму для заполнения табличной области. Она будет создаваться прямо на листе, и представлять собой её диапазон. С помощью данного инструмента пользователь сам сможет реализовать те возможности, которые считает нужными. По функционалу он практически ни в чем не будет уступать встроенному аналогу Excel, а кое в чем, возможно, превосходить его. Единственный недостаток состоит в том, что для каждого табличного массива придется составлять отдельную форму, а не применять один и тот же шаблон, как это возможно при использовании стандартного варианта.
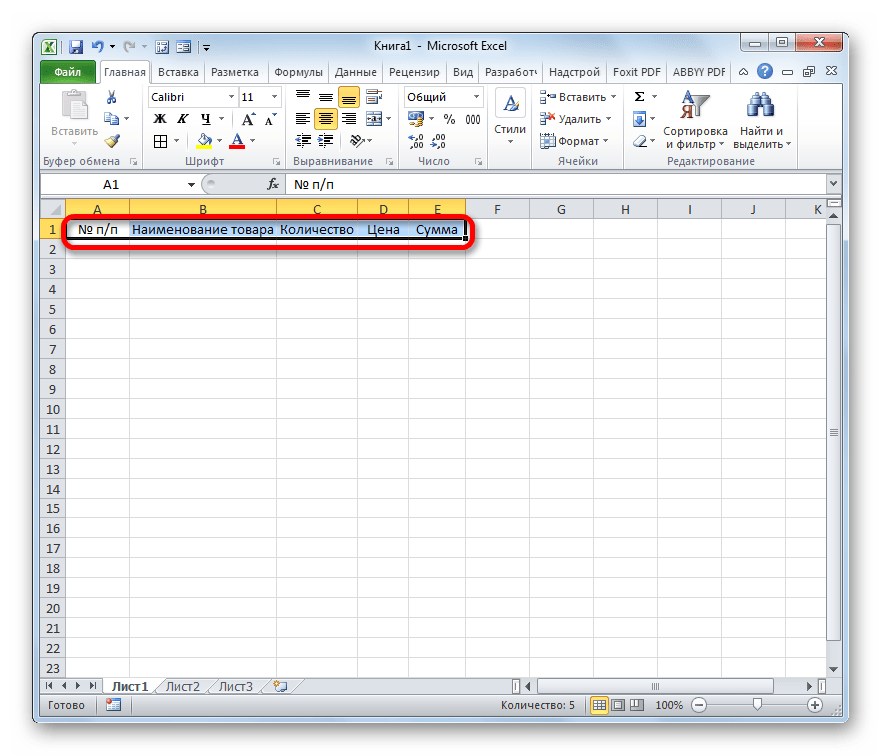
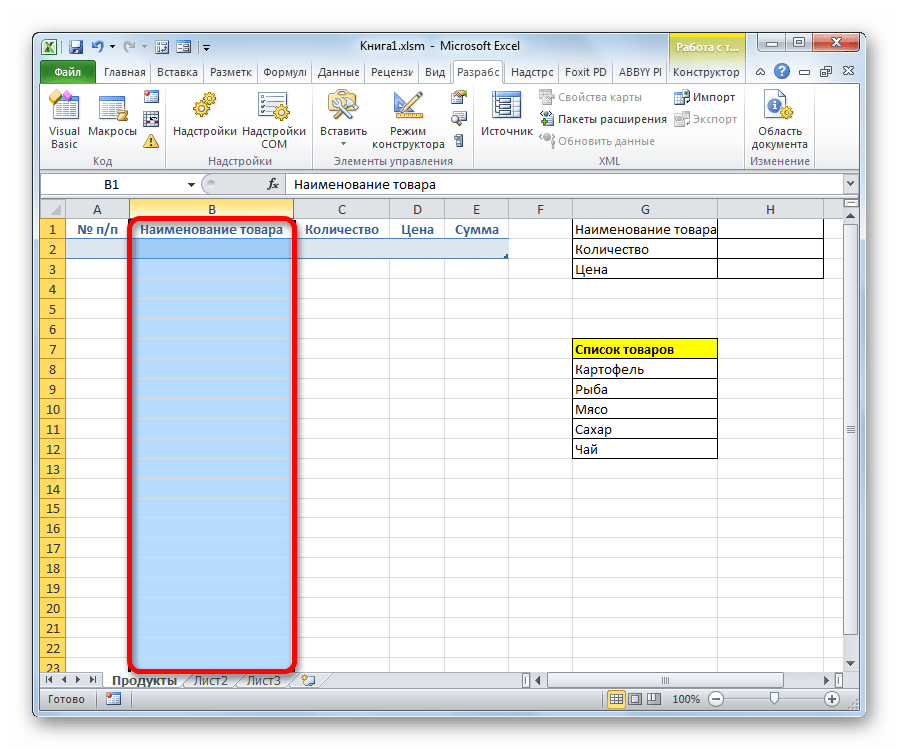
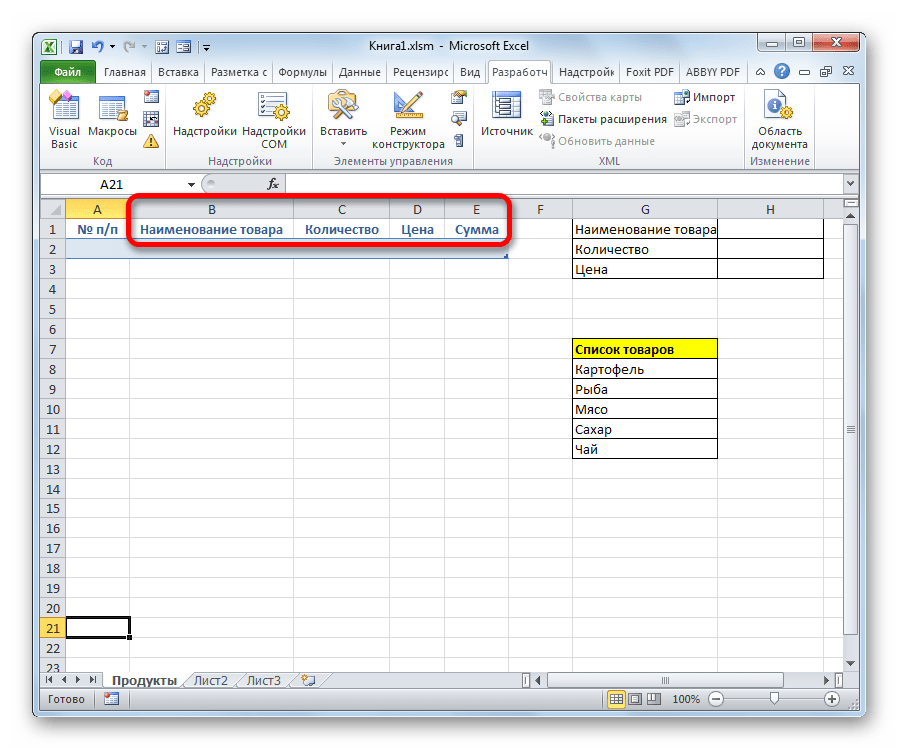
- Как и в предыдущем способе, прежде всего, нужно составить шапку будущей таблицы на листе. Она будет состоять из пяти ячеек с именами: «№ п/п», «Наименование товара», «Количество», «Цена», «Сумма».
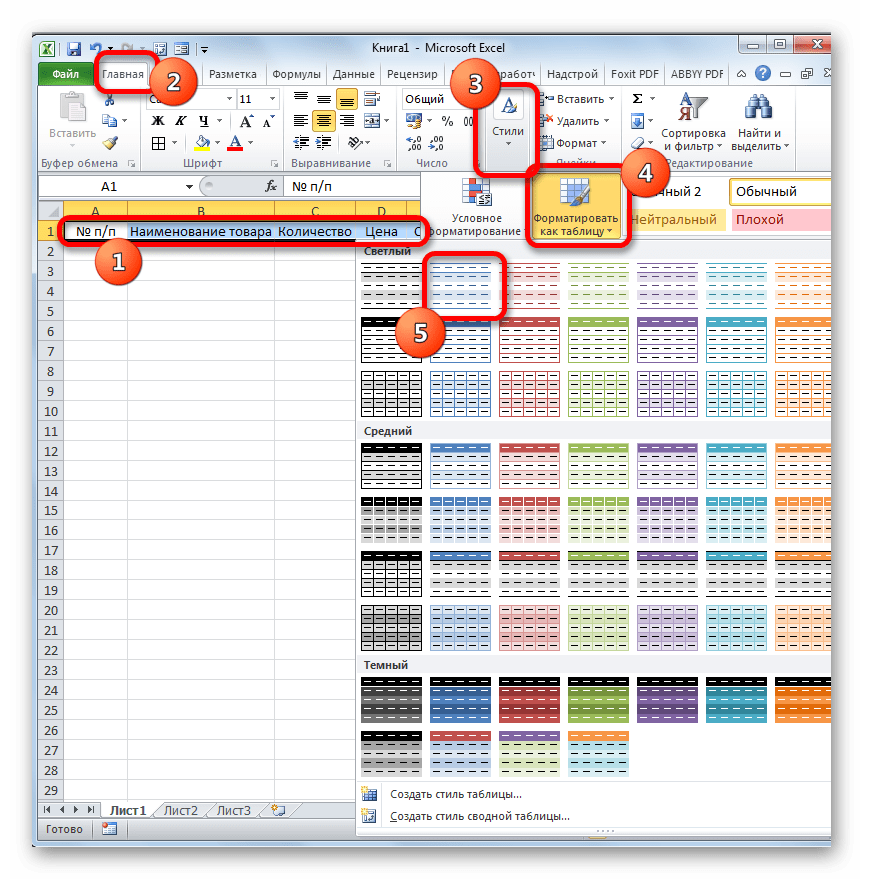
- Далее нужно из нашего табличного массива сделать так называемую «умную» таблицу, с возможностью автоматического добавления строчек при заполнении соседних диапазонов или ячеек данными. Для этого выделяем шапку и, находясь во вкладке «Главная», жмем на кнопку «Форматировать как таблицу» в блоке инструментов «Стили». После этого открывается список доступных вариантов стилей. На функционал выбор одного из них никак не повлияет, поэтому выбираем просто тот вариант, который считаем более подходящим.
- Затем открывается небольшое окошко форматирования таблицы. В нем указан диапазон, который мы ранее выделили, то есть, диапазон шапки. Как правило, в данном поле заполнено все верно. Но нам следует установить галочку около параметра «Таблица с заголовками». После этого жмем на кнопку «OK».
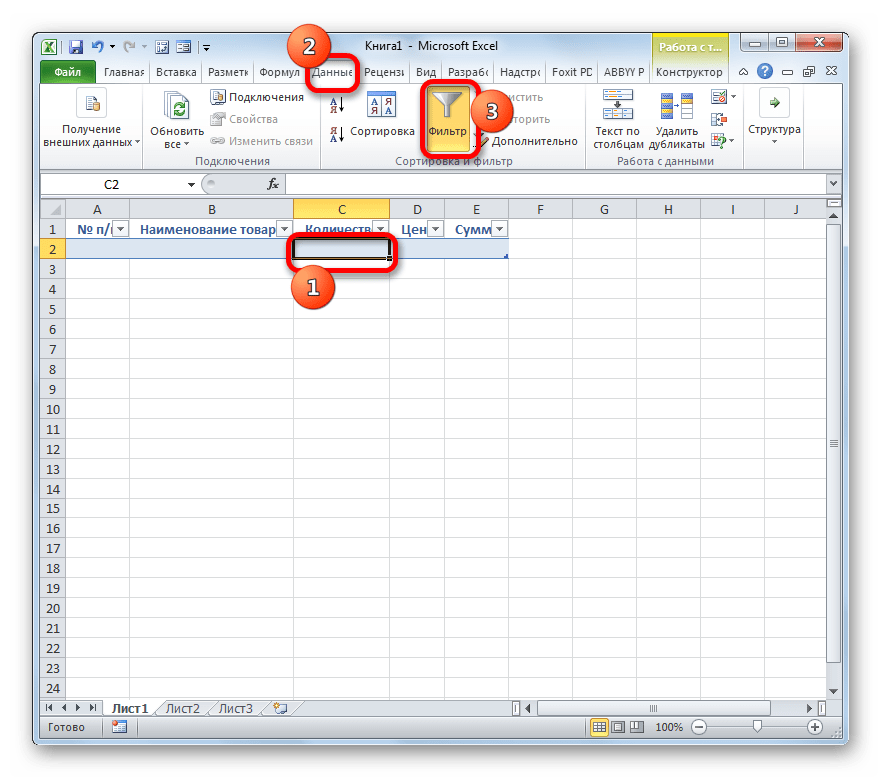
- Итак, наш диапазон отформатирован, как «умная» таблица, свидетельством чему является даже изменение визуального отображения. Как видим, помимо прочего, около каждого названия заголовка столбцов появились значки фильтрации. Их следует отключить. Для этого выделяем любую ячейку «умной» таблицы и переходим во вкладку «Данные». Там на ленте в блоке инструментов «Сортировка и фильтр» щелкаем по значку «Фильтр».
Существует ещё один вариант отключения фильтра. При этом не нужно даже будет переходить на другую вкладку, оставаясь во вкладке «Главная». После выделения ячейки табличной области на ленте в блоке настроек «Редактирование» щелкаем по значку «Сортировка и фильтр». В появившемся списке выбираем позицию «Фильтр».
- Как видим, после этого действия значки фильтрации исчезли из шапки таблицы, как это и требовалось.
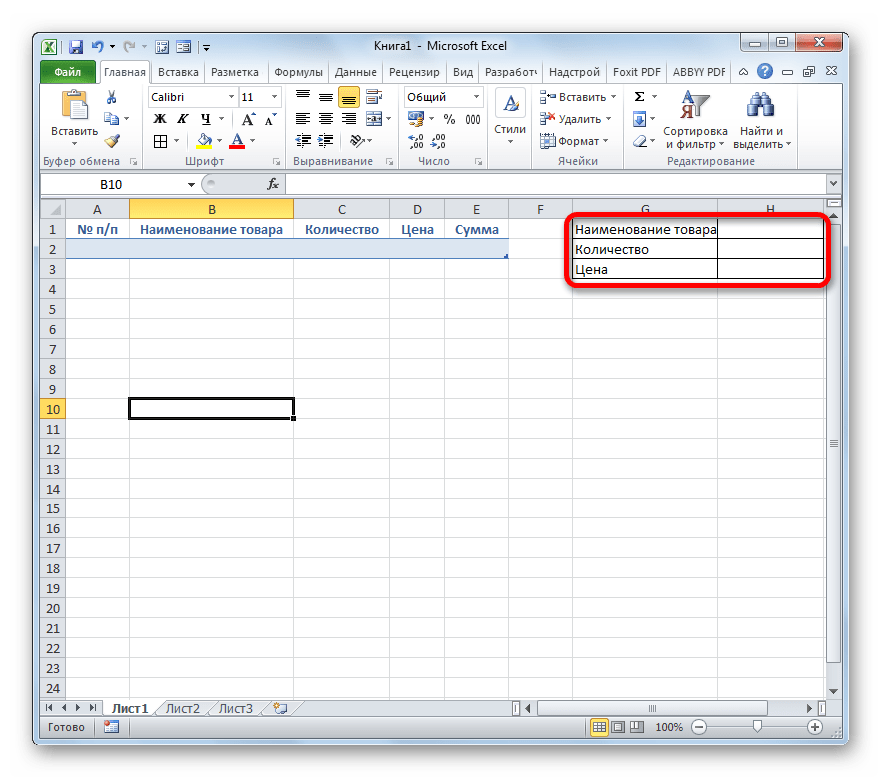
- Затем нам следует создать саму форму ввода данных. Она тоже будет представлять собой своего рода табличный массив, состоящий из двух столбцов. Наименования строк данного объекта будут соответствовать именам столбцов основной таблицы. Исключение составляют столбцы «№ п/п» и «Сумма». Они будут отсутствовать. Нумерация первого из них будет происходить при помощи макроса, а расчет значений во втором будет производиться путем применения формулы умножения количества на цену.
Второй столбец объекта ввода данных оставим пока что пустым. Непосредственно в него позже будут вводиться значения для заполнения строк основного табличного диапазона.
- После этого создаем ещё одну небольшую таблицу. Она будет состоять из одного столбца и в ней разместится список товаров, которые мы будем выводить во вторую колонку основной таблицы. Для наглядности ячейку с заголовком данного перечня («Список товаров») можно залить цветом.
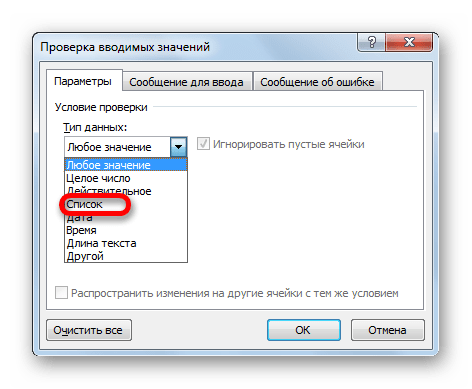
- Затем выделяем первую пустую ячейку объекта ввода значений. Переходим во вкладку «Данные». Щелкаем по значку «Проверка данных», который размещен на ленте в блоке инструментов «Работа с данными».
- Запускается окно проверки вводимых данных. Кликаем по полю «Тип данных», в котором по умолчанию установлен параметр «Любое значение».
- Из раскрывшихся вариантов выбираем позицию «Список».
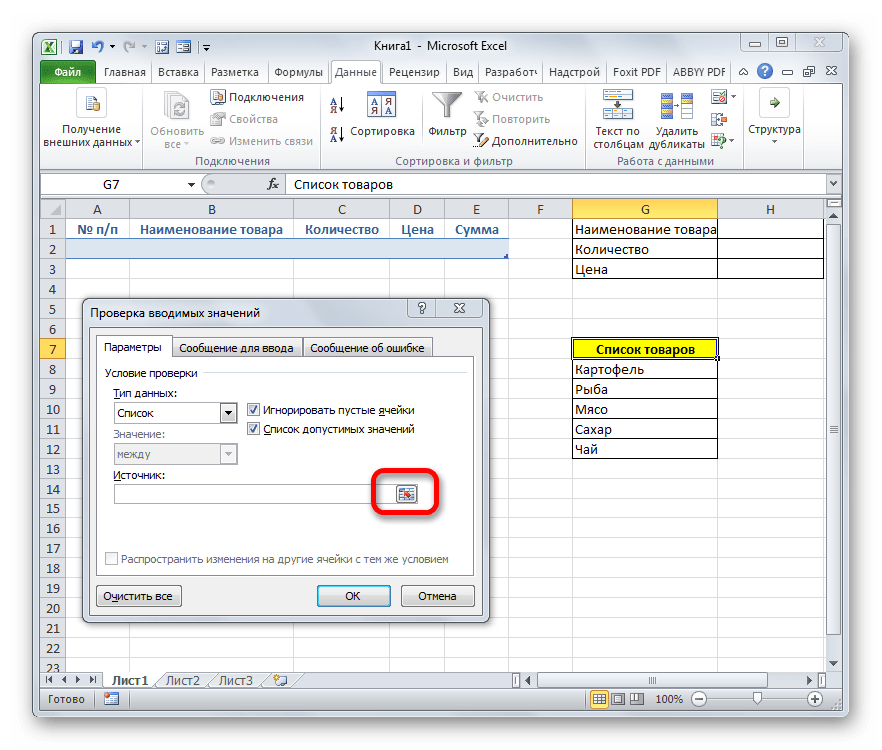
- Как видим, после этого окно проверки вводимых значений несколько изменило свою конфигурацию. Появилось дополнительное поле «Источник». Щелкаем по пиктограмме справа от него левой клавишей мыши.
- Затем окно проверки вводимых значений сворачивается. Выделяем курсором с зажатой левой клавишей мыши перечень данных, которые размещены на листе в дополнительной табличной области «Список товаров». После этого опять жмем на пиктограмму справа от поля, в котором появился адрес выделенного диапазона.
- Происходит возврат к окошку проверки вводимых значений. Как видим, координаты выделенного диапазона в нем уже отображены в поле «Источник». Кликаем по кнопке «OK» внизу окна.
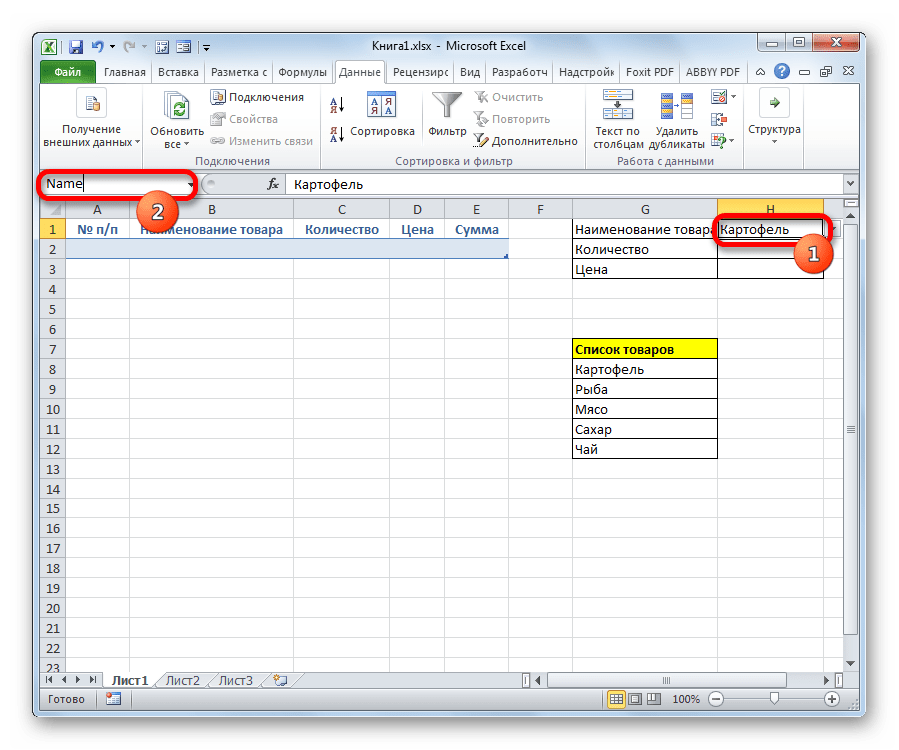
- Теперь справа от выделенной пустой ячейки объекта ввода данных появилась пиктограмма в виде треугольника. При клике на неё открывается выпадающий список, состоящий из названий, которые подтягиваются из табличного массива «Список товаров». Произвольные данные в указанную ячейку теперь внести невозможно, а только можно выбрать из представленного списка нужную позицию. Выбираем пункт в выпадающем списке.
- Как видим, выбранная позиция тут же отобразилась в поле «Наименование товара».
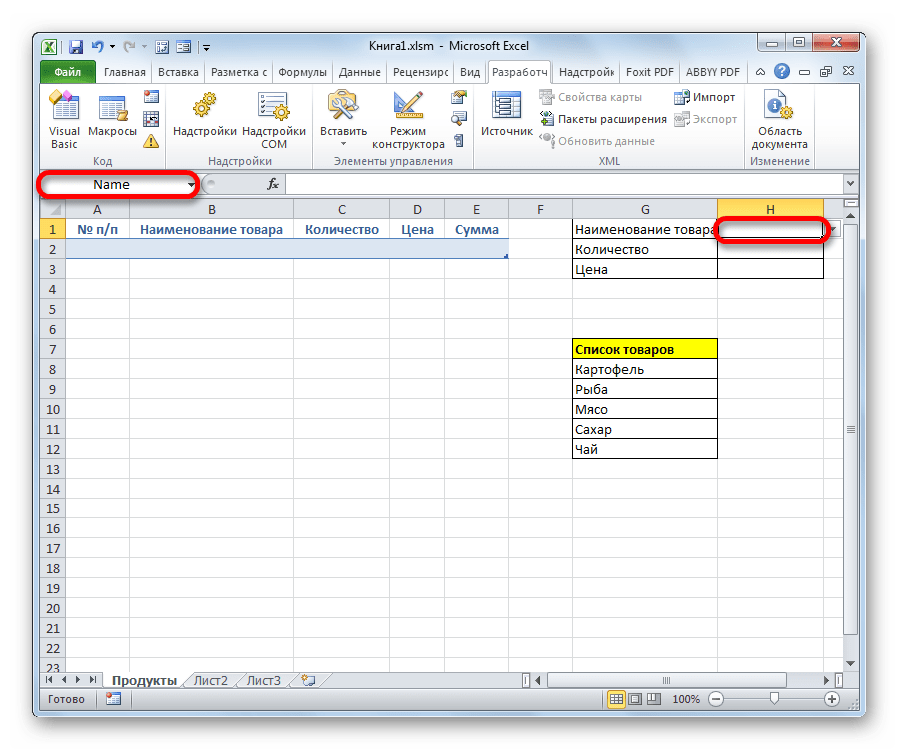
- Далее нам нужно будет присвоить имена тем трем ячейкам формы ввода, куда мы будем вводить данные. Выделяем первую ячейку, где уже установлено в нашем случае наименование «Картофель». Далее переходим в поле наименования диапазонов. Оно расположено в левой части окна Excel на том же уровне, что и строка формул. Вводим туда произвольное название. Это может быть любое наименование на латинице, в котором нет пробелов, но лучше все-таки использовать названия близкие к решаемым данным элементом задачам. Поэтому первую ячейку, в которой содержится название товара, назовем «Name». Пишем данное наименование в поле и жмем на клавишу Enter на клавиатуре.
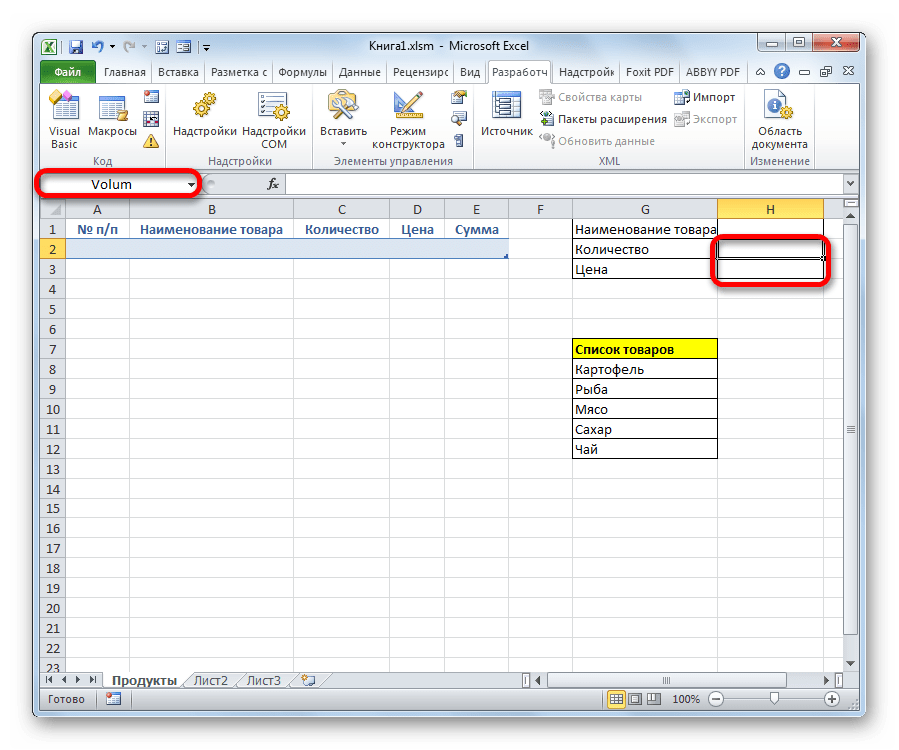
- Точно таким же образом присваиваем ячейке, в которую будем вводить количество товара, имя «Volum».
- А ячейке с ценой – «Price».
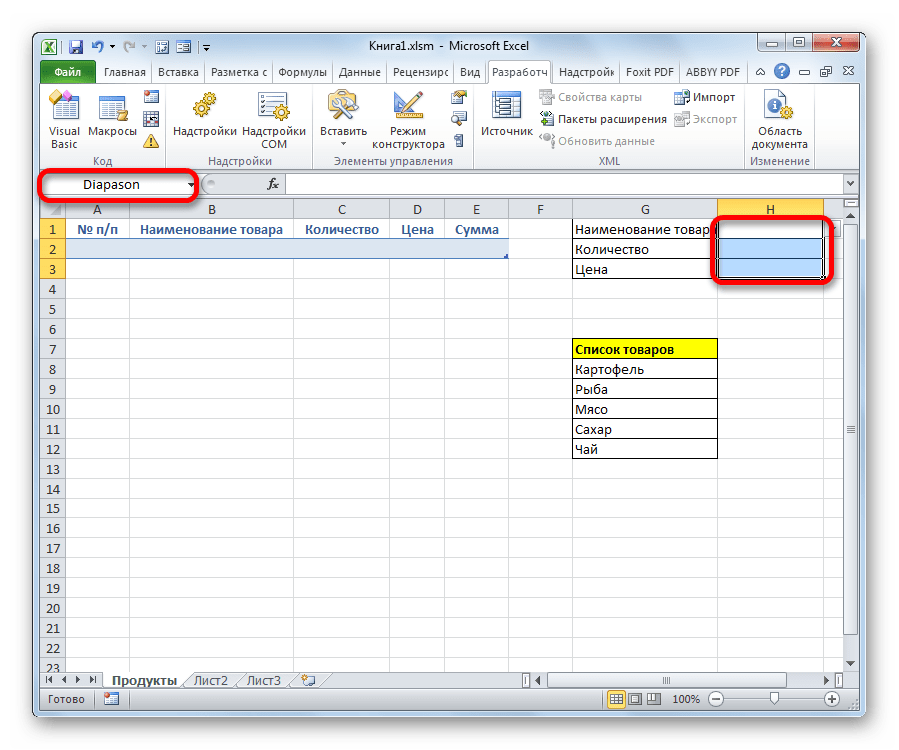
- После этого точно таким же образом даем название всему диапазону из вышеуказанных трех ячеек. Прежде всего, выделим, а потом дадим ему наименование в специальном поле. Пусть это будет имя «Diapason».
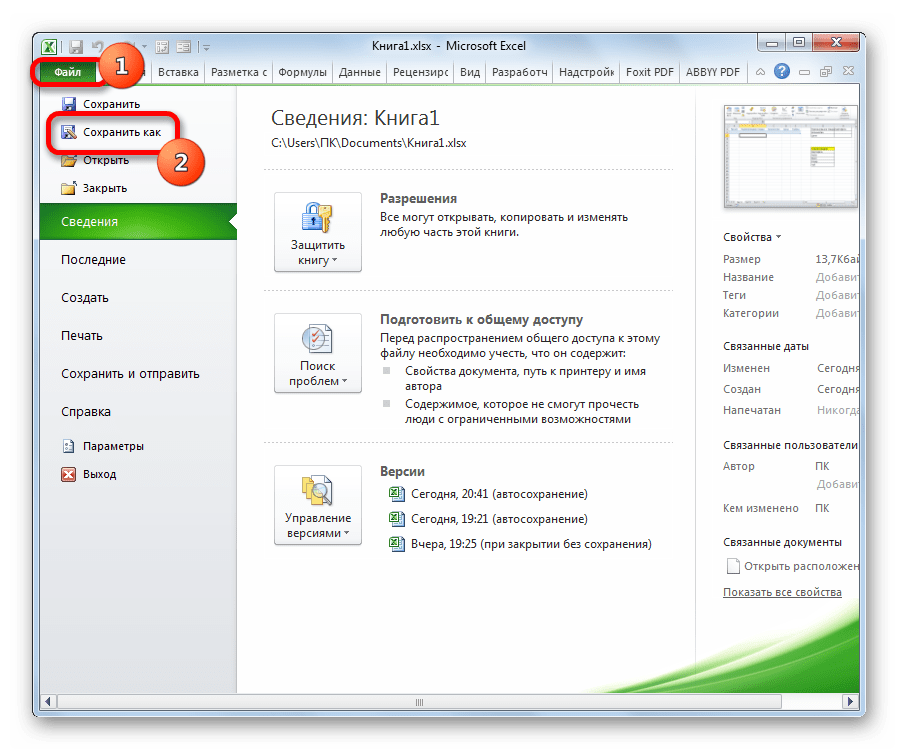
- После последнего действия обязательно сохраняем документ, чтобы названия, которые мы присвоили, смог воспринимать макрос, созданный нами в дальнейшем. Для сохранения переходим во вкладку «Файл» и кликаем по пункту «Сохранить как…».
- В открывшемся окне сохранения в поле «Тип файлов» выбираем значение «Книга Excel с поддержкой макросов (.xlsm)». Далее жмем на кнопку «Сохранить».
- Затем вам следует активировать работу макросов в своей версии Excel и включить вкладку «Разработчик», если вы это до сих пор не сделали. Дело в том, что обе эти функции по умолчанию в программе отключены, и их активацию нужно выполнять принудительно в окне параметров Excel.
- После того, как вы сделали это, переходим во вкладку «Разработчик». Кликаем по большому значку «Visual Basic», который расположен на ленте в блоке инструментов «Код».
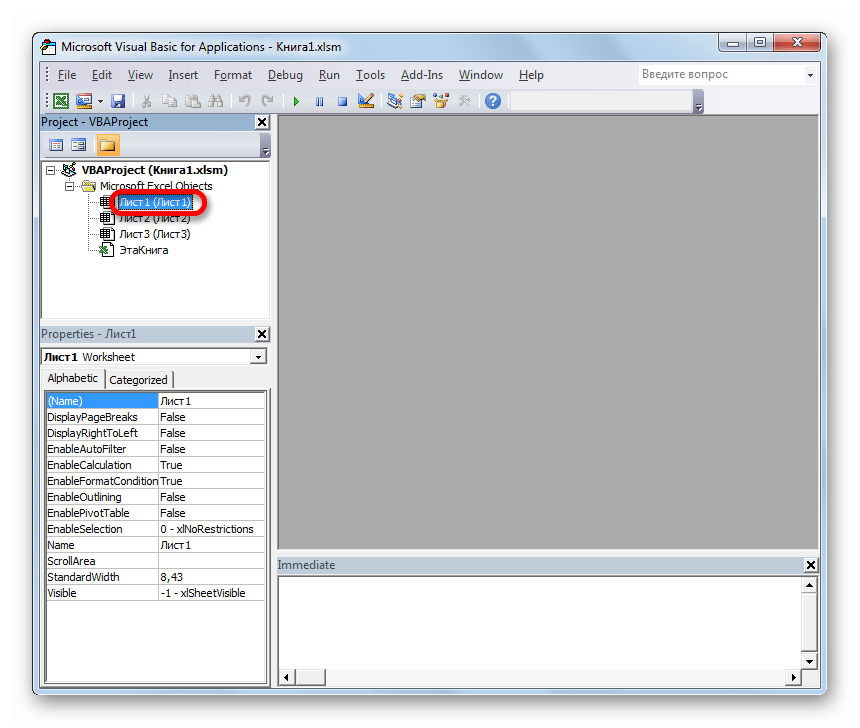
- Последнее действие приводит к тому, что запускается редактор макросов VBA. В области «Project», которая расположена в верхней левой части окна, выделяем имя того листа, где располагаются наши таблицы. В данном случае это «Лист 1».
- После этого переходим к левой нижней области окна под названием «Properties». Тут расположены настройки выделенного листа. В поле «(Name)» следует заменить кириллическое наименование («Лист1») на название, написанное на латинице. Название можно дать любое, которое вам будет удобнее, главное, чтобы в нем были исключительно символы латиницы или цифры и отсутствовали другие знаки или пробелы. Именно с этим именем будет работать макрос. Пусть в нашем случае данным названием будет «Producty», хотя вы можете выбрать и любое другое, соответствующее условиям, которые были описаны выше.
В поле «Name» тоже можно заменить название на более удобное. Но это не обязательно. При этом допускается использование пробелов, кириллицы и любых других знаков. В отличие от предыдущего параметра, который задает наименование листа для программы, данный параметр присваивает название листу, видимое пользователю на панели ярлыков.
Как видим, после этого автоматически изменится и наименование Листа 1 в области «Project», на то, которое мы только что задали в настройках.
- Затем переходим в центральную область окна. Именно тут нам нужно будет записать сам код макроса. Если поле редактора кода белого цвета в указанной области не отображается, как в нашем случае, то жмем на функциональную клавишу F7 и оно появится.
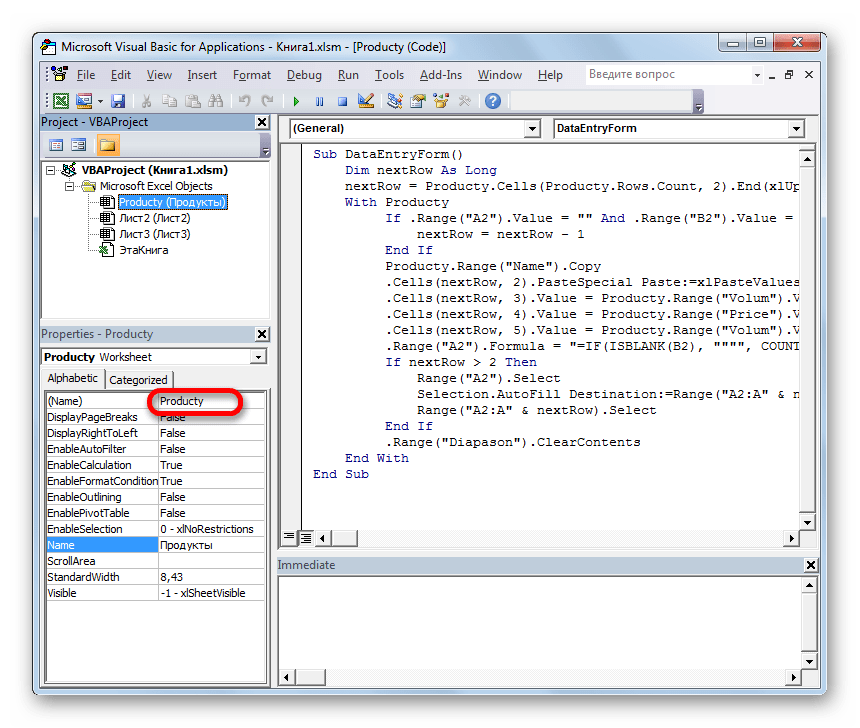
- Теперь для конкретно нашего примера нужно записать в поле следующий код:
Sub DataEntryForm()
Dim nextRow As Long
nextRow = Producty.Cells(Producty.Rows.Count, 2).End(xlUp).Offset(1, 0).Row
With Producty
If .Range("A2").Value = "" And .Range("B2").Value = "" Then
nextRow = nextRow - 1
End If
Producty.Range("Name").Copy
.Cells(nextRow, 2).PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteValues
.Cells(nextRow, 3).Value = Producty.Range("Volum").Value
.Cells(nextRow, 4).Value = Producty.Range("Price").Value
.Cells(nextRow, 5).Value = Producty.Range("Volum").Value * Producty.Range("Price").Value
.Range("A2").Formula = "=IF(ISBLANK(B2), """", COUNTA($B$2:B2))"
If nextRow > 2 Then
Range("A2").Select
Selection.AutoFill Destination:=Range("A2:A" & nextRow)
Range("A2:A" & nextRow).Select
End If
.Range("Diapason").ClearContents
End With
End Sub
Но этот код не универсальный, то есть, он в неизменном виде подходит только для нашего случая. Если вы хотите его приспособить под свои потребности, то его следует соответственно модифицировать. Чтобы вы смогли сделать это самостоятельно, давайте разберем, из чего данный код состоит, что в нем следует заменить, а что менять не нужно.
Итак, первая строка:
Sub DataEntryForm()«DataEntryForm» — это название самого макроса. Вы можете оставить его как есть, а можете заменить на любое другое, которое соответствует общим правилам создания наименований макросов (отсутствие пробелов, использование только букв латинского алфавита и т.д.). Изменение наименования ни на что не повлияет.
Везде, где встречается в коде слово «Producty» вы должны его заменить на то наименование, которое ранее присвоили для своего листа в поле «(Name)» области «Properties» редактора макросов. Естественно, это нужно делать только в том случае, если вы назвали лист по-другому.
Теперь рассмотрим такую строку:
nextRow = Producty.Cells(Producty.Rows.Count, 2).End(xlUp).Offset(1, 0).RowЦифра «2» в данной строчке означает второй столбец листа. Именно в этом столбце находится колонка «Наименование товара». По ней мы будем считать количество рядов. Поэтому, если в вашем случае аналогичный столбец имеет другой порядок по счету, то нужно ввести соответствующее число. Значение «End(xlUp).Offset(1, 0).Row» в любом случае оставляем без изменений.
Далее рассмотрим строку
If .Range("A2").Value = "" And .Range("B2").Value = "" Then«A2» — это координаты первой ячейки, в которой будет выводиться нумерация строк. «B2» — это координаты первой ячейки, по которой будет производиться вывод данных («Наименование товара»). Если они у вас отличаются, то введите вместо этих координат свои данные.
Переходим к строке
Producty.Range("Name").CopyВ ней параметр «Name» означат имя, которое мы присвоили полю «Наименование товара» в форме ввода.
В строках
.Cells(nextRow, 2).PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteValues
.Cells(nextRow, 3).Value = Producty.Range("Volum").Value
.Cells(nextRow, 4).Value = Producty.Range("Price").Value
.Cells(nextRow, 5).Value = Producty.Range("Volum").Value * Producty.Range("Price").Value
наименования «Volum» и «Price» означают названия, которые мы присвоили полям «Количество» и «Цена» в той же форме ввода.
В этих же строках, которые мы указали выше, цифры «2», «3», «4», «5» означают номера столбцов на листе Excel, соответствующих колонкам «Наименование товара», «Количество», «Цена» и «Сумма». Поэтому, если в вашем случае таблица сдвинута, то нужно указать соответствующие номера столбцов. Если столбцов больше, то по аналогии нужно добавить её строки в код, если меньше – то убрать лишние.
В строке производится умножение количества товара на его цену:
.Cells(nextRow, 5).Value = Producty.Range("Volum").Value * Producty.Range("Price").ValueРезультат, как видим из синтаксиса записи, будет выводиться в пятый столбец листа Excel.
В этом выражении выполняется автоматическая нумерация строк:
If nextRow > 2 Then
Range("A2").Select
Selection.AutoFill Destination:=Range("A2:A" & nextRow)
Range("A2:A" & nextRow).Select
End If
Все значения «A2» означают адрес первой ячейки, где будет производиться нумерация, а координаты «A» — адрес всего столбца с нумерацией. Проверьте, где именно будет выводиться нумерация в вашей таблице и измените данные координаты в коде, если это необходимо.
В строке производится очистка диапазона формы ввода данных после того, как информация из неё была перенесена в таблицу:
.Range("Diapason").ClearContentsНе трудно догадаться, что («Diapason») означает наименование того диапазона, который мы ранее присвоили полям для ввода данных. Если вы дали им другое наименование, то в этой строке должно быть вставлено именно оно.
Дальнейшая часть кода универсальна и во всех случаях будет вноситься без изменений.
После того, как вы записали код макроса в окно редактора, следует нажать на значок сохранения в виде дискеты в левой части окна. Затем можно его закрывать, щелкнув по стандартной кнопке закрытия окон в правом верхнем углу.
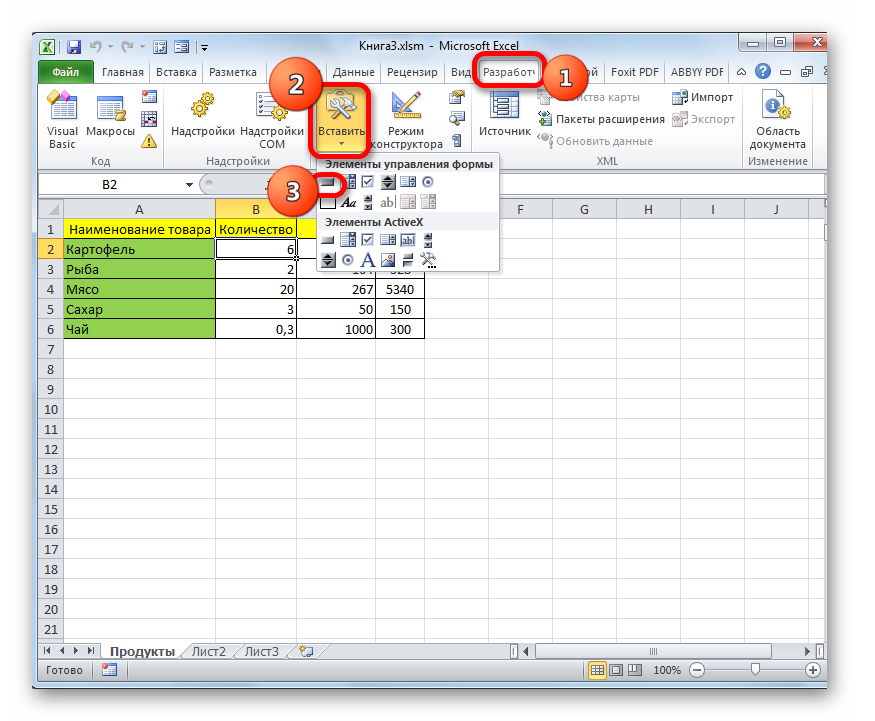
- После этого возвращаемся на лист Excel. Теперь нам следует разместить кнопку, которая будет активировать созданный макрос. Для этого переходим во вкладку «Разработчик». В блоке настроек «Элементы управления» на ленте кликаем по кнопке «Вставить». Открывается перечень инструментов. В группе инструментов «Элементы управления формы» выбираем самый первый – «Кнопка».
- Затем с зажатой левой клавишей мыши обводим курсором область, где хотим разместить кнопку запуска макроса, который будет производить перенос данных из формы в таблицу.
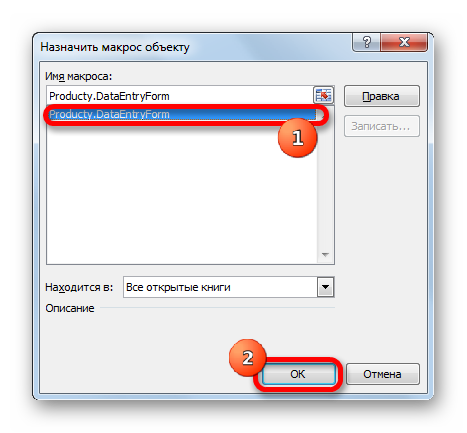
- После того, как область обведена, отпускаем клавишу мыши. Затем автоматически запускается окно назначения макроса объекту. Если в вашей книге применяется несколько макросов, то выбираем из списка название того, который мы выше создавали. У нас он называется «DataEntryForm». Но в данном случае макрос один, поэтому просто выбираем его и жмем на кнопку «OK» внизу окна.
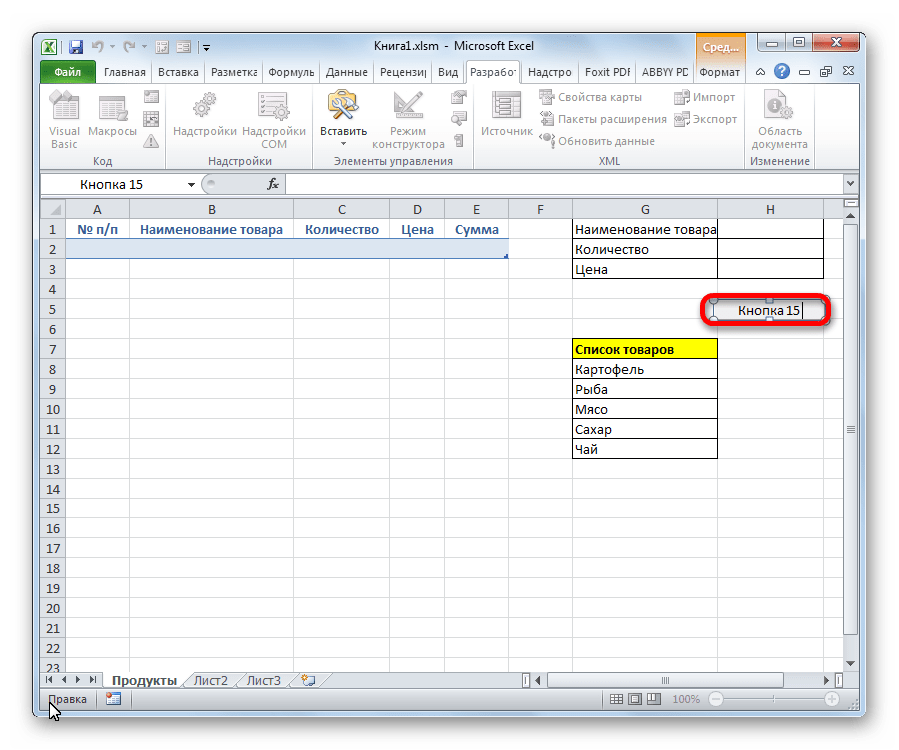
- После этого можно переименовать кнопку, как вы захотите, просто выделив её текущее название.
В нашем случае, например, логично будет дать ей имя «Добавить». Переименовываем и кликаем мышкой по любой свободной ячейке листа.
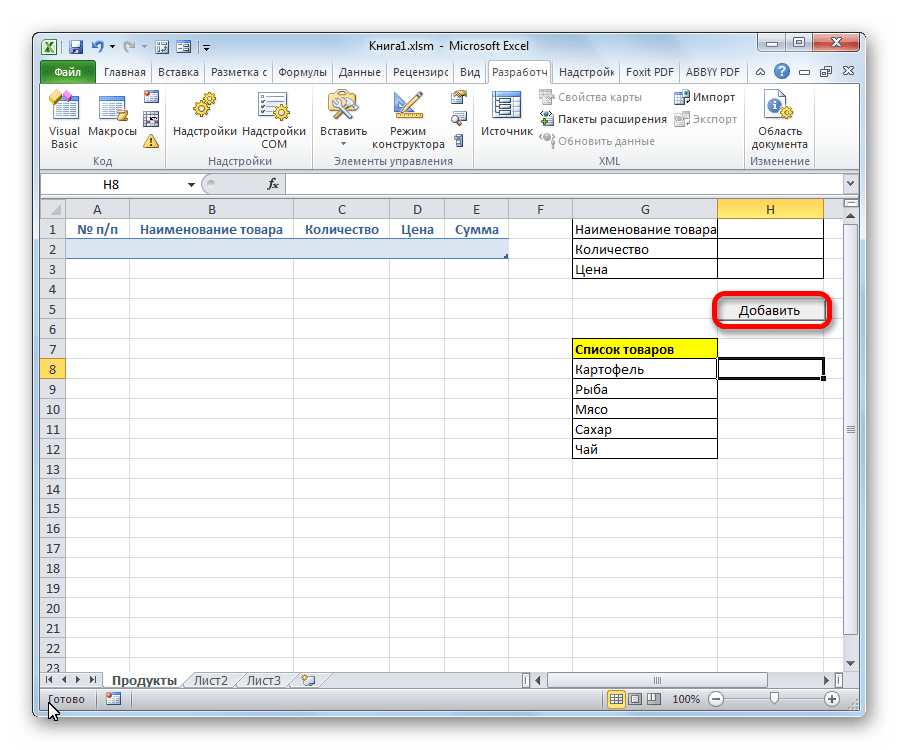
- Итак, наша форма полностью готова. Проверим, как она работает. Вводим в её поля необходимые значения и жмем на кнопку «Добавить».
- Как видим, значения перемещены в таблицу, строке автоматически присвоен номер, сумма посчитана, поля формы очищены.
- Повторно заполняем форму и жмем на кнопку «Добавить».
- Как видим, и вторая строка также добавлена в табличный массив. Это означает, что инструмент работает.
Читайте также:
Как создать макрос в Excel
Как создать кнопку в Excel
В Экселе существует два способа применения формы заполнения данными: встроенная и пользовательская. Применение встроенного варианта требует минимум усилий от пользователя. Его всегда можно запустить, добавив соответствующий значок на панель быстрого доступа. Пользовательскую форму нужно создавать самому, но если вы хорошо разбираетесь в коде VBA, то сможете сделать этот инструмент максимально гибким и подходящим под ваши нужды.
Let’s say you own a hot sauce company.
Having an Excel customer feedback form will tell you how tasty 😋 and spicy 🌶️ your sauce is. Beats asking people individually, any day, right?
So whether you want to survey customers, take client feedback, or collect data from employees, Excel forms can be handy.
But how do you create a form in Excel in the first place?!
In this article, you’ll learn how to create a form in Excel.
We’ll also go over its limitations and suggest an alternative tool to create forms easily.
Make way for the hot sauce feedback with a quick Excel form!
What Are Excel Forms?
An Excel form is a data collection tool from Microsoft Excel. It’s basically a dialog box containing fields for a single record.
In each record, you can enter up to 32 fields, and your Excel worksheet column headers become the form field names.
What are the benefits of using an Excel data entry form?
Now Excel isn’t easy.
Its endless cells make it difficult to know where to feed what data.
Like trying to understand what ‘mild’ means when all you know and love is spicy sauces!
This is why people use Excel forms to make quick data entries in the right fields without scrolling up and down the whole worksheet.
No more entering data into an Excel spreadsheet row after row after row after row…

An Excel data entry form lets you:
- View more data without scrolling up and down
- Include data validation
- Reduce chances of human errors
Sounds quite helpful. So let’s learn how to create an Excel form.
How To Create A Form In Excel?
Before you cook up a form in Excel, you gotta do the prep work.
First, you must have your columns or fields ready.
They’re your raw ingredients, like chili peppers or ginger, ready for your sauce.
You also have to find the ‘Form’ option.
No worries.
We’ll help you make a table, find the ‘Form’ option, and create an Excel form using a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Make a quick Excel table
Open an Excel spreadsheet, and you’ll start on the first sheet tab (by default).
For this form, you’re the owner of a hot sauce company.
And we’re gonna make a customer feedback form for your delicious sauce.
Here’s an example of the columns you can add to your Excel worksheet:
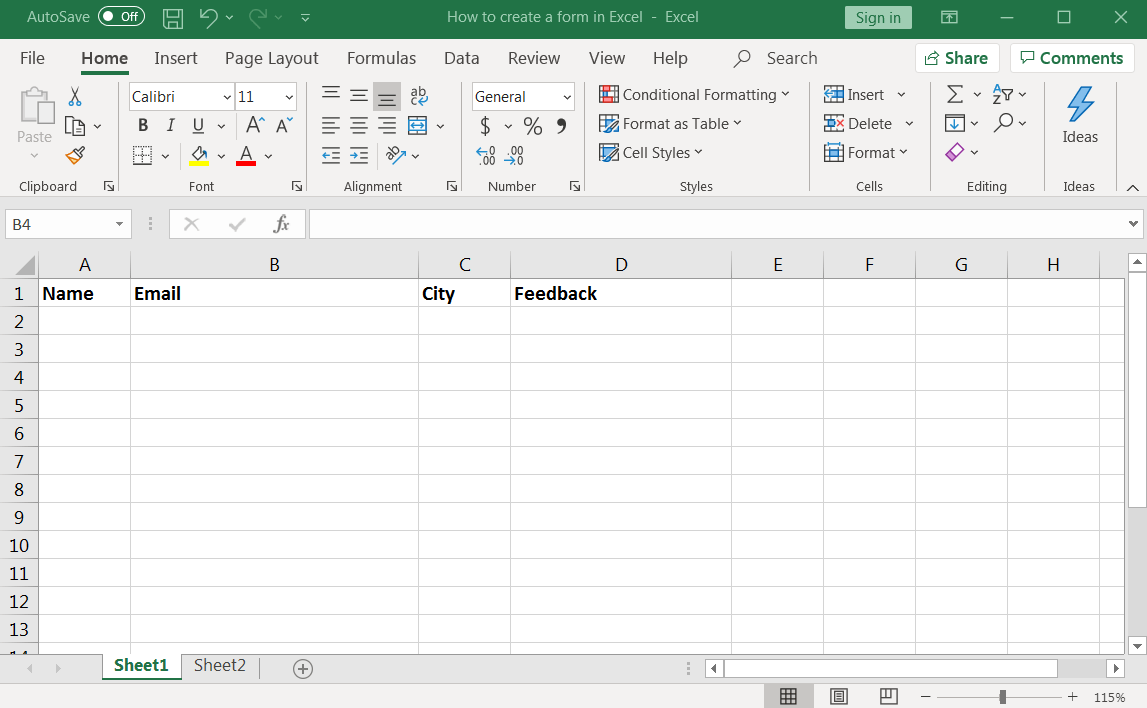
Now you have to convert your column names into a table.
Just select the column headers > click on Insert > Tables > Table.
A tiny dialog box should pop up. Make sure to tick the My table has headers checkbox.

Click on OK, and you should get an Excel table as shown in the image below.
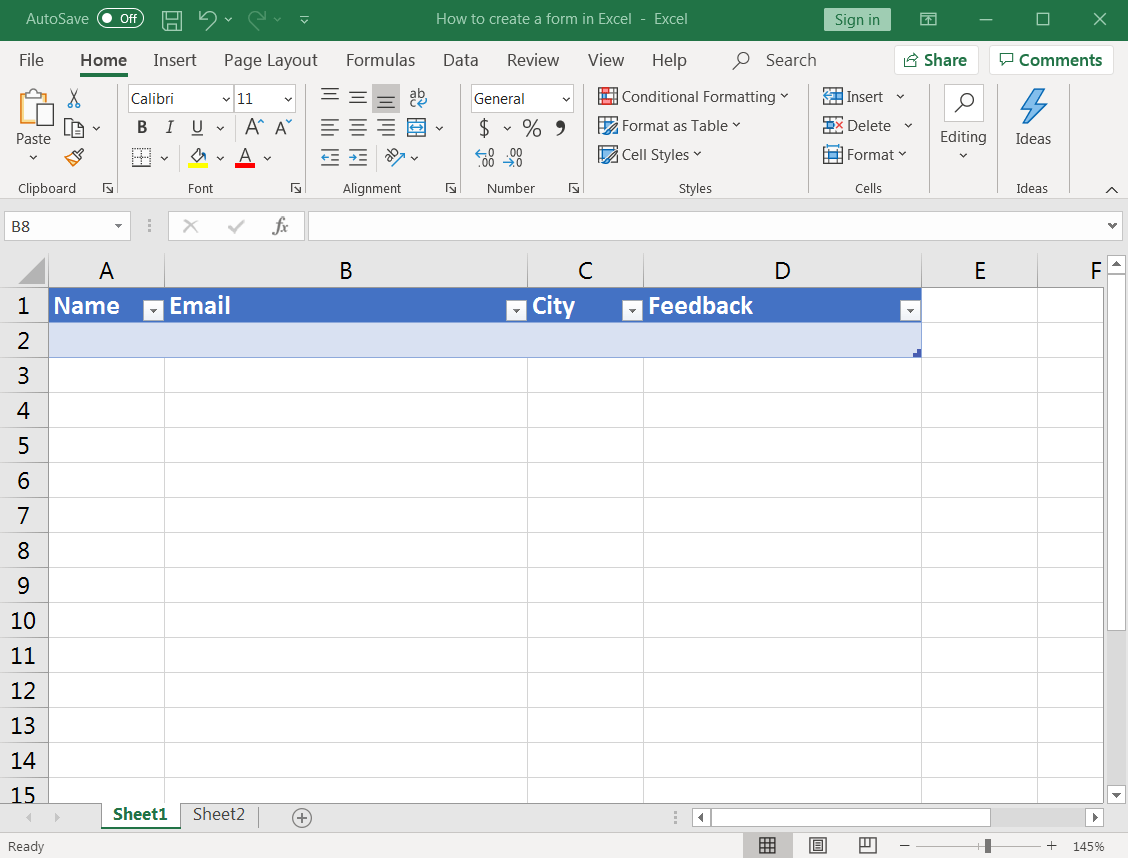
Here, you can adjust the column width depending on the data the field may contain.
Step 2: Add data entry form option to the Excel ribbon
Take a good look at your Excel worksheet.
Check the row of tabs and icons at the top of the Excel window (ribbon). You won’t find the option to use a data entry form in any ribbon tab.

Don’t worry. It’s perfectly normal.
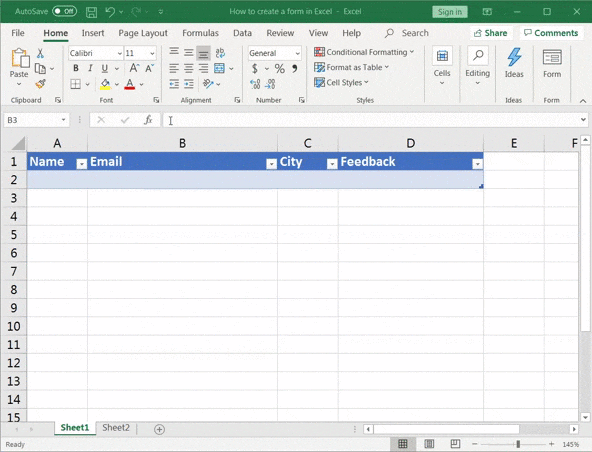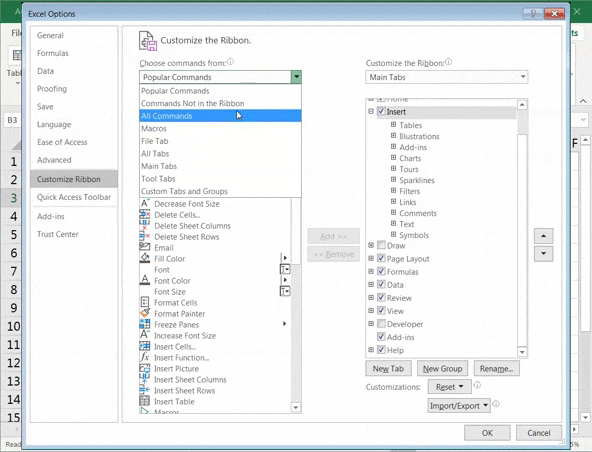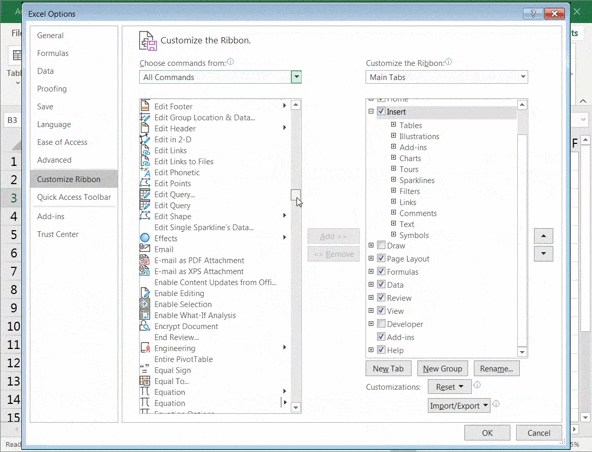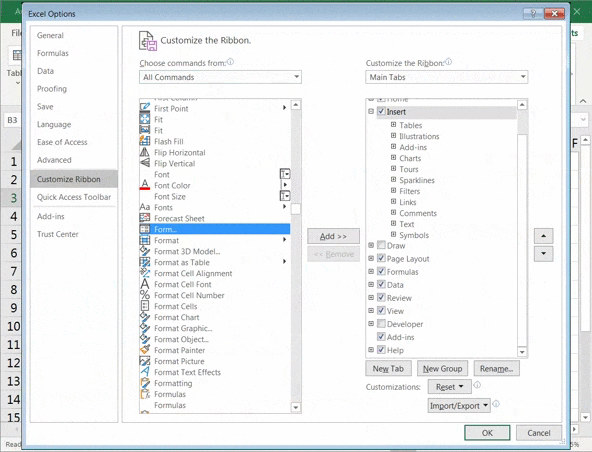
You have to add the ‘form’ option to the Excel sheet ribbon. To do this:
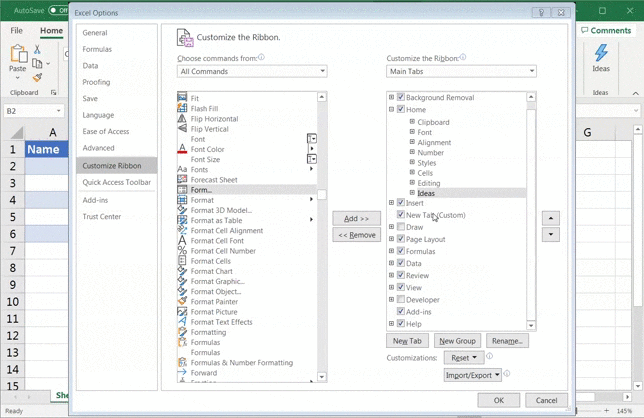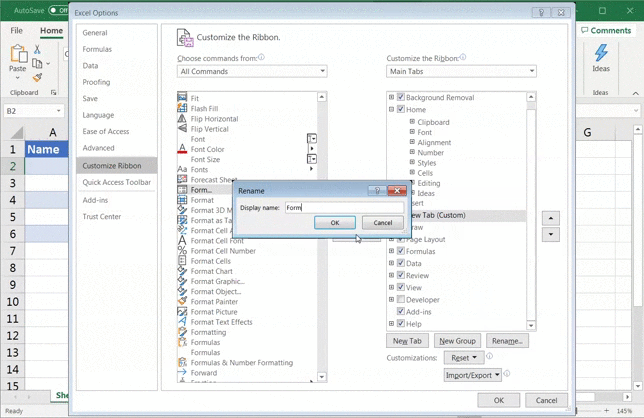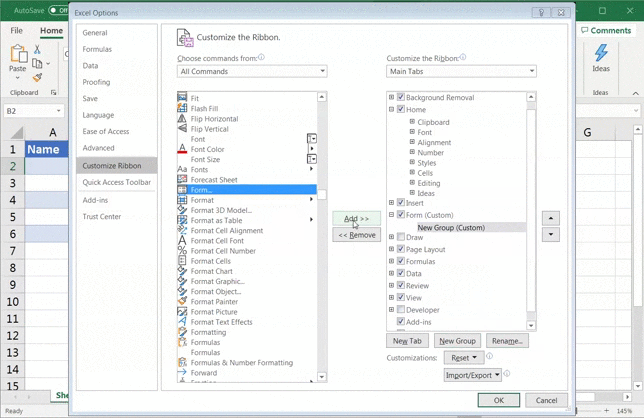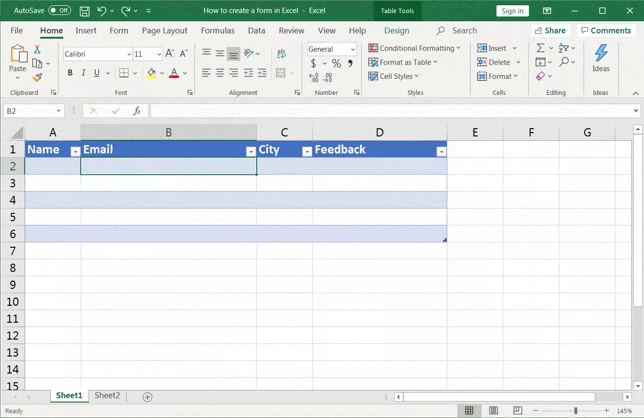
- Right-click on any of the existing icons you see in the ribbon or toolbar
- Click on Customize the Ribbon.
- An Excel Options dialog box should pop up
- Select All Commands from the drop-down list
- Scroll down the list of commands and select Form
- Now click on Add
Did it work? If yes, congratulations!
In case it didn’t allow you to add the Form command button or option, just click on New Tab > Rename > Name it ‘Form’ > click OK.
Then, click on New Group > Add.
Make sure the Form option is selected when you click Add.
And that’s it! You have finally completed adding the Form icon to the ribbon.
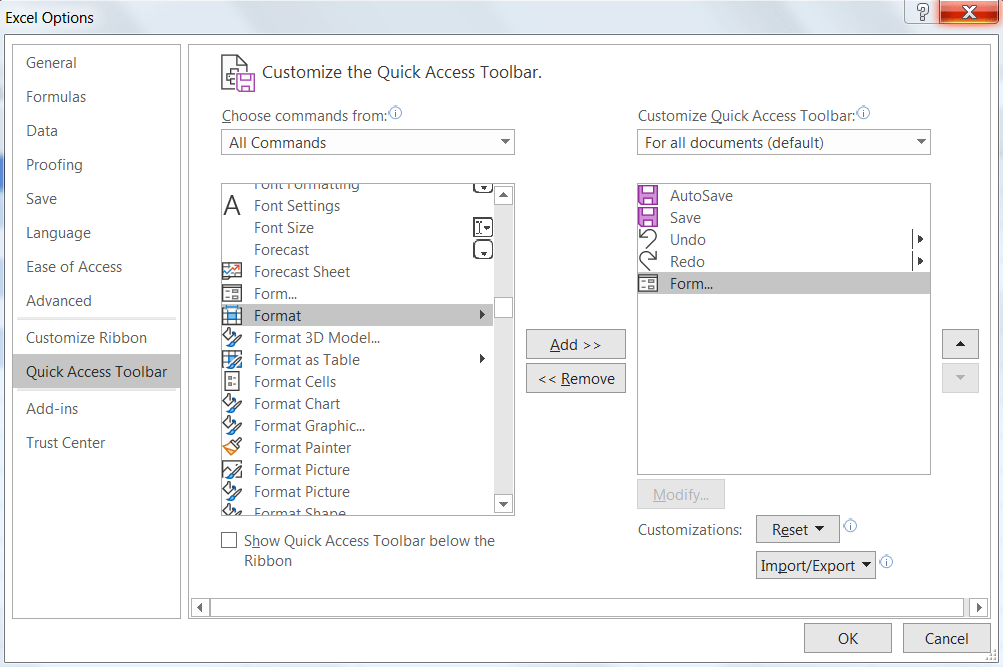
To access it quickly in your workbook, click on Quick Access Toolbar in the same Excel Options dialog box you used earlier.
Select Form under All Commands > click Add. Then, hit enter.
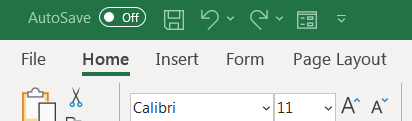
And voila!
You’ll notice the Form button or icon appear on the green area at the top of the Excel workbook in the quick access toolbar.
Bonus: Make a Fillable Form in Word!
Step 3: Enter form data
Now, you can click on any cell in your table and then on the Form icon to input form data.
A dialog box should open with the field names and some button options such as New, Delete, Restore, and criteria button.
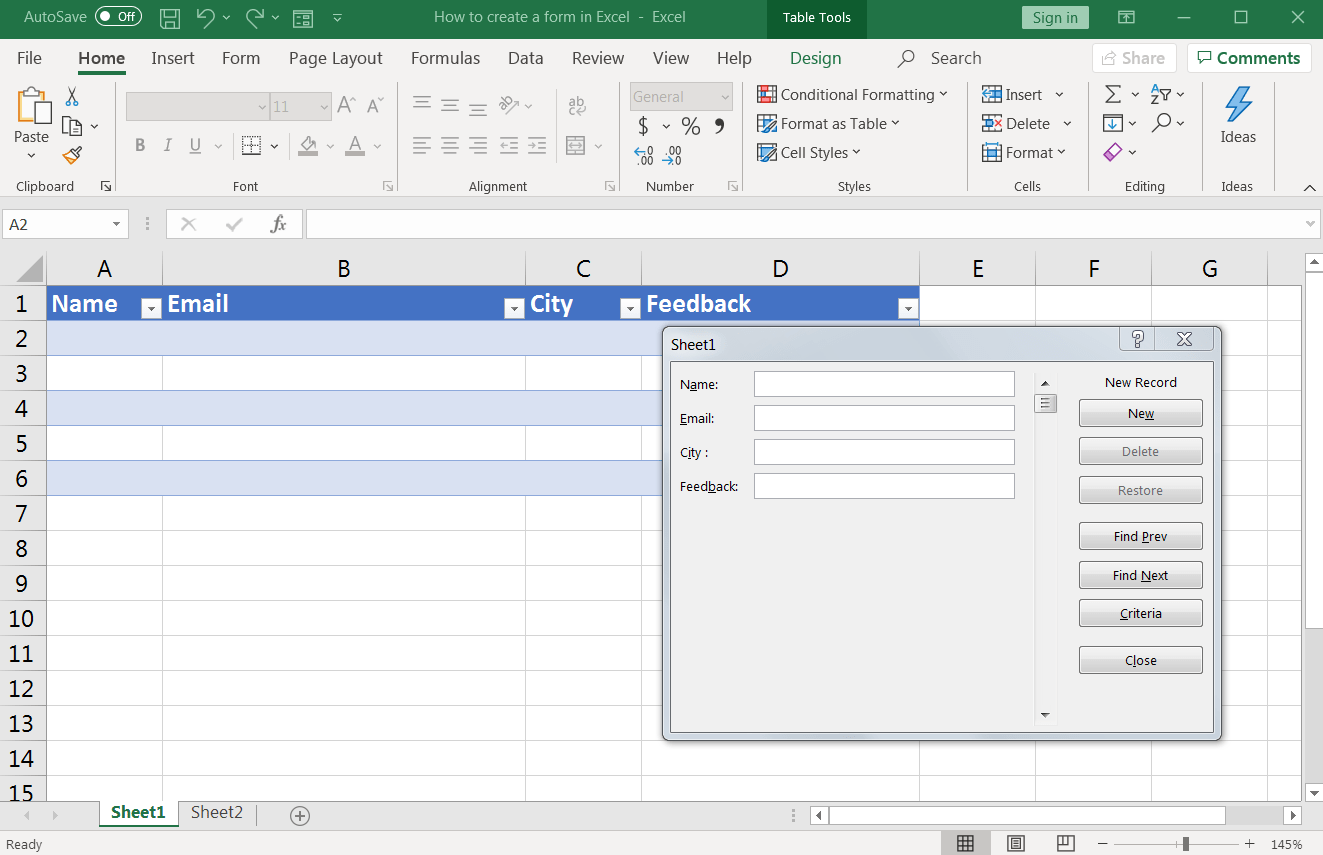
This is a customized data entry form based on the fields in our data.
Enter the desired data in the fields and click on the form button New.
That should make the data appear in your Excel table.
Click on Close to leave the dialog box and view your data table.
Repeat the process till you have entered all the data you want.
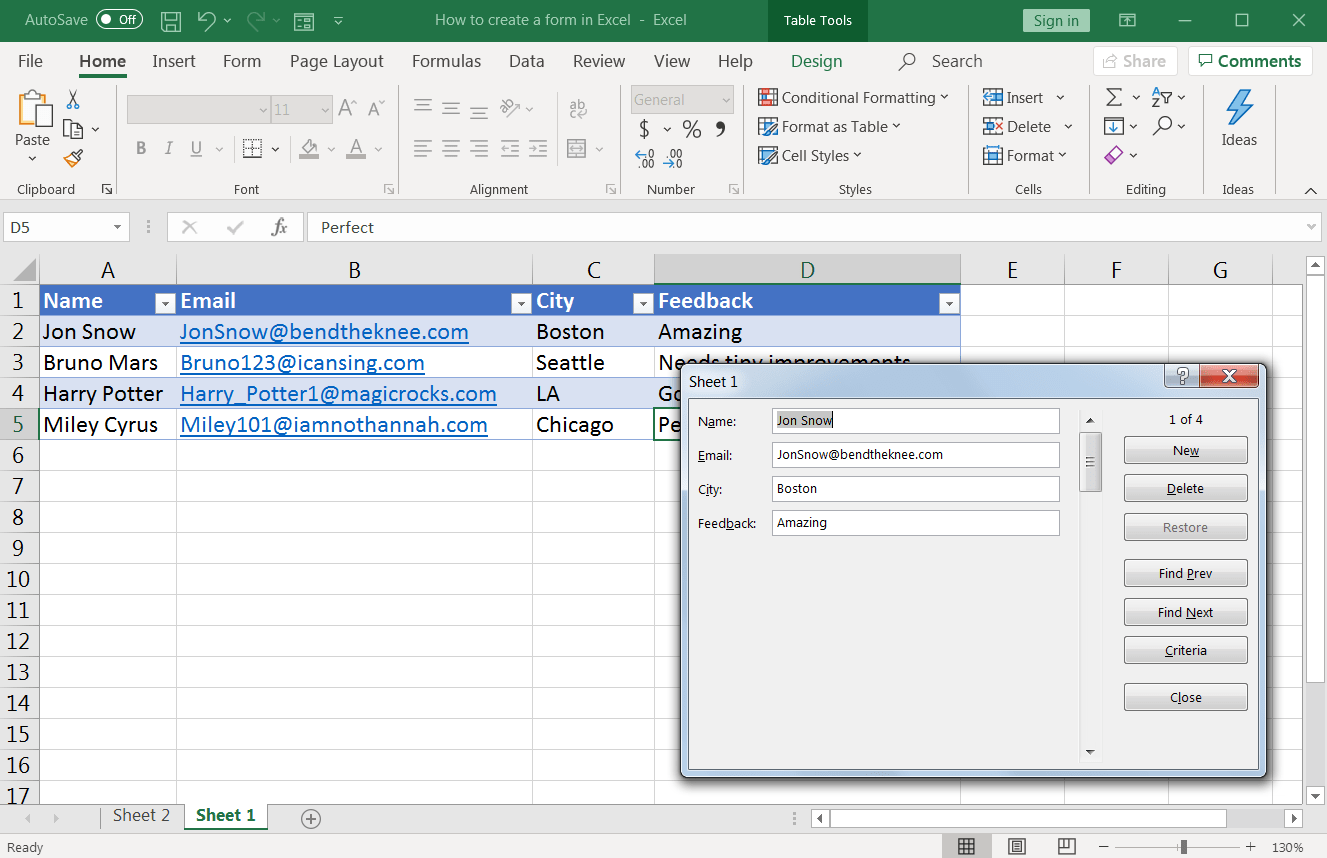
Step 4: Restrict data entry based on conditions
If your hot sauce form contains certain criteria or rules for filling fields, data validation can be useful. It ensures your customers’ data conforms to a few conditions.
For example, you want the sauce feedback field to only accept short texts. So you can create a data validation rule to allow only a specific text length.
If a customer enters feedback longer than what you want, it will not be allowed, and they will see an error.
Here’s how you can set these data entry form control conditions:
- Select the cell or cells where you want to add a data validation rule. In this example, we have selected cells under the feedback column (D2-D5)
- Click the Data tab > Data Validation icon > select Data Validation from the drop-down list
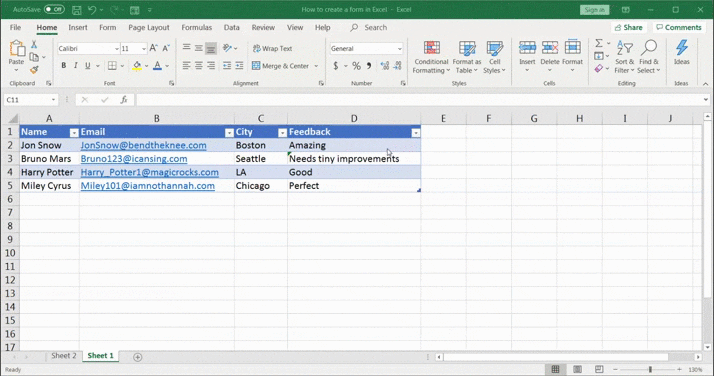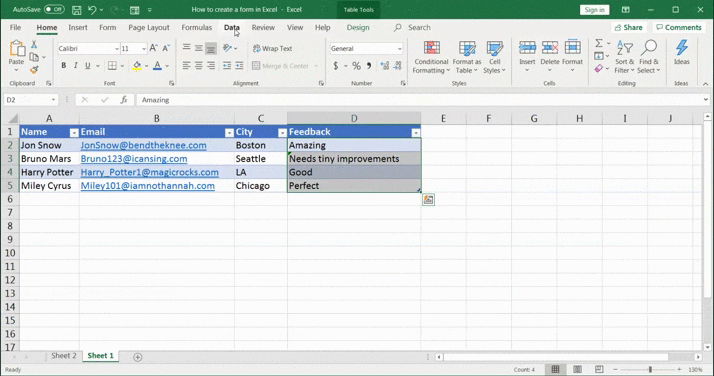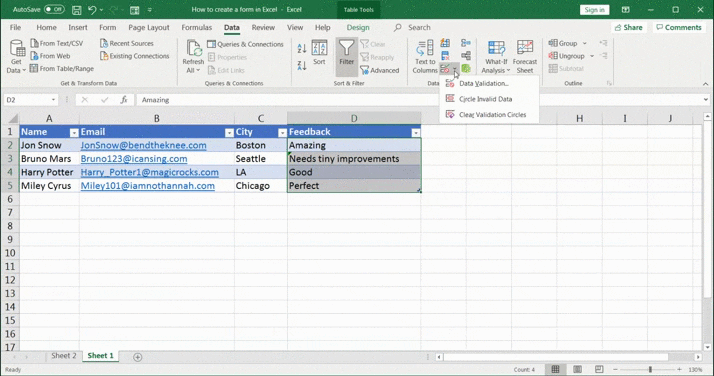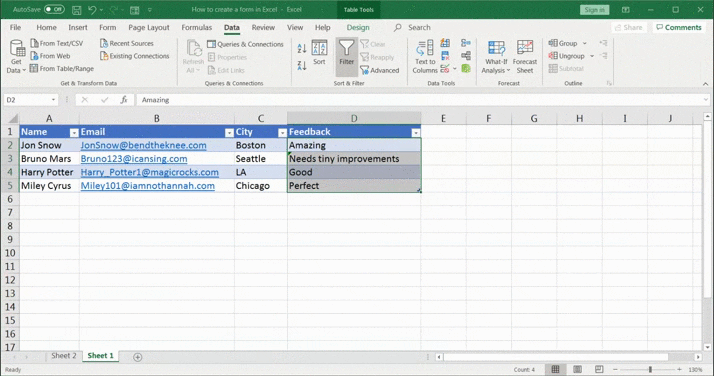
- The Data Validation dialog box will appear. Under Settings, select Text length from the Allow drop-down. Then choose the text length condition under Data and the number of characters. Click OK to apply the rules
Here we chose the condition ‘less than’ and set the feedback character limit to a maximum ‘10’.
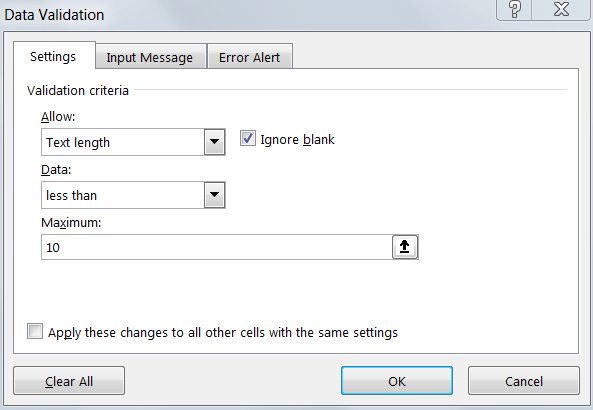
Now, when you use the data entry form to enter text in the feedback column, and if it isn’t a text under ten characters, it won’t be allowed.
You’ll be alerted with a sound and this error message.

But this is just an example.
Don’t stop your customers from singing praises for your sauce! 😛
Data validation only helps ensure people don’t fill in wrong data in the fields.
I mean, what if someone enters the feedback ‘amazing’ in the name field?
Great idea for a name, but no help for your data collection efforts! 😜
Step 5: Start collecting data
You can now collect data using any of these options:
- Ask customers to fill the form by sharing the Excel file with them. Invite them using their email address or copy and share the spreadsheet link
- Send a copy of the form as an email attachment
- Fill in the data yourself as the customers give you feedback
You’ll find all these options by clicking on share on the top right corner of your sheet.

Note: This process is different from creating a custom form using Excel VBA (Visual Basics for Application). Excel VBA is a Microsoft Excel programming language used to automate tasks and perform other functions such as create a text box, userform, etc.
The Excel VBA user form isn’t an ideal option since it’s even more complicated to set up.
Bonus: Use Jotform to create forms!
3 Limitations Of Creating Forms In Excel
Excel does kind of speed up the data entry process using the form functionality.
However, it doesn’t make it fun, and that’s just one of its limitations.
Here are some more limitations that might make you want to reconsider using an Excel data entry form:
1. Formula restrictions
Excel formulas have split the world into two teams.
One finds it convenient, and the other finds it impossible.
Like how some people love hot sauces while others prefer something sweeter.
But with forms, you straight-up can’t enter an Excel formula into a data form field.
You just can’t.
Then why even use Excel?!
2. Field limit
Clearly, there’s a limit to how many fields there can be in an Excel form.
What do you do when you want more than 32 columns (fields)?
Wouldn’t it be easier to have a tool that wasn’t as complex as MS Excel and didn’t restrict fields?
3. Not the most user-friendly form
Excel can be difficult for many users because of the different functions and rules.
To create form in Excel, you must add a feature to the toolbar.
What’s with the hide and seek, Excel?
Oh, and it’s absolutely not user-friendly for Mac users.
Cause guess what?
The form command doesn’t even exist in the Mac version! *scoff*
Having second thoughts about Excel? Here are the top Excel alternatives
Clearly, you need a tool that can make up for all the Excel form drawbacks and do more.
Good news!
Introducing ClickUp, one of the world’s highest-rated productivity tool used by teams in small and big companies.
Related Resources:
- How to Create a Project Timeline in Excel
- How to Make a Calendar in Excel
- How to Create an Org Chart in Excel
- How to Make a Graph in Excel
- How to Make a KPI Dashboard in Excel
- How to Make an Excel Database
- How to Show Dependencies in Excel
Create Effortless Forms Using ClickUp
ClickUp is the ultimate all-in-one tool to create forms.
What you’re looking for is our Form view.
And unlike Excel, we don’t hide it. Because we’re proud of it! 😎

We also want you to find it without reading a guide like you just did.
Check out these ClickUp Form tips for educators!🍎
To build a form in ClickUp, you must add a form view in three simple steps:
- Open a List, Space, or Folder of your choice
- Click on the + button and select Form
- Name it and add a description
Ensure that the name is something catchy or appropriate depending on the purpose of your form.
How’s ‘Fire cannot kill a dragon’ for a catchy hot sauce form title?
(Warning: Only people who love their spice will get this 😎)
Now let’s build this form!
You’ll find a bunch of fields on the left panel in the form view. Drag and drop them on your form, and that’s how easy it is to add a field.
The panel doesn’t have the field you’re looking for? No worries!
Just click on the field’s title to rename it.

But wait, we’re not close to done being awesome.
Did you know you can also add your company branding in the form view?
After you complete it, it’s time to share your form.
Spot the ‘Share’ icon on the top right of the form view. Click on it to copy the direct link for your form to share it with anyone you like.
Or you can build the form into a page via the HTML code through the ‘embed code’ section.
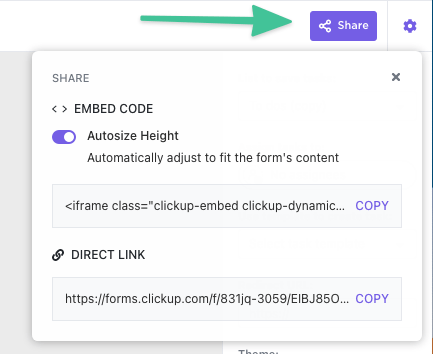
Bonus: Form building tips for ClickUp.
And lastly, we’re pretty sure you won’t need any other tool if you have ClickUp forms.
But if you prefer other apps like Google Forms, ClickUp can easily integrate with them too. The integration converts Google Forms responses into ClickUp tasks automatically.
What’s more?
ClickUp has so many more awesome features in store for you.
Here’s a sneak peek at some of the many features ClickUp has to offer:
- View tasks in a spreadsheet format with the Table view
- Create tasks and reminders without the internet with offline mode
- Assign a single task to multiple assignees
- Create workflows with custom statuses
- Set reminders, so you don’t miss out on important tasks
- Share all your views with anyone using public sharing
- Integrate with all your favorite tools, including Trello, Microsoft Teams, Google Drive, etc.
- Import an Excel file into ClickUp by saving it as a CSV
- Track task durations using the native time tracker
Excel Or ClickUp: What’s Hot? 🔥
An Excel form is less of a form creator and more of an easy data entry application.
It can help you avoid mistakes if data entry is part of your daily work.
However, when it comes to creating forms, Excel doesn’t seem ideal.
Instead, try ClickUp. It’s a powerful project management tool that lets you create custom forms using a simple drag and drop functionality.
If there’s anything you want to do beyond that, ClickUp has a long list of features, including Mind maps, Workload view, Notepad, priorities, and more.
So you never have to leave the platform for anything. Save your precious time, people!
Use ClickUp for free and create red-hot forms that nobody can resist!🌶️

Have you tried Microsoft Forms yet?
It’s a great new tool from Microsoft that allows you to quickly and easily create surveys, quizzes and polls.
There is a wide variety of potential uses for these. You could use them to get customer feedback, collect reviews and testimonials or even use them as data entry forms.
I’m using these using these forms in my courses to get student feedback and reviews so I can improve my teaching. I also suggested them to a friend who was looking for a simple data entry solution.
Let’s take a look!
Sign Up For Microsoft Forms
If you’re signed up with Office 365, then you already have Microsoft Forms and it can either be accessed from OneDrive, SharePoint, Excel Online or the Forms website.
If you don’t have an Office account, then you can still sign up to use forms for free here https://forms.office.com/ by creating a Microsoft account.
Creating a New Form or Quiz
There are a couple different ways to create a form or quiz with Microsoft Forms.
Creating a Form in OneDrive
You can create forms inside OneDrive personal or business. Navigate to the folder where you want to store your form results ➜ click on New ➜ select Forms for Excel.
You will then be asked to name the workbook associated with your form. This workbook will be saved in your chosen folder and will be where all the form submissions will be saved.
Creating a Form in SharePoint
The same thing can be done to create a form if you have an Office 365 business account with SharePoint online. Navigate to the folder where you want to store your form results ➜ click on New ➜ select Forms for Excel.
This also prompts you for a new workbook name where your form submissions will be saved.
Creating a Form in Excel Online
If you’re working with Excel Online, you can also create forms. Go to the Insert tab ➜ click on the Forms button ➜ select New Form from the menu.
This will create a form that’s linked to the current workbook.
Creating a Form from the Website
After you sign into https://forms.office.com/ you should be taken to the home page where you can create new forms and quizzes. If you don’t land on the home page, you can always get there from any screen using the button in the top left corner of the screen that’s labelled Forms.
From the home screen, click on either New Form or New Quiz.
The Different Types of Questions
Microsoft Forms currently has two types of forms. There are Forms and Quizzes. They both allow you to create the same type of questions. The only difference between them is you can assign point values and correct answers to quiz questions in order to calculate a quiz score.
All the questions can be accessed by clicking on the Add new button. This will show the list of available questions choices, but note that some are hidden in a menu accessible by clicking on the Ellipses.
Types of Questions
There are 7 types of questions available. Each has different options.
- The Choice option allows you to define a list of possible answers for the user to select one or more answers from.
- The Text option allows you to create long or short answer text questions.
- The Rating option allows you to create questions with a star or number rating between 2 and 10.
- The Date option allows the user to select a date from a calendar to answer the question.
- The Ranking questions allows a user to drag and drop items to answer questions like order of preference.
- The Likert option allows you to create “agree/disagree” scale type questions.
- The Net Promoter Score option allows you to create questions like “How likely are you to recommend [brand X] to a friend or colleague?” that utilize a net promoter style grading.
Tip: Some question types like the Choice and Ranking options allow you to copy and paste from a range in Excel or a line separated text file. This is handy if you have a long list of choices to add.
Each type of question has a different menu. For example, the above picture shows the available options for the Choice style questions.
- You can copy, delete or move the question from the menu in the top right of the question.
- You can add the actual question along with a subtitle (the subtitle option is found in the Ellipses menu).
- Forms has some built in AI capability to suggest answers for some types of questions. You can select individual items from its suggestions or add them all.
- For the multiple choices you can add or delete choices. You can mark the correct answer (for quizzes) and add comments to the choices.
- You can add more choice options.
- For quizzes, you can assign a point value for the purpose of calculating a quiz score.
- You can allow multiple answers and set the question to require an answer in order to submit the form.
- Further options are available in the Ellipses menu.
Form Sections
Sections in forms or quizzes allow you to break up the form into parts.
If you have a lot of questions in your form and don’t use sections, then the user would see all the questions on one page. Adding sections means you can break this up into multiple pages and the user will only see the next section of questions after completing the current section.
This can help with form submission rates, as seeing long lists of questions can discourage a user from answering all the questions and submitting the form.
You can add sections by clicking on Add new ➜ Ellipses menu ➜ Section.
Previewing a Form
When you’ve done creating your form, you can easily preview it and see exactly what a user will see.
Click on the Preview button in the top right to view and test the form. Careful though, as submitting the form in preview mode will still add the response to your results and you will have to manually delete the response to remove it from your results.
You’ll be able to preview what the form looks like on both mobile and desktop by using the buttons at the top right while in preview mode.
Form and Quiz Settings
Each form has some important settings that can be found in the Ellipses menu.
- For quizzes, you can choose to show the results to respondents automatically after submission.
- Forms and quizzes can either be public or private to an organization. When shared within an organization, you can chose to record the respondent’s name and limit users to one submission.
- There are options to open or close the form to accepting responses. You can set a start and end date for accepting responses. You can shuffle the order in which questions appear. You can add a custom thank you message that appears after a user submits the form.
- You can set notification options to send email notifications to each user or to yourself when a new response is received.
Form Branching
The above is an example of a form that uses branching.
Branching is one of the most useful features in Forms, but it’s unfortunately hidden inside an Ellipses menu. This will allow you to have different questions appear next based on how the user has answered a previous question.
To create a conditional form, click on the Ellipses found in the top right ➜ then select Branching.
This example asks the user if they’ve used Microsoft Forms before and gives two options, either Yes or No. If the user selects yes, then they are asked to rate the product out of 5 stars. If the user answers no, then they are asked why not. This way users are not shown questions that are not relevant to them.
Viewing Form Results
At some point, you’re going to want to take a look at the answers that have been submitted by people using your form. This can be done in the Responses tab of any form where you can see a summarized version of the results.
- You can view the details of each result individually.
- You can view all the results in the associated Excel file.
- You can share the results by creating a summary link. Click on the Ellipses ➜ choose Create a summary link.
In fact, I created a summary link to the above example for which can be viewed here.
Form Themes
There’s not much you can do in order to change the look and feel of your forms, but you can change the colour or background image.
Go to the Theme menu in the top right. Here you can select from a couple preset themes or if you click on the plus icon, you can select a custom colour or background image.
Sharing Your Forms
How do are you going to use your new form?
The whole point of creating a form is to collect information from users, so after creating a form you’re going to need to share it with your user audience! This can all be done from the Share menu in the top right.
- You can choose to make the form available to anyone with the link or only people inside your organization.
- You can copy this link and send it to anyone you want to complete the form.
- Sharing the form can be done via link, QR code, embedded HTML form code (see example of embedded form above), or by email.
- You can share a copy of your form as a template via a link so others can modify it for their own use.
- You can collaborate on form creation within an organization or with external users with an Office account.
- You a link to collaborate on editing the form can be copied and shared with anyone you want to give access to edit the form.
Conclusions
If you need to collect information from different users, then Microsoft Forms might be the tool for you.
With forms, you can quickly and easily create questionnaires that you can share both internally or externally from your work.
These forms will automatically collect and store the responses inside an Excel workbook so they can be easily viewed and analyzed later.
It’s another great tool in the Office suite that works well with Excel and is one you’re definitely going to want to explore using.
About the Author
John is a Microsoft MVP and qualified actuary with over 15 years of experience. He has worked in a variety of industries, including insurance, ad tech, and most recently Power Platform consulting. He is a keen problem solver and has a passion for using technology to make businesses more efficient.
Download Article
A quick and easy guide to create forms in Microsoft Excel
Download Article
This wikiHow teaches you how to create a form in a Microsoft Excel document. A spreadsheet form allows you to enter quickly large amounts of data into a table or list of cells. If you want to create a form with which other people can interact, you can use options found on the Developer tab of Excel to do so. Keep in mind that the data entry form feature is only available in Excel for Windows computers.
-
1
Open Excel. Click or double-click the Excel app icon, which resembles a white «X» on a dark-green background.
-
2
Click Blank workbook. It’s in the upper-left side of the page.
Advertisement
-
3
Add the «Form» button to Excel. By default, the «Form» button isn’t included in Excel. You can add it to Excel’s list of «Quick Access» icons that appear in the top-left corner of the window by doing the following:
- Click File.
- Click Options in the bottom-left side of the window.
- Click Quick Access Toolbar on the left side of the window.
- Click the «Choose commands from» drop-down box at the top of the window.
- Click All Commands.
- Scroll down until you reach Form, then click it.
- Click Add >> in the middle of the window.
- Click OK.
-
4
Enter your column headers. Type the name of the column into which you want to add data into the top cell in each column you want to use.
- For example, if you’re creating a form that lists different baked items, you might type «Pumpkin Bread» into cell A1, «Muffins» into cell B1, and so on.
-
5
Select your column headers. Click and hold the left-most column header, then drag your mouse right to the right-most column header. You can then release your mouse button.
-
6
Click the «Form» button. It’s the box-shaped icon in the upper-left side of the Excel window, just right of the right-facing «Redo» button.
-
7
Click OK when prompted. Doing so opens the Form pop-up window.
-
8
Enter the data for your first row. Type whatever you want to add into each column header’s text box.
-
9
Click New. It’s in the upper-right side of the pop-up window. Doing this will automatically enter your typed data into the spreadsheet under the appropriate column headers.
-
10
Enter subsequent rows of information. Each time you finish filling out the data entry fields, clicking New will enter your data and start a new row.
-
11
Close the data entry form. Click Close on the right side of the window to do so. Your data should now be completely entered below the appropriate column headers.
Advertisement
-
1
Open Excel. Click or double-click the Excel app icon, which resembles a white «X» on a dark-green background.
-
2
Click Blank workbook. It’s in the upper-left side of the page.
-
3
Enable the Developer tab. The Developer tab is where you’ll find the option to insert form buttons, but it isn’t included in Excel by default. To enable it, do the following:[1]
- Windows — Click File, click Options, click Customize Ribbon, check the «Developer» box, and click OK.
- Mac — Click Excel, click Preferences…, click Authoring under the «View» heading, and click Developer tab. You can then close the window.
-
4
Enter your form’s data. Type in whatever data you want users to be able to select in your form.
- This step will vary depending on the information you want to use in your form.
-
5
Click the Developer tab. It’s at the top of the Excel window.
-
6
Click Insert. This option is in the «Controls» section of the Developer toolbar. Clicking it prompts a drop-down menu to appear.
- Skip this step on a Mac.
-
7
Select a form control. Click the type of control you want to use for your spreadsheet.
- For example, if you want to add a checkbox to your form, you would click the checkbox icon.
-
8
Click anywhere on the spreadsheet. Doing so will place your control button on the spreadsheet.
- You can click and drag your control to the location in which you want to anchor it.
-
9
Right-click the form control icon. A drop-down menu will appear.
- On a Mac, hold down Control while clicking the icon.
-
10
Click Format Control…. It’s at the bottom of the drop-down menu.
-
11
Edit your form control button. Depending on the button you selected, your options will vary; in most cases, you’ll be able to select a cell range or a target cell by clicking the arrow to the right of the «Cell range» or «Target cell» text box and then selecting cells (or a cell) that contain your form’s data.
- For example, if you wanted to create a drop-down menu with a list of numbers, you would click the arrow to the right of the «Cell range» text box and then click and drag your mouse down a column of numbers in your spreadsheet.
-
12
Click OK. It’s at the bottom of the window. Doing so saves your settings and applies them to your spreadsheet.
- At this point, you can proceed with adding other form buttons to your spreadsheet.
-
13
Protect your spreadsheet. Once you’ve finished adding form buttons to your spreadsheet, you can prevent people from moving or removing the buttons by protecting the spreadsheet:
- Windows — Click Review in the Excel toolbar, click Protect Sheet, make sure that any options other than «Select locked cells» and «Select unlocked cells» are unchecked, enter a password to unlock the document, and click OK. You can then re-enter the password when prompted to finish locking the sheet.
- Mac — Click Tools at the top of the screen, select Protection, click Protect Sheet in the pop-out menu, make sure that any options other than «Select locked cells» and «Select unlocked cells» are unchecked, enter a password to unlock the document, and click OK. You can then re-enter the password when prompted to finish locking the sheet.
Advertisement
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Open a blank workbook.
2. Add the «Form» button to Excel.
3. Create column headers.
4. Select the column headers.
5. Click Form.
6. Click OK.
7. Enter the first row data and click New.
8. Enter additional rows.
9. Click Close.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 419,721 times.