After you create a table, Microsoft Office Word 2007 offers you many ways to format that table. If you decide to use Table Styles, you can format your table all at once, and even see a preview of what your table will look like formatted in a particular style before you actually apply the style.
You can create a custom look for tables by splitting or merging cells, adding or deleting columns or rows, or adding borders. If you’re working with a long table, you can repeat the table headings on each page on which the table appears. To prevent awkward page breaks that disrupt the flow of your table, you can also specify just how and where the table should break across pages.
What do you want to do?
-
Use Table Styles to format an entire table
-
Add or remove borders
-
Display or hide gridlines
-
Add a cell, row, or column
-
Delete a cell, row, or column
-
Merge or split cells
-
Repeat a table heading on subsequent pages
-
Control where a table is divided
Use Table Styles to format an entire table
After you create a table, you can format the entire table by using Table Styles. By resting your pointer over each of the preformatted table styles, you can preview what the table will look like.
-
Click in the table that you want to format.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Design tab.
-
In the Table Styles group, rest the pointer over each table style until you find a style that you want to use.
Note: To see more styles, click the More arrow
.
-
Click the style to apply it to the table.
-
In the Table Style Options group, select or clear the check box next to each the table element to apply or remove the selected style.
Top of Page
Add or remove borders
You can add or remove borders to format a table the way that you want.
Add table borders
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
In the Table group, click Select, and then click Select Table.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Design tab.
-
In the Table Styles group, click Borders, and then do one of
the following:-
Click one of the predefined border sets.
-
Click Borders and Shading, click the Borders tab, and then choose the options that you want.
-
Remove table borders from the whole table
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
In the Table group, click Select, and then click Select Table.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Design tab.
-
In the Table Styles group, click Borders, and then click No Border.
Add table borders to specified cells only
-
On the Home tab, in the Paragraph group, click Show/Hide.
-
Select the cells that you want, including their end-of-cell marks.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Design tab.
-
In the Table Styles group, click Borders, and then click the border that you want to add.
Remove table borders from specified cells only
-
On the Home tab, in the Paragraph group, click Show/Hide.
-
Select the cells that you want, including their end-of-cell marks.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Design tab.
-
In the Table Styles group, click Borders, and then click No Border.
Top of Page
Display or hide gridlines
Gridlines show the cell boundaries of a table on the screen wherever the table doesn’t have borders applied. If you hide the gridlines in a table that has borders, you won’t see the change because the gridlines are behind the borders. To view the gridlines, remove the borders.
Unlike borders, gridlines appear only on the screen; they are never printed. If you turn off gridlines, the table is displayed as it will be printed.
Note: Gridlines are not visible when you view a document in a Web browser or in Print Preview.
Display or hide table gridlines in a document
-
Under Table Tools, on the Layout tab, in the Table group, click View Gridlines.
Top of Page
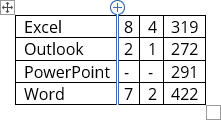
Add a cell, row, or column
Add a cell
-
Click in a cell that is located just to the right of or above where you
want to insert a cell. -
Under Table Tools, on the Layout tab, click the Rows & Columns Dialog Box Launcher.
-
Click one of the following options:
|
Click this |
To do this |
|
Shift cells right |
Insert a cell and move all other cells in that row to the right. Note: This option may result in a row that has more cells than the other rows. |
|
Shift cells down |
Insert a cell and move remaining existing cells in that column down one row each. A new row will be added at the bottom of the table to contain the last existing cell. |
|
Insert entire row |
Insert a row just above the cell that you clicked in. |
|
Insert entire column |
Insert a column just to the right of the cell that you clicked in. |
Add a row
-
Click in a cell that is located just below or above where you want to add a row.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To add a row just above the cell that you clicked in, in the Rows and Columns group, click Insert Above.
-
To add a row just below the cell that you clicked in, in the Rows and Columns group, click Insert Below.
-
Add a column
-
Click in a cell that is located just to the right or left of where you want to add a column.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To add a column just to the left of the cell that you clicked in, in the Rows and Columns group, click Insert Left.
-
To add a column just to the right of the cell that you clicked in, in the Rows and Columns group, click Insert Right.
-
Top of Page
Delete a cell, row, or column
-
Do one of the following:
To select
Do this
A cell
Click the left edge of the cell.
.
A row
Click to the left of the row.
A column
Click the column’s top gridline or top border.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
In the Rows & Columns group, click Delete, and then click Delete Cells, Delete Rows, or Delete Columns, as appropriate.
Top of Page
Merge or split cells
Merge cells
You can combine two or more cells in the same row or column into a single cell. For example, you can merge several cells horizontally to create a table heading that spans several columns.
-
Select the cells that you want to merge by clicking the left edge of a cell and then dragging across the other cells that you want.
-
Under Table Tools, on the Layout tab, in the Merge group, click Merge Cells.
Split cells
-
Click in a cell, or select multiple cells that you want to split.
-
Under Table Tools, on the Layout tab, in the Merge group, click Split Cells.
-
Enter the number of columns or rows that you want to split the selected cells into.
Top of Page
Repeat a table heading on subsequent pages
When you work with a very long table, it will be divided wherever a page break occurs. You can make adjustments to the table so that the table headings are repeated on each page.
Repeated table headings are visible only in Print Layout view and when you print the document.
-
Select the heading row or rows. The selection must include the first row of the table.
-
Under Table Tools, on the Layout tab, in the Data group, click Repeat Header Rows.
Note: Word automatically repeats the table headings on each new page that results from an automatic page break. Word does not repeat a heading if you insert a manual page break within a table.
Top of Page
Control where a table is divided
When you work with a very long table, it must be divided wherever a page break occurs. By default, if a page break occurs within a large row, Microsoft Word allows a page break to divide the row between the two pages.
You can make adjustments to the table to make sure that the information appears as you want it to when the table spans multiple pages.
Prevent a
table row from breaking across pages
-
Click in the table.
-
Under Table Tools, click the Layout tab.
-
In the Table group, click Properties, and then click the Row tab.
-
Clear the Allow row to break across pages check box.
Force a table to break across pages at a particular row
-
Click in the row that you want to appear on the next page.
-
Press CTRL+ENTER.
Top of Page
Many documents present some data in the form of figures or tables. Creating tables is often more efficient than describing the data in the paragraph text, especially when the data is numerical or large. The tabular data presentation makes it easier to read and understand.
A table is a collection of information or data, usually represented by horizontal rows and vertical columns. Each column and each row can have a header. Some tables have only column headings or only row headings. The box at the junction of each column and row is a cell that contains data such as text, numeric information, or images. Some cells can be merged or split (see more about formatting tables). E.g.:
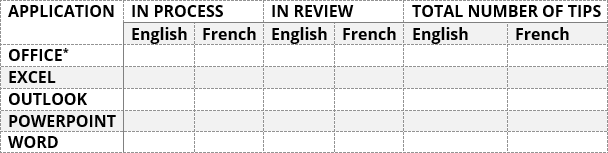
Microsoft Word has many features that make working with tables simple and convenient.
Create a table
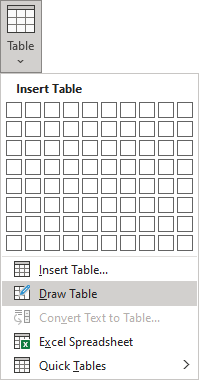
There are several ways how to insert or create a table:
- Create a blank table of up to 10 columns and 8 rows,
- Create a blank table with more than 10 columns or more than 8 rows,
- Create a blank table manually (Draw a table),
- Create a table using predefined templates (Quick Tables),
- Create a table from the existing data (Convert Text to Table),
- Insert a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet.
To create a blank table in a Word document, do the following:
1. Place your cursor where you want to insert the table.
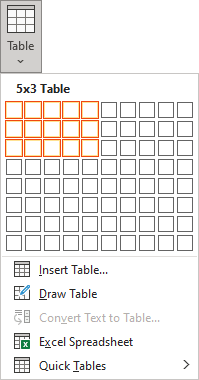
2. On the Insert tab, in the Tables group, click the Table button:

3. Do one of the following:
Create a blank table of up to 10 columns and 8 rows
- To create a table of up to 10 columns and 8 rows, move the cursor right (to select columns) and down (to select rows) the grid to select as many cells as you need. E.g., the table of 5 columns and 3 rows (selected cells will turn orange):
Click on a cell in the grid with the expected number of rows and columns (or press Enter) to insert an empty table to fit the width of the text (paragraph).
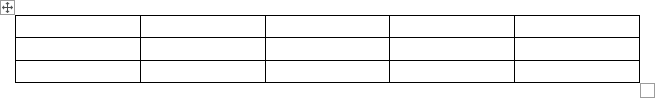
The table has the specified number of single-line text rows in the current paragraph and equal-width columns. E.g., the table of 3 rows and 5 columns:
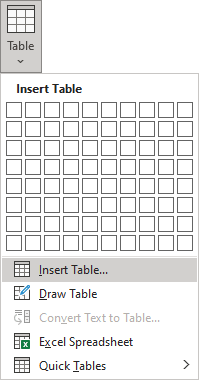
Create a blank table with more than 10 columns or more than 8 rows
- To create a table with more than 10 columns or more than 8 rows, do one of the following:
- Create a table with exactly 10 columns or 8 rows, then add as many columns or rows as you need (see below how to customize table).
- Click the Insert Table… option:
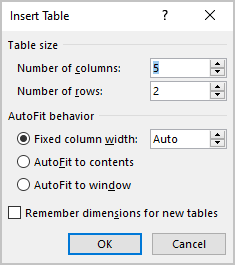
In the Insert Table dialog box:
- In the Table size group, specify the number of columns and rows,
- In the AutoFit behavior group, specify the width of the table and its columns:
- Select the Fixed column width option to customize width in the appropriate field: select Auto (used by default) or specify width. E.g., 0.75″:
- Select the AutoFit contents option to adjust cell sizes to the document content. E.g.:
- Select the AutoFit to window option to adjust the table’s width to the document content width. E.g.:
- Select the Remember dimension for new tables check box if you want to create tables with the same options later. Word will remember your customization.
Create a blank table manually
- To manually create an empty table, click the Draw Table option:
After clicking that option, the cursor changes to the pencil
that allows drawing cells directly in the Word document to create a table:
Click anywhere in a document but the table itself by the pencil to stop drawing a table.
Notes:
- To draw additional lines, select a table, then on the Table Layout tab, in the Draw group, click the Draw Table button:
- If you draw a line in the wrong position, click the Eraser button in the Draw group of the Table Layout tab:
- We recommend displaying the rulers or gridlines to help you place the lines correctly.
- To draw additional lines, select a table, then on the Table Layout tab, in the Draw group, click the Draw Table button:
Create a table using predefined templates
To create a table using predefined Word templates of tables and calendars, do the following:
1. Place your cursor where you want to insert the table.
2. On the Insert tab, in the Tables group, click the Table dropdown list, then select Quick Tables list:
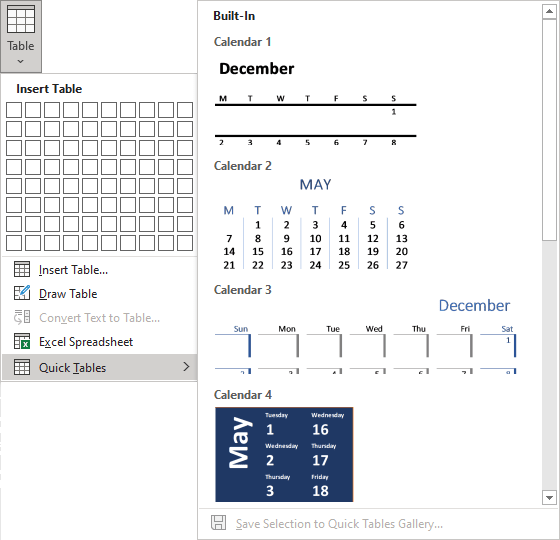
3. From the Quick Tables gallery, select the template you prefer.
For example:
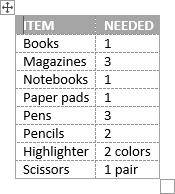
Create a table from the existing data
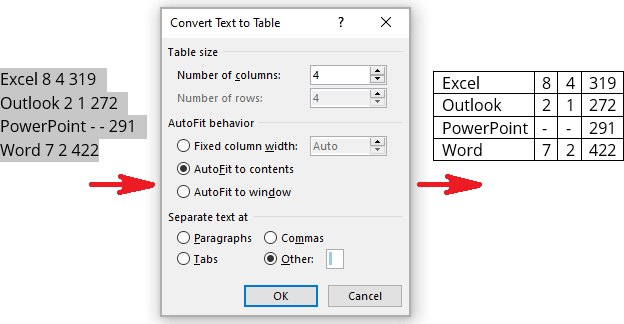
To create a table from the existing data in a document data (either as regular text or as a tabbed list), do the following:
1. Select the document data you want to shape into a new table.
2. On the Insert tab, in the Tables group, click the Table dropdown list, then select Convert Text to Table…:

3. In the Convert Text to Table dialog box:
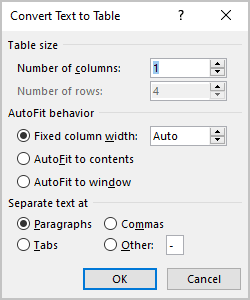
- In the Table size group, specify the number of columns,
- In the AutoFit behavior group, specify whether the width of the columns should be fixed (see details above),
- In the Separate text at group, select the character that separates text into columns in the selected text: paragraph marks, commas, tabs, or some other character.
E.g.:
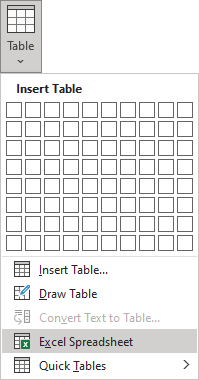
Insert a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet
Note: It is possible to insert a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet in a document. To do so, on the Insert tab, in the Tables group, click the Table dropdown list, then select Excel Spreadsheet:
Word opens the Excel spreadsheet where you can enter the data. You can use Excel features such as functions and formulas to create or manipulate the data. Note that it is not a Word table.
Add rows and columns
To add a row and a column to a table, do the following:
1. Position the cursor:
- to a cell in a row above or below which you need to insert a row,
- to a cell in a column left or right which you need to insert a column.
2. Do one of the following:
- Click the Insert dropdown list in the Mini toolbar:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Rows & Columns group:
- Click the Insert Above button to insert a row above the row with the cursor,
- Click the Insert Below button to insert a row below the row with the cursor,
- Click the Insert Left button to insert a column left to the column with the cursor,
- Click the Insert Right button to insert a column right to the column with the cursor.
- Right-click and select the Insert list:
Notes:
- To insert rows or columns, move the mouse over the table or left of the table until you see the Insertion indicator, then click the icon:
and
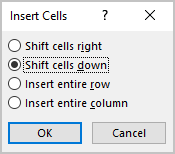
- You can choose the option Insert -> Insert Cells… from the popup menu; Word opens the Insert Cells dialog box:
After selecting the option and clicking the OK button, Word adds an entire row or column, not a cell. Word just moves cells according to the selection.
Delete a table element
To delete a table element, do the following:
1. Select the cell, multiple cells, the entire column or multiple columns, the entire row, or multiple rows.
2. Do one of the following:
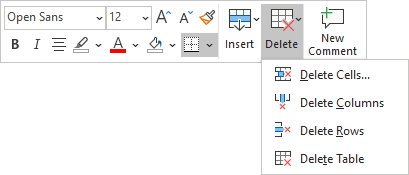
- Click the Delete dropdown list in the Mini toolbar:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Rows & Columns group, click the Delete dropdown list, then select one of the options:
3. Select one of the proposed options:
- Delete Cells… opens the Delete Cells dialog box, in which select the option you need:
- Delete Columns
- Delete Rows
- Delete Table
Note: You can select the element you want to delete, right-click on the selection and select the appropriate item in the popup menu. For example, if the entire table is selected or the column is selected:
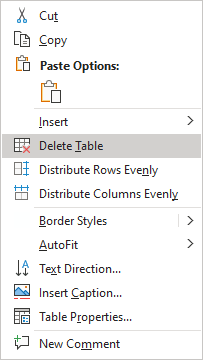
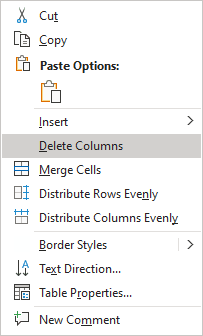
Convert a table into text
To convert a table into text in Word, follow the next steps:
1. Click anywhere in the table.
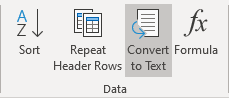
2. On the Layout tab, in the Format group, click the Convert to Text button:
3. In the Convert Table to Text dialog box, select the charter to separate cells data in the text:
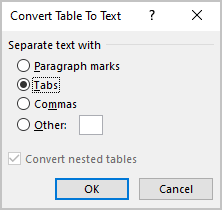
4. Click OK.
Creating and formatting tables seems to be difficult for beginners in Microsoft Word.
A table is an object used to summarize a large amount of data in rows and columns. It is often, an easy object to use when comparing different items. It is also easy for you to understand data summarized in a table than a vague report in a text format. This is because tables help in data analysis for ease of making inferences using available data.
Tables create a portable data structure for ease of storage and retrieval. This is why databases store data in tables. Also, data is stored and displayed in spreadsheets in tabular form.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to easily create, edit, and format tables in any word document.
You can create tables in MS word just as you can create tables in other word applications. After a table is created, there could be a need to edit the data in a table. Creating and formatting tables is therefore an important skill when using a word processing application.
Uses of tables
When working with tables, we can use tables to display and compare data; for example:
- Tables can be used to organize data that is too complicated to be described in a text
- It can also be used to make data comparisons. E.g., compare sales of product A in X and Y periods.
- Tables can also be used to make analyses to draw an inference. E.g., tabular data analysis in percentages.
- It is used to summarize data for clarity and makes it more readable and understandable to the audience.
- Tables can be used to track trends and identify patterns in a time-series data
No matter what you need tables for in your Word document, you should learn how to create and format them.
How to Create Table In MS Word
There are 5 ways to insert or create a table in an MS Word document. Each of these methods is necessary depending on the kind of table you want to create. The five methods include:
- The insert table template
- A preset table design templates
- The draw table command
- Working from an Excel spreadsheet
- Using the insert table command
Let us expatiate on how to use each of these methods to create a table in MS Word application.
Using the insert table template
The insert table template allows you to create a blank table by selecting up to 10 columns and 8 rows. It is the fastest way of creating a table. It inserts an empty table in your document based on the number of columns and rows selected. The inserted table also assumes the width of the current document. You can add more columns and rows depending on your need.
Create a blank table
To create a blank table, do the following:
- Make sure the insertion point is at the position you want to insert your table
- On the Insert tab, under the Tables group, select Table.
- From the dropdown menu, under Insert Table, point to the number of columns and rows you want on the template.
- Then click at the junction of the columns and rows selected, see the diagram below.
- There are 10 columns and 8 rows. The number of columns and rows you selected will be automatically inserted into your document.
- Start entering data in your table.
Create a table with preset design templates
These are preset table designs from which you can choose. It includes a calendar design, a list table, and tables with header designs. You can insert any of these table designs and edit the data in them.
Create a table with a preset table design
To create a table with a preset design, do the following:
- Make sure the insertion point is at the position you want to insert your table
- On the Insert tab, under the Tables group, select Table.
- From the dropdown menu, point to Quick Tables.
- From the list that appears, scroll and select a table design of your choice.
- The selected design automatically appears in your document.
- Edit the available data with yours.
Create a table with the draw table command
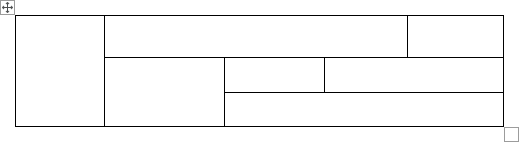
Creating and formatting tables in Word can be achieved using the draw table command. The draw table command gives you the option of using the pencil and eraser tools on the Design tab. You can use the pencil tool to create a new table or add a column or row to an existing table. The eraser tool is used to remove table borders or to completely erase an entire table.
Creating a table with pencil and eraser tools
To use the draw table command to create a table, do the following:
- On the Insert tab, under the Tables group, select Table.
- From the dropdown menu, select Draw Table.
- Your pointer changes to a pencil.
- Take the pointer to the location on your document where you want to create the table.
- Click and drag diagonally, from left to right to draw a rectangle.
- Using the pencil, divide the rectangle into columns and rows.
- To create a column, the point at the top border, click and drag downward to join the bottom border.
- To create a row, the point at the left border, click and drag rightward to join the rightmost border.
- When done, enter your desired data in the table.
Create a table with an Excel spreadsheet
You can also create a table using an Excel spreadsheet. This is most useful when you have a computation or analysis to make.
When you insert a table using an Excel spreadsheet, the Excel app opens, allowing you to adjust your table. You can customize the table based on your desired number of columns and rows.
You can also copy and paste data from Excel to create an Excel spreadsheet table in MS word. To edit an Excel table, double-click on the MS Word document table to open the Excel app.
Insert a table in Word using an Excel spreadsheet
To create a table using an Excel spreadsheet, do the following:
- Ensure that the insertion point is at the position you want to insert your table.
- On the Insert tab, under the Tables group, select Table.
- From the dropdown menu, select Excel Spreadsheet.
- A mini spreadsheet is automatically inserted into your document with Excel features replacing word features.
- Click and drag the small dark boxes to adjust the table width.
- Adjust columns and rows appropriately to fit the width. Make sure no columns and rows are left vacant.
- Enter your desired data in the cells and format it appropriately.
- When done, click outside the mini spreadsheet to return to MS Word. NB: To edit data, double-click on the Excel table.
Using the insert table command
The last method you can use to create a table in MS Word is by using the insert table command. This method allows you to create a table by specifying the features of the table in a dialog box. Let us use this method to create a table as follow:
To create a table using an Excel spreadsheet, do the following:
- Ensure that the insertion point is at the position you want to insert your table.
- On the Insert tab, under the Tables group, select Table.
- From the dropdown menu, select Insert Table… The insert table dialog box appears.
- On the insert table dialog box, specify the following:
- Under Number of columns specify how many columns you want
- Under Number of rows specify how many rows you want
- Choose any of Fixed column width, AutoFit to contents, or AutoFit to window under AutoFit behavior.
- Click OK when done. Your table will be inserted automatically.
- Start entering your data as desired.
NOTE the following:
- If you chose the Fixed column width, select auto or a specific column width in inches, e.g., 1.2”. The columns will be adjusted based on the size.
- If you chose the AutoFit to contents, the columns will adjust based on the contents in the table.
- If you chose AutoFit to window, the table will be adjusted to cover the current document width.
You can use any of the above methods to create your table, but my preferred method is the last. Whenever I use this method, I always set the AutoFit behavior to AutoFit to contents. This is because I prefer content-adjusting columns rather than manually adjusting them.
How to Edit Table in MS Word
Editing a table means updating the content of a table. This can be done either by replacing old content or by adding new content to the existing one.
As soon as you create a table, two command tabs are added to the existing ones, namely Design and Layout. These two tabs appear whenever the table is active. If the cursor is not blinking in the table, the two tabs will disappear. The commands in the Layout tab are what we need to edit our tables in MS Word.
Replacing old content
We can replace old content with new content or completely remove it, and replace it with nothing. This can be achieved in two ways:
- By removing the content of a cell in a table and replacing it with the new content: to achieve this,
- Go to the table and select the cell you want to edit
- Highlight the content of the cell and press Delete on the keyboard
- Type the new content in the empty cell
- Or by removing an entire cell, row, or column in the table. This can be achieved as follow.
Delete a cell in a table
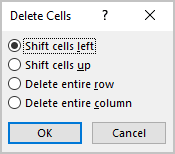
When you delete an unwanted cell in a table, the other cells will shift upwards or leftwards. To delete an unwanted cell in a table, do the following:
- Select the cell you want to delete from your table.
- Do any of the following:
- From the mini-toolbar that appears, select Delete. From the submenu that appears, select Delete Cells…
- On the Layout tab, under Rows & Columns, select Delete. From the Delete submenu, select Delete Cells…
- The delete cells dialog box appears.
- On the dialog box, select either Shift cells left or Shift cells up. The option to choose depends on the direction of the deleted item. If the item to be deleted will affect the row, then shift cells left, else, shift cells up.
- Click OK to delete. The selected cell(s) deletes automatically.
Delete entire row or column
An update might require that an entire row or column be completely removed. In this case, do the following:
- Select the row or column you want to delete. Note that selecting a cell in that row or column is enough.
- Do any of the following:
- From the mini-toolbar that appears, select Insert. From the submenu that appears, select Delete Rows to delete a row, or Delete Columns to delete a column.
- On the Layout tab, under Rows & Columns, select Delete. From the Delete submenu, select Delete Rows or Delete Columns.
- The selected row or column and its content will be automatically deleted.
Merging two or more cells
To merge cells means to join one or more cells together. When the selected cells are merged, it becomes one cell. To merge cells in a table, do the following:
- Select two or more adjacent cells that you want to merge.
- Do any of the following:
- From the mini-toolbar that appears, select Merge Cells.
- On the Layout tab, under Merge, select Merge Cells.
- The selected cells automatically become one, with their content inside the new cell.
Adding new content
In some cases, editing a table may require that you add more columns or/and rows. To add entirely new content, we need to adjust our table. We can add new content by splitting cells or tables and adding columns or rows.
Adding a column or row to a table
To add a column or row to an existing table, do the following:
- Select the row or column next to where you want to add a row or column. Note that selecting a cell in that row or column is enough.
- Do any of the following:
- From the mini-toolbar that appears, select Delete. From the submenu that appears, select any of the following: Insert Above or Insert Below to add a row. Or Insert Left or Insert Right to add a column.
- On the Layout tab, under Rows & Columns, select Insert. From the Insert submenu, select any of Insert Above, Insert Below or Insert Left or Insert Right.
- A row automatically appears above or below the selected row. Or a column appears to the left or right of the selected column.
Splitting Cells
Splitting cells means dividing one or more cells into columns or rows. To divide existing cells in a table, do the following:
- Select the cell or adjacent cells you want to split.
- On the Layout tab, under Merge, select Split Cells. The split cells dialog box will appear.
- On the split cells dialog box, enter the number of columns and rows for the new cells.
- Press OK to apply.
Split a table
You can also divide an existing table into two halves. To do so, follow these steps:
- Select the row from where you want to split a table.
- On the Layout tab, under Merge, select Split Table.
- The table divides into two from the selected row.
Formatting Tables in Word
Formatting tables in Word includes applying designs that will make our table outstanding. We shall use the Design tab to apply preset table designs and manual formatting.
Formatting table cells
Formatting tables also include applying alignment and cell size formatting to selected cells from the Layout tab. In the Layout tab, under the Alignment group, you can perform the following formatting types:
- Align the content of selected cells in a table using alignment commands.
- Change the text direction of selected cells in a table using the Text Direction command.
- Customize the margins within selected cells in a table using the Cell Margins dialog box.
You can also use the Cell Size group to resize selected cells in a table. You can resize a cell’s Height and Width by entering a size in the available text boxes. When you click on the Distribute Rows or Distribute Columns buttons, all rows or columns are distributed equally.
Working with table styles
Microsoft Word has preset table styles you can use to easily format your tables. To use a preset table style, do the following:
- Select the table you want to format/
- On the Design tab, under Table Styles, select the More styles dropdown arrow.
- From the list of styles, select a style that best suits your design.
- The selected style automatically applies to the selected table.
Add cell shading to a table
You can manually apply shading to selected cells, rows, or columns of your table. To do this, follow the following steps:
- Select the cells, or rows or columns you want to apply shading on.
- On the Design tab, under Table Styles, select the Shading dropdown arrow.
- From the color palettes that appear, select a color that best suits your design.
- The selected color applies to the selected cells, rows, or columns.
Formatting table borders
When you create a table in word, the table usually displays the gridlines, otherwise called table borders. You can decide to not display these table borders, change their color or apply them to selected cells.
Remove borders from a table
To remove the borders in a table, do the following:
- Select the table, cell(s), row(s), or column(s) you want to remove borders from.
- On the Design tab, under Borders, select Borders.
- From the dropdown list, select No Border.
- Borders automatically disappear from the selected table, cells, rows, or columns.
You can remove the top, bottom, left, or right border of a selected cell, row, or column. To do this, follow the steps above and select any of Top Border, Bottom Border, Left border, or Right Border.
You can also select Borders and Shading… from the dropdown list to display the borders dialog box. Select the borders you want to remove on the dialog box by clicking on them in the preview window. See Formatting Paragraphs.
Format table borders
You can change the look of your table borders by changing the border style and color. This can be applied to the entire table or selected cells, rows, or columns. This can be done in two ways: using the Borders command or using the Border Painter command.
Using the borders command
To use the borders command to format a table’s border, do the following:
- Highlight the table, cell, row, or columns you want to change their border style.
- On the Design tab, under Borders, select the Border Styles.
- From the dropdown window, select a border style of your choice.
- Select the Border Line Weight, and choose a line weight of your choice.
- Select the Pen Color icon, and choose a color of your choice.
- Select Borders, from the dropdown list, select the type of border you want to apply.
- The selected border applies the style to the selected cell, row, column, or table. NB: You can achieve this styling at once by using the borders and shading dialog box.
Using the border painter
To use the border painter command to format a table’s border, do the following:
- On the Design tab, under Borders, select the Border Styles.
- From the dropdown window, select a border style of your choice.
- Select the Border Line Weight, and choose a line weight of your choice.
- Select the Pen Color icon, and choose a color of your choice.
- Select the Border Painter, your pointer changes to a calligraphic pen.
- Use the pointer to drag over any of the borderlines you want to change. The selected styles will be automatically applied to those borders.
- While the Border Painter is still selected, you can change the style, color, and weight of the border. Dragging it over borderlines will change the lines to the current styles.
Conclusion
I want to believe that today’s tutorial is exciting and challenging. You should have learned new ways to insert and create tables in MS Word. Did you notice that creating and formatting tables in MS word is captivating, especially to beginners?
In this tutorial, we looked at creating, editing, and formatting tables in MS Word. I believe that this tutorial is useful and will help you in your career. Next week we shall finalize this series with the topic of printing your document. Don’t miss it.
Please, kindly help a friend in need by clicking on the share button. Don’t forget the previous series, in case you’ve not seen them:
- What is Microsoft Word: A Practical Overview
- How to Create a Document in Microsoft Word
- The Page Layout: Microsoft Word Tutorials 3
- Inserting and Formatting Text in Word Document
- Paragraph Formatting in a Word Document
Are you struggling to get your message across? When your Microsoft Word project contains information, try presenting it in the form of a Word table. Learn how to make tables in Word quickly with a template.
A table is a kind of chart that organizes and presents data in rows and columns. It makes information easier to grasp, understand, and analyze at a glance, compared to explaining the same data through plain text.
Microsoft Word gives you various ways to insert or create a table. And you’ve got granular control over the formatting, layout, and appearance of Microsoft Word tables. Table charts are useful in different types of Word projects, whether for personal, educational, or business use.
This article will show you how to make a table in Word using a template. Then edit and format it to change its appearance.
(Note: The screenshots and instructions that follow are made using Microsoft Word for Mac version 16.4. If you’re using a different version of Word, then the interface and steps may be different.)
How to Make & Edit MS Word Tables (Video)
In this video, you’ll learn how to quickly make tables in Mircosoft Word. Find out how to start with a premium template. Quickly customize it to make an attractive, professional MS Word table you can use and reuse.
To learn even more about MS Word tables and about templates than can be used for tables, study the step-by-step tutorial below:
How to Make Basic Tables in Word
Let’s start by learning how to make a basic table in Microsoft Word:
1. Insert a Table
You can create a basic Microsoft Word table in one of two ways:
Method 1. The Insert Tab
Click on the Insert tab, then click the Table button on the ribbon.
The Insert Table panel appears. Drag the cursor over the squares to specify the number of columns and rows you want to create. Click to apply.
Method 2. The Insert Menu
Go to Insert > Table….
The Insert Table panel opens. Specify the number of columns and rows you need. (You can always add or remove columns and rows later.)
Also select the Autofit Behavior you want the table to have. You’ve got several options:
- Initial column width. The default setting is Auto, which divides the entire width of your page window across the number of columns in the table. Or, you can specify a different column width.
- AutoFit to contents. Resizes the column width based on the width of the content inside the column.
- AutoFit to window. Distributes the columns equally across the entire width of the page window.
- Set as default for new tables. Check this option if you want the settings to be applied globally to all new tables you create.
When you’re happy with the options you’ve selected, click OK.
2. Draw a Table
Or, you can draw a table in MS Word. This is a useful feature if you want to create an irregular or more complicated table with columns and/or rows of varying widths.
To draw a table, click Insert > Table > Draw Table.
With your mouse or trackpad, click and drag the cursor to start drawing your table. You can begin by drawing the outermost boundary of the table first.
Then, click and drag the cursor to create columns and rows inside the table. When you’re done, click anywhere outside the table.
Here’s an example of an “irregular” table you can draw using this feature.
If you make a mistake, click Layout > Eraser to erase a line from the table.
Click and drag the eraser along the line you wish to erase. The line that’ll be erased appears as a thick, red line. Release the mouse or trackpad to erase.
Click outside the table when you’re done.
3. Convert Text to Tables and Vice Versa
Another way to create a table is by converting text into a table. This means you can take non-tabular data from a CSV or plain TXT file and convert them into a table.
First, copy and paste the non-tabular data into your Word document.
With the text selected, go to Insert > Table > Convert Text to Table….
The Convert Text to Table panel opens. Specify the settings you wish to use. Click OK.
The text is then converted into a table.
You can also do the opposite, which is to convert a table into text.
Select the cells or entire table you want to convert. Next, click on the Layout tab then click the Convert Table to Text icon.
The Convert Table to Text panel opens. This is where you’ll decide how you want to separate text that’s currently in different columns. When you’ve made a selection, click OK.
For this example, I chose to separate text with commas. This is what the converted table looks like.
4. Advanced: How to Insert a Table from Excel
If you’ve already created a table in Excel, you can embed it into your Word document.
Open the Excel file. Click and drag the mouse to select the table.
Go back to your Word document. Go to Edit > Paste Special ….
In the Paste Special panel, select Microsoft Excel Binary Worksheet Object, then click OK.
This embeds the Excel table into Word. It’s still an Excel table, which means you can’t edit or format the table in MS Word. You’ve got to do so in Excel.
Double-click anywhere in the table to launch the source file in Excel. When you make any changes to the table in Excel, the table embedded in your Word project automatically updates to reflect those changes.
Now you know how to make a table in MS Word using various options.
How to Edit Tables
At any time after creating your table, you can edit and customize it to look the way you want it to. Here are some steps for editing tables in Microsoft Word:
1. Add a Column or Row
To add a row or column, click inside a table cell. Right-click on the mouse, then click Insert.
Select one of the following:
- Columns to the Left. Adds a column to the left of the current column
- Columns to the Right. Adds a column to the right of the current column
- Rows Above. Adds a row above the current row
- Rows Below. Adds a row below the current row
- Cells … Inserts a cell and shifts the rest of the cells either to the right or down from where the cursor is
- Table … Inserts a table inside the current cell
Or, with the cursor in one of the cells, you can click on the Layout tab.
Then choose of the following buttons on the ribbon:
- Insert Above. Inserts a row above the current cell
- Insert Below. Inserts a row below the current cell
- Insert Columns to the Left. Inserts a column to the left of the current cell
- Insert Columns to the Right. Inserts a column to the right of the current cell
Finally, you can add a new row when you’ve reached the last cell in the last row of your table. Simply press tab and a new row appears.
2. Delete a Column or Row
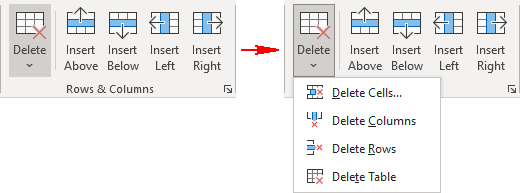
To delete a cell, column, row, or table, click on the Layout tab > Delete.
Select one of the options that appear:
- Delete Cells …
- Delete Columns
- Delete Rows
- Delete Table
You can use the same steps to edit a table you’ve drawn. Or, you can use the Layout tab to add or delete rows and columns.
Merge Cells
Sometimes you may want to merge cells to present information more clearly. To merge cells, click and drag the cursor to select the cells you wish to merge.
On the Layout tab, click on the Merge Cells button.
Or, after selecting the cells to be merged, right-click on your mouse, then click Merge Cells.
Now the cells have been merged into one.
Split Cells
After merging cells, you can always split them again into separate cells.
Place the cursor in the merged cell, then click Layout > Split Cells.
Or, right-click on your mouse, then click Split Cells….
Either way, the Split Cells panel pops up. Specify the number of columns and rows you want to split the cell into. Click OK.
Split Table
You may decide that it makes more sense to split up a table into two separate tables. Microsoft Word lets you do that easily, too.
In this example, I want to split the table right above the Accessories cell. And so, I’ll place the cursor in that cell. Next, click on the Layout tab, then click the Split Table button.
Now, we’ve got two separate tables.
Table Formatting
When you first create a table, it looks plain and boring. But Microsoft Word has many features so you can format tables to look exactly the way you want them. Here are some common ways to format tables:
1. Table Styles
The easiest way to format a table is by using one of the pre-formatted table styles. Put the cursor in any cell in the table. Click on the Table Design tab. Next, click on the arrow to expand the Table Styles group.
Click on a style you want to use and it’s applied immediately.
You can change any style you’ve selected. Again, click on Table Design, expand the Table Style group, then click Modify Style.
The Modify Style panel opens. Make the selections you want, then click OK.
2. Use Your Own Formatting
The Table Design tab gives you control over the appearance of every aspect of your table. Click on the Table Design tab and any of the appropriate buttons on the ribbon.
Resize a Table
You can also resize your table. Click on any cell to select the table, then click and drag one of the corners to resize it.
Or, you can use the Layout tab to resize individual cells, specific rows or columns, or the entire table. Select the columns or rows you wish to resize. Specify the height and/or width you wish to apply.
You can also adjust column width by hand by using the Table Ruler. Click inside a column you want to change. Then, drag the sliders in the Table Ruler to set to desired width.
Text Wrapping
If you want text to flow around the table, you can do so by changing its text wrapping.
Click in any cell to select the table. Click Table > Table Properties….
In the Table Properties panel and under Text Wrapping, click Around > OK.
Now the text flows around the table.
Take note that the Table Properties panel allows you to format other qualities of the table, including:
- Size
- Alignment
- Positioning
- Borders and Shading
On the other tabs, you can change:
- Column, Row, and Cell Size
- Allow row to break across pages
- Repeat as header row at the top of each page
- Cell Vertical Alignment
- Alt Text (Title and Description) — more information about the table, to help people with vision or cognitive impairment who may not see the table
Find Great Styles for Microsoft Word
You don’t have to start from scratch to create an impressive and effective Word document — even if you don’t have design skills. You can find great styles by using a template for Word.
One great source for great Microsoft Word templates and professional graphics is Envato Elements. For one low monthly subscription, you get unlimited downloads of templates, graphics, fonts, and other creative tools you need for your project. It’s a terrific option if you create plenty of materials.
For single projects, GraphicRiver is an outstanding source for templates for Word. This marketplace gives you access to thousands of creative elements on a pay-per-use basis.
Learn More
Microsoft Word has many robust features to help you realize the vision you’ve got for your document. But with power comes complexity. That’s why it’s a good idea to learn how to use Microsoft Word.
These articles will help you get started:
Visualize Your Data with Microsoft Word Tables
Make your information clearer and easier to understand by learning how to make a table in Microsoft Word. Tables organize data into rows and columns, which makes them easier to grasp at a glance. Follow the steps in this article to create, format, and customize tables in Word.
You can also use a premium Word template to get a premium design created by designers. Get Word templates from Envato Elements, if you want unlimited downloads of templates, graphics, and other creative tools you need — all for one flat monthly fee.
Or, get premium templates for Word from GraphicRiver if you prefer to pay for each use of an item. Both sources give you access to thousands of design elements created by professionals, so you can save time, energy, and effort while creating an outstanding Word document.
Did you find this post useful?
Marketing & Communications Professional and Lifelong Learner/Canada
Lexi Rodrigo is a marketing and communications professional, copywriter, and course creator who helps remarkable brands and people get seen, heard, and known. Writing for the web since 2008, she has over 100+ blog posts published on Envato Tuts, Acadium, Mirasee, Vero, Copyblogger, FreelanceFolder, Business2Community, and others.
Lexi has supported multimillion-dollar companies and nonprofits in various marketing and communication roles. She has driven results like tripling the organic search traffic of a blog in three months and generating over $65 million in revenues, donations, and sponsorships.
She has a Bachelor of Arts degree in communications. She is also the co-author of «Blog Post Ideas: 21 Proven Ways to Create Compelling Content and Kiss Writer’s Block Goodbye.» When she’s not reading or writing, Lexi bakes bread, grows food, and takes long walks.

A table is one convenient way to display like information. People can refer to the table within a document and see how it applies to the lesson being taught. They can come to their own conclusions when they see the data stacked up against each other. That’s where knowing how to create and format tables within a Microsoft Word document pays off.
Why You Need to Use Tables in Documents
Let’s face it, some people need visual aids to learn. Even though text is comprised of letters, numbers, and punctuation, it can be very taxing on the eyes. When you’re able to stress a point visually with a table, you’re able to relay data quickly and in a way that other people understand well.
Tables take large amounts of data and categorize it in a way that is easy to understand and digest. It gives readers of a document, catalog or manual an organized way to process what they’ve learned from the author. You don’t have to skim paragraph after paragraph of text to gain the same understanding from a well-made table.
How to Create a Table and Then Format It to Your Liking
To create a table in Microsoft Word, you must first own Microsoft Office. Once you have the software downloaded to your computer, you’ll want to open a new word document by double clicking the MS Word icon and choosing ‘New’ when prompted by the menu to make a selection.
Once your blank document is open, you’ll want to type out your list or text. Converting it to table format takes a few steps, so be prepared. Once you learn how to do it the first time, you’ll have no problem creating and adding tables to documents.
Here’s what you need to do to get the process going:
-
Choose ‘Home’ then ‘Show/Hide’.
This allows you to see the tabs and paragraph makings made in the document.
-
Use separator characters in the form of commas or tabs.
This tells the program where to divide text. It will place it into table columns.
-
When you want to begin a new table row, you’ll need to use paragraph marks.
This allows you to decide how much information you plan to share on the table.
-
Once you’ve done that, you’ll want to create the table.
Select it by highlighting it with the highlighter tool on the ribbon at the top of the document.
-
Then select ‘Insert>Table’ and ‘Convert Text to Table.
You’ll find this in the drop down menu under ‘Insert Table’ and ‘Draw Table’.
-
Set the column width by choosing ‘Fixed column width’ and selecting a number.
You’ll determine how wide you want the columns to be based on the amount of text you’re sharing.
-
Resize the columns if necessary.
Select ‘AutoFit to contents’.
-
Resize the table to fit the width of space.
Do this by choosing ‘AutoFit to window’.
-
Separate text at requires the separator character used in the text you started with.
Make sure to include this before hitting ‘OK’.
Following these steps in order allows you to create and format unique tables to insert into your Word documents. You can enhance the effectiveness of your communications easily. All you need is a few extra minutes and Microsoft Office to begin.
Where to Get Microsoft Office Software and Apps
There are a number of places to get Microsoft Office software and apps. You can buy them directly from Microsoft or from Software Keep where you’re given a significant discount on authentic software and apps. If you shop online with us, you’ll have access to your purchase right away because you digitally download it opposed to waiting for a hardcopy CD or DVD to arrive by mail.
What Software Keep Has to Offer Its Customers
Many Americans prefer buying their MS Office software and apps from Software Keep because they’ve built a relationship with our company. They know our products are authentic and that we give them choices as to whether they download Microsoft Office for Mac or PC. If they find a deal on Student Microsoft Office on another site, they ask us to price match the identical product which we willingly do.
Get Microsoft Office Pro here.
November 28, 2018
|
Categories: News

 .
.
 and
and