Once you start learning VBA one of the coolest things you can do is to write a VBA code to insert new a worksheet in a workbook.
Well, there is already a shortcut key to insert a new worksheet or you can also use the normal option but the benefit of using a VBA code is you can add multiple worksheets with a single click and you can also define that where you want to add it.
For this, you need to use the Sheets.Add method, and in this post, we will be learning how to use it to add one or more worksheets in a workbook.
Sheets.Add Method
Sheets.Add ([Before], [After], [Count], [Type])- Before: To add a new sheet before a sheet.
- After: To add the new sheet before a sheet.
- Count: Number of sheets to add.
- Type: Type of the sheet you want to add (LINK)
Open the visual basic editor and follow these steps.
- First, you need to enter Sheets.Add method.
- Then you need to define the place to add the new sheet (Before or After).
- Next thing is to enter the count of worksheets.
- In the end, the type of sheet.

Different Ways to Add New Sheets in a Workbook using a VBA Code
Below you have different ways to add a new sheet to a workbook:
1. Add a Single Sheet
To add a single sheet, you can use the below code, where you didn’t specify any argument.
Sub SheetAddExample1()
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets.Add
End SubThis code tells Excel to add a sheet in the active workbook, but as you don’t have any argument it will use the default values and add one worksheet(xlWorksheet) before the active sheet.
Here’s one more way to write this, check out the below code.
Sub SheetAddExample2()
Sheets.Add
End SubAs you are already in the active workbook you can use the below code as well. It does the same thing.
2. Add Multiple Sheets
To add multiple sheets in one go, you just need to define the COUNT argument with the number of sheets you want to add.
Sub AddSheets3()
Sheets.Add Count:=5
End SubNow the count of the sheets that you have defined is 5, so when you run this code it instantly adds the five new sheets in the workbook.
3. Add a Sheet with a Name
If you want to rename the sheet after adding it, you can use the following code:
Sub AddNewSheetswithNameExample1()
Sheets.Add.Name = "myNewSHeet"
End SubIn the above code, we have used the name object (LINK) which helps you to specify the name of a sheet.
4. Add a Sheet with a Name from a Cell
You can also take the value to use as the sheet’s name from a cell.
Sub AddNewSheetswithNameExample2()
Sheets.Add.Name = Range("A1")
End SubIn the above code, cell A1 is used to get the name for the new sheet.
5. Add a Sheet After/Before a Specific Sheet
As these arguments are already there in the Sheets.Add where you can specify the sheet to add a new sheet before or after it.
Sub AddSheetsExample5()
Sheets.Add Before:=Worksheets("mySheet")
Sheets.Add After:=Worksheets("mySheet")
End SubNow in the above code, you have two lines of code that you have used before and after an argument in the Sheet.Add method. So, when you run this code it adds two sheets one is before and one is after the “mySheet”.
6. Add a New Sheet at Beginning
By using the before argument using you can also add a sheet at the beginning of the sheets that you have in the workbook.
So basically, what we are going to do is we’re going to specify the sheet number instead of the sheet name.
Sub AddSheetsExample6()
Sheets.Add Before:=Sheets(1)
End SubIn the above code, you have used sheet number (1) that tells VBA to add the sheet before the sheet which is in the first position in all the worksheets. In this way, it will always add the new sheet at the beginning.
7. Add a New Sheet at the End (After the Last Sheet)
To add a new sheet in the end you need to write the code in a different way. So, for this, you need to know how many sheets there in the workbook are so that you can add a new sheet at the end.
Sub AddSheetsExample8()
Sheets.Add After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count)
End SubIn the above code, Sheet.Count returns the count of the sheets that you have in the workbook, and as you have defined the after argument it adds the new sheet after the last sheet in the workbook.
8. Add Multiple Sheets and use Names from a Range
The following code counts rows from the range A1:A7. After that, it loops to add sheets according to the count from the range and uses values from the range to name the sheet while adding it.
Sub AddSheetsExample9()
Dim sheets_count As Integer
Dim sheet_name As String
Dim i As Integer
sheet_count = Range("A1:A7").Rows.Count
For i = 1 To sheet_count
sheet_name = Sheets("mySheet").Range("A1:A7").Cells(i, 1).Value
Worksheets.Add().Name = sheet_name
Next i
End SubBut with the above code, there could be a chance that the sheet name you want to add already exists or you have a blank cell in the name range.
In that case, you need to write a code that can verify if the sheet with the same name already exists or not and whether the cell from where you want to take the sheet name is blank or not.
If both conditions are fulfilled only then it should add a new sheet. Let me put it in steps two steps:
First, you need to write an Excel User Defined Function to check if a sheet with the same name already exists or not.
Function SheetCheck(sheet_name As String) As Boolean
Dim ws As Worksheet
SheetCheck = False
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If ws.Name = sheet_name Then
SheetCheck = True
End If
Next
End FunctionSecond, you need to write a code using this function and that code should also check if the name cell is blank or not.
Sub AddMultipleSheet2()
Dim sheets_count As Integer
Dim sheet_name As String
Dim i As Integer
sheet_count = Range("A1:A7").Rows.Count
For i = 1 To sheet_count
sheet_name = Sheets("mySheet").Range("A1:A10").Cells(i, 1).Value
If SheetCheck(sheet_name) = False And sheet_name <> "" Then
Worksheets.Add().Name = sheet_name
End If
Next i
End SubNow in the above code, you have used the VBA IF Statement and in this statement, you have the sheet check function which checks for the sheet name and then you have a condition to check if the name cell has a blank value.
Sample File
More Tutorials on Worksheets
- VBA Worksheet – Excel VBA Examples – VBA Tutorial
In this Article
- Add Sheet
- Add Sheet with Name
- Create New Sheet with Name from a Cell
- Add Sheet Before / After Another Sheet
- Insert Sheet After Another Sheet
- Add Sheet To End of Workbook
- Add Sheet To Beginning of Workbook:
- Add Sheet to Variable
- More Add Sheet Examples
- Create Sheet if it Doesn’t Already Exist
- Create Worksheets From List of Names
- VBA Coding Made Easy
This tutorial will discuss how to add / insert worksheets using VBA.
This simple macro will add a Sheet before the ActiveSheet:
Sub Add ()
Sheets.Add
End SubAfter inserting a Sheet, the new Sheet becomes the ActiveSheet. You can then use the ActiveSheet object to work with the new Sheet (At the bottom of this article we will show how to insert a new sheet directly to a variable).
ActiveSheet.Name = "NewSheet"Add Sheet with Name
You can also define a Sheet name as you create the new Sheet:
Sheets.Add.Name = "NewSheet"Create New Sheet with Name from a Cell
Or use a cell value to name a new Sheet:
Sheets.Add.Name = range("a3").valueAdd Sheet Before / After Another Sheet
You might also want to choose the location of where the new Sheet will be inserted. You can use the After or Before properties to insert a sheet to a specific location in the workbook.
Insert Sheet After Another Sheet
This code will insert the new sheet AFTER another sheet:
Sheets.Add After:=Sheets("Input")This will insert a new Sheet AFTER another sheet and specify the Sheet name:
Sheets.Add(After:=Sheets("Input")).Name = "NewSheet"Notice the extra parenthesis required in the second example (the first example will generate an error if the second parenthesis are added).
or Before:
Sheets.Add(Before:=Sheets("Input")).Name = "NewSheet"In these examples we explicitly named the Sheet used to determine the sheet location. Often you’ll want to use the Sheet Index number instead, so that you can insert the sheet to the beginning or end of the Workbook:
Add Sheet To End of Workbook
To add a Sheet to the end of the workbook:
Sheets.Add After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count)Add Sheet To Beginning of Workbook:
To add a Sheet to the beginning of the workbook:
Sheets.Add(Before:=Sheets(1)).Name = "FirstSheet"Add Sheet to Variable
This code assigns the new Sheet to a variable as the sheet is created:
Dim ws As Worksheet
Set ws = Sheets.AddFrom here you can reference the new sheet with the variable ‘ws’:
ws.name = "VarSheet"More Add Sheet Examples
Create Sheet if it Doesn’t Already Exist
You might want to create a sheet only if it doesn’t already exist.
VBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Create Worksheets From List of Names
The following routine will look at the contents of a single column set up Excel worksheets within the current workbook with these names. It makes a call to another function to see if a sheet with that name already exists, and if so the sheet isn’t created.
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Call CreateWorksheets(Sheets("Sheet2").Range("A1:a10"))
End Sub
Sub CreateWorksheets(Names_Of_Sheets As Range)
Dim No_Of_Sheets_to_be_Added As Integer
Dim Sheet_Name As String
Dim i As Integer
No_Of_Sheets_to_be_Added = Names_Of_Sheets.Rows.Count
For i = 1 To No_Of_Sheets_to_be_Added
Sheet_Name = Names_Of_Sheets.Cells(i, 1).Value
'Only add sheet if it doesn't exist already and the name is longer than zero characters
If (Sheet_Exists(Sheet_Name) = False) And (Sheet_Name <> "") Then
Worksheets.Add().Name = Sheet_Name
End If
Next i
End SubFunction Sheet_Exists(WorkSheet_Name As String) As Boolean
Dim Work_sheet As Worksheet
Sheet_Exists = False
For Each Work_sheet In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If Work_sheet.Name = WorkSheet_Name Then
Sheet_Exists = True
End If
Next
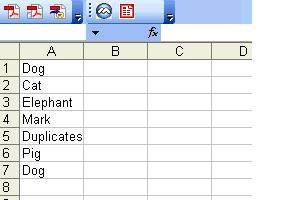
End FunctionSo if we have the following text in cells A1:A30 in Sheet 2:
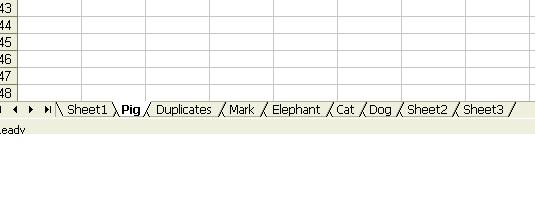
Then the following sheets will be created:
Note that although “Dog” appears twice, only one sheet is created.
To download the .XLS file for this tutorial, click here.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro – A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
<<Return to VBA Examples
I have some very simple code that adds a new Worksheet, after the current worksheets, to an Excel document, and then changes its name to one entered in a text box on a userform. Works fine on a new workbook, however in a workbook that has a number of existing worksheets it creates the new worksheet, but does not rename it.
This only happens the first time you run this code, the next time it will run fine. The thing that makes it even stranger is that if you open the VBA editor to try and debug it, it then runs fine as well. This obviously makes finding the error pretty hard.
The code I’m using is here:
Dim WS As Worksheet
Set WS = Sheets.Add(After:=Sheets(Worksheets.count))
WS.name = txtSheetName.value
Pretty simple. I’m wondering if this problem is that it is trying to rename the sheet before it is properly created? Is there a better way to write this code?
Update:
I’ve started debugging this using msgboxes, as opening the debugger makes the problem stop, and it seems that it just stops processing the code halfway through:
Dim WS As Worksheet
MsgBox (WS Is Nothing)
Set WS = Sheets.Add(After:=Sheets(Worksheets.count))
'***** Nothing after this point gets processed *******
MsgBox (WS Is Nothing)
MsgBox WS.name
WS.name = txtSheetName.value
MsgBox WS.name
- Create New Excel Sheet in VBA
- Use the
Sheets.Add()Method to Add Sheet in VBA
We will introduce how to create a new excel sheet in VBA with examples.
Create New Excel Sheet in VBA
Writing a VBA code to insert a new worksheet in a workbook is one of the smartest things we can do once we start learning VBA. There is a shortcut key to insert a new worksheet, or we can use the standard option, but the advantage of using a VBA code is that we can add multiple worksheets with a click and specify where we wish to add them.
We’ll need to use Sheets for this. In this article, we’ll learn how to apply the Add technique to add one or more worksheets to a workbook.
Use the Sheets.Add() Method to Add Sheet in VBA
We can add a fresh sheet before an already existing sheet by using the before method. Add another sheet after an existing one using the after method.
The added sheet must be counted by using the count method. We want to add the sheet type using the type method.
We can use the syntax for Sheets.Add().
# vba
Sheets.Add ([Before], [After], [Count], [Type])
Follow these instructions in the VBA editor to insert a new sheet, as shown below.
- We must first enter Sheets in VBA.
- We will use Add method.
- Then, we must decide where to position the new sheet (Before or After) by using VBA.
- The next step is to input the total number of worksheets in excel by using VBA.
- Lastly, we will enter the sheet’s type.
Let’s create a function to add a new sheet using the steps we discussed above.
Code:
# vba
Sub CreateNewSheet()
Sheets.Add After:=Worksheets("Sheet2"), Count:=3, Type:=xlWorksheet
End Sub
Output:
We will use different methods to insert the fresh sheet into a Workbook. Several methods for adding an extra sheet to a workbook are listed below.
Add Single Sheet in VBA
We can use the code below to add a single sheet without specifying any arguments.
Code:
# vba
Sub AddSingleSheet()
ActiveWorkbook.Sheets.Add
End Sub
Output:
This code instructs Excel to add a sheet to the active workbook. However, because no arguments are provided, it will take the default values to add one worksheet (Microsoft excel sheet) before the active sheet.
Here is another way to write this.
Code:
# vba
Sub AddSingleSheetWithoutActiveWorkbook()
Sheets.Add
End Sub
Output:
Insert Several Sheets in VBA
Provide the number of sheets we want to add in the COUNT option to add many sheets at once.
Code:
# vba
Sub AddMultipleSheets()
Sheets.Add Count:=2
End Sub
Output:
Insert Sheet With a Title in VBA
We can enter the following code to rename the sheet once we have added it.
Code:
# vba
Sub AddSheetWithTitle()
Sheets.Add.Name = "New Sheet"
End Sub
Output:
Create New Sheet With the Name of a Cell in VBA
We may also utilize a cell to get the value for the sheet’s name.
Code:
# vba
Sub AddSheetWithCellName()
Sheets.Add.Name = Range("B1")
End Sub
Output:
In excel, Cell A1 is applied in the above code to get the new sheet’s name.
Add New Sheet at Start in VBA
We can also insert a sheet to the start of the sheets in the workbook by applying the above argument.
Code:
# vba
Sub BeginByNewSheet()
Sheets.Add Before:=Sheets(1)
End Sub
Output:
Instead of specifying the sheet name, we will supply the sheet number. We used sheet number (1) in the above code to tell VBA to add the sheet just before the sheet in the first place in all worksheets.
This ensures that the fresh sheet is always added first.
Add New Sheet at End in VBA
We must rewrite the code above to add a new sheet at the end.
Code:
# vba
Sub AddSheetAtEnd()
Sheets.Add After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count)
End Sub
Output:
We’ll need to know how many sheets are in the workbook to add a new sheet at the end.
Author: Oscar Cronquist Article last updated on October 16, 2022
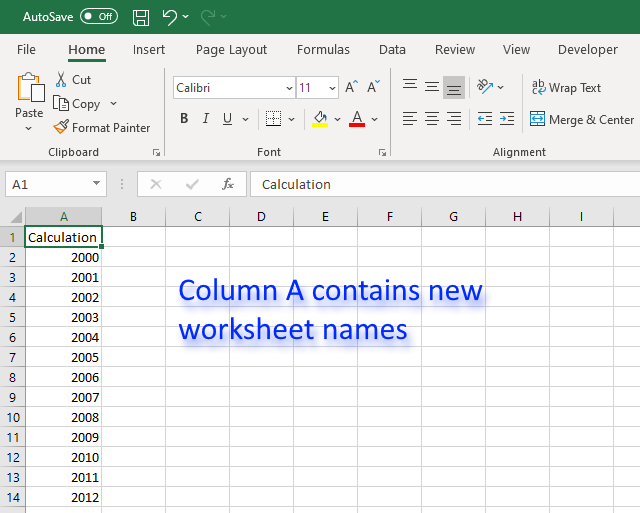
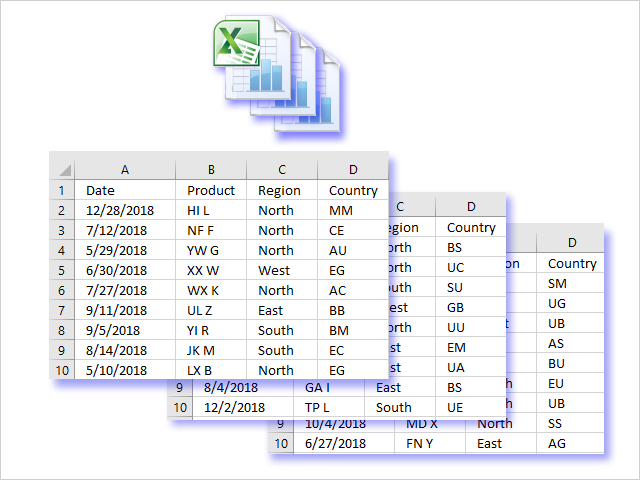
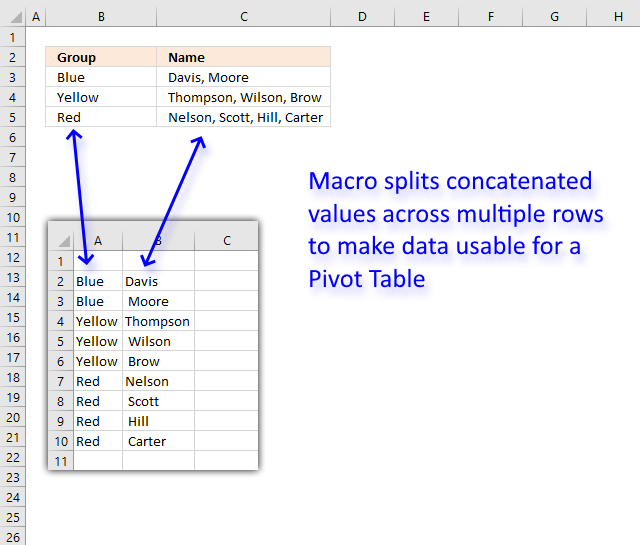
This article demonstrates a macro that inserts new worksheets based on names in a cell range. The cell range may have multiple columns if you like.
This macro allows you to create new worksheets very quickly.
Table of Contents
- Create new worksheets programmatically based on values in a cell range
[VBA]- How this macro works
- VBA macro
- Where to put the code
- Explaining code
- Get Excel file
- Create new worksheets based on a comma delimited list [VBA]
- VBA code
- Get Excel file
- Create new worksheets using an Input box [VBA]
- VBA code
- Get Excel file
- Copy worksheet template and rename [VBA]
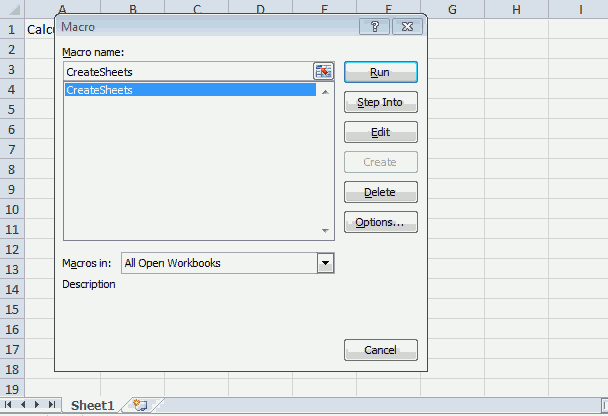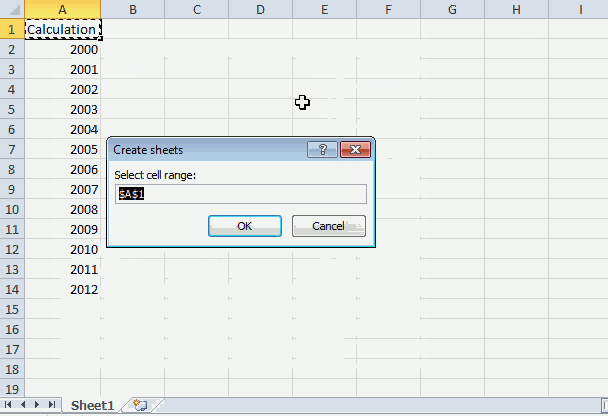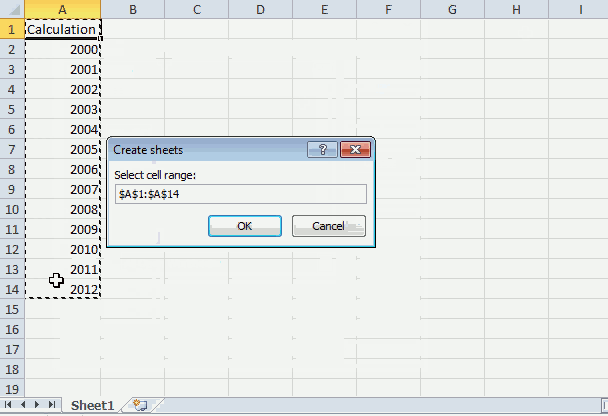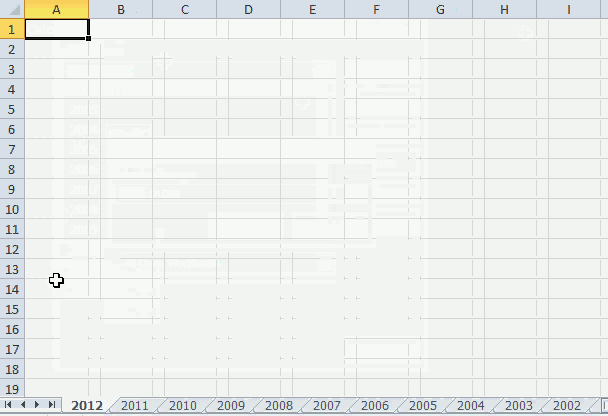
1. Create new worksheets programmatically based on values in a cell range
1.1 How this macro works
The animated image above shows how this macro works.
- Press Alt + F8 to open the Macro dialog box.
- Select macro CreateSheets.
- Press with mouse on «Run» button.
- An input box appears asking for a cell range.
- Select a cell range and press with left mouse button on the «OK» button.
- Worksheets are now added automatically to the workbook and named correspondingly after the values in the cell range.
Back to top
1.2 VBA macro
'Name macro
Sub CreateSheets()
'Dimension variables and declare data types
Dim rng As Range
Dim cell As Range
'Enable error handling
On Error GoTo Errorhandling
'Show inputbox to user and prompt for a cell range
Set rng = Application.InputBox(Prompt:="Select cell range:", _
Title:="Create sheets", _
Default:=Selection.Address, Type:=8)
'Iterate through cells in selected cell range
For Each cell In rng
'Check if cell is not empty
If cell <> "" Then
'Insert worksheet and name the worksheet based on cell value
Sheets.Add.Name = cell
End If
'Continue with next cell in cell range
Next cell
'Go here if an error occurs
Errorhandling:
'Stop macro
End Sub
Back to top
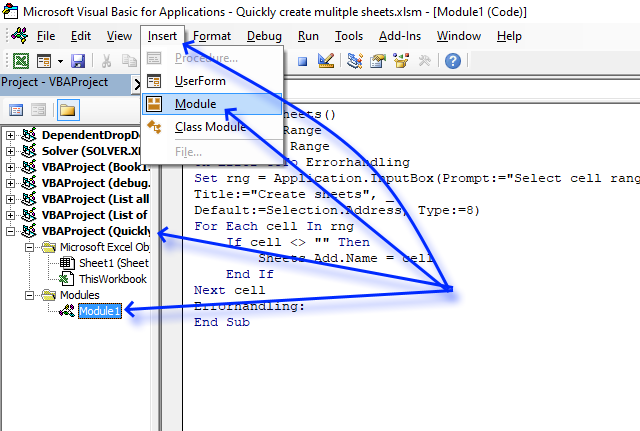
1.3 Where to put the code
- Copy above VBA code.
- Press Alt + F11 to open the Visual Basic Editor.
- Press with mouse on your workbook in the Project Explorer.
- Press with mouse on «Insert» on the menu.
- Press with mouse on «Module».
- Paste VBA code to code window, see image above.
Back to top
1.4 Explaining code
Creating procedures in excel is easy. Open the Visual Basic Editor using one of these instructions:
- Press Alt+F11
- Go to tab Developer and press with left mouse button on Visual basic «button»
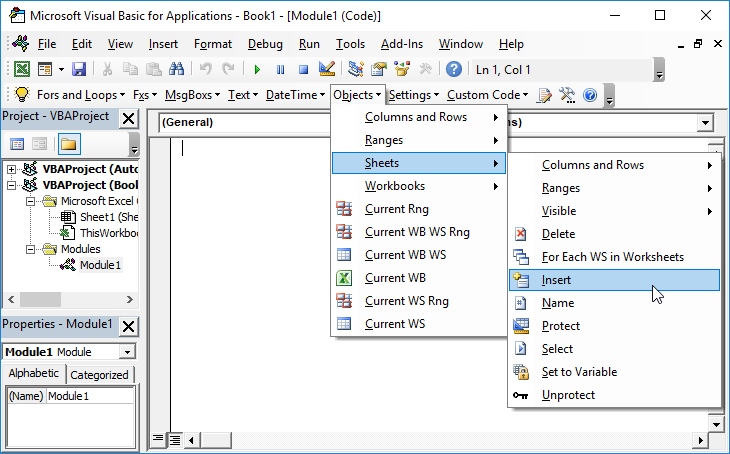
You create macro procedures in a module. First create a module. Press with right mouse button on on your workbook in the project explorer. Press with left mouse button on Insert | Module.
Sub CreateSheets()
Type: Sub CreateSheets() in the module. CreateSheets() is the name of the macro.
Dim rng As Range
Dim cell As Range
These lines declare rng and cell as range objects. A range object can contain a single cell, multiple cells, a column or a row. Read more about declaring variables.
On Error Goto Errorhandling
If the user selects something else than a cell range like a chart, this line makes the procedure go to Errorhandling.
Set rng = Application.InputBox(Prompt:=»Select cell range:», _
Title:=»Create sheets», _
Default:=Selection.Address, Type:=8)
The inputbox asks the user for a cell range. The cell range is stored in the range object rng.
For Each cell In rng
This stores each cell value from the range object rng to the cell object, one by one.
If cell <> «» Then
Checks if the cell variable is NOT empty. If the cell variable is empty the procedure goes to «End If» line. We can’t create a sheet with no name.
Sheets.Add.Name = cell
Creates a new sheet named with the value stored in the cell variable.
End If
The end of the If statement.
Next cell
Go back to the «For each» statement and store a new single cell in the cell object.
Errorhandling:
The procedure goes to this line if a line returns an error.
End Sub
All procedures must end with this line.
Back to top
1.5 Excel file
Back to top
Recommended reading
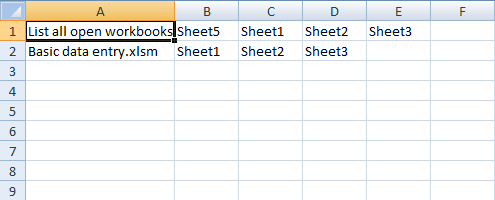
List all open workbooks and corresponding sheets (vba)
2. Create new worksheets programmatically based on a comma-delimited list
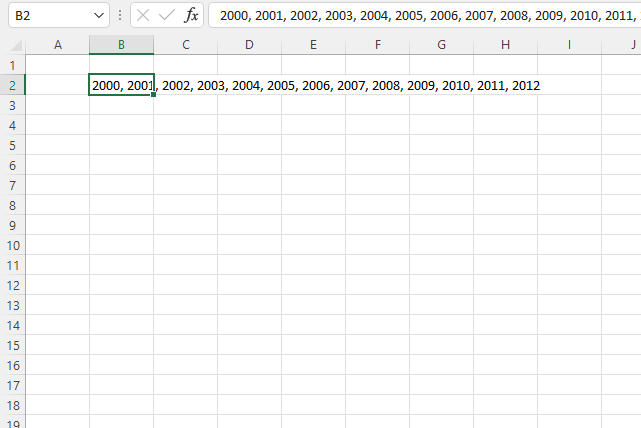
The image above shows a comma delimited list in cell B2, the macro below in section 2.1 lets you select a cell containing a comma delimiting list.
It splits the string based on the comma into an array of values. The values are then used to insert new worksheets with names based on those array values.
Back to top
2.1 VBA code
Sub CreateSheetsFromList()
Dim rng As Range
Dim cell As Range
Dim Arr As Variant
On Error GoTo Errorhandling
Set rng = Application.InputBox(Prompt:="Select cell:", _
Title:="Create sheets", _
Default:=Selection.Address, Type:=8)
Arr = Split(rng.Value, ", ")
For Each Value In Arr
If Value <> "" Then
Sheets.Add.Name = Value
End If
Next Value
Errorhandling:
End Sub
Back to top
Where to put the code?
2.2 Excel file
Back to top
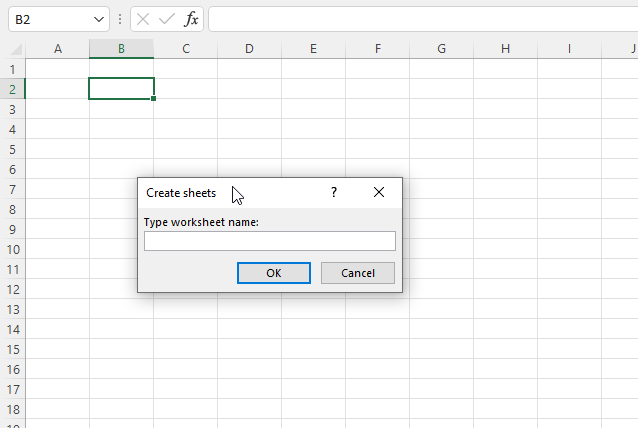
3. Create new worksheets using an Input box
The following macro displays an input box allowing the Excel user to type a worksheet name, the worksheet is created when the «OK» button is pressed.
The macro stops if nothing is typed or the user presses the «Cancel» button. It shows a new input box each time a new worksheet is created.
Back to top
3.1 VBA code
Sub CreateSheetsFromDialogBox()
Dim str As String
Dim cell As Range
Dim Arr As Variant
On Error GoTo Errorhandling
Do
str = Application.InputBox(Prompt:="Type worksheet name:", _
Title:="Create sheets", Type:=3)
If str = "" Or str = "False" Then
GoTo Errorhandling:
Else
Sheets.Add.Name = str
End If
Loop Until str = "False"
Errorhandling:
End Sub
Where to put the code?
Back to top
3.2 Excel file
Back to top
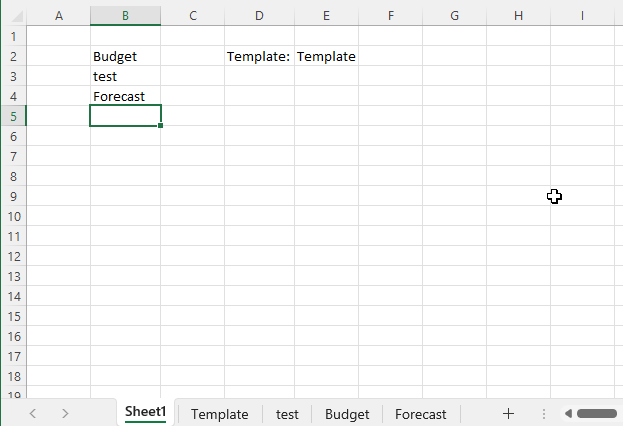
4. Copy the worksheet template and rename
This example demonstrates an Event macro that copies a worksheet based on a value in cell E2 and renames it to a cell value in column B.
Is it possible to not just generate the new sheet from typing in a cell and name the sheet after the cell but to have the new sheet be a copy on a current sheet that is kind of like a template for a form?
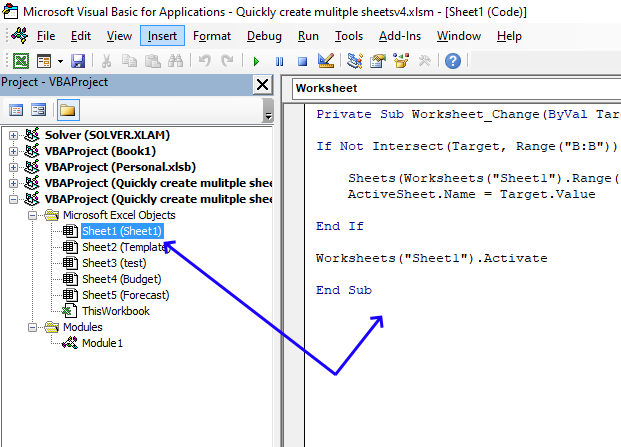
4.1 VBA event code
'Event code that runs if a cell value is changed
Private Sub Worksheet_Change(ByVal Target As Range)
'Check if the cell value is in column B
If Not Intersect(Target, Range("B:B")) Is Nothing Then
'Copy worksheet based on value in cell E2 in worksheet Sheet1 and put it last
Sheets(Worksheets("Sheet1").Range("E2").Value).Copy , Sheets(Sheets.Count)
'Rename worksheet to the value you entered.
ActiveSheet.Name = Target.Value
End If
'Go back to worksheet Sheet1
Worksheets("Sheet1").Activate
End Sub
Back to top
4.2 Where to put the event code?
- Press Alt + F11 to open the Visual Basic Editor.
- Double press with left mouse button on with the left mouse button on the worksheet name where you want to put the event code, in the worksheet Explorer shown in the image above.
- Paste event code to the code window, also shown in the image above.
- Return to Excel.
Remember to save the workbook as a macro-enabled workbook *.xlsm in order to attach the code to the workbook.
Back to top
4.3 How to run macro?
The event code runs whenever a new value is entered in column B. For example, type Trend in cell B5, then press Enter.
The macro automatically copies the worksheet «Template» given in cell E2 and renames it to Trend. That is all.
Back to top
Apply drop-down lists dynamically
This article demonstrates how to automatically create drop-down lists if adjacent data grows, there are two methods explained here. The […]
Auto resize columns as you type
Excel does not resize columns as you type by default as the image above demonstrates. You can easily resize all […]
Automate data entry [VBA]
This article demonstrates how to automatically enter data in cells if an adjacent cell is populated using VBA code. In […]
Basic data entry [VBA]
In this small tutorial, I am going to show you how to create basic data entry with a small amount […]
Calendar with scheduling [vba]
Here is my contribution to all excel calendars out there. My calendar is created in Excel 2007 and uses both […]
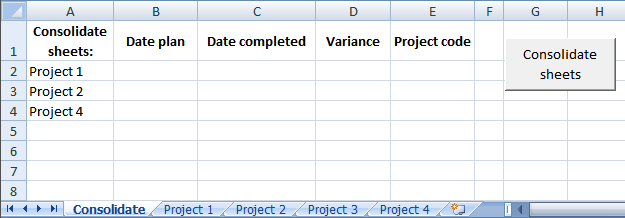
Consolidate sheets [vba]
Question: I have multiple worksheets in a workbook. Each worksheets is project specific. Each worksheet contains almost identical format. The […]
Copy a dynamic cell range [VBA]
In this blog post, I will demonstrate some VBA copying techniques that may be useful if you don’t know the […]
Create a Print button [VBA]
This article describes how to create a button and place it on an Excel worksheet then assign a macro to […]
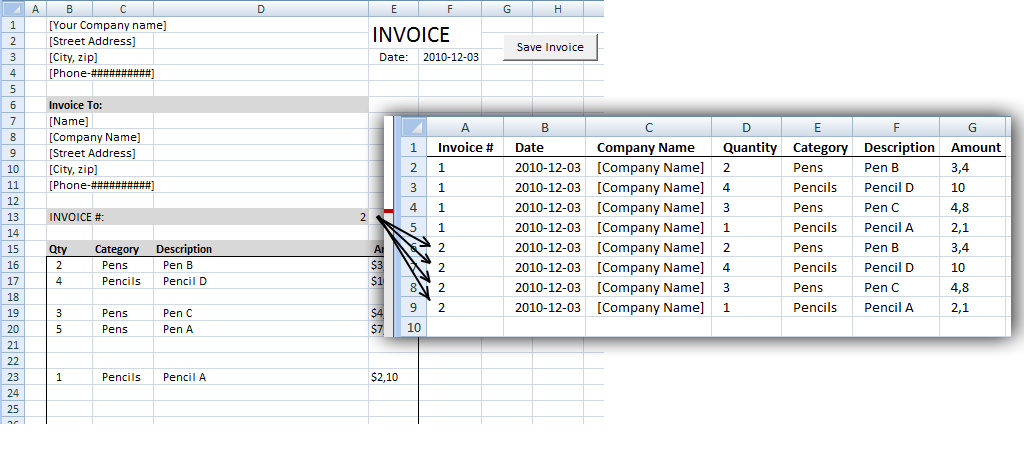
Edit invoice data [VBA]
In a previos post:Excel vba: Save invoice data we added/copied data between sheets. This post describes how to overwrite existing […]
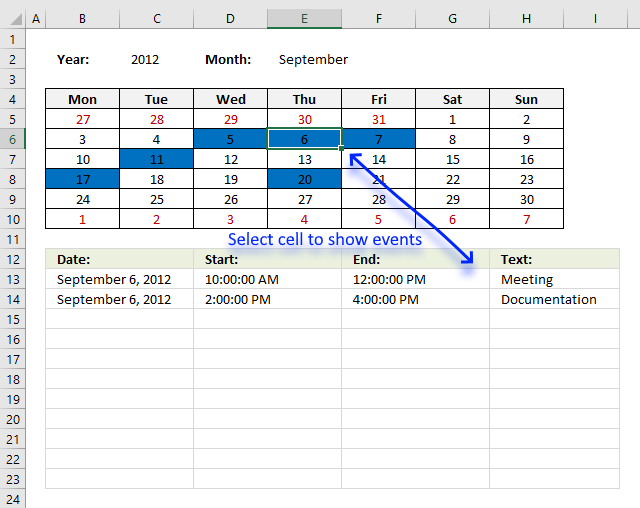
Excel calendar [VBA]
This workbook contains two worksheets, one worksheet shows a calendar and the other worksheet is used to store events. The […]
Hide specific columns programmatically
This article describes a macro that hides specific columns automatically based on values in two given cells. I am also […]
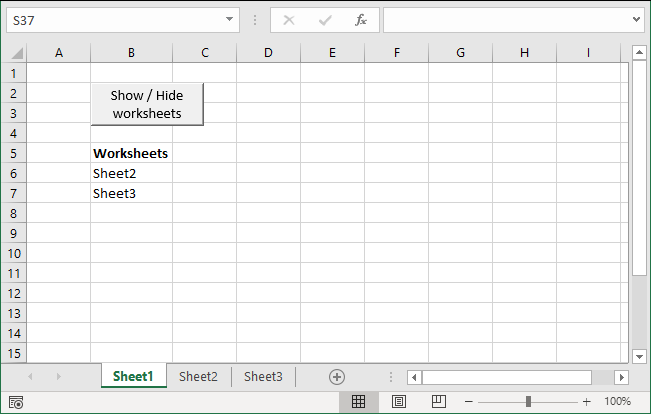
Hide specific worksheets programmatically
This article demonstrates techniques to hide and unhide worksheets programmatically. The image above shows the Excel window and the worksheet […]

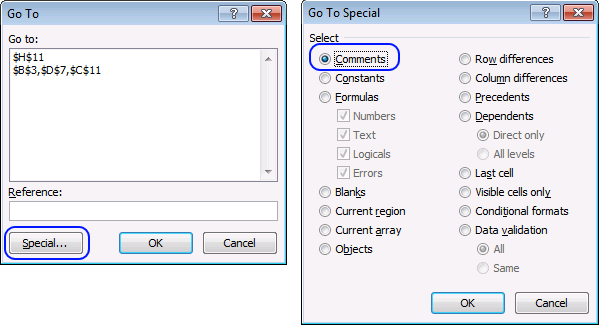
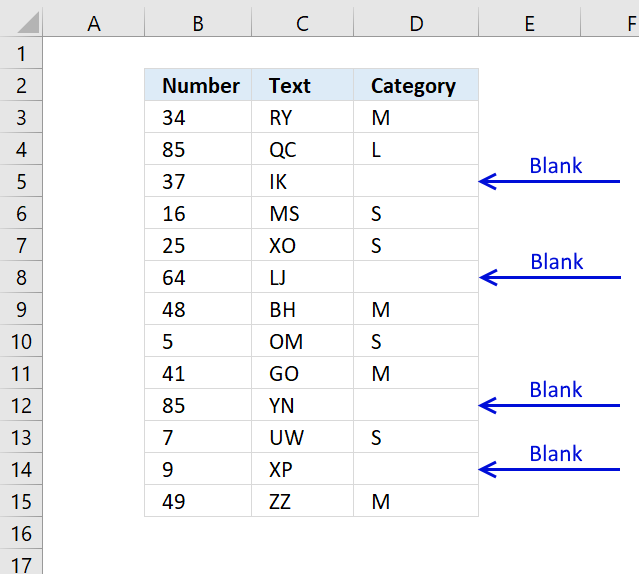
How to quickly select blank cells
In this smaller example, column D (Category) has empty cells, shown in the picture above. If your column contains thousands of […]
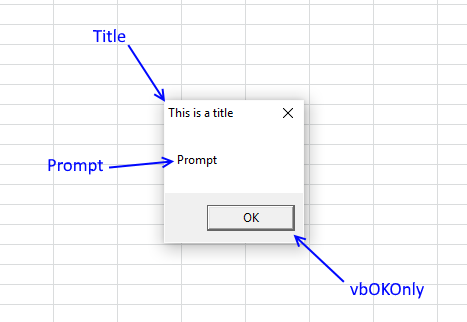
How to use DIALOG BOXES
A dialog box is an excellent alternative to a userform, they are built-in to VBA and can save you time […]
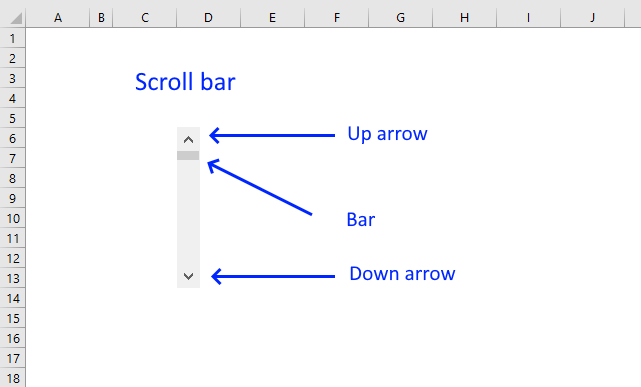
How to use the Scroll Bar
This article demonstrates how to insert and use a scroll bar (Form Control) in Excel. It allows the user to […]
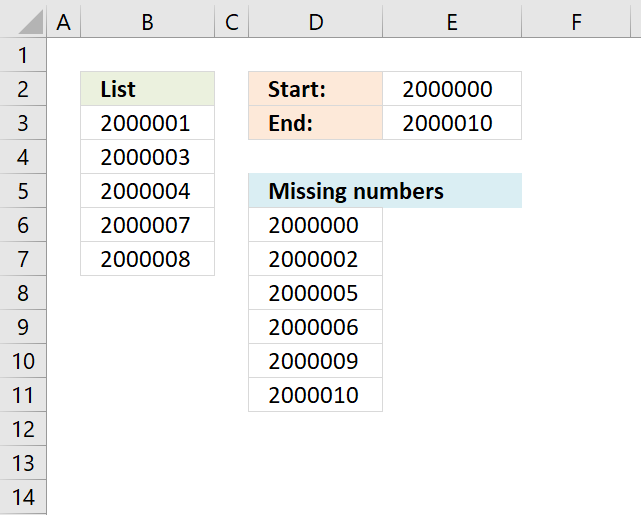
Identify missing numbers in a column
The image above shows an array formula in cell D6 that extracts missing numbers i cell range B3:B7, the lower […]
Locate a shape in a workbook
This article demonstrates how to locate a shape in Excel programmatically based on the value stored in the shape. The […]
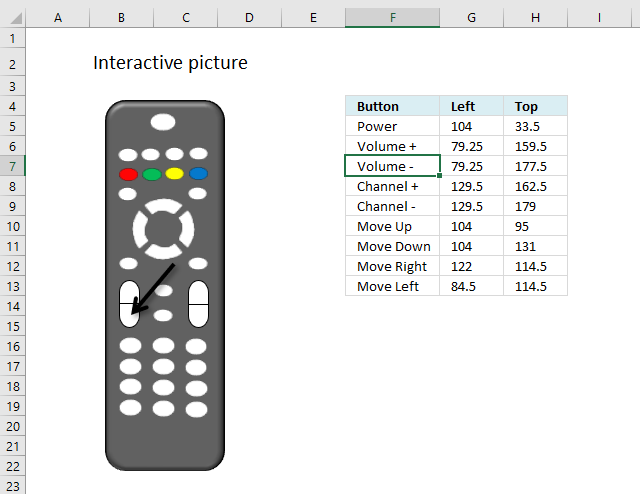
Move a shape [VBA]
This article demonstrates how to move a shape, a black arrow in this case, however, you can use whatever shape […]
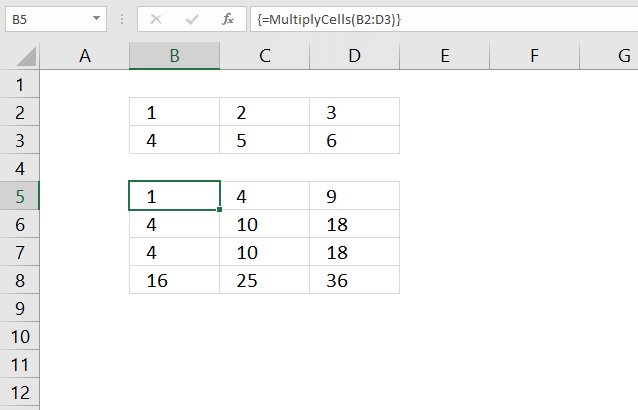
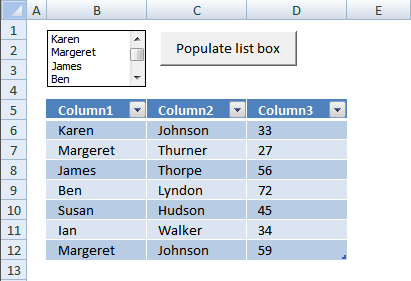
Normalize data [VBA]
To be able to use a Pivot Table the source data you have must be arranged in way that a […]
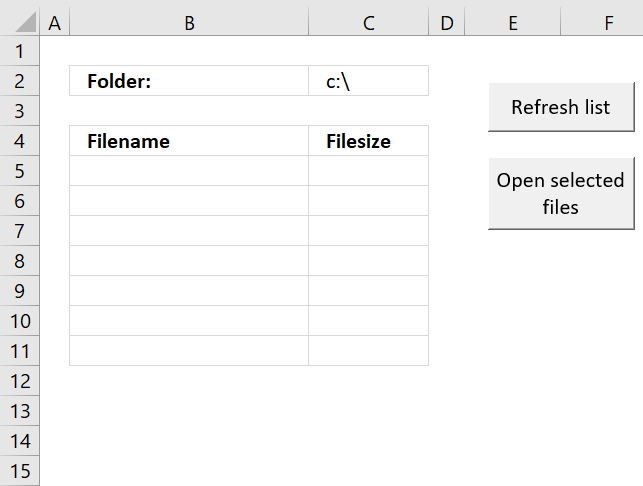
Open Excel files in a folder [VBA]
This tutorial shows you how to list excel files in a specific folder and create adjacent checkboxes, using VBA. The […]
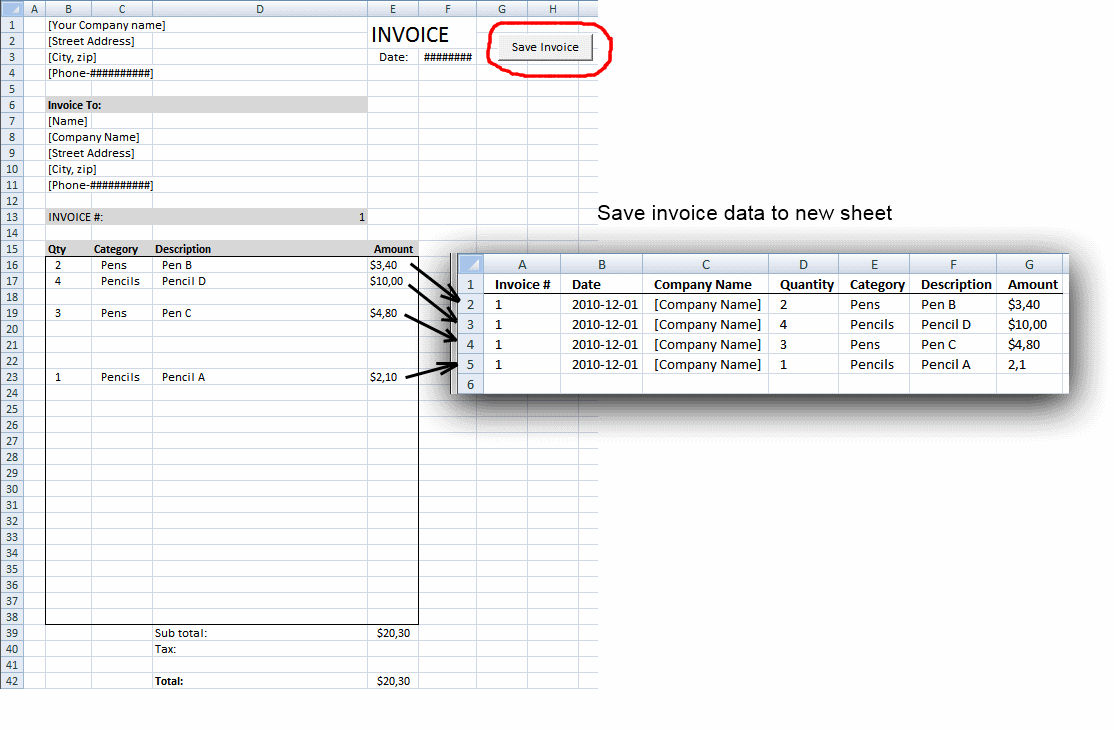
Save invoice data [VBA]
This article demonstrates a macro that copies values between sheets. I am using the invoice template workbook. This macro copies […]
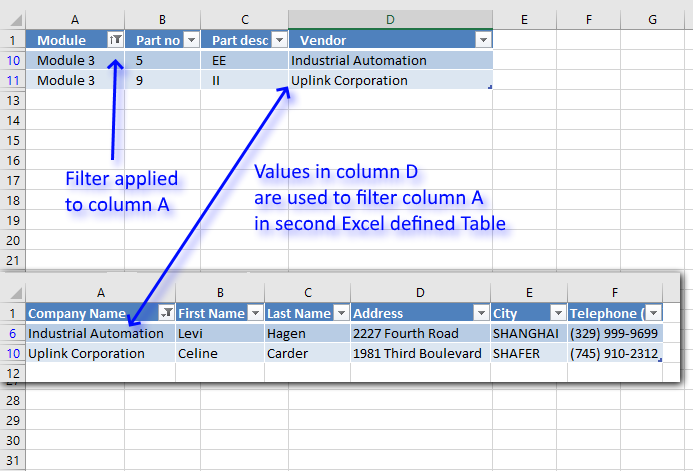
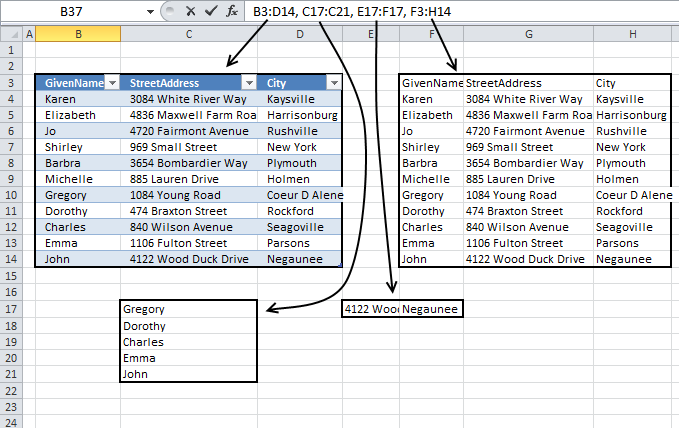
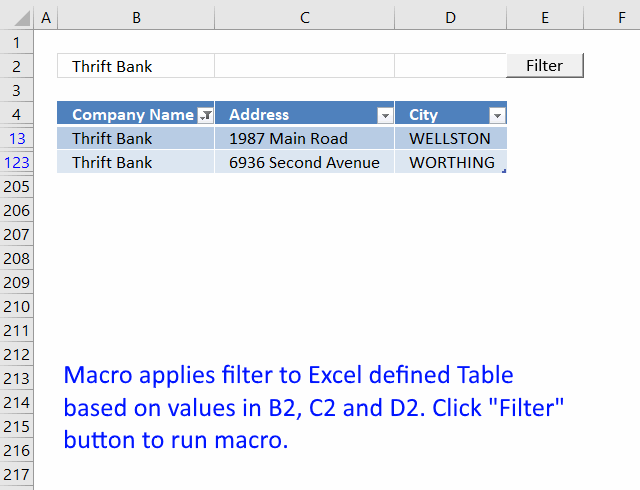
Search two related tables [VBA]
This article demonstrates a macro that automatically applies a filter to an Excel defined Table based on the result from […]
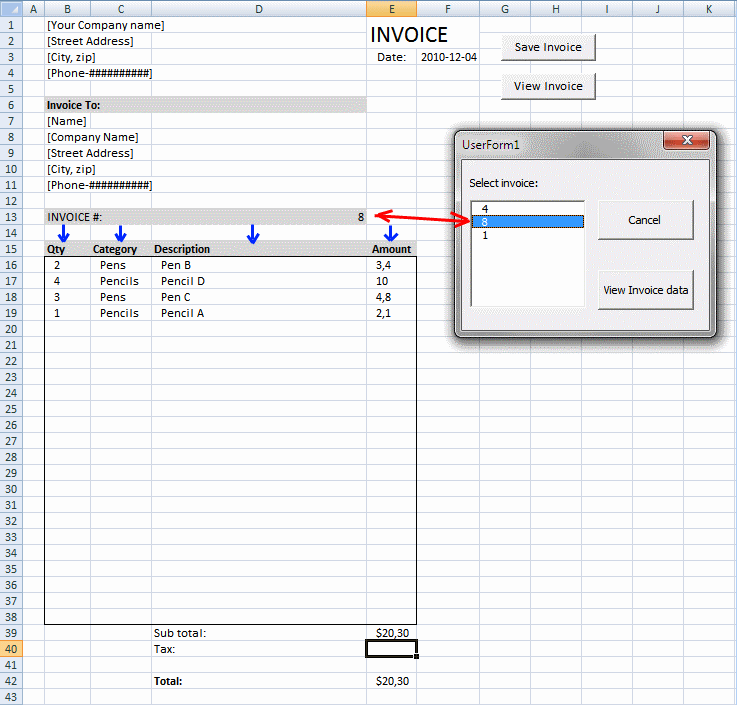
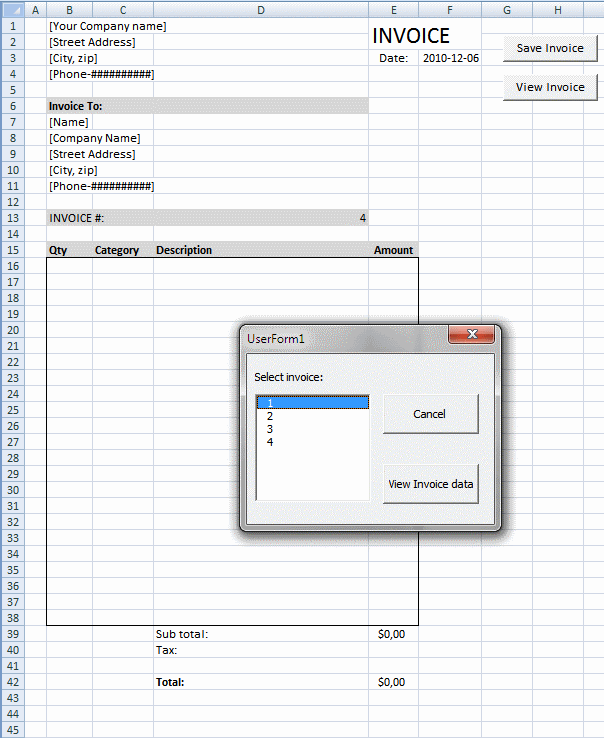
Select and view invoice [VBA]
This post demonstrates how to view saved invoices based on the invoice number using a userform. The userform appears when the […]
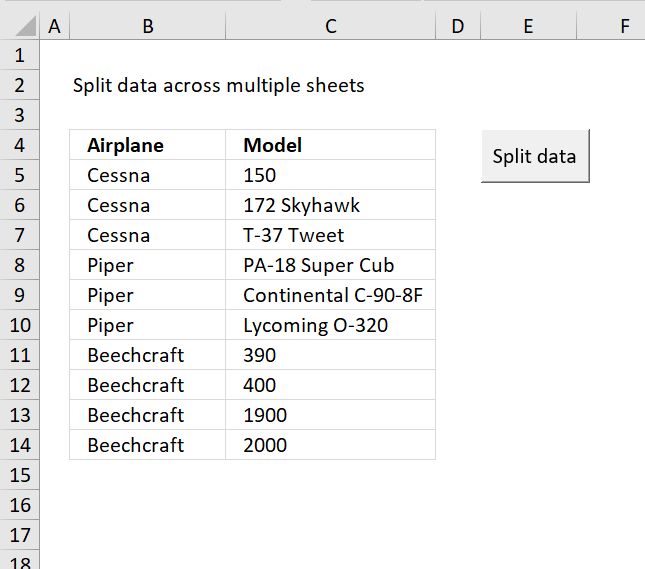
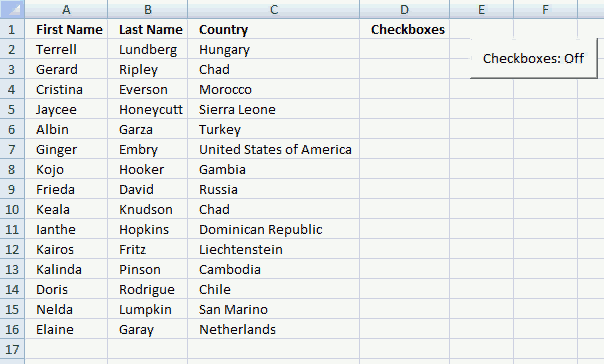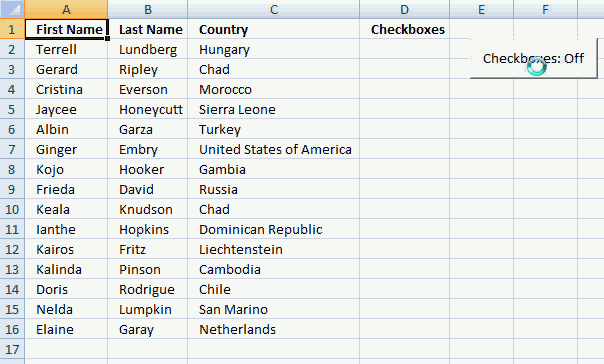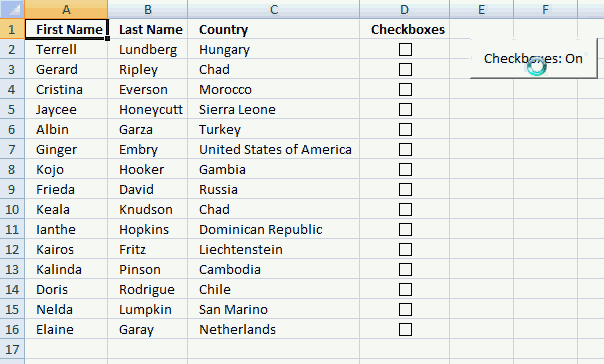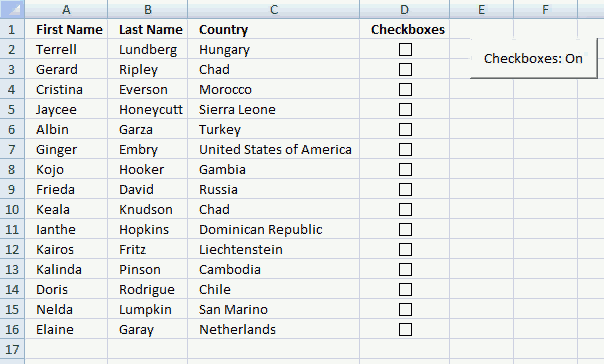
Toggle a macro on/off using a button
This article demonstrates how the user can run a macro by press with left mouse button oning on a button, […]
Working with COMBO BOXES [Form Controls]
This blog post demonstrates how to create, populate and change comboboxes (form control) programmatically. Form controls are not as flexible […]

Working with FILES
In this blog article, I will demonstrate basic file copying techniques using VBA (Visual Basic for Applications). I will also […]
Working with TEXT BOXES [Form Controls]
There are two different kinds of text boxes, Form controls and ActiveX Controls. Form controls can only be used on […]
Latest updated articles.
More than 300 Excel functions with detailed information including syntax, arguments, return values, and examples for most of the functions used in Excel formulas.
More than 1300 formulas organized in subcategories.
Excel Tables simplifies your work with data, adding or removing data, filtering, totals, sorting, enhance readability using cell formatting, cell references, formulas, and more.
Allows you to filter data based on selected value , a given text, or other criteria. It also lets you filter existing data or move filtered values to a new location.
Lets you control what a user can type into a cell. It allows you to specifiy conditions and show a custom message if entered data is not valid.
Lets the user work more efficiently by showing a list that the user can select a value from. This lets you control what is shown in the list and is faster than typing into a cell.
Lets you name one or more cells, this makes it easier to find cells using the Name box, read and understand formulas containing names instead of cell references.
The Excel Solver is a free add-in that uses objective cells, constraints based on formulas on a worksheet to perform what-if analysis and other decision problems like permutations and combinations.
An Excel feature that lets you visualize data in a graph.
Format cells or cell values based a condition or criteria, there a multiple built-in Conditional Formatting tools you can use or use a custom-made conditional formatting formula.
Lets you quickly summarize vast amounts of data in a very user-friendly way. This powerful Excel feature lets you then analyze, organize and categorize important data efficiently.
VBA stands for Visual Basic for Applications and is a computer programming language developed by Microsoft, it allows you to automate time-consuming tasks and create custom functions.
A program or subroutine built in VBA that anyone can create. Use the macro-recorder to quickly create your own VBA macros.
UDF stands for User Defined Functions and is custom built functions anyone can create.
A list of all published articles.