IF function
The IF function is one of the most popular functions in Excel, and it allows you to make logical comparisons between a value and what you expect.
So an IF statement can have two results. The first result is if your comparison is True, the second if your comparison is False.
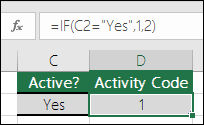
For example, =IF(C2=”Yes”,1,2) says IF(C2 = Yes, then return a 1, otherwise return a 2).
Use the IF function, one of the logical functions, to return one value if a condition is true and another value if it’s false.
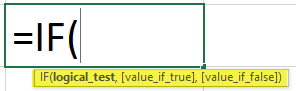
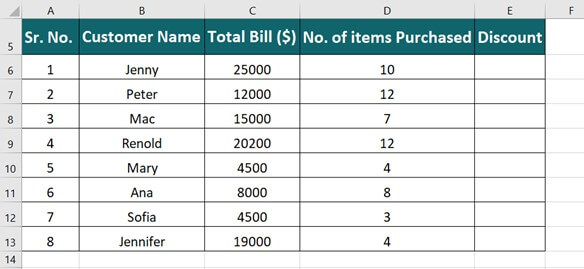
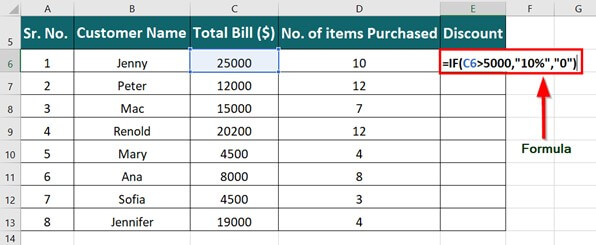
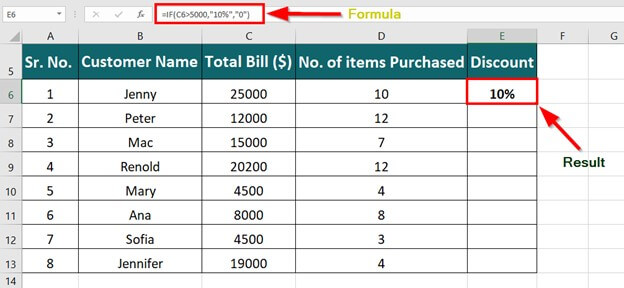
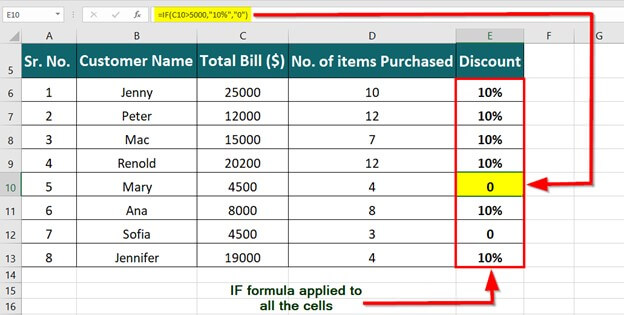
IF(logical_test, value_if_true, [value_if_false])
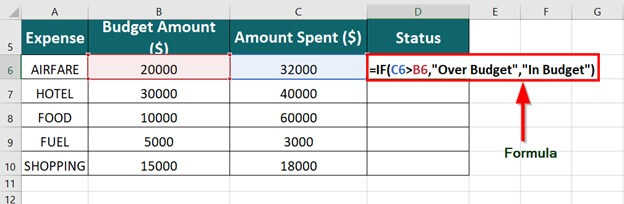
For example:
-
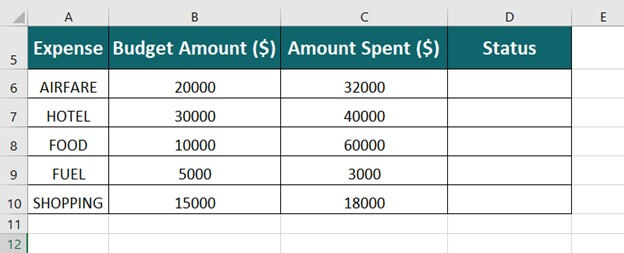
=IF(A2>B2,»Over Budget»,»OK»)
-
=IF(A2=B2,B4-A4,»»)
|
Argument name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
logical_test (required) |
The condition you want to test. |
|
value_if_true (required) |
The value that you want returned if the result of logical_test is TRUE. |
|
value_if_false (optional) |
The value that you want returned if the result of logical_test is FALSE. |
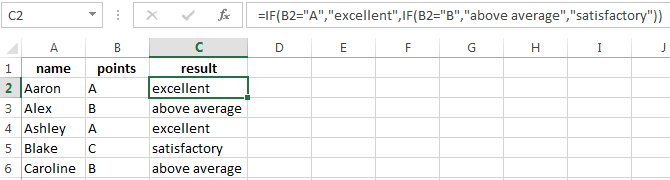
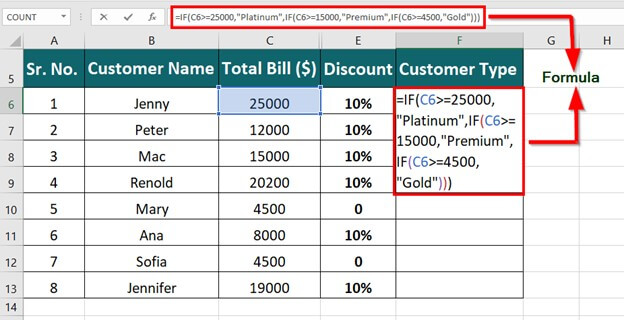
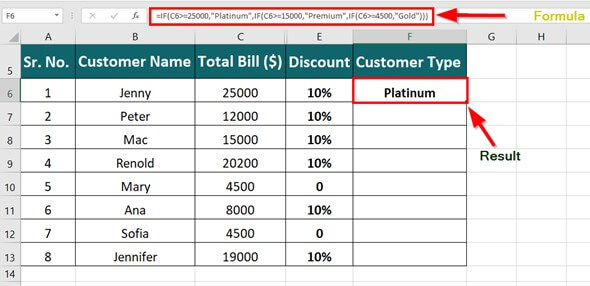
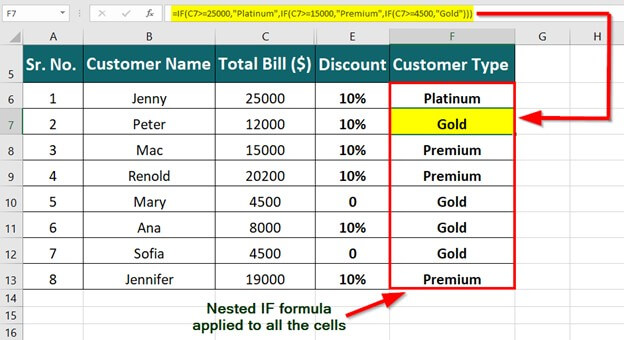
Simple IF examples
-
=IF(C2=”Yes”,1,2)
In the above example, cell D2 says: IF(C2 = Yes, then return a 1, otherwise return a 2)
-
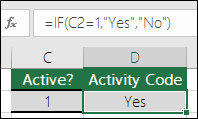
=IF(C2=1,”Yes”,”No”)
In this example, the formula in cell D2 says: IF(C2 = 1, then return Yes, otherwise return No)As you see, the IF function can be used to evaluate both text and values. It can also be used to evaluate errors. You are not limited to only checking if one thing is equal to another and returning a single result, you can also use mathematical operators and perform additional calculations depending on your criteria. You can also nest multiple IF functions together in order to perform multiple comparisons.
-
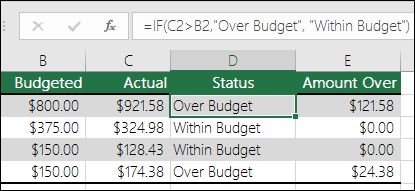
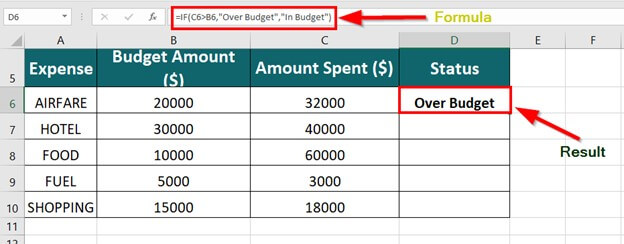
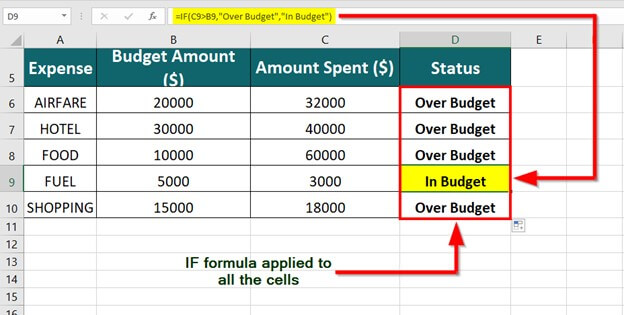
=IF(C2>B2,”Over Budget”,”Within Budget”)
In the above example, the IF function in D2 is saying IF(C2 Is Greater Than B2, then return “Over Budget”, otherwise return “Within Budget”)
-
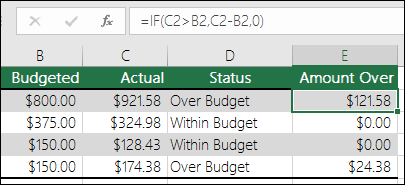
=IF(C2>B2,C2-B2,0)
In the above illustration, instead of returning a text result, we are going to return a mathematical calculation. So the formula in E2 is saying IF(Actual is Greater than Budgeted, then Subtract the Budgeted amount from the Actual amount, otherwise return nothing).
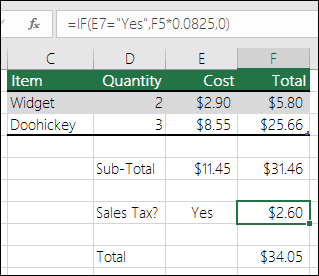
-
=IF(E7=”Yes”,F5*0.0825,0)
In this example, the formula in F7 is saying IF(E7 = “Yes”, then calculate the Total Amount in F5 * 8.25%, otherwise no Sales Tax is due so return 0)
Note: If you are going to use text in formulas, you need to wrap the text in quotes (e.g. “Text”). The only exception to that is using TRUE or FALSE, which Excel automatically understands.
Common problems
|
Problem |
What went wrong |
|---|---|
|
0 (zero) in cell |
There was no argument for either value_if_true or value_if_False arguments. To see the right value returned, add argument text to the two arguments, or add TRUE or FALSE to the argument. |
|
#NAME? in cell |
This usually means that the formula is misspelled. |
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.

See Also
IF function — nested formulas and avoiding pitfalls
IFS function
Using IF with AND, OR and NOT functions
COUNTIF function
How to avoid broken formulas
Overview of formulas in Excel
Need more help?
What is IF Function in Excel?
IF function in Excel evaluates whether a given condition is met and returns a value depending on whether the result is “true” or “false”. It is a conditional function of Excel, which returns the result based on the fulfillment or non-fulfillment of the given criteria.
For example, the IF formula in Excel can be applied as follows:
“=IF(condition A,“value B”,“value C”)”
The IF excel function returns “value B” if condition A is met and returns “value C” if condition A is not met.
It is often used to make logical interpretations which help in decision-making.
Table of contents
- What is IF Function in Excel?
- Syntax of the IF Excel Function
- How to Use IF Function in Excel?
- Example #1
- Example #2
- Example #3
- Example #4
- Example #5
- Guidelines for the Multiple IF Statements
- Frequently Asked Question
- IF Excel Function Video
- Recommended Articles
Syntax of the IF Excel Function
The syntax of the IF function is shown in the following image:
The IF excel function accepts the following arguments:
- Logical_test: It refers to the condition to be evaluated. The condition can be a value or a logical expression.
- Value_if_true: It is the value returned as a result when the condition is “true”.
- Value_if_false: It is the value returned as a result when the condition is “false”.
In the formula, the “logical_test” is a required argument, whereas the “value_if_true” and “value_if_false” are optional arguments.
The IF formula uses logical operators to evaluate the values in a range of cells. The following table shows the different logical operatorsLogical operators in excel are also known as the comparison operators and they are used to compare two or more values, the return output given by these operators are either true or false, we get true value when the conditions match the criteria and false as a result when the conditions do not match the criteria.read more and their meaning.
| Operator | Meaning |
|---|---|
| = | Equal to |
| > | Greater than |
| >= | Greater than or equal to |
| < | Less than |
| <= | Less than or equal to |
| <> | Not equal to |
How to Use IF Function in Excel?
Let us understand the working of the IF function with the help of the following examples in Excel.
You can download this IF Function Excel Template here – IF Function Excel Template
Example #1
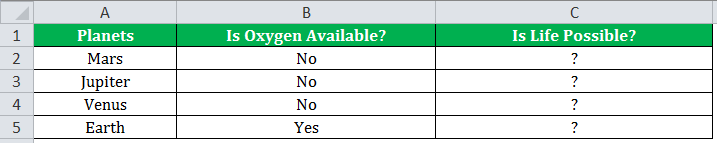
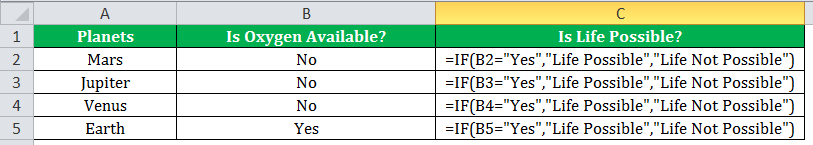
If there is no oxygen on a planet, life is impossible. If oxygen is available on a planet, then life is possible. The following table shows a list of planets in column A and the information on the availability of oxygen in column B. We have to find the planets where life is possible, based on the condition of oxygen availability.
Let us apply the IF formula to cell C2 to find out whether life is possible on the planets listed in the table.
The IF formula is stated as follows:
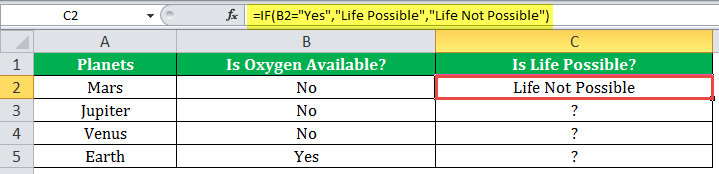
“=IF(B2=“Yes”, “Life is Possible”, “Life is Not Possible”)
The succeeding image shows the IF formula applied to cell C2.
The subsequent image shows how the IF formula is applied to the range of cells C2:C5.
Drag the cells to view the output of all the planets.
The output in the below worksheet shows life is possible on the planet Earth.
Flow Chart of Generic IF Excel Function
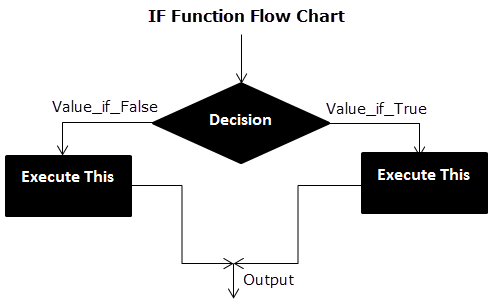
The IF Function Flow Chart for Mars (Example #1)

The flow of IF function flowchart for Jupiter and Venus is the same as the IF function flowchart for Mars (Example #1).
The IF Function Flow Chart for Earth

Hence, the IF excel function allows making logical comparisons between values. The modus operandi of the IF function is stated as: If something is true, then do something; otherwise, do something else.
Example #2
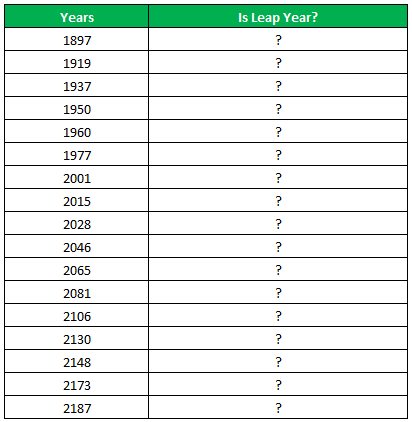
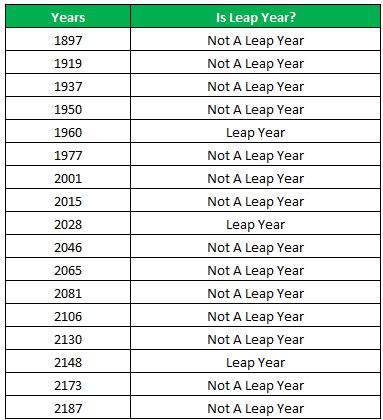
The following table shows a list of years. We want to find out if the given year is a leap year or not.
A leap year has 366 days; the extra day is the 29th of February. The criteria for a leap year are stated as follows:
- The year will be exactly divisible by 4 and not exactly be divisible by 100 or
- The year will be exactly divisible by 400.
In this example, we will use the IF function along with the AND, OR, and MOD functions to find the leap years.
We use the MOD function to find a remainder after a dividend is divided by a divisor.
The AND functionThe AND function in Excel is classified as a logical function; it returns TRUE if the specified conditions are met, otherwise it returns FALSE.read more evaluates both the conditions of the leap years for the value “true”. The OR functionThe OR function in Excel is used to test various conditions, allowing you to compare two values or statements in Excel. If at least one of the arguments or conditions evaluates to TRUE, it will return TRUE. Similarly, if all of the arguments or conditions are FALSE, it will return FASLE.read more evaluates either of the condition for the value “true”.
We will apply the MOD function to the conditions as follows:
If MOD(year,4)=0 and MOD(year,100)<>(is not equal to) 0, then the year is a leap year.
or
If MOD(year,400)=0, then the year is a leap year; otherwise, the year is not a leap year.
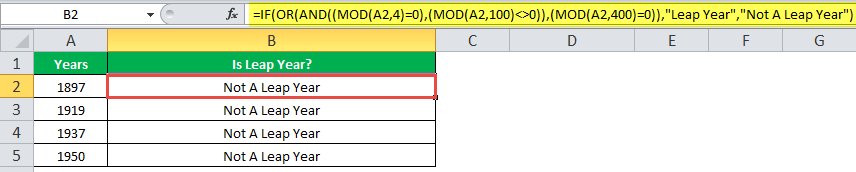
The IF formula is stated as follows:
“=IF(OR(AND((MOD(year,4)=0),(MOD(year,100)<>0)),(MOD(year,400)=0)),“Leap Year”, “Not A Leap Year”)”
The argument “year” refers to a reference value.
The following images show the output of the IF formula applied in the range of cells.
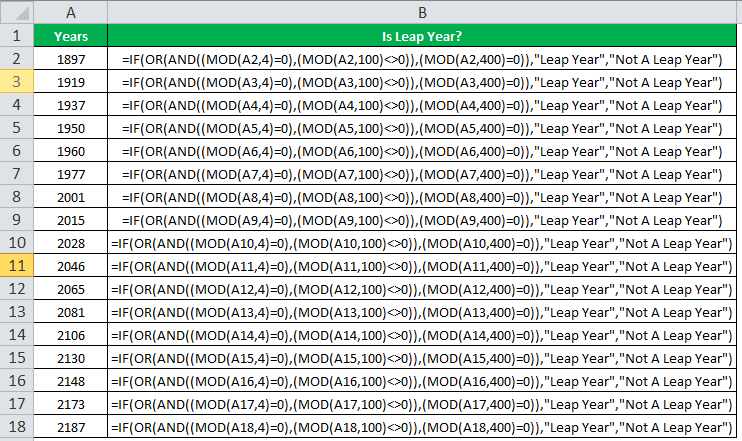
The following image shows how the IF formula is applied to the range of cells B2:B18.
The succeeding table shows the years 1960, 2028, and 2148 as leap years and the remaining as non-leap years.
The result of the IF excel formula is displayed for the range of cells B2:B18 in the following image.
Example #3
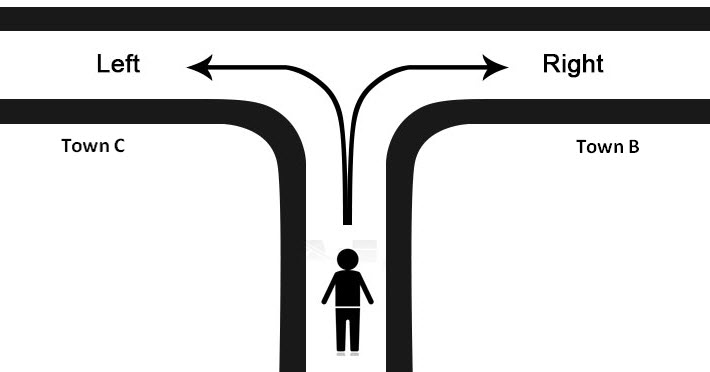
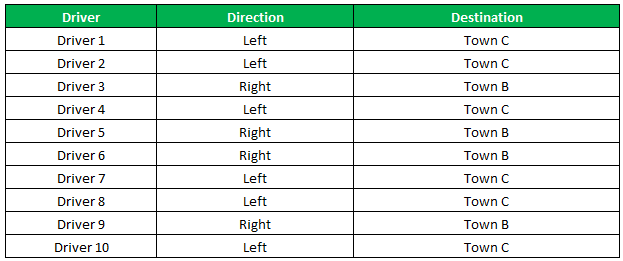
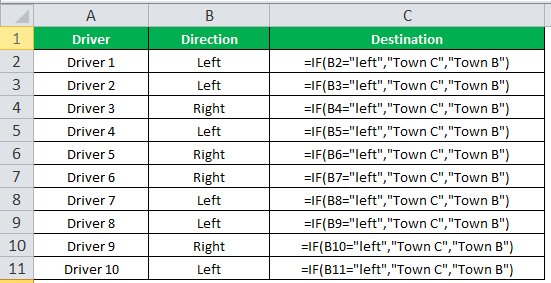
The succeeding table shows a list of drivers and the directions they undertook to reach the destination. It is preceded by an image of the road intersection explaining the turns taken by the drivers and their destinations. The right turn leads to town B, and the left turn leads to town C. Identify the driver’s destination to town B and town C.
Road Intersection Image
Let us apply the IF excel function to find the destination. Here, the condition is mentioned as follows:
- If the driver turns right, he/she reaches town B.
- If the driver turns left, he/she reaches town C.
We use the following IF formula to find the destination:
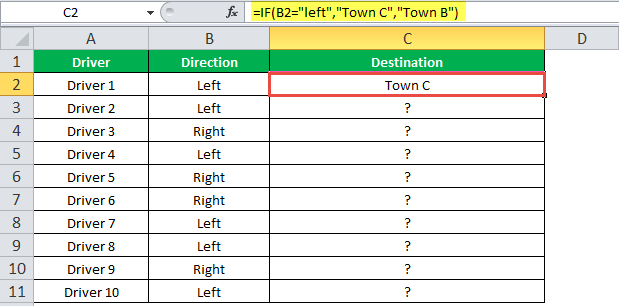
“=IF(B2=“Left”, “Town C”, “Town B”)”
The succeeding image shows the output of the IF formula applied to cell C2.
Drag the cells to use the formula in the range C2:C11. Finally, we get the destinations of each driver for their turning movements.
The below image displays the IF formula applied to the range.
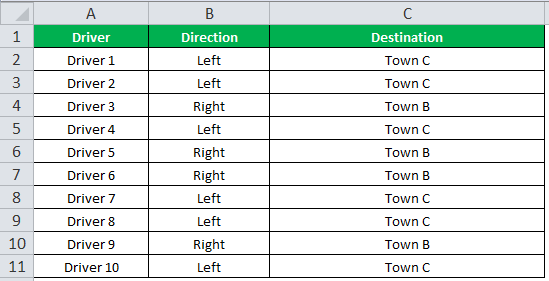
The output of the IF formula and the destinations are displayed in the succeeding image.
The result shows that six drivers reached town C, and the remaining four have reached town B.
Example #4
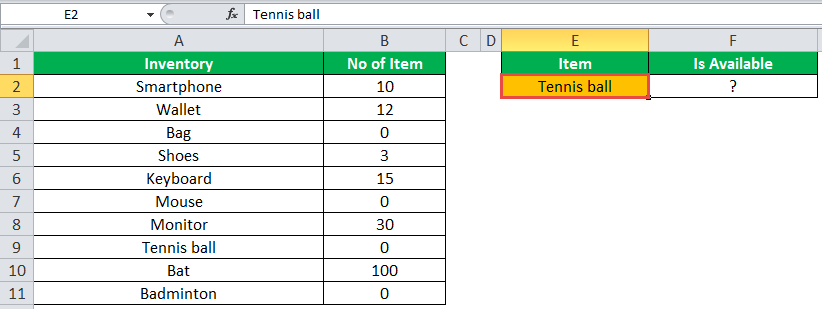
The following table shows a list of items and their inventory levels. We want to check if the specific item is available in the inventory or not using the IF function.
Let us list the name of items in column A and the number of items in column B. The list of data to be validated for the entire items list is shown in the cell E2 of the below image.
We use the Excel IF along with the VLOOKUP functionThe VLOOKUP excel function searches for a particular value and returns a corresponding match based on a unique identifier. A unique identifier is uniquely associated with all the records of the database. For instance, employee ID, student roll number, customer contact number, seller email address, etc., are unique identifiers.
read more to check the availability of the items in the inventory.
The VLOOKUP function looks up the values referring to the number of items, and the IF function will check whether the item number is greater than zero or not.
We will apply the following IF formula in the F2 cell:
“=IF(VLOOKUP(E2,A2:B11,2,0)=0, “Item Not Available”,“Item Available”)”
If the lookup value of an item is equal to 0, then the item is not available; else, the item is available.
The succeeding image shows the result of the IF formula in the cell F2.
Select “bat” in the E2 item cell to know whether the item is available or not in the inventory (as shown in the following image).
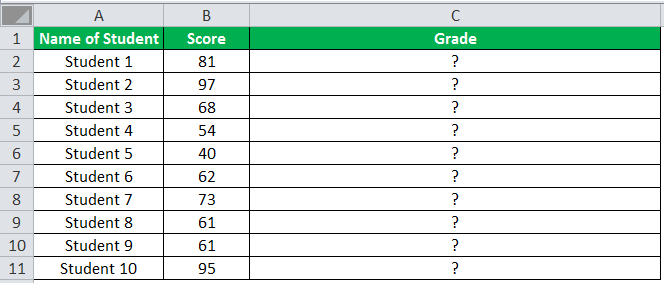
Example #5
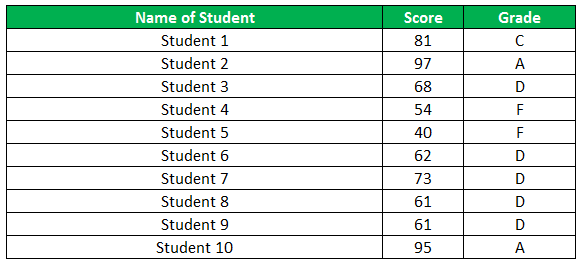
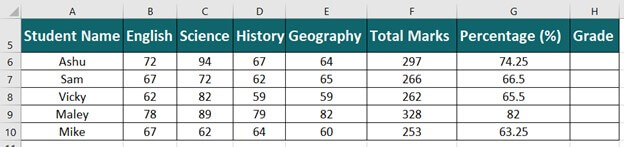
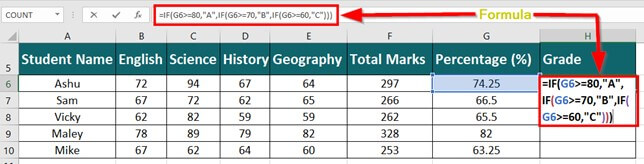
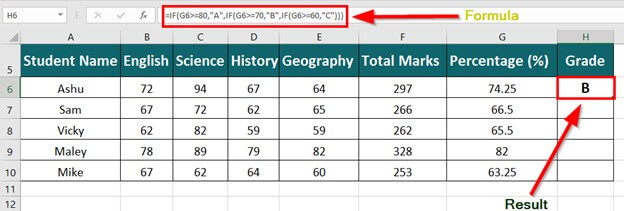
The following table shows the list of students and their marks. The grade criteria are provided based on the marks obtained by the students. We want to find the grade of each student in the list.
We apply the Nested IF in Excel since we have multiple criteria to find and decide each student’s grade.
The Nesting of IF function uses the IF function inside another IF formula when multiple conditions are to be fulfilled.
The syntax of Nesting of IF function is stated as follows:
“=IF( condition1, value_if_true1, IF( condition2, value_if_true2, value_if_false2 ))”
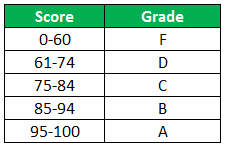
The succeeding table represents the range of scores and the grades, respectively.
Let us apply the multiple IF conditions with AND function in the below-nested formula to find out the grade of the students:
“=IF((B2>=95),“A”,IF(AND(B2>=85,B2<=94),“B”,IF(AND(B2>=75,B2<=84),“C”,IF(AND(B2>=61,B2<=74),“D”,“F”))))”
The IF function checks the logical condition as shown in the formula below:
“=IF(logical_test, [value_if_true],[value_if_false])”
We will split the above-mentioned nested formula and check the IF statements as shown below:
First Logical Test: B2>=95
If the formula returns,
- Value_if_true, execute: “A” (Grade A) else(comma) enter value_if_false
- Value_if_false, then the formula finds another IF condition and enter IF condition
Second Logical Test: B2>=85(logical expression 1) and B2<=94(logical expression 2)
(We use AND function to check the multiple logical expressions as the two given conditions are to be evaluated for “true.”)
If the formula returns,
- Value_if_true, execute: “B” (Grade B) else(comma) enter value_if_false
- Value_if_false, then the formula finds another IF condition and enter IF condition
Third Logical Test: B2>=75(logical expression 1) and B2<=84(logical expression 2)
(We use AND function to check the multiple logical expressions as the two given conditions are to be evaluated for “true.”)
If the formula returns,
- Value_if_true, execute: “C” (Grade C) else(comma) enter value_if_false
- value_if_false, then the formula finds another IF condition and enter IF condition
Fourth Logical Test: B2>=61(logical expression 1) and B2<=74(logical expression 2)
(We use AND function to check the multiple logical expressions as the two given conditions are to be evaluated for “true.”)
If the formula returns,
- Value_if_true, execute: “D” (Grade D) else(comma) enter value_if_false
- Value_if_false, execute: “F” (Grade F)
- Finally, close the parenthesis.
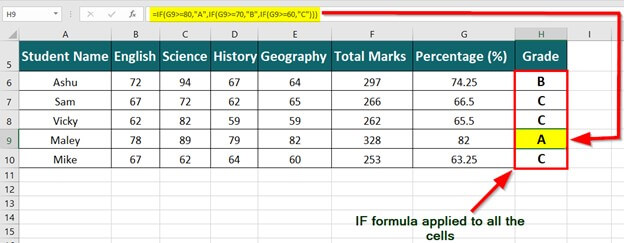
The below image displays the output of the IF formula applied to the range.
The succeeding image shows the IF nested formula applied to the range.
The grades of the students are listed in the following table.
Guidelines for the Multiple IF Statements
The guidelines for the multiple IF statements are listed as follows:
- Use nested IF function to a limited extent as multiple IF statements require a great deal of thought to be accurate.
- Multiple IF statementsIn Excel, multiple IF conditions are IF statements that are contained within another IF statement. They are used to test multiple conditions at the same time and return distinct values. Additional IF statements can be included in the ‘value if true’ and ‘value if false’ arguments of a standard IF formula.read more require multiple parentheses (), which is often difficult to manage. Excel provides a way to check the color of each opening and closing parenthesis to avoid this situation. The last closing parenthesis color will always be black, denoting the end of the formula statement.
- Whenever we pass a string value for the arguments “value_if_true” and “value_if_false” or test a reference against a string value, enclose the string value in double quotes. Passing a string value without quotes will result in “#NAME?” error.
Frequently Asked Question
1. What is the IF function in Excel?
The Excel IF function is a logical function that checks the given criteria and returns one value for a “true” and another value for a “false” result.
The syntax of the IF function is stated as follows:
“=IF(logical_test, [value_if_true], [value_if_false])”
The arguments are as follows:
1. Logical_test – It refers to a value or condition that is tested.
2. Value_if_true – It is the value returned when the condition logical_test is “true.”
3. Value_if_false – It is the value returned when the condition logical_test is “false.”
The “logical_test” is a required argument, whereas the “value_if_true” and “value_if_false” are optional arguments.
2. How to use the IF Excel function with multiple conditions?
The IF Excel statement for multiple conditions is created by using multiple IF functions in a single formula.
The syntax of IF function with multiple conditions is stated as follows:
“=IF (condition 1_“true”, do something, IF (condition 2_“true”, do something, IF (condition 3_ “true”, do something, else do something)))”
3. How to use the function IFERROR in Excel?
IF Excel Function Video
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the IF function in Excel. Here we discuss how to use the IF function along with examples and downloadable templates. You may also look at these useful functions –
- What is the Logical Test in Excel?A logical test in Excel results in an analytical output, either true or false. The equals to operator, “=,” is the most commonly used logical test.read more
- “Not Equal to” in Excel“Not Equal to” argument in excel is inserted with the expression <>. The two brackets posing away from each other command excel of the “Not Equal to” argument, and the user then makes excel checks if two values are not equal to each other.read more
- Data Validation ExcelThe data validation in excel helps control the kind of input entered by a user in the worksheet.read more
The logical IF statement in Excel is used for the recording of certain conditions. It compares the number and / or text, function, etc. of the formula when the values correspond to the set parameters, and then there is one record, when do not respond — another.
Logic functions — it is a very simple and effective tool that is often used in practice. Let us consider it in details by examples.
The syntax of the function «IF» with one condition
The operation syntax in Excel is the structure of the functions necessary for its operation data.
=IF(boolean;value_if_TRUE;value_if_FALSE)
Let us consider the function syntax:
- Boolean – what the operator checks (text or numeric data cell).
- Value_if_TRUE – what will appear in the cell when the text or numbers correspond to a predetermined condition (true).
- Value_if_FALSE – what appears in the box when the text or the number does not meet the predetermined condition (false).
Example:
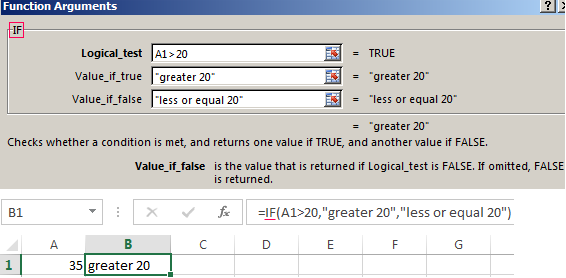
Logical IF functions.
The operator checks the A1 cell and compares it to 20. This is a «Boolean». When the contents of the column is more than 20, there is a true legend «greater 20». In the other case it’s «less or equal 20».
Attention! The words in the formula need to be quoted. For Excel to understand that you want to display text values.
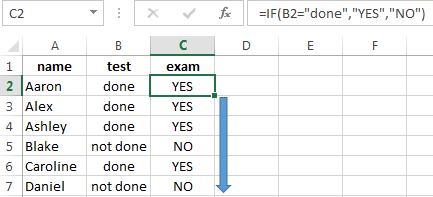
Here is one more example. To gain admission to the exam, a group of students must successfully pass a test. The results are listed in a table with columns: a list of students, a credit, an exam.
The statement IF should check not the digital data type but the text. Therefore, we prescribed in the formula В2= «done» We take the quotes for the program to recognize the text correctly.
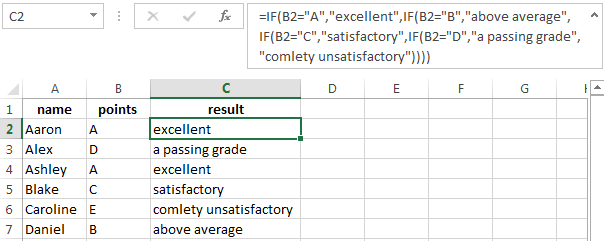
The function IF in Excel with multiple conditions
Usually one condition for the logic function is not enough. If you need to consider several options for decision-making, spread operators’ IF into each other. Thus, we get several functions IF in Excel.
The syntax is as follows:
Here the operator checks the two parameters. If the first condition is true, the formula returns the first argument is the truth. False — the operator checks the second condition.
Examples of a few conditions of the function IF in Excel:
It’s a table for the analysis of the progress. The student received 5 points:
- А – excellent;
- В – above average or superior work;
- C – satisfactory;
- D – a passing grade;
- E – completely unsatisfactory.
IF statement checks two conditions: the equality of value in the cells.
In this example, we have added a third condition, which implies the presence of another report card and «twos». The principle of the operator is the same.
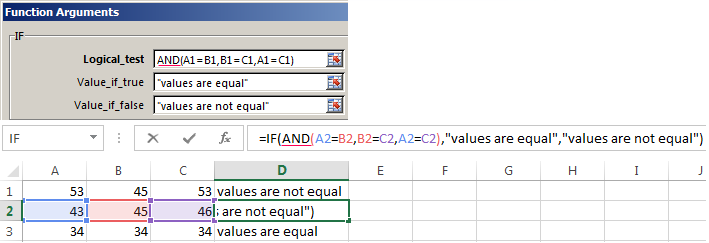
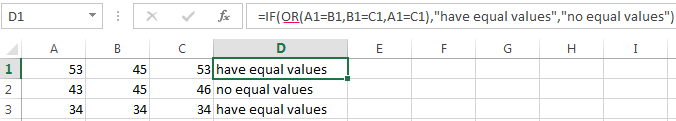
Enhanced functionality with the help of the operators «AND» and «OR»
When you need to check out a few of the true conditions you use the function И. The point is: IF A = 1 AND A = 2 THEN meaning в ELSE meaning с.
OR function checks the condition 1 or condition 2. As soon as at least one condition is true, the result is true. The point is: IF A = 1 OR A = 2 THEN value B ELSE value C.
Functions AND & OR can check up to 30 conditions.
An example of using the operator AND:
It’s the example of using the logical operator OR.
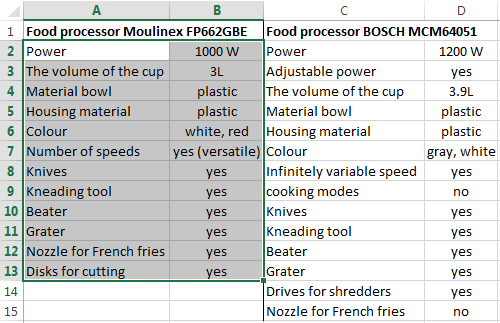
How to compare data in two tables
Users often need to compare the two spreadsheets in an Excel to match. Examples of the «life»: compare the prices of goods in different bringing, to compare balances (accounting reports) in a few months, the progress of pupils (students) of different classes, in different quarters, etc.
To compare the two tables in Excel, you can use the COUNTIFS statement. Consider the order of application functions.
For example, consider the two tables with the specifications of various food processors. We planned allocation of color differences. This problem in Excel solves the conditional formatting.
Baseline data (tables, which will work with):
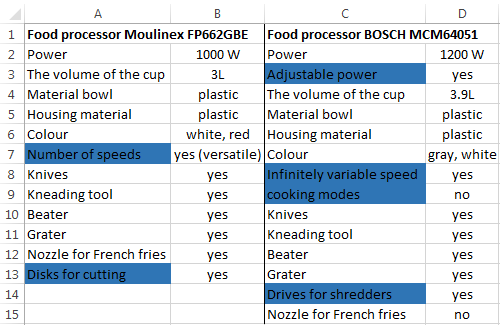
Select the first table. Conditional Formatting — create a rule — use a formula to determine the formatted cells:
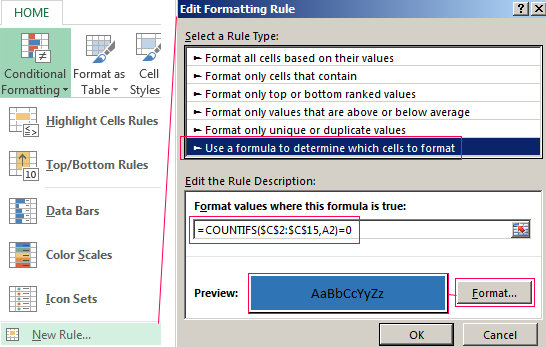
In the formula bar write: = COUNTIFS (comparable range; first cell of first table)=0. Comparing range is in the second table.
To drive the formula into the range, just select it first cell and the last. «= 0» means the search for the exact command (not approximate) values.
Choose the format and establish what changes in the cell formula in compliance. It’s better to do a color fill.
Select the second table. Conditional Formatting — create a rule — use the formula. Use the same operator (COUNTIFS). For the second table formula:
Download all examples in Excel
Now it is easy to compare the characteristics of the data in the table.
In this tutorial, we will learn about the IF function in Excel. Along with IF, the AND and OR functions are important formulas too. A nested IF simply means multiple IF functions in a single syntax.
Introducing IF Function in Excel
Let’s get started with this easy guide to using the IF function and all its related functions in Microsoft Excel, step-by-step with supporting images and examples.
1. IF Function
To learn to use the IF function, we will take an example of a mark list of students below.
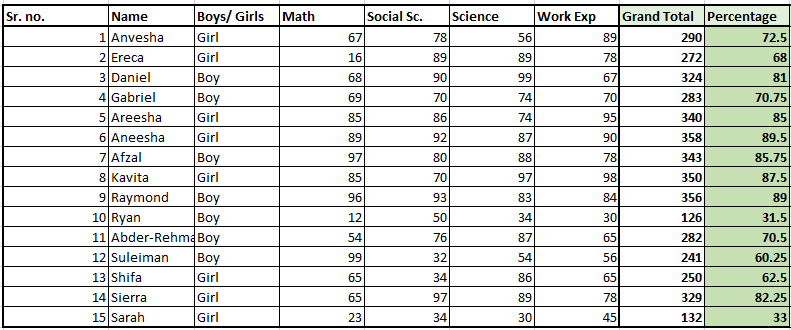
Our goal is to find out which student has passed or failed and what are their grades. Of course, it would be a tedious task to find out pass or fail results and grades for each student in this list.
To ease our task, we have IF functions for that matter. The IF function will automatically identify if a student has passed or failed based on the criteria you provide to it.
It will automatically mark a student as “Pass” if he/she has scored above the minimum pass mark and mark a student as “Fail” if he/she has scored below the minimum pass mark.
The IF function automatically assigns the appropriate grades to students based on their marks if you command it.
Here is a glimpse of how the IF function helps you out with assigning grades and marking “Pass” or “Fail”.
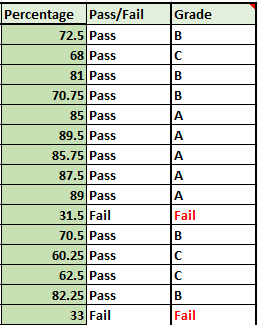
Steps to use IF function in Excel
We have allotted certain grades and marked them as Pass or Fail to students based on the percentages they have secured in their exams, with the help of the IF function.
1. Using the IF function in Excel to identify passed/failed students
Let’s learn how we can use the IF formula to achieve this. We will use the same example. We take the minimum passing percentage as 34%.
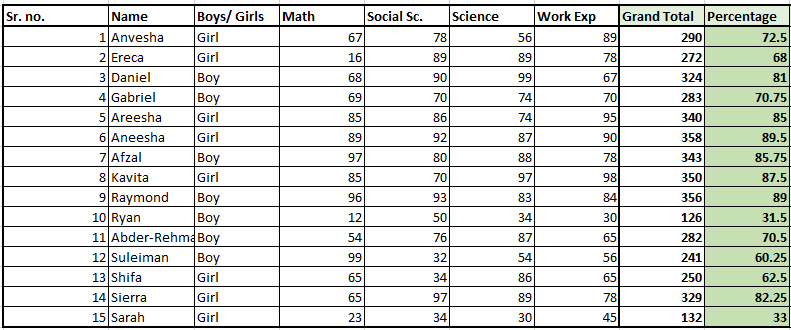
- Find out the percentage of total marks of every student.
- Create a new column named “Pass/Fail”.
- In the blank cell below the title, type the IF formula as follows next.
- Type =IF( and select the first student’s percentage and type >=34.
- Put a comma and move to the next argument named [value_if_true]. This means you’re being asked to put a value to be displayed if the above condition is true. Remember these arguments are case sensitive.
- Once you have put a comma, type “Pass”.
- Put a comma and move to the next argument named [value_if_false] to display a value when the above condition is false. This field is optional in most cases but we need a false value because it is a mark list.
- Close the bracket and hit ENTER.
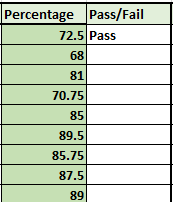
You can see that the formula is displaying “Pass” for the first student because she has secured above 34%.
- Double-click or drag the cell from the right corner below to autofill the formula to all the students below.
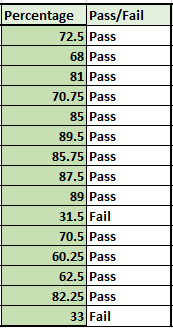
Recommended read: How to Autofill in Excel?
2. Nested IF Function
Now, let us start assigning grades to all students.
We are going to be using multiple IF functions in a single syntax this time to provide multiple criteria to the IF function. This is called Nested IF in Excel.
However, there is no specific function named “Nested IF” in Excel, it is simply that this behavior has been given a name i.e., Nested IF.
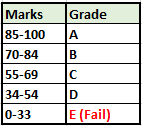
Before we proceed further, we need to first make a table that displays a grading class for each grade. Here is an example below.
- Create a new column named “Grade”.
- Type the IF function in a blank cell below the title as follows.
- Type =IF( and now type AE118>=85,”A”,IF(AE118>=70,”B”,IF(AE118>=55,”C”,IF(AE118>=34,”D”,IF(AE118<=33,”Fail”.
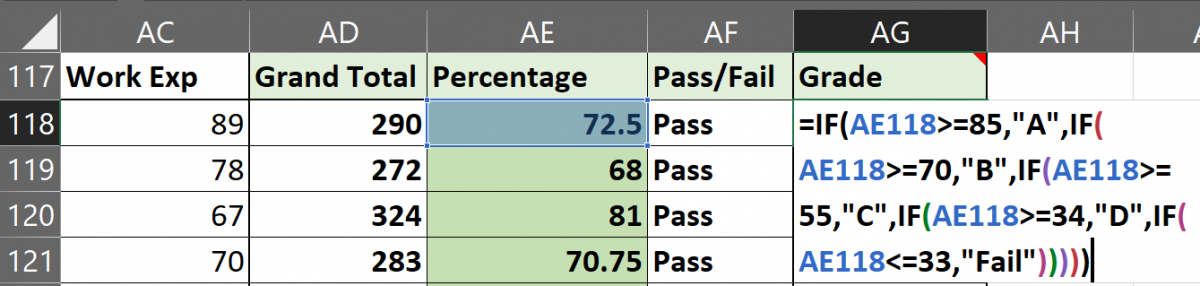
- Note that AE118 is our cell address for the first student’s percentage. It will be different in your case. Refer to the image above to make sense of the formula.
- The formula simply states- if percentage marks are above and equal to 85 then give “A”, if percentage marks are above and equal to 70 then give “B”, and so on and so forth. For the last condition, we have applied the condition- if the marks are less than or equal to 33 then give “Fail”.
- For the last IF statement, you can either put the result as “Fail” or “E” as you like.
- Now, note that we will close the formula with 5 brackets for this example as we have used a total of 5 IF formulas.

- Hit ENTER to complete the formula.
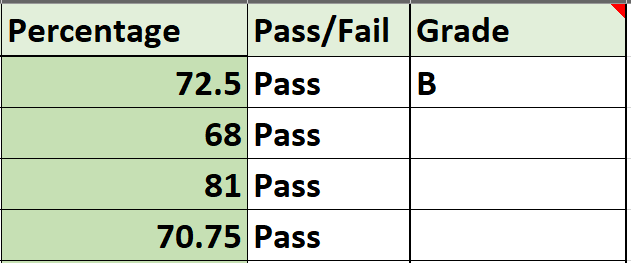
You can now see that the formula has been applied to the first entry and the result is B because the student has secured 72.5% which is less than 75%. This means the nested Ifs are working correctly.
- Now drag the cell from the lower right corner to autofill the formula to the rest of the entries.
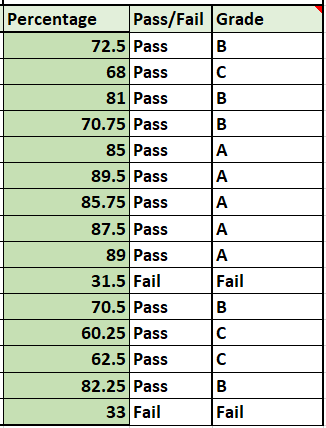
You can see that we now have grades and pass/fail markings for every student on the list successfully.
3. IF with AND in Excel
Let us learn the IF formula with the AND function in a single syntax with a minor example.
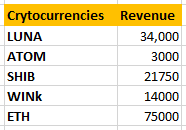
When you have two or more distinct conditions to be used together, you can use the IF function with AND in Excel.
While nested IFs will also work, using AND function will save your time as it is shorter to type. So, let’s get started.
Our goal is to identify currencies with revenues greater than 20,000 and less than 50,000 and mark them as “Good”.
- Type =IF(AND( because we are using the IF with AND function.
- Select the first cell under Revenue, and type >20000.
- Put a comma and select the first cell under Revenue again and type <50000.
- Now, close the bracket to complete the AND function. We’re still working on the IF function so do not put two brackets.
- We come back to the IF function as soon as we close the AND function. Now put the values to be displayed if the condition is true or false.
- Put a comma to move to the argument [value_if_true] and type “Good”.
- You can provide a result in the [value_if_false] argument, but it is completely optional. If nothing is provided then the cells will display FALSE if the condition is false. But if you want the cells to remain blank simply put “” (two double quotation marks) in this argument.
- Close the bracket to complete the IF function as well.
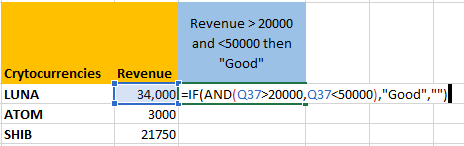
This is how the syntax should look like before pressing ENTER.
- Hit ENTER to view results and drag the cell down to autofill the formula to the rest of the cells.
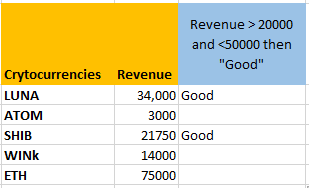
There are only two such cells for which the condition is true and the result is being displayed as “Good” for them and the rest of the cells are blank. This means the formula is working correctly.
4. IF with OR in Excel
Using the OR function with the IF function will give results for either of the conditions that are true.
- Type =IF(OR(.
- Select the first cell under Revenue and type >=20000.
- Put a comma and select the first cell under Revenue again and type <=50000.
- Now, close the bracket to complete the OR function. We’re still working on the IF function so do not put two brackets.
- Coming back to the IF function, we now put the values to be displayed if the condition is true or false.
- Put a comma to move to the argument [value_if_true] and type “Flag”.
- Put a comma to move to the argument [value_if_false] and type “”.

This is how the syntax should look like before pressing ENTER.
- Close the bracket to complete the OR function and hit ENTER.
- Drag the cell below to get the results for the rest.
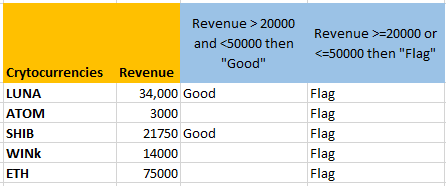
The formula is true for all entries and so it is displaying “Flag” for all of them. This is because all the values are either lower than 50,000 or greater than 20,000.
Conclusion
This was all about IF functions and other related functions to the IF function that are AND and OR functions.
Reference: ExcelJet
This is a step-by-step guide on how to use IF function in Excel. It shows you how to create a formula using the IF function, it includes several IF formula examples, an introduction on how to use nested IF formulas, and the exercise file I used when creating this tutorial.
The Excel IF function performs a logical test and returns one value when the condition is TRUE and another when the condition is FALSE.
How do you write an if-then formula in Excel? Well, the syntax for IF statements is the same in all Excel versions. This means that you can use any of the examples shown in this article in Excel for Microsoft 365 or Excel 2021, 2019, 2016, 2013, 2010, 2007, and 2003.
How to use IF function in Excel:
- Select the cell where you want to insert the IF formula. Using your mouse or keyboard, navigate to the cell where you want to insert your formula.
- Type =IF(
- Insert the condition that you want to check, followed by a comma (,). The first argument of the IF function is the logical_test. This is the condition that you want to validate. For example C6 > 70.
- Insert the value to display when the condition is TRUE, followed by a comma (,). The second argument of the IF function is value_if_true. Here, you can insert a nested formula or a simple message such as “YES”.
- Insert the value to display when the condition is FALSE. The last argument of the IF function is value_if_false. Just like the previous step, you can insert a nested formula or display a message such as “NO”. This can also be set as an empty string (“”), which will display a cell that looks blank.
- Type ) to close the function and press ENTER
The following video shows you exactly how to apply the six steps described above and create your first IF formula.
The syntax that shows how to create an IF function in Excel is explained below:=IF(logical_test, [value_if_true], [value_if_false])
IF is a logical function and implies setting 3 arguments:
logical_test – The logical condition that you want to test. This will return either a TRUE or a FALSE value.
value_if_true – [optional] The value or formula which will be used when logical_test is TRUE.
value_if_false – [optional] The value or formula which will be used when logical_test is FALSE.
Please remember that while both value_if_true and value_if_false are optional, at least one of them needs to be supplied. Otherwise, your IF formula will simply return 0 (zero).
Where is the IF function in Excel? Since this is a logical function, you can find the IF function in the Formulas tab, Function Library section, under Logical.
Logical operators for IF function
The IF function is one of the most used Excel functions, and it allows you to return different values when the logical condition supplied is TRUE or FALSE. An Excel if-then formula can use the following logical operators:
| Logical operators | Definition | Example |
| = | equal to | A1=B1 |
| <> | not equal to | A1<>B1 |
| > | greater than | A1>B1 |
| >= | greater than or equal to | A1>=B1 |
| < | lower than | A1<B1 |
| <= | lower than or equal to | A1<=B1 |
The IF function doesn’t support wildcards.
Your first IF formula
The IF function runs a logical test and returns different values depending on whether the result is TRUE or FALSE. The result from IF can be a value, a cell reference, or even another formula.
Now let’s move on to some examples.
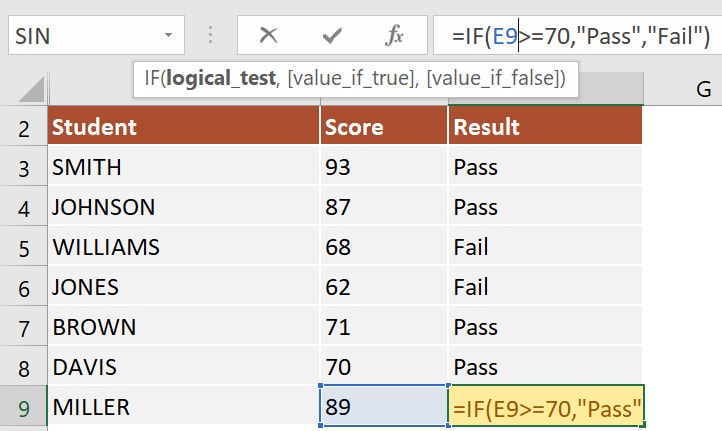
We’ll be evaluating exam grades. If the student obtained a score higher than or equal to 70, then we will return the message “Pass.” If the grade is lower than 70, then we will display “Fail.”
In this example, I have inserted the following formula in cell F9:=IF(E9>=70, "Pass", "Fail")
The 3 arguments for this IF formula are:
logical_test: E9>=70
value_if_true: Pass is returned if E9>=70.
value_if_false: Fail is returned if E9<70.
Please note that when you want to use text in your IF formulas (like a word or sentence), you need to wrap the text in quotes (e.g. “Fail”). The only exception is while using TRUE or FALSE, which are built-in functionalities that Excel recognizes automatically.
How to use the IF function in Excel with another function or formula
The beauty of the IF function is that it allows us to build complex financial models with lots of interdependencies. This includes using different formulas based on conditional logic.
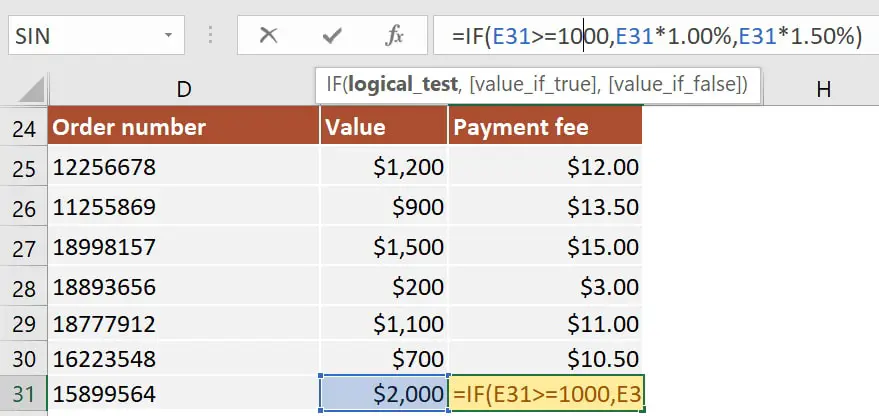
In our next example, we will use the IF function to calculate a payment fee based on the value of the order. If the order value is higher than or equal to $1000, then it should calculate a payment fee of 1.00%. However, if the total order value is lower than $1000, then it should use 1.50%.
The formula in cell F31 is:=IF(E31>=1000, E31*1%, E31*1.5%)
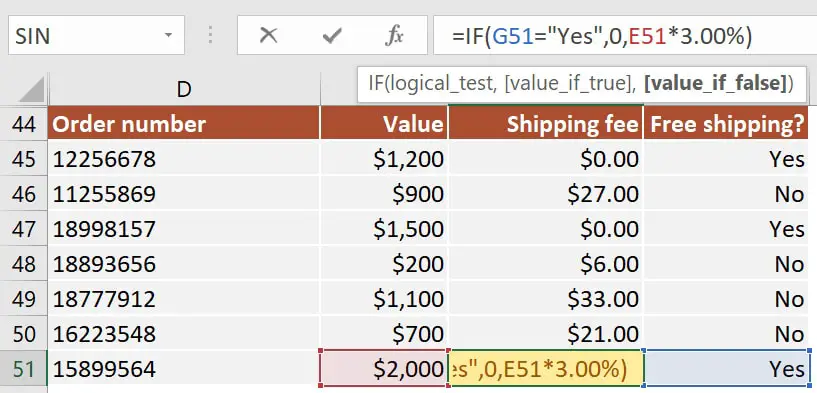
Now let’s look at an IF formula that is dependent on user input. If we select free shipping for the order, then the shipping fee will be set to zero. Otherwise, it will be calculated as 3% of the order value.
This is something really easy to achieve, but it will open up so many opportunities for you to use the IF function in the future.
How to use nested IF statements in Excel
Nesting more IF functions allows you to perform multiple comparisons and create more complex formulas. However, you can only nest up to 64 IF functions in Excel. If you ever reach this limit (I never did), I can guarantee that there is a better and more elegant solution using functions like VLOOKUP, SUMIF, or COUNTIFS.
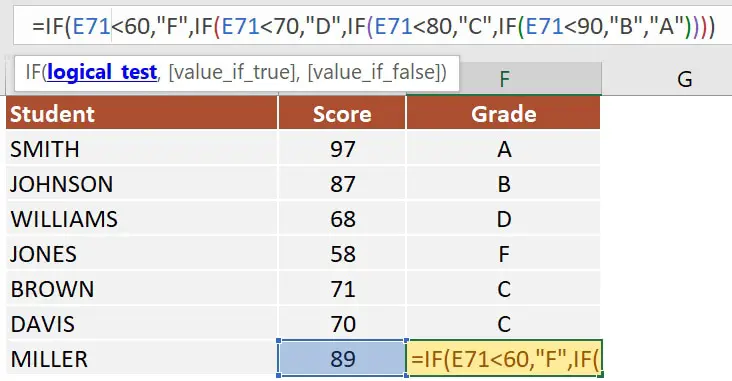
In the next example, I wrote a formula with several nested IF functions to assign a grade to a list of students based on their test results.
=IF(E71<60, "F", IF(E71<70, "D", IF(E71<80, "C", IF(E71<90, "B", "A"))))
The order of the conditions is important. When the conditions overlap, Excel will retrieve the [value_if_true] argument from the first IF statement that returns TRUE. This is why the conditions from the formula above need to be inserted in the same order for the formula to work properly.
Note: If you are running Office 365, then you can also look at the new IFS function. This function runs multiple tests and returns the value corresponding to the first TRUE result. It’s a very useful alternative to nested IF formulas and makes your formulas much easier to understand by others. You can read more about IFS on Microsoft’s website.
How to use IF formula with OR function in Excel
OR allows you to supply alternative conditions to an IF statement. This opens up opportunities to create complex scenarios where certain behavior is triggered by multiple possible conditions.
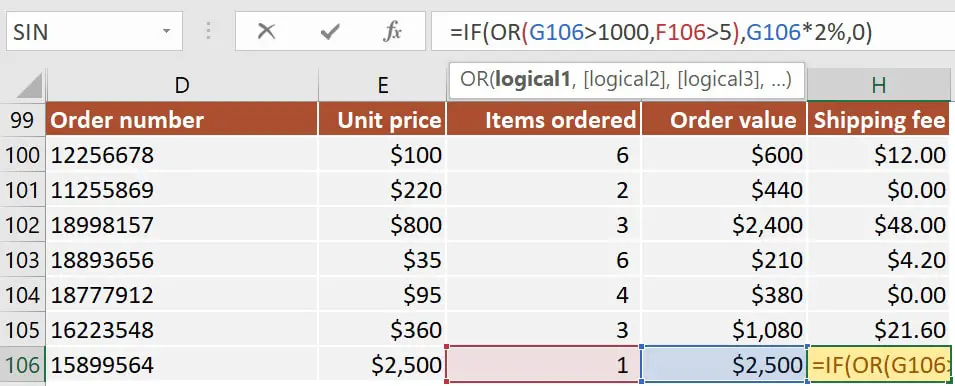
Let’s look at an IF formula that calculates a 2.00% shipping fee when the total order value is higher than $1000 or when there are more than 5 items in the order.
The IF OR statement I’ve used in cell H106 is:=IF(OR(G106>1000, F106>5), G106*2%, 0)
The OR function evaluates if G106>1000 or if F106>5 and the formula returns TRUE when either or both conditions are fulfilled.
How to use IF formula with AND function in Excel
AND allows you to supply multiple criteria to an IF statement. Basically, the IF function returns TRUE if, and only if, all the conditions are met.
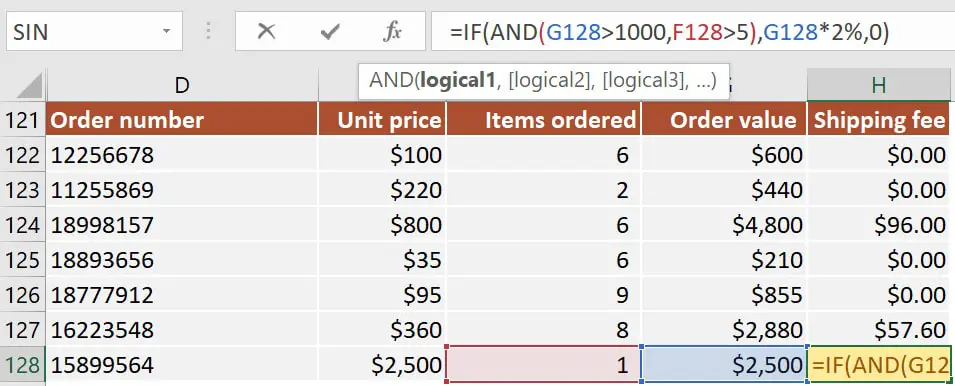
Working with our previous example, let’s apply the shipping fee only when the total order value is higher than $1000 and the order contains more than 5 items.
The IF AND statement I’ve used in cell H106 is:=IF(AND(G128>1000, F128>5), G128*2%, 0)
The AND function evaluates if G106>1000 and if F106>5 and returns TRUE when both conditions are fulfilled.
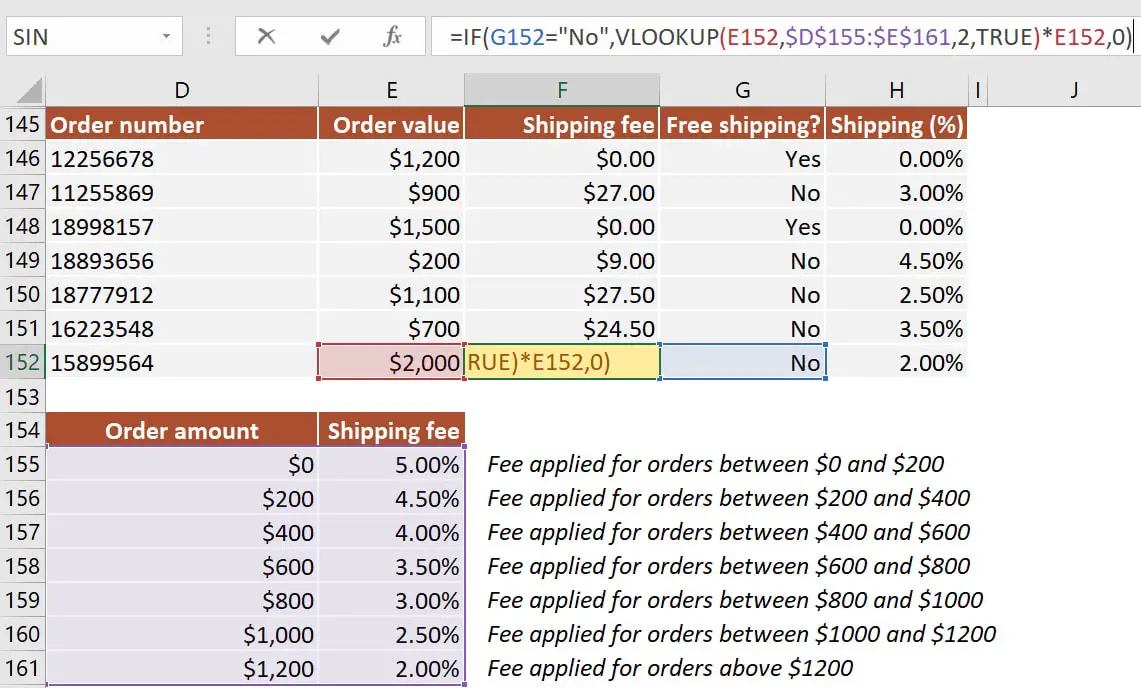
How to use IF function with VLOOKUP in Excel
VLOOKUP can be nested inside an IF formula to retrieve data when a condition is TRUE or FALSE. In the next example, I will show you how to calculate shipping fees based on a different table that contains the thresholds and percentages to be applied depending on the order value.
The formula I’ve used in cell F152:=IF(G152="No", VLOOKUP(E152, $J$146:$K$152, 2, TRUE)*E152, 0)
The formula uses the following arguments:
logical_test: G152="No"
value_if_true: VLOOKUP(E152, $J$146:$K$152, 2, TRUE)*E152 is used to retrieve the corresponding shipping fee percentage when G152=”No”
value_if_false: 0 is returned if G152 is anything else than “No.” In our case, the alternative is selecting “Yes” from the drop-down list.
Note: One thing to remember is that I’ve used a VLOOKUP formula with an approximate match argument. This means that your data must be sorted in ascending order by lookup value (in our case, the Order amount).
In case you need additional help, please also read this article that explains step-by-step how to use VLOOKUP function in Excel.
What to do next?
IF is a versatile function that can be used in a wide range of scenarios. I use it daily, and I can’t imagine a world where Excel would lack this functionality.
Practice writing formulas using the IF function, and your spreadsheets will definitely get better and more complex. For example, why not look at another example using an IF function with 3 conditions? It will show you more examples of how to insert an if formula in Excel using nested IF statements and multiple conditions.
Let me know if you have questions on how to use IF function in Excel or if you need advice on how to nest multiple IF statements in your Excel project by leaving a comment below.
The IF function is useful for making quick decisions or performing comparisons in Microsoft Excel. It’s an easy but versatile logical comparison function for handling many scenarios, ranging from financial models to assigning allowances. In this tutorial, I’ll show how to use the IF function in Excel and a simple adaptation. (Includes practice worksheet)
What is the IF Function?
The IF function is one of the simplest and most useful logical functions. It can fill cell items for you based on evaluating a condition such as a cell’s content and logical operators. What’s appealing about the function is that it can be used with other functions to handle more complex scenarios. You might think of it as a formula building block and you can find it in the Logical category.
The wizard-like dialog allows you to fill 3 Function Arguments or data elements, but you could use the formula bar once you master it. This is the easiest way to learn an Excel formula because you can see if it returns your expected result. For example, at the bottom left of the dialog, a line reads “Formula result =.”
The IF Function Arguments
| Field | Definition |
|---|---|
| Logical_test | A test on a cell value that is either TRUE or FALSE. |
| Value_if_true | The value Excel will put in a cell if the test is true. |
| Value_if_false | The value Excel will put in a cell if the test fails. |
Despite not having Microsoft Excel, my parents routinely employed this type of IF logic when calculating my allowance. Their version read:
IF you empty the garbage AND mow the lawn AND wash the dishes AND walk the dog, you get your full allowance.
And since I grew up in New England, this logic would change with the seasons to account for leaves and snow.
Setting Up the IF Function
Although Excel can’t issue an allowance, it can calculate the amount using a logic test based on whether a cell met a formula condition.
For example, I could create a spreadsheet with the chores needed to get an allowance. If the chores were completed (TRUE situation), a value would be applied toward the allowance. If the chore wasn’t completed (FALSE situation), nothing would be added.
These examples are noted by labels [1] and [2] in the screen snap below.
Using the example above, you might express the logic in the following way:
IF cell B2 equals “Y”, then use the Rate value from cell C2 ($3.00) in D2.
IF cell B2 does not equal “Y”, then place 0 in cell D2.
As you can see in this example, the IF logical condition is either TRUE or FALSE. And it pays to take out the garbage.
Comparison Operators
To help evaluate conditions, Excel uses a list of common operators. You probably know these as we probably used them in math class. These operators will be evaluated to a logical “true” or “false”. In the table below, B2 and C2 in the Example column are cell references.
| Operator | Example |
| = (equals) | B2 = “YES” |
| < (less than) | B2 < 12 |
| > (greater than) | B2 > 112 |
| <= (less than or equal to) | B2 <= 12 |
| >= (greater than or equal to) | B2 >= 12 |
| <> (not equal to) | B2 <> C2 |
How To Enter IF Function Arguments
- Click the spreadsheet cell where you wish to use the Excel formula.
- From the Formulas tab, click Insert function…
- In the Insert Function dialog text box, type “if“.
Note: On Office 365, there is now a Logical button on the Formulas tab. You can select IF from the drop-down menu.
- Make sure your cursor is in the Logical_test text box.
- Click the spreadsheet cell you wish to evaluate. Excel will fill in the cell reference such as “B2”.
- Add the equals sign = and your desired value in quotes. For example =”Y”.
- In the Value_if_true field, type the value you would like entered in your cell if B2 equals “Y”. In our example, I’ll click cell C3.
- In the Value_if_false: field, enter the value the cell should have if B2 does not have a “Y”. I’ll enter 0. I could leave it blank, but the cell would show “FALSE”.
- Review the dialog to see if the Formula result= value (label [1] below) is what you expect. If not, check to see if any errors show to the right of the fields (label [2] below).
- Click OK.
- Copy the formula to the other cells in your column.
✪ Tip: Even though the Value_if_false field is optional, it’s best to provide a value. Otherwise, Excel will use FALSE in the cell value.
Excel IF With Numeric Values
The above spreadsheet might have been Version 1 for my parents. A new incentive program would appear based on some parent/child negotiations and competitive neighborhood rates. I probably would’ve requested pay for partial chores. No doubt, my parents would counter with a penalty clause if something was less than half done.
Excel is flexible when it comes to IF statements and can evaluate more than a simple “Y” or “N.” For example, if we convert our previous Done? column to a % Done column with a number, we can accommodate these new requirements such as:
=IF(B2>0.5,B2*C2,-C2)The new formula returns the allowance based on the % Done in Column B. If the chore completion number is greater than .5, a prorated amount is applied to the allowance.
If the chore completion rate was .5 or below, a negative amount was applied to the allowance. Loosely translated, an “incomplete” performance costs money. You could also apply colors using conditional formatting.
Troubleshooting Tips
There are a couple of reasons why the IF function doesn’t work as expected.
- You don’t have quotes around a text string. For example, you used B2=Y instead of B2=”Y”. The quotes aren’t needed if you use the values TRUE or FALSE as Excel recognizes them.
- You have a data type mismatch. For example, your comparison operator was comparing a number in one cell such as “twelve”, but the comparison cell had 12. However, Excel is forgiving if you’re evaluating number formats such as 1.5 versus $1.50.
As you’ve seen, this is a versatile and useful function. Once you get the hang of how to use IF function in Excel, you’ll start using it in more scenarios. The two examples presented here were foundational. But you can use IF functions to handle other transactions such as applying sales tax, stock values, shipping charges, fixing Excel DIV 0 errors, or even nesting IF functions with Boolean logic.
And if you have kids, let them build the Excel spreadsheet and give them a bonus for using the IF function.
Hand-picked Excel Tutorials
- How to Use Excel VLOOKUP
- Beginner’s Guide to XLOOKUP
- How to Create an Excel Pivot Table
- The Benefits of Creating Excel Tables
- Video: How to Use Conditional Formatting
This Excel tutorial explains how to use the Excel IF function with syntax and examples.
Description
The Microsoft Excel IF function returns one value if the condition is TRUE, or another value if the condition is FALSE.
The IF function is a built-in function in Excel that is categorized as a Logical Function. It can be used as a worksheet function (WS) in Excel. As a worksheet function, the IF function can be entered as part of a formula in a cell of a worksheet.
Subscribe
If you want to follow along with this tutorial, download the example spreadsheet.
Download Example
Syntax
The syntax for the IF function in Microsoft Excel is:
IF( condition, value_if_true, [value_if_false] )
Parameters or Arguments
- condition
- The value that you want to test.
- value_if_true
- It is the value that is returned if condition evaluates to TRUE.
- value_if_false
- Optional. It is the value that is returned if condition evaluates to FALSE.
Returns
The IF function returns value_if_true when the condition is TRUE.
The IF function returns value_if_false when the condition is FALSE.
The IF function returns FALSE if the value_if_false parameter is omitted and the condition is FALSE.
Example (as Worksheet Function)
Let’s explore how to use the IF function as a worksheet function in Microsoft Excel.
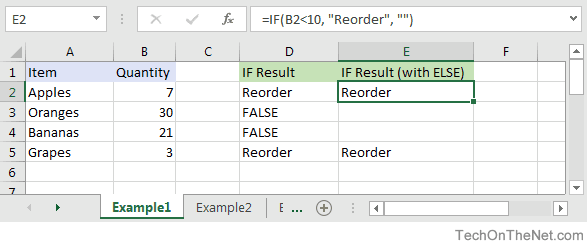
Based on the Excel spreadsheet above, the following IF examples would return:
=IF(B2<10, "Reorder", "") Result: "Reorder" =IF(A2="Apples", "Equal", "Not Equal") Result: "Equal" =IF(B3>=20, 12, 0) Result: 12
Combining the IF function with Other Logical Functions
Quite often, you will need to specify more complex conditions when writing your formula in Excel. You can combine the IF function with other logical functions such as AND, OR, etc. Let’s explore this further.
AND function
The IF function can be combined with the AND function to allow you to test for multiple conditions. When using the AND function, all conditions within the AND function must be TRUE for the condition to be met. This comes in very handy in Excel formulas.
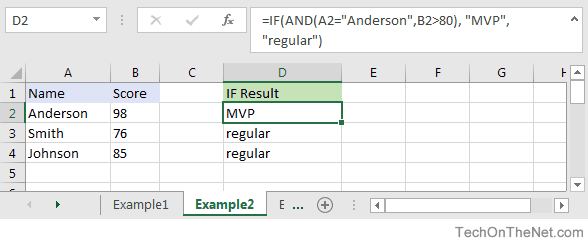
Based on the spreadsheet above, you can combine the IF function with the AND function as follows:
=IF(AND(A2="Anderson",B2>80), "MVP", "regular") Result: "MVP" =IF(AND(B2>=80,B2<=100), "Great Score", "Not Bad") Result: "Great Score" =IF(AND(B3>=80,B3<=100), "Great Score", "Not Bad") Result: "Not Bad" =IF(AND(A2="Anderson",A3="Smith",A4="Johnson"), 100, 50) Result: 100 =IF(AND(A2="Anderson",A3="Smith",A4="Parker"), 100, 50) Result: 50
In the examples above, all conditions within the AND function must be TRUE for the condition to be met.
OR function
The IF function can be combined with the OR function to allow you to test for multiple conditions. But in this case, only one or more of the conditions within the OR function needs to be TRUE for the condition to be met.
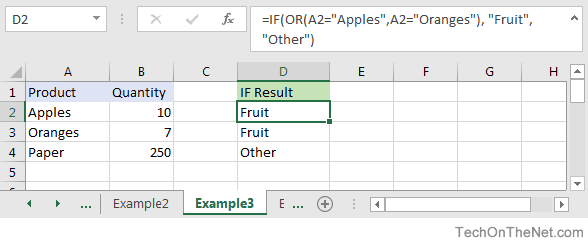
Based on the spreadsheet above, you can combine the IF function with the OR function as follows:
=IF(OR(A2="Apples",A2="Oranges"), "Fruit", "Other") Result: "Fruit" =IF(OR(A4="Apples",A4="Oranges"),"Fruit","Other") Result: "Other" =IF(OR(A4="Bananas",B4>=100), 999, "N/A") Result: 999 =IF(OR(A2="Apples",A3="Apples",A4="Apples"), "Fruit", "Other") Result: "Fruit"
In the examples above, only one of the conditions within the OR function must be TRUE for the condition to be met.
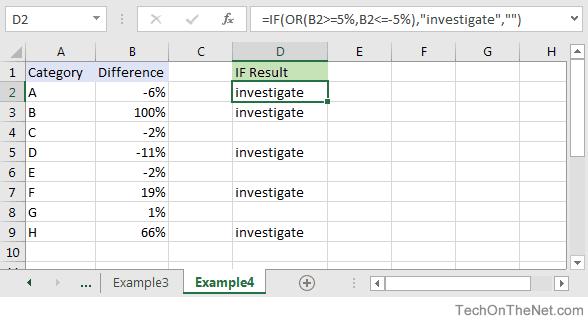
Let’s take a look at one more example that involves ranges of percentages.
Based on the spreadsheet above, we would have the following formula in cell D2:
=IF(OR(B2>=5%,B2<=-5%),"investigate","") Result: "investigate"
This IF function would return «investigate» if the value in cell B2 was either below -5% or above 5%. Since -6% is below -5%, it will return «investigate» as the result. We have copied this formula into cells D3 through D9 to show you the results that would be returned.
For example, in cell D3, we would have the following formula:
=IF(OR(B3>=5%,B3<=-5%),"investigate","") Result: "investigate"
This formula would also return «investigate» but this time, it is because the value in cell B3 is greater than 5%.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: In Microsoft Excel, I’d like to use the IF function to create the following logic:
if C11>=620, and C10=»F»or»S», and C4<=$1,000,000, and C4<=$500,000, and C7<=85%, and C8<=90%, and C12<=50, and C14<=2, and C15=»OO», and C16=»N», and C19<=48, and C21=»Y», then reference cell A148 on Sheet2. Otherwise, return an empty string.
Answer: The following formula would accomplish what you are trying to do:
=IF(AND(C11>=620, OR(C10="F",C10="S"), C4<=1000000, C4<=500000, C7<=0.85, C8<=0.9, C12<=50, C14<=2, C15="OO", C16="N", C19<=48, C21="Y"), Sheet2!A148, "")
Question: In Microsoft Excel, I’m trying to use the IF function to return 0 if cell A1 is either < 150,000 or > 250,000. Otherwise, it should return A1.
Answer: You can use the OR function to perform an OR condition in the IF function as follows:
=IF(OR(A1<150000,A1>250000),0,A1)
In this example, the formula will return 0 if cell A1 was either less than 150,000 or greater than 250,000. Otherwise, it will return the value in cell A1.
Question: In Microsoft Excel, I’m trying to use the IF function to return 25 if cell A1 > 100 and cell B1 < 200. Otherwise, it should return 0.
Answer: You can use the AND function to perform an AND condition in the IF function as follows:
=IF(AND(A1>100,B1<200),25,0)
In this example, the formula will return 25 if cell A1 is greater than 100 and cell B1 is less than 200. Otherwise, it will return 0.
Question: In Microsoft Excel, I need to write a formula that works this way:
IF (cell A1) is less than 20, then times it by 1,
IF it is greater than or equal to 20 but less than 50, then times it by 2
IF its is greater than or equal to 50 and less than 100, then times it by 3
And if it is great or equal to than 100, then times it by 4
Answer: You can write a nested IF statement to handle this. For example:
=IF(A1<20, A1*1, IF(A1<50, A1*2, IF(A1<100, A1*3, A1*4)))
Question: In Microsoft Excel, I need a formula in cell C5 that does the following:
IF A1+B1 <= 4, return $20
IF A1+B1 > 4 but <= 9, return $35
IF A1+B1 > 9 but <= 14, return $50
IF A1+B1 >= 15, return $75
Answer: In cell C5, you can write a nested IF statement that uses the AND function as follows:
=IF((A1+B1)<=4,20,IF(AND((A1+B1)>4,(A1+B1)<=9),35,IF(AND((A1+B1)>9,(A1+B1)<=14),50,75)))
Question: In Microsoft Excel, I need a formula that does the following:
IF the value in cell A1 is BLANK, then return «BLANK»
IF the value in cell A1 is TEXT, then return «TEXT»
IF the value in cell A1 is NUMERIC, then return «NUM»
Answer: You can write a nested IF statement that uses the ISBLANK function, the ISTEXT function, and the ISNUMBER function as follows:
=IF(ISBLANK(A1)=TRUE,"BLANK",IF(ISTEXT(A1)=TRUE,"TEXT",IF(ISNUMBER(A1)=TRUE,"NUM","")))
Question: In Microsoft Excel, I want to write a formula for the following logic:
IF R1<0.3 AND R2<0.3 AND R3<0.42 THEN «OK» OTHERWISE «NOT OK»
Answer: You can write an IF statement that uses the AND function as follows:
=IF(AND(R1<0.3,R2<0.3,R3<0.42),"OK","NOT OK")
Question: In Microsoft Excel, I need a formula for the following:
IF cell A1= PRADIP then value will be 100
IF cell A1= PRAVIN then value will be 200
IF cell A1= PARTHA then value will be 300
IF cell A1= PAVAN then value will be 400
Answer: You can write an IF statement as follows:
=IF(A1="PRADIP",100,IF(A1="PRAVIN",200,IF(A1="PARTHA",300,IF(A1="PAVAN",400,""))))
Question: In Microsoft Excel, I want to calculate following using an «if» formula:
if A1<100,000 then A1*.1% but minimum 25
and if A1>1,000,000 then A1*.01% but maximum 5000
Answer: You can write a nested IF statement that uses the MAX function and the MIN function as follows:
=IF(A1<100000,MAX(25,A1*0.1%),IF(A1>1000000,MIN(5000,A1*0.01%),""))
Question: In Microsoft Excel, I am trying to create an IF statement that will repopulate the data from a particular cell if the data from the formula in the current cell equals 0. Below is my attempt at creating an IF statement that would populate the data; however, I was unsuccessful.
=IF(IF(ISERROR(M24+((L24-S24)/AA24)),"0",M24+((L24-S24)/AA24)))=0,L24)
The initial part of the formula calculates the EAC (Estimate At completion = AC+(BAC-EV)/CPI); however if the current EV (Earned Value) is zero, the EAC will equal zero. IF the outcome is zero, I would like the BAC (Budget At Completion), currently recorded in another cell (L24), to be repopulated in the current cell as the EAC.
Answer: You can write an IF statement that uses the OR function and the ISERROR function as follows:
=IF(OR(S24=0,ISERROR(M24+((L24-S24)/AA24))),L24,M24+((L24-S24)/AA24))
Question: I have been looking at your Excel IF, AND and OR sections and found this very helpful, however I cannot find the right way to write a formula to express if C2 is either 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 and F2 is F and F3 is either D,F,B,L,R,C then give a value of 1 if not then 0. I have tried many formulas but just can’t get it right, can you help please?
Answer: You can write an IF statement that uses the AND function and the OR function as follows:
=IF(AND(C2>=1,C2<=9, F2="F",OR(F3="D",F3="F",F3="B",F3="L",F3="R",F3="C")),1,0)
Question:In Excel, I have a roadspeed of a car in m/s in cell A1 and a drop down menu of different units in C1 (which unclude mph and kmh). I have used the following IF function in B1 to convert the number to the unit selected from the dropdown box:
=IF(C1="mph","=A1*2.23693629",IF(C1="kmh","A1*3.6"))
However say if kmh was selected B1 literally just shows A1*3.6 and does not actually calculate it. Is there away to get it to calculate it instead of just showing the text message?
Answer: You are very close with your formula. Because you are performing mathematical operations (such as A1*2.23693629 and A1*3.6), you do not need to surround the mathematical formulas in quotes. Quotes are necessary when you are evaluating strings, not performing math.
Try the following:
=IF(C1="mph",A1*2.23693629,IF(C1="kmh",A1*3.6))
Question:For an IF statement in Excel, I want to combine text and a value.
For example, I want to put an equation for work hours and pay. IF I am paid more than I should be, I want it to read how many hours I owe my boss. But if I work more than I am paid for, I want it to read what my boss owes me (hours*Pay per Hour).
I tried the following:
=IF(A2<0,"I owe boss" abs(A2) "Hours","Boss owes me" abs(A2)*15 "dollars")
Is it possible or do I have to do it in 2 separate cells? (one for text and one for the value)
Answer: There are two ways that you can concatenate text and values. The first is by using the & character to concatenate:
=IF(A2<0,"I owe boss " & ABS(A2) & " Hours","Boss owes me " & ABS(A2)*15 & " dollars")
Or the second method is to use the CONCATENATE function:
=IF(A2<0,CONCATENATE("I owe boss ", ABS(A2)," Hours"), CONCATENATE("Boss owes me ", ABS(A2)*15, " dollars"))
Question:I have Excel 2000. IF cell A2 is greater than or equal to 0 then add to C1. IF cell B2 is greater than or equal to 0 then subtract from C1. IF both A2 and B2 are blank then equals C1. Can you help me with the IF function on this one?
Answer: You can write a nested IF statement that uses the AND function and the ISBLANK function as follows:
=IF(AND(ISBLANK(A2)=FALSE,A2>=0),C1+A2, IF(AND(ISBLANK(B2)=FALSE,B2>=0),C1-B2, IF(AND(ISBLANK(A2)=TRUE, ISBLANK(B2)=TRUE),C1,"")))
Question:How would I write this equation in Excel? IF D12<=0 then D12*L12, IF D12 is > 0 but <=600 then D12*F12, IF D12 is >600 then ((600*F12)+((D12-600)*E12))
Answer: You can write a nested IF statement as follows:
=IF(D12<=0,D12*L12,IF(D12>600,((600*F12)+((D12-600)*E12)),D12*F12))
Question:In Excel, I have this formula currently:
=IF(OR(A1>=40, B1>=40, C1>=40), "20", (A1+B1+C1)-20)
If one of my salesman does sale for $40-$49, then his commission is $20; however if his/her sale is less (for example $35) then the commission is that amount minus $20 ($35-$20=$15). I have 3 columns that are needed based on the type of sale. Only one column per row will be needed. The problem is that, when left blank, the total in the formula cell is -20. I need help setting up this formula so that when the 3 columns are left blank, the cell with the formula is left blank as well.
Answer: Using the AND function and the ISBLANK function, you can write your IF statement as follows:
=IF(AND(ISBLANK(A1),ISBLANK(B1),ISBLANK(C1)),"",IF(OR(A1>40, B1>40, C1>40), "20", (A1+B1+C1)-20))
In this formula, we are using the ISBLANK function to check if all 3 cells A1, B1, and C1 are blank, and if they are return a blank value («»). Then the rest is the formula that you originally wrote.
Question:In Excel, I need to create a simple booking and and out system, that shows a date out and a date back
«A1» = allows person to input date booked out
«A2» =allows person to input date booked back in
«A3″= shows status of product, eg, booked out, overdue return etc.
I can automate A3 with the following IF function:
=IF(ISBLANK(A2),"booked out","returned")
But what I cant get to work is if the product is out for 10 days or more, I would like the cell to say «send email»
Can you assist?
Answer: Using the TODAY function and adding an additional IF function, you can write your formula as follows:
=IF(ISBLANK(A2),IF(TODAY()-A1>10,"send email","booked out"),"returned")
Question:Using Microsoft Excel, I need a formula in cell U2 that does the following:
IF the date in E2<=12/31/2010, return T2*0.75
IF the date in E2>12/31/2010 but <=12/31/2011, return T2*0.5
IF the date in E2>12/31/2011, return T2*0
I tried using the following formula, but it gives me «#VALUE!»
=IF(E2<=DATE(2010,12,31),T2*0.75), IF(AND(E2>DATE(2010,12,31),E2<=DATE(2011,12,31)),T2*0.5,T2*0)
Can someone please help? Thanks.
Answer: You were very close…you just need to adjust your parentheses as follows:
=IF(E2<=DATE(2010,12,31),T2*0.75, IF(AND(E2>DATE(2010,12,31),E2<=DATE(2011,12,31)),T2*0.5,T2*0))
Question:In Excel, I would like to add 60 days if grade is ‘A’, 45 days if grade is ‘B’ and 30 days if grade is ‘C’. It would roughly look something like this, but I’m struggling with commas, brackets, etc.
(IF C5=A)=DATE(YEAR(B5)+0,MONTH(B5)+0,DAY(B5)+60),
(IF C5=B)=DATE(YEAR(B5)+0,MONTH(B5)+0,DAY(B5)+45),
(IF C5=C)=DATE(YEAR(B5)+0,MONTH(B5)+0,DAY(B5)+30)
Answer:You should be able to achieve your date calculations with the following formula:
=IF(C5="A",B5+60,IF(C5="B",B5+45,IF(C5="C",B5+30)))
Question:In Excel, I am trying to write a function and can’t seem to figure it out. Could you help?
IF D3 is < 31, then 1.51
IF D3 is between 31-90, then 3.40
IF D3 is between 91-120, then 4.60
IF D3 is > 121, then 5.44
Answer:You can write your formula as follows:
=IF(D3>121,5.44,IF(D3>=91,4.6,IF(D3>=31,3.4,1.51)))
Question:I would like ask a question regarding the IF statement. How would I write in Excel this problem?
I have to check if cell A1 is empty and if not, check if the value is less than equal to 5. Then multiply the amount entered in cell A1 by .60. The answer will be displayed on Cell A2.
Answer:You can write your formula in cell A2 using the IF function and ISBLANK function as follows:
=IF(AND(ISBLANK(A1)=FALSE,A1<=5),A1*0.6,"")
Question:In Excel, I’m trying to nest an OR command and I can’t find the proper way to write it. I want the spreadsheet to do the following:
If D6 equals «HOUSE» and C6 equals either «MOUSE» or «CAT», I want to return the value in cell B6. Otherwise, the formula should return the value «BLANK».
I tried the following:
=IF((D6="HOUSE")*(C6="MOUSE")*OR(C6="CAT"));B6;"BLANK")
If I only ask for HOUSE and MOUSE or HOUSE and CAT, it works, but as soon as I ask for MOUSE OR CAT, it doesn’t work.
Answer:You can write your formula using the AND function and OR function as follows:
=IF(AND(D6="HOUSE",OR(C6="MOUSE",C6="CAT")),B6,"BLANK")
This will return the value in B6 if D6 equals «HOUSE» and C6 equals either «MOUSE» or «CAT». If those conditions are not met, the formula will return the text value of «BLANK».
Question:In Microsoft Excel, I’m trying to write the following formula:
If cell A1 equals «jaipur», «udaipur» or «jodhpur», then cell A2 should display «rajasthan»
If cell A1 equals «bangalore», «mysore» or «belgum», then cell A2 should display «karnataka»
Please help.
Answer:You can write your formula using the OR function as follows:
=IF(OR(A1="jaipur",A1="udaipur",A1="jodhpur"),"rajasthan", IF(OR(A1="bangalore",A1="mysore",A1="belgum"),"karnataka"))
This will return «rajasthan» if A1 equals either «jaipur», «udaipur» or «jodhpur» and it will return «karnataka» if A1 equals either «bangalore», «mysore» or «belgum».
Question:In Microsoft Excel I’m trying to achieve the following with IF function:
If a value in any cell in column F is «food» then add the value of its corresponding cell in column G (eg a corresponding cell for F3 is G3). The IF function is performed in another cell altogether. I can do it for a single pair of cells but I don’t know how to do it for an entire column. Could you help?
At the moment, I’ve got this:
=IF(F3="food"; G3; 0)
Answer:This formula can be created using the SUMIF formula instead of using the IF function:
=SUMIF(F1:F10,"=food",G1:G10)
This will evaluate the first 10 rows of data in your spreadsheet. You may need to adjust the ranges accordingly.
I notice that you separate your parameters with semi-colons, so you might need to replace the commas in the formula above with semi-colons.
Question:I’m looking for an Exel formula that says:
If F3 is «H» and E3 is «H», return 1
If F3 is «A» and E3 is «A», return 2
If F3 is «d» and E3 is «d», return 3
Appreciate if you can help.
Answer:This Excel formula can be created using the AND formula in combination with the IF function:
=IF(AND(F3="H",E3="H"),1,IF(AND(F3="A",E3="A"),2,IF(AND(F3="d",E3="d"),3,"")))
We’ve defaulted the formula to return a blank if none of the conditions above are met.
Question:I am trying to get Excel to check different boxes and check if there is text/numbers listed in the cells and then spit out «Complete» if all 5 Boxes have text/Numbers or «Not Complete» if one or more is empty. This is what I have so far and it doesn’t work.
=IF(OR(ISBLANK(J2),ISBLANK(M2),ISBLANK(R2),ISBLANK (AA2),ISBLANK (AB2)),"Not Complete","")
Answer:First, you are correct in using the ISBLANK function, however, you have a space between ISBLANK and (AA2), as well as ISBLANK and (AB2). This might seem insignificant, but Excel can be very picky and will return a #NAME? error. So first you need to eliminate those spaces.
Next, you need to change the ELSE condition of your IF function to return «Complete».
You should be able to modify your formula as follows:
=IF(OR(ISBLANK(J2),ISBLANK(M2),ISBLANK(R2),ISBLANK(AA2),ISBLANK(AB2)), "Not Complete", "Complete")
Now if any of the cell J2, M2, R2, AA2, or AB2 are blank, the formula will return «Not Complete». If all 5 cells have a value, the formula will return «Complete».
Question:I’m very new to the Excel world, and I’m trying to figure out how to set up the proper formula for an If/then cell.
What I’m trying for is:
If B2’s value is 1 to 5, then multiply E2 by .77
If B2’s value is 6 to 10, then multiply E2 by .735
If B2’s value is 11 to 19, then multiply E2 by .7
If B2’s value is 20 to 29, then multiply E2 by .675
If B2’s value is 30 to 39, then multiply E2 by .65
I’ve tried a few different things thinking I was on the right track based on the IF, and AND function tutorials here, but I can’t seem to get it right.
Answer:To write your IF formula, you need to nest multiple IF functions together in combination with the AND function.
The following formula should work for what you are trying to do:
=IF(AND(B2>=1, B2<=5), E2*0.77, IF(AND(B2>=6, B2<=10), E2*0.735, IF(AND(B2>=11, B2<=19), E2*0.7, IF(AND(B2>=20, B2<=29), E2*0.675, IF(AND(B2>=30, B2<=39), E2*0.65,"")))))
As one final component of your formula, you need to decide what to do when none of the conditions are met. In this example, we have returned «» when the value in B2 does not meet any of the IF conditions above.
Question:Here is the Excel formula that has me between a rock and a hard place.
If E45 <= 50, return 44.55
If E45 > 50 and E45 < 100, return 42
If E45 >=200, return 39.6
Again thank you very much.
Answer:You should be able to write this Excel formula using a combination of the IF function and the AND function.
The following formula should work:
=IF(E45<=50, 44.55, IF(AND(E45>50, E45<100), 42, IF(E45>=200, 39.6, "")))
Please note that if none of the conditions are met, the Excel formula will return «» as the result.
Question:I have a nesting OR function problem:
My nonworking formula is:
=IF(C9=1,K9/J7,IF(C9=2,K9/J7,IF(C9=3,K9/L7,IF(C9=4,0,K9/N7))))
In Cell C9, I can have an input of 1, 2, 3, 4 or 0. The problem is on how to write the «or» condition when a «4 or 0» exists in Column C. If the «4 or 0» conditions exists in Column C I want Column K divided by Column N and the answer to be placed in Column M and associated row
Answer:You should be able to use the OR function within your IF function to test for C9=4 OR C9=0 as follows:
=IF(C9=1,K9/J7,IF(C9=2,K9/J7,IF(C9=3,K9/L7,IF(OR(C9=4,C9=0),K9/N7))))
This formula will return K9/N7 if cell C9 is either 4 or 0.
Question:In Excel, I am trying to create a formula that will show the following:
If column B = Ross and column C = 8 then in cell AB of that row I want it to show 2013, If column B = Block and column C = 9 then in cell AB of that row I want it to show 2012.
Answer:You can create your Excel formula using nested IF functions with the AND function.
=IF(AND(B1="Ross",C1=8),2013,IF(AND(B1="Block",C1=9),2012,""))
This formula will return 2013 as a numeric value if B1 is «Ross» and C1 is 8, or 2012 as a numeric value if B1 is «Block» and C1 is 9. Otherwise, it will return blank, as denoted by «».
Question:In Excel, I really have a problem looking for the right formula to express the following:
If B1=0, C1 is equal to A1/2
If B1=1, C1 is equal to A1/2 times 20%
If D1=1, C1 is equal to A1/2-5
I’ve been trying to look for any same expressions in your site. Please help me fix this.
Answer:In cell C1, you can use the following Excel formula with 3 nested IF functions:
=IF(B1=0,A1/2, IF(B1=1,(A1/2)*0.2, IF(D1=1,(A1/2)-5,"")))
Please note that if none of the conditions are met, the Excel formula will return «» as the result.
Question:In Excel, I need the answer for an IF THEN statement which compares column A and B and has an «OR condition» for column C. My problem is I want column D to return yes if A1 and B1 are >=3 or C1 is >=1.
Answer:You can create your Excel IF formula as follows:
=IF(OR(AND(A1>=3,B1>=3),C1>=1),"yes","")
Please note that if none of the conditions are met, the Excel formula will return «» as the result.
Question:In Excel, what have I done wrong with this formula?
=IF(OR(ISBLANK(C9),ISBLANK(B9)),"",IF(ISBLANK(C9),D9-TODAY(), "Reactivated"))
I want to make an event that if B9 and C9 is empty, the value would be empty. If only C9 is empty, then the output would be the remaining days left between the two dates, and if the two cells are not empty, the output should be the string ‘Reactivated’.
The problem with this code is that IF(ISBLANK(C9),D9-TODAY() is not working.
Answer:First of all, you might want to replace your OR function with the AND function, so that your Excel IF formula looks like this:
=IF(AND(ISBLANK(C9),ISBLANK(B9)),"",IF(ISBLANK(C9),D9-TODAY(),"Reactivated"))
Next, make sure that you don’t have any abnormal formatting in the cell that contains the results. To be safe, right click on the cell that contains the formula and choose Format Cells from the popup menu. When the Format Cells window appears, select the Number tab. Choose General as the format and click on the OK button.
Question:I was wondering if you could tell me what I am doing wrong.
Here are the instructions:
A customer is eligible for a discount if the customer’s 2016 sales greater than or equal to 100000 OR if the customers First Order was placed in 2016.
If the customer qualifies for a discount, return a value of Y
If the customer does not qualify for a discount, return a value of N.
Here is the formula I’ve entered:
=IF(OR([2014 Sales]=0,[2015 Sales]=0,[2016 Sales]>=100000),"Y","N")
I only have 2 cells wrong. Can you help me please? I am very lost and confused.
Answer:You are very close with your IF formula, however, it looks like you need to add the AND function to your formula as follows:
=IF(OR([2016 Sales]>=100000,AND([2014 Sales]=0,[2015 Sales]=0),C8>=100000),"Y","N")
This formula should return Y if 2016 sales are greater than or equal to 100000, or if both 2014 sales and 2015 sales are 0. Otherwise, the formula will return N. You will also notice that we switched the order of your conditions in the formula so that it is easier to understand the formula based on your instructions above.
Question:Could you please help me? I need to use «OR» on my formula but I can’t get it to work. This is what I’ve tried:
=IF(C6>=0<=150,150000,IF(C6>=151<=160,158400))
Here is what I need the formula to do:
IF C6 IS >=0 OR <=150 THEN ASSIGN $150000
IF C6 IS >=151 OR <=160 THEN ASSIGN $158400
Answer:You should be able to use the AND function within your IF function as follows:
=IF(AND(ISBLANK(C6)=FALSE,C6>=0,C6<=150),150000,IF(AND(C6>=151,C6<=160),158400,""))
Notice that we first use the ISBLANK function to test C6 to make sure that it is not blank. This is because if C6 if blank, it will evalulate to greater than 0 and thus return 150000. To avoid this, we include ISBLANK(C6)=FALSE as one of the conditions in addition to C6>=0 and C6<=150. That way, you won’t return any false results if C6 is blank.
Question:I am having a problem with a formula, I want it to be IF E5=N then do the first formula, else do the second formula. Excel recognizes the =IF(logical_test,value_if_TRUE,value_if_FALSE) but doesn’t like the formula below:
=IF(e5="N",((AND(AH5-AG5<456, AH5-S5<822)), "Compliant", "not Compliant"),((AH5-S5<822), "Compliant", "not Compliant"))
Any help would be greatly appreciated.
Answer:To have the first formula executed when E5=N and then second formula executed when E5<>N, you will need to nest 2 additional IF functions within the main IF function as follows:
=IF(E5="N", IF((AND(AH5-AG5<456, AH5-S5<822)), "Compliant", "not Compliant"), IF((AH5-S5<822), "Compliant", "not Compliant"))
If E5=»N», the first nested IF function will be executed:
IF((AND(AH5-AG5<456, AH5-S5<822)), "Compliant", "not Compliant")
Otherwise,the second nested IF function will be executed:
IF((AH5-S5<822), "Compliant", "not Compliant"))
Question:I need to write a formula based on the following logic:
There is a maximum discount allowed of £1000 if the capital sum is less that £43000 and a lower discount of £500 if the capital sum is above £43000. So the formula should return either £500 or £1000 in the cell but the £43000 is made up of two numbers, say for e.g. £42750+350 and if the second number is less than the allowed discount, the actual lower value is returned — in this case the £500 or £1000 becomes £350. Or as another e.g. £42000+750 returns £750.
So on my spreadsheet, in this second e.g. I would have A1= £42000, A2=750, A3=A1+A2, A4=the formula with the changing discount, in this case £750.
How can I write this formula?
Answer:In cell A4, you can calculate the correct discount using the IF function and the MIN function as follows:
=IF(A3<43000, MIN(A2,1000), MIN(A2,500))
If A3 is less than 43000, the formula will return the lower value of A2 and 1000. Otherwise, it will return the lower value of A2 and 500.
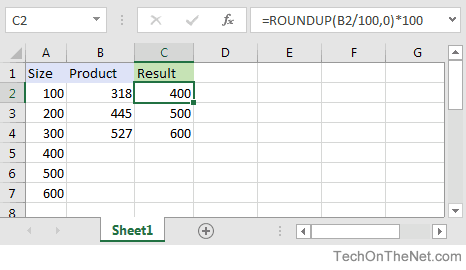
Question: I have a list of sizes in column A with sizes 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600. Then I have another column B, with sizes of my products, and it is random, for example, 318, 445, 527. What I’m trying to create is for a value of 318 in column B, I need to return 400 for that product. If the value in column B is 445, then I should return 500 and so on, as long sizes in column A must be BIGGER to the NEAREST size to column B.
Any idea how to create this function?
Answer:If your sizes are in increments of 100, you can create this function by taking the value in column B, dividing by 100, rounding up to the nearest integer, and then multiplying by 100.
For example in cell C2, you can use the IF function and the ROUNDUP function as follows:
=ROUNDUP(B2/100,0)*100
This will return the correct value of 400 for a value of 318 in cell B2. Just copy this formula to cell C3, C4 and so on.
What is the Excel IF Function?
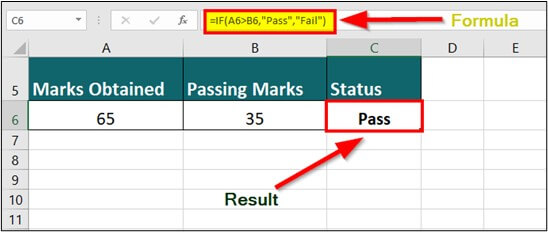
The IF() function is a logical function in Excel that evaluates a specific condition and provides a certain value if the condition is True and another value if it’s False.
For example, the formula =IF(A6>B6,”Pass”,”Fail”) displays the output as Pass if the marks obtained (A6) is greater than the passing marks (B6) otherwise displays the output as Fail.
The Excel IF function is found in Excel’s Logical functions library. We can use the function to perform data analysis, calculate salaries, prepare student academic reports, etc.
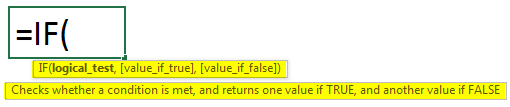
Excel IF Function Syntax
The syntax for the IF function is-
Explanation:
- Logical_test: Test/ compare values using logical operators
- Value_if_true: Value to be returned if the condition is satisfied
- Value_if_false: Value to be returned if the condition is not satisfied
Key Highlights
- The operators in the logical_test argument of the IF function may be:
= Equals to
<> Not Equals to
> Greater than
>= Greater than or equal to
< Less than
<= Less than or equal to
- Every conditional test must contain at least one comparison operator.
- The IF function allows Excel spreadsheets to make decisions when analyzing data.
- The IF function can have more than one logical test in one formula.
How to Use Excel IF Function?
You can download this Excel IF Function Template here – Excel IF Function Template
To understand the use of the IF function in Excel consider the below-given example.
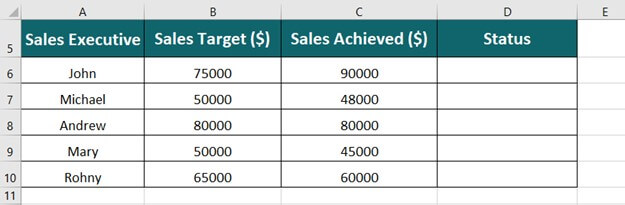
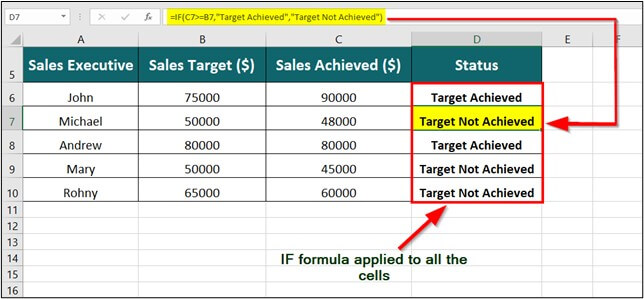
The table below shows the sales achieved by five sales representatives along with their monthly target. We want to find who has achieved the target and who has not achieved the target using the Excel IF function.
Solution:
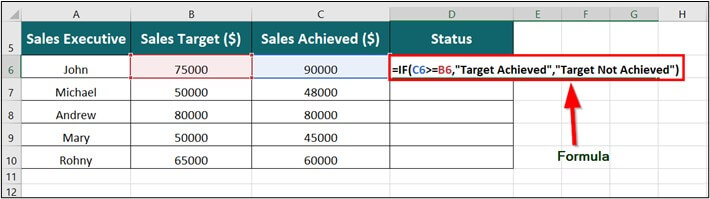
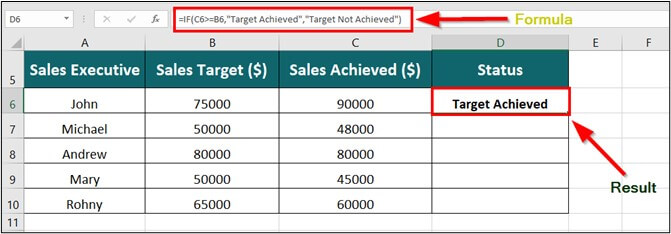
Step 1: Place the cursor in cell D6 and enter the formula,
=IF(C6>=B6,”Target Achieved”, “Target Not Achieved”)
Explanation:
- C6>=B6: It represents the criteria that if the Sales Achieved is greater than or equal to the SalesTarget then display the corresponding result.
- “Target Achieved”: It is the output to display when the given criteria are met.
- “Target Not Achieved”: It is the output to display when the given criteria are not met.
Step 2: Press Enter key to get the below result
The IF function analyzes and finds that Sales Achieved (90000) is greater than the Sales Target (75000) and displays the output Target Achieved.
Now, to get the status of the remaining Sales representatives,
Step 3: Drag the formula into the other cells
In the above table, the sales achieved by Michael i.e., 48000 (C7) not greater than or equal to the sales target i.e., 50000 (B7) which means the given criteria are not met. Therefore, the IF function displays the status of Micheal as Target Not Achieved (highlighted in yellow).
Nested IF Statements
When there is more than one IF function in a formula to test certain conditions it is known as a Nested IF statement. We can use Nested IF statements (formulas) to test more than one condition which gives more than one possible result. To understand the use and working of the Nested IF functions consider the below example.
Example #1
The below table shows the marks, total marks, and the percentage of five students in the subjects- English, Science, History, and Geography. We want to evaluate the student’s respective grades based on their percentages using the Nested IF function.
Solution:
Step 1: Place the cursor in cell H6 and enter the formula,
=IF(G6>=80,”A”,IF(G6>=70,”B”,IF(G6>=60,”C”)))
Note: In the above table there are three IF functions in one formula, therefore, it is known as a Nested IF statement.
Explanation:
The formula states that:
- If the percentage (G6) is greater than or equal to 80, then display the grade as A.
- If the percentage (G6) is greater than or equal to 70, then display the grade as B.
- If the percentage (G6) is greater than or equal to 60, then display the grade as C.
Step 2: Press Enter key to get the below result
Explanation:
The percentage obtained by Ashu is greater than 70. Therefore, the IF function displays the output as B.
Now, to evaluate the grade obtained by other students
Step 3: Drag the formula to other cells
Example #2
The table below shows a list of customers with the number of items they purchased and the total bill for each of them. The customers are offered a 10% discount on their purchase if the total bill is more than or equal to $5000. We want to find out which customers are eligible for the discount using the Excel IF function.
Solution:
Step 1: Place the cursor in cell E6 and enter the formula,
=IF(C6>5000,”10%”,”0″)
Explanation:
- C6>5000: It is the criteria that indicate if the amount of the Total Bill (C6) is greater than 5000 then the customer is eligible for a discount.
- “10%”: It is the value to be displayed if the criteria are satisfied i.e., the eligible customer will get a 10% discount.
- “0”: It is the value to be displayed if the criteria are not satisfied i.e., the customer will not get a discount.
Note: A text in IF (or any other) formula must be enclosed in double quotation.
Step 2: Press Enter key to get the below result
The IF function evaluates the criteria and finds that the Total Bill of Jenny is greater than 5000. Therefore, it provides the result of 10% (discount).
Now, to find eligibility for other customers
Step 3: Drag the formula to other cells to get the below result
The IF function evaluates and finds that the Total Bill of Mary is not greater than 5000. Therefore, it provides the result of 0 (highlighted in yellow) which indicates Mary is not eligible for a discount.
Now, based on the Total Bill amount we want to categorize the customers as Premium, Gold, or Platinum using the Nested IF function.
Step 4: Place the cursor in cell F6 and enter the formula,
=IF(C6>=25000,”Platinum”,IF(C6>=15000,”Premium”,IF(C6>=4500,”Gold”)))
Explanation:
- C6>=25000, “Platinum”: It indicates that if the Total Bill (C6) is greater than or equal to 25000, then categorize the customer as Platinum.
- C6>=15000, “Premium”: It indicates that if the Total Bill (C6) is greater than or equal to 15000, then categorize the customer as Premium.
- C6>=4500, “Gold”: It indicates that if the Total Bill (C6) is greater than or equal to 4500, then categorize the customer as Gold.
Note: In the above example, the IF function is used thrice to evaluate three different criteria, therefore, it is known as Nested IF.
Step 5: Press Enter key to get the below result
The IF function evaluates the criteria and finds that the Total Bill (C6) amount of Jenny is equal to 25000. Therefore, it provides the result as Platinum.
Step 6: Drag the formula in other cells to get the below result.
Example #3
The below table shows the total budget amount and amount spent by a traveler on the expenses- Airfare, Hotel, Food, Fuel, and Shopping. We want to find out if he was Over Budget or In Budget using the Excel IF function.
Solution:
Step 1: Place the cursor in cell D6 and enter the formula,
=IF(C6>B6,”Over Budget”,”In Budget”)
Explanation:
- C6>B6: It is the criteria that indicate if the Amount Spent (C6) is greater than Budget Amount (B6) and then provides a certain result.
- “Over Budget”: It is the value to display if the given criteria are satisfied.
- “In Budget”: It is the value to display if the given criteria are not satisfied.
Step 2: Press Enter key to get the below result
The IF function provides the result of Over Budget (D6) because the Amount Spent (C6) is greater than the Budget Amount (B6) i.e., the criteria are satisfied.
Step 3: Drag the formula into other cells to find the status of other expenses
The IF function provides the status as In Budget (highlighted in yellow) for Fuel because the Amount Spent is less than the Budget Amount i.e., the criteria are not satisfied.
Things to Remember
- When we use Nested IF we can nest up to 64 IF functions using the Nested Formula.
- If we provide an array as any arguments in the IF formula, the function will evaluate each element of the array.
- If we use text values in the IF formula, we must enclose it with double quotes (e.g. “Pass”).
- We can combine the IF functions with logical functions like AND and OR to provide multiple criteria.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1) What is the importance of the IF function?
Answer: The IF function is a decision-making statement that guides Excel to make calculative decisions based on the given criteria. The Excel IF function executes one code if the given condition is satisfied or another code if the given condition is not satisfied.
Q2) What is the use of IF function in Excel?
Answer: The IF function can be used to perform a logical comparison between values and provide specific results depending on the condition to be True or False. In addition, we can also use the IF function to identify blank data cells within the Excel worksheet. To find the blank cells we can nest the ISBLANK function into the IF function. Identifying blank data cells can help prevent calculation errors by finding possible issues before doing the actual calculations.
Q3) What are the 3 parts of the IF function?
Answer: The 3 parts of the IF function are
- A logical test- To perform the logical comparison using an operator sign
- A value to return if the result of the logical test is TRUE;
- A value to return if the result of the logical test is FALSE.
Q4) How many IF functions are there?
Answer: We can nest up to 64 different Excel IF functions. However, maintaining multiple IF statements can be difficult, therefore, it is important to ensure that we nest the formula with 100% accuracy to give correct results.
Recommended Articles
The above article is a guide to the IF Function in Excel. To learn more about logic-based functions EDUCBA recommends the below-given articles.
- COUNTIF Excel Function
- Nested IF Formula in Excel
- VBA IF Statements
- SUMIF Formula in Excel
The IF function runs a logical test and returns one value for a TRUE result, and another value for a FALSE result. The result from IF can be a value, a cell reference, or even another formula. By combining the IF function with other logical functions like AND and OR, you can test more than one condition at a time.
Syntax
The generic syntax for the IF function looks like this:
=IF(logical_test,[value_if_true],[value_if_false])The first argument, logical_test, is typically an expression that returns either TRUE or FALSE. The second argument, value_if_true, is the value to return when logical_test is TRUE. The last argument, value_if_false, is the value to return when logical_test is FALSE. Both value_if_true and value_if_false are optional, but you must provide one or the other. For example, if cell A1 contains 80, then:
=IF(A1>75,TRUE) // returns TRUE
=IF(A1>75,"OK") // returns "OK"
=IF(A1>85,"OK") // returns FALSE
=IF(A1>75,10,0) // returns 10
=IF(A1>85,10,0) // returns 0
=IF(A1>75,"Yes","No") // returns "Yes"
=IF(A1>85,"Yes","No") // returns "No"Notice that text values like «OK», «Yes», «No», etc. must be enclosed in double quotes («»). However, numeric values should not be enclosed in quotes.
Logical tests
The IF function supports logical operators (>,<,<>,=) when creating logical tests. Most commonly, the logical_test in IF is a complete logical expression that will evaluate to TRUE or FALSE. The table below shows some common examples:
| Goal | Logical test |
|---|---|
| If A1 is greater than 75 | A1>75 |
| If A1 equals 100 | A1=100 |
| If A1 is less than or equal to 100 | A1<=100 |
| If A1 equals «Red» | A1=»red» |
| If A1 is not equal to «Red» | A1<>»red» |
| If A1 is less than B1 | A1<B1 |
| If A1 is empty | A1=»» |
| If A1 is not empty | A1<>»» |
| If A1 is less than current date | A1<TODAY() |
Notice text values must be enclosed in double quotes («»), but numbers do not. The IF function does not support wildcards, but you can combine IF with COUNTIF to get basic wildcard functionality. To test for substrings in a cell, you can use the IF function with the SEARCH function.
Pass or Fail example
In the worksheet shown above, we want to assign either «Pass» or «Fail» based on a test score. A passing score is 70 or higher. The formula in D6, copied down, is:
=IF(C5>=70,"Pass","Fail")
Translation: If the value in C5 is greater than or equal to 70, return «Pass». Otherwise, return «Fail».
Note that the logical flow of this formula can be reversed. This formula returns the same result:
=IF(C5<70,"Fail","Pass")
Translation: If the value in C5 is less than 70, return «Fail». Otherwise, return «Pass».
Both formulas above, when copied down, will return correct results.
Note: If you are new to the idea of formula criteria, this article explains many examples.
Assign points based on color
In the worksheet below, we want to assign points based on the color in column B. If the color is «red», the result should be 100. If the color is «blue», the result should be 125. This requires that we use a formula based on two IF functions, one nested inside the other. The formula in C5, copied down, is:
=IF(B5="red",100,IF(B5="blue",125))
Translation: IF the value in B5 is «red», return 100. Else, if the value in B5 is «blue», return 125.
There are three things to notice in this example:
- The formula will return FALSE if the value in B5 is anything except «red» or «blue»
- The text values «red» and «blue» must be enclosed in double quotes («»)
- The IF function is not case-sensitive and will match «red», «Red», «RED», or «rEd».
This is a simple example of a nested IFs formula. See below for a more complex example.
Return another formula
The IF function can return another formula as a result. For example, the formula below will return A1*5% when A1 is less than 100, and A1*7% when A1 is greater than or equal to 100:
=IF(A1<100,A1*5%,A1*7%)
Nested IF statements
The IF function can be «nested». A «nested IF» refers to a formula where at least one IF function is nested inside another in order to test for more conditions and return more possible results. Each IF statement needs to be carefully «nested» inside another so that the logic is correct. For example, the following formula can be used to assign a grade rather than a pass / fail result:
=IF(C6<70,"F",IF(C6<75,"D",IF(C6<85,"C",IF(C6<95,"B","A"))))
Up to 64 IF functions can be nested. However, in general, you should consider other functions, like VLOOKUP or XLOOKUP for more complex scenarios, because they can handle more conditions in a more streamlined fashion. For a more details see this article on nested IFs.
Note: the newer IFS function is designed to handle multiple conditions without nesting. However, a lookup function like VLOOKUP or XLOOKUP is usually a better approach unless the logic for each condition is custom.
IF with AND, OR, NOT
The IF function can be combined with the AND function and the OR function. For example, to return «OK» when A1 is between 7 and 10, you can use a formula like this:
=IF(AND(A1>7,A1<10),"OK","")
Translation: if A1 is greater than 7 and less than 10, return «OK». Otherwise, return nothing («»).
To return B1+10 when A1 is «red» or «blue» you can use the OR function like this:
=IF(OR(A1="red",A1="blue"),B1+10,B1)
Translation: if A1 is red or blue, return B1+10, otherwise return B1.
=IF(NOT(A1="red"),B1+10,B1)
Translation: if A1 is NOT red, return B1+10, otherwise return B1.
IF cell contains specific text
Because the IF function does not support wildcards, it is not obvious how to configure IF to check for a specific substring in a cell. A common approach is to combine the ISNUMBER function and the SEARCH function to create a logical test like this:
=ISNUMBER(SEARCH(substring,A1)) // returns TRUE or FALSEFor example, to check for the substring «xyz» in cell A1, you can use a formula like this:
=IF(ISNUMBER(SEARCH("xyz",A1)),"Yes","No")Read a detailed explanation here.
More information
- Read more about nested IFs
- Learn how to use VLOOKUP instead of nested IFs (video)
- 50 Examples of formula criteria
Notes
- The IF function is not case-sensitive.
- To count values conditionally, use the COUNTIF or the COUNTIFS functions.
- To sum values conditionally, use the SUMIF or the SUMIFS functions.
- If any of the arguments to IF are supplied as arrays, the IF function will evaluate every element of the array.