Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 More…Less
If you need a quick way to count rows that contain data, select all the cells in the first column of that data (it may not be column A). Just click the column header. The status bar, in the lower-right corner of your Excel window, will tell you the row count.
Do the same thing to count columns, but this time click the row selector at the left end of the row.
The status bar then displays a count, something like this:

If you select an entire row or column, Excel counts just the cells that contain data. If you select a block of cells, it counts the number of cells you selected. If the row or column you select contains only one cell with data, the status bar stays blank.
Notes:
-
If you need to count the characters in cells, see Count characters in cells.
-
If you want to know how many cells have data, see Use COUNTA to count cells that aren’t blank.
-
You can control the messages that appear in the status bar by right-clicking the status bar and clicking the item you want to see or remove. For more information, see Excel status bar options.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Need more help?
In this article, we will learn about how to Count table rows & columns in Excel.
In simple words, while working with large data in Excel we need to find the number of rows or columns in excel table.
The ROWS function in excel returns the number of rows in an array.
Syntax:
The COLUMNS function in excel returns the number of columns in an array.
Syntax:
Let’s understand this function using it in an example.
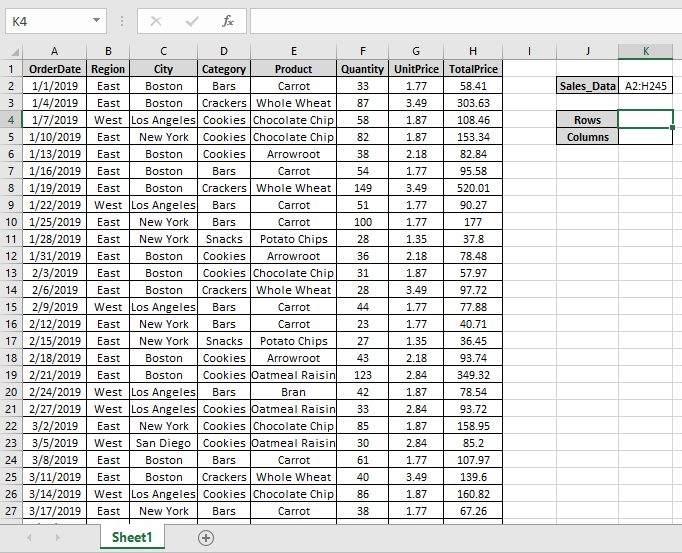
Here we have large data A2:H245 named Sales_Data
Here we need to find out the number of rows & columns of Sales_Data table in Excel.
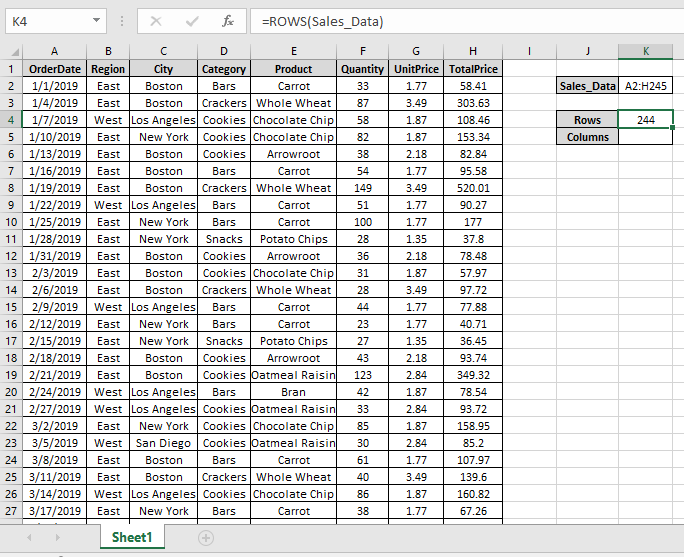
Use the formula to get the number of rows
A2:H245 : Sales_Data table as an array.
We got the number of rows of the Sales_Data.
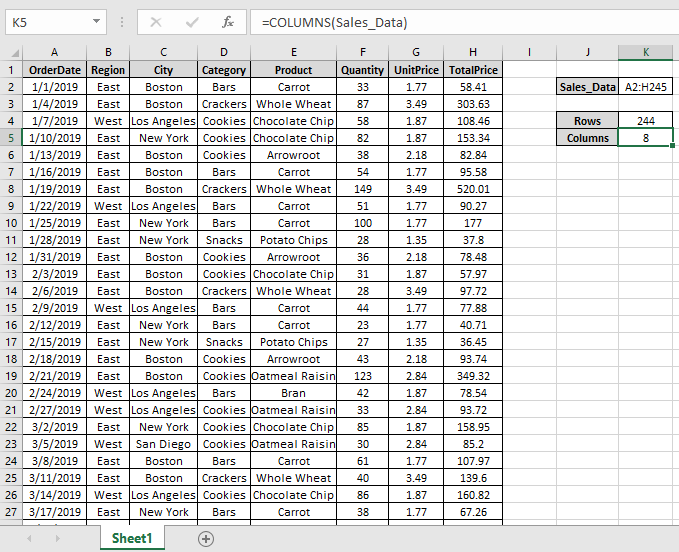
Use the formula to get the number of rows
A2:H245 : Sales_Data table as an array.
As you can see the ROWS & COLUMNS functions returns the number of rows & columns of table.
Hope you understood how to use ROWS function and COLUMNS function in Excel. Explore more articles on Excel cell info function functions here. Please feel free to state your query or feedback for the above article.
Related Articles :
How to use the CELL function in Excel
How to use the ROW function in Excel
How to use the COLUMN Function in Excel
Popular Articles :
50 Excel Shortcut to Increase Your Productivity : Get faster at your task. These 50 shortcuts will make you work even faster on Excel.
How to use the VLOOKUP Function in Excel : This is one of the most used and popular functions of excel that is used to lookup value from different ranges and sheets.
How to use the COUNTIF function in Excel : Count values with conditions using this amazing function. You don’t need to filter your data to count specific values. Countif function is essential to prepare your dashboard.
How to use the SUMIF Function in Excel : This is another dashboard essential function. This helps you sum up values on specific conditions.
How to Count the Number of Rows in Excel?
Here are the different ways of counting rows in Excel using the formula, rows with data, empty rows, rows with numerical values, rows with text values, and many other things related to counting the number of rows in Excel.
You can download this Count Rows Excel Template here – Count Rows Excel Template
Table of contents
- How to Count the Number of Rows in Excel?
- #1 – Excel Count Rows which has only the Data
- #2 – Count all the rows that have the data
- #3 – Count the rows that only have the numbers
- #4 – Count Rows, which only has the Blanks
- #5 – Count rows that only have text values
- #6 – Count all of the rows in the range
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
#1 – Excel Count Rows which has only the Data
Firstly, we will see how to count the number of rows in Excel with the data. There could be empty rows between the data, but we often need to ignore them and find exactly how many rows contain the data in it.
- We can count the number of rows with data by selecting the range of cells in Excel. For example, take a look at the below data.
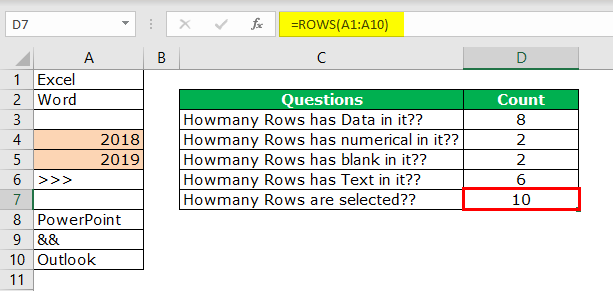
We have a total of 10 rows (border inserted area). In this 10 row, we want to count exactly how many cells have data. Since this is a small list of rows, we can easily calculate the number of rows. But when it comes to the huge database, it is impossible to count manually. So, this article will help you with this.
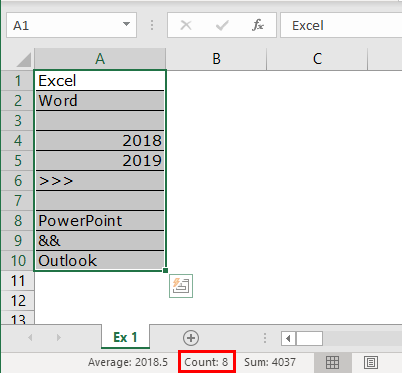
- Firstly, we must select all the rows in Excel.
- It is not telling us how many rows contain the data here. Instead, look at the Excel screen’s right-hand side bottom, i.e., a status bar.
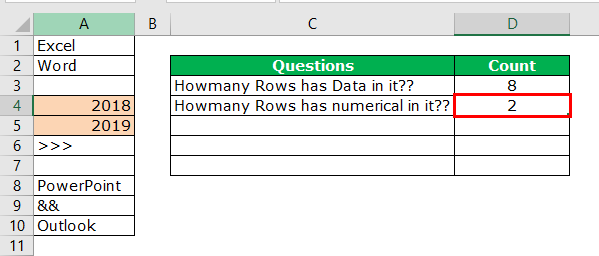
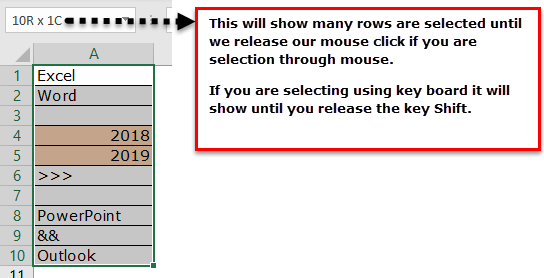
Take a look at the red circled area. It says COUNT as 8, which means that out of 10 selected rows, 8 have data.
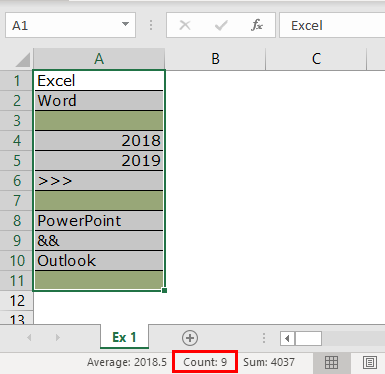
- Now, we will select one more row in the range and see what the count will be.
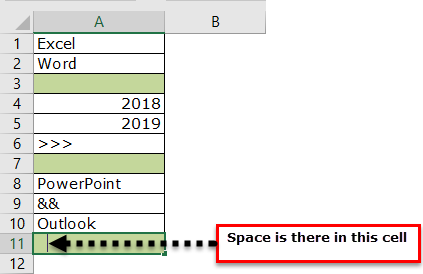
- We have selected 11 rows, but the count says 9, whereas we have data only in 8 rows. When we closely examine the cells, the 11th row contains a space.
Even though there is no value in the cell and it has only space Excel will be treated as the cell which contains the data.
#2 – Count all the rows that have the data
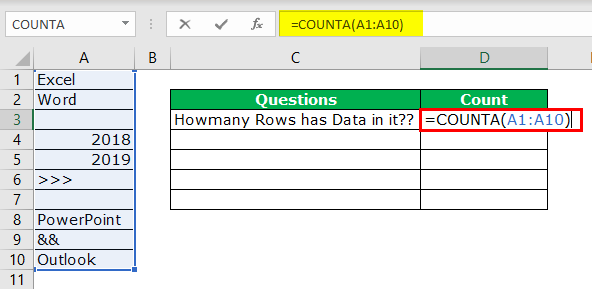
We know how to check how many rows contain the data quickly. But that is not the dynamic way of counting rows that have data. Instead, we need to apply the COUNTA function to count how many rows contain the data.
We will apply the COUNTA function in the D3 cell.
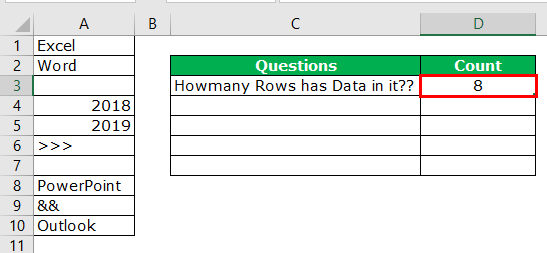
So, the total number of rows containing the data is 8 rows. Even this formula treats space as data.
#3 – Count the rows that only have the numbers
Here we want to count how many rows contain only numerical values.
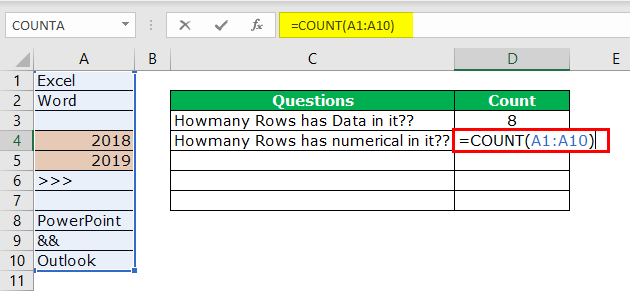
We can easily say 2 rows contain numerical values. Let us examine this by using a formula. We have a built-in formula called COUNT which counts only numerical values in the supplied range.
We will apply the COUNT function in cell B1 and select the range as A1 to A10.
The COUNT function also says 2 as a result. So, out of 10 rows, only rows contain numerical values.
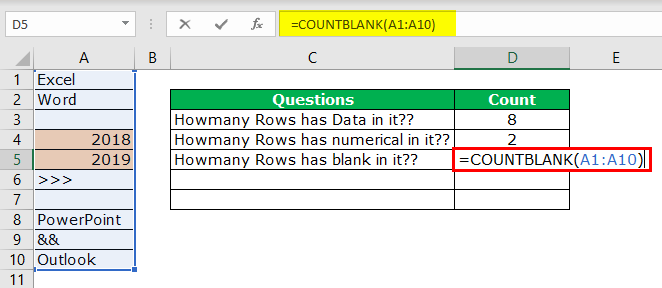
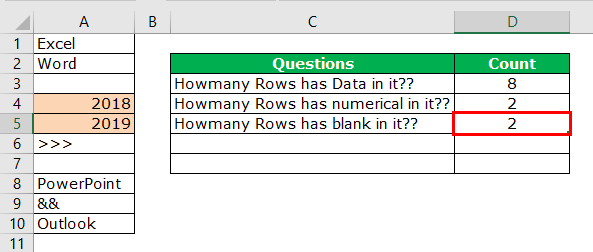
#4 – Count Rows, which only has the Blanks
We can find only blank rows by using the COUNTBLANK function in Excel.
We have 2 blank rows in the selected range, which are revealed by the count blank function.
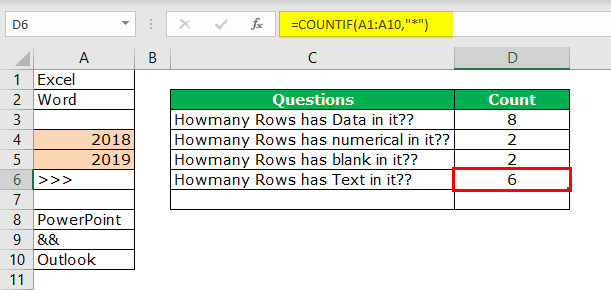
#5 – Count rows that only have text values
Remember, we do not have any straight in the COUNTTEXT function. Unlike in previous cases, we need to think differently here. We can use the COUNTIF functionThe COUNTIF function in Excel counts the number of cells within a range based on pre-defined criteria. It is used to count cells that include dates, numbers, or text. For example, COUNTIF(A1:A10,”Trump”) will count the number of cells within the range A1:A10 that contain the text “Trump”
read more with a wildcard character asterisk (*).
Here all the magic is done by the wildcard character asterisk (*). It matches any of the alphabets in the row and returns the result as a text value row. Even if the row contains numerical and text values, it will be treated as text value only.
#6 – Count all of the rows in the range
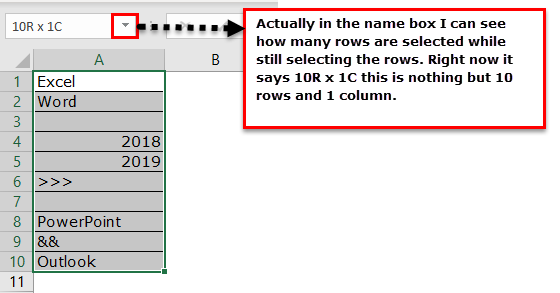
Now comes the important part. How do we count how many rows we have selected? One uses the Name Box in excel, which is limited while still choosing the rows. But how do we measure then?
We have a built-in ROWS formula, which returns how many rows are selected.
Things to Remember
- Even space is treated as a value in the cell.
- If the cell contains numerical and text values, it will be treated as a text value.
- ROW may return the current row we are in, but ROWS will return how many are in the supplied range even though there is no data in the rows.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to Count Rows in Excel. Here, we discuss the top 6 ways of counting rows in Excel using the formula: rows with data, empty rows, rows with numerical values, rows with text values, and many other things related to counting rows in Excel and practical examples and downloadable Excel templates. You may learn more about Excel from the following articles: –
- VBA COUNTIF
- Add Multiple Rows in Excel
- Excel Count Formula
- How to Insert Multiple Rows in Excel?
Excel Row Count (Table of Contents)
- Introduction to Row Count in Excel
- How to Count the Rows in Excel?
Introduction to Row Count in Excel
Excel provides many built-in functions through which we can do multiple calculations. We can also count the rows and columns in Excel. Here in this article, we will discuss the Row Count in Excel. If we want to measure the rows which contain data, select all the cells of the first column by clicking on the column header. It will display the row count on the status bar in the lower right corner.
Let’s take some values in the Excel sheet.
Select the entire column which contains data. Now click on the column label for counting the rows; it will show you the row count. Refer to the below screenshot:
There are two types of functions for counting the rows.
- ROW()
- ROWS()
The ROW() function gives you the row number of a particular cell.
The ROWS() function gives you the count of rows in a range.
How to Count the Rows in Excel?
Let’s take some examples to understand the usage of ROWS functions.
You can download this Row Count Excel Template here – Row Count Excel Template
Example #1
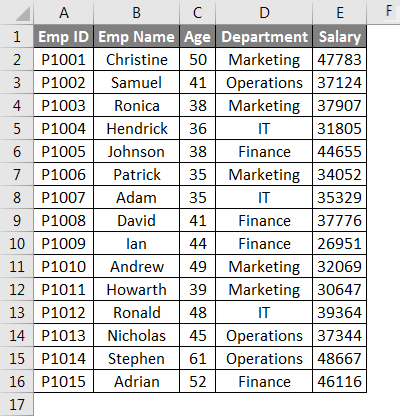
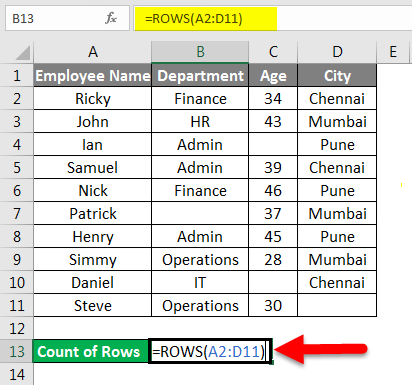
We have given the below employee data.
For counting the rows here, we will use the below function here:
=ROWS(range)
Where range = a range of cells containing data.
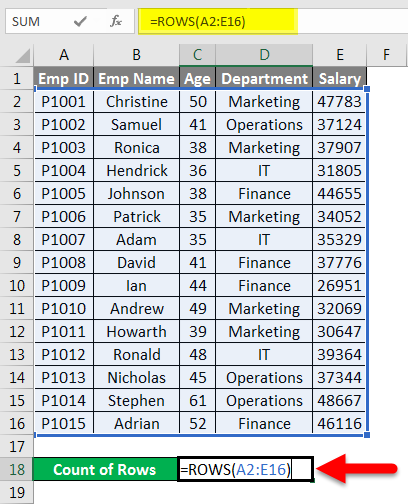
Now we will apply the above function like the below screenshot:
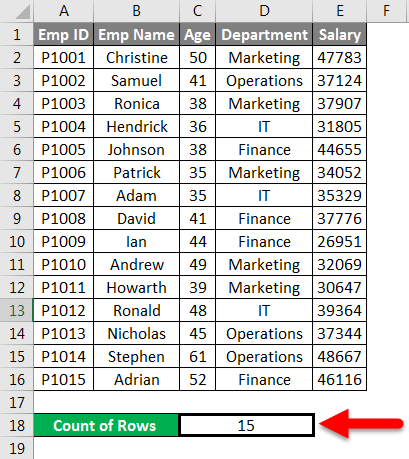
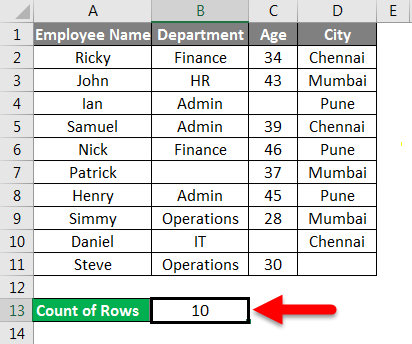
Which returns the number of rows containing the data in the supplied range.
The final result is given below:
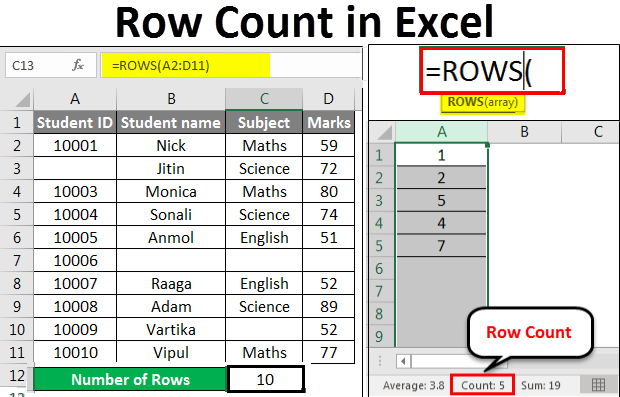
Example #2
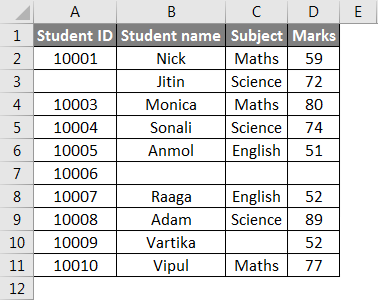
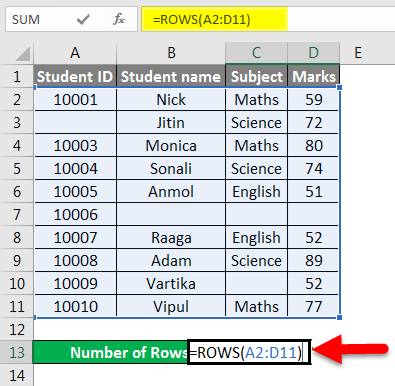
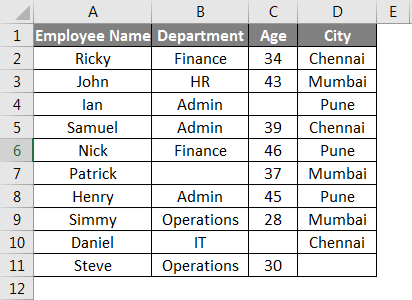
We have given below some student marks subject-wise.
As we can see in the above dataset, certain information is absent.
As per the screenshot below, we will apply the ROWS function for counting the rows containing data.
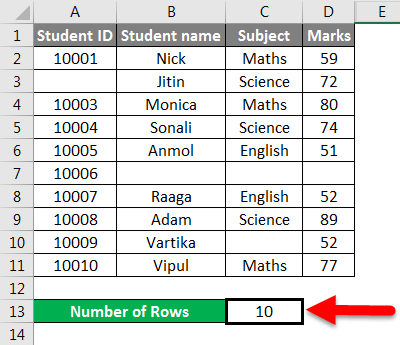
The final result is given below:
Example #3
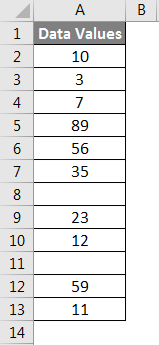
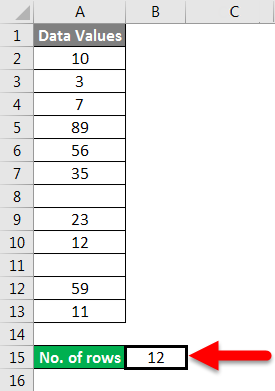
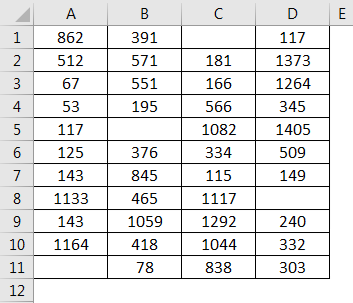
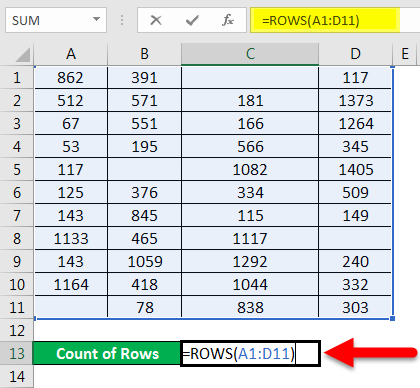
We have given the below data values.
We will pass the range of data values within the function for counting the number of rows.
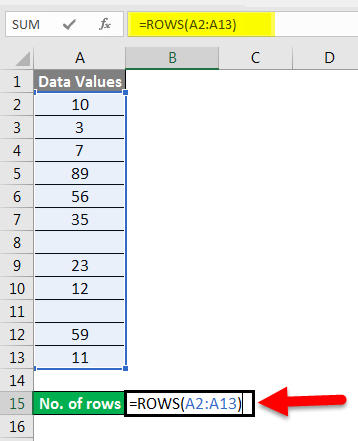
Apply the function like the below screenshot:
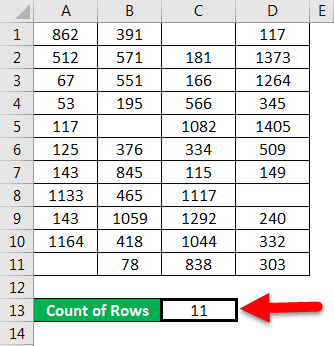
Press ENTER key here, and it will return the count of rows.
The final result is shown below:
Explanation:
When we pass the range of cells, it gives you the count of cells you selected.
Example #4
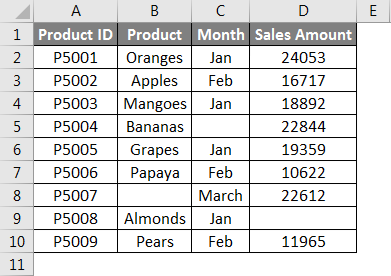
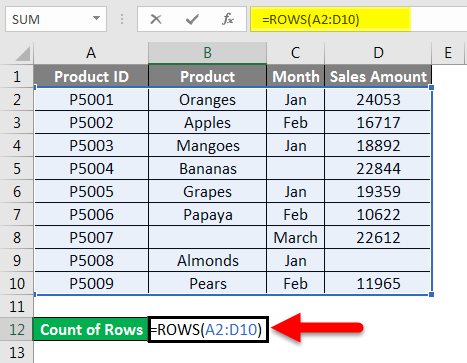
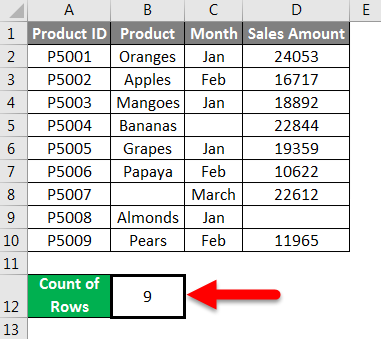
We have given below product details:
Now we will pass the range of the given dataset within the function like the below screenshot:
Press ENTER key, which will give you the count of rows containing data in the passing range.
The final result is given below:
Example #5
We have given some raw data.
Some cell values are missing here, so now, for counting the rows, we will apply the function shown in the below screenshot:
Hit the Enter key, and it will return the count of rows having data.
The final result is given below:
Example #6
We have given a company employee data where some details are missing:
Now apply the ROWS function to count the row containing data of employees:
Hit the Enter key to get the final rows
Things to Remember About Row Count in Excel
- When you click on the column heading for counting the rows, it will give you the count which contains data.
- If you pass a range of cells, it will return the number of cells that you have selected.
- The status bar won’t show you anything if the column contains the data only in one cell. That is, the status bar stays blank.
- If the data are given in the table form, then for counting the rows, you can pass the table range within the ROWS function.
- You can also do the setting of the message in the status bar. Do right-click on the status bar and click the item you want to see or remove.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to Row Count in Excel. Here we discussed How to Count the Rows, practical examples, and a downloadable Excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles–
- COUNTA Function in Excel
- Count Function in Excel
- ROWS Function in Excel
- Add Rows in Excel Shortcut