Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel for Mac 2011 More…Less
This article describes the formula syntax and usage of the DAYS function in Microsoft Excel. For information about the DAY function, see DAY function.
Description
Returns the number of days between two dates.
Syntax
DAYS(end_date, start_date)
The DAYS function syntax has the following arguments.
-
End_date Required. Start_date and End_date are the two dates between which you want to know the number of days.
-
Start_date
Required. Start_date and End_date are the two dates between which you want to know the number of days.
Note: Excel stores dates as sequential serial numbers so that they can be used in calculations. By default, Jan 1, 1900 is serial number 1, and January 1, 2008 is serial number 39448 because it is 39447 days after January 1, 1900.
Remarks
-
If both date arguments are numbers, DAYS uses EndDate–StartDate to calculate the number of days in between both dates.
-
If either one of the date arguments is text, that argument is treated as DATEVALUE(date_text) and returns an integer date instead of a time component.
-
If date arguments are numeric values that fall outside the range of valid dates, DAYS returns the #NUM! error value.
-
If date arguments are strings that cannot be parsed as valid dates, DAYS returns the #VALUE! error value.
Example
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter. If you need to, you can adjust the column widths to see all the data.
|
Data |
||
|---|---|---|
|
31-DEC-2021 |
||
|
1-JAN-2021 |
||
|
Formula |
Description |
Result |
|
=DAYS(«15-MAR-2021″,»1-FEB-2021») |
Finds the number of days between the end date (15-MAR-2021) and start date (1-FEB-2021). When you enter a date directly in the function, you need to enclose it in quotation marks. Result is 42. |
42 |
|
=DAYS(A2,A3) |
Finds the number of days between the end date in A2 and the start date in A3 (364). |
364 |
Top of Page
Need more help?
Summary
The Excel DAYS function returns the number of days between two dates. With a start date in A1 and end date in B1, =DAYS(B1,A1) will return the days between the two dates.
Purpose
Return value
A number representing days.
Arguments
- end_date — The end date.
- start_date — The start date.
Syntax
=DAYS(end_date, start_date)
Usage notes
The DAYS function returns the number of days between two dates. Both dates must be valid Excel dates or text values that can be coerced to dates. The DAYS function only works with whole numbers, fractional time values that might be part of a date are ignored. If start and end dates are reversed, DAYS returns a negative number. The DAYS function returns all days between two dates, to calculate working days between dates, see the NETWORKDAYS function.
Examples
With a start date in A1 and end date in A2:
=DAYS(A2,A1)
Will return the same result as:
=A2-A1
Unlike the simple formula above, the DAYS function can also handle dates in text format, as long as the date is recognized by Excel. For example:
=DAYS("7/15/2016","7/1/2016") // returns 14
The DAYS function returns the number of days between two dates. For example:
=DAYS("1-Mar-21","2-Mar-21") // returns 1
To include the end date in the count, add 1 to the result:
=DAYS("1-Mar-21","2-Mar-21")+1 // returns 2
Storing and parsing text values that represent dates should be avoided, because it can introduce errors and parsing problems. Working with native Excel dates (which are numbers) is a better approach. To create a numeric date from scratch in a formula, use the DATE function.
Notes
- The DAYS function only works with whole numbers and ignores time.
- If dates are not recognized, DAYS returns the #VALUE! error.
- If dates are out of range, DAYS returns the #NUM! error.
Author
Dave Bruns
Hi — I’m Dave Bruns, and I run Exceljet with my wife, Lisa. Our goal is to help you work faster in Excel. We create short videos, and clear examples of formulas, functions, pivot tables, conditional formatting, and charts.
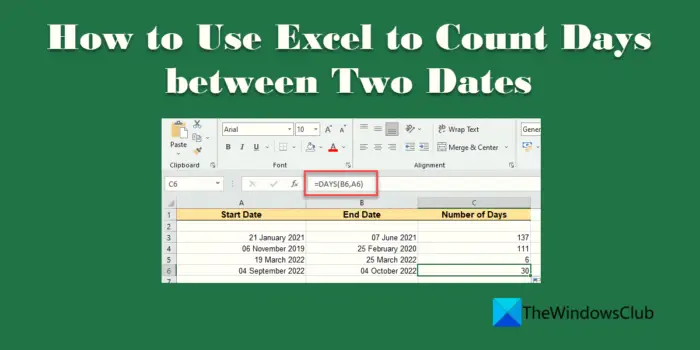
If you want to know how to use Excel to count days between two dates, then this post is going to help you. There may be times when you need to calculate the number of days between two given dates while analyzing some financial data. Excel is an amazing tool that can do that for you in a matter of seconds. How? By using Excel Functions! Excel offers a bunch of useful functions that allow you to quickly find the count, sum, average, maximum value, minimum value, etc., for a range of cells. It also offers some text functions and financial functions that are worth checking.
In this post, we are going to show you 5 different methods to count days between two Dates in Excel. They are:
- Using Subtraction
- Using the DAYS function
- Using the DATEDIF function
- Using the NETWORKDAYS function
- Using the TODAY function
Let us have a detailed look at all the above methods.
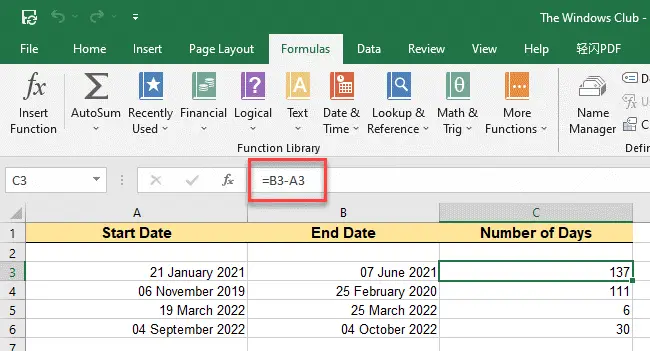
1] Using Subtraction
Subtraction is the easiest way to count days between two dates in Excel. You can use the arithmetic operator – (minus sign) to subtract one date from another to find the number of days between them.
Let’s say we have an Excel sheet with some sample dates listed in two columns, Column A and Column B. The dates in Column B precede the dates in Column A. The third column, Column C, will display the count of days when we subtract the value of Column A from the value of Column B, for each row in the spreadsheet.
The following steps describe the process in detail:
- Place your cursor in cell C3.
- In the formula bar, type =B3-A3.
- Press the Enter key. Excel will calculate the number of days between the dates entered in cells B3 and A3 and display the result in cell C3.
- Take your mouse pointer to the lower-right corner of cell C3. It will turn into a + (plus) symbol.
- Click, hold, and drag the cursor till cell C6. This action will copy the formula of cell C3 to cells C4, C5, and C6 as well, displaying results for all the dates we have taken into consideration.
Note: While using Subtraction, always write the End Date before the Start Date.
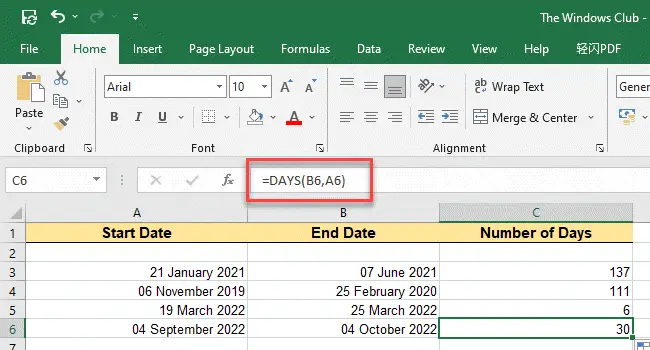
2] Using the DAYS function
DAYS is a date function in Excel that calculates the difference between two given dates in days. It can recognize dates passed as ‘strings’ if they can be parsed as valid dates in Excel.
Syntax
DAYS(end_date, start_date)
- end_date is the last date provided
- start_date is the first date provided
Now for the same example described above, we can use the DAYS formula to count the days as follows:
- Keeping the focus on cell C3, type =DAYS(B3, A3) in the formula bar.
- Press the Enter key. Days count between dates in cells A3 and B3 will appear in C3.
- Copy the same formula to cells C4, C5, and C6 through the mouse cursor drag method, as explained above.
Tip: If your accounting system is based on a 360-day year (twelve 30-day months), you may use the DAYS360 function to count the number of days.
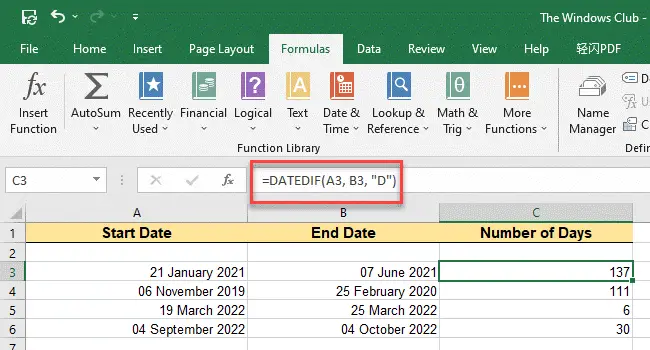
3] Using the DATEDIF function
The DATEDIF function is an advanced version of the DAYS function. It calculates the difference between two date values based on a specified interval, such as days, months, or years. It is useful in formulas that involve age-based calculations.
Syntax
DATEDIF(start_date, end_date, unit)
- start_date is the first or start date of the given period.
- end_date is the last date of the given period.
- unit is the information that you would like to get. For example, if you want the DATEDIF function to calculate the number of days, you can enter D in place of the unit. Similarly, you can enter M for months and Y for years. You can also enter a combination of two units, such as YM. This will calculate the difference in months, ignoring the years and the days.
Now taking the same example as above, follow these steps to use the DATEDIF function to count days in Excel:
- Place your cursor in cell C3.
- Double click and type =DATEDIF(A3, B3, “D”)
- Press the Enter key. The results will be displayed in cell C3.
- Now again take your cursor to the lower-right corner of cell C3, and click and drag it to cell C6 to view all the results.
Also Read: How to count words in Microsoft Excel.
4] Using the NETWORKDAYS function
NETWORKDAYS is another useful function through which you can use Excel to find days between two dates. It calculates the number of whole working days between two given dates. While calculating the number of days between two given dates, it automatically excludes the weekends (Saturday, Sunday) and optionally excludes any other holidays provided as dates (state, federal, and floating holidays).
Syntax
NETWORKDAYS(start_date,end_date,[holidays])
- start_date argument takes the value of the start date.
- end_date argument takes the value of the end date.
- [holidays] is a reference to one or dates to be counted as non-working days.
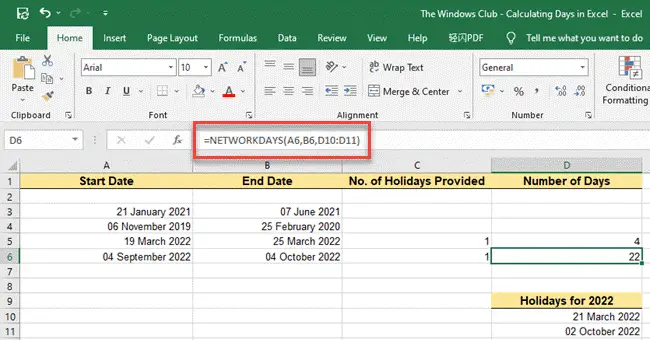
Now let’s say we provide a list of holidays (other than weekends) for the same set of dates as shown in the above example. We can use the NETWORKDAYS function to calculate working days between the given dates as follow:
- Place the cursor in cell D6.
- In the formula bar, type =NETWORKDAYS(A6,B6,D10:D11). As you can see in the above screenshot, the count of days has now been reduced from 30 to 22 (excluding 4 Saturdays, 4 Sundays, and 1 holiday which is occurring on Sunday).
- Now double click on cell D5 and type =NETWORKDAYS(A5,B5,D10:D11).
- Press the Enter key. The function now returns 4, excluding 1 Sunday and 1 holiday.
Notes:
- The NETWORKDAYS function includes the start_date in the count if it happens to be a weekday.
- If you need to provide custom weekends (for example, if you want Excel to mark Wednesday as a weekend and not Saturday, Sunday), then you should use the NETWORKDAYS.INTL function. This function allows you to pass a ‘weekend’ argument to set which days are considered weekends.
5] Using the TODAY function
The TODAY function can be used to calculate the number of days between a past date or a future date, and the current date. By default, it returns the current date (if the cell format is set to General).
Syntax
Today()
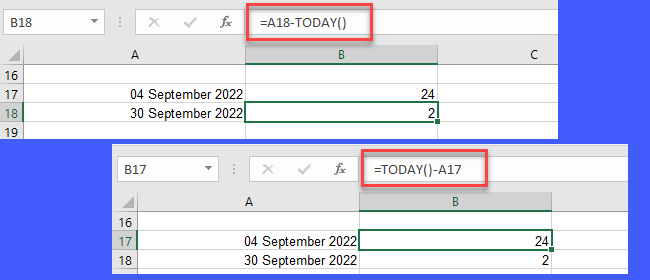
Let’s say the current date is 28 September 2022. And we have the date value 04 September 2022 in cell A17 and the date value 30 September 2022 in cell A18.
To calculate the number of days between today and 04 September 2022 (which is a past date), we will use the formula =TODAY()-A17. The function returns 24 as the resultant value.
Similarly, to calculate the number of days between today and 30 September 2022 (which is a future date), we will use the formula =A18-TODAY(). The function returns 2 as the resultant value.
That’s it! Hope you enjoyed knowing these easy tips to use Excel to count days between two dates. Do let us know in the comments if you have any questions.
What is the formula to calculate days?
Multiple Excel formulas can be used to calculate the days between 2 given dates. These include DAYS, DATEDIF, NETWORKDAYS, and TODAY functions. To know how these functions can be used to count days, refer to the above post. You may also use the Subtraction operator (-) to count days between two dates, as explained in this post.
How do I count days from a date in Excel?
There are five ways to count days from a date in Excel. For example, you can use the simple subtraction method to get the job done. However, if it doesn’t work, you can use the DAYS, DATEIF, NETWORKDAYS, or TODAY function as well. For your information, these functions work on Excel, Excel Online, and Google Sheets.
Read Next: How to multiply numbers in Single or Multiple cells in Excel.
На чтение 5 мин Просмотров 2к. Опубликовано 27.02.2022
Итак, мы имеем несколько серьезных функций, для того чтобы рассчитать кол-во дней между двумя датами, причем с разными параметрами (такими как выходные дни, праздники и так далее).
В этой статье я продемонстрирую вам разные ситуации, где нужно посчитать кол-во дней между датами. Все они будут с разными «уклонами», в одной ситуации нужно посчитать без выходных, в другой количество понедельников и так далее.
Содержание
- Стандартный расчет количества дней
- С помощью функции ДНИ
- С помощью функции РАЗНДАТ
- Расчет кол-ва рабочих дней
- Расчет кол-ва неполных рабочих дней между двумя датами
- Количество понедельников между двумя датами
Стандартный расчет количества дней
Итак, в Excel есть две функции для вычисления кол-ва дней.
С помощью функции ДНИ
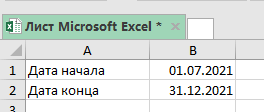
Чтобы получить результат от функции нам понадобится дата начала и дата конца.
Итак, вы указываете эти две даты в аргументах функции и получаете количество дней между ними.
Хороший пример вы можете видеть на картинке ниже:
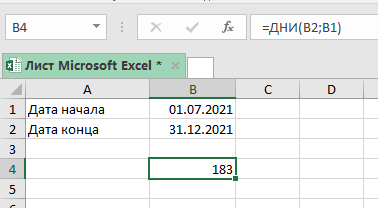
Используем эту формулу:
=ДНИ(B2;B1) Также вы можете вручную прописать даты в функции (без указания ячеек), но тогда вам нужно заключить их в кавычки.
Эта функция вычислит количество дней между этими датами, но если вы хотите чтобы расчет велся «включительно» с датами начала и конца, то добавьте к результату + 1 (просто пропишите это в функции).
С помощью функции РАЗНДАТ
Эта функция аналогична, её отличие в том, что можно указать больше параметров. То есть больше «подстроить» под ситуацию.
Также можно вычислить кол-во месяцев или лет между датами.
Допустим, мы имеем то что указано на картинке ниже:
Пропишем формулу:
=РАЗНДАТ(B1;B2;"D") Эта функция использует три наших аргумента:
- Дата начала — B1
- Дата окончания — B2
- «D» — текстовая строка
Важный момент: этой функции не будет в подсказке при написании названия функции, т.е. если вы будете писать РАЗНДАТ, Excel будет вести себя так, как будто он не знает что это за функция, но это не так.
Функция РАЗНДАТ больше подходит для ситуаций, когда нужно вычислить кол-во лет или месяцев между датами, в других ситуациях удобнее применять ДНИ (функцию).
Вот формула, которая даст результат по месяцам, которые будут между датами:
=РАЗНДАТ(B1;B2;"M") А эта формула, тоже самое что и прошлая, только вычисляет кол-во лет:
=РАЗНДАТ(B1;B2;"Y") Расчет кол-ва рабочих дней
Итак, рабочие дни можно вычислить двумя способами:
- Функция Excel ЧИСТРАБДНИ — ее следует использовать, если выходные дни — суббота и воскресенье.
- Функция Excel ЧИСТРАБДНИ.МЕЖД — используйте ее, когда выходные дни отличаются от субботы и воскресенья.
Сначала быстро рассмотрим синтаксис и аргументы фунции ЧИСТРАБДНИ.
Функция Excel ЧИСТРАБДНИ
=ЧИСТРАБДНИ(нач_дата, конеч_дата, [праздники])
- нач_дата — это дата начала отсчета.
- end_date — это конечная дата отсчета.
- [праздники] — (Необязательно) Отдельная дата или диапазон дат, которые не будут учитываться в расчетах.
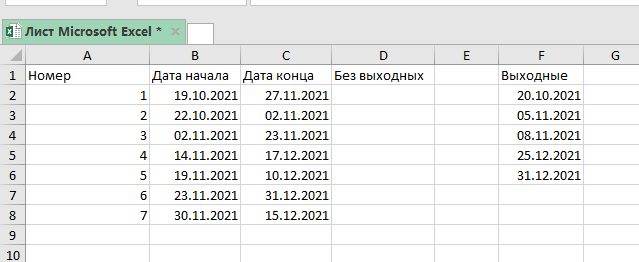
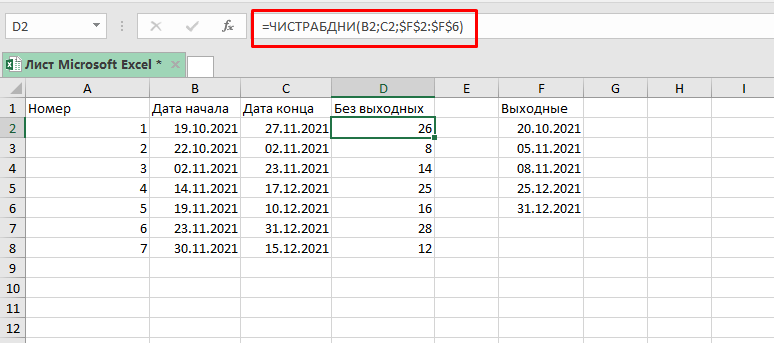
Посмотрим на стандартный пример, когда нужно посчитать кол-во рабочих дней.
Мы будем использовать эту формулу:
=ЧИСТРАБДНИ(B2;C2;$F$2:$F$6) Такая вариация этой функции даст то что вам нужно, если вам нужно посчитать рабочие дни без субботы и воскресенья.
Но бывают и другие ситуации, к примеру, в разных странах выходные на неделе строятся по-разному, это может быть пятница и так далее.
Именно для таких ситуаций и появилась функция ЧИСТРАБДНИ.МЕЖД.
Посмотрим что из себя представляет эта функция.
Функция Excel ЧИСТРАБДНИ.МЕЖД
=ЧИСТРАБДНИ.МЕЖД(нач_дата; конеч_дата; [выходные]; [праздники])
- нач_дата — значение даты, представляющее собой начальную дату.
- конеч_дата — значение даты, представляющее дату окончания.
- [нерабочие дни] — (Необязательно) в этом аргументе указываются исключительные дни(праздники и т.д.), если аргумента не будет, выходные останутся по-стандарту(суббота и воскресенье).
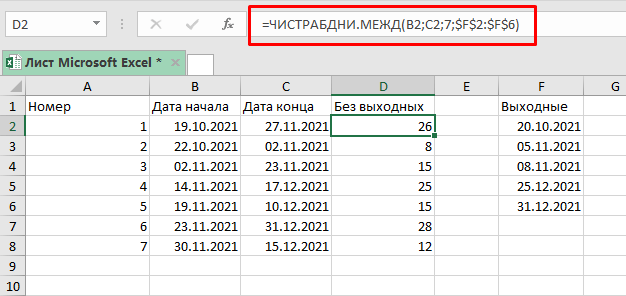
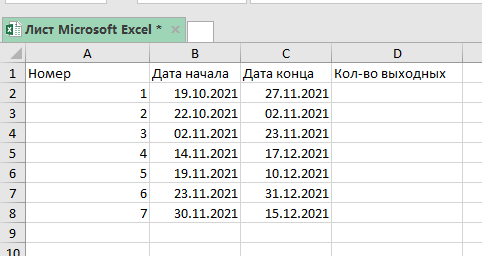
А сейчас, попробуем посчитать кол-во рабочих дней, если выходными будут пятница и суббота.
Допустим, таблица такая же как и в прошлом примере:
Будем использовать формулу:
=ЧИСТРАБДНИ.МЕЖД(B2;C2;7;$F$2:$F$6) 3 аргумент в функции сообщает Excel, что пятница и суббота выходные.
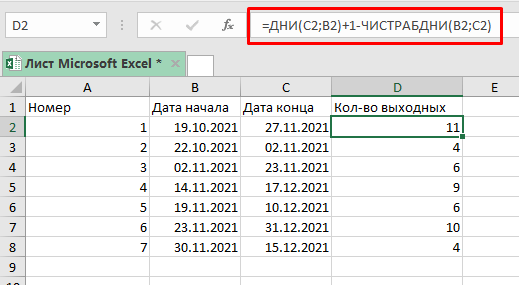
Также, мы можем использовать ЧИСТРАБДНИ.МЕЖД для расчета выходных между двумя датами.
Она конечно вычисляет кол-во рабочих дней, но мы можем адаптировать это «под себя».
Допустим, таблица все та же:
Формула, которая нам подойдет:
=ДНИ(C2;B2)+1-РАЗНДАТ(B2;C2)Расчет кол-ва неполных рабочих дней между двумя датами
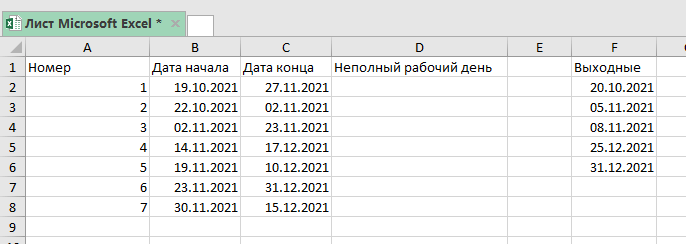
Также, к примеру, можно использовать эту же функцию для расчета неполных рабочих дней.
Допустим, у нас есть похожая таблица с данными:
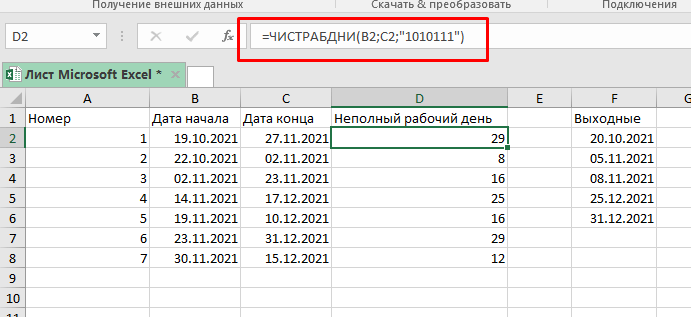
Формула, для нашего случая, будет такой:
=ЧИСТРАБДНИ.МЕЖД($B$3;$C$3;"1010111";$E$3:$E$7) Для обозначения выходных дней, мы использовали «1010111».
- 0 — рабочий день
- 1 — неполный рабочий день
Первая цифра из этого числа — понедельник, последняя — воскресенье
Грубо говоря, «0000011» значит, что с понедельника по пятницу — рабочие дни, а суббота и воскресенье — нерабочие (выходные).
По той же логике, «1010111» означает, что только вторник и четверг являются рабочими, а остальные 5 дней — нерабочими.
Если вам нужно исключить какие-то дни из расчетов, можете исключать их таким образом.
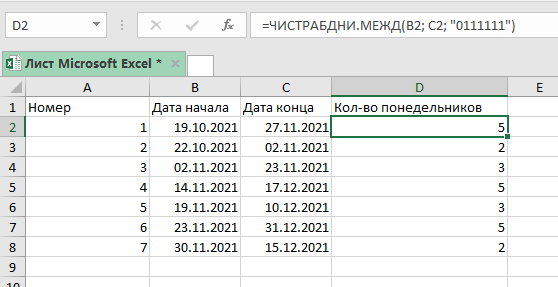
Количество понедельников между двумя датами
Для поиска количества понедельников мы можем использовать ту же логику, которая использовалась выше при подсчете неполных рабочих дней.
Функция, которая выведет кол-во понедельников:
=ЧИСТРАБДНИ(B2;C2;"0111111") В этой формуле «0» означает рабочий день, а «1» — нерабочий день.
Формула рассчитывает количество рабочих дней, с учетом того что единственный рабочий день — это понедельник.
Аналогичным образом можно рассчитать количество любых, интересующих вас дней, между двумя датами.