When you move or copy rows and columns, by default Excel moves or copies all data that they contain, including formulas and their resulting values, comments, cell formats, and hidden cells.
When you copy cells that contain a formula, the relative cell references are not adjusted. Therefore, the contents of cells and of any cells that point to them might display the #REF! error value. If that happens, you can adjust the references manually. For more information, see Detect errors in formulas.
You can use the Cut command or Copy command to move or copy selected cells, rows, and columns, but you can also move or copy them by using the mouse.
By default, Excel displays the Paste Options button. If you need to redisplay it, go to Advanced in Excel Options. For more information, see Advanced options.
-
Select the cell, row, or column that you want to move or copy.
-
Do one of the following:
-
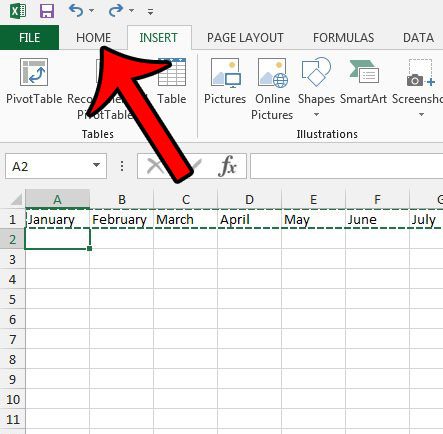
To move rows or columns, on the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Cut
or press CTRL+X.
-
To copy rows or columns, on the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Copy
or press CTRL+C.
-
-
Right-click a row or column below or to the right of where you want to move or copy your selection, and then do one of the following:
-
When you are moving rows or columns, click Insert Cut Cells.
-
When you are copying rows or columns, click Insert Copied Cells.
Tip: To move or copy a selection to a different worksheet or workbook, click another worksheet tab or switch to another workbook, and then select the upper-left cell of the paste area.
-
Note: Excel displays an animated moving border around cells that were cut or copied. To cancel a moving border, press Esc.
By default, drag-and-drop editing is turned on so that you can use the mouse to move and copy cells.
-
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
-
Do one of the following:
-
Cut and replace
Point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a move pointer, drag the rows or columns to another location. Excel warns you if you are going to replace a column. Press Cancel to avoid replacing.
-
Copy and replace Hold down CTRL while you point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a copy pointer
, drag the rows or columns to another location. Excel doesn’t warn you if you are going to replace a column. Press CTRL+Z if you don’t want to replace a row or column.
-
Cut and insert Hold down SHIFT while you point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a move pointer
, drag the rows or columns to another location.
-
Copy and insert Hold down SHIFT and CTRL while you point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a move pointer
, drag the rows or columns to another location.
Note: Make sure that you hold down CTRL or SHIFT during the drag-and-drop operation. If you release CTRL or SHIFT before you release the mouse button, you will move the rows or columns instead of copying them.
-
Note: You cannot move or copy nonadjacent rows and columns by using the mouse.
If some cells, rows, or columns on the worksheet are not displayed, you have the option of copying all cells or only the visible cells. For example, you can choose to copy only the displayed summary data on an outlined worksheet.
-
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
-
On the Home tab, in the Editing group, click Find & Select, and then click Go To Special.
-
Under Select, click Visible cells only, and then click OK.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Copy
or press Ctrl+C. .
-
Select the upper-left cell of the paste area.
Tip: To move or copy a selection to a different worksheet or workbook, click another worksheet tab or switch to another workbook, and then select the upper-left cell of the paste area.
-
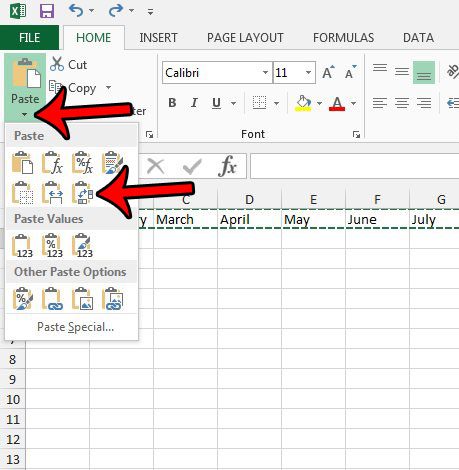
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Paste
or press Ctrl+V.
If you click the arrow below Paste
, you can choose from several paste options to apply to your selection.
Excel pastes the copied data into consecutive rows or columns. If the paste area contains hidden rows or columns, you might have to unhide the paste area to see all of the copied cells.
When you copy or paste hidden or filtered data to another application or another instance of Excel, only visible cells are copied.
-
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Copy
or press Ctrl+C.
-
Select the upper-left cell of the paste area.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click the arrow below Paste
, and then click Paste Special.
-
Select the Skip blanks check box.
-
Double-click the cell that contains the data that you want to move or copy. You can also edit and select cell data in the formula bar.
-
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, do one of the following:
-
To move the selection, click Cut
or press Ctrl+X.
-
To copy the selection, click Copy
or press Ctrl+C.
-
-
In the cell, click where you want to paste the characters, or double-click another cell to move or copy the data.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Paste
or press Ctrl+V.
-
Press ENTER.
Note: When you double-click a cell or press F2 to edit the active cell, the arrow keys work only within that cell. To use the arrow keys to move to another cell, first press Enter to complete your editing changes to the active cell.
When you paste copied data, you can do any of the following:
-
Paste only the cell formatting, such as font color or fill color (and not the contents of the cells).
-
Convert any formulas in the cell to the calculated values without overwriting the existing formatting.
-
Paste only the formulas (and not the calculated values).
Procedure
-
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Copy
or press Ctrl+C.
-
Select the upper-left cell of the paste area or the cell where you want to paste the value, cell format, or formula.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click the arrow below Paste
, and then do one of the following:
-
To paste values only, click Values.
-
To paste cell formats only, click Formatting.
-
To paste formulas only, click Formulas.
-
When you paste copied data, the pasted data uses the column width settings of the target cells. To correct the column widths so that they match the source cells, follow these steps.
-
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, do one of the following:
-
To move cells, click Cut
or press Ctrl+X.
-
To copy cells, click Copy
or press Ctrl+C.
-
-
Select the upper-left cell of the paste area.
Tip: To move or copy a selection to a different worksheet or workbook, click another worksheet tab or switch to another workbook, and then select the upper-left cell of the paste area.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click the arrow under Paste
, and then click Keep Source Column Widths.
You can use the Cut command or Copy command to move or copy selected cells, rows, and columns, but you can also move or copy them by using the mouse.
-
Select the cell, row, or column that you want to move or copy.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To move rows or columns, on the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Cut
or press CTRL+X.
-
To copy rows or columns, on the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Copy
or press CTRL+C.
-
-
Right-click a row or column below or to the right of where you want to move or copy your selection, and then do one of the following:
-
When you are moving rows or columns, click Insert Cut Cells.
-
When you are copying rows or columns, click Insert Copied Cells.
Tip: To move or copy a selection to a different worksheet or workbook, click another worksheet tab or switch to another workbook, and then select the upper-left cell of the paste area.
-
Note: Excel displays an animated moving border around cells that were cut or copied. To cancel a moving border, press Esc.
-
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
-
Do one of the following:
-
Cut and insert
Point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a hand pointer, drag the row or column to another location
-
Cut and replace Hold down SHIFT while you point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a move pointer
, drag the row or column to another location. Excel warns you if you are going to replace a row or column. Press Cancel to avoid replacing.
-
Copy and insert Hold down CTRL while you point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a move pointer
, drag the row or column to another location.
-
Copy and replace Hold down SHIFT and CTRL while you point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a move pointer
, drag the row or column to another location. Excel warns you if you are going to replace a row or column. Press Cancel to avoid replacing.
Note: Make sure that you hold down CTRL or SHIFT during the drag-and-drop operation. If you release CTRL or SHIFT before you release the mouse button, you will move the rows or columns instead of copying them.
-
Note: You cannot move or copy nonadjacent rows and columns by using the mouse.
-
Double-click the cell that contains the data that you want to move or copy. You can also edit and select cell data in the formula bar.
-
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, do one of the following:
-
To move the selection, click Cut
or press Ctrl+X.
-
To copy the selection, click Copy
or press Ctrl+C.
-
-
In the cell, click where you want to paste the characters, or double-click another cell to move or copy the data.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Paste
or press Ctrl+V.
-
Press ENTER.
Note: When you double-click a cell or press F2 to edit the active cell, the arrow keys work only within that cell. To use the arrow keys to move to another cell, first press Enter to complete your editing changes to the active cell.
When you paste copied data, you can do any of the following:
-
Paste only the cell formatting, such as font color or fill color (and not the contents of the cells).
-
Convert any formulas in the cell to the calculated values without overwriting the existing formatting.
-
Paste only the formulas (and not the calculated values).
Procedure
-
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Copy
or press Ctrl+C.
-
Select the upper-left cell of the paste area or the cell where you want to paste the value, cell format, or formula.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click the arrow below Paste
, and then do one of the following:
-
To paste values only, click Paste Values.
-
To paste cell formats only, click Paste Formatting.
-
To paste formulas only, click Paste Formulas.
-
You can move or copy selected cells, rows, and columns by using the mouse and Transpose.
-
Select the cells or range of cells that you want to move or copy.
-
Point to the border of the cell or range that you selected.
-
When the pointer becomes a
, do one of the following:
|
To |
Do this |
|---|---|
|
Move cells |
Drag the cells to another location. |
|
Copy cells |
Hold down OPTION and drag the cells to another location. |
Note: When you drag or paste cells to a new location, if there is pre-existing data in that location, Excel will overwrite the original data.
-
Select the rows or columns that you want to move or copy.
-
Point to the border of the cell or range that you selected.
-
When the pointer becomes a
, do one of the following:
|
To |
Do this |
|---|---|
|
Move rows or columns |
Drag the rows or columns to another location. |
|
Copy rows or columns |
Hold down OPTION and drag the rows or columns to another location. |
|
Move or copy data between existing rows or columns |
Hold down SHIFT and drag your row or column between existing rows or columns. Excel makes space for the new row or column. |
-
Copy the rows or columns that you want to transpose.
-
Select the destination cell (the first cell of the row or column into which you want to paste your data) for the rows or columns that you are transposing.
-
On the Home tab, under Edit, click the arrow next to Paste, and then click Transpose.
Note: Columns and rows cannot overlap. For example, if you select values in Column C, and try to paste them into a row that overlaps Column C, Excel displays an error message. The destination area of a pasted column or row must be outside the original values.
See also
Insert or delete cells, rows, columns
How to Convert Rows to Columns in Excel?
There are two different methods for converting rows to columns in Excel, which are as follows:
- Method #1 – Transposing Rows to Columns Using Paste Special.
- Method #2 – Transposing Rows to Columns Using TRANSPOSE Formula.
Table of contents
- How to Convert Rows to Columns in Excel?
- #1 Using Paste Special
- Example
- #2 Using TRANSPOSE Formula
- Example
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
- #1 Using Paste Special
#1 Using Paste Special
It is an efficient method; it is easy to implement and saves time. Also, this method would be ideal if you want your original formatting to be copied.
You can download this Convert Rows to Columns Excel Template here – Convert Rows to Columns Excel Template
Example
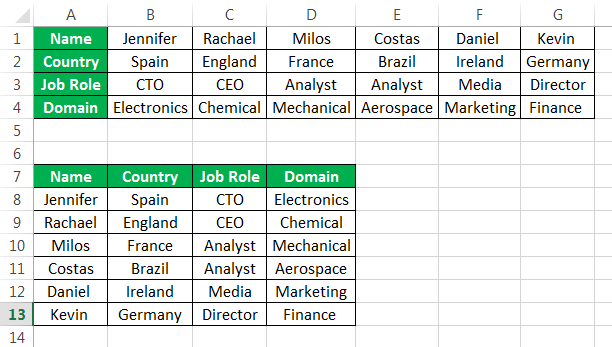
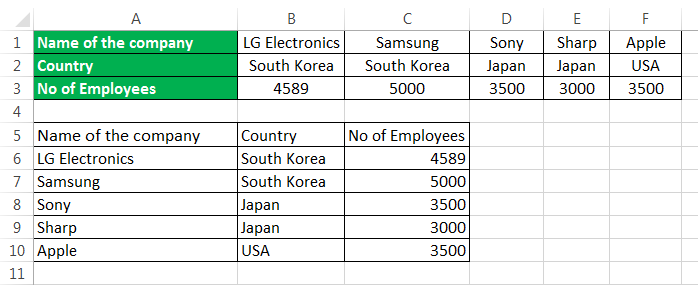
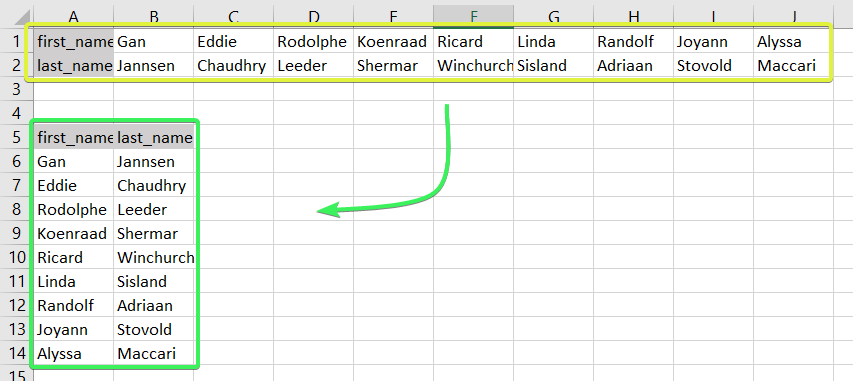
For example, if you have below data of key industry players from various regions, it also shows their job roles as shown in figure1.
| Name | Jennifer | Racheal | Milos | Costas | Daniel | Kevin |
| Country | Spain | England | France | Brazil | Ireland | Germany |
| Job Role | CTO | CEO | Analyst | Analyst | Media | Director |
| Domain | Electronics | Chemical | Mechanical | Aerospace | Marketing | Finance |
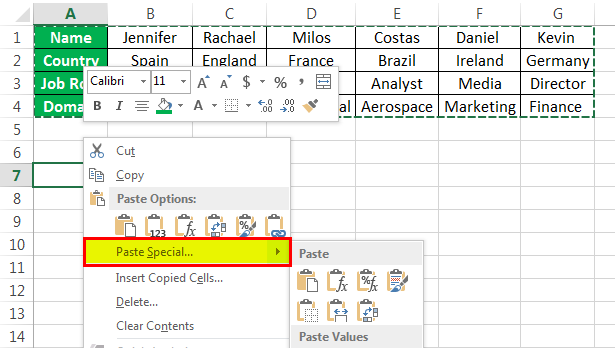
In example 1, the players’ names are written in column form. Still, the list becomes too long, and the data entered also seems unorganized. Hence, we would change the rows to columns using paste special methodsPaste special in Excel allows you to paste partial aspects of the data copied. There are several ways to paste special in Excel, including right-clicking on the target cell and selecting paste special, or using a shortcut such as CTRL+ALT+V or ALT+E+S.read more.
The steps to convert rows to columns in Excel using the Paste Special method are as follows:
- Select the whole data which needs to be transformed or transposed. Then, Copy the selected data by simply pressing Ctrl + C keys.
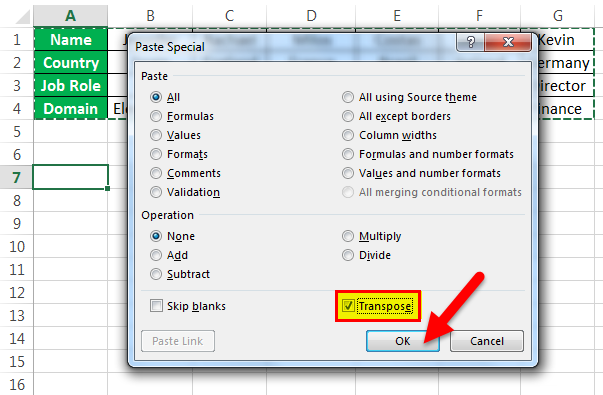
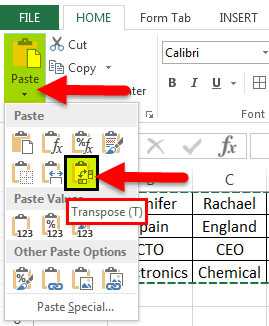
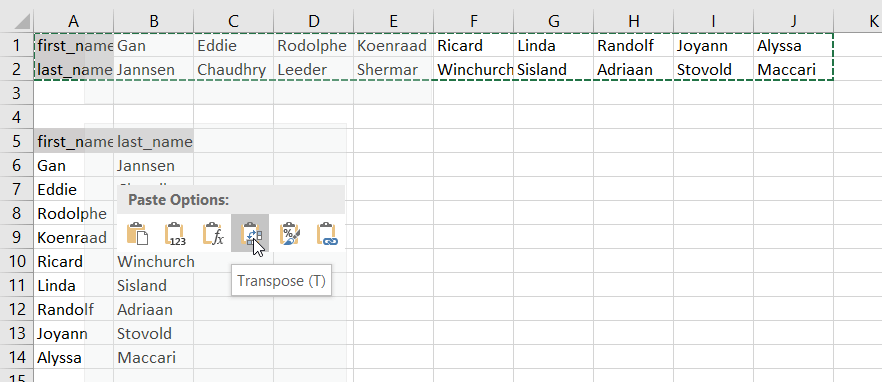
- Select a blank cell and ensure it is outside the original data range. Paste the data by pressing the “Ctrl +V” keys starting at the first blank space or cell. Then, select the down arrow from the toolbar under the “Paste” option and select “Paste Transpose.” But the easy way is to right-click the blank you chose first to paste the data. Then, select “Paste Special” from it.
- Then, a “Paste Special” dialog box will appear from which select the “Transpose” option. And click “OK.”
- In the above figure, copy the data which needs to be transposed and then click on the down arrow of the Paste option and form the options select Transpose. (Paste-Transpose)
It shows how the transpose function is performed to convert rows to columns.
#2 Using TRANSPOSE Formula
When a user wants to keep the same connections of the rotating table with the original table, it can use a transposing method using a formula. This method is also quicker in converting rows to columns in Excel. But, it does not keep the source formatting and links it to a transposed table.
Example
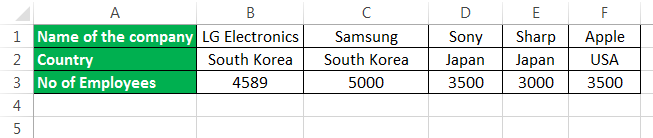
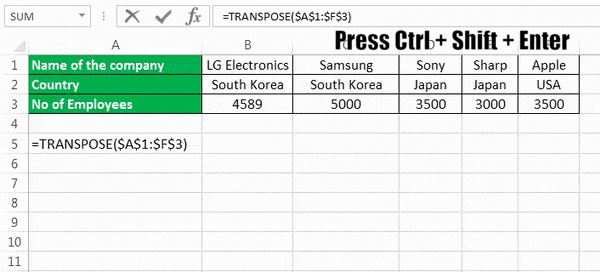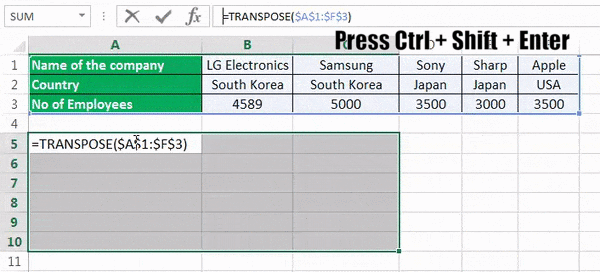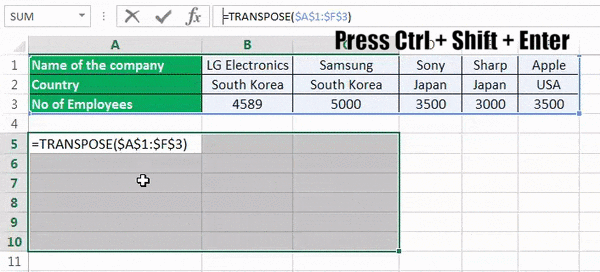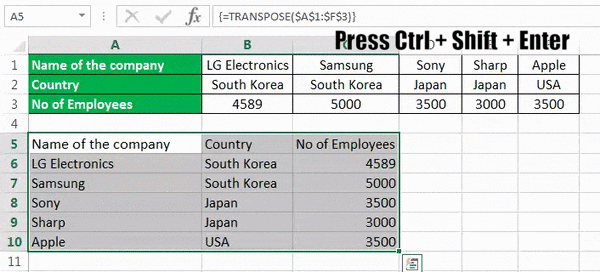
Consider the example below, as shown in figure 6, where it shows the company’s names, location, and the number of employees.
The steps to transpose rows to columns in excel using formula are as follows:
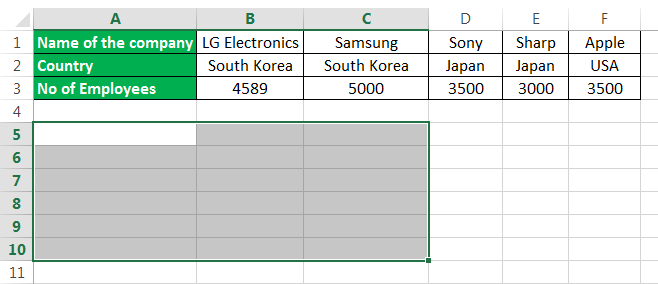
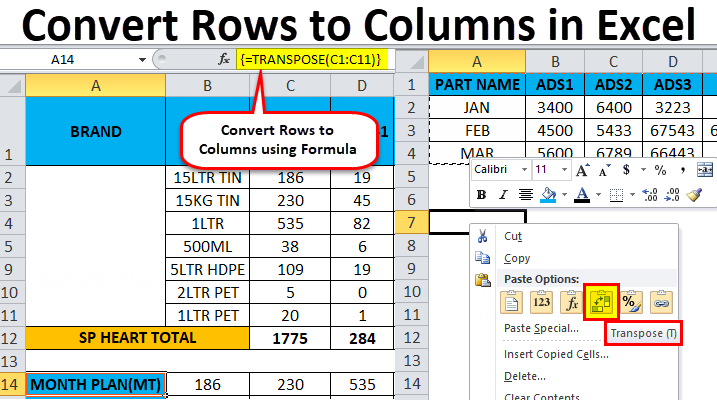
- First, count the number of rows and columns in your original excel table. And then, select the same number of blank cells but ensure you have to transpose the rows to columns to choose the blank cells in the opposite direction. Like in example 2, the number of rows is 3, and the number of columns is 6. So, you will select 6 blank rows and 3 blank columns.
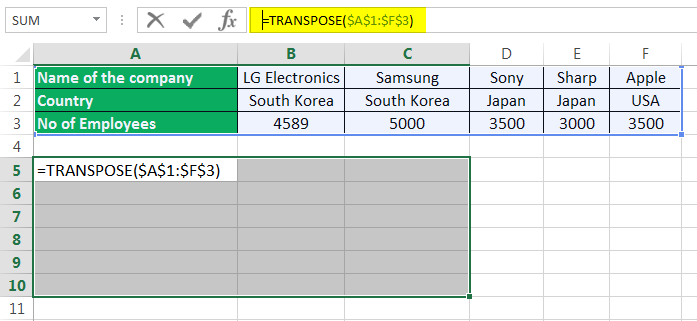
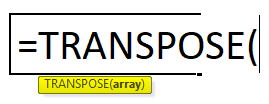
- In the first empty cell, enter the TRANSPOSE formula in excelThe TRANSPOSE function in excel helps rotate (switch) the values from rows to columns and vice versa. Being a part of the Excel lookup and reference functions, its purpose is to organize the data in the desired format. To execute the formula, the exact size of the range to be transposed is selected and the CSE key (“Control+Shift+Enter”) is pressed.
read more ‘=TRANSPOSE($A$1:$F$3)’.
- Since this formula needs to be applied for other blank cells so press ‘Ctrl+Shift+Enter.’
The rows are converted to columns.
Advantages
- The Paste Special method is useful when the user needs the original formatting to be continued.
- In the transpose method, by using the TRANSPOSE function, the converted table will change its data automatically, which means that whenever the user changes the data in the original table, it will automatically change the data in the transposed table, as it is linked to it.
- Converting the rows to columns in Excel sometimes helps the user to make the audience understand their data easily and so that the audience interprets it without much effort.
Disadvantages
- If the number of rows and columns increases, then the transpose method using the Paste Special options cannot perform efficiently. In this case, the “TRANSPOSE” function will be disabled when there are many rows to be converted to columns.
- The “Transpose Paste Special” option does not link the original data to the transposed data. Therefore, if you need to change the data, you must repeat all the steps.
- In the transpose method, the source formatting is not kept the same for the transposed data by using the formula.
- After converting the rows to columns in Excel using a formula, the user cannot edit the data in the transposed table as it is linked to the source data.
Things to Remember
- We can transpose rows to columns using Paste Special methods. We can link the data to the original data by selecting “Paste Link” from the “Paste Special” dialog box.
- We can also use Excel’s INDIRECT formula and ADDRESS functions in ExcelThe address function finds the cell’s address and returns an absolute value. It requires two mandatory arguments: the row number and the column number. For example, if we use =Address(1,2), the result will be $B$1.read more to convert rows to columns and vice-versa.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to Convert Rows to Columns in Excel. Here, we discuss switching rows to columns in Excel using the Paste Special and TRANSPOSE formula, practical examples, and a downloadable Excel template. You may learn more about Excel from the following articles: –
- Group Columns in ExcelIn Excel, grouping one or more columns together in a worksheet is referred to as group column and I t allows you to contract or expand the column.read more
- Compare Two Columns in ExcelTwo columns in excel are compared when their entries are studied for similarities and differences.read more
- Use Columns Formula in Excel
- Column Sort in Excel
Содержание
- Move or copy cells, rows, and columns
- Transpose (rotate) data from rows to columns or vice versa
- Tips for transposing your data
- Need more help?
- How You Can Convert Rows to Columns or Columns to Rows in Excel Workbooks
- How to convert rows into columns or columns to rows in Excel – the basic solution
- Can I convert multiple rows to columns in Excel from another workbook?
- How to switch rows and columns in Excel in more efficient ways
- How to change row to column in Excel with TRANSPOSE
- TRANSPOSE formula to convert multiple rows to columns in Excel desktop
- TRANSPOSE formula to rotate row to column in Excel Online
- Excel TRANSPOSE multiple rows in a group to columns between different workbooks
- Are there other formulas to convert columns to rows in Excel?
- How to convert text in columns to rows in Excel using INDIRECT+ADDRESS
- How to convert Excel data in columns to rows using INDIRECT+ADDRESS from other cells
- How to automatically convert rows to columns in Excel VBA
- VBA macro script to convert multiple rows to columns in Excel
- Convert rows to column in Excel using Power Query
- Error message when trying to convert rows to columns in Excel
- Overlap error
- Wrong data type error
Move or copy cells, rows, and columns
When you move or copy rows and columns, by default Excel moves or copies all data that they contain, including formulas and their resulting values, comments, cell formats, and hidden cells.
When you copy cells that contain a formula, the relative cell references are not adjusted. Therefore, the contents of cells and of any cells that point to them might display the #REF! error value. If that happens, you can adjust the references manually. For more information, see Detect errors in formulas.
You can use the Cut command or Copy command to move or copy selected cells, rows, and columns, but you can also move or copy them by using the mouse.
By default, Excel displays the Paste Options button. If you need to redisplay it, go to Advanced in Excel Options. For more information, see Advanced options.
Select the cell, row, or column that you want to move or copy.
Do one of the following:
To move rows or columns, on the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Cut 
To copy rows or columns, on the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Copy 
Right-click a row or column below or to the right of where you want to move or copy your selection, and then do one of the following:
When you are moving rows or columns, click Insert Cut Cells.
When you are copying rows or columns, click Insert Copied Cells.
Tip: To move or copy a selection to a different worksheet or workbook, click another worksheet tab or switch to another workbook, and then select the upper-left cell of the paste area.
Note: Excel displays an animated moving border around cells that were cut or copied. To cancel a moving border, press Esc.
By default, drag-and-drop editing is turned on so that you can use the mouse to move and copy cells.
Select the row or column that you want to move or copy.
Do one of the following:
Cut and replace Point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a move pointer 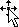
Copy and replace Hold down CTRL while you point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a copy pointer 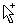
Cut and insert Hold down SHIFT while you point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a move pointer 
Copy and insert Hold down SHIFT and CTRL while you point to the border of the selection. When the pointer becomes a move pointer 
Note: Make sure that you hold down CTRL or SHIFT during the drag-and-drop operation. If you release CTRL or SHIFT before you release the mouse button, you will move the rows or columns instead of copying them.
Note: You cannot move or copy nonadjacent rows and columns by using the mouse.
Источник
Transpose (rotate) data from rows to columns or vice versa
If you have a worksheet with data in columns that you need to rotate to rearrange it in rows, use the Transpose feature. With it, you can quickly switch data from columns to rows, or vice versa.
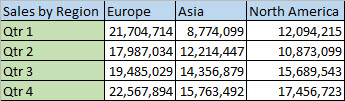
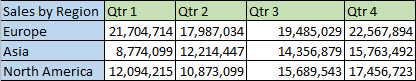
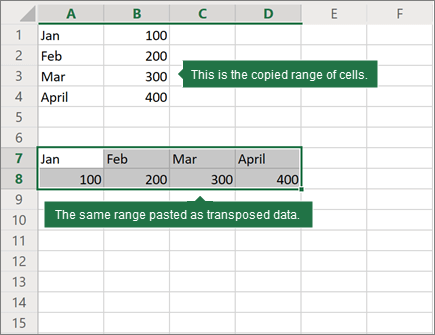
For example, if your data looks like this, with Sales Regions in the column headings and and Quarters along the left side:
The Transpose feature will rearrange the table such that the Quarters are showing in the column headings and the Sales Regions can be seen on the left, like this:
Note: If your data is in an Excel table, the Transpose feature won’t be available. You can convert the table to a range first, or you can use the TRANSPOSE function to rotate the rows and columns.
Here’s how to do it:
Select the range of data you want to rearrange, including any row or column labels, and press Ctrl+C.
Note: Ensure that you copy the data to do this, since using the Cut command or Ctrl+X won’t work.
Choose a new location in the worksheet where you want to paste the transposed table, ensuring that there is plenty of room to paste your data. The new table that you paste there will entirely overwrite any data / formatting that’s already there.
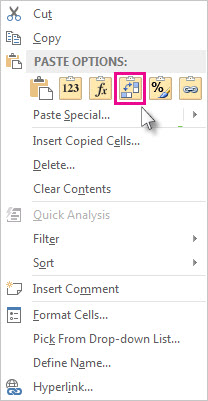
Right-click over the top-left cell of where you want to paste the transposed table, then choose Transpose 
After rotating the data successfully, you can delete the original table and the data in the new table will remain intact.
Tips for transposing your data
If your data includes formulas, Excel automatically updates them to match the new placement. Verify these formulas use absolute references—if they don’t, you can switch between relative, absolute, and mixed references before you rotate the data.
If you want to rotate your data frequently to view it from different angles, consider creating a PivotTable so that you can quickly pivot your data by dragging fields from the Rows area to the Columns area (or vice versa) in the PivotTable Field List.
You can paste data as transposed data within your workbook. Transpose reorients the content of copied cells when pasting. Data in rows is pasted into columns and vice versa.
Here’s how you can transpose cell content:
Copy the cell range.
Select the empty cells where you want to paste the transposed data.
On the Home tab, click the Paste icon, and select Paste Transpose.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Источник
How You Can Convert Rows to Columns or Columns to Rows in Excel Workbooks
Do you have some values arranged as rows in your workbook, and do you want to convert text in rows to columns in Excel like this?
In Excel, you can do this manually or automatically in multiple ways depending on your purpose. Read on to get all the details and choose the best solution for yourself.
How to convert rows into columns or columns to rows in Excel – the basic solution
The easiest way to convert rows to columns in Excel is via the Paste Transpose option. Here is how it looks:
- Select and copy the needed range
- Right-click on a cell where you want to convert rows to columns
- Select the Paste Transpose option to rotate rows to columns
As an alternative, you can use the Paste Special option and mark Transpose using its menu.
It works the same if you need to convert columns to rows in Excel.
This is the best way for a one-time conversion of small to medium numbers of rows both in the Excel desktop and online.
Can I convert multiple rows to columns in Excel from another workbook?
The method above will work well if you want to convert rows to columns in Excel between different workbooks using Excel desktop. You need to have both spreadsheets open and do the copying and pasting as described.
However, in Excel Online, this won’t work for different workbooks. The Paste Transpose option is not available.
Therefore, in this case, it’s better to use the TRANSPOSE function.
How to switch rows and columns in Excel in more efficient ways
To switch rows and columns in Excel automatically or dynamically, you can use one of these options:
- Excel TRANSPOSE function
- VBA macro
- Power Query
Let’s check out each of them in the example of a data range that we imported to Excel from a Google Sheets file using Coupler.io.
Coupler.io is an integration solution that synchronizes data between source and destination apps on a regular schedule. For example, you can set up an automatic data export from Google Sheets every day to your Excel workbook.
Check out all the available Excel integrations.
How to change row to column in Excel with TRANSPOSE
TRANSPOSE is the Excel function that allows you to switch rows and columns in Excel. Here is its syntax:
- array – an array of columns or rows to transpose
One of the main benefits of TRANSPOSE is that it links the converted columns/rows with the source rows/columns. So, if the values in the rows change, the same changes will be made in the converted columns.
TRANSPOSE formula to convert multiple rows to columns in Excel desktop
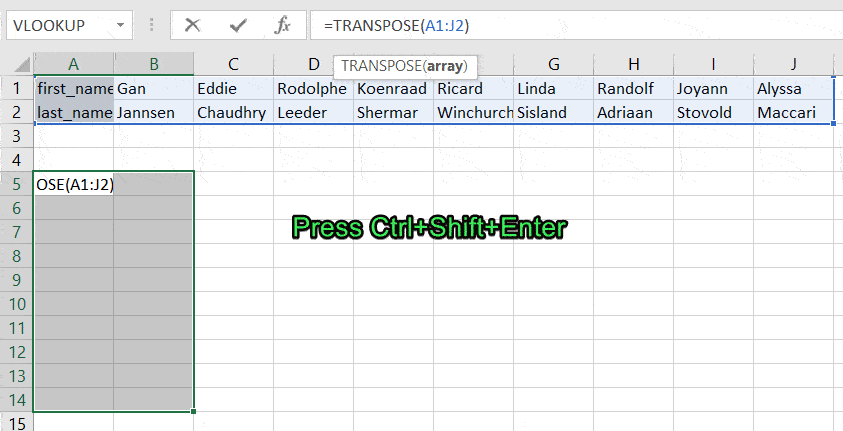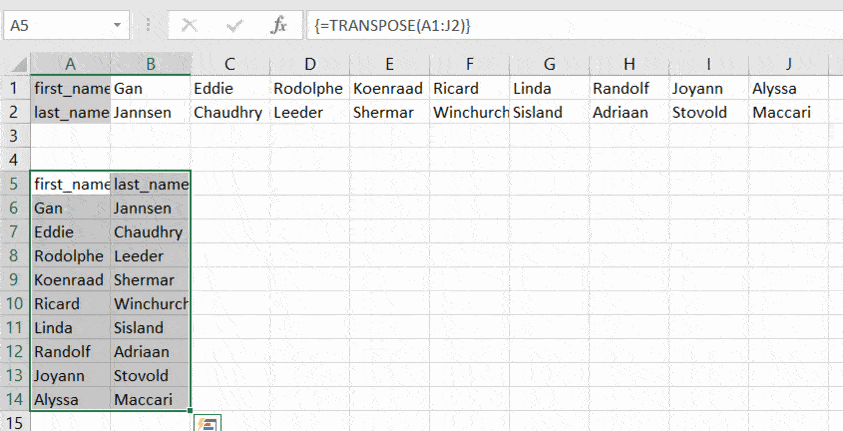
TRANSPOSE is an array formula, which means that you’ll need to select a number of cells in the columns that correspond to the number of cells in the rows to be converted and press Ctrl+Shift+Enter.
Fortunately, you don’t have to go through this procedure in Excel Online.
TRANSPOSE formula to rotate row to column in Excel Online
You can simply insert your TRANSPOSE formula in a cell and hit enter. The rows will be rotated to columns right away without any additional button combinations.
Excel TRANSPOSE multiple rows in a group to columns between different workbooks
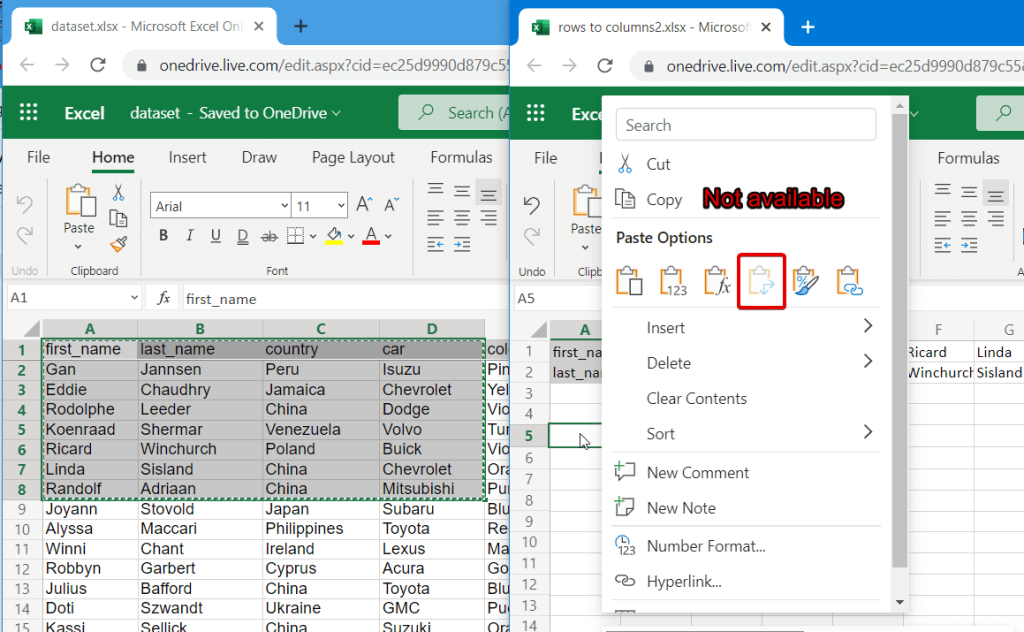
We promised to demonstrate how you can use TRANSPOSE to rotate rows to columns between different workbooks. In Excel Online, you need to do the following:
- Copy a range of columns to rotate from one spreadsheet and paste it as a link to another spreadsheet.
- We need this URL path to use in the TRANSPOSE formula, so copy it.
- The URL path above is for a cell, not for an array. So, you’ll need to slightly update it to an array to use in your TRANSPOSE formula. Here is what it should look like:
You can follow the same logic for rotating rows to columns between workbooks in Excel desktop.
Are there other formulas to convert columns to rows in Excel?
TRANSPOSE is not the only function you can use to change rows to columns in Excel. A combination of INDIRECT and ADDRESS functions can be considered as an alternative, but the flow to convert rows to columns in Excel using this formula is much trickier. Let’s check it out in the following example.
How to convert text in columns to rows in Excel using INDIRECT+ADDRESS
If you have a set of columns with the first cell A1, the following formula will allow you to convert columns to rows in Excel.
But where are the rows, you may ask! Well, first you need to drag this formula down if you are converting multiple columns to rows. Then drag it to the right.
NOTE: This Excel formula only to convert data in columns to rows starting with A1 cell. If your columns start from another cell, check out the next section.
How to convert Excel data in columns to rows using INDIRECT+ADDRESS from other cells
To convert columns to rows in Excel with INDIRECT+ADDRESS formulas from not A1 cell only, use the following formula:
- first_cell – enter the first cell of your columns
Here is an example of how to convert Excel data in columns to rows:
Again, you’ll need to drag the formula down and to the right to populate the rest of the cells.
How to automatically convert rows to columns in Excel VBA
VBA is a superb option if you want to customize some function or functionality. However, this option is only code-based. Below we provide a script that allows you to change rows to columns in Excel automatically.
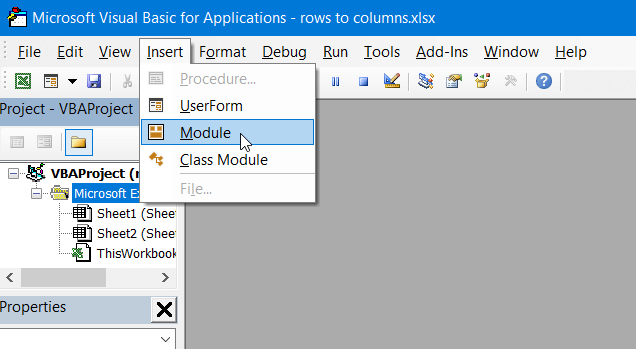
- Go to the Visual Basic Editor (VBE). Click Alt+F11 or you can go to the Developer tab => Visual Basic.
- In VBE, go to Insert => Module.
- Copy and paste the script into the window. You’ll find the script in the next section.
- Now you can close the VBE. Go to Developer => Macros and you’ll see your RowsToColumns macro. Click Run.
- You’ll be asked to select the array to rotate and the cell to insert the rotated columns.
- There you go!
VBA macro script to convert multiple rows to columns in Excel
Convert rows to column in Excel using Power Query
Power Query is another powerful tool available for Excel users. We wrote a separate Power Query Tutorial, so feel free to check it out.
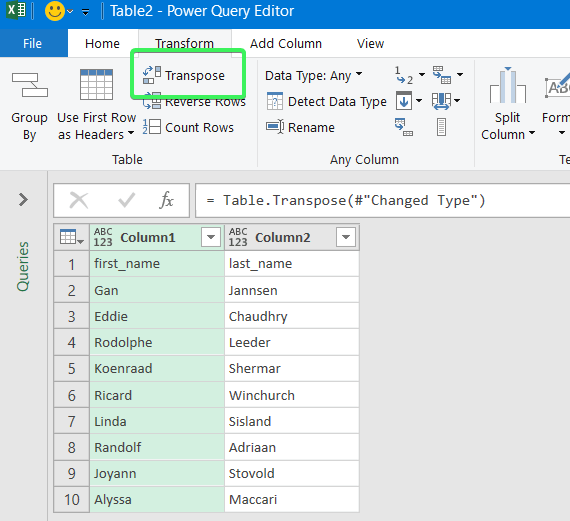
Meanwhile, you can use Power Query to transpose rows to columns. To do this, go to the Data tab, and create a query from table.
- Then select a range of cells to convert rows to columns in Excel. Click OK to open the Power Query Editor.
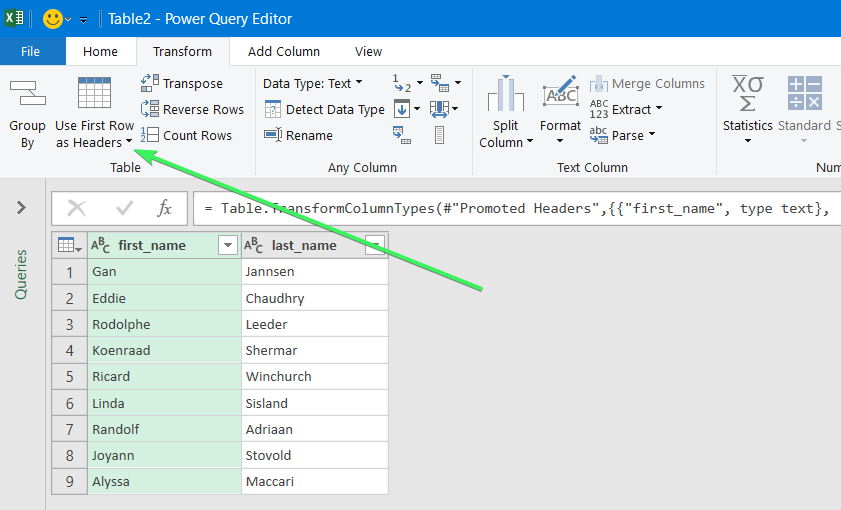
- In the Power Query Editor, go to the Transform tab and click Transpose. The rows will be rotated to columns.
- If you want to keep the headers for your columns, click the Use First Row as Headers button.
- That’s it. You can Close & Load your dataset – the rows will be converted to columns.
Error message when trying to convert rows to columns in Excel
To wrap up with converting Excel data in columns to rows, let’s review the typical error messages you can face during the flow.
Overlap error
The overlap error occurs when you’re trying to paste the transposed range into the area of the copied range. Please avoid doing this.
Wrong data type error
You may see this #VALUE! error when you implement the TRANSPOSE formula in Excel desktop without pressing Ctrl+Shift+Enter.
Other errors may be caused by typos or other misprints in the formulas you use to convert groups of data from rows to columns in Excel. Always double-check the syntax before pressing Enter or Ctrl+Shift+Enter 🙂 . Good luck with your data!
Источник
Do you have some values arranged as rows in your workbook, and do you want to convert text in rows to columns in Excel like this?
In Excel, you can do this manually or automatically in multiple ways depending on your purpose. Read on to get all the details and choose the best solution for yourself.
How to convert rows into columns or columns to rows in Excel – the basic solution
The easiest way to convert rows to columns in Excel is via the Paste Transpose option. Here is how it looks:
- Select and copy the needed range
- Right-click on a cell where you want to convert rows to columns
- Select the Paste Transpose option to rotate rows to columns
As an alternative, you can use the Paste Special option and mark Transpose using its menu.
It works the same if you need to convert columns to rows in Excel.
This is the best way for a one-time conversion of small to medium numbers of rows both in the Excel desktop and online.
Can I convert multiple rows to columns in Excel from another workbook?
The method above will work well if you want to convert rows to columns in Excel between different workbooks using Excel desktop. You need to have both spreadsheets open and do the copying and pasting as described.
However, in Excel Online, this won’t work for different workbooks. The Paste Transpose option is not available.
Therefore, in this case, it’s better to use the TRANSPOSE function.
How to switch rows and columns in Excel in more efficient ways
To switch rows and columns in Excel automatically or dynamically, you can use one of these options:
- Excel TRANSPOSE function
- VBA macro
- Power Query
Let’s check out each of them in the example of a data range that we imported to Excel from a Google Sheets file using Coupler.io.
Coupler.io is an integration solution that synchronizes data between source and destination apps on a regular schedule. For example, you can set up an automatic data export from Google Sheets every day to your Excel workbook.
Check out all the available Excel integrations.
How to change row to column in Excel with TRANSPOSE
TRANSPOSE is the Excel function that allows you to switch rows and columns in Excel. Here is its syntax:
=TRANSPOSE(array)array– an array of columns or rows to transpose
One of the main benefits of TRANSPOSE is that it links the converted columns/rows with the source rows/columns. So, if the values in the rows change, the same changes will be made in the converted columns.
TRANSPOSE formula to convert multiple rows to columns in Excel desktop
TRANSPOSE is an array formula, which means that you’ll need to select a number of cells in the columns that correspond to the number of cells in the rows to be converted and press Ctrl+Shift+Enter.
=TRANSPOSE(A1:J2)
Fortunately, you don’t have to go through this procedure in Excel Online.
TRANSPOSE formula to rotate row to column in Excel Online
You can simply insert your TRANSPOSE formula in a cell and hit enter. The rows will be rotated to columns right away without any additional button combinations.
Excel TRANSPOSE multiple rows in a group to columns between different workbooks
We promised to demonstrate how you can use TRANSPOSE to rotate rows to columns between different workbooks. In Excel Online, you need to do the following:
- Copy a range of columns to rotate from one spreadsheet and paste it as a link to another spreadsheet.

- We need this URL path to use in the TRANSPOSE formula, so copy it.
- The URL path above is for a cell, not for an array. So, you’ll need to slightly update it to an array to use in your TRANSPOSE formula. Here is what it should look like:
=TRANSPOSE('https://d.docs.live.net/ec25d9990d879c55/Docs/Convert rows to columns/[dataset.xlsx]dataset'!A1:D12)
You can follow the same logic for rotating rows to columns between workbooks in Excel desktop.
Are there other formulas to convert columns to rows in Excel?
TRANSPOSE is not the only function you can use to change rows to columns in Excel. A combination of INDIRECT and ADDRESS functions can be considered as an alternative, but the flow to convert rows to columns in Excel using this formula is much trickier. Let’s check it out in the following example.
How to convert text in columns to rows in Excel using INDIRECT+ADDRESS
If you have a set of columns with the first cell A1, the following formula will allow you to convert columns to rows in Excel.
=INDIRECT(ADDRESS(COLUMN(A1),ROW(A1)))
But where are the rows, you may ask! Well, first you need to drag this formula down if you are converting multiple columns to rows. Then drag it to the right.
NOTE: This Excel formula only to convert data in columns to rows starting with A1 cell. If your columns start from another cell, check out the next section.
How to convert Excel data in columns to rows using INDIRECT+ADDRESS from other cells
To convert columns to rows in Excel with INDIRECT+ADDRESS formulas from not A1 cell only, use the following formula:
=INDIRECT(ADDRESS(COLUMN(first_cell) - COLUMN($first_cell) + ROW($first_cell), ROW(first_cell) - ROW($first_cell) + COLUMN($first_cell)))
- first_cell – enter the first cell of your columns
Here is an example of how to convert Excel data in columns to rows:
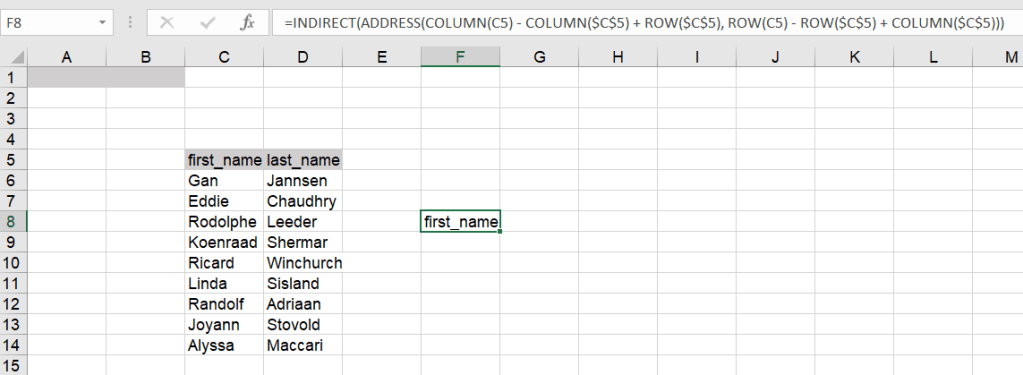
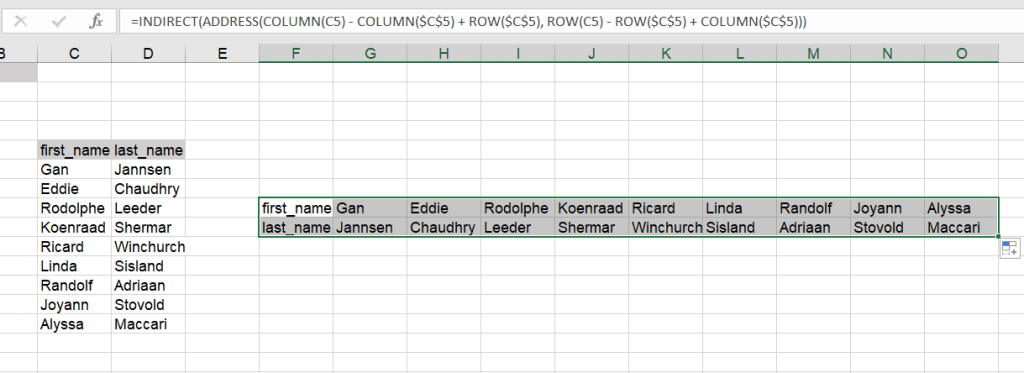
=INDIRECT(ADDRESS(COLUMN(C5) - COLUMN($C$5) + ROW($C$5), ROW(C5) - ROW($C$5) + COLUMN($C$5)))
Again, you’ll need to drag the formula down and to the right to populate the rest of the cells.
How to automatically convert rows to columns in Excel VBA
VBA is a superb option if you want to customize some function or functionality. However, this option is only code-based. Below we provide a script that allows you to change rows to columns in Excel automatically.
- Go to the Visual Basic Editor (VBE). Click Alt+F11 or you can go to the Developer tab => Visual Basic.
- In VBE, go to Insert => Module.
- Copy and paste the script into the window. You’ll find the script in the next section.
- Now you can close the VBE. Go to Developer => Macros and you’ll see your RowsToColumns macro. Click Run.
- You’ll be asked to select the array to rotate and the cell to insert the rotated columns.
- There you go!
VBA macro script to convert multiple rows to columns in Excel
Sub TransposeColumnsRows()
Dim SourceRange As Range
Dim DestRange As Range
Set SourceRange = Application.InputBox(Prompt:="Please select the range to transpose", Title:="Transpose Rows to Columns", Type:=8)
Set DestRange = Application.InputBox(Prompt:="Select the upper left cell of the destination range", Title:="Transpose Rows to Columns", Type:=8)
SourceRange.Copy
DestRange.Select
Selection.PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteAll, Operation:=xlNone, SkipBlanks:=False, Transpose:=True
Application.CutCopyMode = False
End Sub
Sub RowsToColumns()
Dim SourceRange As Range
Dim DestRange As Range
Set SourceRange = Application.InputBox(Prompt:="Select the array to rotate", Title:="Convert Rows to Columns", Type:=8)
Set DestRange = Application.InputBox(Prompt:="Select the cell to insert the rotated columns", Title:="Convert Rows to Columns", Type:=8)
SourceRange.Copy
DestRange.Select
Selection.PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteAll, Operation:=xlNone, SkipBlanks:=False, Transpose:=True
Application.CutCopyMode = False
End Sub
Read more in our Excel Macros Tutorial.
Convert rows to column in Excel using Power Query
Power Query is another powerful tool available for Excel users. We wrote a separate Power Query Tutorial, so feel free to check it out.
Meanwhile, you can use Power Query to transpose rows to columns. To do this, go to the Data tab, and create a query from table.
- Then select a range of cells to convert rows to columns in Excel. Click OK to open the Power Query Editor.
- In the Power Query Editor, go to the Transform tab and click Transpose. The rows will be rotated to columns.
- If you want to keep the headers for your columns, click the Use First Row as Headers button.
- That’s it. You can Close & Load your dataset – the rows will be converted to columns.
Error message when trying to convert rows to columns in Excel
To wrap up with converting Excel data in columns to rows, let’s review the typical error messages you can face during the flow.
Overlap error
The overlap error occurs when you’re trying to paste the transposed range into the area of the copied range. Please avoid doing this.
Wrong data type error
You may see this #VALUE! error when you implement the TRANSPOSE formula in Excel desktop without pressing Ctrl+Shift+Enter.
Other errors may be caused by typos or other misprints in the formulas you use to convert groups of data from rows to columns in Excel. Always double-check the syntax before pressing Enter or Ctrl+Shift+Enter 🙂 . Good luck with your data!
-
A content manager at Coupler.io whose key responsibility is to ensure that the readers love our content on the blog. With 5 years of experience as a wordsmith in SaaS, I know how to make texts resonate with readers’ queries✍🏼
Back to Blog
Focus on your business
goals while we take care of your data!
Try Coupler.io
Excel Rows to Columns (Table of Contents)
- Rows to Columns in Excel
- How to Convert Rows to Columns in Excel using Transpose?
Rows to Columns in Excel
In Microsoft Excel, we can change the rows to column and column to row vice versa, using TRANSPOSE. We can either use the Transpose or Transpose function to get the output.
Definition of Transpose
Transpose function normally returns a transposed range of cells which is used to switch the rows to columns and columns to rows vice versa, i.e. we can convert a vertical range of cells to a horizontal range of cells or a horizontal range of cells to a vertical range of cells in excel.
For example, a horizontal range of cells is returned if a vertical range is entered, or a vertical range of cells is returned if a horizontal range of cells is entered.
How to Convert Rows to Columns in Excel using Transpose?
It is very simple and easy. Let’s understand the working of converting rows to columns in excel by using some examples.
You can download this Convert Rows to Columns Excel?Template here – Convert Rows to Columns Excel?Template
Steps to use transpose:
- Start the cell by selecting and copying an entire range of data.
- Click on the new location.
- Right-click the cell.
- Choose to paste special, and we will find the transpose button.
- Click on the 4th option.
- We will get the result converted to rows to columns.
Example #1
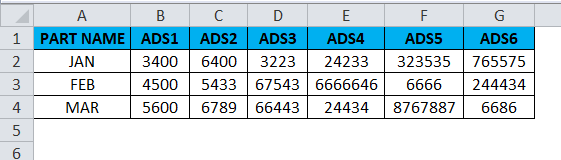
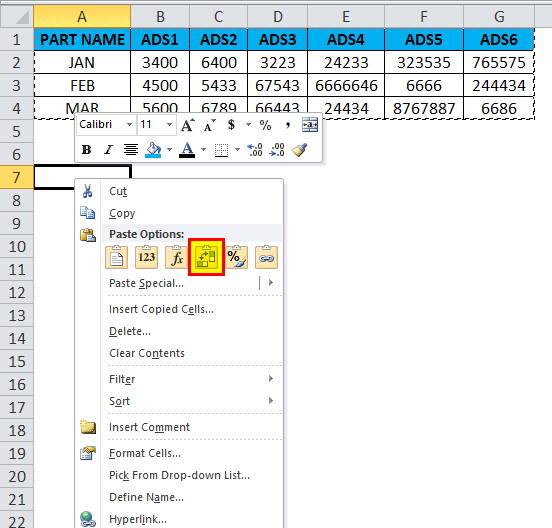
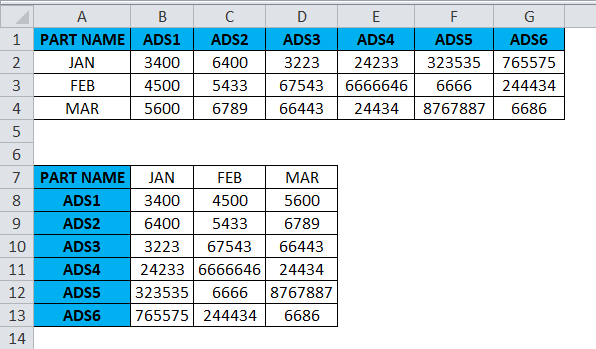
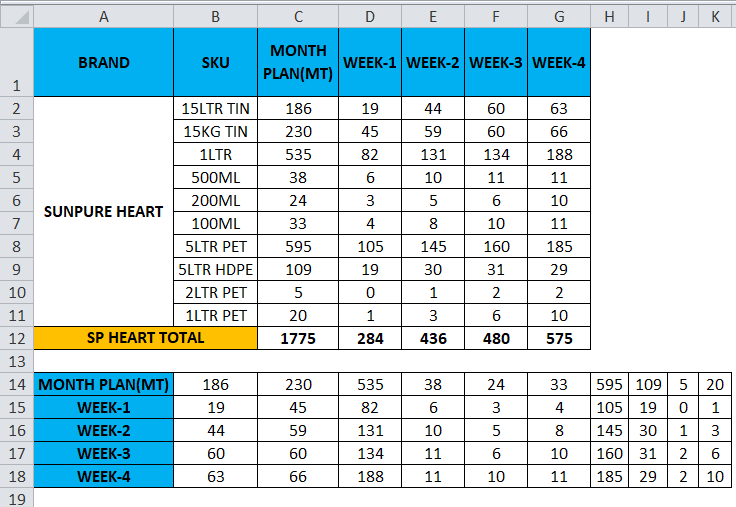
Consider the below example where we have a revenue figure for sales month wise. We can see that month data are row-wise and Part number data are column-wise.
If we want to convert the rows to the column in excel, we can use the transpose function and apply it by following the below steps.
- First, select the entire cells from A To G, which has data information.
- Copy the entire data by pressing the Ctrl+ C Key.
- Now select the new cells where exactly you need to have the data.
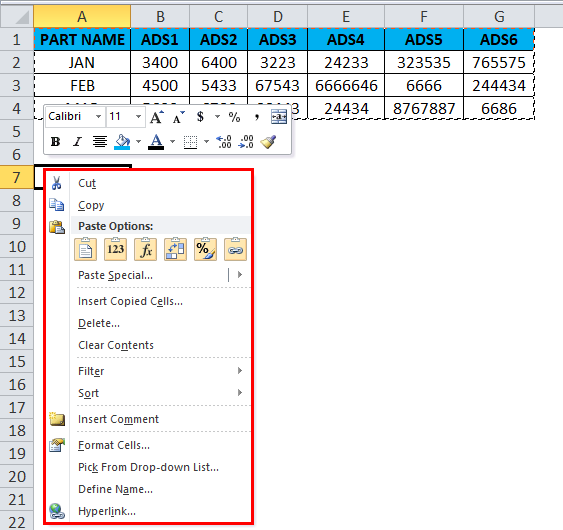
- Right, click on the new cell, and we will get the below option which is shown below.
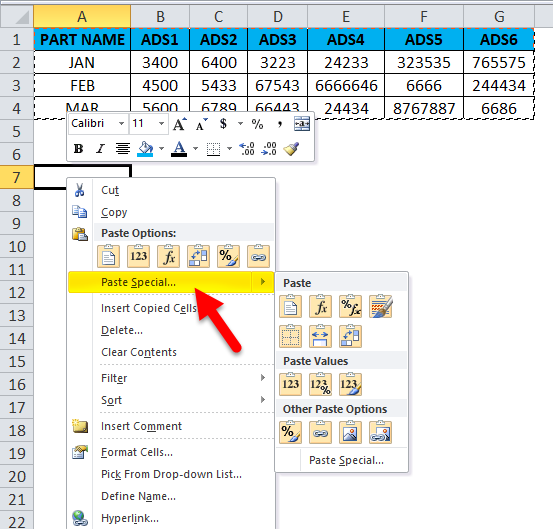
- Choose the option paste special.
- Select the fourth option in paste special, which is called transpose, as shown in the below screenshot highlighted in yellow color.
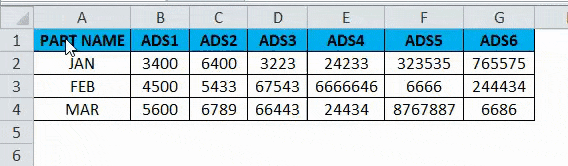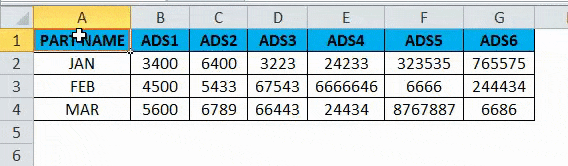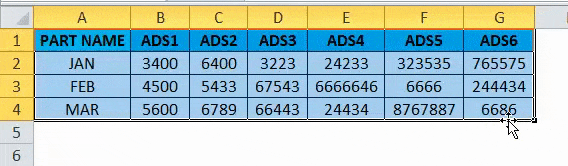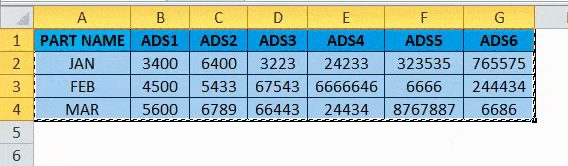
- Once we click on transpose, we will get the below output as follows.
In the above screenshot, we can see that rows have been changed to column and column has been changed to rows in excel. In this way, we can easily convert the given data from row to column and column to row in excel. For the end-user, if there is a huge data, this transpose will be very useful, and it saves a lot of time instead of typing it, and we can avoid duplication.
Example #2
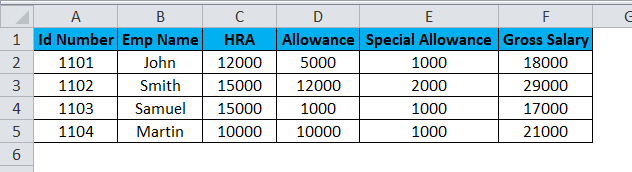
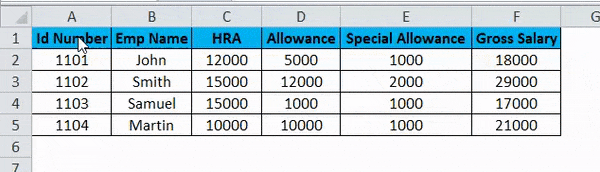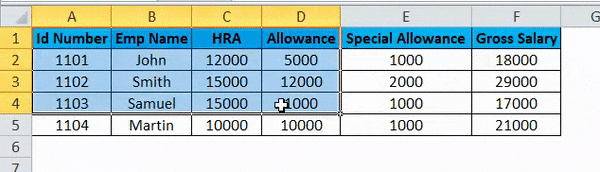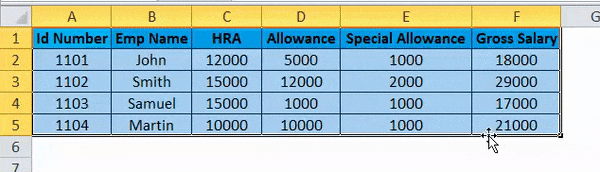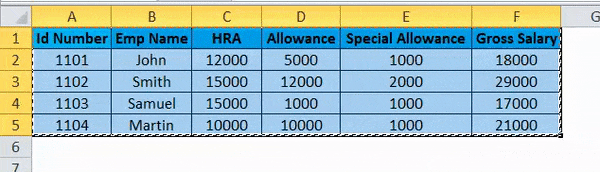
In this example, we will convert rows to the column in excel and see how to use transpose the employee salary data by following the below steps.
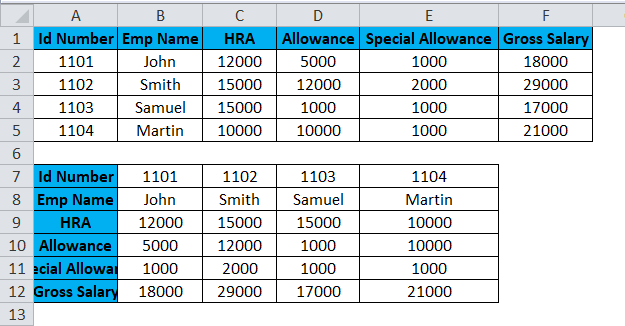
Consider the above screenshot, which has id number, emp name, HRA, Allowance, and Special Allowance. Suppose we need to convert the data column to rows; in these cases TRANSPOSE function will be very useful to convert it, which saves time instead of entering the data. We will see how to convert the column to row with the below steps.
- Click on the cell and copy the entire range of data as shown below.
- Once you copy the data, choose the new cell location.
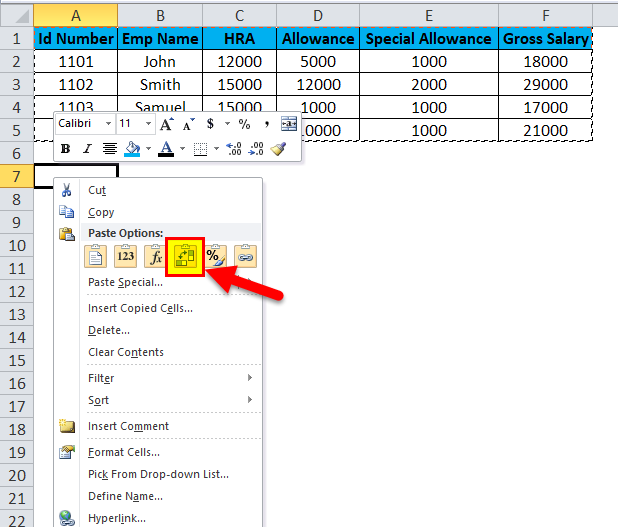
- Right-click on the cell.
- We will get the paste special dialogue box.
- Choose Paste Special option.
- Select the Transpose option in that, as shown below.
- Once you have chosen the transpose option, the excel row data will be converted to the column as shown in the below result.
In the above screenshot, we can see the difference that row has been converted to columns; in this way, we can easily use the transpose to convert horizontal to vertical and vertical to horizontal in excel.
Transpose Function
In excel, a built-in function called Transpose Function converts rows to columns and vice versa; this function works the same as transpose. i.e. we can convert rows to columns or columns into rows vice versa.
Syntax of Transpose Function:
Argument
- Array: The range of cells to transpose.
When a set of an array is transposed, the first row is used as the first column of an array, and in the same way, the second row is used as the second column of a new one and the third row is used as the third column of the array.
If we are using the transpose function formula as an array, then we have CTRL+SHIFT +ENTER to apply it.
Example #3
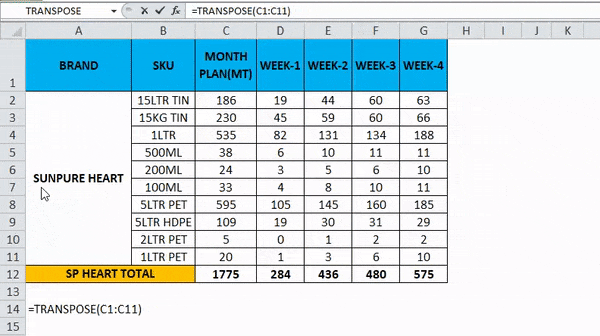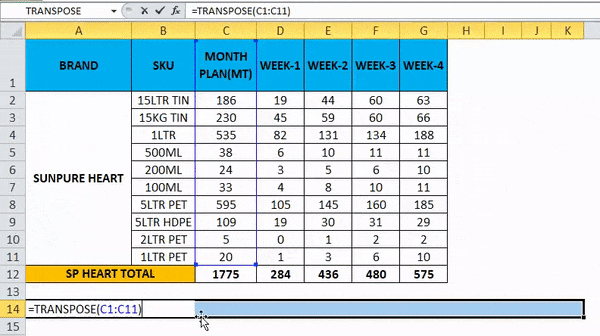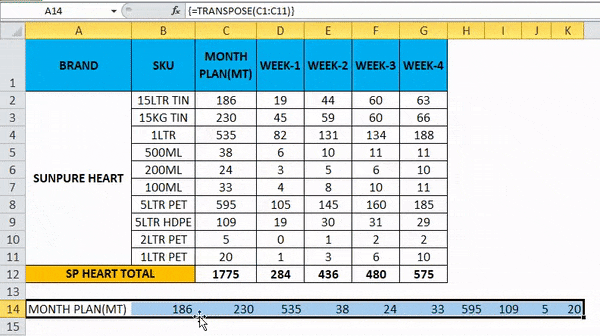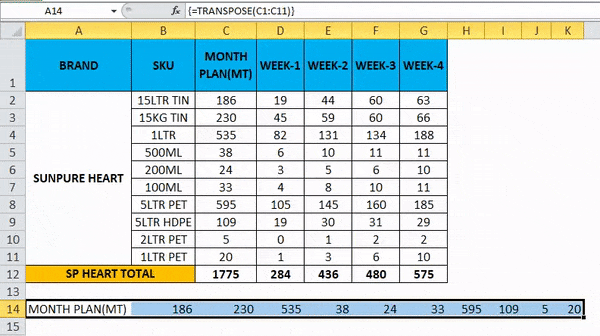
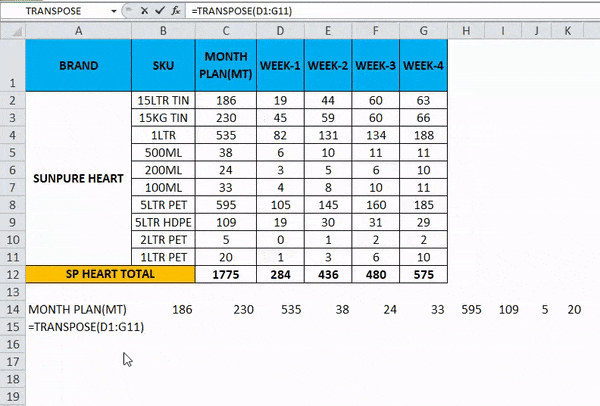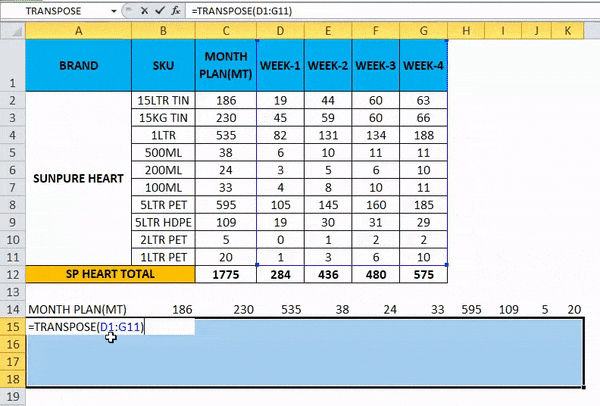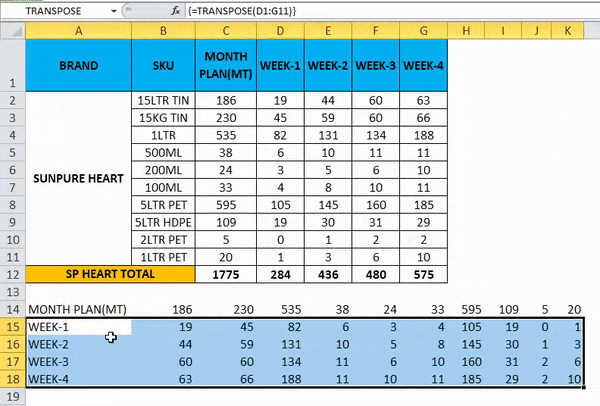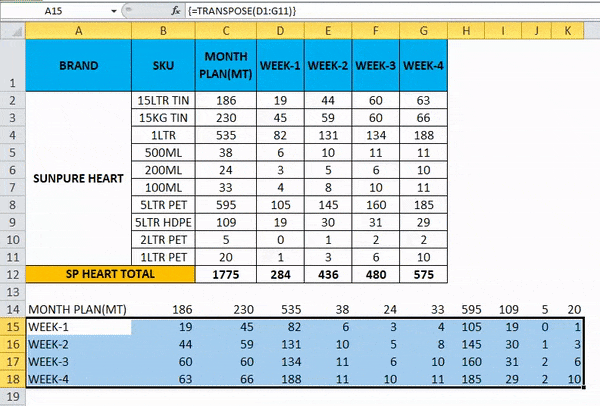
In this example, we are going to see how to use the transpose function with an array with the below example.
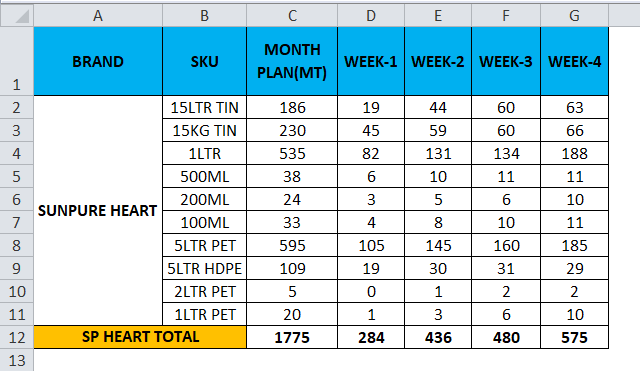
Consider the below example, which shows sales data week wise where we are going to convert the data to columns to row and row to column vice versa by using the transpose function.
- Click on the new cell.
- Select the row you want to transpose.
- Here we are going to convert the MONTH PLAN to the column.
- We can see that there are 11 rows, so in order to use the transpose function, the rows and columns should be in equal cells; if we have 11 rows, then the transpose function needs the same 11 columns to convert it.
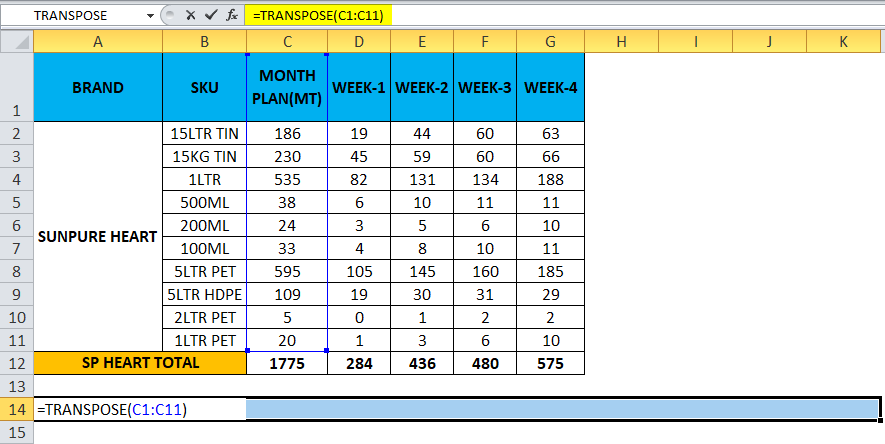
- Choose exactly 11 columns, use the Transpose Formula, and select an array from C1 to C11, as shown in the below screenshot.
- Now use CTRL+SHIFT +ENTER to apply as an array formula.
- Once we use the CTRL+SHIFT +ENTER, we can see the open and close parenthesis in the formulation.
- We will get the output where a row has been changed to the column, which is shown below.
- Use the formula for the entire cells so that we will get the exact result.
So the Final Output will be as below.
Things to Remember about Convert Rows to Columns in Excel
- Transpose function is one of the most useful functions in excel where we can rotate the data, and the data information will not be changed while converting.
- If there are any blank or empty cells, transpose will not work, and it will give the result as zero.
- While using the array formula in transpose function, we cannot delete or edit the cells because all the data are connected with links, and Excel will throw an error message that “YOU CAN NOT CHANGE PART OF AN ARRAY.”
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Rows to Columns in Excel. Here we discuss how to convert rows to columns in excel using transpose along with practical examples and a downloadable excel template. Transpose can help everyone to convert multiple rows to a column in excel easily quickly. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- Excel COLUMNS Function
- Excel ROW Function
- Unhide Columns in Excel
- Excel Rows and Columns
How to Transpose Data in Excel: Turn Rows into Columns (2023)
Did you ever happen to construct a data table in Excel? Where after it was all done, you realized that it would have made more sense the other way round?
In such a situation, don’t rush to recreate the table altogether.
Instead, you can turn the sides of your table with the transpose feature of Excel. And all it takes is a pair of clicks. 😀
Ready to learn all about transpose excel? Let’s dive into the article below.
To practice as you learn, download our free sample workbook here.
Turn rows into columns with copy/paste (transpose)
This section applies where you have rows-long data that you want to be organized as Excel columns.
For example, take a look at the image below.

The image above has the seven days of a week in the shape of a row.
Can you turn this row into a column in Excel? Look below.
1. Select the data to be transposed (the row of weekdays).

2. Right-click on the selection.
3. From the context menu that opens up, select Copy.
Or, select the row and press Ctrl + C.

4. Activate the destination cell (where you want the column to appear).
5. Right-click again to launch the context menu, as shown below.

6. Click on the Option Paste Special under paste options.

7. From the ‘Paste Special’ dialogue box, click ‘Transpose’ and click ‘Okay’

Pro Tip!
To save time, click the arrow next to Paste options. From the drop-down menu choose the icon with a two-ended arrow. ✌️

The weekdays have now taken the shape of a column!
Turn columns into rows with copy/paste (transpose)
That’s how you can turn your row-oriented data into a column.
But does this work the other way around? Can you convert columns into rows?
1. Select the column containing the weekdays.

2. Right-click on the selection, and from the context menu, select Copy.

3. Activate the destination cell (where you want the row to appear).
4. Right-click again to launch the context menu.

5. Click on the Option Paste Special.
6. From the ‘Paste Special’ dialogue box, click ‘ Transpose’ and click ‘Okay’

Ta-da! Excel converts columns to rows. 😎

The transpose function hence works both ways.
Does transpose work on a table?
The above example was a simple one. We took a row and turned it into a column (and vice versa).
But what comes now is not only a row of weekdays but a whole timetable.

The above image shows different weekdays and time slots. For each time slot and each weekday, classes for different subjects are scheduled.
Presently, time slots are arranged in a horizontal range (in a row). And weekdays are in a vertical range (in a column).
To turn the table the other way around, follow these steps.
1. Select the table.
2. Right-click anywhere on the table to launch the context menu and select Copy.

3. Activate the destination range (where you want the transposed cells to appear).
4. Right-click again to launch the context menu

6. Click on the Option Paste Special.
7. From the ‘Paste Special’ dialogue box, click ‘ Transpose’ and click ‘Okay’

The table takes a whole new look.

And here we have the transposed table.
Pay attention to see how the time slots are now organized in a vertical range. Similarly, weekdays take the shape of a row.
The data in between is also transposed accordingly.
Easy enough, isn’t it?
Transpose and keep references with the TRANSPOSE function
Everything seems good until here. But what if you want to retain a table in both the forms – before and after it is transposed?
This means you want to retain references to the source table. So that whenever you make a change to the source table, the transposed data changes accordingly and automatically.
To do so, the simple copy/paste feature of Excel won’t work. Instead, you’d need a dynamic function like the Transpose function.
For the same timetable.
1. Write the Transpose function in the destination cell as follows:
= TRANSPOSE (B2:F9)

Select the entire cell range where the original data is placed.
2. Press Enter to have the table transposed.

Excel has transposed the whole table (columns to rows).
How is it different from the copy/paste transpose feature?
Make changes to any cell in the source table.

Note how Excel automatically brings the same change to the transposed data.

This is because the transposed cells retain the reference to the original table. If the source data in the original table changes, the transposed data would also change.
Transpose (Copy / Paste Special) vs. The Transpose Function
We have already seen two ways how you may transpose a given data set in Excel. Which one’s better? 🤔
Here’s a quick analysis:
1. The transpose function keeps references to the original data. Copy / Pasting lacks this functionality.
2. The transpose function is an array formula that returns an array. You cannot make changes to any individual cell of the array.

3. The transpose function reproduces the transposed data but misses out on the formatting of the original table.
4. Also, the transpose formula will turn any blank cells in the source data to zero (0). Refer to the top left cell of the table in our example.
And so you manually have to reformat the table.
That’s it – Now what?
The article teaches you how to transpose rows, columns, multiple rows, and multiple columns in Excel.
It also explains how to transpose a whole table through copy/pasting. And to transpose a table but keep references through the Transpose function.
Also, let’s not forget the analysis of which of the above methods suits us the best.
The transpose function is a handy one – but you might only use it once in a while. Some other very common and widely used functions of Excel include the VLOOKUP, SUMIF, and IF functions.
My free 30-minutes email course is all that you need to get the hang of these functions (and many more).
Kasper Langmann2023-01-19T12:22:17+00:00
Page load link
While you might have a good idea of the layout of the data that you are adding to a spreadsheet, changes in the scope of a project, or the addition of more data could change that.
It can be frustrating to cut and paste a lot of data in Excel when you need to move it around, and that becomes even more complicated when data that is already in a row needs to go to a column or vice versa.
Luckily Microsoft Excel has a helpful paste option that will let you switch from a row to a column in your spreadsheet.
Our tutorial below will show you how to select existing data in Excel and use the Transpose option to convert it from a row to a column.
How to Convert a Row Into a Column in Excel
- Open your spreadsheet.
- Select the cells to convert.
- Right-click a selected cell and choose Copy.
- Click the cell where you want to paste the data.
- Choose the Home tab.
- Click the Paste button, then select the Transpose option.
Our guide continues below with additional information on how to switch a row to a column in Excel, including pictures of these steps.
Occasionally you might find that you have laid out data in a spreadsheet in a different manner than you actually need it.
This can be frustrating, and the prospect of essentially redoing the exact same task again might not be appealing.
Fortunately, you can convert a row into a column in Excel 2013 by taking advantage of a feature called Transpose.
Transposing data in an Excel spreadsheet allows you to copy a series of data that is currently in a row, then paste that same data into a column instead.
This can be immensely helpful when a spreadsheet has been laid out incorrectly, and it can help to minimize potential mistakes that can occur when you need to re-enter large sequences of information.
Transposing a Row to a Column in Excel 2013 (Guide with Pictures)
In the tutorial below we will be converting data from a row to a column.
Note that the new location of the data cannot overlap the original location of the data.
If this presents a problem, then you can always use the first cell under your target destination row, then delete the original row. Click here to learn how to delete a row in Excel 2013.
These steps will show you how to switch a row to a column in an Excel spreadsheet.
Step 1: Open your spreadsheet in Excel 2013.
Open your Excel file.
Step 2: Highlight the data that you wish to transpose to a column.
Select the row data to convert.
Step 3: Right-click the selected data, then click the Copy option.
Copy the selected data.
Note that you can also copy data by pressing Ctrl + C on your keyboard.
Step 4: Click inside the cell where you would like to display the first cell in the new column.
Choose where to put the data.
Step 5: Click the Home tab at the top of the window.
Choose the Home tab.
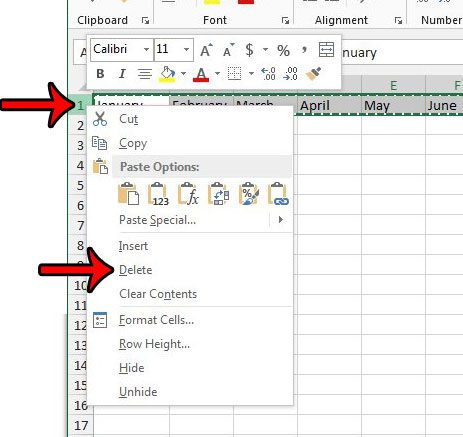
Step 6: Click the arrow under the Paste button at the left side of the ribbon, then click the Transpose button.
Click Paste, then Transpose.
You can now delete the original row by right-clicking the row number at the left side of the spreadsheet, then clicking the Delete option.
Now that you know how to switch a row to a column in Excel you will be able to move your data around a little more easily when you have cells that are in the incorrect type of cell range.
Frequently Asked Questions About Changing a Row to a Column in Microsoft Excel
How do I insert a row in Microsoft Excel?
If your spreadsheet is already full of data and you need to add some data in the middle of it, then you don’t need to cut and paste everything to move it down a row.
If you right-click on the row number below where you wish to add the new row you can select the Insert option to place a new blank row above that row.
How do I add a column in an Excel spreadsheet?
Adding a new column to your spreadsheet is similar to adding a new row.
You can right-click on the column letter to the right of where you wish to add the new column, then choose the Insert option from that menu.
Can I delete a row or a column in Excel?
Yes, it’s possible to delete an entire row and all of the data that is contained within the cells in that row or column.
If you right-click on a row number or a column letter, it will select that entire range and open a contextual menu with some options.
One of those options is “Delete” which you can select the delete the whole column or row from your worksheet.
How do I create a new worksheet tab in an Excel workbook?
If you aren’t copying and pasting data to move it to a different location in the same spreadsheet, then you might be planning to put it into a new blank spreadsheet.
Rather than creating an entirely new Excel workbook file, you can click the plus button to the right of your worksheet tabs at the bottom of the window.
This will create a new, blank worksheet tab where you can paste copied data from other worksheets in your workbook.
Is there a worksheet in an Excel file that you would like to use in a different Excel file? Learn about copying entire worksheets in Excel 2013 and make it easier to reuse your most helpful spreadsheets.
Additional Sources
Matthew Burleigh has been writing tech tutorials since 2008. His writing has appeared on dozens of different websites and been read over 50 million times.
After receiving his Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees in Computer Science he spent several years working in IT management for small businesses. However, he now works full time writing content online and creating websites.
His main writing topics include iPhones, Microsoft Office, Google Apps, Android, and Photoshop, but he has also written about many other tech topics as well.
Read his full bio here.

 or press CTRL+X.
or press CTRL+X. or press CTRL+C.
or press CTRL+C.
 or press Ctrl+V.
or press Ctrl+V. , drag the row or column to another location
, drag the row or column to another location , do one of the following:
, do one of the following: