Функции преобразования типов данных в VBA Excel. Наименования функций, синтаксис, типы возвращаемых данных, диапазоны допустимых значений выражения-аргумента.
Синтаксис функций преобразования
Выражение (аргумент) – это любое строковое или числовое выражение, возвращающее значение, входящее в диапазон допустимых значений для аргумента. Выражение может быть представлено переменной или другой функцией.
Если аргумент, переданный в функцию, не входит в диапазон типа, в который преобразуются данные, происходит ошибка.
Функции преобразования типов
Наименования функций преобразования типов, типы возвращаемых данных, диапазоны допустимых значений для аргумента:
| Функция | Тип данных | Диапазон значений аргумента |
|---|---|---|
| CBool | Boolean | Любое допустимое строковое или числовое выражение. |
| CByte | Byte | От 0 до 255. |
| CCur | Currency | От -922 337 203 685 477,5808 до 922 337 203 685 477,5807. |
| CDate | Date | Любое допустимое выражение даты. |
| CDbl | Double | От -1,79769313486231E308 до -4,94065645841247E-324 для отрицательных значений; от 4,94065645841247E-324 до 1,79769313486232E308 для положительных значений. |
| CDec | Decimal | 79 228 162 514 264 337 593 543 950 335 для чисел без десятичных знаков. Для чисел с 28 десятичными знаками диапазон составляет 7,9228162514264337593543950335. Наименьшим возможным числом, отличным от нуля, является число 0,0000000000000000000000000001. |
| CInt | Integer | От -32 768 до 32 767, дробная часть округляется. |
| CLng | Long | От -2 147 483 648 до 2 147 483 647, дробная часть округляется. |
| CSng | Single | От -3,402823E38 до -1,401298E-45 для отрицательных значений; от 1,401298E-45 до 3,402823E38 для положительных значений. |
| CStr | String | Результат, возвращаемый функцией CStr, зависит от аргумента Выражение. |
| CVar | Variant | Диапазон совпадает с типом Double для числовых значений и с типом String для нечисловых значений. |
Дополнительно для VBA7:
| Функция | Тип данных | Диапазон значений аргумента |
|---|---|---|
| CLngLng | LongLong | От -9 223 372 036 854 775 808 до 9 223 372 036 854 775 807, дробная часть округляется. Действительно только для 64-разрядных платформ. |
| CLngPtr | LongPtr | От -2 147 483 648 до 2 147 483 647 для 32-разрядных платформ, от -9 223 372 036 854 775 808 до 9 223 372 036 854 775 807 для 64-разрядных платформ, дробная часть округляется в обоих типах систем. |
Примеры преобразования типов
Функция CBool
Функция CBool используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Boolean.
|
Dim a a = CBool(10) ‘Результат: True a = CBool(0) ‘Результат: False a = CBool(«True») ‘Результат: True a = CBool(«Test») ‘Результат: Error Dim a, b, c a = «Test1» b = «Test2» c = CBool(a = b) ‘Результат: False c = CBool(a <> b) ‘Результат: True |
Функция CByte
Функция CByte используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Byte.
|
Dim a, b, c a = 654 b = 3.36 c = a / b ‘Результат: 194,642857142857 c = CByte(c) ‘Результат: 195 c = a * b ‘Результат: 2197,44 c = CByte(c) ‘Результат: Error |
Функция CCur
Функция CCur используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Currency.
|
Dim a, b, c a = 254.6598254 b = 569.2156843 c = a + b ‘Результат: 823,8755097 c = CCur(a + b) ‘Результат: 823,8755 |
Функция CDate
Функция CDate используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Date. Она распознает форматы даты в соответствии с национальной настройкой системы.
|
Dim a As String, b As Date, c As Double a = «28.01.2021» b = CDate(a) ‘Результат: #28.01.2021# c = CDbl(b) ‘Результат: 44224 Dim a a = CDate(44298.63895) ‘Результат: #12.04.2021 15:20:05# a = CDate(44298) ‘Результат: #12.04.2021# a = CDate(0.63895) ‘Результат: #15:20:05# |
Функция CDbl
Функция CDbl используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Double.
|
Dim a As String, b As String, c As Double a = «45,3695423» b = «548955,756» c = CDbl(a) + CDbl(b) ‘Результат: 549001,1255423 |
Примечание
Eсли основной язык системы – русский, при записи в редакторе VBA Excel дробного числа в виде текста, ставим в качестве разделителя десятичных разрядов – запятую. Проверьте разделитель по умолчанию для своей национальной системы:
MsgBox Application.DecimalSeparator
Функция CDec
Функция CDec используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Decimal.
|
Dim a As String, b As Double, c a = «5,9228162514264337593543950335» b = 5.92281625142643 c = CDec(a) — CDec(b) ‘Результат: 0,0000000000000037593543950335 Dim a As Double, b As String, c a = 4.2643E—14 b = CStr(a) ‘Результат: «4,2643E-14» c = CDec(a) ‘Результат: 0,000000000000042643 |
Функция CInt
Функция CInt используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Integer.
|
Dim a As String, b As Integer a = «2355,9228» b = CInt(a) ‘Результат: 2356 |
Функция CLng
Функция CLng используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Long.
|
Dim a As Date, b As Long a = CDate(44298.63895) ‘Результат: #12.04.2021 15:20:05# b = CLng(a) ‘Результат: 44299 a = CDate(b) ‘Результат: #13.04.2021# |
Функция CSng
Функция CSng используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Single.
|
Dim a As String, b As Single a = «3,2365625106» b = CSng(a) ‘Результат: 3,236562 |
Функция CStr
Функция CStr используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных String.
|
Dim a As Single, b As String a = 5106.23 b = CStr(a) ‘Результат: «5106,23» |
Функция CVar
Функция CVar используется для преобразования выражений в тип данных Variant.
|
Dim a As Double, b As String, c a = 549258.232546 b = «Новое сообщение» c = CVar(a) ‘Результат: 549258,232546 (Variant/Double) c = CVar(b) ‘Результат: «Новое сообщение» (Variant/String) |
Функции преобразования типов данных используются в тексте процедур VBA Excel для того, чтобы указать, что результатом выполнения той или иной операции должны стать данные определенного типа, отличающегося от типа, заданного по умолчанию.
Return to VBA Code Examples
We have already covered an introduction to string functions in our VBA Strings and Substrings Functions tutorial. In this tutorial, we are going to look at how to convert an integer to a string (click here to learn about converting Strings to Numbers). The reason you would want to convert a number or date to a string is in order to use string manipulation functions on these values.
The VBA CStr Function
The VBA CStr Function allows you to convert a number, date or boolean data type to a string.
MsgBox CStr (88)The syntax of the CStr Function is:
CStr(expression) where expression is the number or date that you want to convert.
The following code shows you how numbers are outputted compared to text, including by using the CStr Function.
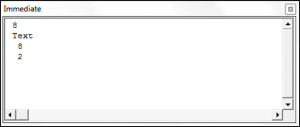
Sub UsingTheConvertToStringFunction()
Debug.Print CStr(8)
Debug.Print "Text"
Debug.Print 8
Debug.Print 2
End SubThis uses Debug.Print to output the results to the Immediate Window.
Both CStr(8) and the word Text are displayed as text and are left aligned whereas the two numbers are right aligned within the immediate window.
VBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
OBJECTS
Worksheets: The Worksheets object represents all of the worksheets in a workbook, excluding chart sheets.
Range: The Range object is a representation of a single cell or a range of cells in a worksheet.
PREREQUISITES
Worksheet Name: Have a worksheet named Analyst.
Number to convert to Text: Ensure that the number that you want to convert to text is captured in cell («B5»).
ADJUSTABLE PARAMETERS
Output Range: Select the output range by changing the cell reference («C5») in the VBA code to any cell in the worksheet, that doesn’t conflict with the formula.
Number to convert to Text: Select the number that you want to convert to text by changing the cell reference («B5») to any cell in the worksheet that contains the number that you want to convert to text and doesn’t conflict with the formula.
Excel VBA CSTR Function
CSTR in VBA is a data type conversion function that one may use to convert any value provided to this function to a string. For example, even if the given input is an integer or float value, this function will convert the value’s data type to a string data type, so the return type of this function is a string.
How do we go about this if we need to convert any value to string data type in VBAData type is the core character of any variable, it represents what is the type of value we can store in the variable and what is the limit or the range of values which can be stored in the variable, data types are built-in VBA and user or developer needs to be aware which type of value can be stored in which data type. Data types assign to variables tells the compiler storage size of the variable.read more? For this, in VBA, we have a function called “CSTR.” In this article, we will guide you through the methodology of the “CSTR” function in VBA.
The String is the data type that holds any String values. When we say string, it generally refers to text values, but that is not true with VBA codingVBA code refers to a set of instructions written by the user in the Visual Basic Applications programming language on a Visual Basic Editor (VBE) to perform a specific task.read more. A string can hold any order of characters as data. For example, “Hello” is treated as String, “123456” is treated as a string and “12-04-2019” as a string. This String data type can hold any order of characters.
Table of contents
- Excel VBA CSTR Function
- What Does CSTR Function Do in VBA?
- VBA CSTR Syntax
- How to Use VBA CSTR Function in Excel?
- Example #1
- Example #2
- Example #3
- Recommended Articles
- What Does CSTR Function Do in VBA?
What Does CSTR Function Do in VBA?
Have you ever thought of converting a different expression to Strings in VBAString functions in VBA do not replace the string; instead, this function creates a new string. There are numerous string functions in VBA, all of which are classified as string or text functions.read more? If you have a doubt, is that possible? Then the answer is an absolute YES!
CSTR is a function covering different format expressions to String format in VBA. With the CSTR function, we can convert the provided expression value to the String data type.
VBA CSTR Syntax
Below is the syntax of the Excel VBA CSTR function.
The syntax of the CSTR function includes only one argument.
Expression: It is the targeted value or cell value we are trying to change to the String data type.
The value could be any data type. So, CSTR goes ahead and converts to String data type. The common data types we usually convert are Integer, Boolean, and Date to String data types.
How to Use VBA CSTR Function in Excel?
Now, we will see some examples of the Excel VBA CSTR function.
You can download this VBA CStr Excel Template here – VBA CStr Excel Template
Example #1
Look at the below code.
Code:
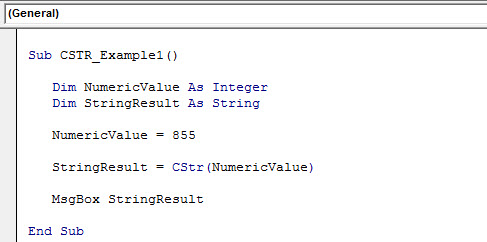
Sub CSTR_Example1() Dim NumericValue As Integer Dim StringResult As String NumericValue = 855 StringResult = CStr(NumericValue) MsgBox StringResult End Sub
Firstly, we assigned the Integer data type to the variable “NumericValue” as 855. Now, the variable “NumericValue” holds the Integer data type. Another variable, “StringResult,” assigned the formula CSTR to convert Integer data type to String data type.
CSTR converted the integer number to String data type. So, even though we can see the number 855, it is no longer an Integer Date Type in VBAIn VBA, an integer is a data type that may be assigned to any variable and used to hold integer values. In VBA, the bracket for the maximum number of integer variables that can be kept is similar to that in other languages. Using the DIM statement, any variable can be defined as an integer variable.read more. Instead, it is now in the String data type.
Example #2
Look at an example of VBA Boolean Data TypeBoolean is an inbuilt data type in VBA used for logical references or logical variables. The value this data type holds is either TRUE or FALSE and is used for logical comparison. The declaration of this data type is similar to all the other data types.read more Conversion.
Code:
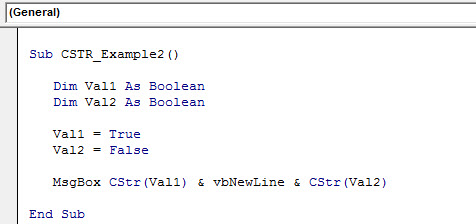
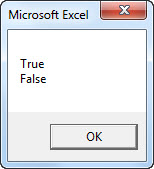
Sub CSTR_Example2() Dim Val1 As Boolean Dim Val2 As Boolean Val1 = True Val2 = False MsgBox CStr(Val1) & vbNewLine & CStr(Val2) End Sub
In the above code, I have declared two variables as Boolean.
Dim Val1 As Boolean Dim Val2 As Boolean
In the next line, we have assigned Boolean values as TRUE and FALSE.
Val1 = True Val2 = False
At this point, both variables are Boolean data types. Therefore, we have applied the VBA CSTR function in this example to convert this Boolean data type to a String data type.
Example #3
Look at the example of Date data type conversion to String data type.
Code:
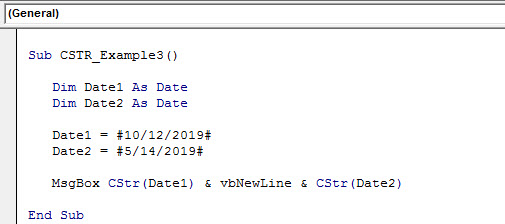
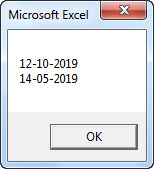
Sub CSTR_Example3() Dim Date1 As Date Dim Date2 As Date Date1 = #10/12/2019# Date2 = #5/14/2019# MsgBox CStr(Date1) & vbNewLine & CStr(Date2) End Sub
We have declared two variables as Date.
Dim Date1 As Date Dim Date2 As Date
Next line, we have assigned the Date values as 10-12-2019 and 05-14-2019, respectively.
Date1 = #10/12/2019# Date2 = #5/14/2019#
At this point, both the variables are Date data types. In the next line, we have applied the CSTR function to convert the Date data type to the String data type. Like CSTR function used to convert any other data type to String data type.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA CStr. Here, we learn how to use the VBA CStr function to convert the value to String data type, along with some simple to advanced examples. Below are some useful Excel articles related to VBA: –
- Convert String in VBA
- Excel VBA StrComp
- VBA Like Operator
- Count Function in VBA
Most times, you won’t need to «convert»; VBA will do safe implicit type conversion for you, without the use of converters like CStr.
The below code works without any issues, because the variable is of Type String, and implicit type conversion is done for you automatically!
Dim myVal As String
Dim myNum As Integer
myVal = "My number is: "
myVal = myVal & myNum
Result:
«My number is: 0»
You don’t even have to get that fancy, this works too:
Dim myString as String
myString = 77
«77»
The only time you WILL need to convert is when the variable Type is ambiguous (e.g., Type Variant, or a Cell’s Value (which is Variant)).
Even then, you won’t have to use CStr function if you’re compounding with another String variable or constant. Like this:
Sheet1.Range("A1").Value = "My favorite number is " & 7
«My favorite number is 7»
So, really, the only rare case is when you really want to store an integer value, into a variant or Cell value, when not also compounding with another string (which is a pretty rare side case, I might add):
Dim i as Integer
i = 7
Sheet1.Range("A1").Value = i
7
Dim i as Integer
i = 7
Sheet1.Range("A1").Value = CStr(i)
«7»