Download PC Repair Tool to quickly find & fix Windows errors automatically
Content Controls in Microsoft Word offer a great way to automate your document creation. It also helps in organizing the content in a structured manner. These and many more features make Content controls easy to understand and use. So, let’s see how to add and change content controls in Word.
Content controls mostly find their use in creating templates and forms as they provide flexibility in content placement. Also, depending on your preferences, you can prevent them from being edited or deleted. Here’s how!
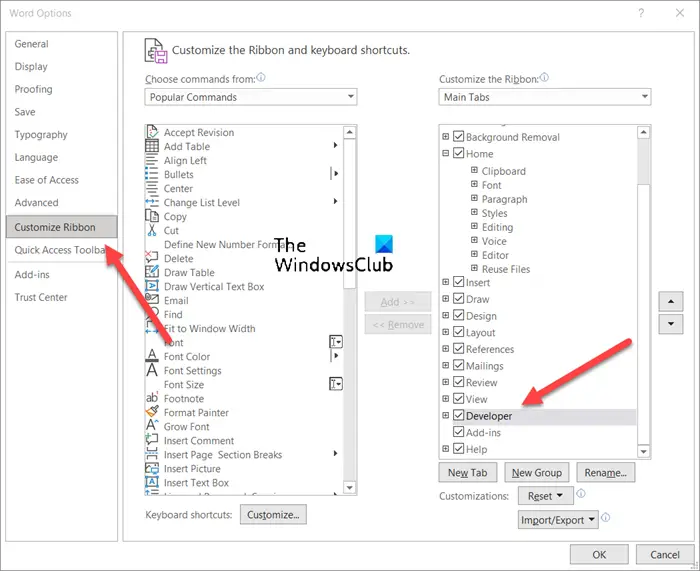
- Click File in Word.
- Scroll down to Options.
- Choose Customize Ribbon.
- Select the Developer box.
- Click OK.
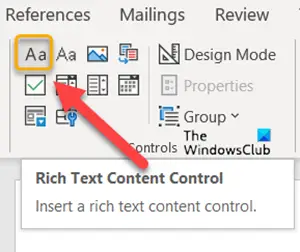
- To add a Content control, click Rich Text Content Control box.
- Place the box at appropriate location, select Properties.
- Add General Information.
- Change Locking permissions.
How do you edit Rich Text Content Control?
Before proceeding with the steps to edit or Rich Text Content Control in Word, you’ll need to add the Developer tab to the Ribbon menu in Word.
For this, click the File tab on the Ribbon menu and choose Options.
When the Options window opens, navigate to Customize Ribbon.
Here, select the Developer box and hit the Ok button as shown in the image above.
Next, to add a Content control, click Rich Text Content Control box.
Place the box at the appropriate location, to create a template.
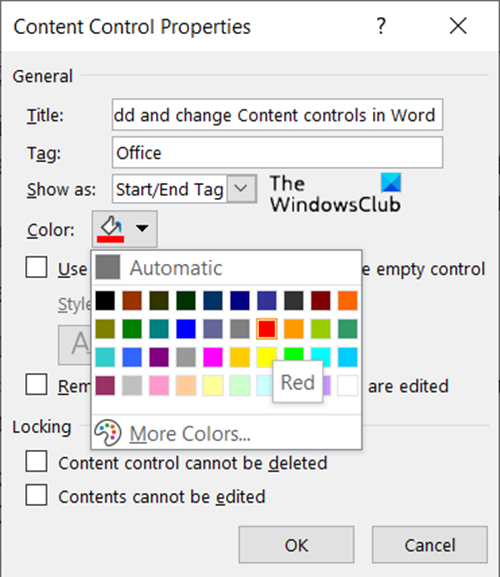
Then, select Properties under Controls block.
Add description like the title for the box, tags to be used, color for the box, etc.
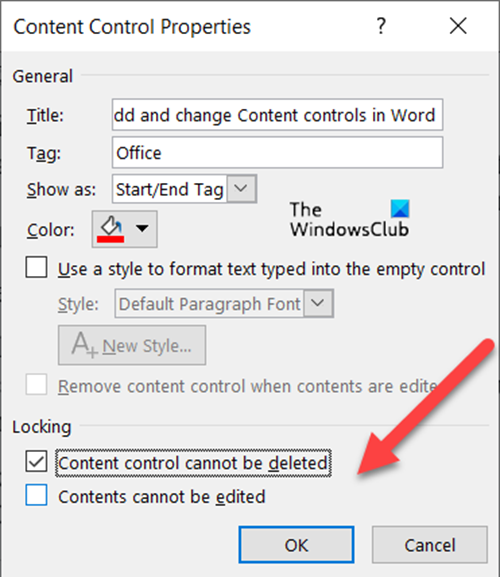
You can also change Content controls by changing its locking permission (editing or deleting them) by checking/un-checking the following boxes.
- Content Controls cannot be deleted.
- Content Controls cannot be edited.
Similarly, you can choose to create a Drop-down List via Content controls.
How do I remove content control in Word?
If you would like to delete or remove Content controls in Word:
- Press Ctrl+A to select the entire document.
- Then, right-click a visible content control.
- Now, in the context menu that appears on your computer screen, click Remove Content Control.
What is a Rich Text Content control?
A block of rich text that can be formatted represents a Rich Text Content control. So, all the custom formatted text like pictures, tables and other such items can be included in this category.
Hope it helps!
A post-graduate in Biotechnology, Hemant switched gears to writing about Microsoft technologies and has been a contributor to TheWindowsClub since then. When he is not working, you can usually find him out traveling to different places or indulging himself in binge-watching.
| title | manager | ms.date | ms.audience | keywords | ms.assetid | description | ms.localizationpriority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Content controls in Word |
lindalu |
09/10/2021 |
Developer |
content controls [word],content controls [Word], what’s new |
c0e6dd3b-fae1-453d-a9b4-7f456b5172db |
Learn how Microsoft Word 2013 content controls enable a larger range of structured document scenarios. |
high |
Content controls in Word
Learn how Microsoft Word 2013 content controls enable a larger range of structured document scenarios.
This topic provides information about changes to content controls in Microsoft Word 2013 and the document scenarios that those changes enable.
Structured documents
Structured documents are documents that control where content can appear on a document, what kind of content can appear in the document, and whether that content can be edited.
Here are some common scenarios for structured content in Microsoft Word:
-
A legal firm needs to create documents that contain legal language that should not be changed by the user.
-
A business needs to create a proposal cover page where only the title, author, and date are entered by the user.
-
A business needs to create invoices where the customer data is included in the invoice at predefined regions.
Using content controls to structure a document
Content controls are Microsoft Word entities that act as containers for specific content in a document. Individual content controls can contain content such as dates, lists, or paragraphs of formatted text. Content controls help you to create rich, structured blocks of content and are designed for use in templates that insert well-defined blocks into your documents, creating structured documents.
Content controls are ideal for creating structured documents because content controls help you fix the position of content, specify the kind of content (for example, a date, a picture, or text), restrict or enable editing, and add semantic meaning to content.
Content controls in Word 2010
The following content controls are available in Word 2010:
-
Rich Text
-
Plain Text
-
Picture
-
Building Block Gallery
-
Combo Box
-
Drop-Down List
-
Date
-
Checkbox
-
Group
Word 2010 content controls enable various potential structured document solutions, but in Word 2013 content controls enable a greater range of scenarios.
Content control improvements in Word 2013
In Word 2013, content controls provide three key improvements: improved visualization, support for XML Mapping for Rich Text content controls, and a new content control for repeating content.
Improved visualization
Word 2013 allows an individual content control to appear in one of three possible states:
-
Bounding box
-
Start/End tags
-
None
[!NOTE]
If not stated otherwise, this section discusses the visualization of content controls when the document is not viewed in Design Mode.You set the display mode for a content control by using the Show as drop-down list control in the Content Control Properties dialog box.
Figure 1. Content Control Properties dialog box
You can also set the display mode for a content control by using the Word 2013 object model (discussed later in New Word 2013 content control object model members).
Bounding box
The default rendering for content controls in Word 2013 is to preserve the look of content controls as they appear in Word 2007 and Word 2010; that is, as a bounding box. When a content control is set to show as Bounding Box, the display changes depending upon the following user interaction:
-
When the content control does not have the focus, no visualization occurs
-
On mouse-over, the content control appears as a shaded rectangle
Figure 2. Content control on mouse-over
- When the content control has the focus (when the user chooses the content control), the control appears as a «bounding box» (with a line around the content and the title showing, if a title has been set)
Figure 3. Content control with focus
Start/End tags
When the content control is set to show as Start/End tag, the tags are displayed regardless of user interaction, and the title never appears; but buttons, such as the Drop-Down List button, appear on mouse over.
Figure 4. Content control set to show as start/end tags
None
When the content control is set to show as None, the content control is not displayed.
Content control colorization
In addition to enabling a different kind of display for a content control, Word 2013 also helps you to set the color for an individual content control. You set the color of a content control by using the Color button in the Content Control Properties dialog box.
You can also set the color of a content control by using the Word 2013 object model (discussed later in New Word 2013 content control object model members).
Figure 5. Content Control Properties dialog box
Support for XML mapping for rich text content controls
Word 2013 helps you to map the content of rich text content controls and document building block content controls to the XML data store. To do this, you set the XML mapping for the content control. You can set this property by using the existing XMLMapping.SetMapping method in the object model. Within the custom XML part, the custom XML is stored as flat Open XML markup converted into a string (by using standard XML encoding), so that it can be stored as a text node in the custom XML part. However, the mapping continues to have the limitation that it can only successfully map to leaf nodes or attributes.
[!NOTE]
Rich text content controls cannot contain other rich text content controls. If one exists inside of another (for example, because of file format manipulation, copy and paste, and so on), it is unlinked until it is no longer contained inside a mapped rich text control.
For more information about how to set up XML mapping, see the section New Word 2013 content control object model members later in this topic.
Supporting repeating content
In addition to visualization enhancements and support for XML mapping to rich text content controls, Word 2013 also adds a new content control that enables you to repeat content. The repeating section content control repeats the content contained within it, including other content controls.
You insert the repeating section content control around entire paragraphs or table rows. Once the control surrounds a section, you can insert copies of the section above or below the contained section.
Figure 6. Repeating section content control context menu
You can repeat the inserted section by using either the control on the end of the content control (displayed as a button with a plus sign (
Figure 7. Assign a section title in the Content Control Properties dialog box
Once you have given the section a title, if you select Allow users to add and remove sections in the Content Control Properties dialog box, users can add or delete the section by name.
Figure 8. Use the repeating section content control context menu to delete a section
When a repeating section content control surrounds other content controls, the enclosed content controls are repeated in each new item; but any such content controls have their contents reset to placeholder text. There are two exceptions where child control contents are preserved:
-
When a child control is a repeating section control.
-
When a child control is XML-mapped to a node outside the repeating section content control.
Figure 9. Repeating section content control containing child controls before repeat
Figure 10. Repeating section content control containing child controls after repeat
Repeating section content controls around XML-mapped controls
For XML mappings that are contained in a repeating section, Word 2013 maps them as follows.
If the mapping does not intersect with an item in the node set as part of its parent chain, the binding is an «absolute binding» and shows the same content in all repeating section items.
If the mapping does intersect with an item in the node set as part of its parent chain, the binding is a «relative binding», and is remapped as follows:
-
The absolute binding for the node is determined (flattening out any query expressions)─this should happen on initial mapping
-
The axis of the binding that intersects with the node set is removed
-
The remainder of the XPath is evaluated relative to the XPath of the repeating section content item
For example, the following mappings might occur:
-
The repeating section is mapped to rootnextpath
-
The control in the sample item is mapped to rootnextpath[2]baz
-
Word matches rootnextpath[2] to an item in the node set
The binding is therefore evaluated as .baz, where the base is the node of the repeating content item.
The following suggestions for working with repeating content controls can help you prevent data loss and avoid frustration.
Working with repeating section content controls that are mapped to XML data
If you insert a repeating section content control that is mapped to XML data, every time your user reopens the document, Word recreates the repeating section items, based on the information in the data store. Even if you save the document, any changes that the user makes in the repeating section items in the document that aren’t also mapped into the data store are lost.
To help prevent this from happening, lock the repeating section content control and allow the user to edit only in unlocked child content controls that are mapped to the XML as well.
Binding a repeating section content control to a table
If you want to bind a repeating section content control to a table, insert the table and then the insert repeating section content control, and not the other way around. (Otherwise, you won’t be able to select only the table).
Nesting repeating section content controls within a table
Nesting repeating section content controls tightly within a table (for example, when the end of the parent and child repeating section content control is in the same cell) causes the outer repeating section to be deleted when the inner section has an item added or removed.
You can prevent this from happening by adding a paragraph marker between the end of one repeating section content control and the next. To hide the paragraph marker, deselect the Show/Hide option on the Home tab of the ribbon.
Open XML File Format schema additions
The following elements were added to the WordprocessingML Open XML File Format schema.
Table 1. New elements in the WordprocessingML Open XML File Format schema for content controls
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| <w:appearance> | <w:appearance> is a child element of <w:sdtPr>. The following values are valid for the val attribute: <w:appearance val= boundingBox|tags|hidden. The default value is boundingBox. |
| <w:color> | <w:color> is a child element of <w:sdtPr>. The content model matches the existing CT_Color complex type. The default value is the color used in Word 2010. |
New Word 2013 content control object model members
With the new enhancements and additions to content controls in Word 2013, the object model for Word has been updated to allow for programmatic manipulation of the new feature set. In addition, changes have also been made to the underlying Open XML File Format for word processing documents.
The following sections provide more information about the specific object model changes related to each content control enhancement.
Visualization enhancements
Several object model additions are included in Word 2013 for content control visualization enhancements. The following table list new members of the ContentControl object for visualization.
Table 2. New ContentControl object members
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| . Appearance as WdContentControlAppearance | Gets or sets the visualization of the content control. |
| . Color as WdColor | Gets or sets the color of the content control. |
The following table lists constants in the new WdContentControlAppearance enumeration.
Table 3. New WdContentControlAppearance enumeration constants
| Constant | Description |
|---|---|
| wdContentControlBoundingBox | Represents a content control shown as a shaded rectangle/bounding box (with optional title). |
| wdContentControlTags | Represents a content control shown as start/end markers. |
| wdContentControlHidden | Represents a content control that is not shown. |
Code sample
The following code sample shows how to create rich text content controls and set visualization programmatically.
Sub testVisualization() Dim objcc As ContentControl Dim objRange As Range ' Get the first paragraph as a range object. Set objRange = ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(1).Range ' Create a rich text content control around the first paragraph. Set objcc = ActiveDocument.ContentControls.Add(wdContentControlRichText, objRange) objcc.Title = "Default Bounding Box" ' Set visualization to the default. objcc.Appearance = wdContentControlBoundingBox ' Create a new paragraph. objRange.InsertParagraphAfter Set objRange = ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(2).Range ' Create a rich text content control around the second paragraph. Set objcc = ActiveDocument.ContentControls.Add(wdContentControlRichText, objRange) objcc.Title = "Non Bounding" ' Set visualization to invisible. objcc.Appearance = wdContentControlHidden ' Create a new paragraph. objRange.InsertParagraphAfter Set objRange = ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(3).Range ' Create a rich text content control around the third paragraph. Set objcc = ActiveDocument.ContentControls.Add(wdContentControlRichText, objRange) objcc.Title = "Tags Only with Pink color" ' Set visualization to Start/End tags with pink color. objcc.Appearance = wdContentControlTags objcc.Color = wdColorPink End Sub
XML mapping
No additions were made to the Word 2013 object model to accommodate rich text mapping to XML nodes in the document data store. Instead, use the existing object model to map a rich text content control to an XML node in the document data store. Additionally, no changes were made to the underlying Open XML File Format WordprocessingML schema as part of the newly included rich text content control support specifically for XML mapping.
Code sample
The following code sample shows how to map a rich text content control to an XML node programmatically.
Sub testRichBinding() Dim objRange As Range Dim objcc As ContentControl Dim objCustomPart As CustomXMLPart Dim blnMap As Boolean ' Add a custom XML part to the data store. Set objCustomPart = ActiveDocument.CustomXMLParts.Add ' Load XML fragment into the custom XML part. objCustomPart.LoadXML ("<x>Rich Text Databinding</x>") ' Get the first paragraph as a range object. Set objRange = ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(1).Range ' Create a rich text content control around the first paragraph. Set objcc = ActiveDocument.ContentControls.Add(wdContentControlRichText, objRange) ' Bind the XML node to the rich text content control. blnMap = objcc.XMLMapping.SetMapping("/x") ' Return whether mapping worked. MsgBox objcc.XMLMapping.IsMapped End Sub
Repeating section content controls represented in the object model
The repeating section content control is available in the object model by using the following additions to the ContentControl object and the new RepeatingSectionItem and RepeatingSectionItemColl objects. Table 4 lists the most important new members of the ContentControl object for repeating section content controls.
Table 4. ContentControl object members
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| AllowInsertDeleteSection as Boolean | Gets or sets whether users can add or remove sections from the content control by using the UI. If this property is called for a content control that is not of type repeating section, the call fails with the following error message: «This property can only be used with repeating section content controls.» |
| RepeatingSectionItemTitle as String | Gets or sets the name of repeating section items used in the context menu. If this property is called for a content control that is not of type repeating section, the call fails with: «This property can only be used with repeating section content controls.» |
| InsertRepeatingSectionItemBefore as ContentControl | Adds a repeating section item before the current item and returns the new repeating section item. If this method is called for a content control that is not of type repeating section item, the call fails with: «This property can only be used with repeating section item content controls.» |
| InsertRepeatingSectionItemAfter as ContentControl | Adds a repeating section item after the current item and returns the new repeating section item. If this method is called for a content control that is not of type repeating section item, the call fails with: «This property can only be used with repeating section item content controls.» |
Table 5 lists the most important members of the RepeatingSectionItem object.
Table 5. RepeatingSectionItem object members
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Range as Range | Returns the range of the specified repeating section item, excluding the start and end tags. |
| Delete | Deletes the specified repeating section item. |
| InsertItemAfter as RepeatingSectionItem | Adds a repeating section item after the specified item and returns the new item. |
| InsertItemBefore as RepeatingSectionItem | Adds a repeating section item before the specified item and returns the new item. |
Table 6 lists the most important members of the RepeatingSectionItemColl object.
Table 6. RepeatingSectionItemColl object members
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Item as RepeatingSectionItem | Returns an individual repeating section item. |
Table 7 shows the new member of the WdContentControlType enumeration for repeating section content controls.
Table 7. WdContentControlType enumeration addition
| Constant | Description |
|---|---|
| wdContentControlRepeatingSection | Represents a content control that contains a single item in a repeating section. |
Code sample
The following code sample shows how to use repeating section content controls programmatically.
Sub testRepeatingSectionControl() Dim objRange As Range Dim objTable As Table Dim objCustomPart As CustomXMLPart Dim objCC As ContentControl Dim objCustomNode As CustomXMLNode Set objCustomPart = ActiveDocument.CustomXMLParts.Add objCustomPart.LoadXML ("<books>" & _ "<book><title>Everyday Italian</title>" & _ "<author>Giada De Laurentiis</author></book>" & _ "<book><title>Harry Potter</title>" & _ "<author>J K. Rowling</author></book>" & _ "<book><title>Learning XML</title>" & _ "<author>Erik T. Ray</author></book></books>") Set objRange = ActiveDocument.Paragraphs(1).Range Set objTable = ActiveDocument.Tables.Add(objRange, 2, 2) With objTable.Borders .InsideLineStyle = wdLineStyleSingle .OutsideLineStyle = wdLineStyleDouble End With Set objRange = objTable.Cell(1, 1).Range Set objCustomNode = objCustomPart.SelectSingleNode("/books[1]/book[1]/title[1]") Set objCC = ActiveDocument.ContentControls.Add(wdContentControlText, objRange) objCC.XMLMapping.SetMappingByNode objCustomNode Set objRange = objTable.Cell(1, 2).Range Set objCustomNode = objCustomPart.SelectSingleNode("/books[1]/book[1]/author[1]") Set objCC = ActiveDocument.ContentControls.Add(wdContentControlText, objRange) objCC.XMLMapping.SetMappingByNode objCustomNode Set objRange = objTable.Rows(1).Range Set objCC = ActiveDocument.ContentControls.Add(wdContentControlRepeatingSection, objRange) objCC.XMLMapping.SetMapping ("/books[1]/book") End Sub
Open XML File Format changes for repeating section content controls
The file format representation of a repeating section content control generally uses the same element names, values, and so on as the existing XML markup; however, the <sdt> element representing the outer repeating section container exists in the Word 2013 namespace, to ensure compatibility with earlier versions of Word.
The individual repeating items within the repeating section content control (that surround each individual item) are saved as rich text content controls using the existing WordprocessingML representation. Table 8 lists new elements in the WordprocessingML schema for repeating section content controls.
Table 8. New elements in the WordprocessingML schema for repeating section content controls
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| <w15:repeatingSection> | Specifies a repeating section content control. This element is mutually exclusive with all other control types and has no child elements or attributes. |
| <w15:repeatingSectionItem> | Specifies a repeating section item content control. This element is mutually exclusive with all other control types, and has no child elements or attributes. |
| <w15:doNotAllowInsertDeleteSection> | Specifies that the user cannot add or delete sections by using the user interface in Word 2013. |
| <w15:sectionTitle> | Specifies the name of repeating section items (and is used in the context menu when the control is chosen). |
Add and change Content Controls in Word
- Click File in Word.
- Scroll down to Options.
- Choose Customize Ribbon.
- Select the Developer box.
- Click OK.
- To add a Content control, click Rich Text Content Control box.
- Place the box at appropriate location, select Properties.
- Add General Information.
Contents
- 1 What does control contents mean in a Word document?
- 2 How do I turn a Word document into a fillable form?
- 3 How do you insert rich text content control in Word?
- 4 How do I make a Word document fillable and not editable?
- 5 How do I create a fillable PDF from Word?
- 6 How do I turn a Word document into a fillable PDF?
- 7 How do I edit content control text in Word?
- 8 How do I insert plain text content control in Word 2013?
- 9 What is a fillable PDF?
- 10 How do I convert a Word document to a fillable PDF without Acrobat?
- 11 How do I use developer tools in Word?
- 12 How do I edit content control drop-down in Word?
- 13 How can I make CV on my laptop?
- 14 How do I copy and paste content control?
- 15 How do you use combo box content control?
- 16 Is fillable a word?
- 17 Are all PDFs editable?
What does control contents mean in a Word document?
Individual content controls can contain content such as dates, lists, or paragraphs of formatted text. Content controls help you to create rich, structured blocks of content and are designed for use in templates that insert well-defined blocks into your documents, creating structured documents.
How do I turn a Word document into a fillable form?
Creating Fillable Forms Using Microsoft Word
- Enable Developer Tab. Open Microsoft Word, then go to the File Tab > Options > Customize Ribbon > check the Developer Tab in the right column > Click OK.
- Insert a Control.
- Edit Filler Text.
- Design Mode button again to exit the mode.
- Customize Content Controls.
How do you insert rich text content control in Word?
If the Controls task pane is not visible, click More Controls on the Insert menu, or press ALT+I, C. Under Insert controls, click Rich Text Box. In the Rich Text Box Binding dialog box, select the field in which you want to store rich text box data, and then click OK.
How do I make a Word document fillable and not editable?
Head on to the “Protect” section on the ribbon and click the button labeled “Protect Document.” You should then click the button named “Restrict Formatting and Editing.” On the options that appear, select the one that says “Allow only this type of editing in the document” and pick “Filling in forms.” Once you’re done,
How do I create a fillable PDF from Word?
Create a Fillable PDF Form from a Word Document
- Open the Word document that you want to make into a PDF form.
- Go to File -> Print, make sure “Adobe PDF” is selected as your printer, and then click the Print button.
- Word will ask you where to save the PDF file you’re creating.
How do I turn a Word document into a fillable PDF?
How to create fillable PDF files:
- Open Acrobat: Click on the “Tools” tab and select “Prepare Form.”
- Select a file or scan a document: Acrobat will automatically analyze your document and add form fields.
- Add new form fields: Use the top toolbar and adjust the layout using tools in the right pane.
- Save your fillable PDF:
How do I edit content control text in Word?
On the Developer tab, in the Controls group, click Design Mode. Click the content control where you want to revise the placeholder instructional text. Edit the placeholder text and format it any way you want.
How do I insert plain text content control in Word 2013?
Inserting a Content Control
- Position the insertion point where you want the new control.
- On the Developer tab, make sure Design Mode is selected.
- Click one of the content control buttons on the Controls group to insert it into the document.
What is a fillable PDF?
Answer. A fillable PDF is a PDF document that includes certain fields that are editable without PDF-editor software. Any fillable PDF that opens in modern PDF viewers (Acrobat, Preview, Chrome, Bluebeam) will be usable in the Forms tool. Note: XFA-based PDFs are only compatible with Adobe.
How do I convert a Word document to a fillable PDF without Acrobat?
To create a fillable PDF using this tool, follow these steps:
- Open ApowerPDF.
- Click on Create.
- Select Blank Document.
- Select the Forms tab.
- Add the forms fields that you need – double-click on the field to change its appearance, name, and layout.
- When you are finished, click on File and then choose Save.
How do I use developer tools in Word?
The Developer tab isn’t displayed by default, but you can add it to the ribbon.
- On the File tab, go to Options > Customize Ribbon.
- Under Customize the Ribbon and under Main Tabs, select the Developer check box.
How do I edit content control drop-down in Word?
If you want to make any changes to the drop-down box, just select it while in Developer Mode and click “Properties” again. Select “Content control can’t be deleted” to ensure readers cannot delete the drop-down box or its options. Don’t select the “Contents cannot be edited” option.
How can I make CV on my laptop?
To access these CV templates from your computer:
- Open Microsoft Word, then click on “New from Template.”
- Then, type “CV” or “curriculum vitae) into the search bar to browse for available templates.
- Finally, choose the template you want to use, and Word will launch your ready-to-use template.
How do I copy and paste content control?
Press Ctrl+C to copy the control to the Clipboard. Position the cursor where you want to repeat the control’s selected value. Don’t press Ctrl+V as you normally would to paste something. Instead, choose Paste Special from the Paste dropdown in the Clipboard group on the Home tab (Figure D).
How do you use combo box content control?
Under Insert controls, click Combo Box.
- Click Add.
- In the Value box, type the text that you want to store if a user selects this entry.
- In the Display name box, type the text that you want to display for this entry, and then click OK.
- Repeat steps 1 through 3 for each entry that you want to add to the list box.
Is fillable a word?
Able to be filled.
Are all PDFs editable?
Adobe Acrobat has all kinds of tools to mark up PDFs and even do light editing (as well as tools to lock down PDFs to prevent any alternations). But the general point is true – Adobe Acrobat is not a word processor and PDFs aren’t meant to be edited directly.It’s called an editable PDF.