HelpDesk
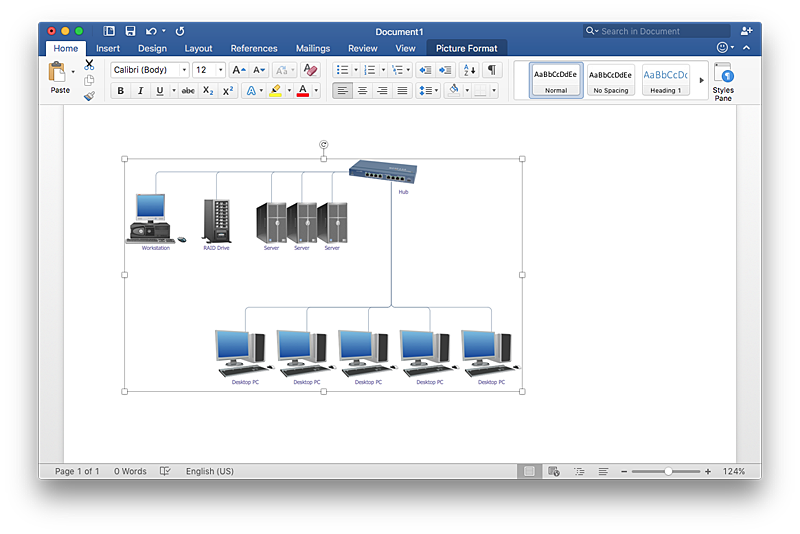
Effective management of the computer network of any size includes the creation and maintenance of the network documentation package. Computer network diagrams may be the part of the network documentation that is often presented as MS Word document. Network diagrams describing the topology of the network and equipment installed in the network, are the essential part of this package. ConceptDraw PRO provides network administrators with ability to easily create computer network diagrams and then insert them into a MS Word document.
HelpDesk
How to Add a Rack Diagram to a MS Word Document Using ConceptDraw PRO
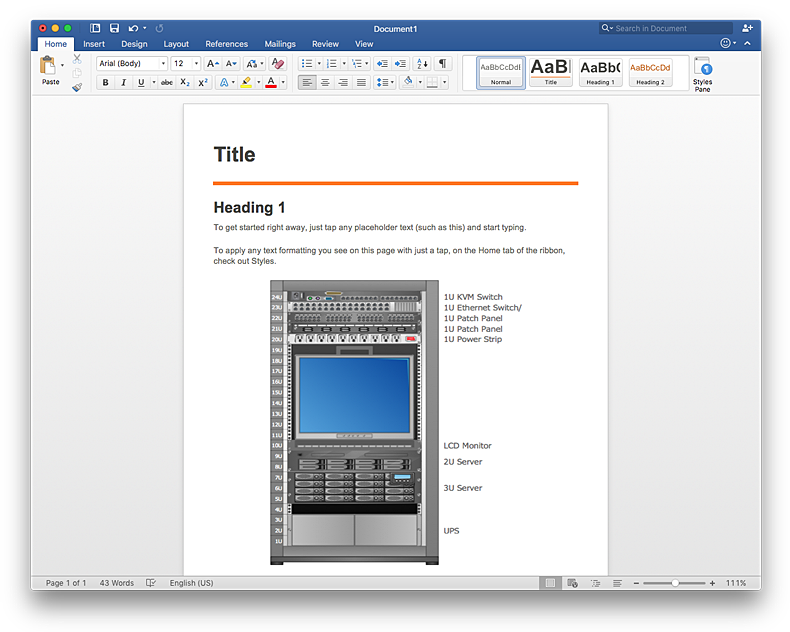
Rack Diagram depicts the structure of network equipment installation, and provides network administrator with the base to support electronic equipment, power, cooling, and cable management. ConceptDraw PRO allows you to easily create diagram that will help to detail the type of rack equipment that best fits your needs and then lets you to insert the scheme of rack configuration into the network documentation pack. ConceptDraw PRO allows you to easily create rack configuration diagrams and then insert them into a MS Word document.

Network Layout Floor Plans
Network Layout Floor Plans
Network Layout Floor Plans solution extends ConceptDraw PRO software functionality with powerful tools for quick and efficient documentation the network equipment and displaying its location on the professionally designed Network Layout Floor Plans. Never before creation of Network Layout Floor Plans, Network Communication Plans, Network Topologies Plans and Network Topology Maps was not so easy, convenient and fast as with predesigned templates, samples, examples and comprehensive set of vector design elements included to the Network Layout Floor Plans solution. All listed types of plans will be a good support for the future correct cabling and installation of network equipment.
- How To Create Network Topologies In Microsoft Word
- Wireless Network Diagram Examples | How to Create a Wireless …
- Network Topology Report In Word File
- Network Topology With Ms Word File Download
- Hybrid Network Topology | Star Network Topology | Cisco Network …
- Star Network Topology | Hybrid Network Topology | Tree Network …
- Cisco Network Templates | How to Create a Vehicular Network …
- How To Create a MS Visio Rack Diagram Using ConceptDraw PRO …
- Hybrid Network Topology | Star Network Topology | Computer …
- How Topology Diagram Draw To Microsoft Word
- Network Icon | Cisco Network Icons | Network Icons | Microsoft …
- Telecommunication networks . Computer and Network Examples …
- Network Topology Mapper | Hotel Network Topology Diagram …
- Star Network Topology | Cisco Network Objects in ConceptDraw …
- Cisco Network Templates | How to Add a Network Diagram to a MS …
- How to Add a Network Diagram to a MS Word Document Using …
- Create Network Topology Map Using Free Script How To
- Star Network Topology | Hybrid Network Topology | Cisco Network …
- How To Create a MS Visio Telecommunication Network Diagram …
- How to Add a Wireless Network Diagram to a MS Word Document …
- ERD | Entity Relationship Diagrams, ERD Software for Mac and Win
- Flowchart | Basic Flowchart Symbols and Meaning
- Flowchart | Flowchart Design — Symbols, Shapes, Stencils and Icons
- Flowchart | Flow Chart Symbols
- Electrical | Electrical Drawing — Wiring and Circuits Schematics
- Flowchart | Common Flowchart Symbols
- Flowchart | Common Flowchart Symbols
A computer
network consists of two or more computers that are interconnected in
order to share resources (such as printers), exchange files, or allow
electronic communications. In a computer network the individual
stations, called ‘nodes’, may be computers, terminals, or
communication units of various kinds. The computers on a network may
be linked through cables, telephone lines, radio waves, satellites,
or infrared light beams. So, a computer network is a group of
computers and other devices connected together in order to share
information.
In addition
to physically connecting computers and communication devices, a
network system has the function of establishing a cohesive
architecture that allows almost seamless data transmission while
using various equipment types. ISO Open Systems Interconnection (OSI)
and IBM’s Systems Network Architecture (SNA) are two popular
architectures used at present.
Local area
network (LANs) and wide area network are two basic network types.
A local
area network (LAN) is a computer network that covers a local area. It
may be a home, office or small group of buildings such as a college
or factory. The topology of a network dictates its physical
structure. The generally accepted maximum size for a LAN is 1 km2.
At present, there are two common wiring technologies for a LAN,
Ethernet and Token Ring. A LAN typically includes two or more PCs,
printers, CD-ROMs and high-capacity storage devices called file
servers, which enable each computer on the network to have access to
a common set of files. A LAN is controlled by LAN operating system
software. LAN users may also have access to other LANs or tap into
wide
area
networks. LANs with similar architectures are linked by transfer
points, called ‘bridges’, and LANs with different architectures
use ‘gateways’ to convert data as it passes between systems. A
router is used to make the connection between LANs.
A wide area
network (WAN) is a computer network that covers a wide geographical
area, involving a large number of computers. Computer networks may
link the computers by means of cables, optical fibres, or satellites
and modems, devices that allow computers to communicate over
telephone lines. The best example of a WAN is the Internet, a
collection of networks and gateways linking millions of computer
users on every continent.
Typically,
WANs are used to connect LANs together. Many WANs are built for one
particular organization and are private, others, built by Internet
service providers, provide connections from an organization’s LAN
to the Internet. WANs are most often built of leased lines. At each
end of the leased line, a router is used to connect to the LAN on one
side and a hub within the WAN on the other. The defining
characteristics of LANs in contrast to WANs are: a) much higher data
rates; b) smaller geographic range – at most a few kilometers –
and c) they do not involve leased telecommunication lines.
A number of
network protocols such as TCP/IP, X.25, ATM and Frame relay can be
used for WANs. A protocol is a set of communication rules to regulate
the cooperation of two devices, to make sure that everyone speaks the
same language.
Exercise 3. Answer the
following questions.
-
What does
a computer network consist of? 2. What may the individual stations
in the computer network be? What are they called? 3. How are the
computers on a network linked? 4. What is a computer network? 5.
What are the functions of a network system? 6. What is an
architecture of a network system and what data transmission does it
allow? 7. What are two popular architectures used at present? 8.
What two basic network types are there? 9. What is a local area
network? (In size, wiring technology, the way of access to a common
set of files and to other LANs). 10. What does a LAN include? 11.
What is a wide area network? 12. What may computers on the network
be linked by? 13. What are modems? 14. What is the Internet? 15.
What are WANs used for? 16. What is a protocol?
Exercise 4.
Give Ukrainian / Russian equivalents for the following word
combinations:
a) the
individual stations called ‘nodes’, infrared light beams, a group
of computers connected together, in order to exchange files, in
addition to physically connecting computers and communication
devices; the function of establishing a cohesive architecture, almost
seemless data transmission, while using various equipment types, two
popular architectures used at present, a small group of buildings
such as a college or factory, the topology of a network, the
generally accepted maximum size for a LAN, high-capacity storage
devices called file servers, a collection of networks and gateways
linking millions of computer users, on every continent, Internet
service providers, at each end of the leased line, on one side, on
the other side, a number of network protocols, a set of communication
rules;
b) to be
interconnected in order to share resources, to be linked through
cables, to cover a local area, to enable each computer on the network
to access a common set of files, to be controlled by LAN operating
system software, to have access to other LANs, to tap into wide area
networks, to be linked by transfer points called ‘bridges’, to
use ‘gateways’ to convert data, to be used to make the connection
between LANs, to cover a wide geographical area, to link computers by
means of cables, to be built for one particular organization, to be
built of leased lines, to regulate the cooperation of two devices, to
perform traffic control, to allow computers to communicate over
telephone lines.
Exercise 5.
Write English equivalents for the following words and word
combinations.
|
|
Exercise
6. Form verbal word combinations as used in the text. Translate them.
Use them in sentences of your own.
|
1. |
1. |
|
2. |
2. |
|
3. |
3. |
|
4. |
4. |
|
5. |
5. |
|
6. |
6. |
|
7. |
7. |
|
8. |
8. |
|
9. |
9. |
|
10. |
10. |
Exercise 7. Fill in the blanks
with the words given below.
(at, by, by means of, on, of,
for, to, through, into, from).
1. The
computers … a network may be linked … cables, telephone lines,
radio waves, satellites, or infrared light beams. 2. The topology …
a network dictates its physical structure. 3. … present, there are
two common wiring technologies … a LAN. 4. A LAN is controlled …
LAN operating system software. 5. LAN users may also have access …
other LANs or tap … wide
area
networks. 6. Computer networks may link the computers … cables,
optical fibres, or satellites and modems. 7. Many WANs are built …
one particular organization, others provide connections … an
organization’s LAN … the Internet. 8. … each end … the leased
line a router is used.
Exercise 8. Compose questions
to the following sentences.
1. The
computers on a network may be linked through cables, telephone lines,
radiowaves, satellites. 2. The topology of a network dictates its
physical structure. 3. At present there are two common wiring
technologies for LAN. 4. Modems allow computers to communicate over
telephone lines. 5. WANs are used to connect LANs together. 6. A LAN
is controlled by LAN operating system software.
Exercise 9.
Translate the following sentences into English.
|
1. |
1. |
|
2.В |
2. |
|
3. |
3. |
|
4. |
4. |
|
5. |
5. |
|
6. |
6. |
|
7. |
7. |
|
8. |
8. |
|
9. |
9. |
|
10. |
10. |
|
11. |
11. |
|
12. |
12. |
|
13. |
13. |
|
14. |
14.Глобальная |
|
15. |
15. |
|
16. |
16. |
|
17. |
17. |
|
18. |
18. |
|
19. |
19. |
|
20. |
20. |
|
21. |
21. |
|
22. |
22. |
|
23. |
23. |
|
24. |
24. |
Exercise
10. Speak on Computer Networks.
Exercise
11. Memorize the following:
|
a) terms: |
||
|
superhighway |
супермагістраль |
супермагистраль |
|
metropolitan area network |
міська |
городская |
|
common carrier |
приватна |
частная компания, |
|
single-user |
однокористувацький |
однопользовательский |
|
public |
загальнодоступний, |
общедоступный, |
|
public carrier |
загальнодоступний |
общедоступный |
|
data (transfer) rate |
швидкість |
скорость передачи |
|
link |
лінія зв’язку, |
линия связи, |
|
b) verbs: |
||
|
search |
шукати, вивчати |
искать, изучать |
|
digitize |
оцифровувати, |
отцифровывать, |
|
route |
відправляти |
отправлять по |
|
restrict |
обмежувати |
ограничивать |
|
range (from …to, between) |
коливатися в |
колебаться в |
|
allow for |
передбачати, |
предусматривать, |
|
span |
охоплювати |
охватывать |
|
c) |
||
|
dedicated |
виділений, |
выделенный, |
|
´disparate |
незрівнянний, |
несравненный, |
Exercise
12. Read and translate text 1.
Text 1
The
communication of data over telephone lines and by radio is one of the
most important and influential uses of computers. Using modems,
people can send text and graphics files, exchange messages, and
search databases over worldwide computer networks.
As more of the world’s
information is digitized, more people seek access to the global
‘digital library’. The combination of computers, modems,
databases, and communications lines has become known as the
information superhighway.
A network
in computing is two or more computers connected for the purpose of
routing, managing, and storing rapidly changing data. A local area
network (LAN), which is restricted by distances of up to one mile,
and a metropolitan area network (MAN), which is restricted to
distances of up to 60 miles, connect personal computers and
workstations (each called a node) over dedicated, private
communications links. A wide area network (WAN) connects large
numbers of nodes over long-distance communications links, such as
common carrier telephone lines, over distances ranging from that
between major metropolitan centers to that between continents. An
internet is a connection between networks. The Internet is a WAN that
connects thousands of disparate networks in the U.S., Canada, Europe,
Asia, and elsewhere, providing global communication between nodes on
government, educational, and industrial networks. Networks allow for
resource sharing (e.g., multiple computers sharing one printer), data
sharing and communication or data exchange (e.g., electronic mail).
Local area
network is a computer network dedicated to sharing data among several
single-user workstations or personal computers, each of which is
called a node. A LAN can have from two to several hundred such nodes,
each separated by distances of several feet to as much as a mile, and
should be distinguished from connections among computers over public
carriers, such as telephone circuits, that are used for other
purposes. Because of the relatively small areas involved, the nodes
in a LAN can be connected by special high-data-rate cables. A
metropolitan area network is defined as being restricted to a larger
area (maximum distances of 50-60 miles) than a LAN but one still
small enough so that dedicated links (such as microwave links) can be
used. A computer network that spans a relatively large geographical
area is called WAN.
Businesses
establish much smaller networks for their own use. One type, a local
area network, connects a company’s workstations within the same
building or in neighboring buildings. A wide area network links
workstations over large areas. Both LAN’s and WAN’s enable
co-workers to exchange information rapidly. They also enable
computers to share printers and storage devices.
Exercise 13. Answer the
following questions.
1. What is
one of the most important uses of computers. 2. What is known as the
information superhighway? 3. How can people exchange messages and
search databases? 4. What is a network in computing? 5. What is a
personal computer or workstation in a network called? 6. What do a
local area network and a wide area network differ in? 7. What is a
metropolitan area network defined as? 8. What is the Internet? 9.
What do networks allow the user to do?
Exercise 14. Fill in the
blanks with prepositions and adverbs given below. Translate the
sentences.
(Over, by,
of, as, within, on, to)
1. The
communication of data … telephone lines and … radio is one …
the most important uses … computers. 2. People can search databases
… computer networks. 3. People seek access … the global ‘digital
library’. 4. The combination … computers, modems, databases, and
communications lines has become known … the information
superhighway. 5. A local area network is restricted … distances of
up to one mile. 6. A local area network connects company’s
workstations … the same building. 7. File servers enable each
computer … the network to have access … a common set … files.
Exercise
15. Memorize the following:
|
ARPAnet |
мережа |
сеть ARPAnet |
|
bulletin board |
електронна дошка |
электронная |
|
newsgroup |
тематична |
тематическая |
|
host |
головний, |
главный, основной; |
Exercise
16.
Read and translate text 2.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
A list server (mailing list server) is a program that handles subscription requests for
a mailing list and distributes new messages, newsletters, or other postings from the
list’s members to the entire list of subscribers as they occur or are scheduled. (A list
server should not be confused with a mail server, which handles incoming and
outgoing e-mail for Internet users.)
A mailing list or listserver (named after the software used to run the electronic
mailing and discussion lists) or list forum on the Internet are the most common
ways for mass email communication and permit mail recipients to discuss issues of
common interest. The modus-operandi of such a system works like this. A
listserver has two e-mail addresses, viz. the listserv address and the list address.
The former generally accepts commands for joining/exiting a list, to receive
acknowledgements, etc. whereas the latter accepts messages of actual discussion
which will be scanned by a list moderator (optional) and distributed to all members
of the list. Any message sent to the e-mail list address will be distributed to every
member of that list and hence one should be cautious in not sending commands
meant for the server to the list address. The members depending on their interest
can reply or comment on these messages; they do not have to actively participate
by sending messages all the time; or they can just browse the discussion and stay
as a silent spectator to the activity; they are also free to leave the list at their choice.
The user does not have to learn software and hardware in detail to join a forum. A
person conversant with the basics of how to send and receive e-mail messages can
successfully join and interact with a list forum of her/ his interest. Due to the
swiftness by which an electronic mail is delivered, electronic mailing lists can do a
lot more than the traditional paper distribution lists. A common mistake made by a
new user is that s/he sends subscription requests to the regular list address
annoying other list members. Care should be taken to observe the basic etiquettes
(netiquette) while dealing with listservers: do not spam; do not send an
advertisement or other unsolicited material without any consideration of the Web
Tools 144 appropriateness of the material; commands are sent to the listserv and
not to the list; access to a mailing list is a privilege and not a right; use language
with care; be cautious when communicating to list servers or newsgroups; and be
able to support what you speak; etc. The Internet hosts several mailing lists on
various subjects ranging from astronomy to zoology and from music to genealogy.
The “CataList” service maintained by Listserv lists all public lists running on
Listserv servers worldwide (http://www.lsoft.com/lists/ listref.html). The lists
could also be located by any of the web search engines like Google. The
yahoogroups feature provided by the famous web portal Yahoo has enabled to run
By
- Kinza Yasar,
-
Alexander S. Gillis,
Technical Writer and Editor
What is a computer network?
A computer network is a group of interconnected nodes or computing devices that exchange data and resources with each other. A network connection between these devices can be established using cable or wireless media. Once a connection is established, communication protocols — such as TCP/IP, Simple Mail Transfer Protocol and Hypertext Transfer Protocol — are used to exchange data between the networked devices.
The first example of a computer network was the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network. This packet-switched network was created in the late 1960s by ARPA, a U.S. Department of Defense agency.
A computer network can be as small as two laptops connected through an Ethernet cable or as complex as the internet, which is a global system of computer networks.
How does a computer network work?
Devices attached to a computer network use IP addresses that are resolved into hostnames through a domain name system server to communicate with each other over the internet and on other computer networks. A variety of protocols and algorithms are also used to specify the transmission of data among endpoints.
Network systems must follow certain standards or guidelines to operate. Standards are a set of data communication rules required for the exchange of information between devices and are developed by various standards organizations, including IEEE, the International Organization for Standardization and the American National Standards Institute. For example, the Ethernet standard establishes a common communication language for wired or physical networks, and the 802.11 standard specifies connectivity for wireless local area networks (WLANs).
A computer network must be physically and logically designed in such a way that makes it possible for the underlying network elements to communicate with each other. This layout of a computer network is known as the computer network architecture.
The following are the two most common computer network architectures:
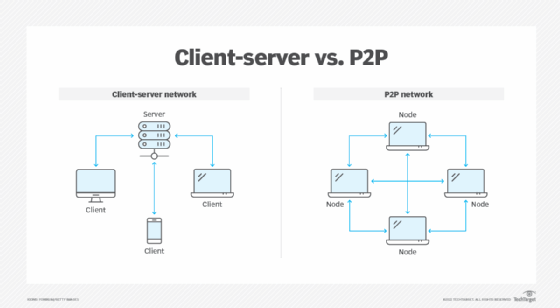
- Client-server. This model consists of many clients — or nodes — where at least one network node acts as the central server. The clients in this model don’t share resources, but request the central server, as all the resources are installed on it.
- Peer-to-peer (P2P). Each connected device on this network behaves as the client, as well as the server, and enjoys similar privileges. The resources of each peer are shared among the entire network, including memory, processing power and printing. Many companies use the P2P architecture to host memory-intensive applications, such as three-dimensional rendering, across multiple network devices.
A well-defined computer network also takes network capacity into account. A network’s capacity is how much traffic the network can support at any given time, while still meeting service-level agreements. It’s measured in terms of bandwidth, which is quantified by the theoretical maximum number of bits per second that can pass through a network device.
Core components of a computer network
The following building blocks — network devices, links and communication protocols — make computer network operations possible:
- Network devices. These physical devices or nodes are the data communication equipment that is connected inside a computer network. Examples of network devices include modems, routers, PCs, servers, firewalls, switches and gateways. Each device in a computer network is identified by a network address and often has easily identifiable hostnames.
- Links. A link is the transmission medium used for connecting the nodes and enabling them to transmit to each other. The links can be either wired, wireless or optical, such as an Ethernet cable or a Wi-Fi signal. The links can be configured in different ways, both physically and logically, and the network topology dictates the manner in which links and nodes relate to each other.
- Communication protocols. These are the rules or protocols that all nodes on a network must follow for information transfer. Common protocols include the TCP/IP suite, IEEE 802, Ethernet, WLAN and cellular standards.
TCP/IP is a conceptual model that suggests the following four functional layers for these communication links:
- Network access layer. This layer defines how the data is physically transferred through the network, as well as how hardware devices send bits through a network medium, such as coaxial, optical, fiber or twisted-pair cables.
- Internet layer. This is the layer where routing takes place. It packages data into packets and enables them to be sent and received over the network. The internet layer includes IP, Address Resolution Protocol and Internet Control Message Protocol.
- Transport layer. This layer ensures the stable, sequenced and error-free delivery of data packets. It achieves this by swapping acknowledgment of data reception and retransmitting lost or dropped packets. Typical protocols used at the transport layer include TCP and User Datagram Protocol.
- Application layer. Security protocols, such as Transport Layer Security, operate at this layer and play an integral part in ensuring network security. This is the abstraction layer that communicates directly with applications and defines how high-level apps should access the network to start a data transfer. For example, the application layer is used to define where, when and how much data should be sent at a specific rate.
The modern internet architecture is mostly built on the TCP/IP model, which is the simplified version of the more conceptual Open Systems Interconnection model.
Advantages of using a computer network
Computer networks are ideal for the quick exchange of information and the efficient use of resources.
The following are benefits of using a computer network:
- Resource sharing. Enterprises of all sizes can use a computer network to share resources and critical assets. Resources for sharing can include printers, files, scanners and photocopy machines. Computer networks are especially beneficial for larger and globally spread-out organizations, as they can use a single common network to connect with their employees.
- Flexibility. Today’s computer networks enable people to use flexible communication and resource-sharing methods based on their needs and preferences. For example, some people might use email or instant messaging to communicate, while others might prefer using an app such as WhatsApp.
- Higher connectivity. Thanks to computer networks, people can stay connected regardless of their location. For example, video calling and document-sharing apps, such as Zoom and Google Docs, enable employees to connect and collaborate remotely.
- Data security and management. In a computer network, data is centralized on shared servers. This helps network administrators to better manage and protect their company’s critical data assets. They can perform regular data backups and enforce security measures, such as multifactor authentication, across all devices collectively.
- Storage capacity. Most organizations scale over time and have an abundance of data that needs storage. Computer networks, especially those that employ cloud-based technologies, can store massive amounts of data and backups on a centralized remote server that’s accessible to everyone, at any given time.
- Entertainment. Computer networks, especially the internet, offer various sources of entertainment, ranging from computer games to streaming music and videos. Multiplayer games, for example, can only be operated through a local or home-based LAN or a wide area network (WAN), such as the internet.
Types of computer networks
There are several types of computer networks. Which network an organization uses depends on factors such as the number of devices, types of operating systems, transmission medium used, network topology, the distance between each device and their geographic scale.
Some examples of computer networks are the following:
- LANs. LANs interconnect endpoints in a single domain. Examples of LANs include schools, hospitals and office buildings.
- WANs. WANs interconnect multiple LANs and span larger geographical areas, such as big cities, states and countries.
- Metropolitan area networks (MANs). A MAN connects computer resources in a large geographic area, such as a city.
- Storage area networks (SANs). SANs are specialized and dedicated networks that connect multiple high-performance data storage devices and resources. They provide built-in security and block-level access. A SAN provides disaster recovery because it includes different storage devices, such as disk drives, magnetic tapes and optical storage.
- Personal area networks (PANs). A PAN is used by one person to connect multiple devices, such as printers and scanners.
- WLANs. This is a group of colocated devices that use radio transmission instead of wired connections.
- Campus area networks (CANs). A CAN is a collection of interconnected LANs that are commonly used by larger organizations, such as governments and universities.
- Virtual private networks (VPNs). A VPN extends a private network over a public network to improve the privacy and security of a network connection.
- Passive optical networks (PONs). A PON is a fiber optic network that delivers broadband access to end users.
- Service provider networks. These are network providers that lease network capacity and functionality to customers. Providers typically consist of telecommunication companies, data carriers, internet service providers and cable television providers.
- Cloud networks. This is a type of WAN, but its infrastructure is delivered by a cloud-based service, such as Amazon Web Services. Cloud networks are a standard approach for modern networks.
Networks can be divided into subnetworks, also called subnets.
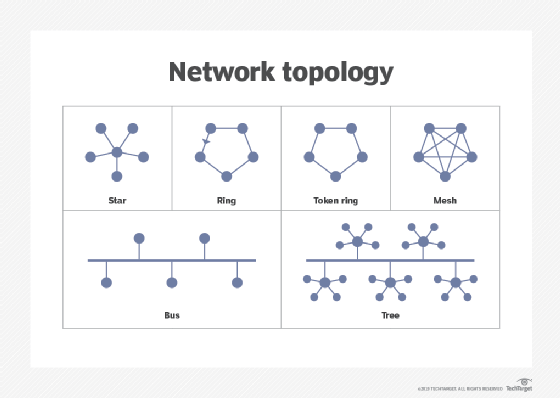
What are the different types of network topologies?
A network topology is the physical and logical arrangement of a network. All topologies come with different pros and cons. Organizations should consider the scope of a network — including its size, scaling needs and business goals — before selecting a particular topology.
Network topologies include the following types:
- Star network. A star network topology connects all nodes to a common central computer.
- Ring network. Network devices are connected to two other devices on either side through a coaxial cable or an RJ-45 cable.
- Full mesh network. All nodes in a full mesh network are connected directly to other nodes.
- Partial mesh network. Only some nodes connect directly to one another, while others are only connected to one or two other nodes in the network.
- Point-to-point network. This network provides a dedicated connection between two endpoints.
- Bus network. A bus network follows the LAN topology, where devices in a single LAN are attached directly to a transmission line known as a bus. All signals pass through all devices, and the recipient device recognizes the signals intended for it.
- Tree network. This is a hybrid network topology where two or more star networks are connected.
Computer networks come in all shapes and sizes. Explore the seven common types of networks, along with their pros and cons.
This was last updated in March 2023
Continue Reading About computer network
- An introduction to 8 types of network devices
- What software-defined LAN means for campus virtualization
- Wireless access point vs. router: What’s the difference?
- 4 categories of network monitoring
- Ethernet vs. Carrier Ethernet: How do they differ?
Dig Deeper on Network Infrastructure
-
physical layer
By: Alexander Gillis
-
Fibre Channel
By: Stephen Bigelow
-
wireless mesh network (WMN)
By: Wesley Chai
-
Spine-leaf (spine-leaf architecture)
By: Alexander Gillis
What is a computer network? The simple answer is that when two or more computing devices are connected by cable or wireless, a computer network is produced. In this article, you will get the perfect answer to the question “What is a computer network”, types of computer networks, their applications, and some common terms in the field of networking.
What is Network?
A network is a collection of people or objects that work together in a well-planned and intelligent way to achieve a specific goal. The most important principle in any network is information sharing and exchange.
By sharing information among the members of the network, helps to achieve the specified goal more quickly and accurately. Moreover, a network has no time or space constraints.
What is Computer Network?
Computer networks are one of the most important pillars of information technology. In short, computer networks are a group of interconnected computers. These computers can be PC or servers that are connected to each other via devices such as switches and routers to form a computer network.
But nowadays, many other devices, including CCTV systems, VoIP-based phones, tablets, smartphones, and game consoles, can connect to the network. Even more than that, the Internet of Things (IoT) provides the ability to connect anything to computer networks. So it’s better to say for the next few years, “We can’t find anything today that doesn’t deal with computer networks.”
Components Of A Computer Network
As stated earlier, a computer network is a collection of interconnected computers, so we divide these components of a computer network into three general categories:
- Connecting devices (client computers, servers)
- Devices that provide the possibility of connection (switches and routers)
- Media that allows the possibility of physical connection between these devices (cables and waves)
In the following, we will explain these components in general:
- Client: The term client refers to devices used by end-users. For example, personal computers (PCs), laptops (laptops), tablets (Tablets), and other such devices are considered clients. Of course, a more professional definition of a client is to interpret it as a client point in computer networks.
- Server: Powerful computers that, as their name implies, are responsible for servicing computer networks. Services such as Web, Email, File Server, etc.
- Switch: The job of a switch is to connect the various components of a computer network to each other and exchange traffic between them. This traffic exchange is done by the switch, in layer 2 (Data Link) and based on MAC Address.
- Router: The application of a router is to connect different computer networks to each other. This connection and the decision to exchange traffic between computer networks is made based on the IP Address and Routing Table of a router.
- Media: For physical connection between all the devices mentioned above, you need to use communication media that can be copper cables, fiber optics, or radio waves in wireless networks.
- WAN Link: To connect a computer network to the World Wide Web or other wide area networks such as the national information network in our beloved country, a communication gateway must be provided. This port can be through ADSL, MPLS, or other technologies.
Purpose Of Computer Networks
The purpose of creating computer networks is to create connections and resource sharing. This connection can be between a computer and a server on an organization network or connecting a laptop to the Internet via WiFi technology.
Sharing a printer and a file sharing on a computer network, accessing office automation software on the Web, and Sending e-mail (E-mail), are some of the important facilities that computer networks provide to us.
Also, with the help of various VoIP and Video Conferencing technologies, it is possible to have audio and video communication on the computer network.
Functions Of Computer Network
Computer networks may be branches of electrical engineering, telecommunications, computer science, information technology, or computer engineering. Because these disciplines are based on theoretical and practical science.
- A computer network facilitates interpersonal communication and allows users to communicate more effectively and easily through a variety of solutions. Such as email, Messenger, Online chat, Phone, Video communication, and Video conference.
- Another function of a computer network is that it allows us to share computing and information resources for the use of users and other software. Such as printing a document by a shared printer or storing information on a device on the network.
- A network allows us to share a variety of information and files in a variety of formats and documents for other systems and users on the network, creating access levels for each person or system.
- Distributed computing systems in the network use the resource computing system or server to calculate and perform the tasks necessary to buy and read several books.
- Computer networks can affect the survival of the environment. Thanks to the computer network and the Internet, we can access a large amount of information with just a little time and without the need to cut down trees to produce paper.
- Thanks to the integrated storage of information, we no longer have to worry about deleting or losing our information. Our data is kept completely secure on the server and a backup is made of it.
- The distance between different branches in a factory, organization, or company no longer makes sense. Because the computer network and the presence of network equipment can shorten the distances and cause a secure exchange of information between employees.
Applications Of Computer Network
Computer networks have many uses. Including:
- File And Application Sharing: Users can share their files and applications over the network. Today, relatively new phenomena such as online collaboration and telecommuting are taking advantage of this feature of networks.
- Hardware Sharing: In a computer network, hardware such as printers and hard disks can be shared with network users.
- Voice Over IP (VoIP): Users can communicate with other VoIP voice users using computer networks and the Internet Protocol (IP).
- Communication: Users can communicate with each other by text, video, and audio using computer networks.
- E-Commerce: Users can buy and sell goods using computer networks.
Computer networks are divided into different types according to different indicators. For example, they can be divided into several species in terms of connectivity or physical topology, as well as in terms of geographical area.
Types Of Computer Networks
There are different types of computer networks and they are classified according to different criteria. But in general computer networks are divided into three general groups based on size.
- LAN or Local Area Network
- MAN or Metropolitan Area Networks
- WAN or Wide Area Network
Local Area Network or LAN
LAN or Local Area Network is the smallest type of computer network. A LAN is used to communicate between the computers of a company, school, residential or commercial building. In general, LANs are limited in terms of geographical location and number of computers.
Local area networks or LANs are set up to transmit data within a small set of computers. LANs use technologies such as Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) and WiFi (IEEE 802.11). So you do not need to get a license from anywhere or coordinate with telecommunications to set up a LAN.
You can easily buy a few meters of cable, a few network cards, and a switch, and easily connect a computer bag. Computers within a school, shop, company, cafe, etc. work in the form of a LAN.
LANs are very cheap, very fast, and less likely to cause errors and problems. In addition, if there is a problem with a LAN, it is very easy and fast to troubleshoot
Metropolitan Area Network or MAN
MAN or Metropolitan Area Networks are larger than LANs and can cover an area of the size of a city (or larger). In fact, it can be said that a MAN network is formed by connecting several LAN networks to each other.
To set up a MAN network, you must coordinate with the Radio Communications Regulatory Authority and obtain the necessary permits. The MAN network connects several LANs.
For example, imagine a company that has 10 branches in the city. A MAN network must be set up to connect the employees of these branches. By setting up a MAN network, the local network of each branch can be connected to other branches.
MAN networks are slower than LAN, more likely to fail, and naturally more difficult to troubleshoot. The cost of setting up MAN networks is relatively high and only affordable for companies and organizations.
Wide Area Network or WAN
The WAN or Wide Area Network is the largest and most complex type of network. The area covered by WANs is the size of the country or even the continent. As is typical of WAN networks, requires a lot of legal licenses.
And it can be said that only governments and very large companies can get these licenses. WANs actually connect organizations’ local area networks to the Internet. The Internet is the largest WAN in the world.
Transmission speeds in global networks (WANs) are much slower than MAN and LAN networks but have a wide coverage range. In other words, in a WAN network, a user in Pakistan can communicate with another user in another country like UK and exchange Information or have an Internet telephone conversation (such as Viber, Telegram, etc.).
Unfortunately, in WANs, the error rate is very high and the system is more difficult to troubleshoot.