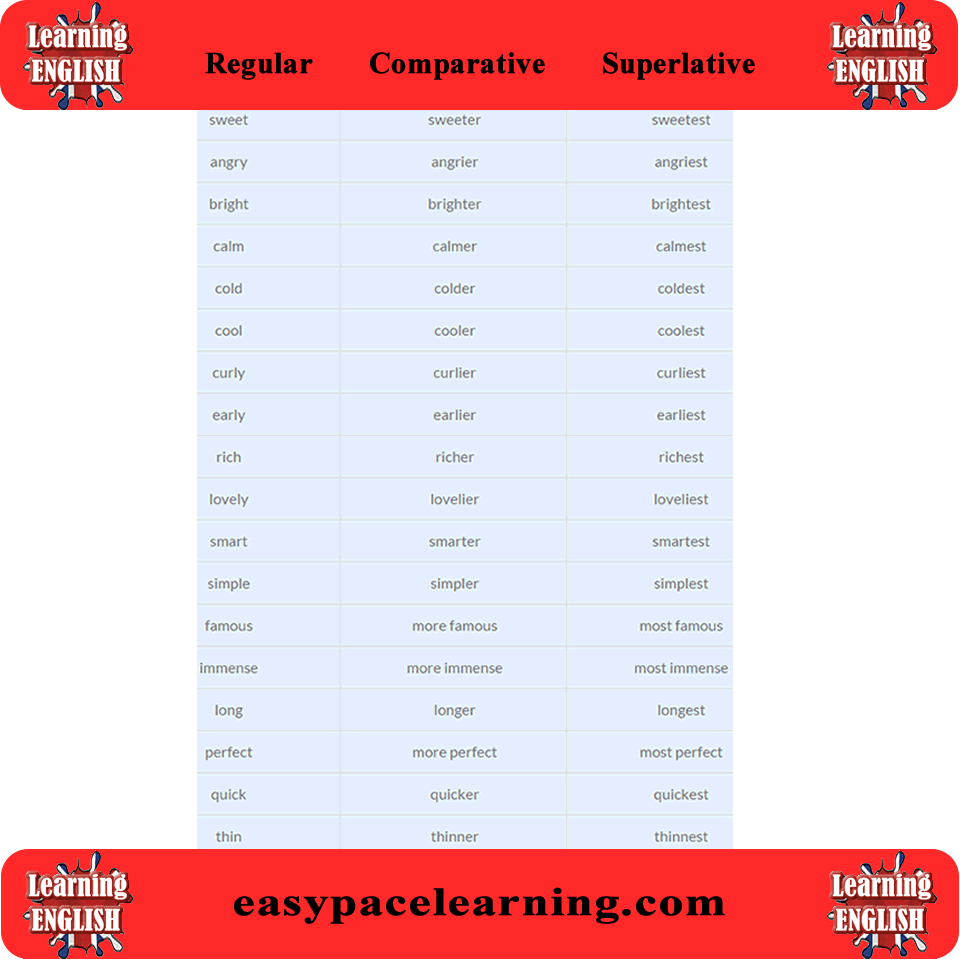
Test 1. Write the comparative and superlative forms of these adjectives.
1. cold – 6. comfortable – 11. new —
2. big – 7. easy – 12. expensive —
3. wonderful – 8. fat – 13. hungry —
4. happy – 9. bad – 14. hot —
5. good – 10. nice – 15. little —
Светило науки — 2667 ответов — 7338 раз оказано помощи
1cold-colder-the coldest
2big-bigger-the biggest
3wonderful-more wonderful-the most wonderful
4happy-happier-the happiest
5good-better-the best
6comfortable-more comfortable-the most comfortable
7easy-easier-the easiest
8fat-fatter-the fattest
9bad-worse-the worst
10nice-nicer-the nicest
11new-newer-the newest
12expensive-more expensive-the most expensive
13hungry-hungrier-the hungriest
14hot-hotter-the hottest
15little-less the least
Comparative Superlative and adjectives list from A to Z
Adjective |
Comparative |
Superlative |
|
angry |
angrier |
angriest |
|
bad |
worse |
worst |
|
big |
bigger |
biggest |
|
bitter |
bitterer |
bitterest |
|
black |
blacker |
blackest |
|
bland |
blander |
blandest |
|
bloody |
bloodier |
bloodiest |
|
blue |
bluer |
bluest |
|
bold |
bolder |
boldest |
|
bossy |
bossier |
bossiest |
|
brave |
braver |
bravest |
|
brief |
briefer |
briefest |
|
bright |
brighter |
brightest |
|
broad |
broader |
broadest |
|
busy |
busier |
busiest |
|
calm |
calmer |
calmest |
|
cheap |
cheaper |
cheapest |
|
chewy |
chewier |
chewiest |
|
chubby |
chubbier |
chubbiest |
|
classy |
classier |
classiest |
|
clean |
cleaner |
cleanest |
|
clear |
clear |
clearest |
|
clever |
cleverer |
cleverest |
|
close |
closer |
closest |
|
cloudy |
cloudier |
cloudiest |
|
clumsy |
clumsier |
clumsiest |
|
coarse |
coarser |
coarsest |
|
cold |
colder |
coldest |
|
cool |
cooler |
coolest |
|
crazy |
crazier |
craziest |
|
creamy |
creamier |
creamiest |
|
creepy |
creepier |
creepiest |
|
crispy |
crispier |
crispiest |
|
cruel |
crueller |
cruellest |
|
crunchy |
crunchier |
crunchiest |
|
curly |
curly |
curliest |
|
curvy |
curvier |
curviest |
|
cute |
cuter |
cutest |
|
damp |
damper |
dampest |
|
dark |
darker |
darkest |
|
deadly |
deadlier |
deadliest |
|
deep |
deeper |
deepest |
|
dense |
denser |
densest |
|
dirty |
dirtier |
dirtiest |
|
dry |
drier |
driest |
|
dull |
duller |
dullest |
|
dumb |
dumber |
dumbest |
|
dusty |
dustier |
dustiest |
|
early |
earlier |
earliest |
|
easy |
easier |
easiest |
|
faint |
fainter |
faintest |
|
fair |
fairer |
fairest |
|
fancy |
fancier |
fanciest |
|
far |
further/farther |
furthest/farthest |
|
fast |
faster |
fastest |
|
fat |
fatter |
fattest |
|
few |
fewer |
fewest |
|
fierce |
fiercer |
fiercest |
|
filthy |
filthier |
filthiest |
|
fine |
finer |
finest |
|
firm |
firmer |
firmest |
|
fit |
fitter |
fittest |
|
flaky |
flakier |
flakiest |
|
flat |
flatter |
flattest |
|
fresh |
fresher |
freshest |
|
friendly |
friendlier |
friendliest |
|
full |
fuller |
fullest |
|
funny |
funnier |
funniest |
|
gentle |
gentler |
gentlest |
|
gloomy |
gloomier |
gloomiest |
|
good |
better |
best |
|
grand |
grander |
grandest |
|
grave |
graver |
gravest |
|
greasy |
greasier |
greasiest |
|
great |
greater |
greatest |
|
greedy |
greedier |
greediest |
|
gross |
grosser |
grossest |
|
guilty |
guilter |
guiltiest |
|
hairy |
hairier |
hairiest |
|
handy |
handier |
handiest |
|
happy |
happier |
happiest |
|
hard |
harder |
hardest |
|
harsh |
harsher |
harshest |
|
healthy |
healthier |
healthiest |
|
heavy |
heavier |
heaviest |
|
high |
higher |
highest |
|
hip |
hipper |
hippest |
|
hot |
hotter |
hottest |
|
humble |
humbler |
humblest |
|
hungry |
hungrier |
hungriest |
|
icy |
icier |
iciest |
|
itchy |
itchier |
itchiest |
|
juicy |
juicier |
juiciest |
|
kind |
kinder |
kindest |
|
large |
larger |
largest |
|
late |
later |
latest |
|
lazy |
lazier |
laziest |
|
light |
lighter |
lightest |
|
likely |
likelier |
likeliest |
|
little |
littler |
littlest |
|
lively |
livelier |
liveliest |
|
lonely |
lonlier |
loneliest |
|
long |
longer |
longest |
|
loud |
louder |
loudest |
|
lovely |
lovelier |
loveliest |
|
low |
lower |
lowest |
|
mad |
madder |
maddest |
|
mean |
meaner |
meanest |
|
messy |
messier |
messiest |
|
mild |
milder |
mildest |
|
moist |
moister |
moistest |
|
narrow |
narrower |
narrowest |
|
nasty |
nastier |
nastiest |
|
naughty |
naughtier |
naughtiest |
|
near |
nearer |
nearest |
|
neat |
neater |
neatest |
|
needy |
needier |
neediest |
|
new |
newer |
newest |
|
nice |
nicer |
nicest |
|
noisy |
noisier |
noisiest |
|
odd |
odder |
oddest |
|
oily |
oilier |
oiliest |
|
old |
older/elder |
oldest/eldest |
|
plain |
plainer |
plainest |
|
polite |
politer |
politest |
|
poor |
poorer |
poorest |
|
pretty |
prettier |
prettiest |
|
proud |
prouder |
proudest |
|
pure |
purer |
purest |
|
quick |
quicker |
quickest |
|
quiet |
quieter |
quietest |
|
rare |
rarer |
rarest |
|
raw |
rawer |
rawest |
|
rich |
richer |
richest |
|
ripe |
riper |
ripest |
|
risky |
riskier |
riskiest |
|
roomy |
roomier |
roomiest |
|
rough |
rougher |
roughest |
|
rude |
ruder |
rudest |
|
rusty |
rustier |
rustiest |
|
sad |
sadder |
saddest |
|
safe |
safer |
safest |
|
salty |
saltier |
saltiest |
|
sane |
saner |
sanest |
|
scary |
scarier |
scariest |
|
shallow |
shallower |
shallowest |
|
sharp |
sharper |
sharpest |
|
shiny |
shinier |
shiniest |
|
short |
shorter |
shortest |
|
shy |
shyer |
shyest |
|
silly |
sillier |
silliest |
|
simple |
simpler |
simplest |
|
sincere |
sincerer |
sincerest |
|
skinny |
skinnier |
skinniest |
|
sleepy |
sleepier |
sleepiest |
|
slim |
slimmer |
slimmest |
|
slimy |
slimier |
slimiest |
|
slow |
slower |
slowest |
|
small |
smaller |
smallest |
|
smart |
smarter |
smartest |
|
smelly |
smellier |
smelliest |
|
smoky |
smokier |
smokiest |
|
smooth |
smoother |
smoothest |
|
soft |
softer |
softest |
|
soon |
sooner |
soonest |
|
sore |
sorer |
sorest |
|
sorry |
sorrier |
sorriest |
|
sour |
sourer |
sourest |
|
spicy |
spicier |
spiciest |
|
steep |
steeper |
steepest |
|
stingy |
stingier |
stingiest |
|
strange |
stranger |
strangest |
|
strict |
stricter |
strictest |
|
strong |
stronger |
strongest |
|
sunny |
sunnier |
sunniest |
|
sweaty |
sweatier |
sweatiest |
|
sweet |
sweeter |
sweetest |
|
tall |
taller |
tallest |
|
tan |
tanner |
tannest |
|
tasty |
tastier |
tastiest |
|
thick |
thicker |
thickest |
|
thin |
thinner |
thinnest |
|
thirsty |
thirstier |
thirstiest |
|
tiny |
tinier |
tiniest |
|
tough |
tougher |
toughest |
|
true |
truer |
truest |
|
ugly |
uglier |
ugliest |
|
warm |
warmer |
warmest |
|
weak |
weaker |
weakest |
|
wealthy |
wealthier |
wealthiest |
|
weird |
weirder |
weirdest |
|
wet |
wetter |
wettest |
|
wide |
wider |
widest |
|
wild |
wilder |
wildest |
|
windy |
windier |
windiest |
|
wise |
wiser |
wisest |
|
worldly |
worldlier |
worldliest |
|
worthy |
worthier |
worthiest |
|
young |
younger |
youngest |
Print the list of comparative superlative and adjectives from A to Z
To print the lesson on the list of comparative superlative and adjectives from A to Z. Right click on a white space and choose print. You can click on the printer icon just below and to the right of the contact us menu button at the top of the page.
Lessons that are related to this those that and these
Food adjectives for describing food A to Z list
Order of adjectives English grammar
Adjectives learning what are adjectives
Click on the following link for the Online English dictionary — English lesson
Еще раз напомним, что прилагательное (Adjective) – это слово, которое обозначает признак предмета, лица или явления. Оно отвечает на вопрос «какой?». Давайте рассмотрим, как образовать степени сравнения прилагательных в английском языке.
Все прилагательные делятся на две группы: качественные (qualitative) и относительные (relative). Но не все из них мы можем сравнивать. Например, «деревянный» – относительное прилагательное, и мы не можем сказать «более деревянный». А качественные прилагательные можно представить в положительной (красивый), сравнительной (красивее) и превосходной (самый красивый) степенях сравнения. А теперь мы расскажем о каждой степени подробно.
Сравнительная степень прилагательных в английском языке. Comparative degree
Сначала кратко расскажем о положительной степени. Положительная степень – это простая форма прилагательного: умный, веселый, мягкий. Эту форму вы встречаете в словарях. Например: brave (храбрый), new (новый), cold (холодный).
Сравнительная степень используется, когда сравнивают характеристики двух или более предметов, лиц. Такие слова, как «быстрее», «выше», «сильнее» – прилагательные в сравнительной степени. Как ее образовать?
- К коротким прилагательным (состоят из одного или двух слогов) нужно добавить окончание -er: cheap (дешевый) – cheaper (дешевле), narrow (узкий) – narrower (уже), long (длинный) – longer (длиннее).
- Если прилагательное заканчивается на -e, то мы просто добавляем -r: close (близкий) – closer (ближе).
- Если прилагательное заканчивается на -у, то -y меняется на -i: lucky (везучий) – luckier (более везучий), easy (простой) – easier (проще).
- Если прилагательное заканчивается на сочетание гласная + согласная, то конечная согласная удваивается: big (большой) – bigger (больше), hot (горячий) – hotter (горячее).
- Сравнительная степень длинных прилагательных (более 2-х слогов) образуется при помощи слов more (более) и less (менее): expensive (дорогой) – more expensive (дороже), serious (серьезный) – less serious (менее серьезный), comfortable (удобный) – more comfortable (более удобный).
Превосходная степень прилагательных в английском языке. Superlative degree
Если для сравнительной степени нужно два объекта, чтобы сравнивать характеристики, то для превосходной нужно несколько объектов, среди которых мы будем выделять один «самый-самый». Для образования этой степени мы выполняем следующее:
- К коротким прилагательным добавляем окончание -est: thin (тонкий) – the thinnest (самый тонкий), fast (быстрый) – the fastest (самый быстрый). При этом прилагательные на -e, -у и на согласную букву подчиняются тем же правилам, что и при образовании сравнительной степени: the simplest (самый простой), the busiest (самый занятый).
- Длинные прилагательные мы употребляем со словами most (самый) и least (менее всего): talented (талантливый) – the most talented (самый талантливый), interesting (интересный) – the least interesting (наименее интересный).
При образовании этой степени обязательно нужно употреблять артикль the, как и написано в вышеуказанных примерах.
Особые прилагательные
А еще в английском есть список прилагательных, которые могут употребляться и с суффиксами, и с со словами more/most, less/least.
| Слово | Перевод |
|---|---|
| Able | Способный |
| Angry | Злой |
| Clever | Умный |
| Common | Общий |
| Cruel | Жестокий |
| Friendly | Дружелюбный |
| Gentle | Нежный |
| Handsome | Красивый |
| Narrow | Узкий |
| Pleasant | Приятный |
| Polite | Вежливый |
| Quiet | Тихий |
| Serious | Серьезный |
| Simple | Простой |
| Sour | Кислый |
Прилагательные-исключения
Также есть прилагательные, степени сравнения которых образуются не по общему правилу. Эти прилагательные, как и их формы, следует знать наизусть.
- Good – better – the best (хороший – лучше – лучший).
- Bad – worse – the worst (плохой – хуже – худший).
- Little – less – the least (маленький – меньше – наименьший).
- Many/much – more – the most (много – больше – наибольший).
- Old – older – the oldest (старый – старше – самый старый).
- Old – elder – the eldest (старый – старше – самый старший) – о членах семьи.
- Late – later – the latest/last (поздний – более поздний – последний/последний по времени).
- Late – the latter – the last (поздний – второй из двух перечисленных – последний по порядку).
- Near – nearer – the nearest (близкий – более близкий – ближайший по расстоянию).
- Near – nearer – next/the next (близкий – более близкий – следующий по времени/следующий по порядку).
- Far – farther – the farthest (дальний – более дальний – самый дальний).
- Far – further – the furthest (дальний, далекий – дальнейший – дальнейший/добавочный).
Предлагаем вам изучить табличку со степенями сравнения.
| Прилагательное | Степени сравнения | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Положительная | Сравнительная | Превосходная | |
| Короткие, из 1-2 слогов | Прилагательное
cheap |
+ er
cheaper |
+ est
the cheapest |
| Длинные слова из 2-х и более слогов | Прилагательное
expensive |
More/less + прилагательное
more/less expensive |
The most/least + прилагательное
the most/least expensive |
↓ Скачать таблицу «Степени сравнения прилагательных в английском» (*.pdf, 180 Кб)
Это основные правила образования степеней сравнения прилагательных в английском языке. Не забудьте в конце пройти тест, чтобы проверить, как хорошо вы запомнили этот материал.
Тест
Степени сравнения прилагательных в английском языке
Если вы нашли ошибку, пожалуйста, выделите фрагмент текста и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Объясним правила образования и использования английских прилагательных.
Содержание:
- 1. Образование сравнительной степени прилагательных
- 2. Образование превосходной степени прилагательных
- 3. Less и the least
Есть три степени сравнения прилагательных в английском языке: положительная (positive degree), сравнительная (comparative degree) и превосходная (superlative degree).
Положительная степень прилагательного в английском языке — это форма, в которой слово записано в словаре, например, big (большой), small (маленький) или pretty (симпатичный). Мы используем положительную степень, чтобы сказать, что предмет или человек обладает определенным признаком или качеством. Сравнительную степень используем, когда хотим отметить, что предмет или человек обладает определенным качеством в большей степени, чем другие. А превосходная степень прилагательного показывает, что объект обладает качеством в наибольшей степени.
Английские прилагательные делят на две категории:
- качественные прилагательные описывают качество, например: narrow (узкий), beautiful (красивый), friendly (дружелюбный).
- относительные прилагательные называют признак, например: wooden (деревянный), French (французский).
Только у качественных прилагательных есть три степени сравнения.
My car is fast but your car is faster. — Моя машина быстрая, но твоя машина быстрее.
My car is German and your car is French. — Моя машина немецкая, а твоя машина французская.
French и German — относительные прилагательные, сравнивать их невозможно. Нельзя сказать, что какой-то предмет более немецкий или самый французский.
Образование сравнительной степени прилагательных в английском языке
Рассмотрим образование сравнительной степени прилагательных на примере. Возьмем две дороги: одна из них двухполосная, вторая — четырехполосная. Следовательно, вторая дорога шире, чем первая. Сравнить предметы можно при помощи слова than (чем, нежели):
This road is broader than that one. — Эта дорога шире, чем та.
При образовании сравнительной степени прилагательных в английском языке необходимо учитывать длину прилагательного. Измерять эту длину надо слогами. Если вы сомневаетесь в количестве слогов, воспользуйтесь ресурсом How Many Syllables.
Прилагательное длиной в один слог — big (большой), small (маленький), thin (тонкий), cute (забавный), cold (холодный) — называется односложным.
Прилагательное длиной в два слога — mod-ern (современный), bus-y (занятой), clev-er (умный), pret-ty (красивый) — двусложное.
Прилагательное длиной в три и более слогов — beau-ti-ful (красивый), con-fi-den-tial (секретный), de-fen-sive (защищающий) — многосложное.
Особенности образования сравнительной степени прилагательных:
- Односложные прилагательные
Если прилагательное односложное, сравнительная степень образуется путем добавления суффикса -(e)r:
cold (холодный) – colder (холоднее)
warm (теплый) – warmer (теплее)
cool (прохладный) – cooler (прохладнее)
safe (безопасный) – safer (безопаснее)
cute (забавный) – cuter (забавнее)
wide (широкий) – wider (шире)In Canada I got used to colder winters. — В Канаде я привык к более холодным зимам.
Kate’s dog is cuter than Ann’s. — Пес Кейт милее, чем пес Энн.Если односложное прилагательное оканчивается на сочетание краткая гласная + согласная, то конечная согласная удваивается:
big (большой) – bigger (больше)
thin (тонкий, худой) – thinner (тоньше, худее)
fat (толстый, жирный) – fatter (толще, жирнее)The cuts were thinner but deeper. — Разрезы были тоньше, но более глубокие.
July this year is hotter, I think. — Июль в этом году жарче, мне кажется.Конечная согласная не удваивается, если односложное прилагательное оканчивается на сочетание долгая гласная + согласная:
slow (медленный) – slower (медленнее)
cheap (дешевый) – cheaper (дешевле)The bus started moving slower. — Автобус стал двигаться медленнее.
Property is cheaper in Turkey than here. — Недвижимость в Турции дешевле, чем здесь. - Двусложные прилагательные
- К двусложным прилагательным, которые оканчиваются на звуки /r/, /l/ или безударный гласный звук, добавляем суффикс -(e)r:
clever /ˈklevər/ (умный) – cleverer (умнее)
noble /ˈnəʊbl/ (благородный) – nobler (самый благородный)
narrow /ˈnærəʊ/ (узкий) – narrower (у́же)The road became narrower, so we had to turn around. — Дорога стала уже, и нам пришлось повернуть назад.
You will appear to be nobler if you just admit that you are wrong. — Вы будете выглядеть благороднее, если просто признаете свою неправоту. - Если прилагательное оканчивается на гласную -y, она меняется на -i и добавляется суффикс -(e)r:
busy (занятой) – busier (более занятой)
cosy (уютный) – cosier (уютнее)The house in the mountains was cosier compared to the house we rented at the seaside. — Дом в горах был уютнее по сравнению с домом, который мы снимали на побережье.
A cleverer student will get an opportunity to go to the contest. — Более умный студент получит возможность поехать на состязание. - Прилагательные, которые оканчиваются на -ing, -ed, -ful и -less, образуют сравнительную степень с помощью more:
thankful (благодарный) – more thankful (более благодарный)
amusing (забавный) – more amusing (более забавный)My previous job was more stressful than this one. — Моя предыдущая работа была более напряженной, чем эта.
The situation was more amusing than I thought it would be. — Ситуация оказалась более забавной, чем я предполагала.Однако некоторые двусложные прилагательные с другими окончаниями также образуют сравнительную степень только при помощи more:
modern (современный) – more modern (более современный)
central (центральный) – more central (более центральный)
famous (известный) – more famous (более известный)
human (человеческий) – more human (более человечный)
honest (честный) – more honest (более честный)During the last speech, Kate was more honest than during the previous one. — Во время последнего разговора Кейт была более честна, чем во время предыдущего.
My father’s attitude to life is more modern than his colleagues’. — У моего отца более современных подход к жизни, чем у его коллег. - У некоторых двусложных прилагательных есть две формы образования сравнительной степени — с окончанием -(e)r и с помощью слова more:
polite (вежливый) – politer / more polite (более вежливый)
friendly (дружелюбный) – friendlier / more friendly (более дружелюбный)
noble (благородный) – nobler / more noble (более благородный)
narrow (узкий) – narrower / more narrow (более узкий)
gentle (нежный) – gentler / more gentle (более нежный)
cruel (жестокий) – crueler / more cruel (более жестокий)
quiet (тихий) – quieter / more quiet (более тихий)
clever (умный) – cleverer / more clever (более умный)
angry (злой) – angrier / more angry (более злой)I wish some nurses were a bit more gentle and polite. — Я бы хотел, чтобы некоторые медсестры были помягче и повежливее.
The kids became quieter and suddenly nodded off. — Дети стали вести себя спокойнее и внезапно заснули.
- К двусложным прилагательным, которые оканчиваются на звуки /r/, /l/ или безударный гласный звук, добавляем суффикс -(e)r:
- Многосложные прилагательные
Если прилагательное многосложное, тогда сравнительную степень от него образовываем, ставя перед ним слово more:
interesting (интересный) – more interesting (интереснее)
beautiful (красивый) – more beautiful (красивее)
unexpected (неожиданный) – more unexpected (неожиданнее)It is a more interesting book, believe me. — Это более интересная книга, поверь мне.
You are more beautiful than she ever was. — Ты красивее, чем она когда-либо была.Самая известная ошибка в английской грамматике — фраза, сказанная Алисой Льюиса Кэролла:
Алиса, презрев правила грамматики, прибавляет к многосложному прилагательному суффикс -(e)r, вместо того чтобы сказать more and more curious.
- Исключения
good (хороший) – better (лучше)
bad (плохой) – worse (хуже)
far (далекий) – farther/further (дальше)
old (старый) – older (старее/старше)There is no better option. — Нет лучшего варианта.
They say I can find a doctor in a farther village. — Они говорят, что я смогу найти врача в более отдаленной деревне.Обратите внимание, что прилагательное far имеет два варианта сравнительной степени. Выбор нужной формы зависит от смысла слова. Когда речь идет о расстоянии, не имеет значения, какую форму выбрать.
It was a farther/further school. — Это была более отдаленная школа.
Если мы хотим употребить это прилагательное в значении «дальнейший», «добавочный», тогда используем исключительно further.
For further information, turn to the secretary. — За дальнейшей информацией обратитесь к секретарю.
Образование превосходной степени прилагательных в английском языке
Вернемся к примеру с дорогами. Первая — двухполосная, вторая — четырехполосная, а третья — шестиполосная.
The first road is broader than the second one, but the third road is the broadest. — Первая дорога шире второй, но третья дорога самая широкая.
Особенности формирования превосходной степени английских прилагательных:
- Односложные прилагательные
Если прилагательное односложное, его превосходная степень образуется путем прибавления суффикса -(e)st, а перед словом ставится определенный артикль the. Если есть другие слова-определители, например притяжательное местоимение, артикль the опускается:
cold (холодный) – the coldest (самый холодный)
warm (теплый) – the warmest (самый теплый)
cool (прохладный) – the coolest (самый прохладный)
safe (безопасный) – the safest (самый безопасный)
cute (забавный) – the cutest (самый забавный)
wide (широкий) – the widest (самый широкий)The kitchen with its stone floor was the coolest place in the house. — Кухня с каменным полом была самым прохладным местом в доме.
This is my cutest dog Charlie. — Это моя самая милая собака Чарли.Если прилагательное оканчивается на сочетание гласная + согласная, конечная согласная удваивается:
big (большой) – the biggest (самый большой)
thin (тонкий, худой) – the thinnest (самый тонкий, самый худой)
fat (толстый, жирный) – the fattest (самый толстый, самый жирный)I want to find a recipe of a cake with the fattest layer of chocolate. — Хочу найти рецепт торта с самым толстым слоем шоколада.
She chose the biggest teddy. — Она выбрала самого большого плюшевого медведя.Последняя согласная не удваивается в односложных прилагательных с долгим гласным звуком:
new (новый) – the newest (самый новый)
brief (краткий) – the briefest (самый краткий)
deep (глубокий) – the deepest (самый глубокий)This is the briefest love story that I have ever heard. — Это самая короткая история любви, которую я когда-либо слышала.
Could I express my deepest sympathy? — Могу ли я выразить свою глубочайшую признательность? - Двусложные прилагательные
- К двусложным прилагательным, которые оканчиваются на звуки /r/, /l/ или безударный гласный звук, присоединяем суффикс -(e)st. Не забываем, что перед прилагательным необходимо поставить определенный артикль the:
clever (умный) – the cleverest (умнейший)
noble (благородный) – the noblest (благороднейший)
narrow (узкий) – the narrowest (самый узкий)It was the narrowest street I had ever seen in my life. — Это была самая узкая улица, которую я когда-либо видел в своей жизни.
Who is the cleverest student in your class? — Кто самый умный ученик в вашем классе? - Если прилагательное оканчивается на букву -y, она меняется на -i, к слову добавляется суффикс -(e)st и артикль the:
friendly (дружелюбный ) – the friendliest (самый дружелюбный)
trendy (модный) – the trendiest (самый модный)Cindy is the friendliest kid in the class. — Синди — самый дружелюбный ребенок в классе.
They chose the narrowest path because it was the shortest. — Они выбрали самую узкую тропу, потому что она была самой короткой. - Прилагательные, которые оканчиваются на -ing, -ed, -ful и -less, образуют превосходную степень с помощью the most:
thankful (благодарный) – the most thankful (самый благодарный)
amusing (забавный) – the most amusing (самый забавный)He has such unusual facial expressions! Sam is the most amusing kid in the group. — У него такая интересная мимика! Сэм — самый забавный малыш в группе.
He is the most grateful student I have ever taught. — Он самый благодарный ученик, которого я когда-либо учила.Однако некоторые двусложные прилагательные с другими окончаниями также образуют сравнительную степень только при помощи the most:
modern (современный) – the most modern (самый современный)
central (центральный) – the most central (самый центральный)
famous (известный) – the most famous (самый известный)
human (человеческий) – the most human (самый человечный)
honest (честный) – the most honest (самый честный)This building is the most modern in his district. — Это здание самое современное в районе.
She is the most honest member of her family. — Она самая честная из всех членов семьи. - У некоторых двусложных прилагательных есть две формы сравнительной степени — the перед прилагательным с окончанием -(e)st или the most перед прилагательным:
polite (вежливый) – the politest / the most polite (самый вежливый)
common (обычный) – the commonest / the most common (самый обычный)
simple (простой) – the simplest / the most simple (самый простой)
stupid (глупый) – the stupidest / the most stupid (самый глупый)
clever (умный) – the cleverest / the most clever (самый умный)The task appeared to be the simplest. — Задача оказалась самой легкой.
That’s the most stupid thing I’ve ever heard. — Это самая глупая вещь, которую я когда-либо слышал.
- К двусложным прилагательным, которые оканчиваются на звуки /r/, /l/ или безударный гласный звук, присоединяем суффикс -(e)st. Не забываем, что перед прилагательным необходимо поставить определенный артикль the:
- Многосложные прилагательные
Многосложные прилагательные образуют превосходную степень с помощью the most:
interesting (интересный) – the most interesting (самый интересный)
beautiful (красивый) – the most beautiful (самый красивый)
unexpected (неожиданный) – the most unexpected (самый неожиданный)For my grandmother, her son is the most darling person in the world. — Для моей бабушки ее сын — самый дорогой человек в мире.
Monica Bellucci is the most famous and the most beautiful Italian actress. — Моника Белуччи — самая знаменитая и самая красивая итальянская актриса. - Исключения
good (хороший) – the best (лучший)
bad (плохой) – the worst (худший)
far (далекий) – the farthest / the furthest (самый дальний)
old (старый) – the oldest (самый старый) / the eldest (самый старший)Gary is not the worst lawyer in the town, but he is not the best, though. — Гэри не худший юрист в городе, но и не лучший.
As usual, she found what she needed in the farthest store. — Как обычно, она нашла то, что ей было нужно, в самом дальнем магазине.
Less и the least
Используем less, когда хотим отметить, что предмет/человек обладает каким-то качеством в меньшей степени, чем другие, а the least — в наименьшей степени.
hard (тяжелый) – less hard (менее тяжелый) – the least hard (наименее тяжелый)
famous (известный) – less famous (менее известный) – the least famous (наименее известный)
beautiful (красивый) – less beautiful (менее красивый) – the least beautiful (наименее красивый)
Let’s choose a less expensive hotel. — Давай выберем менее дорогой отель.
She is now a less famous actress than 20 years ago. — Сейчас она менее известная актриса, чем 20 лет назад.
The least tiring journey was to Los Angeles because they took the train. — Наименее выматывающим было путешествие в Лос-Анджелес, потому что они поехали на поезде.
First, I offer to choose the least beautiful dress. — Сначала я предлагаю выбрать наименее красивое платье.
Надеемся, что после нашего подробного объяснения, вы сможете без труда использовать сравнительную и превосходную степени прилагательных в английском языке. Чтобы упорядочить в голове изученный материал, пройдите небольшой тест.
Тест по теме «Степени сравнения прилагательных в английском языке»
© 2023 englex.ru, копирование материалов возможно только при указании прямой активной ссылки на первоисточник.
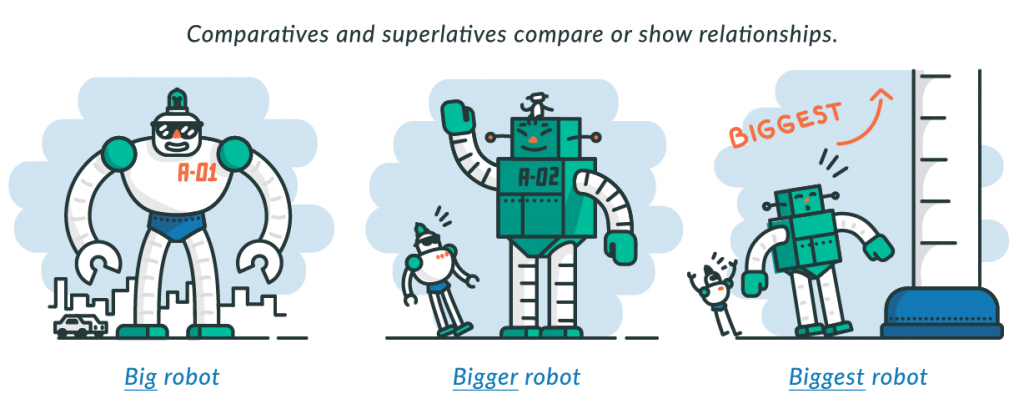
Comparatives and superlatives are special types of adjectives used when comparing two or more things. The trickiest thing when using comparatives and superlatives is making sure we are writing them the correct way, but with a little practice, comparatives and superlatives can quickly be mastered.
In this post we’ll review what comparatives and superlatives are, the rules for how to form these adjectives the correct way, and how to use them effectively in a sentence.
After reviewing the information below, test yourself with a post-assessment quiz and practice with our high quality, standards-aligned questions here.
The Basics of Comparatives and Superlatives

What is a Comparative?
Comparative Adjectives are words used to describe a noun by comparing it to another noun. We usually think of ‘er’ words like bigger or smaller, but they can be a little trickier than that.
The way we form comparative adjectives is based on the number of syllables in the adjective and whether or not the adjective ends with the letter ‘y’.
What is a Superlative?
Superlative Adjectives are words used to describe a noun when comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree. Think: big, bigger, biggest, or small, smaller, smallest.
Like with comparative adjectives, it’s not always as simple as adding ‘est’. The number of syllables and whether or not the adjective ends with the letter ‘y’ also help us determine how to form a superlative adjective.
One Syllable Adjectives
Let’s look at a chart showing the comparative and superlative forms of the word for the most basic one syllable adjectives, where we add ‘er’ for the comparative and ‘est’ for the superlative. *Note: when the adjective follows the CVC, or consonant, vowel, consonant spelling, the final consonant is doubled.
|
ADJECTIVE |
COMPARATIVE |
SUPERLATIVE |
|
Big |
Bigger |
Biggest |
|
Tall |
Taller |
Tallest |
|
Small |
Smaller |
Smallest |
|
Hot |
Hotter |
Hottest |
Comparative Adjectives:
- I am faster than my friend.
- Arizona is hotter than Alaska.
Superlative Adjectives:
- She is the tallest student.
- That was the shortest movie in the series.
Notice the other words around the comparative and superlative adjectives. Most comparatives are followed by ‘than’, and most superlatives follow the word ‘the’.
Two Syllable Adjectives
Now let’s look at a chart showing the comparative and superlative forms of the word for adjectives with two syllables. Comparative adjectives with two syllables can be formed by making the ‘er’ ending or by adding the words ‘more’ or ‘less’ before the adjective.
For superlative adjectives, you make the ‘est’ ending but use the word ‘most’ or ‘least’ instead of ‘more’ or ‘less’.
|
ADJECTIVE |
COMPARATIVE |
SUPERLATIVE |
|
Happy |
Happier |
Happiest |
|
Crazy |
Crazier |
Craziest |
|
Nervous |
More/Less Nervous |
Most/Least Nervous |
|
Massive |
More/Less Massive |
Most/Least Massive |
|
Quiet |
Quieter or More/Less Quiet |
Quietest or Most/Least Quiet |
*Note: In many cases, either form of the comparative or superlative can be used, but there is generally a ‘most common’ usage. Additionally, the adjective does not need to end in ‘y’ in order to use the ‘er’ or ‘est’ usage, as the last example in the table shows. Your ear will often be able to recognize what sounds best.
Comparative Adjectives:
- She tends to be less passive than her brother.
- This quiz is simpler than the last one.
Superlative Adjectives:
- Fall is the busiest shopping season.
- This is the most rapid method of delivery.
Notice again how the comparative adjectives are followed by ‘than’, and superlative adjectives follow the word ‘the’.
Three or More Syllable Adjectives
The chart below shows the comparative and superlative forms of the word for adjectives that are three or more syllables long. In these cases, we always add ‘more’ or ‘less’ before a comparative adjective and ‘most’ or ‘least’ before a superlative adjective.
|
ADJECTIVE |
COMPARATIVE |
SUPERLATIVE |
|
Mysterious |
More/Less Mysterious |
Most/Least Mysterious |
|
Complicated |
More/Less Complicated |
Most/Least Complicated |
|
Wonderful |
More/Less Wonderful |
Most/Least Wonderful |
Comparative Adjectives:
- I tend to be more reluctant than my friends when trying new things.
- The noise at the pool was less bothersome than the noise on the beach.
Superlative Adjectives:
- Her second compilation was the most exceptional of them all.
- Those were the least comfortable couches I have ever sat on.
Irregular Adjectives
When using comparative and superlative adjectives, it is important to note that there are a handful of irregular adjectives that don’t follow the rules above. The chart below shows these irregular adjectives along with their comparative and superlative forms.
|
ADJECTIVE |
COMPARATIVE |
SUPERLATIVE |
|
Good |
Better |
Best |
|
Bad or Ill |
Worse |
Worst |
|
Little (Amount) |
Less |
Least |
|
Far (Distance) |
Farther |
Farthest |
|
Far (Extent) |
Further |
Furthest |
|
Many or Much |
More |
Most |
Comparative Adjectives:
- I did better than the rest of my class on the final.
- She ran farther in this race than she did in the last one.
Superlative Adjectives:
- That was the best birthday present ever!
- I bought the least expensive souvenir that I could find.
Return to the Table of Contents
2 Tips for Recognizing and Using Comparative & Superlative Adjectives
Tip #1: Rearrange your sentence to use different forms of the adjective
We can use different forms of the adjective if we adjust our sentence to fit the adjective.
Here are some examples we used for one syllable adjectives:
Comparative Example:
- I ran faster than my friend.
Now, let’s rearrange the sentence in a way that allows us to use the superlative form of the adjective.
- Between my friend and I, I ran the fastest.
Here, the comparison is still being made between two people; however, when we limit the nouns that we are comparing, we can use the superlative form of the adjective. Notice this sentence follows the other superlative characteristic of using the word ‘the’ before the adjective.
Superlative Example:
- That was the shortest movie in the series.
Now, let’s rearrange the sentence in a way that allows us to use the comparative form of the adjective.
- That was shorter than any other movie in the series.
Here, the comparison is still being made to two or more movies, and we are still describing it to the lowest degree. By adding ‘any other’ before ‘movie in the series’, we can use the comparative form of the adjective. Notice that this sentence also now follows the other comparative characteristic of using the word ‘than’ after the adjective.
Tip #2: Remember your spelling rules before making the comparative or superlative form of the adjective
Any time we change the ending of a word, we need to take into account how the word is normally spelled.
If the adjective already ends with an ‘e’, only add ‘r’ for the comparative and ‘st’ for the superlative.
- Wide becomes Wider or Widest.
- Brave becomes Braver or Bravest.

If the adjective ends with a consonant + short vowel + consonant (CVC), we typically double the last consonant.
- Big becomes Bigger or Biggest.
- Hot becomes Hotter or Hottest.
If the adjective ends with a ‘y’, we change the ‘y’ to and ‘i’.
- Early becomes Earlier or Earliest.
- Silly becomes Sillier or Silliest.
Return to the Table of Contents
Applying the Basics: Comparative and Superlative Adjective Review & Practice
Now that you understand what comparatives and superlatives are, and how to use them properly in a sentence, let’s practice identifying them and checking for proper usage.
Remember, comparative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to another noun. Superlative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree.
Comparative Adjectives Exercises & Review
Complete the quick exercise below to assess your mastery of comparative adjectives.
In the sentences below, select the option that accurately shows the comparative form of the adjective. Remember, a comparative adjective describes a noun by comparing it to another noun.
1. Lucas is (oldest/older) than Lily.
- older
2. Alaska is (colder/more cold) than Florida.
- colder
3. I am (more worried/worrieder) about this exam than the last one.
- more worried
4. This map is (more confusing/most confusing) than my calculus homework.
- more confusing
5. I ran (further/farther) than my best friend did yesterday.
- Farther
Superlative Adjectives Exercises & Review
Complete the quick exercise below to assess your mastery of superlative adjectives.
In the sentences below, select the option that accurately shows the superlative form of the adjective. Remember, a superlative adjective describes a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree.
1. Playing games with your family is the (funner/funnest) way to pass the time when you’re cooped up at home.
- funnest
2. My brother is the (most annoying/annoyingest) person to have around when looking for peace and quiet.
- most annoying
3. As soon as possible, we hope to go to the (beautifulest/most beautiful) tropical island.
- most beautiful
4. Reading a good book is the (most leisurely/more leisurely) way to relax.
- most leisurely
5. Multitasking is the (less efficient/least efficient) method of productivity.
- least efficient
Comparative & Superlative Exercises
Use your knowledge of both comparative and superlative adjectives in the exercise below.
Identify the comparative and superlative adjectives in the sentences below. There may be more than one in a sentence. Make sure you specify which are comparative and which are superlative.
1. I worked on the least complicated homework before starting the more challenging work.
- Comparative: more challenging
- Superlative: least complicated
2. She is taller than the other girls in her class, but she is not the tallest student in the class.
- Comparative: taller
- Superlative: tallest
3. I find direct instruction to be the most straightforward way learning new material.
- Superlative: most straightforward
4. I believe the most obvious answer is correct more often than not.
- Comparative: more often
- Superlative: most obvious
5. Finishing first in the finals was the most fulfilling accomplishment after a sectional performance that was harder than she expected.
- Comparative: harder
- Superlative: most fulfilling
For additional practice, check out the Comparative and Superlative content on Albert.
Return to the Table of Contents
Try for Yourself: Comparative and Superlative Adjectives Quiz
Feeling confident in your understanding of comparative and superlative adjectives?
Take this short quiz to see what you’ve learned:
1. Do comparative or superlative adjectives show the highest degree of a quality?
- Answer: Superlative Adjectives
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! Superlative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree. Comparative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to another noun.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right. Remember, comparative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to another noun. Superlative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree.
2. Do comparative or superlative adjectives sometimes use the additional modifier ‘more’?
- Answer: Comparative Adjectives
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! Since comparative adjectives do not describe a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree, they can use modifiers such as ‘more’.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right. Remember, superlative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree, so they would use modifiers such as ‘most’ or ‘least’. Comparative adjectives do not describe a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree, they can use modifiers such as ‘more’.
3. Does the following sentence use a comparative or superlative adjective?
People from Chicago often agree that deep dish pizza is better than thin crust pizza.
- Answer: Comparative Adjective
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! In this sentence, deep dish pizza is being compared to thin crust pizza. The word ‘better’ is a comparative adjective since it is comparing one type of pizza to another.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right. Remember, superlative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree. In this sentence, deep dish pizza is being compared to thin crust pizza. The word ‘better’ is a comparative adjective since it is comparing one type of pizza to another.
4. Is the underlined section of the sentence below a comparative or superlative adjective?
The tree in front of my house is the tallest tree in the neighborhood.
- Answer: Superlative Adjective
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! Superlative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree. The word ‘tallest’ describes the tree to the highest degree compared to the other trees in the neighborhood.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right. Remember, Remember, comparative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to another noun. Superlative adjectives describe a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree. The word ‘tallest’ describes the tree to the highest degree compared to the other trees in the neighborhood.
5. Which of the following sentences correctly uses a comparative adjective?
A. I thought your portion was the biggest than mine.
B. I thought your portion was bigger than mine.
- Answer: B
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! Comparative adjectives usually end with the letters ‘er’ because they are describing a comparison with one other noun.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right. Superlative adjectives usually end with the letters ‘est’ because they are describing a comparison with two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree. Additionally, superlative adjectives are not typically followed by the word ‘than’. Comparative adjectives usually end with the letters ‘er’ because they are describing a comparison with one other noun.
6. Which of the following sentences correctly uses a superlative adjective?
A. That was the least memorable movie I’ve seen in a long time.
B. That was the less memorable movie I’ve seen in a long time.
- Answer: A
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! Superlative adjectives with three syllables use the words ‘least’ or ‘most’ because they are describing a comparison with two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right. Comparative adjectives with three syllables use the words ‘more’ or ‘less’ because they are describing a comparison with one other noun. Superlative adjectives with three syllables use the words ‘least’ or ‘most’ because they are describing a comparison with two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree.
For additional practice with comparative and superlative adjectives, check out our practice on Albert.io: Comparatives and Superlatives.
Return to the Table of Contents
Teacher’s Corner for Comparatives and Superlatives
While it’s true that comparative and superlative adjectives are a foundational grammar skill, the Common Core English Language Progressive Skills Chart shows that even elementary-level skills “require continued attention in higher grades as they are applied to increasingly sophisticated writing and speaking.”
For specific standards addressing comparative and superlative adjectives, check out the Common Core State Standards site!
Albert’s Comparative and Superlative practice can be used for much more than homework!
Our assessments can be used as pre-and post-tests to measure student progress. Our pre-made quizzes can be used as bell-ringers, exit tickets, and more!
In addition to our pre-made assessments, you can also use our assignments feature to create your own quizzes and assessments.
Return to the Table of Contents
Summary on Comparative Adjectives and Superlative Adjectives
A Comparative Adjective is a word that describes a noun by comparing it to another noun. Comparative adjectives typically end in ‘er’ and are followed by the word ‘than’.
A Superlative Adjective is a word that describes a noun by comparing it to two or more nouns to the highest or lowest degree. Superlative adjectives typically end in ‘est’ and are preceded by the word ‘the’.
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives are words we often see and use in our writing. Make sure you are structuring your comparative and superlative adjectives appropriately for the number of syllables in the adjective.
Practice makes perfect! Use our Comparative and Superlative practice on Albert’s grammar course!
Need help preparing for your Grammar exam?
Albert has hundreds of grammar practice questions with detailed explanations to help you master concepts.