Boutros International, headed by Mourad and Arlette Boutros, is a leader in the fields of Arabic typography, calligraphy and design. For more than 40 years, working globally, Boutros’ projects have ranged from the creation of Arabic typeface collections for internationally renowned software and design houses, to corporate Arabic logotypes and private commissions.
During his formative years, Boutros was classically trained as an Arabic calligrapher. The development of the personal computer set him on a mission to specialize in projects that combined traditional calligraphic techniques with new technologies. His highly acclaimed books, “Arabic for Designers” and “Talking about Arabic,” aim to share his passion for design with a wider audience and his glorious calligraphy can be found in major institutions throughout the Arabic speaking world.
Before we go any further, it’s essential to clarify that Boutros is a designer of typefaces. Many people are confused between typefaces and fonts. The typographer Norbert Florendo has explained the difference succinctly: “Font is what you use and typeface is what you see.” Stephen Coles elaborates further: “When you talk about how much you like a tune, you don’t say: ‘That’s a great MP3.’ You say: ‘That’s a great song.’ The MP3 is the delivery mechanism, not the creative work. Just as in type, a font is the delivery mechanism and a typeface is the creative work.”
So Boutros’ typefaces are a form of graphic artistry, a creation of his own talent and imagination. He licenses his intellectual property to enable others to be expressive through written Arabic. And therein lies the problem. Many people don’t realize that just as they pay a fee to own a copy of a movie or a video game, they should pay a licensing fee to use a typeface.
Boutros was creating typefaces decades before the PC or the Internet. According to Boutros, in the early 1970s Arabic calligraphers and typographers used to design typeface in a size three to six times larger than the finished size that would be needed. Then the typeface would be reduced photographically to the required size, many copies would be printed on white glossy paper, and finally the characters would be cut out and pasted together by hand to form the word or sentence needed in a magazine or advertisement. It was a slow, labor intensive process.
Then, in 1976, the British company Letraset started work on a wide range of Arabic typefaces using a silk screen process. This made it much easier to use specialty typefaces in advertising, signage, headlines and other written creative content. Mourad and Arlette Boutros in collaboration with Letraset created the Arabic typeface, “Boutros Advertisers Naskh,” to work in harmony with English typefaces.
“The design is based on the classical Naskh style, respecting Arabic calligraphy and cultural rules,” explained Boutros. “The addition of linked straight lines to match the Latin baseline level is designed to achieve harmony when used alongside a Latin equivalent typeface such as Garamond, Palatino and Times Roman as well as Helvetica, Futura and Frutiger. The light and medium weights are suitable for body text. The other weights are suitable for headlines and sub-headings. The outline, shadow and inline versions can be used to give extra decoration to all types of communication materials.”
Boutros Advertisers Naskh became very popular particularly for indoor and outdoor signs at airports, offices and hospitals. It wasn’t long before the use of typefaces took an even bigger jump with the coming of software to handle word processing and graphic arts. Boutros should have become a multimillionaire because his typefaces were everywhere. That didn’t happen. Instead Boutros Advertisers Naskh became the most pirated typeface worldwide.
“People need to know that when they are downloading fonts from online sites claiming to offer free fonts, most of those offers are not legal,” said Boutros. “People should be prepared to respect other people’s creativity and accept that they have to pay for people’s creativity. Individuals would not be happy to go to an office and work without pay. Creative people are not happy when they see individuals and businesses using the fruits of their labor, their creativity, without any compensation.”
Boutros is not upset with the poor boy in the developing world, who has no money to afford a typeface and steals one belonging to Boutros International for personal use. This is just survival. But if that same poor boy copies the font and sells it for profit, then that is piracy. Even worse in his opinion is when someone takes a typeface design, alters it slightly, gives it another name and then offers it as a legal font. Boutros showed Arab News an example from someone who has done exactly that with one of Boutros International’s typefaces.
He has had some amusement in recent years with one typeface that Boutros International created. The typeface has a small flaw in an otherwise beautiful character set. Any company who comes to Boutros International and requests licensing for that typeface is advised of the issue and instead is offered licensing for what Boutros considers to be a superior piece of work. Unfortunately, a significant number of companies don’t care about using typefaces legally and steal the flawed typeface. Since the flaw is minor, they may not even be aware of the problem or choose to overlook it, but the moment they use the typeface publicly, they are exposed to Boutros as thieves.
At the end of our discussion, Boutros did want to highlight one piracy issue which is growing and it is one that he lays at the feet of the US government.
“In nations on the US embargo list, it is impossible to buy licensed software created by American companies,” Boutros said. “I have been invited to speak at an upcoming conference in Syria about advertising. I am not sure if I will go, and if I do go what will I tell the audience? Pirated software and products are all over Syria. The reason is they need to use them and they are not allowed to buy them because of the embargo. What option do they have? Where is the right and the wrong in that situation?”
What does Boutros recommend to avoid intellectual property issues when it comes to software?
“Whenever you have the opportunity, use open source software,” he said. “I use OpenOffice and other programs with a General Public License (GNU GPL). Now there’s a lot of open source software that’s as good as commercial software. It’s a way to be sure you aren’t stealing someone’s creativity.”
Resource Library
Article
Ron Widup
Marketing & Industry Awareness Committee Chair
Shermco Industries
It’s an age-old problem for all of us in the service business – effectively communicating. Clear communications about complex electrical service issues with the customer, the industry and even our employees should always be grammatically correct and free from slang.
When you don’t communicate well, you may inadvertently misrepresent the quality of workmanship of your shop and field services. We frequently communicate via written means like proposals, marketing materials, datasheets and failure summary reports. Each of these needs to be clear and concise.
LOGIN TO VIEW AND DOWNLOAD THE ARTICLE
Related Reference and Training Materials
PREVIOUS ITEM
EASA/AEMT Rewind Study

The Effect of Repair/Rewinding on Premium Efficiency/IE3 Motors
Tests prove Premium Efficiency/IE3 Motors can be rewound without degrading efficiency.
DOWNLOAD THE FULL RESULTS
ANSI/EASA AR100-2020
Recommended Practice for the Repair of Rotating Electrical Apparatus
This is a must-have guide to the repair of rotating electrical machines. Its purpose is to establish recommended practices in each step of the rotating electrical apparatus rewinding and rebuilding processes.
DOWNLOAD — ENGLISH
DESCARGAR - ESPAÑOL
EASA Technical Manual
Revised September 2022
The EASA Technical Manual is the association’s definitive and most complete publication. It’s available FREE to members in an online format. Members can also download PDFs of the entire manual or individual sections.
VIEW & DOWNLOAD
Download

Skip this Video
Loading SlideShow in 5 Seconds..
Communication by the written word PowerPoint Presentation
Download Presentation
Communication by the written word
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — E N D — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
Presentation Transcript
-
Communication by the written word
-
Model of Communication Information source Transmitter Noise Receiver Destination
-
Noise and redundancy spoil communication Noise comes from • Confused arguments. • Red herrings. • Pomposity. • Attempting to be too clever. • Repetition (it is also boring, though used sparingly, it can emphasise a point).
-
A Report should be impressive The written word will be impressive if the layout and style are clear and simple. We may mistakenly fear that our work will be devalued if the writing is straightforward.
-
The writer must identify • the aim of writing. • the audience. • the reader’s aims. • the reader’s background knowledge. • what the reader needs to know. • the reader’s attitudes.
-
The approach to writing a report is • make a plan • discuss a synopsis • draft the text • forget it! • revise and edit
-
The Ten Commandments • The Reader is the most important person. • Make the Report as clear as possible. • Organise for the convenience of the Report user. • All references should be correct in all details. • The writing should be accurate, concise and unobtrusive.
-
The Ten Commandments 6. The right diagrams with the right labels should be in the right place for the reader. 7. Summaries should give the whole picture in miniature. 8. Reports should be checked for technical and typing errors and inconsistencies. 9. The report should be attractively presented. 10. The Reader is the most important person.
-
Style for readability • Avoid long sentences • The sentence length should be flexible • Complicated information should be communicated in short sentences or as bullet points • Long words confuse rather than impress • Use words sparingly — is there a simpler, better word? (thesaurus) • Avoid redundant words • Use words accurately • Sections and Paragraphs • A good paragraph will convey just one idea Ideally this will be stated in a topic sentence, then developed logically • Avoid the passive voice and use the active voice • Use impersonal writing when appropriate
-
Active Voice In sentences written in active voice, the subject performs the action expressed in the verb; the subject acts. In each example above, the subject of the sentence performs the action expressed in the verb.
-
Passive Voice In sentences written in passive voice, the subject receives the action expressed in the verb; the subject is acted upon. The agent performing the action may appear in a «by the . . .» phrase or may be omitted. Examples taken from http://owl.english.purdue.edu/handouts/grammar/g_actpass.html
-
The structure of a Report
-
Contents of a typical Report • Title page : summary, contents • Introduction • Literature Review • Description of work/study done • Results/findings and Discussion • Conclusions and Recommendations • References and Bibliography • Appendices
-
Report Foundations Work/Findings/Discussion Aim Conclusions
-
Title page • The initial impact is important. • The front page tries to grab the reader’s attention. • The most important information should be at the golden section.
-
The potential reader asks….. • What is the report about? • Is it relevant to me? • Does it contain useful and important • information? • Should I spend time reading it now?
-
The title page must win the attention of the reader. Prominence is achieved by • the position on the page. • the font and size of the type.
-
Titles should be short but instructive Construction and instrumentation of an experimental concrete road on the trunk road D7 Uxbridge by-pass to determine the effects of omitting expansion joints. Rapid measurement of carbon in steel. An investigation into the suitability of CSPFA as a base material.
-
1 Summary 2 Introduction 3 Method 4 Results 5 Discussion 6 Conclusions 7 Recommendations 8 References 1 Summary 2 Introduction 3 Method of treatment 3.1 Survey of reducing agents 3.2 Survey of precipitating agents 4 Plant requirements. 4.1 Pre-treatment storage…….. Contents pages should be informative
-
The Summary The summary is a synopsis of the whole report outlining • the aims • the work (methods) • the findings (results) and • the conclusions Informative summaries are best; give hard information rather than vague generalities.
-
Introduction • Define what the problem is (the questions you are addressing) • Outline specific considerations that lead to this investigation • How it differs from previous work • What the report will contain • Perhaps some (hint) of the conclusions
-
Describe the approach taken. Justify that it is appropriate. Establish constraints or assumptions. Enable others to repeat the work and check the conclusions. Link with the aim of the work. Motivate the work — what is its importance? Establish approaches used in previous research — the literature search. Method
-
Do not swamp the argument. Place the details in Appendices. Give sufficient information to support the argument. What is implied by the findings? Do not simply repeat the findings. Compare with the findings of other work. Conclusions are drawn and justified during the discussion. Findings/Results Discussion
-
Presentation of results. • Use the format that illustrates the point to be made. • Tables. • Graphs. • Drawings. • Schematic diagrams.
-
Conclusions • Conclusions are those things that have been discovered as a result of having done the work. What do I know now that I didn’t know before. • A common mistake is to provide a summary of the work. • Conclusions is a short section. • When the conclusions can be written down, it is time to write the report.
-
Conclusions — example 1 Accidents in fog totalled 192 in the three year period 1969-71, making up 4% of the total: 129 of these occurred during daylight hours. Accidents were on average more serious, with more casualties per accident, than those occurring in other weather conditions. About 45% of the fog accidents and 22% of the non-fog accidents occurred on about one-seventh (160km) of the motorway network.
-
Conclusions — example 2 1. If an oil-cooling system is caught at the ‘incipient failure’ stage but does not show gross contamination, the oil should be changed without flushing (section 3.4). 2. Sludge bound oil coolers should be cleaned by a flushing procedure (described in section 3.5) 3. Systems that are grossly contaminated after component failure should be stripped and cleaned on site (section 3.7) 4. Metal-contaminated oil coolers should be returned to the manufacturer for complete stripping and cleaning (section 3.8)
-
References [29] Lam, K Y, Hung, S L, (1995), Concurrency control for time constrained transactions, Computer Journal, 38, 704-715. [30] Lam, K, Lee, V C S, (1996), Distributed real-time concurrency control protocol, in Proc, 4th International Workshop on Parallel and Distributed Real-time Systems, pp122-125, IEEE Computer Society Press, Hawaii. [31] Roberts, Andrew, Mary and Charles Lamb Web site, http://www.mdx.ac.uk/www.study/ylamb.htm [Accessed on 12/12/2004] When you provide information such as the author and title when referencing a web page, it enables the reader to search for the web page, even if the web address is changed.
-
References [28] Umar, A, (1997), Object-oriented Client/server internet environments, Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ. • Umar [28] states that … • Client/server environments [28] are important …. • Umar (1997) suggests that …… • …had significant results (Umar et al. 1998).
-
— Last thoughts — • Think of the report holistically • Initial impression is very important • Title page • Contents • summary • Two very important parts of any report • Introduction • Conclusions
-
Literature Surveys
-
The hierarchy of information
-
The purpose of publication • Expand the body of knowledge. • Prevent replication of effort. • Enable independent checks on results. • Disseminate opinions. • Provoke discussion. • Gain wider recognition for work.
-
Why survey the literature? • Discover the state-of-the-art. • Identify gaps in the body of knowledge. • Identify relevant work. • Locate useful expertise. • Keep abreast of developments.
-
The world of literature • Textbooks. • Learned Journals. • Conference proceedings. • World wide web. • Trade papers. • Newspapers.
-
Types of academic publication • Original paper. • Review of a research topic. • Bibliography. • Thesis. • Dissertation. • Technical Report.
-
Presentation of the literature survey : 1. The project context • What related work is being undertaken? • What is the motivation for the work? • How does it help me/science? • Why am I studying this aspect of the problem?
-
Presentation of the literature survey : 2. The area of investigation • What techniques are in use? • What are the findings of other people? • What are the views of other people? • How do they compare with my views? Literature surveys are a critical appraisal rather than a simple list of papers.
-
A literature survey demonstrates: • an awareness of an adequate body of knowledge, and • the ability to apply that knowledge to the project.
-
The End! Bet you’re glad!
Written communication is communication by means of written symbols or sign that is communicated by or to or between people or groups.
In written communication, a message can be transmitted via email, letter, report, memo, etc. The message, in written communication, is influenced by the vocabulary and grammar used, writing style, precision and clarity of the language used.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Written Communication?
- 2 Characteristics of Written Communication
- 2.1 Written or Recorded
- 2.2 Creative Activity
- 2.3 Human Activity
- 2.4 Language
- 2.5 Permanent Record
- 2.6 Legal Evidence
- 2.7 Lengthy Process
- 2.8 Accuracy
- 3 Advantages of Written Communication
- 3.1 Can maintain records
- 3.2 Has legal validity
- 3.3 Is accurate and dependable
- 3.4 Can be well drafted
- 3.5 Can be used to assign responsibility
- 3.6 Allows little chance of misunderstanding
- 3.7 Allows editing and omissions
- 4 Disadvantages of Written Communication
- 4.1 It is a time-taking medium
- 4.2 It uses too many resources
- 4.3 It requires good writing skills
- 5 Purpose of Written Communication
- 5.1 To widen contact scope
- 5.2 Building Goodwill
- 5.3 Documentary Evidence
- 5.4 Lasting Impression
- 5.5 Provide information
- 5.6 Reference and Record
- 5.7 Economic Communication
- 6 Business Communication Notes
- 7 Reference
Written communication is the most common form of communication being used in business. So, it is believed core among business skills. Memos, reports, bulletins, job descriptions, employee manuals, and electronic mail are the types of written communication used for internal communication.
For communicating with the external environment in writing, electronic mail, Internet Websites, letters, proposals, telegrams, faxes, postcards, contracts, advertisements, brochures, and news releases are used.
In the written form, it may require the drafting of letters and circulars, proposals, memos and business reports of varying kinds and includes
- MemoReport
- Office order
- Circulars
- Graphs/Charts
- Staff Newsletter
- Form/Questionnaire
- Letter
- Notice, Agenda, Notes on Agenda
- Minutes of Meetings
- Advertisement
- Customer Newsletter
- Press Release
- Invitation
- Leaflet/Brochure/Handbills
- Manuals
Characteristics of Written Communication
Written communication is a creative activity. It needs creative facts. The creative facts are produced by a human mind. The main characteristics of a written communication are as follows:
- Written or Recorded
- Creative Activity
- Human Activity
- Language
- Permanent Record
- Legal Evidence
- Lengthy Process
- Accuracy

Written or Recorded
Written communication is an effective process of transferring a message. The sender writes the message in the form of a letter, report, chart, diagram, questionnaire and passes to the receiver.
Creative Activity
Written communication is a creative activity. All the creative activities are produced by the human mind.
Human Activity
Human-being can write or explain an idea, opinion and information in written form. Therefore, written communication is a human activity.
Language
Written communication can be expressed in a language. It may be Hindi, English, any code language, chart, figure etc. The selection of the language depends on the convenience of the sender and the receiver.
Permanent Record
Written communication has proof of evidence. It provides a permanent record for a future reference.
Legal Evidence
When the message is transferred through written communication, these are also used as legal evidence.
Lengthy Process
The process of written communication is very lengthy. The message is transferred in this process through several channels. Therefore, it takes more time.
Accuracy
Written messages are generally prepared in a peaceful environment. It is more effective for achieving future goals of an organization. Therefore, it is prepared by the sender with and accuracy.
Advantages of Written Communication
Written communication is one of the most extensively used modes of communication in most organisations. There are different forms of written communication that are primarily used to exchange information related to business operations, such as memos, reports, circulars, notices, manuals, e-mails, etc. Some of the benefits that written communication offers are as follows:
Some of the advantages of written communication are:
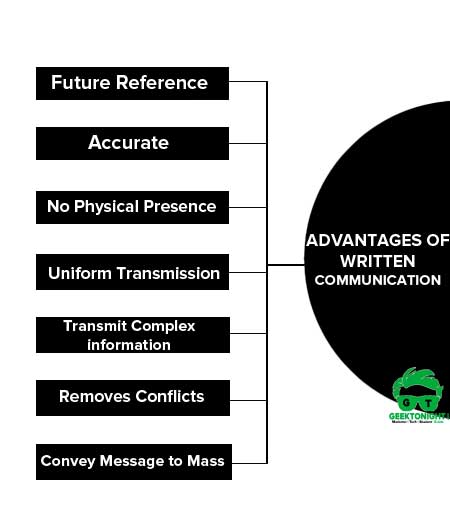
Can maintain records
Most written correspondence can be on record, such as information exchanged with stakeholders, minutes of meetings, mails, etc. Just imagine getting an oral appointment letter. Written documents provide a long-lasting record that can be used for future references.
Has legal validity
Written records provide legal authority, which can be used as proof of any information by organisations for any legal defence. E-mails, for instance, are the most inexpensive and quickest medium of written communication in cases where in-person communication is not possible.
Is accurate and dependable
Written communication is considered more accurate and reliable than oral communication because information exchanged cannot be changed unlike in the case of the latter.
Can be well drafted
Oral words can be spontaneous, unlike written communication which can be edited, modified and carefully articulated offering maximum clarity and accuracy of meaning.
Can be used to assign responsibility
It may not always be possible to communicate the work responsibilities to all employees in person. To take care of such situations, written communication can be used to effectively assign responsibilities.
Allows little chance of misunderstanding
In case the words to be written are carefully chosen and present the meaning precisely, there are very little chances of misunderstanding using written communication.
Allows editing and omissions
Written words can be edited or modified to suit the receiver before the message is sent across to the receivers.
Disadvantages of Written Communication
Some of the disadvantages of written communication are:

It is a time-taking medium
Written communication requires a lot of time. Putting one’s thoughts into words and formulation of the same is, of course, a time-consuming process, as proper structuring is required.
It uses too many resources
A large number of resources are wasted in an organisation on stationery and storage of files and records. Though the use of computers helps save or rather just cut down on some of these expenses, but still written communication costs a lot to organisations and also to the environment as the use of paper means cutting of trees.
It requires good writing skills
Proper grammatical knowledge of a language is required to communicate effectively. Written communication is constrained by grammar and handwriting if the message is not properly typed. Moreover, a poorly drafted message may lead to the loss of business for an organisation.
Purpose of Written Communication
Business letters are not in any way less vital than the blood circulation system in body when we talk and count it with reference to business activities. Needs for sending letter in business is felt for several purposes. Some of such purposes are as under.
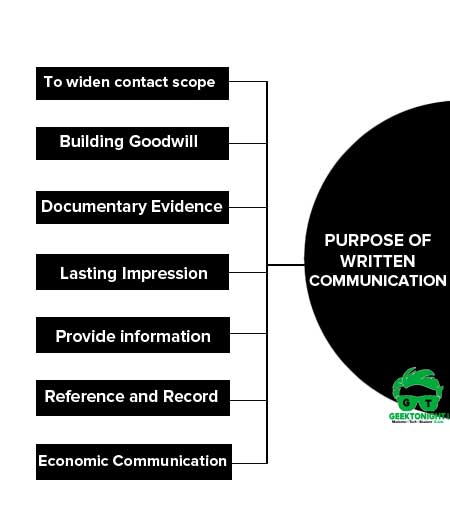
- To widen contact scope
- Building Goodwill
- Documentary Evidence
- Lasting Impression
- Provide information
- Reference and Record
- Economic Communication
To widen contact scope
As already mentioned told, several parties are contacted in business and it is not possible to contact with all parties concerned. Thus, letters are the means that extend the scope of business activities to the desired extent.
Building Goodwill
Letters contribute largely in building goodwill for a business and making friendly relations with concerned parties if these are written in influence manner. These act as an advertisement for building goodwill of the business concerned.
Documentary Evidence
Letters may be filed before a court as written evidence in the form of a business contract. Letters bear the signature of the authorised person. Hence, letters act as evidence in the course of deciding on liabilities.
Lasting Impression
As the letters are retained by the readers, these have a lasting impression on them. These are repeatedly read by readers unless a response is given. They are also remembered by them or make a niche for them in their memory.
Provide information
In business, several parties communicate one another on a number of topics or matters. Business letters with information written on them make such transactions of information very easy. Hence, letters are the most important medium in view of providing information.
Reference and Record
Everyone may agree that it is not possible to keep memory afresh every time in respect of the contracts executed, transaction made and the events taking place in the course of running the business. Letters, however, can easily be used as record for future references. These can use as a reference whenever such need is felt.
Economic Communication
Communication through letters is always economic as no extra cost is incurred in this mode sending information from one place to another. It is cheaper than personal contact with the parties.
Business Communication Notes
(Click on Topic to Read)
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
- Types of Communication
- 7 C of Communication
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- Written Communication
- Soft Skills
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal Communication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- Emotional Intelligence
- Public Speaking
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
Reference
- Business Communication: “ K.K. Sinha, Golgotia Publishing Company.
- Dr K.C. Goyal, Dr Ummed Singh, Dr Kapil Dev, Business Communication.
- Essentials of Business Communication: Rajendra Pal, J.S Korlahalli, Sultan Chand & Sons.
Go On, Share & Help your Friend
Did we miss something in Business Communication Tutorial or You want something More? Come on! Tell us what you think about our post on Written Communication | Business Communication in the comments section and Share this post with your friends.

This kind of communication involves any kind of exchange of information in written form. To put it simply, written language communication is communication by means of written symbols that are communicated by or to, or between people or groups. Thus, written communication is the presentation of ideas or essays that make a clear point, supply details supporting that point, and demonstrate unity and coherence of thought.
[toc]
For example, e-mails, texts, letters, reports, SMS, posts on social media platforms, documents, handbooks, posters, flyers, etc. Written communication requires careful consideration. Writing is a result of long practice and patience in learning. The written word is an indelible record of proceedings in a business environment and therefore needs to be carefully planned.
Definition of Written Communication
These are some simple and understandable definitions of written communication:
Written communication involves any type of massage which makes use of the written word. Written communication is the most important and the most effective for any mode of business communication.
Written communication is the expression of language by means of visible signs. Despite the far wider use of oral communication, modern civilization cannot function without the written form. Business organizations need it to run their systems efficiently and effectively. It should be noted that written communication is not merely oral communication written down. It has its own dynamics. Its importance is mainly in organizing and documenting knowledge.
Written communication is a type of verbal communication. The communication which is performed through various written documents is called written communication. It is a word-based communication that takes place in a written form.
Examples of written communications generally used with clients or other businesses include proposals, letters, advertisements emails, the internet, websites, etc. Written communication within an organization includes circular letters, order letters, inquiry letters, collection letters, etc. All these letters serve important and multidimensional business purposes.
Types of Written Communication
Some important types of Written Communication include:
- Emails
- Proposals
- Reports
- Brochures
Emails
Emails are the most common type of written business communication, according to Startupbizhub, an online reference site. Business professionals use emails to communicate with each other, set up meetings, send documents, confirm appointments, and contact job candidates. Despite their relative casualness, your emails should still come across as professional.
Make sure you address your emails to all intended parties. Leaving just one person out can hinder your email’s effectiveness. Also, list the specific topic of your email in the “Subject” area. Avoid writing long paragraphs in emails. Instead, break your text up with bullet points and shorter paragraphs, according to Forbes online magazine.
Proposals
Proposals are documents that outline upcoming projects. For example, business consultants and advertising agencies submit proposals to companies for projects or special assignments. A marketing manager may submit a proposal to the research and development department to conduct product research.
Proposals are often just one or two pages long. Many companies use specific forms for their proposals. Make sure you clearly identify all the project steps and tasks in your proposal. Include the associated costs of each specific task as well. For example, list the printing, mailing, and postage costs if you are writing up a proposal for a direct mail project.
Reports
Reports are another type of written business communication. Companies use reports to inform employees about various aspects of the business. For example, the finance department will write financial reports to summarize a company’s profit and sales.
Similarly, a marketing research manager may write a report which summarizes the results of a customer phone survey. Write your reports in a structured format. Provide a brief introduction to your report. For example, tell department managers how and when you conducted a customer phone survey.
Include the key objectives you intended for the project. Summarize your findings in the body of your report. Add graphs and charts to clarify more complex concepts. Include an executive summary section in your report that highlights key findings or results. Moreover, always include a cover letter with your report to introduce it to managers or executives.
Brochures
Brochures are literature that features your products and services. Companie uses brochures to sell products or assist sales reps with sales calls. Companies produce brochures in many shapes and sizes. Some brochures are letter size while others are folded in half or thirds. Use color and pictures in your brochures that feature your main products or services. Break up each page of your brochure with plenty of blank space, which makes the brochure more readable.
6 Principles of Written Communication
The following are the six principles of written communication:
- Clarity
- Completeness
- Conciseness
- Consideration
- Courtesy
- Correctness

Clarity
Written communication requires clarity of thought and clarity of expression like using simple words, active construction, avoiding ambiguity and Jargon, using simple sentences, etc.
Completeness
The writer needs to check the completeness of the message. He should verify whether all questions are answered in the message or not.
Conciseness
Conciseness is communicating complete information about the idea in a few words. Concise writing also involves being mindful of word choice. Brevity is very important for effective writing. The writer should include only relevant facts and avoid repetitions.
Consideration
This principle advocates that the writer should consider the reader in his writing. It is always better to emphasize positive and pleasant facts. The writings should reflect the integrity of the writer.
Courtesy
According to this principle, courtesy will be observed through promptness in writing and giving replies, avoidance of imitating expressions, sincere apology for an omission, and generous thanks for a favor.
Correctness
According to this principle, the writer should give correct facts in the message. The message should be sent to the reader at the right time and in the correct style.
Written communication is accurate and serves as a permanent record. One can reach a large number of people through this media simultaneously. You can also fix responsibility for the people through this communication. However, written communication is much more time-consuming and more expensive when compared to oral communication.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Written Communication
These are the followings advantages and disadvantages of written communication:
- Advantages of Written Communication
- Disadvantages of Written Communication
Advantages of Written Communication
There are several advantages of written communication some are given below:
- Suitable for Lengthy Message
- Written Proof
- Clear Message
- Less Expensive Method
- Time-Saving
- Presence of Both Parties Not Necessary
- True and Effective
- Communication in Different Places
- Use as a Reference
- Longevity
- Delegation of Authority
- Effective Communication
- Maintaining Image
- Proper Information
- No Opportunity to Misinterpret
- Controlling Tool
- Easy to Verify

Suitable for Lengthy Message
Suitable for Lengthy Message: The lengthy message can clearly communicated with the help of written communication.
Written Proof
Written Proof: Some documents with regard to some special facts have to be kept for future reference. This is possible only through written communication.
Clear Message
Clear Message: A message may be long or short, it can be made understandable in written communication. There is no fear of anything being left out in such a system.
Less Expensive Method
Less Expensive Method: Messages are to be sent to distant places, if there is no urgency involved, it can be sent at a little expense through this method. But if the message is to be sent to a distant place quickly, this method is not useful.
Time-Saving
Time-Saving: Underwritten communication, there is no open conversation with a big human group. Hence, time is not lost in useless talks.
Presence of Both Parties Not Necessary
Presence of both parties not necessary: In this system, it is not necessary that the receiver should be present before the sender.
True and Effective
True and effective: The written communication is true and hence effective. A sender sends the information after careful consideration because of the written proof it carries with it.
Communication in Different Places
Communication in different places: When messages have to be sent to different places, written communication proves to be useful.
Use as a Reference
Use as a reference: If it is needed, written communication can be used as a future reference.
Longevity
Longevity: Written documents can be preserved for a long time easily. That is why; all the important issues of an organization should be back and white.
Delegation of Authority
Delegation of Authority: Written communication can help the authority delegate the power and authority to the subordinate. It is quite impossible to delegate power without a written document.
Effective Communication
Effective communication: Written communication helps to make communication effective. It is more dependable and effective than those other forms of communication.
Maintaining Image
Maintaining image: Written communication helps to maintain the images of both the person and the organization. It also protects the image of the company or organization.
Proper Information
Proper information: It is a proper and complete communication system. There is no opportunity to include any unnecessary information in a written document.
No Opportunity to Misinterpret
No opportunity to misinterpret: there is an opportunity to misinterpret the information or messages of written communication.
Controlling Tool
Controlling tool: Written communication can help to control the organizational activity. The written document may be used as a tool for controlling.
Easy to Verify
The information and messages that are preserved can be verified easily. If there arises any misunderstanding any party can easily verify the information.
Others: Clear understanding, Legal document, Acceptability, Reduction of risk, Creating confidence, Easy circulation, Wide access or coverage, etc.
Disadvantages of Written Communication
Now let’s clarify the disadvantages of written communication which are given below:
- Unfit for Uneducated Persons
- Lack of Secrecy
- Wastage of Time
- No Quick Information About Feedback
- Expensive
- Red-Tapism
- Lack of Flexibility
- Delay in Response
- Delay in Decision Making
- Complex Words
- Lack of Direct Relation
- Other

Unfit for Uneducated Persons
Unfit for Uneducated Persons: Written communication has no significance for uneducated people. They can only be made to understand orally.
Lack of Secrecy
Lack of secrecy: Because of written proof, nothing can remain secret.
Wastage of Time
Wastage of time: Because of the organizational constraints it is essential to send less important facts in writing, it shall be the waste of time, labor, and money.
No Quick Information About Feedback
No quick information about feedback: Some difficulty is felt when the reactions of the receivers are not known immediately. It also becomes difficult to bring an immediate change in the message.
Expensive
Expensive: Written communication is comparatively expensive. For this communication paper, pen, ink, typewriter, computer and a large number of employees are needed.
Red-Tapism
Red-Tapism: Red-Tapism is one of the most disadvantages of written communication. It means to take time for approval of a project.
Lack of Flexibility
Lack of flexibility: Since writing, documents cannot be changed easily at any time. Lack of flexibility is one of the most important limitations of written communication.
Delay in Response
Delay in response: It takes much time to get a response from the message receiver; prompt response is not possible in the case of written communication but is possible in oral communication.
Delay in Decision Making
Delay in decision-making: Written communication takes much time to communicate with all the parties concerned. So the decision maker cannot take decisions quickly.
Complex Words
Complex words: Sometimes the writer uses complex words in writing a message. It becomes difficult to mean out to the reader. So the objectives of the communication may lose.
Lack of Direct Relation
Lack of direct relation: If there is no direct relation between the writer and the reader, writer communication cannot help to establish a direct relation between them.
Other
Other: Prompt feedback is impossible, Slowness, Bureaucratic attitude, Understanding-problem between boss and subordinates, lack of quick clarification and correction, formality problem, lack of personal intimacy, etc.
Ways to Improve Written Communication
When trying to get your point across to others in writing, here are some ways to improve written communication:
- Vocabulary, Spelling, and Grammar
- Proof-Reading and Editing
- Brevity and Simplicity
- Logical Progression of Ideas
- Authenticity
- Confusing Language
- Poor Sentence Structure
- Information Overload

Vocabulary, Spelling, and Grammar
Vocabulary, spelling, and grammar these things do matter. A written document with a lot of spelling mistakes or grammatical errors loses credibility. It can look as if the writer doesn’t care about the quality of his or her work.
Proof-Reading and Editing
Few pieces of written work are born perfectly formed. Usually, you will need to read over a piece of writing a few times, making changes every time, to obtain a good quality finished product. If you can, it’s often a good idea to go away from a piece of writing for a few hours, days, or even weeks, so that you come back to it again with ‘fresh eyes.
Brevity and Simplicity
Try to get your written points across as simply and concisely as possible. As you gain writing experience and confidence, you can experiment with making your sentences and paragraphs more complex, but if in doubt, do keep it simple.
Logical Progression of Ideas
Most pieces of good writing from the shortest email to the longest thesis follow a very simple rule. This is that your written work should have a clear beginning or introduction, middle or main body, and end or conclusion.
Authenticity
Don’t pass other people’s written work or ideas off as your own – learn how to cite and reference other people’s work appropriately. Work on developing a fluid, personal writing style, and on finding your own voice.
Confusing Language
Confusing language means confusing words that can mislead the reader and cause communication breakdown or barriers between the writer and the reader. Some words are ambiguous, bombastic, vague, sexist, trendy, exaggerated, inflated, and archaic.
Again, we must always remember to write to convey meaning in plain English. It is better to use the familiar word for the far-fetched, the concrete word for the abstract, the single word for the circumlocution, and the short word for the long.
Poor Sentence Structure
Poor sentence structure relates to writing fragments instead of complete sentences and writing sentences that lack unity. Try to keep your sentence(s) short and compact to ensure that they are correct, logical, and easy to read. Long, complicated sentences can be difficult to read and understand. Word order is important for meaning.
Information Overload
Information overload means giving too much information, hence, the reader becomes overwhelmed and confused. This may also cause frustration and cast doubts on the writer’s credibility. Therefore, as a writer, you must decide what sort of information is required in order to produce a clear, concise, and relevant written work.
Read More Related Articles
What is Communication? | Mass Communication
Types of Communication | Principles of Communication
Types of Communication
- Types of Communication
- Verbal Communication
- Non-Verbal Communication
- Written Communication
- Visual Communication
- Feedback Communication
- Mass Communication
- Group Communication
Nonverbal Communication | Verbal Communication
Written Communication | Oral Communication
Business Communication | Organizational Communication
Formal Communication | Informal Communication
Interpersonal Communication | Informal Communication
Downward Communication | Upward Communication
Barriers to Communication | Horizontal or Lateral Communication
Self Development | Effective Communication
Difference Between Oral and Written Communication | Theories of Communication
FAQ Section
What is written communication explained?
This kind of communication involves any kind of exchange of information in written form. To put it simply, written language communication is communication by means of written symbols that are communicated by or to, or between people or groups. Thus, written communication is the presentation of ideas or essays that make a clear point, supply details supporting that point, and demonstrate unity and coherence of thought.
Why do you want to improve your written communication?
Because of these reasons: letters, reports, SMS, posts on social media platforms, documents, handbooks, posters, flyers, etc. written communication requires careful consideration. Writing is a result of long practice and patience in learning. The written word is an indelible record of proceedings in a business environment and therefore needs to be carefully planned.
What is written communication simple words?
Written communication involves any form of message which makes use of the written word. Written communication is the most important and the most effective for any type of business communication.
How can you improve written communication in the workplace?
Following are the ways to improve written communication:
1. Vocabulary, Spelling and Grammar
2. Proof-Reading and Editing
3. Brevity and Simplicity
4. Logical Progression of Ideas
5. Authenticity
6. Confusing Language
7. Poor Sentence Structure
8. Information Overload.
What are the principles of written communication?
These are the six principles of written communication:
1. Clarity
2. Completeness
3. Conciseness
4. Consideration
5. Courtesy
6. Correctness.
What are the advantages of written communication?
Advantages of written communication given below:
1. Suitable for Lengthy Message
2. Written Proof
3. Clear Message
4. Less Expensive Method
5. Time-Saving
6. Presence of Both Parties Not Necessary
7. True and Effective
8. Communication in Different Places
9. Use as a Reference
10. Longevity
11. Delegation of Authority
12. Effective Communication
13. Maintaining Image
14. Proper Information
15. No Opportunity to Misinterpret
16. Controlling Tool
17. Easy to Verify.
What are the disadvantages of written communication?
These are the disadvantages of written communication:
1. Unfit for Uneducated Persons
2. Lack of Secrecy
3. Wastage of Time
4. No Quick Information About Feedback
5. Expensive
6. Red-Tapism
7. Lack of Flexibility
8. Delay in Response
9. Delay in Decision Making
10. Complex Words.
Written communication skills are among the most important skills to learn. These skills are powerful tools that can be used to share information with a large number of people.
Students need written communication skills to communicate with their lecturers and apply for scholarships, internships, jobs, etc. Poor communication skills can cost you a lot, you may lose a scholarship or internship because your application letter was poorly written.
Written communication is one of the most common and effective methods of communication. This type of communication is becoming increasingly important in the digital age.
According to the National Association of Colleges and Employers, 77.5% of employers want a candidate with strong written communication skills.
In this article, you will learn the definition of written communication, examples, importance, limitations, and ways to improve written communication skills.
What are Written Communication Skills
Written communication is a type of communication method that utilizes written words. It involves communicating through written words, either digitally (e.g emails) or on paper.
Written communication skills are those skills required to effectively communicate with written words.
Effective written communication requires the following skills or qualities:
- Sentence construction
- Appropriate use of punctuation
- Knowledge of basic grammar rules
- Appropriate use of tone
- Usage of certain editing tools or software.
Importance of Written Communication
Below is the importance of written communication:
- Creates a permanent record
- Lessen misunderstandings
- Accurate
- Create professional relationships
- Suitable for long-distance communication
- Very easy to distribute.
1. Creates a Permanent Record
Any form of written communication is a permanent record and can serve as a future reference. Written communication documents can be used as evidence in any legal case or whenever it is needed.
2. Lessen Misunderstandings
Written communication is the best way to present a complex matter without any misunderstanding. Effective written communication is easily understood because it is written in simple words.
Also, in case of any misunderstanding, a reader can easily go through it several times till he/she fully understands.
3. Accurate
Written communication has little or no space for errors. Accuracy is guaranteed in written communication because there are multiple chances to correct or edit words. You can easily edit an email, memos, brochures, etc.
4. Create professional relationships
Adequate communication with your clients or customers can foster a professional relationship. Written communication is the most effective way to achieve a professional relationship. Greetings, congratulatory messages, etc. can be sent via email without interrupting the receiver.
5. Suitable for Long Distance Communication
Written communication is a faster way to communicate with people far away from you. For instance, you can easily send messages via WhatsApp regardless of the location.
6. Very Easy to Distribute
Written communication is the best way to distribute information to a large number of people at the same time. For instance, an email can be forwarded to several people at the same time.
Limitations of Written Communication
Although written communication has several advantages, there are still some limitations.
Below are the limitations (disadvantages) of written communication:
-
Late Feedback
Written communication cannot provide instant feedback. The recipient will have to read and understand a message before he/she can reply to the sender.
This type of communication should not be used when you need immediate clarification.
-
Time-consuming
Composing and delivering a written message can take a lot of time. You will have to write, edit, and proofread before you can send most forms of written communication.
-
Expensive
Written communication is expensive because you will have to buy some equipment like ink, paper, printer, computer, etc.
You may also need to employ someone to write or type for you.
-
Meaningless to Illiterate
Written communication is useless if the receiver cannot read or write.
This method of communication requires the ability to read and write. Written communication should not be used when communicating with an illiterate.
Examples of Written Communication in Schools.
Here we will be sharing the most common forms of written communication used in schools.
Note: There are several examples of written communication but below are the most common examples of written communication used in schools.
Below are examples of written communication in schools:
-
Emails
Email is one of the most effective and cheapest means of written communication. Emails can be used for different purposes: communicating with professors and supervisors, sending electronic files, applying for jobs, internships, and scholarships e.t.c
-
Memos
Memos can be used to communicate important information to people within a school. It is an effective way to communicate with school departments.
-
Bulletin
A bulletin is a short official statement used to inform a group of people about a specific matter.
-
Questionnaires
A questionnaire is a set of questions used to get the required information from students, during research or survey.
-
Instructional Materials
Instructional Materials like textbooks, workbooks, handouts, study guides, manuals e.t.c are also examples of written communication. They are any collection of materials that a teacher may use in teaching.
-
Instant Messaging
Instant messaging is a form of written communication in which two or more persons participate in a conversation over their mobile phones or computers. It can be sent via Facebook messenger, Snapchat, WhatsApp, Telegram, WeChat, etc.
-
Website Content
Website Content can be used to educate site visitors about the services a school render.
-
Brochures
Brochures can be used to assist parents to understand how a school operates. It contains information about the school, its staff, and the board of governors.
-
Classroom Webpages
Classroom Webpages can be used for different purposes: posting important updates, uploading assignments, providing access to grades, communicating with parents and students, etc.
-
Newsletters
Newsletters are an effective way of informing students and parents about various school activities, news, events, schedule changes, etc.
-
Press Release
A press release is an official statement given by a company or organization to the media. It can be used by schools to share information that is newsworthy.
Report card comments inform parents about their children’s academic performance.
-
Letters
Letters can be used to send information, complaints, greetings, etc.
-
Postcards
Classroom postcards are a quick and easy way to send short personal messages (e.g welcome back to school message) to your students.
-
Proposals
Proposals can be used to get approval for a specific education project
Tips to Improve your Written Communication Skills
To develop effective written communication skills follow these tips:
- Identify your goal
- Use the right tone
- Avoid the use of jargon
- Stick to the topic
- Use active voice
- Easy to read
- Proofread.
1. Identify Your Goal
Effective written communication must have a purpose. This purpose must be identified and communicated to the recipient in a simple way.
2. Use the Right Tone
The tone you use depends on your target audience and the purpose of writing. Some forms of written communication (like proposals, resumes etc.) requires a formal tone.
3. Avoid the Use of Jargon
In written communication, your choice of words should be simple and easy to understand. Avoid the use of jargon and complex words.
4. Stick to the topic
You must stick to the topic and avoid sharing irrelevant information. This can make it difficult to understand the purpose of the message.
Effective written communication must be concise. So, you need to state your points clearly without including irrelevant information.
5. Use Active Voice
Write most sentences in active voice instead of passive voice. Sentences written in active voice are easier to understand than sentences written in passive voice.
For example, “I fed the dogs” (active voice) is easier to read and understand than “The dogs were fed by me” (passive voice).
6. Easy to Read
Effective written communication must be easy to read. Make use of spacing, short sentences, short paragraphs, bullet points, headings, and subheadings. This will make it easier and less boring to read any form of written communication.
7. Proofread
Carefully check for grammar, spelling, and punctuation mistakes before you share any written communication document.
You can either ask someone to proofread your writing or do it yourself by making use of proofreading software like Grammarly, Paper Rater, ProWriting Aid, Hemingway etc.
In addition, practice writing a variety of documents to improve your written communication skills. You can start by sending emails to your friends and family.
We Also Recommend:
- Top 10 Importance of Writing Essays
- Top 10 Importance of Writing Skills
- MBA Online Student’s Guide
- 2022 GMAT Score Chart: All to Know & Easy Usage Tips
- The 20 Importance of Higher Education: College or University
Conclusion
The digital age has transformed how we communicate with each other. Some years back, we share information via letters, which can take days to be delivered. Now, you can easily share information with just one click.
Modern written communication methods e.g emails, text messages e.t.c are more convenient than older methods of written communication e.g letters.
Beyond high GPA scores, Employers look out for communication skills, especially written communication skills. No doubt, written communication is an essential part of our lives. This is why you have to improve your written communication skills.
We have now come to the end of this article, Do you find this article helpful? Let us know in the Comment Section.
What a wonderfully poor medium it is to communicate with written words. I’m sometimes amazed that we’re able to communicate meaning at all. Here are two good examples of how hard it is to communicate with written words. A few weeks ago I was traveling and decided it was time to schedule another Certified ScrumMaster class. I emailed my assistant, Tonya, and said, «Please book the Hyatt in Denver for July 31-August 2.» A day or two later she emailed back saying, «The hotel is booked.» With that crossed off my mental to-do list I moved on to the next thing.
About two weeks later I’m again on the road and Tonya emails me saying, «Did you want me to find a different hotel in Denver or are you just not going to do that class?» I’m very confused because she’s told me the «hotel is booked.» Since that’s the case why is she asking me about booking a different hotel? We exchange a few more emails until I finally realize that her reply to me («The hotel is booked») did not mean «I’ve finished with that task; the hotel is booked.» It instead meant «The hotel is already booked by someone else; now what should I do?» What’s interesting is to look back over the communication—nothing is wrong with what either of us typed into our emails except that we were each coming out the question from a completely different context.
Here’s a second example of how easy it is to miscommunicate: I’m in London this week teaching some classes for my good friends at Conchango. Since I can’t watch the basketball playoffs as I normally would this time of year I’ve been taking the opportunity to try to learn the rules to cricket. To someone with absolutely no prior exposure to the game it’s quite confusing especially as it seems to go on forever. I mentioned to my class today that I’m trying to figure the game out. One of the participants in the class shared with me the following instructions. These are apparently marketed as «Cricket Rules for Foreigners» throughout the UK:
You have two sides, one out in the field and one in. Each man that’s in the side that’s in goes out, and when he’s out he comes in and the next man goes in until he’s out. When they are all out, the side that’s out comes in and the side thats been in goes out and tries to get those coming in, out. Sometimes you get men still in and not out. When a man goes out to go in, the men who are out try to get him out, and when he is out he goes in and the next man in goes out and goes in. There are two men called umpires who stay all out all the time and they decide when the men who are in are out. When both sides have been in and all the men have been out, and both sides have been out twice after all the men have been in, including those who are not out, that is the end of the game!
These rules are obviously intentionally obtuse. Notice how they are (probably) perfectly correct yet they say nothing about how to really play cricket. What strikes me is how similar these rules are to many requirements documents I’ve seen in the past—they may be accurate and perhaps clear to someone who already knows what is being said but they sure don’t convey any true understanding to the reader.
Did you know that 75% of millennials would rather text than talk on the phone? Studies show that texting and other forms of written communication have become widely popular among smartphone users. Written communication enables you to communicate at your own pace as you can think and take time before writing a message. It’s more effective than verbal communication because it helps recall information with greater efficiency. Writing also helps communicate complex ideas more easily.
Let’s explore the meaning and benefits of effective written communication and see why it’s one of the best forms of self-expression.
Before we set out to define written communication, let’s look at what ‘communication’ means and entails. In a nutshell, communication is the process of exchanging ideas, information or concepts between a sender (who creates and sends the information) and the receiver (who receives and interprets the information). This exchange takes place through a medium or a channel— it could be verbal, nonverbal, visual and written.
Written communication is the process of exchanging messages (information, thoughts or concepts) between a sender and receiver(s) by making use of the written word. Effective written communication is important for businesses as it helps to bring everybody on the same page regarding overall goals and objectives. In this day and age, everybody is expected to navigate emails, bulletins, reports, circulars and office memos.
Here are a few examples of written communication that will highlight its importance in professional settings:
-
Imagine that a new client is interested in collaborating with your organization. You are likely to give them a snapshot of the history and success of your organization and how it has overcome challenges. A business deck or brochure is an effective way of communicating important as well as attractive details about the organization. Not only will it help you provide a summary, but also persuade your client to work with you.
-
Organizations often use business memorandums (memos) for internal communication. Although a majority of memos are now communicated via emails, it’s an effective tool to give instructions or remind people of events, actions or observance. If you want to broadcast a message to a large number of people, memos are the way to go.
What Are The Types Of Written Communication?
Different types of written communication are used in different contexts and needs.
-
Transactional
When you communicate something only to get a response from your receiver, it is known as transactional communication. The online medium is the most effective way to send your message quickly, and emails or texting platforms work wonderfully. Since you expect a response, you need to be careful about the way you frame your message. Be mindful of the tone, language and style. Some examples of transactional communication are asking for a favor, scheduling a meeting or requesting a quick clarification.
-
Informational
When you communicate something for the benefit of the reader or to inform them about something, the message is known as informational communication. The onus is on you to deliver the message and the receiver doesn’t have any role to play, except for raising doubts or asking for clarifications, if any. You need to communicate clearly, avoid complex terms and be direct so that your readers can understand the message easily. Memos are excellent examples of informational communication. They are a quick and efficient form of internal communication.
-
Instructional
When your communication is meant to instruct or direct someone to do a specific task, it’s called instructional communication. These messages should be detailed, giving the reader a fair idea about the topic. It should be easy to follow and should clearly instruct the reader what’s expected of them. The most crucial aspect of instructional communication is the format. Using bullet points to lay down the instructions step by step can help. Using smaller paragraphs or short sentences are a powerful way to help your reader understand your instructions.
What Are Written Communication Skills?
You have probably come across the phrase “we require excellent written communication skills” in several job descriptions and advertisements. Employers value written communication skills because it’s instrumental in driving professional relationships, brand image, and business goals. Written communication skills refer to the ability to effectively get your point across through the written word. Anyone can develop these skills with adequate practice and attention to detail. Here are a few examples of written communication tips that can help you develop good written communication skills and enhance the quality of your business writing:
-
Use active voice so that readers follow your writing at a quicker pace
-
Use the appropriate tone, also known as the voice, which will indicate the degree of formality or friendliness
-
Use the correct grammar and punctuation to ensure that your point is sent across the way you intend it to; poor grammar reflects badly on you as well as the organization
-
Be precise; it helps you to not divulge too much or too little information when communicating your main agenda
-
Keep it simple; it will prevent you from confusing your readers
Written communication skills are essential for every stage of career development. Whether you are applying for a new job or building new professional networks, you need to showcase your writing skills at every stage. For example, you need to learn how to be precise when building your resume so that your strengths and accomplishments are highlighted. Even during presentations, you can’t dump all your data on the slides and expect the audience to follow everything. All your written communication should be easy to read and should contain appropriate terms that get your message across.
The Five Cs of Written Communication
In some ways, written communication is more important than verbal communication. It helps you record information and refer to it in the future. It creates accountability and establishes a powerful channel to engage your audience. Effective written communication depends on various factors. You can remember them through these five Cs.
-
Connection
It is the way you connect with your readers or audience and engage them through written communication.
-
Clarity
You should have clarity of thought while engaging in written communication—it shouldn’t confuse your reader.
-
Cause
Before you write something down, ask yourself what it is that you want to convey. Your goal or purpose should be clear to you as well as your reader. If there are any actionable items, they should also be laid out clearly.
-
Conciseness
Written communication is effective when it is direct and to the point. You need to be clear and put forward your points succinctly.
-
Correctness
Always use appropriate grammar, inoffensive language and the proper tone while communicating. Always proofread what you have written.
How To Write Proficiently
Now that you know the importance of written communication in business, let’s look at how you can improve your approach. Here are some questions that you need to ask yourself to write and communicate proficiently:
-
What Is My Goal?
Having an end-goal in mind helps you focus on the things you want to communicate. For example, if you want someone to take action after reading your email, you need to communicate that objective clearly. Often, emails begin with the main purpose or the big idea so that the reader knows exactly what the communication is about. Irrespective of what format you use, organize your message so that your main idea is communicated even if the reader simply skims through the message.
-
Is My Message Clear?
After you have identified your purpose and written your first draft, you should check for a few things:
-
Whether your message contains unnecessary details, and if extra words or sentences can be removed
-
Whether the message is direct and leaves no room for misinterpretation, and if there are words that can be replaced with more accessible ones
A useful trick to organize your thoughts is to use an outline. Organize information in a logical order, ensuring that you have covered all the major points. This is especially helpful in communicating large chunks of information. For example, you can summarize complicated business reports by outlining the introduction, body and conclusion.
-
How Do I Maintain Professionalism?
Whether it’s an email to a client or a close work-friend, it’s safe to assume that all written communication will be shared with others or forwarded. Before hitting ‘send’, check whether the content is free of inappropriate and insensitive information. What you think is a harmless joke can hurt someone’s sentiments.
Written communication in business is tricky. Sometimes, we may come off as condescending even if we didn’t intend to. We must pay close attention to our tone, style and language and keep our messages respectful. Proofreading and editing are good ways to ensure that the information has been double-checked.
Master The Art!
To write clearly, concisely and compellingly is an art. But anybody can learn how to master the art of effective written communication! Harappa Education’s tried-and-tested methods will teach you how to improve your business communication in ways that everyone will sit up and take notice. The Writing Proficiently course will help you structure your thoughts better and deliver your ideas with precision. The GRT (Goal, Recipient and Tone) Framework will guide you in determining your readers and purpose. The PREP (Point, Reason, Example and Point) Model will help you write with clarity and conciseness. Your words will not only convince but also impress others!
Explore Harappa Diaries to learn more about topics & skills related to the COMMUNICATE Habit such as Writing Skills, Report Writing, How to Take Effective Meeting Minutes, What is a Memo & How to Write a Follow-Up Email to polish your written communication skills.
Because you, like most people, write every day, to some extent, it’s not always easy to realize that you need to improve your written communication skills. Effective written communication is a skill that is learned over time, and one that requires you to organize your thoughts effectively in order to convey your message properly.
If you’re looking to improve your writing skills, this blog post is for you. In this article, we’re going to cover why written communication is a common challenge along with a wide range of best practices so that whether you’re sending an email or writing a formal proposal, you feel confident communicating effectively, every single time.
- Why is written communication a challenge?
- Best practices to improve your writing
Why is written communication a common challenge?
Written communication is a common issue, with many common mistakes, no matter which industry you’re working in. The reason why business writing is especially challenging is because unlike when we speak in person, there’s no such thing as non-verbal cues, tone of voice, or the ability to clarify what you meant right away. Unlike dialogue, a written word only communicates its literal meaning. This means that when you write, you need to really think about if your message is appropriate, has the right tone, and delivers your message effectively. Moreover, sometimes the quality of written communication at work can be a challenge because of time restraints. Often, we’re in a rush and shoot off an email without reading it over or thinking twice. While it seems like a good idea at the time, this is not an effective way to write.
8 best practices to improve written communication
- Think about the purpose of your message
- Put yourself in your reader’s shoes
- Keep it simple
- Keep a place to jot down thoughts and ideas
- Write and read often
- Edit fiercely and read the message out loud
- Ask for help
- Constructive criticism as growth
1 Think about the purpose of your message
Firstly, the message that you’re writing needs to be written with a purpose in mind. What is the message that you’re trying to convey? What is the most effective way that you can convey it? In order to answer these questions, it’s important that you organize your thoughts beforehand and think about the audience that will be receiving the message. The purpose of the communication should be central to the message, clear and obvious. Start with the main goal or purpose of the message so that you can then create an appropriate introduction and conclusion to the message, leaving the most important part in the center.
2 Put yourself in your reader’s shoes
It’s really important to put yourself in your reader’s shoes. Here, think about what kind of background information they have on the topic, as they may need some additional information to paint the picture properly. By putting yourself in the reader’s shoes, you should also think about what kind of audience you are working with, so that you can use the appropriate tone and formalities, where necessary. Reading your writing and pretending that you are the reader will help you edit your message so that it is easier to read and better understood.
3 Keep it simple
A lot of people believe that writing with fancy words, in poetically written sentences makes their message seem more intelligent. Unfortunately, that’s not the case. Disguising a simple message with a ton of jargon is really ineffective because it takes away from the key message that you’re trying to deliver. This point also starts with thinking about the purpose of the message and then attempting to write it in as few words as possible. A tactic for keeping your messages simple is beginning with bullet points or key points. From there, think about which points are absolutely necessary for your message to be successful and delete the rest. Then, you can start making those bullet points into concise sentences.
4 Keep a place to jot down thoughts and ideas
It’s a great idea to keep a place where you can jot down any thoughts and ideas that you have as you go about your workday. This way, when the time comes to write something, you can go through your notes to see if you’ve written down anything that relates to the topic and purpose of the message. This is going to add value to the message because it adds more context and more background information. Knowing that you can pull from your notes is going to improve your writing skills as well as your confidence in your writing abilities. Don’t forget to take some time to actually organize your notes once in a while so that you can remember what’s where.
Pro tip
Use a meeting management tool like Fellow as a digital notepad that you can use to seamlessly jot down ideas that pop into your head throughout the day!
5 Write and read often
Reading and writing to improve your writing skills is simply practicing the craft. Like any other skill that you’d like to acquire or improve, it’s important that you practice your writing and find ways of doing this that resonate and feel good for you. This includes every
day practices, such as taking notes at every meeting that you attend, keeping a personal journal or a written agenda, reading for leisure and also reading blog posts or articles, which can help in enriching your professional knowledge. This practice is going to help you start writing with more ease.
6 Edit fiercely and read the message out loud
There’s no such thing as editing too much when it comes to writing effectively and communicating to be impactful. Start with your rough notes or bullet points, then take some time to organize your thoughts. After you’ve written your message, edit your piece of writing for readability, tone, grammar, punctuality and fluidity. It’s important to ensure that the purpose of the message is crystal clear. Once you’re happy with the content of your communication, read through and edit at least another three or four times. Once you think you’ve got yourself a final draft, don’t forget to read your message out loud, so that you get a sense of how the message will read to others.
7 Ask for help
If you feel like your writing could use some improvement, don’t be afraid to ask for some help. Like anything else that you’re trying to improve, written communication skills take both time and effort to develop. Don’t be discouraged, don’t be embarrassed, and definitely don’t despair because as you continue to practice your reading and writing you’ll be sure to notice that written communication becomes easier and more enjoyable for you. Like any other skill at work, your manager will be more than willing to guide you in improving your writing. A great way to start is by asking a colleague or a manager to proofread your messages- especially the ones that hold a little more importance! It’s very possible that down the line, a colleague may ask you to help them in improving their writing- It all comes full circle!
8 See constructive criticism as an opportunity to grow
If you’re receiving constructive feedback about your writing, it doesn’t mean that you’re a bad writer and it definitely doesn’t mean that you’re bad at your job. Try not to take it too personally! Any constructive criticism or feedback you receive is only meant to help you and to contribute to your learning and professional growth. Take the feedback as an opportunity to learn and try to really implement the comments that you receive, to see if it can make a difference. Ultimately, this feedback is going to make your job easier and more enjoyable for you.
Parting advice
If you want to improve your written communication skills, there are many ways to do so. Try a few of these best practices to see which ones are the most effective for you. As you continue to practice, you’ll develop more confidence and a unique writing style. Effective written communication takes both time and effort, as it’s a skill that is learned and developed over time. As you continue to write every day and apply some of these best practices, you’ll notice that writing will not only become much easier for you, but it will also become much more enjoyable!