MS Excel columns have a pattern like A, B, C, …, Z, AA, AB, AC, …., AZ, BA, BB, … ZZ, AAA, AAB ….. etc. In other words, column 1 is named “A”, column 2 as “B”, and column 27 as “AA”.
Given a column number, find its corresponding Excel column name. The following are more examples.
Input Output 26 Z 51 AY 52 AZ 80 CB 676 YZ 702 ZZ 705 AAC
Thanks to Mrigank Dembla for suggesting the below solution in a comment.
Suppose we have a number n, let’s say 28. so corresponding to it we need to print the column name. We need to take the remainder with 26.
If the remainder with 26 comes out to be 0 (meaning 26, 52, and so on) then we put ‘Z’ in the output string and new n becomes n/26 -1 because here we are considering 26 to be ‘Z’ while in actuality it’s 25th with respect to ‘A’.
Similarly, if the remainder comes out to be non-zero. (like 1, 2, 3, and so on) then we need to just insert the char accordingly in the string and do n = n/26.
Finally, we reverse the string and print.
Example:
n = 700
The remainder (n%26) is 24. So we put ‘X’ in the output string and n becomes n/26 which is 26.
Remainder (26%26) is 0. So we put ‘Z’ in the output string and n becomes n/26 -1 which is 0.
Following is the implementation of the above approach.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define MAX 50
using namespace std;
void printString(int n)
{
char str[MAX];
int i = 0;
while (n > 0) {
int rem = n % 26;
if (rem == 0) {
str[i++] = 'Z';
n = (n / 26) - 1;
}
else
{
str[i++] = (rem - 1) + 'A';
n = n / 26;
}
}
str[i] = '';
reverse(str, str + strlen(str));
cout << str << endl;
return;
}
int main()
{
printString(26);
printString(51);
printString(52);
printString(80);
printString(676);
printString(702);
printString(705);
return 0;
}
Java
public class ExcelColumnTitle {
private static void printString(int columnNumber)
{
StringBuilder columnName = new StringBuilder();
while (columnNumber > 0) {
int rem = columnNumber % 26;
if (rem == 0) {
columnName.append("Z");
columnNumber = (columnNumber / 26) - 1;
}
else
{
columnName.append((char)((rem - 1) + 'A'));
columnNumber = columnNumber / 26;
}
}
System.out.println(columnName.reverse());
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
printString(26);
printString(51);
printString(52);
printString(80);
printString(676);
printString(702);
printString(705);
}
}
Python
MAX = 50
def printString(n):
string = [""] * MAX
i = 0
while n > 0:
rem = n % 26
if rem == 0:
string[i] = 'Z'
i += 1
n = (n / 26) - 1
else:
string[i] = chr((rem - 1) + ord('A'))
i += 1
n = n / 26
string[i] = ''
string = string[::-1]
print "".join(string)
printString(26)
printString(51)
printString(52)
printString(80)
printString(676)
printString(702)
printString(705)
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static String reverse(String input)
{
char[] reversedString = input.ToCharArray();
Array.Reverse(reversedString);
return new String(reversedString);
}
private static void printString(int columnNumber)
{
String columnName = "";
while (columnNumber > 0)
{
int rem = columnNumber % 26;
if (rem == 0)
{
columnName += "Z";
columnNumber = (columnNumber / 26) - 1;
}
else
{
columnName += (char)((rem - 1) + 'A');
columnNumber = columnNumber / 26;
}
}
columnName = reverse(columnName);
Console.WriteLine(columnName.ToString());
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
printString(26);
printString(51);
printString(52);
printString(80);
printString(676);
printString(702);
printString(705);
}
}
Javascript
<script>
function printString(columnNumber)
{
let columnName = [];
while (columnNumber > 0) {
let rem = columnNumber % 26;
if (rem == 0) {
columnName.push("Z");
columnNumber = Math.floor(columnNumber / 26) - 1;
}
else
{
columnName.push(String.fromCharCode((rem - 1) + 'A'.charCodeAt(0)));
columnNumber = Math.floor(columnNumber / 26);
}
}
document.write(columnName.reverse().join("")+"<br>");
}
printString(26);
printString(51);
printString(52);
printString(80);
printString(676);
printString(702);
printString(705);
</script>
Output
Z AY AZ CB YZ ZZ AAC
Time Complexity: O(log26n), as we are using a loop and in each traversal, we decrement by floor division of 26.
Auxiliary Space: O(50), as we are using extra space for storing the result.
Method 2
The problem is similar to converting a decimal number to its binary representation but instead of a binary base system where we have two digits only 0 and 1, here we have 26 characters from A-Z.
So, we are dealing with base 26 instead of base binary.
That’s not where the fun ends, we don’t have zero in this number system, as A represents 1, B represents 2 and so on Z represents 26.
To make the problem easily understandable, we approach the problem in two steps:
- Convert the number to base 26 representation, considering we have 0 also in the system.
- Change the representation to the one without having 0 in its system.
HOW? Here is an example
Step 1:
Consider we have number 676, How to get its representation in the base 26 system? In the same way, we do for a binary system, Instead of division and remainder by 2, we do division and remainder by 26.
Base 26 representation of 676 is : 100
Step2
But Hey, we can’t have zero in our representation. Right? Because it’s not part of our number system. How do we get rid of zero? Well it’s simple, but before doing that let’s remind one simple math trick:
Subtraction: 5000 - 9, How do you subtract 9 from 0 ? You borrow from next significant bit, right.
- In a decimal number system to deal with zero, we borrow 10 and subtract 1 from the next significant.
- In the Base 26 Number System to deal with zero, we borrow 26 and subtract 1 from the next significant bit.
So Convert 10026 to a number system that does not have ‘0’, we get (25 26)26
Symbolic representation of the same is: YZ
Here is the implementation of the same:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void printString(int n)
{
int arr[10000];
int i = 0;
while (n) {
arr[i] = n % 26;
n = n / 26;
i++;
}
for (int j = 0; j < i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] <= 0) {
arr[j] += 26;
arr[j + 1] = arr[j + 1] - 1;
}
}
for (int j = i; j >= 0; j--) {
if (arr[j] > 0)
cout << char('A' + arr[j] - 1);
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
printString(26);
printString(51);
printString(52);
printString(80);
printString(676);
printString(702);
printString(705);
return 0;
}
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static void printString(int n)
{
int []arr = new int[10000];
int i = 0;
while (n > 0)
{
arr[i] = n % 26;
n = n / 26;
i++;
}
for(int j = 0; j < i - 1; j++)
{
if (arr[j] <= 0)
{
arr[j] += 26;
arr[j + 1] = arr[j + 1] - 1;
}
}
for(int j = i; j >= 0; j--)
{
if (arr[j] > 0)
System.out.print(
(char)('A' + arr[j] - 1));
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
printString(26);
printString(51);
printString(52);
printString(80);
printString(676);
printString(702);
printString(705);
}
}
Python3
def printString(n):
arr = [0] * 10000
i = 0
while (n > 0):
arr[i] = n % 26
n = int(n // 26)
i += 1
for j in range(0, i - 1):
if (arr[j] <= 0):
arr[j] += 26
arr[j + 1] = arr[j + 1] - 1
for j in range(i, -1, -1):
if (arr[j] > 0):
print(chr(ord('A') +
(arr[j] - 1)), end = "");
print();
if __name__ == '__main__':
printString(26);
printString(51);
printString(52);
printString(80);
printString(676);
printString(702);
printString(705);
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static void printString(int n)
{
int []arr = new int[10000];
int i = 0;
while (n > 0)
{
arr[i] = n % 26;
n = n / 26;
i++;
}
for(int j = 0; j < i - 1; j++)
{
if (arr[j] <= 0)
{
arr[j] += 26;
arr[j + 1] = arr[j + 1] - 1;
}
}
for(int j = i; j >= 0; j--)
{
if (arr[j] > 0)
Console.Write((char)('A' +
arr[j] - 1));
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
printString(26);
printString(51);
printString(52);
printString(80);
printString(676);
printString(702);
printString(705);
}
}
Javascript
<script>
function printString(n){
let arr = [];
let i = 0;
while (n) {
arr[i] = n % 26;
n = Math.floor(n / 26);
i++;
}
for (let j = 0; j < i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] <= 0) {
arr[j] += 26;
arr[j + 1] = arr[j + 1] - 1;
}
}
let ans = '';
for (let j = i; j >= 0; j--) {
if (arr[j] > 0)
ans += String.fromCharCode(65 + arr[j] - 1);
}
document.write(ans + "<br>");
}
printString(26);
printString(51);
printString(52);
printString(80);
printString(676);
printString(702);
printString(705);
</script>
Output
Z AY AZ CB YZ ZZ AAC
Time Complexity: O(log26n), as we are using a loop and in each traversal, we decrement by floor division of 26.
Auxiliary Space: O(10000), as we are using extra space for the array.
Method 3:
We can use a recursive function which definitely reduces the time and increase the efficiency:
Alphabets are in sequential order like: ‘ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ’. You have experienced while using excel when you see columns and rows numbering are done in Alphabetical ways.
Here’s How I purposefully think about the logic of how it is arranged.
(In Mathematical terms, [a , b ] means from ‘a’ to ‘b’).
[1,26] = [A,Z] (Understand by ‘1’ stands for ‘A’ and ’26” stands for “Z”). For [27,52] ,it will be like [AA,AZ], For [57,78] it will be [BA,BZ]
Logic is to append an Alphabet sequentially whenever it ends up numbering at 26.
For example, if the number is ’27’ which is greater than ’26’, then we simply need to divide by 26, and we get the remainder as 1, We see “1” as “A” and can be recursively done.
we will be using python for this.
Algorithm is:
1. Take an array and Sort the letters from A to Z . (You can also use the import string and string function to get “A to Z” in uppercase.)
2. If the number is less than or equal to ’26’, simply get the letter from the array and print it.
3. If it is greater than 26, use the Quotient Remainder rule, if the remainder is zero, there are 2 possible ways, if the quotient is “1”, simply hash out the letter from the index [r-1]( ‘r’ is remainder), else call out the function from the num =(q-1) and append at the front to the letter indexing [r-1].
4. If the remainder is not equal to “0”, call the function for the num = (q) and append at the front to the letter indexing [r-1].
The code concerned with this is:
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
string alpha = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
string num_hash(int num){
if(num < 26){
string res = "";
res += alpha[num-1];
return res;
}
else{
int q = (num / 26);
int r = num % 26;
string res = "";
if(r == 0){
if(q == 1){
res.append(1,alpha[(26 + r-1)%26]);
}
else{
res = num_hash(q-1);
res.append(1,alpha[(26 + r-1)%26]);
}
}
else{
res = num_hash(q);
res.append(1,alpha[(26 + r-1)%26]);
}
return res;
}
}
int main () {
cout<< num_hash(26) << endl;
cout<< num_hash(51) << endl;
cout<< num_hash(52) << endl;
cout<< num_hash(80) << endl;
cout<< num_hash(676) << endl;
cout<< num_hash(702) << endl;
cout<< num_hash(705) << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
static String alpha = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
static String num_hash(int num){
if(num < 26)
return Character.toString(alpha.charAt(num-1));
else{
int q = Math.floorDiv(num, 26);
int r = num % 26;
if(r == 0){
if(q == 1){
return Character.toString(alpha.charAt((26 + r-1)%26));
}
else
return num_hash(q-1) + alpha.charAt((26 + r-1)%26);
}
else
return num_hash(q) + alpha.charAt((26 + r-1)%26);
}
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
System.out.println(num_hash(26));
System.out.println(num_hash(51));
System.out.println(num_hash(52));
System.out.println(num_hash(80));
System.out.println(num_hash(676));
System.out.println(num_hash(702));
System.out.println(num_hash(705));
}
}
Python3
alpha = 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'
def num_hash(num):
if num < 26:
return alpha[num-1]
else:
q, r = num//26, num % 26
if r == 0:
if q == 1:
return alpha[r-1]
else:
return num_hash(q-1) + alpha[r-1]
else:
return num_hash(q) + alpha[r-1]
print(num_hash(26))
print(num_hash(51))
print(num_hash(52))
print(num_hash(80))
print(num_hash(676))
print(num_hash(702))
print(num_hash(705))
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static string alpha = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
static string num_hash(int num){
if(num < 26)
return Char.ToString(alpha[num-1]);
else{
int q = num/26;
int r = num % 26;
if(r == 0){
if(q == 1){
return Char.ToString(alpha[(26 + r-1)%26]);
}
else
return num_hash(q-1) + alpha[(26 + r-1)%26];
}
else
return num_hash(q) + alpha[(26 + r-1)%26];
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args) {
Console.WriteLine(num_hash(26));
Console.WriteLine(num_hash(51));
Console.WriteLine(num_hash(52));
Console.WriteLine(num_hash(80));
Console.WriteLine(num_hash(676));
Console.WriteLine(num_hash(702));
Console.WriteLine(num_hash(705));
}
}
Javascript
<script>
let alpha = 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'
function num_hash(num)
{
if(num < 26)
return alpha[num-1]
else{
let q = Math.floor(num/26),r = num % 26
if(r == 0){
if(q == 1)
return alpha[(26 + r-1)]
else
return num_hash(q-1) + alpha[(26 + r-1)]
}
else
return num_hash(q) + alpha[r-1]
}
}
document.write(num_hash(26),"</br>")
document.write(num_hash(51),"</br>")
document.write(num_hash(52),"</br>")
document.write(num_hash(80),"</br>")
document.write(num_hash(676),"</br>")
document.write(num_hash(702),"</br>")
document.write(num_hash(705),"</br>")
</script>
Output
Z AY AZ CB YZ ZZ AAC
Time Complexity: O(log26n), as we are using recursion and in each recursive call, we decrement by floor division of 26.
Auxiliary Space: O(1), as we are not using any extra space.
Related Article :
Find the Excel column number from the column title
This article is contributed by Kartik. Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or if you want to share more information about the topic discussed above.
I have several named columns on a sheet. I want to send the column number to a function that will return the column name.
For example, if column 1 is named «apple», I want to pass the column number 1 to a function that returns the column name «apple». My attempt:
Function getColName(colNumber As Integer) As String
'return column name when passed column number
getColName = Cells(1, colNumber).Column.Name
End Function
How can I get this code to work?
asked Feb 11, 2016 at 21:56
7
ColumnNumber = i 'where i need to be a integer number > 0 and <= 16,384
ColumnName = cells(1,i).Address(False, False)
The parameters inside Adress() are related if the rows and columns references are going to be absolute or relatives. In this case above they’ll be relatives.
And it’s over. Simple like that.
answered Jan 14, 2022 at 13:40
Sub GetColumnNameFromRange()
Dim Colname As String
For Each cell In Selection.Cells
If cell.EntireColumn.Hidden = False Then
Colname = Mid(cell.Address, 2, Len(cell.Address) - (Len(cell.Row) + 2))
MsgBox Colname
End If
Next cell
End Sub
Adrian Mole
49.1k147 gold badges50 silver badges78 bronze badges
answered Sep 4, 2021 at 10:38
1
Dim ColAdr as String, ColNo as Long, ColName as String
Function ColName (ColNo as Long)
ColAdr = ThisWorkbook.Sheets("Sheet1").Cells(1, ColNo).Address(RowAbsolute:=True, ColumnAbsolute:=False)
ColName = Left(ColAdr, InStr(1, ColAdr, "$") - 1)
End function
answered Oct 5, 2021 at 23:00
1
If you need the column letter(s) from the index,
here’s a function I’ve written for that:
Function colNameOf(ByVal colindex As Long) As String
Dim overAlphabetic, charId As Long
charId = colindex Mod 26
colindex = colindex - charId
overAlphabetic = colindex / 26
If charId = 0 Then
charId = 26
overAlphabetic = overAlphabetic - 1
End If
Dim overAlphStr As String
overAlphStr = ""
If overAlphabetic > 0 Then
overAlphStr = colNameOf(overAlphabetic)
End If
Dim lastChar
lastChar = ChrW(charId + 64)
colNameOf = overAlphStr & lastChar
End Function
Note, that there is yet no error handling for values smaller than 1. In that case the function just returns any nonsense. DIY…
answered Aug 13, 2020 at 10:10
1
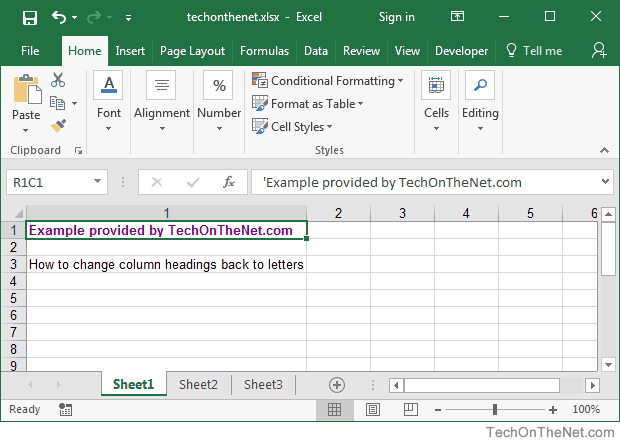
This Excel tutorial explains how to change column headings from numbers (1, 2, 3, 4) back to letters (A, B, C, D) in Excel 2016 (with screenshots and step-by-step instructions).
Question: In Microsoft Excel 2016, my Excel spreadsheet has numbers for both rows and columns. How do I change the column headings back to letters such as A, B, C, D?
Answer: Traditionally, column headings are represented by letters such as A, B, C, D. If your spreadsheet shows the columns as numbers, you can change the headings back to letters with a few easy steps.
In the example below, the column headings are numbered 1, 2, 3, 4 instead of the traditional A, B, C, D values that you normally see in Excel. When the column headings are numeric values, R1C1 reference style is being displayed in the spreadsheet.
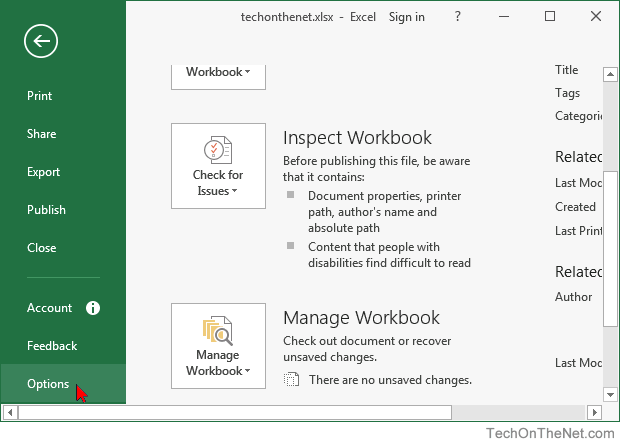
To change the column headings to letters, select the File tab in the toolbar at the top of the screen and then click on Options at the bottom of the menu.
When the Excel Options window appears, click on the Formulas option on the left. Then uncheck the option called «R1C1 reference style» and click on the OK button.
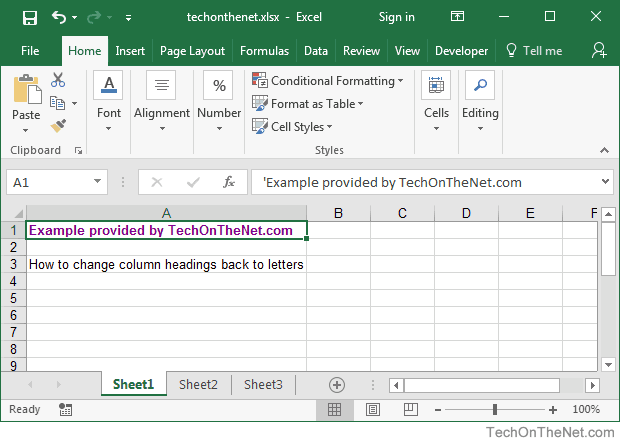
Now when you return to your spreadsheet, the column headings should be letters (A, B, C, D) instead of numbers (1, 2, 3, 4).
- from random import randint.
- # Function to convert a given number to an Excel column.
- def getColumnName(n):
- # initialize output string as empty.
- result = “”
- while n > 0:
- # find the index of the next letter and concatenate the letter.
- # to the solution.
How do I number a column in Excel?
Show column number
- Click File tab > Options.
- In the Excel Options dialog box, select Formulas and check R1C1 reference style.
- Click OK.
What is the column name for 28 column in Excel sheet?
Excel Columns AA-AZ
| Column Letter | Column Number |
|---|---|
| AA | 27 |
| AB | 28 |
| AC | 29 |
| AD | 30 |
What is column formula in Excel?
The COLUMN function returns the column number of the given cell reference. For example, the formula =COLUMN(D10) returns 4, because column D is the fourth column.
How do you create a list of columns in Excel?
You create a list in much the same way you create a worksheet. You enter information into a list by entering data into cells….Method
- In the first cell of the first row of the list, enter a column label.
- Move one cell to the right.
- Enter the second column label.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 until finished.
What is column name in Excel?
In Microsoft Excel, the column headers are named A, B, C, and so on by default. Some users want to change the names of the column headers to something more meaningful. Unfortunately, Excel does not allow the header names to be changed.
How do I make a column header row value in Excel?
With a cell in your table selected, click on the “Format as Table” option in the HOME menu. When the “Format As Table” dialog comes up, select the “My table has headers” checkbox and click the OK button. Select the first row; which should be your header row.
How do you add a header to a formula in Excel?
Click in your table, select Design under Table Tools on the ribbon, and then uncheck “Header Row”. That should allow you to enter a formula in the cell above your table data.
How do I sort data in an Excel chart?
Hover over the top edge of a chart until you see sort by in the upper-left corner, then the name of a field, and then either asc or desc. Click the field name to sort on a different value. Click asc or desc to sort in the opposite direction. Chart sorted descending on the CountryRegion category value by default.
How do you reverse the order of a bar graph?
Right-click and select the option on very bottom of the pop-up menu called Format Axis. Then, on the Format Axis window, check the box for Categories in Reverse Order. That’s a jargony name with a straightforward purpose. It just re-sorts your bar chart in the opposite order of your table.
How do you reverse data in a bar graph?
Tip: In bar chart, reserve the x axis with righting click the x axis and selecting the Format Axis from context menu, then checking the Values in reverse order in the Format Axis dialog box. 3. Close the dialog, now the y axis order is reversed.
How do you mirror a graph on Excel?
On the Insert tab of the ribbon, in the Charts group, click on the Insert Bar Chart button and in the opened menu, click on the second option, which is Stacked Bar, among the 2-D Bar charts. This inserts a mirror bar chart into the worksheet. 3. Move the vertical axis labels to the left of the chart.
Why is my Excel backwards?
This happens because a setting in the Excel options menu called “Show sheet right to left” has been turned on. …

Convert an Excel column number to a column name or letter: C# and VB.NET examples
Posted on Wednesday, November 13th, 2013 at 8:46 am by .
Excel worksheet size has increased dramatically from Excel 2000 to Excel 2007. In fact, the number of rows an Excel 2013 worksheet can support has increased 16 times and the number of columns 64 times more than the number Excel 2000 could handle. Below is a table displaying the number of columns and rows the different versions of Excel can contain:
| Microsoft Excel version | Number of worksheet rows | Number of worksheet columns |
| Excel 2013 | 1 048 576 | 16 384 |
| Excel 2010 | 1 048 576 | 16 384 |
| Excel 2007 | 1 048 576 | 16 384 |
| Excel 2003 | 65 536 | 256 |
| Excel 2000 | 65 536 | 256 |
- Getting the column letter by column number
- Getting the column index by column name
Getting the column letter by column index
There are a lot of examples floating around on the internet on how to convert Excel column numbers to alphabetical characters. There are a few ways to get the column letter, using either vanilla C# or VB.NET, Excel formulas or the Excel object model. Let’s take a look at some of the solutions.
Using C# or VB.NET
C# example:
static string ColumnIndexToColumnLetter(int colIndex) { int div = colIndex; string colLetter = String.Empty; int mod = 0; while (div > 0) { mod = (div - 1) % 26; colLetter = (char)(65 + mod) + colLetter; div = (int)((div - mod) / 26); } return colLetter; }
C# usage:
string columnLetter = ColumnIndexToColumnLetter(100); // returns CV
VB.NET example:
Private Function ColumnIndexToColumnLetter(colIndex As Integer) As String Dim div As Integer = colIndex Dim colLetter As String = String.Empty Dim modnum As Integer = 0 While div > 0 modnum = (div - 1) Mod 26 colLetter = Chr(65 + modnum) & colLetter div = CInt((div - modnum) 26) End While Return colLetter End Function
VB.NET usage:
Dim columnLetter As String = ColumnIndexToColumnLetter(85) ' returns CG
Using an Excel formula to convert a column number to column letter
Of course, if you’re in Excel and need to get the column letter based on a number, you can always use the ADDRESS function. The function is pretty straight forward; it requires a row and column number, and in our case, we need to specify the abs_num parameter, which can be one of four possible options:
| abs_num | Returns |
| 1 or omitted | Absolute |
| 2 | Absolute row and relative column |
| 3 | Relative row and absolute column |
| 4 | Relative |
Consider the following formula:
=ADDRESS(1,5,1)
By changing the abs_num parameter, you’ll see the following result:
| abs_num | Formula | Result | Description |
| 1 or omitted | =ADDRESS(1,5,1) | $E$1 | Absolute |
| 2 | =ADDRESS(1,5,2) | E$1 | Absolute row and relative column |
| 3 | =ADDRESS(1,5,3) | $E1 | Relative row and absolute column |
| 4 | =ADDRESS(1,5,4) | E1 | Relative |
Notice that in all the four cases, we get the column letter, in this case E, back as well as the row number. By setting the abs_num parameter to 4 and replacing the row number, we can effectively return the column letter using the following formula:
=SUBSTITUTE(ADDRESS(1,5,4),”1″,””)
Using the Excel Object Model to convert column numbers to alphabetic format
Of course, you could always use the Excel object model to get the column letter. Much like the ADDRESS function, you use the Address property of the Range object to determine the address of the column and then simply replace the row number as illustrated below:
C# example:
private void columnLetterRibbonButton_OnClick(object sender, IRibbonControl control, bool pressed) { Worksheet sheet = null; Range range = null; string colLetter = string.Empty; try { sheet = (Worksheet)ExcelApp.ActiveSheet; range = sheet.Cells[1, 50] as Excel.Range; colLetter = range.Address[false, false, XlReferenceStyle.xlA1]; colLetter = colLetter.Replace("1", ""); MessageBox.Show(String.Format( "Column letter for column number 50 is : {0}", colLetter)); } finally { if (sheet != null) Marshal.ReleaseComObject(sheet); if (range != null) Marshal.ReleaseComObject(range); }
VB.NET example:
Private Sub GetColumnLetterRibbonButton_OnClick(sender As Object, _ control As IRibbonControl, pressed As Boolean) Handles _ GetColumnLetterRibbonButton.OnClick Dim sheet As Excel.Worksheet = Nothing Dim range As Excel.Range = Nothing Dim colLetter As String = String.Empty Try sheet = DirectCast(ExcelApp.ActiveSheet, Excel.Worksheet) range = TryCast(sheet.Cells(1, 50), Excel.Range) colLetter = range.Address(False, False, Excel.XlReferenceStyle.xlA1) colLetter = colLetter.Replace("1", "") MessageBox.Show(String.Format( _ "Column letter for column number 50 is : {0}", colLetter)) Finally If sheet IsNot Nothing Then Marshal.ReleaseComObject(sheet) End If If range IsNot Nothing Then Marshal.ReleaseComObject(range) End If End Try End Sub
Getting the column index by column letter
What should you do in order to reverse the scenario? How do you get the Excel column letter when all you have is the column index? Let’s take a look at how you can accomplish this using C#, VB.NET, an Excel formula and the Excel object model.
Using C# or VB.NET
C# example:
public static int ColumnLetterToColumnIndex(string columnLetter) { columnLetter = columnLetter.ToUpper(); int sum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < columnLetter.Length; i++) { sum *= 26; sum += (columnLetter[i] - 'A' + 1); } return sum; }
C# usage:
int columnIndex = ColumnLetterToColumnIndex("XFD"); // returns 16384
VB.NET example:
Public Function ColumnLetterToColumnIndex(columnLetter As String) As Integer columnLetter = columnLetter.ToUpper() Dim sum As Integer = 0 For i As Integer = 0 To columnLetter.Length - 1 sum *= 26 Dim charA As Integer = Char.GetNumericValue("A") Dim charColLetter As Integer = Char.GetNumericValue(columnLetter(i)) sum += (charColLetter - charA) + 1 Next Return sum End Function
VB.NET usage:
Dim columnIndex As Integer = ColumnLetterToColumnIndex("ADX") ' returns 703
Using an Excel formula to get the column number
Getting the column index directly in Excel is very easy. Excel has a built-in COLUMN() function. This function accepts a column reference, which is the column address. One catch though, is you have to combine the row number with the column address in order for it to work, e.g.:
=COLUMN(ADX1)
Using the Excel Object Model to convert a column letter to column number
Getting the column index is easily accomplished using the Excel object model. You first need to get a reference to a range object and then get the column number via the Column property of the Range object.
C# example:
private void getColumnIndexRibbonButton_OnClick(object sender, IRibbonControl control, bool pressed) { Worksheet sheet = null; Range range = null; int colIndex = 0; try { sheet = (Worksheet)ExcelApp.ActiveSheet; range = sheet.Range["ADX1"] as Excel.Range; colIndex = range.Column; MessageBox.Show(String.Format( "Column index for column letter ADX is : {0}", colIndex)); } finally { if (sheet != null) Marshal.ReleaseComObject(sheet); if (range != null) Marshal.ReleaseComObject(range); } }
VB.NET example:
Private Sub GetColumnIndexRibbonButton_OnClick(sender As Object, _ control As IRibbonControl, pressed As Boolean) Handles _ GetColumnIndexRibbonButton.OnClick Dim sheet As Excel.Worksheet = Nothing Dim range As Excel.Range = Nothing Dim colIndex As Integer = 0 Try sheet = DirectCast(ExcelApp.ActiveSheet, Excel.Worksheet) range = TryCast(sheet.Range("ADX1"), Excel.Range) colIndex = range.Column MessageBox.Show([String].Format( _ "Column index for column letter ADX is : {0}", colIndex)) Finally If sheet IsNot Nothing Then Marshal.ReleaseComObject(sheet) End If If range IsNot Nothing Then Marshal.ReleaseComObject(range) End If End Try End Sub
Thank you for reading. Until next time, keep coding!
Available downloads:
This sample Excel add-in was developed using Add-in Express for Office and .net:
Sample add-ins and applications (C# and VB.NET)
You may also be interested in:
- Creating COM add-ins for Excel 2013 – 2007. Customizing Excel Ribbon
- Excel add-in development in Visual Studio
Учитывая положительное число, преобразуйте число в соответствующее имя столбца Excel.
Например, на следующем изображении показаны числа, соответствующие столбцам Excel:
Потренируйтесь в этой проблеме
Основная хитрость в этой задаче заключается в обработке граничных случаев, таких как число 26 соответствует столбцу Z, и число 27 соответствует столбцу AA. Точно так же число 1014 соответствует столбцу ALZ, и число 1015 соответствует столбцу AMA.
Ниже приведена программа на C++, Java и Python, которая прекрасно обрабатывает все эти случаи:
C++
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 |
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> using namespace std; // Функция для преобразования заданного числа в столбец Excel string getColumnName(int n) { // инициализируем выходную строку как пустую string result = «»; while (n > 0) { // найти индекс следующей буквы и соединить букву // к решению // здесь индекс 0 соответствует `A`, а 25 соответствует `Z` int index = (n — 1) % 26; result = char(index + ‘A’) + result; n = (n — 1) / 26; } return result; } int main() { // начальное значение для случайного ввода srand(time(NULL)); // генерируем имена столбцов для 10 случайных чисел от 1 до 1000 for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { int r = rand() % 1000 + 1; cout << r << » — « << getColumnName(r) << endl; } return 0; } |
Скачать Выполнить код
Java
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
import java.util.Random; class Main { // Функция для преобразования заданного числа в столбец Excel public static String getColumnName(int n) { // инициализируем выходную строку как пустую StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(); while (n > 0) { // найти индекс следующей буквы и соединить букву // к решению // здесь индекс 0 соответствует `A`, а 25 соответствует `Z` int index = (n — 1) % 26; result.append((char)(index + ‘A’)); n = (n — 1) / 26; } return result.reverse().toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // генерируем имена столбцов для 10 случайных чисел от 1 до 1000 for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { int r = new Random().nextInt(1000) + 1; System.out.println(r + » — « + getColumnName(r)); } } } |
Скачать Выполнить код
Python
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
from random import randint # Функция для преобразования заданного числа в столбец Excel def getColumnName(n): # инициализирует выходную строку как пустую result = » while n > 0: # найти индекс следующей буквы и соединить букву # к решению # здесь индекс 0 соответствует `A`, а 25 соответствует `Z` index = (n — 1) % 26 result += chr(index + ord(‘A’)) n = (n — 1) // 26 return result[::—1] if __name__ == ‘__main__’: # генерирует имена столбцов для 10 случайных чисел в диапазоне от 1 до 1000. for i in range(1, 11): r = randint(1, 1000) print(r, ‘—’, getColumnName(r)) |
Скачать Выполнить код
Output (will vary):
585 — VM
873 — AGO
269 — JI
849 — AFQ
288 — KB
962 — AJZ
549 — UC
572 — UZ
485 — RQ
704 — AAB
Спасибо за чтение.
Пожалуйста, используйте наш онлайн-компилятор размещать код в комментариях, используя C, C++, Java, Python, JavaScript, C#, PHP и многие другие популярные языки программирования.
Как мы? Порекомендуйте нас своим друзьям и помогите нам расти. Удачного кодирования 🙂
Содержание
- Convert an Excel column number to a column name or letter: C# and VB.NET examples
- Getting the column letter by column index
- Using C# or VB.NET
- Using an Excel formula to convert a column number to column letter
- Using the Excel Object Model to convert column numbers to alphabetic format
- Getting the column index by column letter
- Using C# or VB.NET
- Using an Excel formula to get the column number
- Using the Excel Object Model to convert a column letter to column number
- Available downloads:
- MS Excel 2016: How to Change Column Headings from Numbers to Letters
- Convert spreadsheet number to column letter
- 17 Answers 17
- Linked
- Related
- Hot Network Questions
- Subscribe to RSS
- Find Excel column name from a given column number
- Python
- Javascript
- How to convert Excel column numbers into alphabetical characters
- Introduction
- More Information
Convert an Excel column number to a column name or letter: C# and VB.NET examples
Excel worksheet size has increased dramatically from Excel 2000 to Excel 2007. In fact, the number of rows an Excel 2013 worksheet can support has increased 16 times and the number of columns 64 times more than the number Excel 2000 could handle. Below is a table displaying the number of columns and rows the different versions of Excel can contain:
| Microsoft Excel version | Number of worksheet rows | Number of worksheet columns |
| Excel 2013 | 1 048 576 | 16 384 |
| Excel 2010 | 1 048 576 | 16 384 |
| Excel 2007 | 1 048 576 | 16 384 |
| Excel 2003 | 65 536 | 256 |
| Excel 2000 | 65 536 | 256 |
- Getting the column letter by column number
- Getting the column index by column name
Getting the column letter by column index
There are a lot of examples floating around on the internet on how to convert Excel column numbers to alphabetical characters. There are a few ways to get the column letter, using either vanilla C# or VB.NET, Excel formulas or the Excel object model. Let’s take a look at some of the solutions.
Using C# or VB.NET
Using an Excel formula to convert a column number to column letter
Of course, if you’re in Excel and need to get the column letter based on a number, you can always use the ADDRESS function. The function is pretty straight forward; it requires a row and column number, and in our case, we need to specify the abs_num parameter, which can be one of four possible options:
| abs_num | Returns |
| 1 or omitted | Absolute |
| 2 | Absolute row and relative column |
| 3 | Relative row and absolute column |
| 4 | Relative |
Consider the following formula:
=ADDRESS(1,5,1)
By changing the abs_num parameter, you’ll see the following result:
| abs_num | Formula | Result | Description |
| 1 or omitted | =ADDRESS(1,5,1) | $E$1 | Absolute |
| 2 | =ADDRESS(1,5,2) | E$1 | Absolute row and relative column |
| 3 | =ADDRESS(1,5,3) | $E1 | Relative row and absolute column |
| 4 | =ADDRESS(1,5,4) | E1 | Relative |
Notice that in all the four cases, we get the column letter, in this case E, back as well as the row number. By setting the abs_num parameter to 4 and replacing the row number, we can effectively return the column letter using the following formula:
Using the Excel Object Model to convert column numbers to alphabetic format
Of course, you could always use the Excel object model to get the column letter. Much like the ADDRESS function, you use the Address property of the Range object to determine the address of the column and then simply replace the row number as illustrated below:
Getting the column index by column letter
What should you do in order to reverse the scenario? How do you get the Excel column letter when all you have is the column index? Let’s take a look at how you can accomplish this using C#, VB.NET, an Excel formula and the Excel object model.
Using C# or VB.NET
Using an Excel formula to get the column number
Getting the column index directly in Excel is very easy. Excel has a built-in COLUMN() function. This function accepts a column reference, which is the column address. One catch though, is you have to combine the row number with the column address in order for it to work, e.g.:
=COLUMN(ADX1)
Using the Excel Object Model to convert a column letter to column number
Getting the column index is easily accomplished using the Excel object model. You first need to get a reference to a range object and then get the column number via the Column property of the Range object.
Thank you for reading. Until next time, keep coding!
Available downloads:
This sample Excel add-in was developed using Add-in Express for Office and .net:
Источник
MS Excel 2016: How to Change Column Headings from Numbers to Letters
This Excel tutorial explains how to change column headings from numbers (1, 2, 3, 4) back to letters (A, B, C, D) in Excel 2016 (with screenshots and step-by-step instructions).
See solution in other versions of Excel :
Question: In Microsoft Excel 2016, my Excel spreadsheet has numbers for both rows and columns. How do I change the column headings back to letters such as A, B, C, D?
Answer: Traditionally, column headings are represented by letters such as A, B, C, D. If your spreadsheet shows the columns as numbers, you can change the headings back to letters with a few easy steps.
In the example below, the column headings are numbered 1, 2, 3, 4 instead of the traditional A, B, C, D values that you normally see in Excel. When the column headings are numeric values, R1C1 reference style is being displayed in the spreadsheet.
To change the column headings to letters, select the File tab in the toolbar at the top of the screen and then click on Options at the bottom of the menu.
When the Excel Options window appears, click on the Formulas option on the left. Then uncheck the option called «R1C1 reference style» and click on the OK button.
Now when you return to your spreadsheet, the column headings should be letters (A, B, C, D) instead of numbers (1, 2, 3, 4).
Источник
Convert spreadsheet number to column letter
17 Answers 17
The xlsxwriter library includes a conversion function, xlsxwriter.utility.xl_col_to_name(index) and is on github
here is a working example:
Notice that it’s using zero-indexing.
The openpyxl library includes the conversion function (amongst others) which you are looking for, get_column_letter :
My recipe for this was inspired by another answer on arbitrary base conversion (https://stackoverflow.com/a/24763277/3163607)
Just for people still interest in this. The chosen answer by @Marius gives wrong outputs in some cases, as commented by @jspurim. Here is the my answer.
Edited after some tough love from Meta
The procedure for this involves dividing the number by 26 until you’ve reached a number less than 26, taking the remainder each time and adding 65, since 65 is where ‘A’ is in the ASCII table. Read up on ASCII if that doesn’t make sense to you.
Note that like the originally linked question, this is 1-based rather than zero-based, so A -> 1 , B -> 2 .
Recursive one line solution w/o libraries
Recursive Implementation
Iterative Implementations
Version 1: uses chr , ord
Version 2: Uses string.ascii_uppercase
Version 3: Uses divmod , chr , ord
Output: A AA AX CV IZ JJ
This simple Python function works for columns with 1 or 2 letters.
Here is a recursive solution:
The inverse can also be defined recursively, in a similar way:
Just to complicate everything a little bit I added caching, so the name of the same column will be calculated only once. The solution is based on a recipe by @Alex Benfica
an easy to understand solution:
part of the output:
Here is a modified version of the accepted answer that won’t break after ZZ .
- It uses a single while loop and the divmod() function to simplify the calculations.
- start_index can be 0 or 1.
- The divmod() function returns both the quotient and the remainder when dividing two numbers, which in this case are column_int — start_index and 26.
- The remainder is used to generate the next character for the column name, and the quotient is used as the new column_int for the next iteration.
- The loop continues until column_int becomes zero.
Linked
Hot Network Questions
To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader.
Site design / logo © 2023 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA . rev 2023.3.20.43331
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
Источник
Find Excel column name from a given column number
MS Excel columns have a pattern like A, B, C, …, Z, AA, AB, AC, …., AZ, BA, BB, … ZZ, AAA, AAB ….. etc. In other words, column 1 is named “A”, column 2 as “B”, and column 27 as “AA”.
Given a column number, find its corresponding Excel column name. The following are more examples.
Thanks to Mrigank Dembla for suggesting the below solution in a comment.
Suppose we have a number n, let’s say 28. so corresponding to it we need to print the column name. We need to take the remainder with 26.
If the remainder with 26 comes out to be 0 (meaning 26, 52, and so on) then we put ‘Z’ in the output string and new n becomes n/26 -1 because here we are considering 26 to be ‘Z’ while in actuality it’s 25th with respect to ‘A’.
Similarly, if the remainder comes out to be non-zero. (like 1, 2, 3, and so on) then we need to just insert the char accordingly in the string and do n = n/26.
Finally, we reverse the string and print.
Example:
n = 700
The remainder (n%26) is 24. So we put ‘X’ in the output string and n becomes n/26 which is 26.
Remainder (26%26) is 0. So we put ‘Z’ in the output string and n becomes n/26 -1 which is 0.
Following is the implementation of the above approach.
Python
Javascript
Time Complexity: O(log26n), as we are using a loop and in each traversal, we decrement by floor division of 26.
Auxiliary Space: O(50), as we are using extra space for storing the result.
Method 2
The problem is similar to converting a decimal number to its binary representation but instead of a binary base system where we have two digits only 0 and 1, here we have 26 characters from A-Z.
So, we are dealing with base 26 instead of base binary.
That’s not where the fun ends, we don’t have zero in this number system, as A represents 1, B represents 2 and so on Z represents 26.
To make the problem easily understandable, we approach the problem in two steps:
- Convert the number to base 26 representation, considering we have 0 also in the system.
- Change the representation to the one without having 0 in its system.
HOW? Here is an example
Step 1:
Consider we have number 676, How to get its representation in the base 26 system? In the same way, we do for a binary system, Instead of division and remainder by 2, we do division and remainder by 26.
Step2
But Hey, we can’t have zero in our representation. Right? Because it’s not part of our number system. How do we get rid of zero? Well it’s simple, but before doing that let’s remind one simple math trick:
- In a decimal number system to deal with zero, we borrow 10 and subtract 1 from the next significant.
- In the Base 26 Number System to deal with zero, we borrow 26 and subtract 1 from the next significant bit.
So Convert 10026 to a number system that does not have ‘0’, we get (25 26)26
Symbolic representation of the same is: YZ
Источник
How to convert Excel column numbers into alphabetical characters
Introduction
This article discusses how to use the Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) function in Microsoft Excel to convert column numbers into their corresponding alphabetical character designator for the same column.
For example, the column number 30 is converted into the equivalent alphabetical characters «AD».
More Information
Microsoft provides programming examples for illustration only, without warranty either expressed or implied. This includes, but is not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. This article assumes that you are familiar with the programming language that is being demonstrated and with the tools that are used to create and to debug procedures. Microsoft support engineers can help explain the functionality of a particular procedure, but they will not modify these examples to provide added functionality or construct procedures to meet your specific requirements.
The ConvertToLetter function works by using the following algorithm:
- Let iCol be the column number. Stop if iCol is less than 1.
- Calculate the quotient and remainder on division of (iCol — 1) by 26, and store in variables a and b .
- Convert the integer value of b into the corresponding alphabetical character (0 => A, 25 => Z) and tack it on at the front of the result string.
- Set iCol to the divisor a and loop.
For example: The column number is 30.
(Loop 1, step 1) The column number is at least 1, proceed.
(Loop 1, step 2) The column number less one is divided by 26:
29 / 26 = 1 remainder 3. a = 1, b = 3
(Loop 1, step 3) Tack on the (b+1) letter of the alphabet:
3 + 1 = 4, fourth letter is «D». Result = «D»
(Loop 1, step 4) Go back to step 1 with iCol = a
(Loop 2, step 1) The column number is at least 1, proceed.
(Loop 2, step 2) The column number less one is divided by 26:
0 / 26 = 0 remainder 0. a = 0, b = 0
(Loop 2, step 3) Tack on the b+1 letter of the alphabet:
0 + 1 = 1, first letter is «A» Result = «AD»
(Loop 2, step 4) Go back to step 1 with iCol = a
(Loop 3, step 1) The column number is less than 1, stop.
The following VBA function is just one way to convert column number values into their equivalent alphabetical characters:
Note This function only converts integers that are passed to it into their equivalent alphanumeric text character. It does not change the appearance of the column or the row headings on the physical worksheet.
Источник
Long long time ago, when I was building some Excel VBA spreadsheet tool for a leading retailer, I was having some cheat-sheet in Excel, in order to find the number of the column in Excel – e.g. A-1, B-2, C-3 etc.
Today I was building something similar and I was really close to build that cheat sheet again, but I remembered that in my e-mail signature is written “Developer”, so building a cheat sheet for something like this should not be the case.
Thus, I managed to find in google the VBA function that I need to get the column name in Excel 🙂 After some time it worked and I managed to make the reverse function by myself. It all took me about 10 minutes, while building a cheat sheet would have taken 2. Anyway, it looks better this way. Here lies the code:
|
Function GetCol(ColumnNumber) As String Dim FuncRange As String Dim FuncColLength As Integer FuncRange = Cells(1, ColumnNumber).AddressLocal(False, False) FuncColLength = Len(FuncRange) GetCol = Left(FuncRange, FuncColLength — 1) End Function Function GiveCol(ColumnLetters) As String GiveCol = Range(«A1:» & ColumnLetters & «1»).Columns.Count End Function |
How the code works? If you are in trouble, you may write ?GiveCol(“B”) in the immediate window and you will get the result 2. For the first function, if you write GetCol(3), you will get C. As simple as that, if you know what you are looking for. Otherwise, have fun making cheat sheets and using them.
Note:
The GetCol function was found initially here:
http://www.mrexcel.com/forum/excel-questions/16444-getting-column-name-given-column-number.html
I simply changed some of the code, but the idea stays the same.
My column headings are labeled with numbers instead of letters
- On the Excel menu, click Preferences.
- Under Authoring, click General .
- Clear the Use R1C1 reference style check box. The column headings now show A, B, and C, instead of 1, 2, 3, and so on.
Contents
- 1 How do you change Excel to Numbers?
- 2 How do I show column numbers in Excel?
- 3 How do I convert text to values in Excel?
- 4 How do I convert a column of numbers to column names in Excel?
- 5 How do I change the number format in Excel?
- 6 Why does Excel have numbers for columns?
- 7 How do I show columns and row numbers in Excel?
- 8 How do I get columns and row numbers in Excel?
- 9 How do I get row numbers in Excel?
- 10 How do I format numbers in Excel?
- 11 What are the different ways in formatting numbers?
- 12 How do I change the column title in Excel?
- 13 How do I change rows and column names in Excel?
- 14 How do I change Excel columns from numbers to alphabets?
- 15 How do I get rid of column 1 headers in Excel?
- 16 How do I change the row numbers in Excel?
- 17 What is an Xlookup in Excel?
- 18 Why can’t I see row numbers in Excel?
- 19 How do I add a numbered list in Excel?
- 20 How do I automatically number in sheets?
Change numbers with text format to number format in Excel for the…
- Select the cells that have the data you want to reformat.
- Click Number Format > Number. Tip: You can tell a number is formatted as text if it’s left-aligned in a cell.
How do I show column numbers in Excel?
Show column number
- Click File tab > Options.
- In the Excel Options dialog box, select Formulas and check R1C1 reference style.
- Click OK.
How do I convert text to values in Excel?
Use the Format Cells option to convert number to text in Excel
- Select the range with the numeric values you want to format as text.
- Right click on them and pick the Format Cells… option from the menu list. Tip. You can display the Format Cells…
- On the Format Cells window select Text under the Number tab and click OK.
How do I convert a column of numbers to column names in Excel?
To convert a column number to an Excel column letter (e.g. A, B, C, etc.) you can use a formula based on the ADDRESS and SUBSTITUTE functions. With this information, ADDRESS returns the text “A1”.
How do I change the number format in Excel?
You can use the Format Cells dialog to find the other available format codes:
- Press Ctrl+1 ( +1 on the Mac) to bring up the Format Cells dialog.
- Select the format you want from the Number tab.
- Select the Custom option,
- The format code you want is now shown in the Type box.
Why does Excel have numbers for columns?
Cause: The default cell reference style (A1), which refers to columns as letters and refers to rows as numbers, was changed. Solution: Clear the R1C1 reference style selection in Excel preferences. On the Excel menu, click Preferences.The column headings now show A, B, and C, instead of 1, 2, 3, and so on.
How do I show columns and row numbers in Excel?
On the Ribbon, click the Page Layout tab. In the Sheet Options group, under Headings, select the Print check box. , and then under Print, select the Row and column headings check box .
How do I get columns and row numbers in Excel?
It is quite easy to figure out the row number or column number if you know a cell’s address. If the cell address is NK60, it shows the row number is 60; and you can get the column with the formula of =Column(NK60). Of course you can get the row number with formula of =Row(NK60).
How do I get row numbers in Excel?
Use the ROW function to number rows
- In the first cell of the range that you want to number, type =ROW(A1). The ROW function returns the number of the row that you reference. For example, =ROW(A1) returns the number 1.
- Drag the fill handle. across the range that you want to fill.
How do I format numbers in Excel?
Formatting the Numbers in an Excel Text String
- Right-click any cell and select Format Cell.
- On the Number format tab, select the formatting you need.
- Select Custom from the Category list on the left of the Number Format dialog box.
- Copy the syntax found in the Type input box.
What are the different ways in formatting numbers?
How to change number formats. You can select standard number formats (General, Number, Currency, Accounting, Short Date, Long Date, Time, Percentage, Fraction, Scientific, Text) on the home tab of the ribbon using the Number Format menu. Note: As you enter data, Excel will sometimes change number formats automatically.
How do I change the column title in Excel?
Select a column, and then select Transform > Rename. You can also double-click the column header. Enter the new name.
How do I change rows and column names in Excel?
Rename columns and rows in a worksheet
- Click the row or column header you want to rename.
- Edit the column or row name between the last set of quotation marks. In the example above, you would overwrite the column name Gold Collection.
- Press Enter. The header updates.
How do I change Excel columns from numbers to alphabets?
To change the column headings to letters, select the File tab in the toolbar at the top of the screen and then click on Options at the bottom of the menu. When the Excel Options window appears, click on the Formulas option on the left. Then uncheck the option called “R1C1 reference style” and click on the OK button.
How do I get rid of column 1 headers in Excel?
Go to Table Tools > Design on the Ribbon. In the Table Style Options group, select the Header Row check box to hide or display the table headers. If you rename the header rows and then turn off the header row, the original values you input will be retained if you turn the header row back on.
How do I change the row numbers in Excel?
Here are the steps to use Fill Series to number rows in Excel:
- Enter 1 in cell A2.
- Go to the Home tab.
- In the Editing Group, click on the Fill drop-down.
- From the drop-down, select ‘Series..’.
- In the ‘Series’ dialog box, select ‘Columns’ in the ‘Series in’ options.
- Specify the Stop value.
- Click OK.
What is an Xlookup in Excel?
Use the XLOOKUP function to find things in a table or range by row.With XLOOKUP, you can look in one column for a search term, and return a result from the same row in another column, regardless of which side the return column is on.
Why can’t I see row numbers in Excel?
In order to show (or hide) the row and column numbers and letters go to the View ribbon. Set the check mark at “Headings”. That’s it!
How do I add a numbered list in Excel?
Click the Home tab in the Ribbon. Click the Bullets and Numbering option in the new group you created. The new group is on the far right side of the Home tab. In the Bullets and Numbering window, select the type of bulleted or numbered list you want to add to the text box and click OK.
How do I automatically number in sheets?
Use autofill to complete a series
- On your computer, open a spreadsheet in Google Sheets.
- In a column or row, enter text, numbers, or dates in at least two cells next to each other.
- Highlight the cells. You’ll see a small blue box in the lower right corner.
- Drag the blue box any number of cells down or across.