Работа с фигурами в VBA Excel: создание фигур методом Shapes.AddShape, типы фигур (MsoAutoShapeType), обращение к фигурам и изменение их свойств. Примеры.
Объекты для работы с фигурами
Фигуры в VBA Excel представлены тремя объектами:
| Объект | Описание |
|---|---|
| Shapes | Коллекция всех фигур на рабочем листе. Используется для создания новых фигур, для обращения к одной фигуре по имени и для перебора фигур циклом. |
| ShapeRange | Коллекция нескольких фигур, аргументом которой является массив имен выбранных объектов. Используется для редактирования сразу всех фигур, входящих в эту коллекцию. |
| Shape | Объект, представляющий одну фигуру. Используется для редактирования одной этой фигуры. |
Фигуры в VBA Excel создаются методом Shapes.AddShape.
Синтаксис метода AddShape
|
Shapes.AddShape (Type, Left, Top, Width, Height) |
Shapes — выражение, возвращающее коллекцию фигур на рабочем листе, например: ActiveSheet.Shapes.
Параметры метода AddShape
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| Type | Константа из коллекции MsoAutoShapeType, определяющая тип создаваемой фигуры. |
| Left | Расстояние от левой границы фигуры до левой границы табличной части рабочего листа в пунктах.. Тип данных — Single. |
| Top | Расстояние от верхней границы фигуры до верхней границы табличной части рабочего листа в пунктах.. Тип данных — Single. |
| Width | Ширина фигуры по внешним границам в пунктах. |
| Height | Высота фигуры по внешним границам в пунктах. |
Все параметры метода Shapes.AddShape являются обязательными.
Константы MsoAutoShapeType
Константы коллекции MsoAutoShapeType, определяющие основные типы создаваемых фигур:
| Константа | Значение | Тип фигуры |
|---|---|---|
| msoShapeRectangle | 1 | Прямоугольник |
| msoShapeParallelogram | 2 | Параллелограмм |
| msoShapeTrapezoid | 3 | Трапеция |
| msoShapeDiamond | 4 | Ромб |
| msoShapeRoundedRectangle | 5 | Прямоугольник: скругленные углы |
| msoShapeOctagon | 6 | Восьмиугольник (октаэдр) |
| msoShapeIsoscelesTriangle | 7 | Равнобедренный треугольник |
| msoShapeRightTriangle | 8 | Прямоугольный треугольник |
| msoShapeOval | 9 | Овал |
| msoShapeHexagon | 10 | Шестиугольник (гексаэдр) |
| msoShapeCross | 11 | Крест |
| msoShapeRegularPentagon | 12 | Пятиугольник (пентаэдр) |
| msoShapeCan | 13 | Цилиндр |
| msoShapeCube | 14 | Куб |
| msoShapeDonut | 18 | Круг: прозрачная заливка (кольцо) |
| msoShapeLightningBolt | 22 | Молния |
| msoShapeSun | 23 | Солнце |
| msoShapeMoon | 24 | Месяц (луна) |
| msoShape5pointStar | 92 | Звезда: 5 точек (пятиконечная) |
| msoShapeCloud | 179 | Облако |
Все доступные константы из коллекции MsoAutoShapeType смотрите на сайте разработчиков.
Создание объекта ShapeRange
Создание коллекции ShapeRange из выбранных фигур:
|
Dim myShapeRange As ShapeRange Set myShapeRange = ActiveSheet.Shapes.Range(Array(«Пятиугольник 140», «Солнце 141», «Облако 144»)) |
Объектная переменная myShapeRange не обязательна, можно обратиться непосредственно к возвращенной коллекции, например, присвоив всем ее элементам синий цвет:
|
ActiveSheet.Shapes.Range(Array(«Пятиугольник 140», «Солнце 141», «Облако 144»)).Fill.ForeColor.RGB = vbBlue |
Примеры работы с фигурами
Пример 1
Создание пяти разных фигур из кода VBA Excel методом Shapes.AddShape:
|
Sub Primer1() With ActiveSheet.Shapes ‘При создании фигуры без присвоения ее переменной скобки не нужны .AddShape msoShapeCube, 30, 40, 72, 72 .AddShape msoShapeIsoscelesTriangle, 130, 40, 72, 72 .AddShape msoShapeSun, 230, 40, 72, 72 .AddShape msoShapeLightningBolt, 330, 40, 72, 72 ‘Чтобы выбрать фигуру, параметры необходимо заключить в скобки .AddShape(msoShapeCloud, 430, 40, 72, 72).Select End With End Sub |
Результат работы кода:
Пример 2
Работа с одной фигурой:
|
Sub Primer2() Dim myShape As Shape ‘Создаем фигуру «Месяц» и присваивает ссылку на нее переменной myShape Set myShape = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeMoon, 50, 50, 80, 80) With myShape ‘Меняем высоту и ширину фигуры .Height = 150 .Width = 100 ‘Меняем цвет фигуры .Fill.ForeColor.RGB = vbYellow ‘Поворачиваем фигуру влево на 40 градусов .Rotation = —40 End With End Sub |
Пример 3
Редактирование одновременно нескольких фигур с помощью коллекции ShapeRange:
|
Sub Primer3() With ActiveSheet.Shapes.Range(Array(«Овал 1», «Овал 2», «Овал 3»)) ‘Меняем цвет всех фигур из коллекции ShapeRange .Fill.ForeColor.RGB = vbBlue ‘Задаем высоту и ширину овалов .Height = 150 .Width = 50 ‘Поворачиваем фигуры вправо на 45 градусов .Rotation = 45 End With End Sub |
Пример 4
Редактирование одновременно всех фигур на рабочем листе с помощью коллекции ShapeRange:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
Sub Primer4() Dim myShapeRange As ShapeRange, i As Integer, _ myShape As Shape, myArray() As String ‘Задаем массиву размерность от 1 до количества фигур на листе ReDim myArray(1 To ActiveSheet.Shapes.Count) ‘Проходим циклом по всем фигурам коллекции и записываем их имена в массив For Each myShape In ActiveSheet.Shapes i = i + 1 myArray(i) = myShape.Name Next ‘Создаем коллекцию ShapeRange и присваиваем ссылку на нее переменной myShapeRange Set myShapeRange = ActiveSheet.Shapes.Range(myArray) With myShapeRange ‘Изменяем цвет всех фигур на рабочем листе .Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(100, 150, 200) ‘Поворачиваем все фигуры вокруг вертикальной оси .Flip msoFlipVertical End With End Sub |
Пример 5
Добавление надписи (текста) на фигуру:
|
Sub Primer5() Dim myShape As Shape Set myShape = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeCloud, 50, 30, 300, 300) With myShape.TextFrame2 ‘Добавление текста на фигуру .TextRange.Characters.Text = «Объект TextFrame представляет текстовую рамку в объекте Shape. Содержит текст в текстовом кадре, а также свойства и методы, которые контролируют выравнивание и закрепление текстового кадра.» ‘Задаем курсивное начертание .TextRange.Characters.Font.Italic = True ‘Указываем размер шрифта .TextRange.Characters.Font.Size = 13 ‘Отступ левой границы текстового поля от левой внутренней границы фигуры .MarginLeft = 30 ‘Отступ верхней границы текстового поля от верхней внутренней границы фигуры .MarginTop = 20 End With End Sub |
Результат работы кода:
Изменить цвет текста, например на черный, можно двумя способами:
|
‘С помощью константы MsoThemeColorIndex myShape.TextFrame2.TextRange.Characters.Font.Fill.ForeColor.ObjectThemeColor = msoThemeColorDark1 ‘С помощью цветовой модели RGB myShape.TextFrame2.TextRange.Characters.Font.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(0, 0, 0) |
С константами из коллекции MsoThemeColorIndex вы можете ознакомиться на сайте разработчиков.
Пример 6
Удаление фигур с рабочего листа из кода VBA Excel с помощью метода Delete.
Удаление одной фигуры:
|
ActiveSheet.Shapes(«Ромб 5»).Delete |
Удаление нескольких фигур:
|
ActiveSheet.Shapes.Range(Array(«Овал 1», «Овал 2», «Овал 3»)).Delete |
Удаление всех фигур с рабочего листа с помощью цикла:
|
Sub Primer6() Dim myShape As Shape For Each myShape In ActiveSheet.Shapes myShape.Delete Next End Sub |
В 7 примере рассмотрено удаление всех фигур без цикла.
Пример 7
Выделение всех фигур на рабочем листе:
|
ActiveSheet.Shapes.SelectAll |
Выбор всех фигур и удаление выбранного (всех фигур):
|
Sub Primer7() ActiveSheet.Shapes.SelectAll Selection.Delete End Sub |
Продолжение темы в статье VBA Excel. Копирование, перемещение и поворот фигур.
Содержание
- Working with shapes (drawing objects)
- Setting properties for a shape
- Applying a property or method to several shapes at the same time
- Creating a ShapeRange collection that contains all shapes on a sheet
- Applying a property or method to a ShapeRange collection
- Looping through a Shapes or ShapeRange collection
- Aligning, distributing, and grouping shapes in a ShapeRange
- See also
- Support and feedback
- Объект Shape (Проект)
- Замечания
- Пример
- Методы
- Свойства
- См. также
- Поддержка и обратная связь
- Shape object (Excel)
- Remarks
- Example
- Methods
- Properties
- See also
- Support and feedback
Working with shapes (drawing objects)
Shapes, or drawing objects, are represented by three different objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
| Shapes collection | Use to create shapes and to iterate through all the shapes on a given worksheet. |
| ShapeRange collection | Use to modify multiple shapes the same way you work with multiple shapes in the user interface. |
| Shape object | Use to format or modify a single shape. |
Setting properties for a shape
Many formatting properties of shapes are not set by properties that apply directly to the Shape or ShapeRange object. Instead, related shape attributes are grouped under secondary objects, such as the FillFormat object, which contains all the properties that relate to the shape’s fill, or the LinkFormat object, which contains all the properties that are unique to linked OLE objects.
To set properties for a shape, you must first return the object that represents the set of related shape attributes and then set properties of that returned object. For example, you use the Fill property to return the FillFormat object, and then you set the ForeColor property of the FillFormat object to set the fill foreground color for the specified shape, as shown in the following example.
Applying a property or method to several shapes at the same time
In the user interface, you can perform some operations with several shapes selected; for example, you can select several shapes and set all their individual fills at once. You can perform other operations with only a single shape selected; for example, you can edit the text in a shape only if a single shape is selected.
In Visual Basic, there are two ways to apply properties and methods to a set of shapes. These two ways allow you to perform any operation that you can perform on a single shape on a range of shapes, whether or not you can perform the same operation in the user interface.
If the operation works on multiple selected shapes in the user interface, you can perform the same operation in Visual Basic by constructing a ShapeRange collection that contains the shapes you want to work with, and applying the appropriate properties and methods directly to the ShapeRange collection.
If the operation does not work on multiple selected shapes in the user interface, you can still perform the operation in Visual Basic by looping through the Shapes collection or through a ShapeRange collection that contains the shapes you want to work with, and applying the appropriate properties and methods to the individual Shape objects in the collection.
Many properties and methods that apply to the Shape object and ShapeRange collection fail if applied to certain kinds of shapes. For example, the TextFrame property fails if applied to a shape that cannot contain text.
If you are not positive that each of the shapes in a ShapeRange collection can have a certain property or method applied to it, don’t apply the property or method to the ShapeRange collection. If you want to apply one of these properties or methods to a collection of shapes, you must loop through the collection and test each individual shape to make sure it is an appropriate type of shape before applying the property or method to it.
Creating a ShapeRange collection that contains all shapes on a sheet
You can create a ShapeRange object that contains all the Shape objects on a sheet by selecting the shapes and then using the ShapeRange property to return a ShapeRange object containing the selected shapes.
In Microsoft Excel, the Index argument is not optional for the Range property of the Shapes collection, so you cannot use this property without an argument to create a ShapeRange object containing all shapes in a Shapes collection.
Applying a property or method to a ShapeRange collection
If you can perform an operation on multiple selected shapes in the user interface at the same time, you can do the programmatic equivalent by constructing a ShapeRange collection and then applying the appropriate properties or methods to it. The following example constructs a shape range that contains the shapes named «Big Star» and «Little Star» on myDocument and applies a gradient fill to them.
The following are general guidelines for how properties and methods behave when they are applied to a ShapeRange collection.
Applying a method to the collection is equivalent to applying the method to each individual Shape object in that collection.
Setting the value of a property of the collection is equivalent to setting the value of the property of each individual shape in that range.
A property of the collection that returns a constant returns the value of the property for an individual shape in the collection if all shapes in the collection have the same value for that property. If not all shapes in the collection have the same value for the property, it returns the «mixed» constant.
A property of the collection that returns a simple data type (such as Long, Single, or String) returns the value of the property for an individual shape if all shapes in the collection have the same value for that property.
The value of some properties can be returned or set only if there is exactly one shape in the collection. If the collection contains more than one shape, a run-time error occurs. This is generally the case for returning or setting properties when the equivalent action in the user interface is possible only with a single shape (actions such as editing text in a shape or editing the points of a freeform).
The preceding guidelines also apply when you are setting properties of shapes that are grouped under secondary objects of the ShapeRange collection, such as the FillFormat object. If the secondary object represents operations that can be performed on multiple selected objects in the user interface, you’ll be able to return the object from a ShapeRange collection and set its properties.
For example, you can use the Fill property to return the FillFormat object that represents the fills of all the shapes in the ShapeRange collection. Setting the properties of this FillFormat object will set the same properties for all the individual shapes in the ShapeRange collection.
Looping through a Shapes or ShapeRange collection
Even if you cannot perform an operation on several shapes in the user interface at the same time by selecting them and then using a command, you can perform the equivalent action programmatically by looping through a Shapes or ShapeRange collection that contains the shapes you want to work with, applying the appropriate properties and methods to the individual Shape objects in the collection.
The following example loops through all the shapes on myDocument and changes the foreground color for each AutoShape shape.
The following example constructs a ShapeRange collection that contains all the currently selected shapes in the active window and sets the foreground color for each selected shape.
Aligning, distributing, and grouping shapes in a ShapeRange
Use the Align and Distribute methods to position a set of shapes relative to one another or relative to the document that contains them.
Use the Group method or the Regroup method to form a single grouped shape from a set of shapes.
See also
Support and feedback
Have questions or feedback about Office VBA or this documentation? Please see Office VBA support and feedback for guidance about the ways you can receive support and provide feedback.
Источник
Объект Shape (Проект)
Представляет объект в отчете Project, например диаграмму, таблицу отчета, текстовое поле, рисунок свободной формы или рисунок.
Замечания
Объект Shape является членом коллекции Shapes , которая включает все фигуры в отчете.
Запись макроса для объекта Shape не реализована. То есть, когда вы записываете макрос в Project и вручную добавляете фигуру или редактируете элементы фигуры, шаги по добавлению фигуры и управлению ими не записываются.
Есть три объекта, которые представляют фигуры: коллекция Shapes , которая представляет все фигуры в документе; объект ShapeRange , представляющий указанное подмножество фигур в документе (например, объект ShapeRange может представлять фигуры один и четыре в документе, или он может представлять все выбранные фигуры в документе); и объект Shape , представляющий одну фигуру в документе. Если вы хотите работать с несколькими фигурами одновременно или с фигурами в выделенном фрагменте, используйте коллекцию ShapeRange .
Используйте Shapes(Index) , где Индекс — это имя фигуры или номер индекса, чтобы вернуть один объект Shape .
Пример
В следующем примере макрос TestTextShape создает фигуру текстового поля, добавляет текст и изменяет свойства стиля фигуры, заливки, линии, тени и отражения. Макрос FlipShape переворачивает фигуру сверху вниз.
На рисунке 1 показан результат, в котором выбрана фигура, чтобы сделать вкладку ФОРМАТ ленты в разделе СРЕДСТВА РИСОВАНИЯ доступной, хотя активной вкладкой является КОНСТРУКТОР в разделе ИНСТРУМЕНТЫ ОТЧЕТОВ. Если фигура не выбрана, инструменты рисования и вкладка ФОРМАТ не будут видны.
Рис. 1. Тестирование объектной модели фигур
Методы
Свойства
См. также
Поддержка и обратная связь
Есть вопросы или отзывы, касающиеся Office VBA или этой статьи? Руководство по другим способам получения поддержки и отправки отзывов см. в статье Поддержка Office VBA и обратная связь.
Источник
Shape object (Excel)
Represents an object in the drawing layer, such as an AutoShape, freeform, OLE object, or picture.
The Shape object is a member of the Shapes collection. The Shapes collection contains all the shapes in a workbook.
There are three objects that represent shapes: the Shapes collection, which represents all the shapes on a workbook; the ShapeRange collection, which represents a specified subset of the shapes on a workbook (for example, a ShapeRange object could represent shapes one and four in the workbook, or it could represent all the selected shapes in the workbook); and the Shape object, which represents a single shape on a worksheet. If you want to work with several shapes at the same time or with shapes within the selection, use a ShapeRange collection.
| To return. | Use. |
|---|---|
| A Shape object that represents one of the shapes attached by a connector | The BeginConnectedShape or EndConnectedShape property of the ConnectorFormat object. |
| A newly created freeform | The BuildFreeform and AddNodes methods to define the geometry of a new freeform, and use the ConvertToShape method to create the freeform and return the Shape object that represents it. |
| A Shape object that represents a single shape in a grouped shape | GroupItems (index), where index is the shape name or the index number within the group. |
| A newly formed group of shapes | The Group or Regroup method of the ShapeRange object to group a range of shapes and return a single Shape object that represents the newly formed group. After a group has been formed, you can work with the group the same way that you work with any other shape. |
| A Shape object that represents an existing shape | Shapes (index), where index is the shape name or the index number. |
| A Shape object that represents a shape within the selection | Selection.ShapeRange (index), where index is the shape name or the index number. |
Example
The following example horizontally flips shape one and the shape named Rectangle 1 on myDocument.
Each shape is assigned a default name when you add it to the Shapes collection. To give the shape a more meaningful name, use the Name property. The following example adds a rectangle to myDocument, gives it the name Red Square, and then sets its foreground color and line style.
The following example sets the fill for the first shape in the selection in the active window, assuming that there’s at least one shape in the selection.
Methods
Properties
See also
Support and feedback
Have questions or feedback about Office VBA or this documentation? Please see Office VBA support and feedback for guidance about the ways you can receive support and provide feedback.
Источник
VBA Coding With Shape Objects
In this comprehensive guide, you will be learning all the ways you can create and manipulate shapes with VBA macros.
Shapes are objects you can insert into your spreadsheet through the Insert Tab via the Shapes gallery button. These objects can add visualizations to your dashboards, store text, or even serve as buttons to launch macro code.
Here is an outline of the topics covered in this guide:
Creating A New Shape With AddShape()
To create a shape object in Excel using VBA, you must call the AddShape function.
The AddShape function has 4 required inputs in order to generate a new shape:
-
Type — Name of the type of shape you wish to generate
-
Left — Where on the spreadsheet the left side of the shape should be located
-
Top — Where on the spreadsheet the top of the shape should be located
-
Width — How wide your shape should be
-
Height — How tall your shape should be
Here is a snippet of VBA code showing how to create 2 shapes and store the newly created shape to a variable for easy reference later on in your code.
Sub CreateShape()
Dim shp1 As Shape
Dim shp2 As Shape
‘Create & Store New Shape to Variable
Set shp1 = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(msoShape16pointStar, _
ActiveCell.Left, ActiveCell.Top, 80, 27)
‘Create & Store New Shape to Variable (use Enum Code)
Set shp2 = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(94, _
ActiveCell.Left, ActiveCell.Top, 80, 27)
End Sub
Continue reading through the next few sections to learn how to determine the type, size, and position values you should be using to create your desired shape.
Choosing A Shape Type
There are a TON of shape types available to you through VBA. There are so many in fact, that I have painstakenly gone through and visually cataloged them for your ease in the below slide show.
Once you have determined which shape you would like to create, grab either the shape textual name or the enumeration number. You will use this MSOAutoShapeType reference to code the exact shape you want.
If you have a shape already created on your spreadsheet, you can use the following code to figure out its enumeration code that you can reference in your VBA code.
Sub DetermineShapeType()
‘PURPOSE: Display The Shape Type of Selected Shape
‘SOURCE: www.TheSpreadsheetGuru.com
Dim ActiveShape As Shape
Dim UserSelection As Variant
‘Pull-in what is selected on screen
Set UserSelection = ActiveWindow.Selection
‘Determine if selection is a shape
On Error GoTo NoShapeSelected
Set ActiveShape = ActiveSheet.Shapes(UserSelection.Name)
On Error Resume Next
‘Tell User the Shape Type Enumeration Number
MsgBox «The Select Shape Type = » & ActiveShape.AutoShapeType
Exit Sub
‘Error Handler
NoShapeSelected:
MsgBox «You do not have a shape selected!»
End Sub
Determining Shape Position
There are two properties you can modify to change the location of a shape on the spreadsheet with VBA. These two properties are the Left and Top values of the shape.
If you are unsure what the size of your shape should be, there are two popular ways you can size your shape:
Method 1: You can base it on the left and top positions of a cell on your spreadsheet.
The following VBA code shows you how to use the Left value of Cell B1 and the Top value of Cell B10 to reposition the rectangle shape that is created.
Sub ShapePositionFromCell()
Dim shp As Shape
‘Create Shape
Set shp = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeRectangle, _
Range(«B1»).Left, Range(«B10»).Top, 100, 50)
End Sub
Method 2: You can position the shape to your liking manually on the spreadsheet and read the left and top positions using VBA.
The following VBA code will output a message box that displays the Left and Top positions of a currently selected shape (ActiveShape).
Sub DetermineShapePosition()
‘PURPOSE: Display Selected Shape’s Position
‘SOURCE: www.TheSpreadsheetGuru.com
Dim ActiveShape As Shape
Dim UserSelection As Variant
‘Pull-in what is selected on screen
Set UserSelection = ActiveWindow.Selection
‘Determine if selection is a shape
On Error GoTo NoShapeSelected
Set ActiveShape = ActiveSheet.Shapes(UserSelection.Name)
On Error Resume Next
‘Tell User the Shape Position Values
MsgBox «Left Position = » & ActiveShape.Left & vbNewLine & _
«Top Position = » & ActiveShape.Top
Exit Sub
‘Error Handler
NoShapeSelected:
MsgBox «You do not have a shape selected!»
End Sub
Determining Shape Size
There are two properties you can modify to change the size of a shape with VBA. These two properties are the Width and Height values of the shape.
If you are unsure what the size of your shape should be, there are two popular ways you can size your shape:
Method 1: You can base it on the size of a range of cells
Sub ShapeSizeFromRange()
Dim shp As Shape
Dim rng As Range
‘Provide Range for Shape Size
Set rng = Range(«A1:C4»)
‘Create Shape
Set shp = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeRectangle, _
ActiveCell.Left, ActiveCell.Top, rng.Width, rng.Height)
End Sub
Method 2: You can create the shape to your liking manually and read the width and height using VBA
Sub DetermineShapeSize()
‘PURPOSE: Display Selected Shape’s Size
‘SOURCE: www.TheSpreadsheetGuru.com
Dim ActiveShape As Shape
Dim UserSelection As Variant
‘Pull-in what is selected on screen
Set UserSelection = ActiveWindow.Selection
‘Determine if selection is a shape
On Error GoTo NoShapeSelected
Set ActiveShape = ActiveSheet.Shapes(UserSelection.Name)
On Error Resume Next
‘Tell User the Shape Position Values
MsgBox «Width = » & ActiveShape.Width & vbNewLine & _
«Height = » & ActiveShape.Height
Exit Sub
‘Error Handler
NoShapeSelected:
MsgBox «You do not have a shape selected!»
End Sub
Text Formatting
Sub CreateShapeWithText()
Dim shp As Shape
‘Create & Store New Shape to Variable
Set shp = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(msoShape16pointStar, _
ActiveCell.Left, ActiveCell.Top, 80, 27)
‘Add Text To Shape
shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Text = «My Awesome Shape!»
‘Bold/Italicize/Underline Text
shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Bold = True
shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Italic = True
shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.UnderlineStyle = msoUnderlineDottedLine
‘Change Text Color
shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(225, 140, 71)
‘Change Text Size
shp.TextFrame2.TextRange.Font.Size = 14
‘Center Align Text
shp.TextFrame.HorizontalAlignment = xlHAlignCenter
shp.TextFrame.VerticalAlignment = xlVAlignCenter
End Sub
Fill Color & Borders
Sub CreateShapeWithBorder()
Dim shp As Shape
‘Create & Store New Shape to Variable
Set shp = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeRoundedRectangle, _
ActiveCell.Left, ActiveCell.Top, 80, 27)
‘Light Orange Fill
shp.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(253, 234, 218)
‘Add Dotted Border
shp.Line.DashStyle = msoLineDashDotDot
‘Dark Orange Border
shp.Line.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(252, 213, 181)
‘Adjust Border Thickness
shp.Line.Weight = 2
‘Remove Border
shp.Line.Visible = False
End Sub
Change Shape Type
If you are looking to change the shape type of an existing type, you can do so by setting the AutoShapeType to a different shape type value.
Sub ChangeShapeType()
Dim shp As Shape
‘Store specific shape on spreadsheet to a variable
Set shp = ActiveSheet.Shapes(«Shape1»)
‘Change shape type to oval
shp.AutoShapeType = msoShapeOval
End Sub
Create Your Own Macro Button With VBA Code
I personally cannot stand the native Excel form control button. It looks so outdated and really makes your spreadsheets look unprofessional. That is why I prefer to use VBA code to create a shape that looks like a button.
I thought this would be a great example to show you a real-world coding example where I need to create and format a shape to have a specific appearance. The following VBA macro code puts everything we have covered in this guide together and provides you with some sample code that comprises of a true shape-building solution.
Sub Create_Button()
‘PURPOSE: Creates a SpreadsheetGuru macro button shape
‘SOURCE: www.TheSpreadsheetGuru.com
Dim bttn As Shape
‘Create & Position Macro Button
Set bttn = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeRoundedRectangle, _
ActiveCell.Left, ActiveCell.Top, 80, 27)
‘Modify Text Formatting
With bttn.TextFrame2.TextRange
.Text = «Macro»
.Font.Bold = msoTrue
.Font.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(0, 0, 0)
.Font.Size = 14
End With
‘Center Alignment
bttn.TextFrame.HorizontalAlignment = xlHAlignCenter
bttn.TextFrame.VerticalAlignment = xlVAlignCenter
‘Light Gray Fill
bttn.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(217, 217, 217)
‘No Border
bttn.Line.Visible = msoFalse
End Sub
Loop Through All Shapes Of Specific Type
If you need to target a specific shape type on your spreadsheet, you can create a loop that tests the AutoShapeType value to filter your results.
The following VBA code example loops through all shape objects in the currently selected spreadsheet and only changes the fill color of the rectangle shapes.
Sub ChangeRectangleShapes()
Dim shp As Shape
‘Loop through each shape on ActiveSheet
For Each shp In ActiveSheet.Shapes
‘Only modify rectangle shapes
If shp.AutoShapeType = msoShapeRectangle Then
shp.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(253, 234, 218)
End If
Next shp
End Sub
I Hope This Microsoft Excel Article Helped!
Hopefully, I was able to explain how you use VBA code to create and format shapes on your Excel spreadsheets. If you have any questions about these techniques or suggestions on how to improve them, please let me know in the comments section below.
About The Author
Hey there! I’m Chris and I run TheSpreadsheetGuru website in my spare time. By day, I’m actually a finance professional who relies on Microsoft Excel quite heavily in the corporate world. I love taking the things I learn in the “real world” and sharing them with everyone here on this site so that you too can become a spreadsheet guru at your company.
Through my years in the corporate world, I’ve been able to pick up on opportunities to make working with Excel better and have built a variety of Excel add-ins, from inserting tickmark symbols to automating copy/pasting from Excel to PowerPoint. If you’d like to keep up to date with the latest Excel news and directly get emailed the most meaningful Excel tips I’ve learned over the years, you can sign up for my free newsletters. I hope I was able to provide you with some value today and I hope to see you back here soon!
— Chris
The Excel VBA Shape object represents an object in the
drawing layer, such as an AutoShape, freeform, OLE object, or picture. It is a
member of the Shapes collection, which contains all the shapes in a workbook,
but represents a single shape in a worksheet.
How to refer to the Shape
object
We refer to the Shapes collection in a given worksheet as indicated below:
ActiveSheet.Shapes
Then, we can use properties and methods of the Shapes collection as per the Excel object model structure. Some useful methods of the Shapes collection are: AddShape,
AddTextBox, AddFormControl, AddPicture, Item, SelectAll. See below an example
of the structure (for AddShape see next section).
ActiveSheet.Shapes.SelectAll ‘selects all the shapes in
the active sheet
ActiveSheet.Shapes.Item(1).Select ‘selects the first shape in the
active sheet
The latest can simply be referred to as either of the below two
options: the first one using the index, and the second using the shape name. Thus, we refer to a single Shape object.
ActiveSheet.Shapes(1)
ActiveSheet.Shapes(«Rectangle 1»)
Add new shapes
We use the method AddShape of the Excel VBA Shapes
collection to create or add a new shape in a given worksheet. Excel
automatically gives a default name depending on the type of shape (for example,
Rectangle 1, TextBox 2, etc), but we can easily change the name of the shape
and many other properties (see later). See below the standard statement to add
a new AutoShape in the active worksheet.
ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape MsoAutoShapeType, pLeft, pTop, pWidth, pHeight
Where MsoAutoShapeType specifies the type of
an AutoShape object (MsoAutoShapeType enumeration for Microsoft Office), and pLeft, pTop, pWidth, and pHeight determine the position and
size of the shape in points. Note that the pLeft and pTop refer to the upper
left corner of the shape in reference to the upper left edge of the worksheet.
In the following example, we add a rectangle
to the active worksheet.
ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape
msoShapeRectangle, 20, 20, 200, 100
In order to add the shape to a specific cell
or range in the worksheet, we need to specify the position and size of the
shape as follows:
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = ActiveSheet.Range(«D4:H8»)
rngLeft = rng.Left
rngTop = rng.Top
rngHeight = rng.Height
rngWidth = rng.Width
ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape msoShapeRectangle,
rngLeft, rngTop, rngWidth, rngHeight
It is more practical to add the shape to an
object variable in order to easily apply formatting properties or methods later.
In the following example, we define an object variable called “MyShape” to add
a rectangle to the active worksheet, then we change the name of the shape and
apply any other properties (for this see next section).
Dim MyShape As Shape
Set MyShape =
ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddShape(msoShapeRectangle, 50, 50, 140, 80)
With MyShape
.Name =
«MyFirstShape»
‘other
properties
End With
We can add other types of shapes such as text
boxes, form controls, smart art shapes, pictures, etc, with the corresponding
method of the Shapes collection. Here are some useful examples.
The code below adds a textbox into the active
worksheet with given dimensions (100×60) and some inner text. Note that we use
the TextFrame.Characters method to work with text inside the box.
Dim
txtbox As Shape
Set
txtbox = ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddTextbox(msoTextOrientationHorizontal, 50, 50,
100, 60)
With
txtbox.TextFrame.Characters
.Text = «This is my first textbox»
.Font.Color = vbRed
End
With
We can add form controls such as buttons,
check boxes, combo boxes, etc, with the AddFormControl method of the Shapes
collection. For example, to add a command button we can use a similar structure
than the one we have seen earlier:
ActiveSheet.Shapes.AddFormControl
xlButtonControl, 20, 20, 100, 40
In this particular case we
can also use the Buttons.Add method directly. The following subroutine adds a command button to the active worksheet,
and assigns another procedure (ButtonAction) to be run when clicked.
Sub
AddButtonToWorksheet()
Dim
btn As Object
Set
btn = ActiveSheet.Buttons.Add(20, 20, 100, 40)
btn.OnAction = «ButtonAction»
End Sub
Sub
ButtonAction()
MsgBox «You have pressed the button»
End Sub
Select, copy, and delete shapes
We can select, copy, or delete a shape using
the corresponding methods of the Shape object, and specifying that particular
shape with either the number or name (as we have seen earlier).
ActiveSheet.Shapes(«Rectangle 1»).Select ‘selects Rectangle 1
ActiveSheet.Shapes(2).Select ‘selects
the second shape
ActiveSheet.Shapes.SelectAll ‘selects all shapes in the
active sheet
ActiveSheet.Shapes(«Rectangle 1»).Copy
ActiveSheet.Paste
ActiveSheet.Shapes(«Rectangle
1»).Delete
In order to copy or delete all shapes in the
worksheet we need to loop through all shapes using a For Each loop. If you are
not familiar with loops, please check the lesson 6 (Conditions and Loops) in
the training for beginners. The following example deletes all shapes in the
active worksheet:
Dim shp As Shape
For Each shp In ActiveSheet.Shapes
shp.Delete
Next shp
If we want to select and work with a subset of shapes (more
than just one), we have to construct a ShapeRange
collection that contains the shapes we want to work with. In the example below,
we select a rectangular shape (Rectangle 1) and a textbox (TextBox 2) through
an array of shapes. We can now work with those shapes and apply for example
formatting properties to both at the same time.
Dim ShpSubsetArray() As Variant
Dim ShpSubset As Object
ShpSubsetArray = Array(«Rectangle 1»,
«TextBox 2»)
Set ShpSubset =
ActiveSheet.Shapes.Range(ShpSubsetArray)
ShpSubset.Select
Format shapes
There are a bunch of properties to format
shapes in Excel VBA. We can specify the position in the worksheet with the Top
and Left properties as we have seen earlier. Similarly, we can set the width
and height of the shape with the respective properties of the Shape
object.
With ActiveSheet.Shapes(«Rectangle 1»)
.Top = 100
.Left = 100
.Width = 200
.Height = 120
End With
We can also change the aspect of the interior
and border of the shape. The following example changes the interior color of the
rectangle to blue and sets a thick red border around using the Fill and Line
properties.
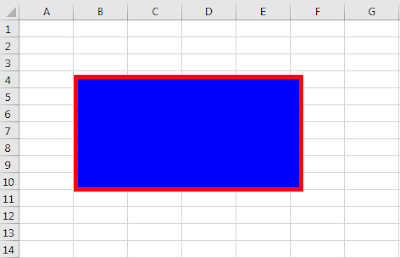
With ActiveSheet.Shapes(«Rectangle 1»)
.Fill.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(0, 0, 255)
.Line.ForeColor.RGB = RGB(255, 0, 0)
.Line.Weight = xlThick
End With
In order to add text to the shape we need to
use the TextFrame property. This may be particularly useful when dealing with
textboxes. We use the TextFrame.Characters method to add text, change font
properties, etc. The example below adds some text red and bold inside the
textbox.
With ActiveSheet.Shapes(«TextBox 2»)
With .TextFrame.Characters
.Text = «This is my textbox»
.Font.Color = vbRed
.Font.Bold = True
End With
End With
Other VBA Objects
Application
Workbook
Worksheet
WorksheetFunction
Range
Chart
Почему же не нужно? Представьте, что автофигура с размеров во весь лист, у неё TopLeftCell — это ячейка A1. Если не учитывать BottomRightCell, то в выделенном диапазонк B2:G20 её как бы и нет, но на самом деле она перекрывает все ячейки. Впрочем, «выбрать все рисунки в выделенном диапазоне ячеек» может иметь и иной смысл — Вам виднее.
Вот пример того, как загнать все объекты DrawingObjects заданного диапазона в коллекцию:
Sub Test()
Dim x, Rng As Range, Col As New Collection
Set Rng = Range(«B2:G20»)
For Each x In ActiveSheet.DrawingObjects
If Not Intersect(Range(x.TopLeftCell, x.BottomRightCell), Rng) Is Nothing Then
Debug.Print x.Name
Col.Add x
End If
Next
End Sub
А если кроме рисунков нужны ещё и автофигуры, то у прямоугольников, например, имена могут повторяться (вариант — при копировании), поэтому dic.Add x.Name, … не есть гуд 
В варианте же с коллекцией без ключа собираются все объекты, а не только с уникальными именами
Sub t()
Dim x, dic
Set dic = CreateObject(«scripting.dictionary»)
For Each x In ActiveSheet.DrawingObjects.ShapeRange
If Not Intersect(Selection, x.TopLeftCell) Is Nothing Then
dic.Add x.Name, x
End If
Next
ActiveSheet.Shapes.Range(dic.keys).Select
Set dic = Nothing
End Sub
Sub t()
Dim x, dic
On Error Resume Next
Set dic = CreateObject(«scripting.dictionary»)
For Each x In ActiveSheet.DrawingObjects.ShapeRange
If Not Intersect(Selection, x.TopLeftCell) Is Nothing Then
dic.Add x.DrawingObject.Index, 0
End If
Next
ActiveSheet.Shapes.Range(dic.keys).Select
Set dic = Nothing
End Sub
Почти то же самое, но без словаря и с учётом области пересечения по 2-м углам:
Sub tt()
Dim x, r As Range
Set r = ActiveWindow.RangeSelection
On Error Resume Next
For Each x In ActiveSheet.DrawingObjects.ShapeRange
If Not Intersect(Range(x.TopLeftCell, x.BottomRightCell), r) Is Nothing Then x.Select (False)
Next x
End Sub
Алексей, не понятно, зачем Вам нужно выделять картинки, обычно select — лишнее действие, если это не интерфесная необходимость, конечно.
Для коллекции приведу еще пример кода для общего случая, когда нужно хранить группу картинок в переменной ShpsRng для последующих групповых операций.
ShpsRng можно было бы объявить и вне процедуры на уровне модуля или глобально.
Sub SelectPictures()
‘ Выделение рисунков видимой области экрана
Dim a(), i&, n&
Dim Shp As Shape, Shps As Shapes, ShpsRng As ShapeRange, Rng As Range
Set Shps = ActiveSheet.Shapes
If Shps.Count = 0 Then Exit Sub
ReDim a(1 To Shps.Count)
Set Rng = Windows(1).VisibleRange
For i = 1 To Shps.Count
With Shps.Item(i)
If .Type = msoPicture Then
If Not Intersect(Range(.TopLeftCell, .BottomRightCell), Rng) Is Nothing Then
n = n + 1
a(n) = i
End If
End If
End With
Next
If n Then
ReDim Preserve a(1 To n)
Set ShpsRng = Shps.Range(a) ‘ ShpsRng может быть и глобальной
ShpsRng.Select ‘ <— для примера
End If
End Sub
Попытал разные варианты кода и всё-таки остановился на Володином (с ActiveWindow.RangeSelection). Так получается и короче, и немного корректнее: программа не отказывается работать если выбран не диапазон, а обрабатывает графические объекты, попадающие в диапазон, который был выбран до того, как выбран графический объект:
Private Sub Draws_In_Selection_Select() ‘ выделить все рисунки в выбранном диапазоне
Dim oDraw, rSel As Range
Set rSel = ActiveWindow.RangeSelection
For Each oDraw In ActiveSheet.DrawingObjects.ShapeRange
If Not Intersect(Range(oDraw.TopLeftCell, oDraw.BottomRightCell), rSel) Is Nothing Then oDraw.Select (False)
Next
End Sub
Меня вполне удовлетворил выбор с Shape.Select(False)
Не столько в конце-концов на листе шэйпов чтобы заметить медленность метода.
Поэтому оставил так:
Private Sub Draws_In_Selection_Select() ‘ выделить В ВЫБРАННОМ ДИАПАЗОНЕ все рисунки
Dim oDraw, rSel As Range
Set rSel = ActiveWindow.RangeSelection
For Each oDraw In ActiveSheet.DrawingObjects.ShapeRange
If Not Intersect(Range(oDraw.TopLeftCell, oDraw.BottomRightCell), rSel) Is Nothing Then oDraw.Select (False)
Next
End Sub
Ну и заодно по такому же принципу слепил макрос, выделяющий на листе все рисунки с нулевыми размерами (они остаются на листе после удаления строк/столбцов):
Private Sub Draws_0D_Select() ‘ выделить НА ЛИСТЕ все рисунки с нулевыми размерами
Dim oDraw As Shape
For Each oDraw In ActiveSheet.DrawingObjects.ShapeRange
If oDraw.Width = 0 Or oDraw.Height = 0 Then oDraw.Select (False)
Next
End Sub