1
Most scholars distinguish between the terms development
of
meaning (when
a new meaning and the one on the basis of which it is formed
coexist in the semantic structure of the word, as in mill,
carriage, etc.) and
change
of
meaning (when
the old meaning is completely replaced by the new one, as in the
noun meat
which
in Old English had the general meaning of «food» but in
Modern English is no longer used in that sense and has instead
developed the meaning «flesh of animals used as a food
product»).
The
second question we must answer in this chapter is how
new
meanings develop. To find the answer to this question we must
investigate the inner mechanism of this process, or at least its
essential features. Let us examine the examples given above from a
new angle, from within, so to speak.
Why
was it that the word mill
—
and not some other word — was selected to denote the first textile
factories? There must have been some connection between the
former sense of mill
and
the new phenomenon to which it was applied. And there was
apparently
such a connection. Mills which produced flour, were mainly driven by
water. The textile factories also firstly used water power. So, in
general terms, the meanings of mill,
both
the old and the new one, could be defined as «an establishment
using water power to produce certain goods». Thus, the
first textile factories were easily associated with mills producing
flour, and the new meaning of mill
appeared
due to this association. In actual fact, all cases of
development or change of meaning are based on some association. In
the history of the word carriage,
the
new travelling conveyance was also naturally associated in people’s
minds with the old one: horse-drawn vehicle > part of a railway
train. Both these objects were related to the idea of travelling.
The job of both, the horse-drawn carriage and the railway carriage,
is the same: to carry passengers on a journey. So the association
was logically well-founded.
Stalls
and
box
formed
their meanings in which they denoted parts of the theatre on the
basis of a different type of association. The meaning of the word
box
«a
small separate enclosure forming a part of the theatre»
developed on the basis of its former meaning «a rectangular
container used for packing or storing things». The two objects
became associated in the speakers’ minds because boxes in the
earliest English theatres really resembled packing cases. They
were enclosed on all sides and heavily curtained even on the side
facing the audience so as to conceal the privileged spectators
occupying them from curious or insolent stares.
The
association on which the theatrical meaning of stalls
was
based is even more curious. The original meaning was «compartments
in stables or sheds for the accommodation of animals (e. g. cows,
horses, etc.)’*.
There does not seem to be much in common between the privileged and
expensive part of a theatre and stables intended for cows and
horses, unless we take into consideration the fact that
theatres in olden times greatly differed from what they are now.
What is now known as the stalls
was,
at that time, standing space divided by barriers into sections so as
to prevent the enthusiastic crowd from knocking one other down and
hurting themselves. So, there must have been a certain outward
resemblance between theatre stalls and cattle stalls. It is also
possible that the word was first used humorously or satirically in
this new sense.
The
process of development of a new meaning (or a change of meaning) is
traditionally termed transference.
Some
scholars mistakenly use the term «transference of meaning»
which is a serious mistake. It is very important to note that in any
case of semantic change it is not the meaning but the word that is
being transferred from one referent onto another (e. g. from a
horse-drawn vehicle onto a railway car). The result of such a
transference is the appearance of a new meaning.
Two
types of transference are distinguishable depending on the two
types of logical associations underlying the semantic process.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Semantic change (also semantic shift, semantic progression, semantic development, or semantic drift) is a form of language change regarding the evolution of word usage—usually to the point that the modern meaning is radically different from the original usage. In diachronic (or historical) linguistics, semantic change is a change in one of the meanings of a word. Every word has a variety of senses and connotations, which can be added, removed, or altered over time, often to the extent that cognates across space and time have very different meanings. The study of semantic change can be seen as part of etymology, onomasiology, semasiology, and semantics.
Examples in English[edit]
- Awful — Literally «full of awe», originally meant «inspiring wonder (or fear)», hence «impressive». In contemporary usage, the word means «extremely bad».
- Awesome — Literally «awe-inducing», originally meant «inspiring wonder (or fear)», hence «impressive». In contemporary usage, the word means «extremely good».
- Terrible — Originally meant «inspiring terror», shifted to indicate anything spectacular, then to something spectacularly bad.
- Terrific — Originally meant «inspiring terror», shifted to indicate anything spectacular, then to something spectacularly good.[1]
- Nice — Originally meant «foolish, ignorant, frivolous, senseless.» from Old French nice (12c.) meaning «careless, clumsy; weak; poor, needy; simple, stupid, silly, foolish,» from Latin nescius («ignorant or unaware»). Literally «not-knowing,» from ne- «not» (from PIE root *ne- «not») + stem of scire «to know» (compare with science). «The sense development has been extraordinary, even for an adj.» [Weekley] — from «timid, faint-hearted» (pre-1300); to «fussy, fastidious» (late 14c.); to «dainty, delicate» (c. 1400); to «precise, careful» (1500s, preserved in such terms as a nice distinction and nice and early); to «agreeable, delightful» (1769); to «kind, thoughtful» (1830).
- Naïf or Naïve —Initially meant «natural, primitive, or native» . From French naïf, literally «native«. The masculine form of the French word, but used in English without reference to gender. As a noun, «natural, artless, naive person,» first attested 1893, from French, where Old French naif also meant «native inhabitant; simpleton, natural fool.»
- Demagogue — Originally meant «a popular leader». It is from the Greek dēmagōgós «leader of the people», from dēmos «people» + agōgós «leading, guiding». Now the word has strong connotations of a politician who panders to emotions and prejudice.
- Egregious — Originally described something that was remarkably good (as in Theorema Egregium). The word is from the Latin egregius «illustrious, select», literally, «standing out from the flock», which is from ex—»out of» + greg—(grex) «flock». Now it means something that is remarkably bad or flagrant.
- Gay — Originally meant (13th century) «lighthearted», «joyous» or (14th century) «bright and showy», it also came to mean «happy»; it acquired connotations of immorality as early as 1637, either sexual e.g., gay woman «prostitute», gay man «womaniser», gay house «brothel», or otherwise, e.g., gay dog «over-indulgent man» and gay deceiver «deceitful and lecherous». In the United States by 1897 the expression gay cat referred to a hobo, especially a younger hobo in the company of an older one; by 1935, it was used in prison slang for a homosexual boy; and by 1951, and clipped to gay, referred to homosexuals. George Chauncey, in his book Gay New York, would put this shift as early as the late 19th century among a certain «in crowd», knowledgeable of gay night-life. In the modern day, it is most often used to refer to homosexuals, at first among themselves and then in society at large, with a neutral connotation; or as a derogatory synonym for «silly», «dumb», or «boring».[2]
- Guy — Guy Fawkes was the alleged leader of a plot to blow up the English Houses of Parliament on 5 November 1605. The day was made a holiday, Guy Fawkes Day, commemorated by parading and burning a ragged manikin of Fawkes, known as a Guy. This led to the use of the word guy as a term for any «person of grotesque appearance» and then by the late 1800s—especially in the United States—for «any man», as in, e.g., «Some guy called for you.» Over the 20th century, guy has replaced fellow in the U.S., and, under the influence of American popular culture, has been gradually replacing fellow, bloke, chap and other such words throughout the rest of the English-speaking world. In the plural, it can refer to a mixture of genders (e.g., «Come on, you guys!» could be directed to a group of mixed gender instead of only men).
Evolution of types[edit]
A number of classification schemes have been suggested for semantic change.
Recent overviews have been presented by Blank[3] and Blank & Koch (1999). Semantic change has attracted academic discussions since ancient times, although the first major works emerged in the 19th century with Reisig (1839), Paul (1880), and Darmesteter (1887).[4] Studies beyond the analysis of single words have been started with the word-field analyses of Trier (1931), who claimed that every semantic change of a word would also affect all other words in a lexical field.[5] His approach was later refined by Coseriu (1964). Fritz (1974) introduced Generative semantics. More recent works including pragmatic and cognitive theories are those in Warren (1992), Dirk Geeraerts,[6] Traugott (1990) and Blank (1997).
A chronological list of typologies is presented below. Today, the most currently used typologies are those by Bloomfield (1933) and Blank (1999).
Typology by Reisig (1839)[edit]
Reisig’s ideas for a classification were published posthumously. He resorts to classical rhetorics and distinguishes between
- Synecdoche: shifts between part and whole
- Metonymy: shifts between cause and effect
- Metaphor
Typology by Paul (1880)[edit]
- Generalization: enlargement of single senses of a word’s meaning
- Specialization on a specific part of the contents: reduction of single senses of a word’s meaning
- Transfer on a notion linked to the based notion in a spatial, temporal, or causal way
Typology by Darmesteter (1887)[edit]
- Metaphor
- Metonymy
- Narrowing of meaning
- Widening of meaning
The last two are defined as change between whole and part, which would today be rendered as synecdoche.
Typology by Bréal (1899)[edit]
- Restriction of sense: change from a general to a special meaning
- Enlargement of sense: change from a special to a general meaning
- Metaphor
- «Thickening» of sense: change from an abstract to a concrete meaning
Typology by Stern (1931)[edit]
- Substitution: Change related to the change of an object, of the knowledge referring to the object, of the attitude toward the object, e.g., artillery «engines of war used to throw missiles» → «mounted guns», atom «inseparable smallest physical-chemical element» → «physical-chemical element consisting of electrons», scholasticism «philosophical system of the Middle Ages» → «servile adherence to the methods and teaching of schools»
- Analogy: Change triggered by the change of an associated word, e.g., fast adj. «fixed and rapid» ← faste adv. «fixedly, rapidly»)
- Shortening: e.g., periodical ← periodical paper
- Nomination: «the intentional naming of a referent, new or old, with a name that has not previously been used for it» (Stern 1931: 282), e.g., lion «brave man» ← «lion»
- Regular transfer: a subconscious Nomination
- Permutation: non-intentional shift of one referent to another due to a reinterpretation of a situation, e.g., bead «prayer» → «pearl in a rosary»)
- Adequation: Change in the attitude of a concept; distinction from substitution is unclear.
This classification does not neatly distinguish between processes and forces/causes of semantic change.
Typology by Bloomfield (1933)[edit]
The most widely accepted scheme in the English-speaking academic world[according to whom?] is from Bloomfield (1933):
- Narrowing: Change from superordinate level to subordinate level. For example, skyline formerly referred to any horizon, but now in the US it has narrowed to a horizon decorated by skyscrapers.[7]
- Widening: There are many examples of specific brand names being used for the general product, such as with Kleenex.[7] Such uses are known as generonyms: see genericization.
- Metaphor: Change based on similarity of thing. For example, broadcast originally meant «to cast seeds out»; with the advent of radio and television, the word was extended to indicate the transmission of audio and video signals. Outside of agricultural circles, very few use broadcast in the earlier sense.[7]
- Metonymy: Change based on nearness in space or time, e.g., jaw «cheek» → «mandible».
- Synecdoche: Change based on whole-part relation. The convention of using capital cities to represent countries or their governments is an example of this.
- Hyperbole: Change from weaker to stronger meaning, e.g., kill «torment» → «slaughter»
- Meiosis: Change from stronger to weaker meaning, e.g., astound «strike with thunder» → «surprise strongly».
- Degeneration: e.g., knave «boy» → «servant» → «deceitful or despicable man»; awful «awe-inspiring» → «very bad.»
- Elevation: e.g., knight «boy» → «nobleman»; terrific «terrifying» → «astonishing» → «very good».
Typology by Ullmann (1957, 1962)[edit]
Ullmann distinguishes between nature and consequences of semantic change:
- Nature of semantic change
- Metaphor: change based on a similarity of senses
- Metonymy: change based on a contiguity of senses
- Folk-etymology: change based on a similarity of names
- Ellipsis: change based on a contiguity of names
- Consequences of semantic change
- Widening of meaning: rise of quantity
- Narrowing of meaning: loss of quantity
- Amelioration of meaning: rise of quality
- Pejoration of meaning: loss of quality
Typology by Blank (1999)[edit]
However, the categorization of Blank (1999) has gained increasing acceptance:[8]
- Metaphor: Change based on similarity between concepts, e.g., mouse «rodent» → «computer device».
- Metonymy: Change based on contiguity between concepts, e.g., horn «animal horn» → «musical instrument».
- Synecdoche: A type of metonymy involving a part to whole relationship, e.g. «hands» from «all hands on deck» → «bodies»
- Specialization of meaning: Downward shift in a taxonomy, e.g., corn «grain» → «wheat» (UK), → «maize» (US).
- Generalization of meaning: Upward shift in a taxonomy, e.g., hoover «Hoover vacuum cleaner» → «any type of vacuum cleaner».
- Cohyponymic transfer: Horizontal shift in a taxonomy, e.g., the confusion of mouse and rat in some dialects.
- Antiphrasis: Change based on a contrastive aspect of the concepts, e.g., perfect lady in the sense of «prostitute».
- Auto-antonymy: Change of a word’s sense and concept to the complementary opposite, e.g., bad in the slang sense of «good».
- Auto-converse: Lexical expression of a relationship by the two extremes of the respective relationship, e.g., take in the dialectal use as «give».
- Ellipsis: Semantic change based on the contiguity of names, e.g., car «cart» → «automobile», due to the invention of the (motor) car.
- Folk-etymology: Semantic change based on the similarity of names, e.g., French contredanse, orig. English country dance.
Blank considered it problematic to include amelioration and pejoration of meaning (as in Ullman) as well as strengthening and weakening of meaning (as in Bloomfield). According to Blank, these are not objectively classifiable phenomena; moreover, Blank has argued that all of the examples listed under these headings can be grouped under other phenomena, rendering the categories redundant.
Forces triggering change[edit]
Blank[9] has tried to create a complete list of motivations for semantic change. They can be summarized as:
- Linguistic forces
- Psychological forces
- Sociocultural forces
- Cultural/encyclopedic forces
This list has been revised and slightly enlarged by Grzega (2004):[10]
- Fuzziness (i.e., difficulties in classifying the referent or attributing the right word to the referent, thus mixing up designations)
- Dominance of the prototype (i.e., fuzzy difference between superordinate and subordinate term due to the monopoly of the prototypical member of a category in the real world)
- Social reasons (i.e., contact situation with «undemarcation» effects)
- Institutional and non-institutional linguistic pre- and proscriptivism (i.e., legal and peer-group linguistic pre- and proscriptivism, aiming at «demarcation»)
- Flattery
- Insult
- Disguising language (i.e., «misnomers»)
- Taboo (i.e., taboo concepts)
- Aesthetic-formal reasons (i.e., avoidance of words that are phonetically similar or identical to negatively associated words)
- Communicative-formal reasons (i.e., abolition of the ambiguity of forms in context, keyword: «homonymic conflict and polysemic conflict»)
- Wordplay/punning
- Excessive length of words
- Morphological misinterpretation (keyword: «folk-etymology», creation of transparency by changes within a word)
- Logical-formal reasons (keyword: «lexical regularization», creation of consociation)
- Desire for plasticity (creation of a salient motivation of a name)
- Anthropological salience of a concept (i.e., anthropologically given emotionality of a concept, «natural salience»)
- Culture-induced salience of a concept («cultural importance»)
- Changes in the referents (i.e., changes in the world)
- Worldview change (i.e., changes in the categorization of the world)
- Prestige/fashion (based on the prestige of another language or variety, of certain word-formation patterns, or of certain semasiological centers of expansion)
The case of reappropriation[edit]
A specific case of semantic change is reappropriation, a cultural process by which a group reclaims words or artifacts that were previously used in a way disparaging of that group, for example like with the word queer. Other related processes include pejoration and amelioration.[11]
Practical studies[edit]
Apart from many individual studies, etymological dictionaries are prominent reference books for finding out about semantic changes. A recent survey lists practical tools and online systems for investigating semantic change of words over time.[12] WordEvolutionStudy is an academic platform that takes arbitrary words as input to generate summary views of their evolution based on Google Books ngram dataset and the Corpus of Historical American English.[13]
See also[edit]
- Calque
- Dead metaphor
- Euphemism treadmill
- False friend
- Genericized trademark
- Language change
- Lexicology and lexical semantics
- List of calques
- Newspeak
- Phono-semantic matching
- Q-based narrowing
- Semantic field
- Skunked term
- Retronym
Notes[edit]
- ^ «13 Words That Changed From Negative to Positive Meanings (or Vice Versa)». Mental Floss. July 9, 2015. Retrieved May 7, 2022.
- ^ Lalor, Therese (2007). «‘That’s So Gay’: A Contemporary Use of Gay in Australian English». Australian Journal of Linguistics. 27 (200): 147–173. doi:10.1080/07268600701522764. hdl:1885/30763. S2CID 53710541.
- ^ Blank (1997:7–46)
- ^ in Ullmann (1957), and Ullmann (1962)
- ^ An example of this comes from Old English: meat (or rather mete) referred to all forms of solid food while flesh (flæsc) referred to animal tissue and food (foda) referred to animal fodder; meat was eventually restricted to flesh of animals, then flesh restricted to the tissue of humans and food was generalized to refer to all forms of solid food Jeffers & Lehiste (1979:130)
- ^ in Geeraerts (1983) and Geeraerts (1997)
- ^ a b c Jeffers & Lehiste (1979:129)
- ^ Grzega (2004) paraphrases these categories (except ellipses and folk etymology) as «similar-to» relation, «neighbor-of» relation, «part-of» relation, «kind-of» relation (for both specialization and generalization), «sibling-of» relation, and «contrast-to» relation (for antiphrasis, auto-antonymy, and auto-converse), respectively
- ^ in Blank (1997) and Blank (1999)
- ^ Compare Grzega (2004) and Grzega & Schöner (2007)
- ^ Anne Curzan (May 8, 2014). Fixing English: Prescriptivism and Language History. Cambridge University Press. pp. 146–148. ISBN 978-1-107-02075-7.
- ^ Adam Jatowt, Nina Tahmasebi, Lars Borin (2021). Computational Approaches to Lexical Semantic Change: Visualization Systems and Novel Applications. Language Science Press. pp. 311–340.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Adam Jatowt (2018). «Every Word has its History: Interactive Exploration and Visualization of Word Sense Evolution» (PDF). ACM Press. pp. 1988–1902.
References[edit]
- Blank, Andreas (1997), Prinzipien des lexikalischen Bedeutungswandels am Beispiel der romanischen Sprachen (Beihefte zur Zeitschrift für romanische Philologie 285), Tübingen: Niemeyer
- Blank, Andreas (1999), «Why do new meanings occur? A cognitive typology of the motivations for lexical Semantic change», in Blank, Andreas; Koch, Peter (eds.), Historical Semantics and Cognition, Berlin/New York: Mouton de Gruyter, pp. 61–90
- Blank, Andreas; Koch, Peter (1999), «Introduction: Historical Semantics and Cognition», in Blank, Andreas; Koch, Peter (eds.), Historical Semantics and Cognition, Berlin/New York: Mouton de Gruyter, pp. 1–16
- Bloomfield, Leonard (1933), Language, New York: Allen & Unwin
- Bréal, Michel (1899), Essai de sémantique (2nd ed.), Paris: Hachette
- Coseriu, Eugenio (1964), «Pour une sémantique diachronique structurale», Travaux de Linguistique et de Littérature, 2: 139–186
- Darmesteter, Arsène (1887), La vie des mots, Paris: Delagrave
- Fritz, Gerd (1974), Bedeutungswandel im Deutschen, Tübingen: Niemeyer
- Geeraerts, Dirk (1983), «Reclassifying Semantic change», Quaderni di Semantica, 4: 217–240
- Geeraerts, Dirk (1997), Diachronic prototype Semantics: a contribution to historical lexicology, Oxford: Clarendon
- Grzega, Joachim (2004), Bezeichnungswandel: Wie, Warum, Wozu? Ein Beitrag zur englischen und allgemeinen Onomasiologie, Heidelberg: Winter
- Grzega, Joachim; Schöner, Marion (2007), English and general historical lexicology: materials for onomasiology seminars (PDF), Eichstätt: Universität
- Jeffers, Robert J.; Lehiste, Ilse (1979), Principles and methods for historical linguistics, MIT press, ISBN 0-262-60011-0
- Paul, Hermann (1880), Prinzipien der Sprachgeschichte, Tübingen: Niemeyer
- Reisig, Karl (1839), «Semasiologie oder Bedeutungslehre», in Haase, Friedrich (ed.), Professor Karl Reisigs Vorlesungen über lateinische Sprachwissenschaft, Leipzig: Lehnhold
- Stern, Gustaf (1931), Meaning and change of meaning with special reference to the English language, Göteborg: Elander
- Traugott, Elizabeth Closs (1990), «From less to more situated in language: the unidirectionality of Semantic change», in Adamson, Silvia; Law, Vivian A.; Vincent, Nigel; Wright, Susan (eds.), Papers from the Fifth International Conference on English Historical Linguistics, Amsterdam: Benjamins, pp. 496–517
- Trier, Jost (1931), Der deutsche Wortschatz im Sinnbezirk des Verstandes (dissertation)
- Ullmann, Stephen (1957), Principles of Semantics (2nd ed.), Oxford: Blackwell
- Ullmann, Stephen (1962), Semantics: An introduction to the science of meaning, Oxford: Blackwell
- Vanhove, Martine (2008), From Polysemy to Semantic change: Towards a Typology of Lexical Semantic Associations, Studies in Language Companion Series 106, Amsterdam, New York: Benjamins.
- Warren, Beatrice (1992), Sense Developments: A contrastive study of the development of slang senses and novel standard senses in English, [Acta Universitatis Stockholmiensis 80], Stockholm: Almqvist & Wiksell
- Zuckermann, Ghil’ad (2003), Language Contact and Lexical Enrichment in Israeli Hebrew. Palgrave Macmillan, ISBN 1-4039-1723-X.
Further reading[edit]
- AlBader, Yousuf B. (2015) «Semantic Innovation and Change in Kuwaiti Arabic: A Study of the Polysemy of Verbs»
- AlBader, Yousuf B. (2016) «From dašš l-ġōṣ to dašš twitar: Semantic Change in Kuwaiti Arabic»
- AlBader, Yousuf B. (2017) «Polysemy and Semantic Change in the Arabic Language and Dialects»
- Grzega, Joachim (2000), «Historical Semantics in the Light of Cognitive Linguistics: Aspects of a new reference book reviewed», Arbeiten aus Anglistik und Amerikanistik 25: 233–244.
- Koch, Peter (2002), «Lexical typology from a cognitive and linguistic point of view», in: Cruse, D. Alan et al. (eds.), Lexicology: An international handbook on the nature and structure of words and vocabularies/lexikologie: Ein internationales Handbuch zur Natur und Struktur von Wörtern und Wortschätzen, [Handbücher zur Sprach- und Kommunikationswissenschaft 21], Berlin/New York: Walter de Gruyter, vol. 1, 1142–1178.
- Wundt, Wilhelm (1912), Völkerpsychologie: Eine Untersuchung der Entwicklungsgesetze von Sprache, Mythus und Sitte, vol. 2,2: Die Sprache, Leipzig: Engelmann.
External links[edit]
- Onomasiology Online (internet platform by Joachim Grzega, Alfred Bammesberger and Marion Schöner, including a list of etymological dictionaries)
- Etymonline, Online Etymology Dictionary of the English language.
- Exploring Word Evolution An online analysis tool for studying evolution of any input words based on Google Books n-gram dataset and the Corpus of Historical American English (COHA).
Chapter 8 how words develop new meanings
It has been mentioned that the systems of meanings of polysemantic words evolve gradually. The older a word is, the better developed is its semantic structure. The normal pattern of a word’s semantic development is from monosemy to a simple semantic structure encompassing only two or three meanings, with a further movement to an increasingly more complex semantic structure.
In this chapter we shall have a closer look at the complicated processes by which words acquire new meanings.
There are two aspects to this problem, which can be generally described in the following way: a) Why should new meanings appear at all? What circumstances cause and stimulate their development? b) How does it happen? What is the nature of the very process of development of new meanings?
Let us deal with each of these questions in turn.
Causes of Development of New Meanings
The first group of causes is traditionally termed historical or extra-linguistic.
Different kinds of changes in a nation’s social life, in its culture, knowledge, technology, arts lead to gaps appearing in the vocabulary which beg to be filled. Newly created objects, new concepts and phenomena must be named. We already know of two ways for providing new names for newly created concepts:
making new words (word-building) and borrowing foreign ones. One more way of filling such vocabulary gaps is by applying some old word to a new object or notion.
When the first textile factories appeared in England, the old word mill was applied to these early industrial enterprises. In this way, mill (a Latin borrowing of the first century В. С.) added a new meaning to its former meaning «a building in which corn is ground into flour». The new meaning was «textile factory».
A similar case is the word carriage which had (and still has) the meaning «a vehicle drawn by horses», but, with the first appearance of railways in England, it received a new meaning, that of «a railway car».
The history of English nouns describing different parts of a theatre may also serve as a good illustration of how well-established words can be used to denote newly-created objects and phenomena. The words stalls, box, pit, circle had existed for a long time before the first theatres appeared in England. With their appearance, the gaps in the vocabulary were easily filled by these widely used words which, as a result, developed new meanings.1
New meanings can also be developed due to linguistic factors (the second group of causes).
Linguistically speaking, the development of new meanings, and also a complete change of meaning, may be caused through the influence of other words, mostly of synonyms.1
Let us consider the following examples.
The Old English verb steorfan meant «to perish». When the verb to die was borrowed from the Scandinavian, these two synonyms, which were very close in their meaning, collided, and, as a result, to starve gradually changed into its present meaning: «to die (or suffer) from hunger».
The history of the noun deer is essentially the same. In Old English (O. E. deor) it had a general meaning denoting any beast. In that meaning it collided with the borrowed word animal and changed its meaning to the modern one («a certain kind of beast», R. олень).
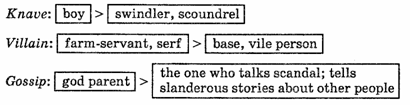
The noun knave (O. E. knafa) suffered an even more striking change of meaning as a result of collision with its synonym boy. Now it has a pronounced negative evaluative connotation and means «swindler, scoundrel».
The Process of Development and Change of Meaning
The second question we must answer in this chapter is how new meanings develop. To find the answer to this question we must investigate the inner mechanism of this process, or at least its essential features. Let us examine the examples given above from a new angle, from within, so to speak.
Why was it that the word mill — and not some other word — was selected to denote the first textile factories? There must have been some connection between the former sense of mill and the new phenomenon to which it was applied. And there was apparently such a connection. Mills which produced flour, were mainly driven by water. The textile factories also firstly used water power. So, in general terms, the meanings of mill, both the old and the new one, could be defined as «an establishment using water power to produce certain goods». Thus, the first textile factories were easily associated with mills producing flour, and the new meaning of mill appeared due to this association. In actual fact, all cases of development or change of meaning are based on some association. In the history of the word carriage, the new travelling conveyance was also naturally associated in people’s minds with the old one: horse-drawn vehicle > part of a railway train. Both these objects were related to the idea of travelling. The job of both, the horse-drawn carriage and the railway carriage, is the same: to carry passengers on a journey. So the association was logically well-founded.
Stalls and box formed their meanings in which they denoted parts of the theatre on the basis of a different type of association. The meaning of the word box «a small separate enclosure forming a part of the theatre» developed on the basis of its former meaning «a rectangular container used for packing or storing things». The two objects became associated in the speakers’ minds because boxes in the earliest English theatres really resembled packing cases. They were enclosed on all sides and heavily curtained even on the side facing the audience so as to conceal the privileged spectators occupying them from curious or insolent stares.
The association on which the theatrical meaning of stalls was based is even more curious. The original meaning was «compartments in stables or sheds for the accommodation of animals (e. g. cows, horses, etc.)», There does not seem to be much in common between the privileged and expensive part of a theatre and stables intended for cows and horses, unless we take into consideration the fact that theatres in olden times greatly differed from what they are now. What is now known as the stalls was, at that time, standing space divided by barriers into sections so as to prevent the enthusiastic crowd from knocking one other down and hurting themselves. So, there must have been a certain outward resemblance between theatre stalls and cattle stalls. It is also possible that the word was first used humorously or satirically in this new sense.
The process of development of a new meaning (or a change of meaning) is traditionally termed transference.
Some scholars mistakenly use the term «transference of meaning» which is a serious mistake. It is very important to note that in any case of semantic change it is not the meaning but the word that is being transferred from one referent onto another (e. g. from a horse-drawn vehicle onto a railway car). The result of such a transference is the appearance of a new meaning.
Two types of transference are distinguishable depending on the two types of logical associations underlying the semantic process.
Transference Based on Resemblance (Similarity)
This type of transference is also referred to as linguistic metaphor. A new meaning appears as a result of associating two objects (phenomena, qualities, etc.) due to their outward similarity. Box and stall, as should be clear from the explanations above, are examples of this type of transference.
Other examples can be given in which transference is also based on the association of two physical objects. The noun eye, for instance, has for one of its meanings «hole in the end of a needle» (cf. with the R. ушко иголки), which also developed through transference based on resemblance. A similar case is represented by the neck of a bottle.
The noun drop (mostly in the plural form) has, in addition to its main meaning «a small particle of water or other liquid», the meanings: «ear-rings shaped as drops of water» (e. g. diamond drops) and «candy of the same shape» (e. g. mint drops). It is quite obvious that both these meanings are also based on resemblance. In the compound word snowdrop the meaning of the second constituent underwent the same shift of meaning (also, in bluebell). In general, metaphorical change of meaning is often observed in idiomatic compounds.
The main meaning of the noun branch is «limb or subdivision of a tree or bush». On the basis of this meaning it developed several more. One of them is «a special field of science or art» (as in a branch of linguistics). This meaning brings us into the sphere of the abstract, and shows that in transference based on resemblance an association may be built not only between two physical objects, but also between a concrete object and an abstract concept.
The noun bar from the original meaning barrier developed a figurative meaning realized in such contexts as social bars, colour bar, racial bar. Here, again, as in the abstract meaning of branch, a concrete object is associated with an abstract concept.
The noun star on the basis of the meaning «heavenly body» developed the meaning «famous actor or actress». Nowadays the meaning has considerably widened its range, and the word is applied not only to screen idols (as it was at first), but, also, to popular sportsmen (e. g. football stars), pop-singers, etc. Of course, the first use of the word star to denote a popular actor must have been humorous or ironical: the mental picture created by the use of the word in this new meaning was a kind of semi-god surrounded by the bright rays of his glory. Yet, very soon the ironical colouring was lost, and, furthermore the association with the original meaning considerably weakened and is gradually erased.
The meanings formed through this type of transference are frequently found in the informal strata of the vocabulary, especially in slang (see Ch. 1). A red-headed boy is almost certain to be nicknamed carrot or ginger by his schoolmates, and the one who is given to spying and sneaking gets the derogatory nickname of rat. Both these meanings are metaphorical, though, of course, the children using them are quite unconscious of this fact.
The slang meanings of words such as nut, onion (= head), saucers (= eyes), hoofs (= feet) and very many others were all formed by transference based on resemblance.
Transference Based on Contiguity
Another term for this type of transference is linguistic metonymy. The association is based upon subtle psychological links between different objects and phenomena, sometimes traced and identified with much difficulty. The two objects may be associated together because they often appear in common situations, and so the image of one is easily accompanied by the image of the other; or they may be associated on the principle of cause and effect, of common function, of some material and an object which is made of it, etc.
Let us consider some cases of transference based on contiguity. You will notice that they are of different kinds.
The Old English adjective glad meant «bright, shining» (it was applied to the sun, to gold and precious stones, to shining armour, etc.). The later (and more modern) meaning «joyful» developed on the basis of the usual association (which is reflected in most languages) of light with joy (cf. with the R. светлое настроение; светло на душе).
The meaning of the adjective sad in Old English was «satisfied with food» (cf. with the R. сыт(ый) which is a word of the same Indo-European root). Later this meaning developed a connotation of a greater intensity of quality and came to mean «oversatisfied with food; having eaten too much». Thus, the meaning of the adjective sad developed a negative evaluative connotation and now described not a happy state of satisfaction but, on the contrary, the physical unease and discomfort of a person who has had too much to eat. The next shift of meaning was to transform the description of physical discomfort into one of spiritual discontent because these two states often go together. It was from this prosaic source that the modern meaning of sad «melancholy», «sorrowful» developed, and the adjective describes now a purely emotional state. The two previous meanings («satisfied with food» and «having eaten too much») were ousted from the semantic structure of the word long ago.
The foot of a bed is the place where the feet rest when one lies in the bed, but the foot of a mountain got its name by another association: the foot of a mountain is its lowest part, so that the association here is founded on common position.
By the arms of an arm-chair we mean the place where the arms lie when one is sitting in the chair, so that the type of association here is the same as in the foot of a bed. The leg of a bed (table, chair, etc.), though, is the part which serves as a support, the original meaning being «the leg of a man or animal». The association that lies behind this development of meaning is the common function: a piece of furniture is supported by its legs just as living beings are supported by theirs.
The meaning of the noun hand realized in the context hand of a clock (watch) originates from the main meaning of this noun «part of human body». It also developed due to the association of the common function:
the hand of a clock points to the figures on the face of the clock, and one of the functions of human hand is also that of pointing to things.
Another meaning of hand realized in such contexts as factory hands, farm hands is based on another kind of association: strong, skilful hands are the most important feature that is required of a person engaged in physical labour (cf. with the R. рабочие руки).
The adjective dull (see the scheme of its semantic structure in Ch. 7) developed its meaning «not clear or bright» (as in a dull green colour; dull light; dull shapes) on the basis of the former meaning «deficient in eyesight», and its meaning «not loud or distinct» (as in dull sounds) on the basis of the older meaning «deficient in hearing». The association here was obviously that of cause and effect: to a person with weak eyesight all colours appear pale, and all shapes blurred; to a person with deficient hearing all sounds are indistinct.
The main (and oldest registered) meaning of the noun board was «a flat and thin piece of wood; a wooden plank». On the basis of this meaning developed the meaning «table» which is now archaic. The association which underlay this semantic shift was that of the material and the object made from it: a wooden plank (or several planks) is an essential part of any table. This type of association is often found with nouns denoting clothes: e. g. a taffeta («dress made of taffeta»); a mink («mink coat»), a jersy («knitted shirt or sweater»).
Meanings produced through transference based on contiguity sometimes originate from geographical or proper names. China in the sense of «dishes made of porcelain» originated from the name of the country which was believed to be the birthplace of porcelain.
Tweed («a coarse wool cloth») got its name from the river Tweed and cheviot (another kind of wool cloth) from the Cheviot hills in England.
The name of a painter is frequently transferred onto one of his pictures: a Matisse = a painting by Matisse.1
Broadening (or Generalization) of Meaning.
Narrowing (or Specialization) of Meaning
Sometimes, the process of transference may result in a considerable change in range of meaning. For instance, the verb to arrive (French borrowing) began its life in English in the narrow meaning «to come to shore, to land». In Modern English it has greatly widened its combinability and developed the general meaning «to come» (e. g. to arrive in a village, town, city, country, at a hotel, hostel, college, theatre, place, etc.). The meaning developed through transference based on contiguity (the concept of coming somewhere is the same for both meanings), but the range of the second meaning is much broader.
Another example of the broadening of meaning is pipe. Its earliest recorded meaning was «a musical wind instrument». Nowadays it can denote any hollow oblong cylindrical body (e. g. water pipes). This meaning developed through transference based on the similarity of shape (pipe as a musical instrument is also a hollow oblong cylindrical object) which finally led to a considerable broadening of the range of meaning.
The word bird changed its meaning from «the young of a bird» to its modern meaning through transference based on contiguity (the association is obvious). The second meaning is broader and more general.
It is interesting to trace the history of the word girl as an example of the changes in the range of meaning in the course of the semantic development of a word.
In Middle English it had the meaning of «a small child of either sex». Then the word underwent the process of transference based on contiguity and developed the meaning of «a small child of the female sex», so that the range of meaning was somewhat narrowed. In its further semantic development the word gradually broadened its range of meaning. At first it came to denote not only a female child but, also, a young unmarried woman, later, any young woman, and in modern colloquial English it is practically synonymous to the noun woman (e. g. The old girl must be at least seventy), so that its range of meaning is quite broad.
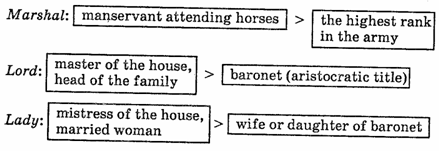
The history of the noun lady somewhat resembles that of girl. In Old English the word (hlxfdiZq)denoted the mistress of the house, i. e. any married woman. Later, a new meaning developed which was much narrower in range: «the wife or daughter of a baronet» (aristocratic title). In Modern English the word lady can be applied to any woman, so that its range of meaning is even broader than that of the O. E. hlxfdiZq. In Modern English the difference between girl and lady in the meaning of woman is that the first is used in colloquial style and sounds familiar whereas the second is more formal and polite. Here are some more examples of narrowing of meaning:
Deer: | any beast | > | a certain kind of beast |
Meat: | any food | > | a certain food product) |
Boy: | any young person of the male sex | > | servant of the male sex |
It should be pointed out once more that in all these words the second meaning developed through transference based on contiguity, and that when we speak of them as examples of narrowing of meaning we simply imply that the range of the second meaning is more narrow than that of the original meaning.
The So-called «Degeneration» («Degradation») and «Elevation» of Meaning
These terms are open to question because they seem to imply that meanings can become «better» or «worse» which is neither logical nor plausible. But, as a matter-of-fact, scholars using these terms do not actually mean the degeneration or elevation of meaning itself, but of the referent onto which a word is transferred, so that the term is inaccurate.
But let us try and see what really stands behind the examples of change of meaning which are traditionally given to illustrate degeneration and elevation of meaning.
I. «Degeneration» of meaning.
These examples show that the second meaning, in contrast with the one from which it developed, denotes a person of bad repute or character. Semantically speaking, the second meaning developed a negative evaluative connotation which was absent in the first meaning.
Such a readjustment in the connotative structure accompanying the process of transference can be sometimes observed in other parts of speech, and not only in nouns.
E. g. Silly: | happy | > | foolish |
II. «Elevation» of meaning.
Fond: | foolish] > | loving, affectionate |
Nice: | foolish] > | fine, good |
In these two cases the situation is reversed: the first meaning has a negative evaluative connotation, and the second meaning has not. It is difficult to see what is actually «elevated» here. Certainly, not the meaning of the word. Here are two more examples.
Tory: | brigand, highwayman | > | member of the Tories |
Knight: | manservant | > |»noble, courageous man]
In the case of Tory, the first meaning has a pronounced negative connotation which is absent in the second meaning. But why call it «elevation»? Semantically speaking, the first meaning is just as good as the second, and the difference lies only in the connotative structure.
The case of knight, if treated linguistically, is quite opposite to that of Tory: the second meaning acquired a positive evaluative connotation that was absent in the first meaning. So, here, once more, we are faced with a mere readjustment of the connotative components of the word.
There are also some traditional examples of «elevation» in which even this readjustment cannot be traced.
In these three words the second meaning developed due to the process of transference based on contiguity. Lord and lady are also examples of narrowing of meaning if we compare the range of the original and of the resultant meanings. No connotations of evaluation can be observed in either of the meanings. The fact that in all these three cases the original meaning denoted a humble ordinary person and the second denotes a person of high rank is absolutely extralinguistic.
All that has been said and the examples that have been given show that the terms «degradation» and «elevation» of meaning are imprecise and do not seem to be an objective reflection of the semantic phenomena they describe.
It would be more credible to state that some cases of transference based on contiguity may result in development or loss of evaluative connotations.
Exercises
I. Consider your answers to the following.
1. What causes the development of new meanings? Give examples.
2. What is the basis of development or change of meaning? Explain what we mean by the term transference.
3. What types of transference can you name?
4. What is meant by the widening and the narrowing of meaning?
5. Give examples of the so-called «degradation» and «elevation» of meaning. Why are these terms imprecise?
II. Read the following extracts and explain the semantic processes by which the italicized words acquired their meanings
1. ‘Bureau’, a desk, was borrowed from French in the 17thc. In Modern French (and English) it means not only the desk but also the office itself and the authority exercised by the office. Hence the familiar bureaucracy is likely to become increasingly familiar. The desk was called so because covered with bureau, a thick coarse cloth of a brown russet.
(From The Romance of Words by E. Weekley)
2. An Earl of Spencer made a short overcoat fashionable for some time. An Earl of Sandwich invented a form of light refreshment which enabled him to take a meal without leaving the card-table. Hence we have such words as spencer and sandwich in English.
(From The Romance of Words by E. Weekley)
3. A common name for overalls or trousers is jeans. In the singular jean is also a term for a durable twilled cotton and is short for the phrase jean fustian which first appeared in texts from the sixteenth century. Fustian (a Latin borrowing) is a cotton or cotton and linen fabric, and jean is the modern spelling of Middle English Jene or Gene, from Genes, the Middle French j name of the Italian city Genoa, where it was made and shipped abroad.
(From The Merriam-Webster Book of Word Histories)
4. Formally barn meant «a storehouse for barley»; today it has widened to mean «any kind of storehouse» for animals or equipment as well as any kind of grain. | The word picture used to refer only to a representation ;:: made with paint; today it can be a photograph or a representation made with charcoal, pencil or any other ; means. A pen used to mean «feather» but now has become generalized to include several kinds of writing implements — fountain, ballpoint, etc. The meaning of sail as limited to moving on water in a ship with sails has now generalized to mean «moving on water in any ship».
(From Teaching English Linguistically by J. Malmstrom, J. Lee)
III. Read the following extract and criticize the author’s treatment of the examples. Provide your own explanations.
Words degenerate in meaning also. In the past villain meant «farm labourer»; counterfeiter meant «imitator» without criminal connotations, and sly meant «skilful». A knave meant a «boy» and immoral meant «not customary», and hussy was a «housewife».
Other words improve in meanings. Governor meant «pilot» and constable meant «stable attendant». Other elevations are enthusiasm which formally meant «fanaticism», knight which used to mean «youth», angel which simply meant «messenger» and pretty which meant «sly». No one can predict the direction of change of meaning, but changes occur constantly.
(From Teaching English Linguistically by J. Malmstrom, J. Lee)
IV. Explain the logical associations in the following groups of meaning for the same words. Define the type of transference which has taken place.
1. The wing of a bird — the wing of a building; the eye of a man — the eye of a needle; the hand of a child — the hand of a clock; the heart of a man — the heart of the matter; the bridge across-the-river — the bridge of the nose; the tongue of a person — the tongue of a bell; the tooth of a boy — the tooth of a comb; the coat of a girl — the coat of a dog.
2. Green grass — green years; black shoes — black despair; nickel (metal) — a nickel (coin); glass — a glass; copper (metal) — a copper (coin); Ford (proper name) — a Ford (car); Damascus (town in Syria) — damask; Kashmir (town in North India) — cashmere.
V. Analyse the process of development of new meanings in the italicized words in the examples given below.
1.I put the letter well into the mouth of the box and let it go and it fell turning over and over like an autumn leaf. 2. Those v/ho had been the head of the line paused momentarily on entry and looked around curiously. 3. A cheerful-looking girl in blue jeans came up to the stairs whistling. 4. Seated behind a desk, he wore a light patterned suit, switch from his usual tweeds. 5. Oh, Steven, I read a Dickens the other day. It was awfully funny. 6. They sat on the rug before the fireplace, savouring its warmth, watching the rising tongues of flame. 7. He inspired universal confidence and had an iron nerve. 8. A very small boy in a green jersey with light red hair cut square across his forehead was peering at Steven between the electric fire and the side of the fireplace. 9. While the others were settling down, Lucy saw Pearson take another bite from his sandwich. 10. As I walked nonchalantly past Hugo’s house on the other side they were already carrying out the Renoirs.
VI. Explain the basis for the following jokes. Trace the logical associations between the different meanings of the same word.
1. Father was explaining to his little son the fundamentals of astronomy.
«That’s a comet.»
«A what?»
«A comet. You know what a comet is?» «No.»
«Don’t you know what they call a star with a tail?»
«Sure — Mickey Mouse.»
2. «Pa, what branches did you take when you went to school?»
«I never went to high school, son, but when I attended the little log school-house they used mostly hickory and beech and willow.»
3. What has eyes yet never sees? (Potato)
4. H e (in telephone booth)’. I want a box for two.
Voice (at the other end): Sorry, but we don’t have boxes for two.
He: But aren’t you the box office of the theatre? Voice: No, we are the undertakers.
VII. In the examples given below identify the eases of widening and narrowing of meaning.
1. While the others waited the elderly executive filled his pipe and lit it. 2. Finn was watching the birds. 3. The two girls took hold of one another, one acting gentleman, the other lady; three or four more pairs of girls immediately joined them and began a waltz. 4. He was informed that the president had not arrived at the bank, but was on his way. 5. Smokey had followed a dictum all his life: If you want a woman to stick beside you, pick an ugly one. Ugly ones stay to slice the meat and stir the gravy.
VIII. Have the italicized words evaluative connotations in their meanings? Motivate your answer and comment on the history of the words.
1. The directors now assembling were admirals and field marshals of commerce. 2. For a businessman to be invited to serve on a top-flight bank board is roughly equivalent to being knighted by the British Queen. 3.1 had a nice newsy gossip with Mrs. Needham before you turned up last night. 4. The little half-starved guy looked more a victim than a. villain. 5. Meanwhile I nodded my head vigorously and directed a happy smile in the direction of the two ladies. 6.1 shook hands with Tom; it seemed silly not to, for I felt suddenly as though I were talking to a child.
IX. Read the following. Find examples of «degeneration» and «elevation» of meaning. Comment on the history of the words.
1. King Arthur invented Conferences because he was secretly a Weak King and liked to know what his memorable thousand and one knights wanted to do next. As they were all jealous knights he had to have the memorable Round Table made to have the Conferences at, so that it was impossible to say which was top knight.
(From 1066 and All That by C. W. Sellar, R. J. Yeatman)
2. Alf: Where are you going, Ted?
Ted: Fishing at the old mill.
Alf: But what about school?
Ted: Don’t be silly. There aren’t any fish there!
X. Try your hand at the following scientific research. Write a short essay on the development of the meanings of three of the following words. Try to explain each shift of meaning. Use «The Shorter Oxford Dictionary» or «The Merriam-Webster Book of Word Histories».
Fee, cattle, school, pupil, nice, pen, gossip, coquette, biscuit, apron, merry, silly, doom, duke, pretty, yankee.