Find and replace text
-
Go to Home > Replace.
-
Enter the word or phrase you want to replace in Find what.
-
Enter your new text in Replace with.
-
Choose Replace All to change all occurrences of the word or phrase. Or, select Find Next until you find the one you want to update, and then choose Replace.
-
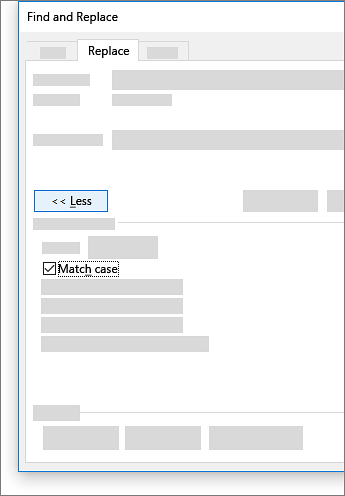
To specify only upper or lowercase in your search, select More > Match case. There are several other ways to search in this menu.
For other options, see Find and replace text
Find and replace basic text
In the upper-right corner of the document, in the search box 
To replace found text:
-
Select the magnifying glass, and then select Replace.
-
In the Replace With box, type the replacement text.
-
Select Replace All or Replace.
Tips:
-
You can also open the basic Find and Replace pane with the keyboard shortcut CONTROL + H.
-
When you replace text, it’s a good idea to select Replace instead of Replace All. That way you can review each item before replacing it.
-
You can find text with special formatting, such as bold or highlight, by using the Format menu.
-
Select View > Navigation Pane.
-
In the Navigation Pane, select the magnifying glass.
-
Select Settings
, and then select Advanced Find & Replace.
Notes:
-
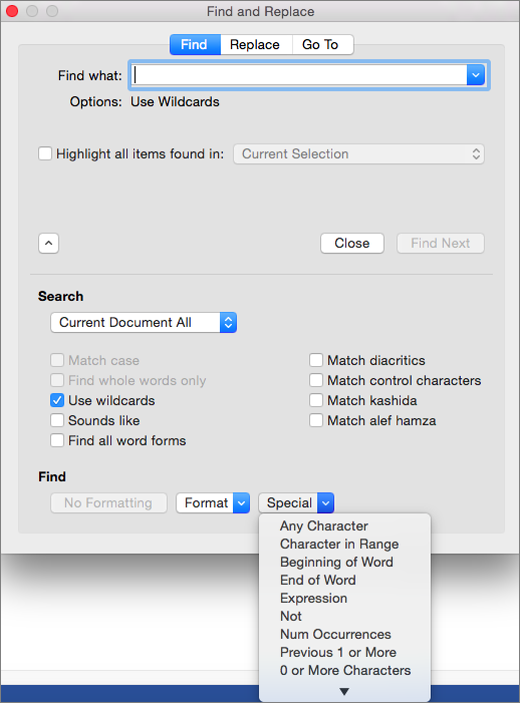
Select the arrow at the bottom of the Find and Replace dialog box to show all options.
-
-
-
On the Format menu, select the option that you want.
If a second dialog box opens, select the options that you want, and then select OK.
-
In the Find and Replace dialog box, select Find Next or Find All.
You can find and replace text with special formatting, such as bold or highlight, by using the Format menu.
-
Select View > Navigation Pane.
-
In the Navigation Pane, select the magnifying glass.
-
Select Settings
, and then select Advanced Find & Replace.
-
At the top of the dialog box, select Replace.
Notes:
-
Select the arrow at the bottom of the Find and Replace dialog box to show all options.
-
-
-
On the Find what box, type the text that you want to find.
-
On the Format menu, select the formatting that you want to find.
If a second dialog box opens, select the options that you want, and then select OK.
-
Select in the box next to Replace with.
-
On the Format menu, select the replacement formatting. If a second dialog box appears, select the formats that you want, and then select OK.
-
Select Replace, Replace All, or Find Next.
-
Select View > Navigation Pane.
-
In the Navigation Pane, select the magnifying glass.
-
Select Settings
, and then select Advanced Find & Replace.
Notes:
-
Select the arrow at the bottom of the Find and Replace dialog box to show all options.
-
-
-
On the Special menu, select the special character that you want to find.
-
Select Find Next.
-
Select View > Navigation Pane.
-
In the Navigation Pane, select the magnifying glass.
-
Select Settings
, and then select Advanced Find & Replace.
Notes:
-
Select the arrow at the bottom of the Find and Replace dialog box to show all options.
-
-
-
At the top of the Find and Replace dialog box, select Replace and then select in the Find What box, but don’t type anything there. Later, when you select a special character, Word will automatically put the character code in the box for you.
Note: Select the arrow at the bottom of the Find and Replace dialog box to show all options.
-
On the Special menu, select the special character that you want to find.
-
Select in the Replace with box.
-
On the Special menu, select the special character that you want to use as a replacement.
-
Select Replace or Find Next.
-
Select View > Navigation Pane.
-
In the Navigation Pane, select the magnifying glass.
-
Select Settings
, and then select Advanced Find & Replace.
-
Select the Use wildcards check box.
If you don’t see the Use wildcards check box, select
.
-
Select the Special menu, select a wildcard character, and then type any additional text in the Find what box.
-
Select Find Next.
Tips:
-
To cancel a search in progress, press
+ PERIOD.
-
You can also enter a wildcard character directly in the Find what box instead of selecting an item from the Special pop-up menu.
-
To search for a character that’s defined as a wildcard character, type a backslash () before the character. For example, type ? to find a question mark.
-
You can use parentheses to group the wildcard characters and text and to indicate the order of evaluation. For example, search for <(pre)*(ed)> to find «presorted» and «prevented.»
-
You can search for an expression and use the n wildcard character to replace the search string with the rearranged expression. For example, type (Newman) (Belinda) in the Find what box and 2 1 in the Replace with box. Word will find «Newman Belinda» and replace it with «Belinda Newman.»
-
-
To replace found text:
-
Select the Replace tab, and then select the Replace with box.
-
Select Special, select a wildcard character, and then type any additional text in the Replace with box.
-
Select Replace All, Replace, or Find Next.
Tip: When you replace text, it’s a good idea to select Replace instead of Replace All. That way you can confirm each replacement to make sure that it’s correct.
-
You can refine a search by using any of the following wildcard characters.
|
To find |
Use this |
For example |
|---|---|---|
|
Any single character |
? |
s?t finds «sat» and «set.» |
|
Any string of characters |
* |
s*d finds «sad» and «started.» |
|
One of the specified characters |
[ ] |
w[io]n finds «win» and «won.» |
|
Any single character in this range |
[-] |
[r-t]ight finds «right» and «sight» and «tight.» Ranges must be in ascending order. |
|
Any single character except the characters inside the brackets |
[!] |
m[!a]st finds «mist» and «most» but not «mast.» |
|
Any single character except characters in the range inside the brackets |
[!x-z] |
t[!a-m]ck finds «tock» and «tuck» but not «tack» or «tick.» Ranges must be in ascending order. |
|
Exactly n occurrences of a character or expression |
{ n} |
fe{2}d finds «feed» but not «fed.» |
|
At least n occurrences of a character or expression |
{ n,} |
fe{1,}d finds «fed» and «feed.» |
|
A range of occurrences of a character or expression |
{ n, n} |
10{1,3} finds «10,» «100,» and «1000.» |
|
One or more occurrences of a character or expression |
@ |
lo@t finds «lot» and «loot.» |
|
The beginning of a word |
< |
<(inter) finds «interesting» and «intercept» but not «splintered.» |
|
The end of a word |
> |
(in)> finds «in» and «within,» but not «interesting.» |
Word for the web lets you find and replace basic text. You can match case or fine whole words only. For more varied options, open your document in Word for the desktop.
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
Aiseo chrome | Rewrite like a pro, everywhere you write
X
Choose source
language
Import From URL
Advanced
Standard
Shorten
Shorten is a Premium Feature
Make any sentence shorter with the Shorten operator.
Expand
Expand is a Premium Feature
Make any sentence longer with the Expand operator.
Simplify
Simplify Tone is a Premium Feature
This tone would focus on paraphrasing and making the text easier to understand for a general audience
Bypass AI

Bypass
is Premium Feature
Evade AI detection and create unique content with the Bypass AI operator.
Creative
Creative tone is a premium feature
Paraphrases text with the most inventiveness and
expression with Creative tone operator.
new
Limit is 900 characters for free accounts. To get 40K characters limit
subscripe to
scale
Characters Count
—
Word Count
—
—
Goals
Adjust Goals
0 of 4 set
Choose target
language
Uploaded Successfully!
Show similarity
Open in editor
Word Count
—
Uniqueness
—
Coming soon These text tools are on the way
Calculate Levenstein Distance
Find Levenstein distance of two text fragments.
Tokenize Text
Create a list of all words in text.
Lemmatize Text
Lemmatize all words in text.
Stem Words in Text
Apply stemming to all words in text.
Color Symbols in Text
Add color to punctuation symbols in text.
Color Letters in Text
Add color to letters in text.
Color Words in Text
Add color to words in text.
Color Sentences in Text
Add color to sentences in text.
Color Paragraphs in Text
Add color to paragraphs in text.
Generate Glitch Text
Mess up characters in your text.
Generate Random Text
Generate text using random words.
Generate Lorem Ipsum Text
Generate lorem ipsum placeholder text.
Create a Crossword Puzzle
Generate a crossword puzzle from the given words.
Convert Text to Code Points
Convert text characters to their corresponding code points.
Convert Code Points to Text
Convert numeric character code points to text.
Convert CSV to Text Columns
Convert CSV data to plain text columns.
Convert Text Columns to CSV
Convert plain text columns to a CSV file.
Generate Text Trigrams
Create a list of all 3-grams.
Generate Text Skip-grams
Create a list of all n-skip-m-grams.
Convert Text to a Number
Encode the entire text to a single number.
Convert a Number to Text
Decode text that was encoded as a number back to text.
Chunkify Text
Divide text into chunks of certain size.
Format Text
Apply formatting and modification functions to text.
Find the Number of Symbols in Text
Count the number of punctuation marks and other sybmols in text.
Find the Number of Letters in Text
Count the number of letters in text.
Find the Number of Sentences in Text
Count the number of sentences in text.
Find the Number of Paragraphs in Text
Count the number of paragraphs in text.
Statistical Text Analysis
Analyze text for most frequent letters, words, and phrases.
Find Patterns in Text
Analyze text for interesting patterns.
Add Diacritics to Text
Add accent marks to text letters.
Enumerate Letters
Add a counter before every letter in text.
Enumerate Words
Add a counter before every word in text.
Enumerate Sentences
Add a counter before every sentence in text.
Enumerate Paragraphs
Add a counter before every paragraph in text.
Interweave Text Fragments
Interleave the letters or words of the given text fragments.
Randomize Letter Spacing
Mess up the spacing between letters in any text.
Find All Email Addresses in Text
Extract all emails from text.
Find All Web Addresses in Text
Extract all URLs from text.
Find All Numbers in Text
Extract all numbers from text.
Find All Countries in Text
Extract all countries from text.
Find All Cities in Text
Extract all cities from text.
Encode Text to Punycode
Convert text to punycode.
Decode Punycode to Text
Convert punycode to text.
Convert Text to Baudot Code
Encode text to Baudot encoding.
Convert Baudot Code to Text
Decode Baudot-encoded text.
Convert Text to Base32
Encode text to base32 encoding.
Convert Base32 to Text
Decode base32-encoded text.
Convert Text to Base45
Encode text to base45 encoding.
Convert Base45 to Text
Decode base45-encoded text.
Convert Text to Base58
Encode text to base58 encoding.
Convert Base58 to Text
Decode base58-encoded text.
Convert Text to Base85
Encode text to Ascii85 encoding.
Convert Base85 to Text
Decode Ascii85-encoded text.
Convert Text to Base65536
Encode text to base65536 encoding.
Convert Base65536 to Text
Decode base65536-encoded text.
Convert Text to Nettext
Encode text to nettext encoding.
Convert Nettext to Text
Decode nettext-encoded text.
Convert Text to Speech
Convert written text into natural sounding voice.
Convert Speech to Text
Convert a voice recording to text.
UTF8-encode Text
Encode text to UTF8 encoding.
UTF8-decode Text
Decode UTF8-encoded text.
UTF16-encode Text
Encode text to UTF16 encoding.
UTF16-decode Text
Decode UTF8-encoded text.
UTF32-encode Text
Encode text to UTF32 encoding.
UTF32-decode Text
Decode UTF32-encoded text.
Uuencode Text
Convert text to Unix-to-Unix encoding.
Uudecode Text
Decode Unix-to-Unix-encoded text.
Xxencode Text
Convert text to Xxencoding.
Convert Text to Quoted Printable
Encode text to QP encoding.
Convert Quoted Printable to Text
Strip HTML Tags from Text
Remove all HTML tags from Text.
Strip XML Tags from Text
Remove all XML tags from Text.
Remove Carriage Returns from Text
Remove new line symbols from the end of each text line.
Compare Text
Find the difference between two text fragments.
Create Text Typos
Generate various text typos.
Create a Mirror Copy of Text
Generate a mirror reflection of text.
Grep Text
Grep text for regular expression matches.
Head Text
Extract first symbols, words, or lines from text.
Tail Text
Extract last symbols, words, or lines from text
Generate Text Mnemonic
Return the first letter of each word in text.
Duplicate Sentences in Text
Make every sentence to be two sentences in the given text.
Remove Sentences from Text
Delete certain sentences from text.
Duplicate Paragraphs in Text
Make every paragraph to be two paragraphs in the given text.
Create a Word Cloud
Create an image from all words in text.
Create a Letter Circle
Create a circle from all letters in text.
Create a Letter Spiral
Create a spiral from all letters in text.
Create a Word Circle
Create a circle from all words in text.
Create a Letter Matrix
Create a matrix of any dimensions from letters in text.
Create a Word Matrix
Create a matrix of any dimensions from words in text.
Create a Word Spiral
Create a spiral from all words in text.
Split Words into Syllables
Split the input text into syllables.
Draw LCD Text
Write any text on an LCD display (with LCD font).
Draw a 2D Text
Convert text to 2-dimensional drawing.
Draw a 3D Text
Convert text to 3-dimensional drawing.
Create a Text Marquee
Create a horizontally or vertically scrolling text.
Animate Text
Create a GIF animation of a text message.
Slowly Reveal Text Message
Create a GIF animation that slowly reveals a text message.
Mojibake Text
Decode text using the wrong encoding and create garbled text.
Unbake Mojibaked Text
Try to find original text from garbled mojibaked text.
Obfuscate Text
Make text harder to read.
Print the Alphabet
Generate the entire alphabet from a to z.
Randomize the Alphabet
Print the alphabet in random order.
Scramble Text
Make text barely readable.
Remove Curse Words from Text
Delete swear words from text.
Edit Text
Edit text in a neat browser-based editor.
I came across this variation of edit-distance problem:
Design an algorithm which transforms a source word to a target word. for example: from head to tail, in each step, you just can replace one character, and the word must be valid. You’ll be given a dictionary.
It clearly is a variation of the edit distance problem, but in edit distance I do not care about if the word is valid or not. So how do I add this requirement to edit distance.
asked Feb 5, 2010 at 7:02
This can be modelled as a graph problem. You can think of the words as nodes of the graph and two nodes are connected if and only if they are of same length and differ in one char.
You can preprocess the dictionary and create this graph, should look like:
stack jack
| |
| |
smack back -- pack -- pick
You can then have a mapping from the word to the node representing the word, for this you can use a hash table, height balanced BST …
Once you have the above mapping in place, all you have to do is see if there exists a path between the two graph nodes, which can easily be done using BFS or DFS.
So you can summarize the algorithm as:
preprocess the dictionary and create the graph.
Given the two inputs words w1 and w2
if length(w1) != length(w2)
Not possible to convert
else
n1 = get_node(w1)
n2 = get_node(w2)
if(path_exists(n1,n2))
Possible and nodes in the path represent intermediary words
else
Not possible
answered Feb 5, 2010 at 7:05
codaddictcodaddict
442k81 gold badges490 silver badges528 bronze badges
6
codaddict’s graph approach is valid, though it takes O(n^2) time to build each graph, where n is the number of words of a given length. If that’s a problem, you can build a bk-tree much more efficiently, which makes it possible to find all words with a given edit distance (in this case, 1) of a target word.
answered Feb 8, 2010 at 10:38
Nick JohnsonNick Johnson
101k16 gold badges128 silver badges198 bronze badges
4
Create a graph with each node representing word in the dictionary. Add an edge between two word nodes, if their corresponding words are at edit distance of 1. Then minimum number of transformations required would length of shortest path between source node and destination node.
answered Apr 16, 2013 at 0:30
prasadvkprasadvk
1,5682 gold badges13 silver badges13 bronze badges
You could simply use recursive back-tracking but this is far from the most optimal solution.
# Given two words of equal length that are in a dictionary, write a method to transform one word into another word by changing only
# one letter at a time. The new word you get in each step must be in the
# dictionary.
# def transform(english_words, start, end):
# transform(english_words, 'damp', 'like')
# ['damp', 'lamp', 'limp', 'lime', 'like']
# ['damp', 'camp', 'came', 'lame', 'lime', 'like']
def is_diff_one(str1, str2):
if len(str1) != len(str2):
return False
count = 0
for i in range(0, len(str1)):
if str1[i] != str2[i]:
count = count + 1
if count == 1:
return True
return False
potential_ans = []
def transform(english_words, start, end, count):
global potential_ans
if count == 0:
count = count + 1
potential_ans = [start]
if start == end:
print potential_ans
return potential_ans
for w in english_words:
if is_diff_one(w, start) and w not in potential_ans:
potential_ans.append(w)
transform(english_words, w, end, count)
potential_ans[:-1]
return None
english_words = set(['damp', 'camp', 'came', 'lame', 'lime', 'like'])
transform(english_words, 'damp', 'lame', 0)
answered Oct 16, 2015 at 21:12
I don’t think this is edit distance.
I think this can be done using a graph. Just construct a graph from your dictionary, and attempt to navigate using your favorite graph traversal algorithm to the destination.
answered Feb 5, 2010 at 7:05
YuliyYuliy
17.3k6 gold badges41 silver badges47 bronze badges
@Codeaddict solution is correct but it misses on the opportunity to simplify and optimize the solution.
DFS vs BFS:
If we go with DFS, there are chances that we meet target string (or to_string) far deeper in the graph. Then we have to keep track of the levels at which it is found and the reference to that node, and finally find the minimum level possible and then trace it from root.
For example, consider this conversion from -> zoom:
from
/
fram foom
/ /
dram drom [zoom] food << To traverse upto this level is enough
... | ...
doom
|
[zoom]
Using BFS, we can simplify this process by a great deal. All we need to do is :
- Start with
fromstring at level0. Add this string tovisitedSetOfStrings. - Add non-visited valid strings to next level which are at edit distance +1 from the strings of current level.
- Add all these strings to
visitedSetOfStrings. - If this set contains the
targetstring, stop further processing of nodes/strings. Otherwise continue to step 2.
To make the path tracing easier, we can add extra information of parent string in each node.
answered Sep 11, 2020 at 7:21
Saurav SahuSaurav Sahu
12.7k5 gold badges60 silver badges78 bronze badges
1
This is C# code to solve the problem using BFS:
//use a hash set for a fast check if a word is already in the dictionary
static HashSet<string> Dictionary = new HashSet<string>();
//dictionary used to find the parent in every node in the graph and to avoid traversing an already traversed node
static Dictionary<string, string> parents = new Dictionary<string, string>();
public static List<string> FindPath(List<string> input, string start, string end)
{
char[] allcharacters = {'a','b','c','d','e','f','g','h','i','j','k','l','m','n','o','p','q','r','s','t','u','v','w','x','y','z'};
foreach (string s in input)
Dictionary.Add(s);
List<string> currentFrontier = new List<string>();
List<string> nextFrontier = new List<string>();
currentFrontier.Add(start);
while (currentFrontier.Count > 0)
{
foreach (string s in currentFrontier)
{
for (int i = 0; i < s.Length; i++)
{
foreach (char c in allcharacters)
{
StringBuilder newWordBuilder = new StringBuilder(s);
newWordBuilder[i] = c;
string newWord = newWordBuilder.ToString();
if (Dictionary.Contains(newWord))
{
//avoid traversing a previously traversed node
if (!parents.Keys.Contains(newWord))
{
parents.Add(newWord.ToString(), s);
nextFrontier.Add(newWord);
}
}
if (newWord.ToString() == end)
{
return ExtractPath(start, end);
}
}
}
}
currentFrontier.Clear();
currentFrontier.Concat(nextFrontier);
nextFrontier.Clear();
}
throw new ArgumentException("The given dictionary cannot be used to get a path from start to end");
}
private static List<string> ExtractPath(string start,string end)
{
List<string> path = new List<string>();
string current = end;
path.Add(end);
while (current != start)
{
current = parents[current];
path.Add(current);
}
path.Reverse();
return path;
}
answered Apr 10, 2014 at 20:18
I don’t think we need graph or some other complicated data structure. My idea is to load the dictionary as a HashSet and use contains() method to find out if the word exists in the dictionary or not.
Please, check this pseudocode to see my idea:
Two words are given: START and STOP.
//List is our "way" from words START to STOP, so, we add the original word to it first.
list.add(START);
//Finish to change the word when START equals STOP.
while(!START.equals(STOP))
//Change each letter at START to the letter to STOP one by one and check if such word exists.
for (int i = 0, i<STOP.length, i++){
char temp = START[i];
START[i] = STOP[i];
//If the word exists add a new word to the list of results.
//And change another letter in the new word with the next pass of the loop.
if dictionary.contains(START)
list.add(START)
//If the word doesn't exist, leave it like it was and try to change another letter with the next pass of the loop.
else START[i] = temp;}
return list;
As I understand my code should work like that:
Input: DAMP, LIKE
Output: DAMP, LAMP, LIMP, LIME, LIKE
Input: BACK, PICK
Output: BACK, PACK, PICK
Regolith
2,9349 gold badges33 silver badges50 bronze badges
answered Dec 5, 2017 at 7:38
Boris Boris
3841 gold badge6 silver badges20 bronze badges
2
class Solution {
//static int ans=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
HashMap<String,Integer> h=new HashMap<String,Integer>();
HashMap<String,Integer> h1=new HashMap<String,Integer>();
for(int i=0;i<wordList.size();i++)
{
h1.put(wordList.get(i),1);
}
int count=0;
Queue<String> q=new LinkedList<String>();
q.add(beginWord);
q.add("-1");
h.put(beginWord,1);
int ans=ladderLengthUtil(beginWord,endWord,wordList,h,count,q,h1);
return ans;
}
public int ladderLengthUtil(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList,HashMap<String,Integer> h,int count,Queue<String> q,HashMap<String,Integer> h1)
{
int ans=1;
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
String s=q.peek();
q.poll();
if(s.equals(endWord))
{
return ans;
}
else if(s.equals("-1"))
{
if(q.isEmpty())
{
break;
}
ans++;
q.add("-1");
}
else
{
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<26;j++)
{
char a=(char)('a'+j);
String s1=s.substring(0,i)+a+s.substring(i+1);
//System.out.println("s1 is "+s1);
if(h1.containsKey(s1)&&!h.containsKey(s1))
{
h.put(s1,1);
q.add(s1);
}
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
}
answered May 11, 2019 at 8:48
1
This is clearly a permutation problem. Using a graph is overkill. The problem statment is missing one important constraint; that you can change each position only once. This then makes it implicit that the solution is within 4 steps. Now all that needs to be decided is the sequence of the replace operations:
Operation1 = change «H» to «T»
Operation2 = change «E» to «A»
Operation3 = change «A» to «I»
Operation4 = change «D to «L»
The solution, the sequence of operations, is some permutation of the string «1234», where each digit represents the position of the character being replaced. e.g. «3124» indicates that first we apply operation3, then operation1, then operation2, then operation 4. At each step, if resulting word is not in dictionary, skip to next permutation. Reasonably trivial. Code anyone?
answered Feb 14, 2012 at 19:52
2
Back to Top
A white circle with a black border surrounding a chevron pointing up. It indicates ‘click here to go back to the top of the page.’
Back to Top
Home
Chevron icon
It indicates an expandable section or menu, or sometimes previous / next navigation options.
Tech
Ye Naiquan /EyeEm/Getty Images
- Find and Replace in Word is a tool that searches a document for a specific word or phrase.
- You can use the tool to replace a word or phrase with another.
- You can review each instance of a word before replacing it, or replace all instances at once.
Find and Replace is a helpful tool in Microsoft Word that searches your document for a specific word or phrase.
You can use the tool to replace one word with another, which can be helpful in situations where you need to go back to change the spelling of a word or check a document for instances of a repeated word to avoid redundancy. For example, if you’re deep into writing a paper and realize you’ve been misspelling someone’s name (let’s say Mark when it should have been Marc), you can use Find and Replace to easily find all instances of Mark and replace it with Marc with a few clicks.
Below, we’ve outlined how to use Find and Replace in Word on macOS and Windows.
Marissa Perino is a former editorial intern covering executive lifestyle. She previously worked at Cold Lips in London and Creative Nonfiction in Pittsburgh. She studied journalism and communications at the University of Pittsburgh, along with creative writing. Find her on Twitter: @mlperino.
Read more
Read less
Abigail Abesamis Demarest is a contributing writer for Insider based in New York. She loves a good glazed donut and nerdy deep dives into the science of food and how it’s made.
Read more
Read less
Related articles
Microsoft Word
Word
More…
Close icon
Two crossed lines that form an ‘X’. It indicates a way to close an interaction, or dismiss a notification.


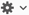 , and then select Advanced Find & Replace.
, and then select Advanced Find & Replace.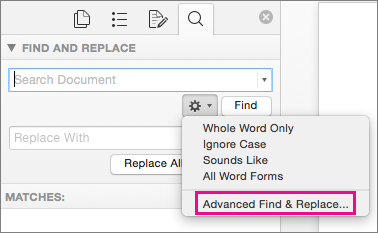
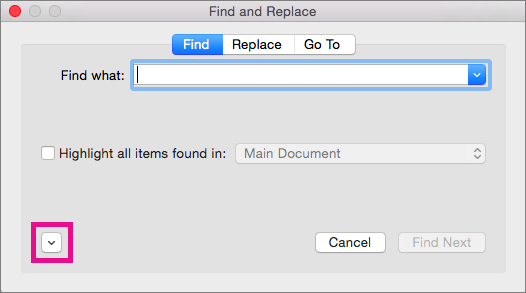

 .
.
 + PERIOD.
+ PERIOD.