Return to VBA Code Examples
In this Article
- VBA Clear Cells / Ranges
- VBA ClearContents
- VBA Clear
- VBA Clear Formatting
- Clear Selection
- Clear Entire Sheet
In VBA it’s easy to clear cells or cell properties with the .Clear methods.
VBA Clear Cells / Ranges
Type the following into the VBA Editor.
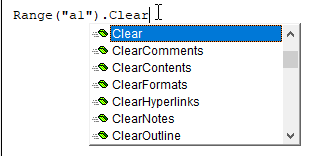
Range("a1").ClearThis will display all of the Clear methods available to you:
As you can see, You can clear:
- Everything ( .Clear)
- Comments ( .ClearComments)
- Contents ( .ClearContents)
- Formats ( .ClearFormats)
- Hyperlinks ( .ClearHyperlinks)
- Notes ( .ClearNotes)
- Outline ( .ClearOutline)
VBA ClearContents
The most common clear method is ClearContents. ClearContents clears only the contents of cells (cell values / text). It does not clear formatting, comments, or anything else.
Range("b2").ClearContentsClearContents is the same as pressing the Delete key on your keyboard.
You can also clear the contents of an entire range of cells:
Range("b2:c10").ClearContentsVBA Clear
Clear will clear all cell properties from a cell:
Range("b2").ClearVBA Clear Formatting
To clear cell formatting use ClearFormats
Range("b2").ClearFormatsClear Selection
To clear the current selection:
Selection.ClearClear Entire Sheet
To clear an entire worksheet:
Sheets("Sheet1").Cells.ClearVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!
Component of Excel Sheets
Excel sheets are a part of an Excel workbook or a document. There can be any number of Excel sheets in a workbook. A Excel sheet may or may not have any of the below components/contents:
- Data in cells
- Formatted cells
- Background color
- Font face
- Font style like bold / italic / underline
- Font color
- Cell borders ( various styles)
- Conditional formatting based on cell contents
- Shapes
- Buttons
- Form objects like text boxes, check boxes, radio buttons
- Data validation with a list
- Formulas in cells
- Pivot tables
- Graphs
- Charts
- Connections to external databases
- Comments
- Hyperlinks
- Formatted tables, etc…
Clearing the Contents of a Worksheet
In case we need to clear contents, formatting, and other data from one or many sheets based on some condition, it might be tiring to do it manually. In that case, it would great if we could clean up the sheet using a pre-defined program. Here is where VBA comes to our rescue.
Clearing Only Cell Contents
Syntax
[Sheets(“<sheet name>”)].Cells.ClearContents
Where the sheet name is optional and if not provided, the active and open sheet is considered.
Example
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Cells.ClearContents
This statement clears only the data (text) in all cells of the sheet named “Sheet1.” It would still retain the other components of the sheet such as charts, graphs, format of cells etc.
Clearing Only Cell Format
Syntax
[Sheets(“<sheet name>”)].Cells.ClearFormats
Where the sheet name is optional and if not provided, the active and open sheet is considered.
Example
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Cells.ClearFormats
This statement clears only the formatting of all cells of the sheet named “Sheet1.” It would still retain the data and other components of the sheet.
Delete a Sheet’s Used Range
Syntax
Activesheet.UsedRange.Delete
This statement has the capacity to delete all contents and objects of the active sheet within the used range.
Syntax
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Cells.ClearComments
Where the sheet name is optional and if not provided, the active and open sheet is considered.
Example
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Cells.ClearComments
This statement would clear up only the comments of all cells in the sheet named “Sheet1.” It would still retain the data, formatting, and other components of the sheet.
Clear the Hyperlinks in a Worksheet
Syntax
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Cells.ClearHyperlinks
Where the sheet name is optional and if not provided, the active and open sheet is considered.
Example
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Cells.ClearHyperlinks
This statement would clear up only the hyperlinks of all cells in the sheet named “Sheet1.” It would still retain the data, formatting, comments, and other components of the sheet.
Clear the Outline in a Worksheet
Syntax
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Cells.ClearOutline
Where the sheet name is optional and if not provided, the active and open sheet is considered.
Example
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Cells.ClearOutline
This statement would clear up only the Outline of all cells in the sheet named “Sheet1.” It would still retain the data, formatting, comments, and other components of the sheet.
Clear the Notes in a Worksheet
Syntax
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Cells.ClearNotes
Where the sheet name is optional and if not provided, the active and open sheet is considered.
Example
Sheets(“Sheet1”).Cells.ClearNotes
This statement would clear up only the notes on all cells in the sheet named “Sheet1.” It would still retain the data, formatting, comments, and other components of the sheet.
Clearing an Entire Sheet
If all the content including data, format, shapes, and other objects need to be cleared, the clear property of the cells (object in worksheet) can be used.
Syntax
[Sheets(“<sheet name>”)].Cells.Clear
Where the sheet name is the name of the worksheet on which the action needs to be done. Cells refer to all the cells of the sheet.
In the place of the sheet’s name within double quotes, we can also provide the index number of the sheet without double quotes
“Activesheet” can also be used in the place of the sheet’s name.
Example:
Sheets(“Sheet2”).Cells.Clear Activesheet.Cells.Clear
Let’s imagine that we need to clear all comments / notes / hyperlinks from 3 sheets that contain the work “Unit”. The code below can help us get the task done quickly.
Note: This can be done on any number of sheets.
One sheet has some data and borders in it.
The next sheet named Unit 2 has a comment in one of the cells.
There is one more sheet named “unit 15” that has some data with conditional formatting.
Now we use this VBA code to clear all these in the three sheets.
This image also shows the other clearing options which I explained above.
Sub clear_all_demo()
' declare all required variables
Dim worksheet_count As Integer
Dim iterator As Integer
Dim ws_name As String
Dim ws As Worksheet
' Set worksheet_count equal to the number of worksheets in the active or open workbook.
worksheet_count = ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets.Count
' Start the loop.
For iterator = 1 To worksheet_count
' find the name of the worksheet
Set ws = ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets(iterator)
ws_name = ws.name
' check if it has the word "unit" in it
If InStr(ws_name, "Unit") > 0 Then
' clear all contents of the sheet
ws.Cells.Clear
End If
Next iterator
End Sub
Code Explained:
Here we declare necessary variables and initialize values for workbook, worksheet, counter, etc.
Then we enter into a loop. Inside the loop, we place a condition to check if the name of the worksheet contains the word “Unit” in it. If so, we clear all contents of the sheet.
On running the code, we see that all kinds of data are cleared from all the three forms.
Conclusion
VBA directly reduces the time and effort of clearing any specific or all kinds of data (list components of a worksheet) easily in no time. But it is worthwhile to say that we need to be very cautious before running the script on the VBA editor as this can be undone/not reversible (i.e) data once lost, is lost forever. The only possibility to save ourselves from such a situation is to make a backup of the workbook before trying anything on the VBA editor.
Метод Range.Clear для полной очистки диапазона ячеек из кода VBA Excel. Методы очистки отдельных свойств и их групп в ячейках. Примеры использования.
Методы очистки ячеек
| Метод | Очищаемые свойства | Примечание |
|---|---|---|
| Range.Clear | Почти все свойства | Ширина и высота ячеек не изменяются |
| Range.ClearComments | Комментарии | Для Excel в составе Office 365 |
| Range.ClearContents | Формулы и значения | Исходное форматирование сохраняется |
| Range.ClearFormats | Свойства, задающие форматы | В том числе отмена объединения ячеек |
| Range.ClearHyperlinks | Гиперссылки | Текст и форматирование сохраняются |
| Range.ClearNotes | Примечания и заметки | Примечания – для локальных программ Excel, заметки – для Excel в составе Office 365 |
| Range.ClearOutline | Структура данных | Смотрите, что такое структурирование данных |
Range – выражение, возвращающее диапазон ячеек.
Примеры использования
1. Удаление гиперссылки из ячейки A1
Cells(1, 1).ClearHyperlinks
2. Очистка диапазона A1:L50 от формул и значений
Range("A1:L50").ClearContents
3. Очистка всех свойств ячеек в столбцах A:K
Columns("A:K").Clear
4. Очистка форматирования ячеек в строках 1:20
Rows("1:20").ClearFormats
Методы очистки диапазонов ячеек в VBA Excel возвращают очищаемые свойства ячеек к значениям по умолчанию. К таким, как на вновь созданном стандартном рабочем листе. При любых методах очистки высота строк и ширина столбцов не изменяются.
Фразы для контекстного поиска: очистка ячеек, очистка ячейки, очистка формул, очистка от формул, удаление формул, очистка значений, удаление значений, очистка форматов, удаление форматирования, удаление форматов.

This VBA Tutorial is accompanied by Excel workbooks containing the macros I use in the examples below. You can get immediate access to these example workbooks by subscribing to the Power Spreadsheets Newsletter.
Use the following Table of Contents to navigate to the section you’re interested in.
Related VBA and Macro Tutorials
The following VBA and Macro Tutorials may help you better understand and implement the contents below:
- General VBA constructs and structures:
- Learn about important VBA constructs here.
- Learn how to work with the Visual Basic Editor here.
- Learn how to work with Excel Sub procedures here.
- Learn about the Excel Object Model, and how to create object references, here.
- Learn about the Range object, and how to refer to cells, here.
- Learn how to work with properties here.
- Learn how to work with methods here.
- Learn how to declare and work with variables here.
- Learn about data types here.
- Learn how to work with loops here.
- Practical VBA applications and macro examples:
- Learn how to work with worksheets using VBA here.
- Learn how to check if a cell is empty here.
- Learn how to delete rows here.
- Learn how to delete blank or empty rows here.
You can find additional VBA and Macro Tutorials in the Archives.
VBA Code to Clear Cell
To clear cells using VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Cells.Clear
Process Followed by VBA to Clear Cell
VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Cells.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cells you want to clear.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with Range.Item), Range.Offset, Range.Resize or Application.ActiveCell properties. If you explicitly declare an object variable to represent Cells, use the Range object data type.
- Item: Clear.
- VBA Construct: Range.Clear method.
- Description: The Range.Clear method clears the Range object you specify (Cells). Range.Clear clears the entire Range object, including values, formulas and formatting.
Macro Example to Clear Cell
The following macro example clears cells A5 to C9 (myRange) in the worksheet named “Clear Cell” of the workbook containing the macro (ThisWorkbook).
Sub clearCell()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-clear-cell/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cells to clear
Dim myRange As Range
'identify cells to clear
Set myRange = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Clear Cell").Range("A5:C9")
'clear cells (including formatting)
myRange.Clear
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Clear Cell
The following images illustrate the results of executing the macro example.
- Before macro execution: Cells A5 to C9 contain the string “data”, have a light blue fill, and the font is formatted as bold.
- After macro execution: Cells A5 to C9 (including both data and formatting) are cleared.
#2: Clear Cell Contents and Keep Formatting
VBA Code to Clear Cell Contents and Keep Formatting
To clear cell contents (but not formatting) using VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Cells.ClearContents
Process Followed by VBA to Clear Cell Contents and Keep Formatting
VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Cells.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cells where you want to clear the contents but not the formatting.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with Range.Item), Range.Offset, Range.Resize or Application.ActiveCell properties. If you explicitly declare an object variable to represent Cells, use the Range object data type.
- Item: ClearContents.
- VBA Construct: Range.ClearContents method.
- Description: The Range.ClearContents method clears values and formulas from the Range object you specify (Cells). Range.ClearContents leaves formatting intact.
Macro Example to Clear Cell Contents and Keep Formatting
The following macro example clears the contents (but not the formatting) of cells A10 to C14 (myRange) in the worksheet named “Clear Cell” of the workbook containing the macro (ThisWorkbook).
Sub clearCellContentsKeepFormatting()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-clear-cell/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cells to clear contents but not formatting
Dim myRange As Range
'identify cells to clear contents and keep formatting
Set myRange = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Clear Cell").Range("A10:C14")
'clear cell contents (but not formatting)
myRange.ClearContents
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Clear Cell Contents and Keep Formatting
The following images illustrate the results of executing the macro example.
- Before macro execution: Cells A10 to C14 contain the string “data”, have a light gold fill, and the font is formatted as bold.
- After macro execution: Cell contents of cells A10 to C14 are cleared. The formatting is kept.
#3: Clear Cell Formatting
VBA Code to Clear Cell Formatting
To clear cell formatting using VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Cells.ClearFormats
Process Followed by VBA to Clear Cell Formatting
VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Cells.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cells where you want to clear cell formatting.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with Range.Item), Range.Offset, Range.Resize or Application.ActiveCell properties. If you explicitly declare an object variable to represent Cells, use the Range object data type.
- Item: ClearFormats.
- VBA Construct: Range.ClearFormats method.
- Description: The Range.ClearFormats method clears the formatting of the Range object you specify (Cells). Range.ClearFormats doesn’t clear values or formulas.
Macro Example to Clear Cell Formatting
The following macro clears the cell formatting of cells A15 to C19 (myRange) of the worksheet named “Clear Cell” in the workbook containing the macro (ThisWorkbook).
Sub clearCellFormatting()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-clear-cell/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cells to clear formatting
Dim myRange As Range
'identify cells to clear formatting
Set myRange = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Clear Cell").Range("A15:C19")
'clear cell formatting
myRange.ClearFormats
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Clear Cell Formatting
The following images illustrate the results of executing the macro example.
- Before macro execution: Cells A15 to C19 contain the string “data”, have a light green fill, and the font is formatted as bold.
- After macro execution: The formatting of cells A15 to C19 is cleared.
#4: Clear Cell Color
VBA Code to Clear Cell Color
To clear cell color using VBA, use a statement with the following structure:
Cells.Interior.Color = xlColorIndexNone
Process Followed by VBA to Clear Cell Color
VBA Statement Explanation
- Item: Cells.
- VBA Construct: Range object.
- Description: Range object representing the cells where you want to clear cell formatting.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with Range.Item), Range.Offset, Range.Resize or Application.ActiveCell properties. If you explicitly declare an object variable to represent Cells, use the Range object data type.
- Item: Interior.
- VBA Construct: Range.Interior property and Interior object.
- Description: The Range. Interior property returns an Interior object representing the interior of the cell range you specify (Cells).
- Item: Color.
- VBA Construct: Interior.Color property.
- Description: The Interior.Color property allows you to set the primary color of the cell interior represented by the Interior object returned by Range.Interior.
- Item: =.
- VBA Construct: Assignment operator.
- Description: The assignment operator assigns the xlColorIndexNone value to the Interior.Color property.
- Item: xlColorIndexNone.
- VBA Construct: xlColorIndexNone constant.
- Description: The xlColorIndexNone constant specifies that the color of the Interior object representing the interior of Cells is none.
Macro Example to Clear Cell Color
The following macro clears the cell color of cells A20 to C24 (myRange) in the worksheet named “Clear Cell” of the workbook containing the macro (ThisWorkbook).
Sub clearCellColor()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-clear-cell/
'declare object variable to hold reference to cells to clear cell color
Dim myRange As Range
'identify cells to clear cell color
Set myRange = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Clear Cell").Range("A20:C24")
'clear cell color
myRange.Interior.Color = xlColorIndexNone
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Clear Cell Color
The following images illustrate the results of executing the macro example.
- Before macro execution: Cells A20 to C24 contain the string “data”, have a light orange fill, and the font is formatted as bold.
- After macro execution: The fill color of cells A20 to C24 is cleared.
#5: Clear Cells with Zero
VBA Code to Clear Cells with Zero
To clear cells with zero within a cell range using VBA, use a macro with the following statement structure:
For Each Cell In Range
If Cell.Value = myValue Then Cell.Clear
Next Cell
Process Followed by VBA to Clear Cells with Zero
VBA Statement Explanation
Lines #1 and #3: For Each Cell In Range | Next Cell
- Item: For Each… In… Next.
- VBA Construct: For Each… Next statement.
- Description: The For Each… Next statement repeats the statement within the loop (line #2) for each element (Cell) in the cell range (Range) you want to search for zeroes in.
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Element of the For Each… Next statement and object variable of the Range object data type.
- Description: The Element of the For Each… Next statement is an object variable used to iterate through the elements (Cell) of the cell range (Range) you want to search for zeroes in.
If you explicitly declare an object variable to represent Cell, use the Range object data type.
- Item: Range.
- VBA Construct: Group of the For Each… Next statement and Range object.
- Description: The For Each… Next statement repeats the statements within the loop (line #2) for each element (Cell) in the Group (Range). Range is a Range object representing the cells where you want to search for zeroes.
You can usually return a Range object with constructs such as the Worksheet.Range, Worksheet.Cells (with Range.Item), Range.Offset, Range.Resize or Application.ActiveCell properties. If you explicitly declare an object variable to represent Range, use the Range object data type.
Line #2: If Cell.Value = myValue Then Cell.Clear
- Item: If… Then.
- VBA Construct: If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: The If… Then… Else statement conditionally executes a group of statements depending on the value of an expression. For these purposes:
- The If… Then… Else statement tests the specified condition (Cell.Value = myValue).
- If the condition is met and returns True: Cell.Clear is executed.
- If the condition is not met and returns False: Execution continues with the statement following the If… Then… Else statement (Next Cell).
- Item: Cell.
- VBA Construct: Object variable of the Range object data type.
- Description: Cell is an object variable used to iterate through the elements of the cell range (Range) you want to search for zeroes in. Within the If… Then… Else statement, Cell represents the individual cell the For Each… Next loop is currently iterating through.
If you explicitly declare an object variable to represent Cell, use the Range object data type.
- Item: Value.
- VBA Construct: Range.Value property.
- Description: The Range.Value property returns the value in the cell the For Each…Next loop is currently iterating through.
- Item: myValue.
- VBA Construct: Variable of a numeric data type.
- Description: myValue represents the value you want to search for and use to determine which cells to clear. Within the macro structure used in this VBA Tutorial, myValue is 0 (zero).
If you explicitly declare a variable to represent myValue, use a numeric data type such as Long, Single or Double (depending on the value you’re searching for).
- Item: Cell.Value = myValue.
- VBA Construct: Condition of If… Then… Else statement.
- Description: This condition is an expression that evaluates to True or False. Cell.Value = myValue returns True or False, as follows:
- True: Value of Cell is equal to myValue (zero).
- False: Value of Cell isn’t equal to myValue (zero).
- Item: Clear.
- VBA Construct: Range.Clear method.
- Description: The Range.Clear method clears the cell the For Each… Next loop is currently iterating through. Range.Clear clears the entire Range object, including values, formulas and formatting.
If you don’t want to clear the entire Range object, but only its contents, formatting or cell color, please refer to the appropriate sections above.
Macro Example to Clear Cells with Zero
The following macro example clears the cells with zero (0) in cells A25 to C29 (myRange) in the worksheet named “Clear Cell” of the workbook containing the macro (ThisWorkbook).
Sub clearCellsWithZero()
'Source: https://powerspreadsheets.com/
'For further information: https://powerspreadsheets.com/excel-vba-clear-cell/
'declare object variables to hold references to cell range where you search for zeroes
Dim myRange As Range
'declare object variable used to iterate through the elements of the cell range
Dim iCell As Range
'declare variable to hold value (zero) you search for
Dim myValue As Long
'identify cells to search for zeroes
Set myRange = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Clear Cell").Range("A25:C29")
'set value (zero) to search for
myValue = 0
'loop through each cell (iCell) of the cell range (myRange)
For Each iCell In myRange
'test if value is zero. If condition is met, clear cell
If iCell.Value = myValue Then iCell.Clear
Next iCell
End Sub
Effects of Executing Macro Example to Clear Cells with Zero
The following images illustrate the results of executing the macro example.
- Before macro execution: Cells A25 to C29 contain the string “data” or the value zero (0), have a light gray fill, and the font is formatted as bold.
- After macro execution: Cells between A25 to C29 containing a zero (0) are cleared (including both data and formatting).
References to VBA Constructs Used in this VBA Tutorial
Use the following links to visit the appropriate webpage in the Microsoft Developer Network:
- Identify the workbook and worksheet where the cells to clear are located:
- Workbook object.
- Application.ActiveWorkbook property.
- Application.ThisWorkbook property.
- Application.Workbooks property.
- Worksheet object.
- Application.ActiveSheet property.
- Workbook.Worksheets property.
- Identify the cells to clear:
- Range object.
- Worksheet.Range property.
- Worksheet.Cells property.
- Application.ActiveCell property.
- Application.Selection property.
- Range.Range property.
- Range.Cells property.
- Range.Item property.
- Range.Offset property.
- Range.Resize property.
- For Each… Next statement.
- If… Then… Else statement.
- Range.Value property.
- Clear cells:
- Range.Clear method.
- Range.ClearContents method.
- Range.ClearFormats method.
- Interior object.
- Range.Interior property.
- Interior.Color property.
- xlColorIndex enumeration.
- Work with variables and data types:
- Dim statement.
- Set statement.
- = operator.
- Data types:
- Double data type.
- Long data type.
- Single data type.
Home / VBA / How to CLEAR an Entire Sheet using VBA in Excel
To clear an entire sheet using a VBA code in one go, you need to use two things, first is the CLEAR method, and then CELLS to refer to all the cells of a worksheet.
Clear the Activesheet
Let’s say if you want to clear all the content from the activate sheet, the code would be like the below.
Cells.ClearWhen you run this code, it will clear everything from all the cells from the active sheet, as I have already mentioned that we have used clear to refer to the entire worksheet and clear to clear it.
Clear a Specific Sheet
There’s one thing that you need to note down that to clear a sheet that sheet needs to be activated. So let’s say you want to clear the “Sheet1”, the code would be like:
Sheets("Sheet1").Activate
Cells.ClearIn this code, the first activates the “Sheet1” and the second line clears everything.
Helpful Links: Run a Macro – Macro Recorder – Visual Basic Editor – Personal Macro Workbook
Other Things to Clear
You can also use the below methods to clear different things.
Cells.ClearContents 'to clear contents
Cells.ClearComments 'to clear Comments
Cells.ClearFormats 'to clears formatting
Cells.ClearHyperlinks 'to clear hyperlinks
Cells.ClearNotes 'to clear notes
Cells.ClearOutline 'to clears outlineClear a Sheet from a Specific Workbook
The below code can refer to the workbook “Book1” and clear the sheet “Sheet1”. But make sure to have the workbook open at the time run this code.
Workbooks("Book1").Sheets("Sheet1").Activate
Cells.ClearThis code first activates the “Sheet1” from the book and clears it.
Clear a Sheet from a Workbook that is Closed
And in the below code, we have referred to the “Sheet1” from the workbook “sample-file”, stored in a specific location.
Sub vba_clear_sheet()
Dim wb As Workbook
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Set wb = Workbooks.Open("C:UsersDellDesktopsample-file.xlsx")
wb.Sheets("Sheet1").Activate
Cells.Clear
wb.Close SaveChanges:=True
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
End SubMore Tutorials on VBA Worksheets
- Back to VBA Worksheet / VBA Tutorial
ClearContents is a method in VBA used to delete or remove the values stored in the cells provided to it. This method makes the cell range empty. It is used with the range property to access the specified cell range. An example of this method is range(“A1:B2”). The ClearContents method will clear the contents of cells from A1 to B2.
In Excel, adding and deleting data is a common routine task.
Sometimes we delete a single cell value, sometimes many cell values, and sometimes we may require to delete the entire worksheet content. This article will show you how to use the “ClearContents” method in Excel VBA. In VBA, we have many methods to do this, like “Clear,” “Delete,” and “Clear Contents.”
Table of contents
- Excel VBA Clear Contents
- What are Clear Contents in Excel VBA?
- Difference Between Clear & Delete Methods
- Use VBA Clear Contents Method to Retain Formatting of Cells
- Loop Through all the Worksheets and Clear Contents of Specific Range
- Recommended Articles
What are Clear Contents in Excel VBA?
Before we tell you about ClearContents in VBA, let me show how we can delete or clear off the data in the specific range.
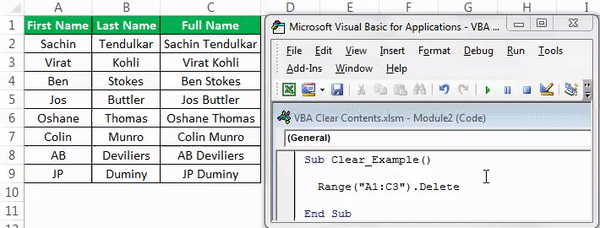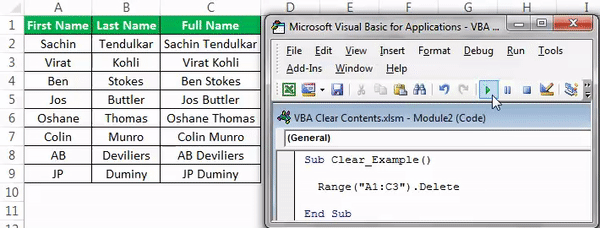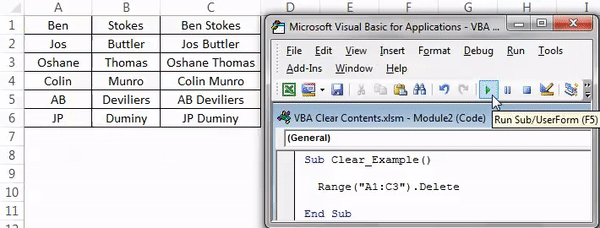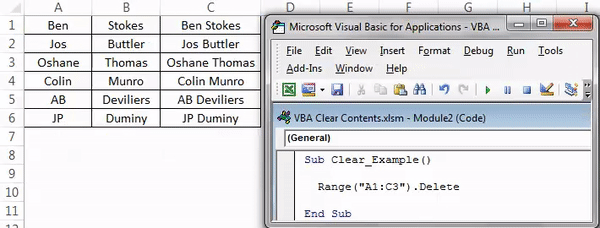
Look at the below data.
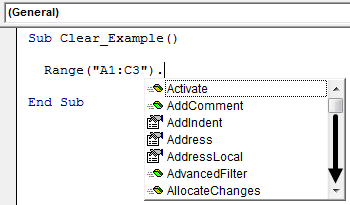
Now, if we want to clear off cells A1 to C3, we need first to mention the range of cells using the VBA RANGERange is a property in VBA that helps specify a particular cell, a range of cells, a row, a column, or a three-dimensional range. In the context of the Excel worksheet, the VBA range object includes a single cell or multiple cells spread across various rows and columns.read more object.
Code:
Range (“A1:C3”)
After mentioning the range of cells by using the RANGE object, we need to select the method “Clear” to clear off the mention of the cell values.
Code:
Range (“A1:C3”).Clear
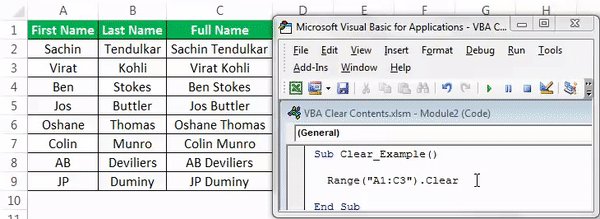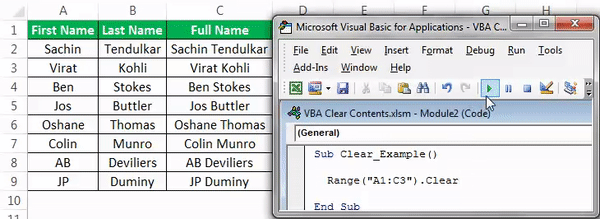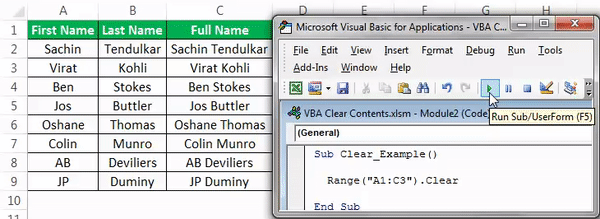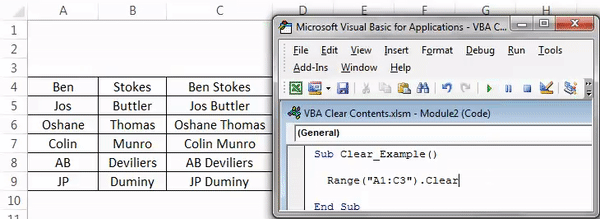
It will clear off the mentioned cell values.
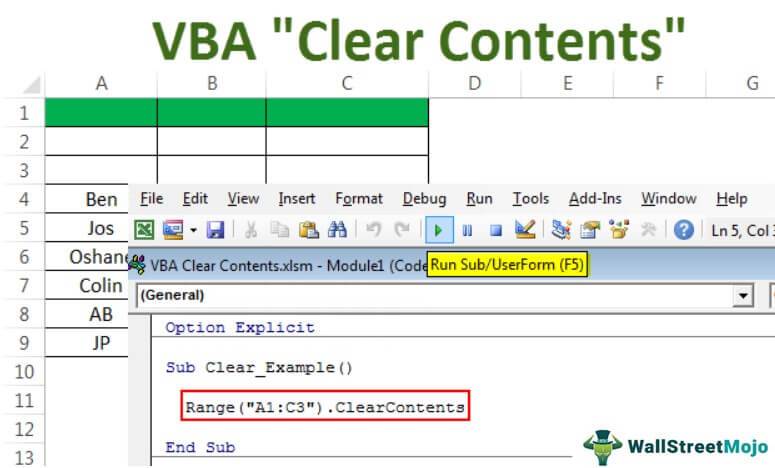
Code:
Sub Clear_Example() Range("A1:C3").Clear End Sub
Apart from the clear method, we can also use the “DELETE” method.
Code:
Range (“A1:C3”).Delete
It will delete the mentioned cell values, just like our clear method.
You can use the VBA CELLS propertyCells are cells of the worksheet, and in VBA, when we refer to cells as a range property, we refer to the same cells. In VBA concepts, cells are also the same, no different from normal excel cells.read more with a worksheet name if you want to delete all the cell’s data.
Worksheets(“Sheet1”).Cells.Delete
Worksheets(“Sheet1”).Cells.Clear
Both the above codes will delete the entire worksheet “Sheet1” data. In addition, it will delete the cell values from the first cell to the last cell of the worksheet.
If you want to delete the present sheet cells, you can use the Active Sheet object.
ActiveSheet.Cells.Delete or ActiveSheet.Cells.Clear
Difference Between Clear & Delete Methods
We know this question should have already played in your mind.
However, there is a difference between these two methods.
When you use the method “Delete,” it will delete the cell, and the below cell will take over the position of the deleted cell.
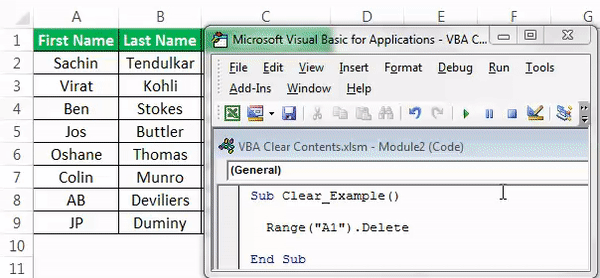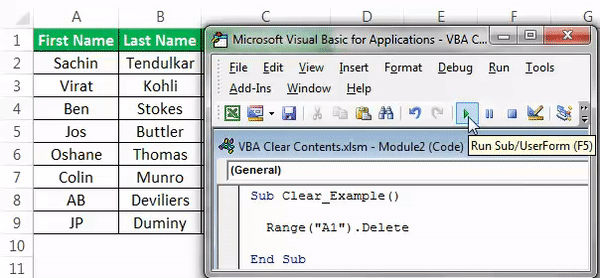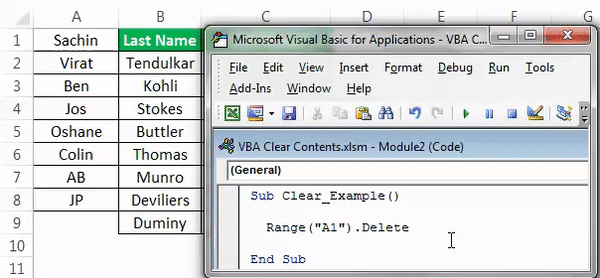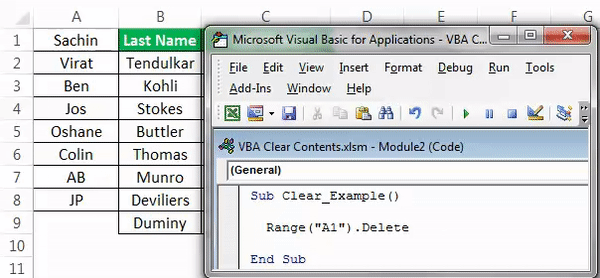
For example, look at the below image.
Now, we will use the delete method to delete cell A1.
Code:
Sub Clear_Example() Range("A1").Delete End Sub
We will run this code and see what happens.
Look what happened here. As we said, when we deleted cell A1, it got deleted, but cell A2 moved one cell up and occupies the deleted cell. So, it will lead to a data mismatch. So, be careful while using the “Delete” method.
Now, for the same data, we will clear the method.
Code:
Sub Clear_Example() Range("A1").Clear End Sub
Now, see what happens when we run this code.
This code has just vacated cell A1 without altering other cells. Therefore, this looks like a proper method to delete only the part of the cells of the entire data range.
Use VBA Clear Contents Method to Retain Formatting of Cells
If you have observed the previous two methods, those two methods not only deleted or cleared off the cells provided. It also deleted the formatting of the cells we have provided.
To retain the formatting of the cells, we need not use neither “Delete” nor “Clear,” but we need to use the VBA “ClearContents” method.
When you enter the range of cells using a RANGE object, it will show all its properties and methods.
We can access “Delete,” we can access “Clear,” and we can also access “ClearContents” methods.
Select this method.
Code:
Sub Clear_Example() Range("A1:C3").ClearContents End Sub
It will clear content from A1 to C3 cell, but we will have all the existing formatting.
As you can see in the above picture, we have cell color in VBA, borders, and every formatting associated with those mentioned cells.
Similarly, we can clear the contents of other sheets as well.
Worksheets(“Sheet1”).Range(“A1:D10”).ClearContents
It will clear the contents from cells A1 to D10 in sheet “Sheet1”.
Similarly, we can delete the other open workbook cells as well.
Workbooks(“Book1.xlsx”).Worksheets(“Sheet1”).Range(“A1:D10”).ClearContents
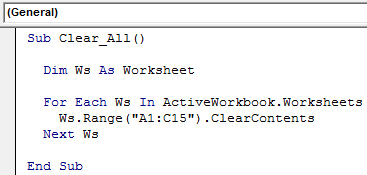
Loop Through all the Worksheets and Clear Contents of Specific Range
Assume you have many sheets in your workbook. You want to delete the range of cells from A1 to C15. To do this, we must use For Each Loop in VBAVBA For Each Loop helps the user to inspect and analyze the groups of objects or values individually. It even facilitates performing the specific activity for every object or value by passing a statement or group of statements in this reference.read more in all the sheets.
The below code will do the job.
Code:
Sub Clear_All() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets Ws.Range("A1:C15").ClearContents Next Ws End Sub
Note: You can change the range of cells as per your wish.
If you want to clear off the entire worksheet data, then you need to use the code below.
Code:
Sub Clear_All() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ActiveWorkbook.Worksheets Ws.Cells.ClearContents Next Ws End Sub
You can download this VBA Clear Contents Excel template here – VBA Clear Contents Template.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA Clear Contents. Here, we learn how to use the Clear, Delete, and ClearContents method in VBA to clear data in Excel and some simple to advanced examples. Below are some useful Excel articles related to VBA: –
- New Line in VBA MsgBox
- How to Use Timer in VBA?
- Excel VBA Break For Loop
- Excel VBA Do Loop