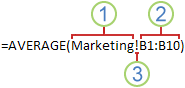For quick access to related information in another file or on a web page, you can insert a hyperlink in a worksheet cell. You can also insert links in specific chart elements.
Note: Most of the screen shots in this article were taken in Excel 2016. If you have a different version your view might be slightly different, but unless otherwise noted, the functionality is the same.
-
On a worksheet, click the cell where you want to create a link.
You can also select an object, such as a picture or an element in a chart, that you want to use to represent the link.
-
On the Insert tab, in the Links group, click Link
.
You can also right-click the cell or graphic and then click Link on the shortcut menu, or you can press Ctrl+K.
-
-
Under Link to, click Create New Document.
-
In the Name of new document box, type a name for the new file.
Tip: To specify a location other than the one shown under Full path, you can type the new location preceding the name in the Name of new document box, or you can click Change to select the location that you want and then click OK.
-
Under When to edit, click Edit the new document later or Edit the new document now to specify when you want to open the new file for editing.
-
In the Text to display box, type the text that you want to use to represent the link.
-
To display helpful information when you rest the pointer on the link, click ScreenTip, type the text that you want in the ScreenTip text box, and then click OK.
-
On a worksheet, click the cell where you want to create a link.
You can also select an object, such as a picture or an element in a chart, that you want to use to represent the link.
-
On the Insert tab, in the Links group, click Link
.
You can also right-click the cell or object and then click Link on the shortcut menu, or you can press Ctrl+K.
-
-
Under Link to, click Existing File or Web Page.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To select a file, click Current Folder, and then click the file that you want to link to.
You can change the current folder by selecting a different folder in the Look in list.
-
To select a web page, click Browsed Pages and then click the web page that you want to link to.
-
To select a file that you recently used, click Recent Files, and then click the file that you want to link to.
-
To enter the name and location of a known file or web page that you want to link to, type that information in the Address box.
-
To locate a web page, click Browse the Web
, open the web page that you want to link to, and then switch back to Excel without closing your browser.
-
-
If you want to create a link to a specific location in the file or on the web page, click Bookmark, and then double-click the bookmark that you want.
Note: The file or web page that you are linking to must have a bookmark.
-
In the Text to display box, type the text that you want to use to represent the link.
-
To display helpful information when you rest the pointer on the link, click ScreenTip, type the text that you want in the ScreenTip text box, and then click OK.
To link to a location in the current workbook or another workbook, you can either define a name for the destination cells or use a cell reference.
-
To use a name, you must name the destination cells in the destination workbook.
How to name a cell or a range of cells
-
Select the cell, range of cells, or nonadjacent selections that you want to name.
-
Click the Name box at the left end of the formula bar
.
Name box
-
In the Name box, type the name for the cells, and then press Enter.
Note: Names can’t contain spaces and must begin with a letter.
-
-
On a worksheet of the source workbook, click the cell where you want to create a link.
You can also select an object, such as a picture or an element in a chart, that you want to use to represent the link.
-
On the Insert tab, in the Links group, click Link
.
You can also right-click the cell or object and then click Link on the shortcut menu, or you can press Ctrl+K.
-
-
Under Link to, do one of the following:
-
To link to a location in your current workbook, click Place in This Document.
-
To link to a location in another workbook, click Existing File or Web Page, locate and select the workbook that you want to link to, and then click Bookmark.
-
-
Do one of the following:
-
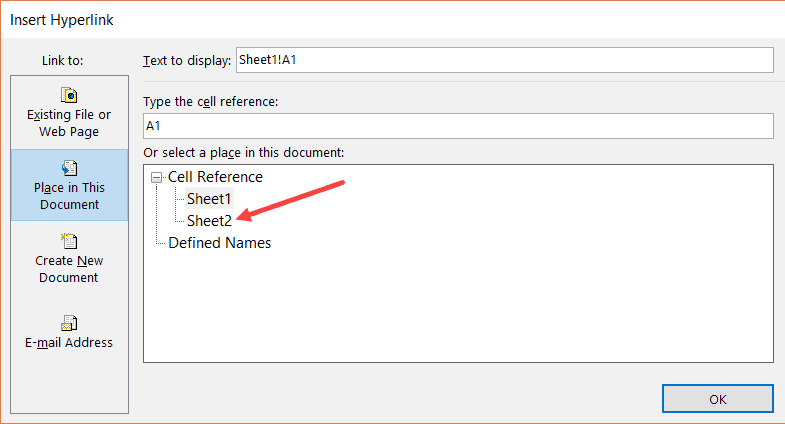
In the Or select a place in this document box, under Cell Reference, click the worksheet that you want to link to, type the cell reference in the Type in the cell reference box, and then click OK.
-
In the list under Defined Names, click the name that represents the cells that you want to link to, and then click OK.
-
-
In the Text to display box, type the text that you want to use to represent the link.
-
To display helpful information when you rest the pointer on the link, click ScreenTip, type the text that you want in the ScreenTip text box, and then click OK.
You can use the HYPERLINK function to create a link that opens a document that is stored on a network server, an intranet, or the Internet. When you click the cell that contains the HYPERLINK function, Excel opens the file that is stored at the location of the link.
Syntax
HYPERLINK(link_location,friendly_name)
Link_location is the path and file name to the document to be opened as text. Link_location can refer to a place in a document — such as a specific cell or named range in an Excel worksheet or workbook, or to a bookmark in a Microsoft Word document. The path can be to a file stored on a hard disk drive, or the path can be a universal naming convention (UNC) path on a server (in Microsoft Excel for Windows) or a Uniform Resource Locator (URL) path on the Internet or an intranet.
-
Link_location can be a text string enclosed in quotation marks or a cell that contains the link as a text string.
-
If the jump specified in link_location does not exist or can’t be navigated, an error appears when you click the cell.
Friendly_name is the jump text or numeric value that is displayed in the cell. Friendly_name is displayed in blue and is underlined. If friendly_name is omitted, the cell displays the link_location as the jump text.
-
Friendly_name can be a value, a text string, a name, or a cell that contains the jump text or value.
-
If friendly_name returns an error value (for example, #VALUE!), the cell displays the error instead of the jump text.
Examples
The following example opens a worksheet named Budget Report.xls that is stored on the Internet at the location named example.microsoft.com/report and displays the text «Click for report»:
=HYPERLINK(«http://example.microsoft.com/report/budget report.xls», «Click for report»)
The following example creates a link to cell F10 on the worksheet named Annual in the workbook Budget Report.xls, which is stored on the Internet at the location named example.microsoft.com/report. The cell on the worksheet that contains the link displays the contents of cell D1 as the jump text:
=HYPERLINK(«[http://example.microsoft.com/report/budget report.xls]Annual!F10», D1)
The following example creates a link to the range named DeptTotal on the worksheet named First Quarter in the workbook Budget Report.xls, which is stored on the Internet at the location named example.microsoft.com/report. The cell on the worksheet that contains the link displays the text «Click to see First Quarter Department Total»:
=HYPERLINK(«[http://example.microsoft.com/report/budget report.xls]First Quarter!DeptTotal», «Click to see First Quarter Department Total»)
To create a link to a specific location in a Microsoft Word document, you must use a bookmark to define the location you want to jump to in the document. The following example creates a link to the bookmark named QrtlyProfits in the document named Annual Report.doc located at example.microsoft.com:
=HYPERLINK(«[http://example.microsoft.com/Annual Report.doc]QrtlyProfits», «Quarterly Profit Report»)
In Excel for Windows, the following example displays the contents of cell D5 as the jump text in the cell and opens the file named 1stqtr.xls, which is stored on the server named FINANCE in the Statements share. This example uses a UNC path:
=HYPERLINK(«\FINANCEStatements1stqtr.xls», D5)
The following example opens the file 1stqtr.xls in Excel for Windows that is stored in a directory named Finance on drive D, and displays the numeric value stored in cell H10:
=HYPERLINK(«D:FINANCE1stqtr.xls», H10)
In Excel for Windows, the following example creates a link to the area named Totals in another (external) workbook, Mybook.xls:
=HYPERLINK(«[C:My DocumentsMybook.xls]Totals»)
In Microsoft Excel for the Macintosh, the following example displays «Click here» in the cell and opens the file named First Quarter that is stored in a folder named Budget Reports on the hard drive named Macintosh HD:
=HYPERLINK(«Macintosh HD:Budget Reports:First Quarter», «Click here»)
You can create links within a worksheet to jump from one cell to another cell. For example, if the active worksheet is the sheet named June in the workbook named Budget, the following formula creates a link to cell E56. The link text itself is the value in cell E56.
=HYPERLINK(«[Budget]June!E56», E56)
To jump to a different sheet in the same workbook, change the name of the sheet in the link. In the previous example, to create a link to cell E56 on the September sheet, change the word «June» to «September.»
When you click a link to an email address, your email program automatically starts and creates an email message with the correct address in the To box, provided that you have an email program installed.
-
On a worksheet, click the cell where you want to create a link.
You can also select an object, such as a picture or an element in a chart, that you want to use to represent the link.
-
On the Insert tab, in the Links group, click Link
.
You can also right-click the cell or object and then click Link on the shortcut menu, or you can press Ctrl+K.
-
-
Under Link to, click E-mail Address.
-
In the E-mail address box, type the email address that you want.
-
In the Subject box, type the subject of the email message.
Note: Some web browsers and email programs may not recognize the subject line.
-
In the Text to display box, type the text that you want to use to represent the link.
-
To display helpful information when you rest the pointer on the link, click ScreenTip, type the text that you want in the ScreenTip text box, and then click OK.
You can also create a link to an email address in a cell by typing the address directly in the cell. For example, a link is created automatically when you type an email address, such as someone@example.com.
You can insert one or more external reference (also called links) from a workbook to another workbook that is located on your intranet or on the Internet. The workbook must not be saved as an HTML file.
-
Open the source workbook and select the cell or cell range that you want to copy.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Copy.
-
Switch to the worksheet that you want to place the information in, and then click the cell where you want the information to appear.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Paste Special.
-
Click Paste Link.
Excel creates an external reference link for the cell or each cell in the cell range.
Note: You may find it more convenient to create an external reference link without opening the workbook on the web. For each cell in the destination workbook where you want the external reference link, click the cell, and then type an equal sign (=), the URL address, and the location in the workbook. For example:
=’http://www.someones.homepage/[file.xls]Sheet1′!A1
=’ftp.server.somewhere/file.xls’!MyNamedCell
To select a hyperlink without activating the link to its destination, do one of the following:
-
Click the cell that contains the link, hold the mouse button until the pointer becomes a cross
, and then release the mouse button.
-
Use the arrow keys to select the cell that contains the link.
-
If the link is represented by a graphic, hold down Ctrl, and then click the graphic.
You can change an existing link in your workbook by changing its destination, its appearance, or the text or graphic that is used to represent it.
Change the destination of a link
-
Select the cell or graphic that contains the link that you want to change.
Tip: To select a cell that contains a link without going to the link destination, click the cell and hold the mouse button until the pointer becomes a cross
, and then release the mouse button. You can also use the arrow keys to select the cell. To select a graphic, hold down Ctrl and click the graphic.
-
On the Insert tab, in the Links group, click Link.
You can also right-click the cell or graphic and then click Edit Link on the shortcut menu, or you can press Ctrl+K.
-
-
In the Edit Hyperlink dialog box, make the changes that you want.
Note: If the link was created by using the HYPERLINK worksheet function, you must edit the formula to change the destination. Select the cell that contains the link, and then click the formula bar to edit the formula.
You can change the appearance of all link text in the current workbook by changing the cell style for links.
-
On the Home tab, in the Styles group, click Cell Styles.
-
Under Data and Model, do the following:
-
To change the appearance of links that have not been clicked to go to their destinations, right-click Link, and then click Modify.
-
To change the appearance of links that have been clicked to go to their destinations, right-click Followed Link, and then click Modify.
Note: The Link cell style is available only when the workbook contains a link. The Followed Link cell style is available only when the workbook contains a link that has been clicked.
-
-
In the Style dialog box, click Format.
-
On the Font tab and Fill tab, select the formatting options that you want, and then click OK.
Notes:
-
The options that you select in the Format Cells dialog box appear as selected under Style includes in the Style dialog box. You can clear the check boxes for any options that you don’t want to apply.
-
Changes that you make to the Link and Followed Link cell styles apply to all links in the current workbook. You can’t change the appearance of individual links.
-
-
Select the cell or graphic that contains the link that you want to change.
Tip: To select a cell that contains a link without going to the link destination, click the cell and hold the mouse button until the pointer becomes a cross
, and then release the mouse button. You can also use the arrow keys to select the cell. To select a graphic, hold down Ctrl and click the graphic.
-
Do one or more of the following:
-
To change the link text, click in the formula bar, and then edit the text.
-
To change the format of a graphic, right-click it, and then click the option that you need to change its format.
-
To change text in a graphic, double-click the selected graphic, and then make the changes that you want.
-
To change the graphic that represents the link, insert a new graphic, make it a link with the same destination, and then delete the old graphic and link.
-
-
Right-click the hyperlink that you want to copy or move, and then click Copy or Cut on the shortcut menu.
-
Right-click the cell that you want to copy or move the link to, and then click Paste on the shortcut menu.
By default, unspecified paths to hyperlink destination files are relative to the location of the active workbook. Use this procedure when you want to set a different default path. Each time that you create a link to a file in that location, you only have to specify the file name, not the path, in the Insert Hyperlink dialog box.
Follow one of the steps depending on the Excel version you are using:
-
In Excel 2016, Excel 2013, and Excel 2010:
-
Click the File tab.
-
Click Info.
-
Click Properties, and then select Advanced Properties.
-
In the Summary tab, in the Hyperlink base text box, type the path that you want to use.
Note: You can override the link base address by using the full, or absolute, address for the link in the Insert Hyperlink dialog box.
-
-
In Excel 2007:
-
Click the Microsoft Office Button
, click Prepare, and then click Properties.
-
In the Document Information Panel, click Properties, and then click Advanced Properties.
-
Click the Summary tab.
-
In the Hyperlink base box, type the path that you want to use.
Note: You can override the link base address by using the full, or absolute, address for the link in the Insert Hyperlink dialog box.
-
To delete a link, do one of the following:
-
To delete a link and the text that represents it, right-click the cell that contains the link, and then click Clear Contents on the shortcut menu.
-
To delete a link and the graphic that represents it, hold down Ctrl and click the graphic, and then press Delete.
-
To turn off a single link, right-click the link, and then click Remove Link on the shortcut menu.
-
To turn off several links at once, do the following:
-
In a blank cell, type the number 1.
-
Right-click the cell, and then click Copy on the shortcut menu.
-
Hold down Ctrl and select each link that you want to turn off.
Tip: To select a cell that has a link in it without going to the link destination, click the cell and hold the mouse button until the pointer becomes a cross
, and then release the mouse button.
-
On the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click the arrow below Paste, and then click Paste Special.
-
Under Operation, click Multiply, and then click OK.
-
On the Home tab, in the Styles group, click Cell Styles.
-
Under Good, Bad, and Neutral, select Normal.
-
A link opens another page or file when you click it. The destination is frequently another web page, but it can also be a picture, or an email address, or a program. The link itself can be text or a picture.
When a site user clicks the link, the destination is shown in a Web browser, opened, or run, depending on the type of destination. For example, a link to a page shows the page in the web browser, and a link to an AVI file opens the file in a media player.
How links are used
You can use links to do the following:
-
Navigate to a file or web page on a network, intranet, or Internet
-
Navigate to a file or web page that you plan to create in the future
-
Send an email message
-
Start a file transfer, such as downloading or an FTP process
When you point to text or a picture that contains a link, the pointer becomes a hand 
What a URL is and how it works
When you create a link, its destination is encoded as a Uniform Resource Locator (URL), such as:
http://example.microsoft.com/news.htm
file://ComputerName/SharedFolder/FileName.htm
A URL contains a protocol, such as HTTP, FTP, or FILE, a Web server or network location, and a path and file name. The following illustration defines the parts of the URL:
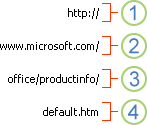
1. Protocol used (http, ftp, file)
2. Web server or network location
3. Path
4. File name
Absolute and relative links
An absolute URL contains a full address, including the protocol, the Web server, and the path and file name.
A relative URL has one or more missing parts. The missing information is taken from the page that contains the URL. For example, if the protocol and web server are missing, the web browser uses the protocol and domain, such as .com, .org, or .edu, of the current page.
It is common for pages on the web to use relative URLs that contain only a partial path and file name. If the files are moved to another server, any links will continue to work as long as the relative positions of the pages remain unchanged. For example, a link on Products.htm points to a page named apple.htm in a folder named Food; if both pages are moved to a folder named Food on a different server, the URL in the link will still be correct.
In an Excel workbook, unspecified paths to link destination files are by default relative to the location of the active workbook. You can set a different base address to use by default so that each time that you create a link to a file in that location, you only have to specify the file name, not the path, in the Insert Hyperlink dialog box.
-
On a worksheet, select the cell where you want to create a link.
-
On the Insert tab, select Hyperlink.
You can also right-click the cell and then select Hyperlink… on the shortcut menu, or you can press Ctrl+K.
-
Under Display Text:, type the text that you want to use to represent the link.
-
Under URL:, type the complete Uniform Resource Locator (URL) of the webpage you want to link to.
-
Select OK.
To link to a location in the current workbook, you can either define a name for the destination cells or use a cell reference.
-
To use a name, you must name the destination cells in the workbook.
How to define a name for a cell or a range of cells
Note: In Excel for the Web, you can’t create named ranges. You can only select an existing named range from the Named Ranges control. Alternately, you can open the file in the Excel desktop app, create a named range there, and then access this option from Excel for the web.
-
Select the cell or range of cells that you want to name.
-
On the Name Box box at the left end of the formula bar
, type the name for the cells, and then press Enter.
Note: Names can’t contain spaces and must begin with a letter.
-
-
On the worksheet, select the cell where you want to create a link.
-
On the Insert tab, select Hyperlink.
You can also right-click the cell and then select Hyperlink… on the shortcut menu, or you can press Ctrl+K.
-
Under Display Text:, type the text that you want to use to represent the link.
-
Under Place in this document:, enter the defined name or cell reference.
-
Select OK.
When you click a link to an email address, your email program automatically starts and creates an email message with the correct address in the To box, provided that you have an email program installed.
-
On a worksheet, select the cell where you want to create a link.
-
On the Insert tab, select Hyperlink.
You can also right-click the cell and then select Hyperlink… on the shortcut menu, or you can press Ctrl+K.
-
Under Display Text:, type the text that you want to use to represent the link.
-
Under E-mail address:, type the email address that you want.
-
Select OK.
You can also create a link to an email address in a cell by typing the address directly in the cell. For example, a link is created automatically when you type an email address, such as someone@example.com.
You can use the HYPERLINK function to create a link to a URL.
Note: The Link_location can be a text string enclosed in quotation marks or a reference to a cell that contains the link as a text string.
To select a hyperlink without activating the link to its destination, do any of the following:
-
Select a cell by clicking it when the pointer is an arrow.
-
Use the arrow keys to select the cell that contains the link.
You can change an existing link in your workbook by changing its destination, its appearance, or the text that is used to represent it.
-
Select the cell that contains the link that you want to change.
Tip: To select a hyperlink without activating the link to its destination, use the arrow keys to select the cell that contains the link.
-
On the Insert tab, select Hyperlink.
You can also right-click the cell or graphic and then select Edit Hyperlink… on the shortcut menu, or you can press Ctrl+K.
-
In the Edit Hyperlink dialog box, make the changes that you want.
Note: If the link was created by using the HYPERLINK worksheet function, you must edit the formula to change the destination. Select the cell that contains the link, and then select the formula bar to edit the formula.
-
Right-click the hyperlink that you want to copy or move, and then select Copy or Cut on the shortcut menu.
-
Right-click the cell that you want to copy or move the link to, and then select Paste on the shortcut menu.
To delete a link, do one of the following:
-
To delete a link, select the cell and press Delete.
-
To turn off a link (delete the link but keep the text that represents it), right-click the cell and then select Remove Hyperlink.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
See Also
Remove or turn off links
Содержание
- HYPERLINK function
- Description
- Syntax
- Remark
- Examples
- Create an external reference (link) to a cell range in another workbook
- Create an external reference between cells in different workbooks
- Create a link to a worksheet in the same workbook
- Need more help?
- Create or change a cell reference
- Need more help?
HYPERLINK function
This article describes the formula syntax and usage of the HYPERLINK function in Microsoft Excel.
Description
The HYPERLINK function creates a shortcut that jumps to another location in the current workbook, or opens a document stored on a network server, an intranet, or the Internet. When you click a cell that contains a HYPERLINK function, Excel jumps to the location listed, or opens the document you specified.
Syntax
The HYPERLINK function syntax has the following arguments:
Link_location Required. The path and file name to the document to be opened. Link_location can refer to a place in a document — such as a specific cell or named range in an Excel worksheet or workbook, or to a bookmark in a Microsoft Word document. The path can be to a file that is stored on a hard disk drive. The path can also be a universal naming convention (UNC) path on a server (in Microsoft Excel for Windows) or a Uniform Resource Locator (URL) path on the Internet or an intranet.
Note Excel for the web the HYPERLINK function is valid for web addresses (URLs) only. Link_location can be a text string enclosed in quotation marks or a reference to a cell that contains the link as a text string.
If the jump specified in link_location does not exist or cannot be navigated, an error appears when you click the cell.
Friendly_name Optional. The jump text or numeric value that is displayed in the cell. Friendly_name is displayed in blue and is underlined. If friendly_name is omitted, the cell displays the link_location as the jump text.
Friendly_name can be a value, a text string, a name, or a cell that contains the jump text or value.
If friendly_name returns an error value (for example, #VALUE!), the cell displays the error instead of the jump text.
In the Excel desktop application, to select a cell that contains a hyperlink without jumping to the hyperlink destination, click the cell and hold the mouse button until the pointer becomes a cross 
Examples
=HYPERLINK(«http://example.microsoft.com/report/budget report.xlsx», «Click for report»)
Opens a workbook saved at http://example.microsoft.com/report. The cell displays «Click for report» as its jump text.
=HYPERLINK(«[http://example.microsoft.com/report/budget report.xlsx]Annual!F10», D1)
Creates a hyperlink to cell F10 on the Annual worksheet in the workbook saved at http://example.microsoft.com/report. The cell on the worksheet that contains the hyperlink displays the contents of cell D1 as its jump text.
=HYPERLINK(«[http://example.microsoft.com/report/budget report.xlsx]’First Quarter’!DeptTotal», «Click to see First Quarter Department Total»)
Creates a hyperlink to the range named DeptTotal on the First Quarter worksheet in the workbook saved at http://example.microsoft.com/report. The cell on the worksheet that contains the hyperlink displays «Click to see First Quarter Department Total» as its jump text.
=HYPERLINK(«http://example.microsoft.com/Annual Report.docx]QrtlyProfits», «Quarterly Profit Report»)
To create a hyperlink to a specific location in a Word file, you use a bookmark to define the location you want to jump to in the file. This example creates a hyperlink to the bookmark QrtlyProfits in the file Annual Report.doc saved at http://example.microsoft.com.
Displays the contents of cell D5 as the jump text in the cell and opens the workbook saved on the FINANCE server in the Statements share. This example uses a UNC path.
Opens the workbook 1stqtr.xlsx that is stored in the Finance directory on drive D, and displays the numeric value that is stored in cell H10.
Creates a hyperlink to the Totals area in another (external) workbook, Mybook.xlsx.
=HYPERLINK(«[Book1.xlsx]Sheet1!A10″,»Go to Sheet1 > A10»)
To jump to a different location in the current worksheet, include both the workbook name, and worksheet name like this, where Sheet1 is the current worksheet.
=HYPERLINK(«[Book1.xlsx]January!A10″,»Go to January > A10»)
To jump to a different location in the current worksheet, include both the workbook name, and worksheet name like this, where January is another worksheet in the workbook.
=HYPERLINK(CELL(«address»,January!A1),»Go to January > A1″)
To jump to a different location in the current worksheet without using the fully qualified worksheet reference ([Book1.xlsx]), you can use this, where CELL(«address») returns the current workbook name.
To quickly update all formulas in a worksheet that use a HYPERLINK function with the same arguments, you can place the link target in another cell on the same or another worksheet, and then use an absolute reference to that cell as the link_location in the HYPERLINK formulas. Changes that you make to the link target are immediately reflected in the HYPERLINK formulas.
Источник
Create an external reference (link) to a cell range in another workbook
You can refer to the contents of cells in another workbook by creating an external reference formula. An external reference (also called a link) is a reference to a cell or range on a worksheet in another Excel workbook, or a reference to a defined name in another workbook.
Open the workbook that will contain the external reference (the destination workbook) and the workbook that contains the data that you want to link to (the source workbook).
Select the cell or cells where you want to create the external reference.
Type = (equal sign).
If you want to use a function, such as SUM, then type the function name followed by an opening parenthesis. For example, =SUM(.
Switch to the source workbook, and then click the worksheet that contains the cells that you want to link.
Select the cell or cells that you want to link to and press Enter.
Note: If you select multiple cells, like =[SourceWorkbook.xlsx]Sheet1!$A$1:$A$10, and have a current version of Microsoft 365, then you can simply press ENTER to confirm the formula as a dynamic array formula. Otherwise, the formula must be entered as a legacy array formula by pressing CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER. For more information on array formulas, see Guidelines and examples of array formulas.
Excel will return you to the destination workbook and display the values from the source workbook.
Note that Excel will return the link with absolute references, so if you want to copy the formula to other cells, you’ll need to remove the dollar ($) signs:
=[SourceWorkbook.xlsx]Sheet1! $A $1
If you close the source workbook, Excel will automatically append the file path to the formula:
Open the workbook that will contain the external reference (the destination workbook) and the workbook that contains the data that you want to link to (the source workbook).
Select the cell or cells where you want to create the external reference.
Type = (equal sign).
Switch to the source workbook, and then click the worksheet that contains the cells that you want to link.
Press F3, select the name that you want to link to and press Enter.
Note: If the named range references multiple cells, and you have a current version of Microsoft 365, then you can simply press ENTER to confirm the formula as a dynamic array formula. Otherwise, the formula must be entered as a legacy array formula by pressing CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER. For more information on array formulas, see Guidelines and examples of array formulas.
Excel will return you to the destination workbook and display the values from the named range in the source workbook.
Open the destination workbook and the source workbook.
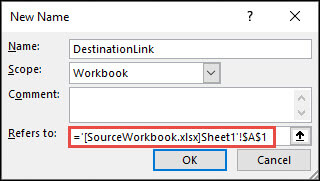
In the destination workbook, Go to Formulas > Defined Names > Define Name.
In the New Name dialog box, in the Name box, type a name for the range.
In the Refers to box, delete the contents, and then keep the cursor in the box.
If you want the name to use a function, enter the function name, and then position the cursor where you want the external reference. For example, type =SUM(), and then position the cursor between the parentheses.
Switch to the source workbook, and then click the worksheet that contains the cells that you want to link.
Select the cell or range of cells that you want to link, and click OK.
External references are especially useful when it’s not practical to keep large worksheet models together in the same workbook.
Merge data from several workbooks You can link workbooks from several users or departments and then integrate the pertinent data into a summary workbook. That way, when the source workbooks are changed, you won’t have to manually change the summary workbook.
Create different views of your data You can enter all of your data into one or more source workbooks, and then create a report workbook that contains external references to only the pertinent data.
Streamline large, complex models By breaking down a complicated model into a series of interdependent workbooks, you can work on the model without opening all of its related sheets. Smaller workbooks are easier to change, don’t require as much memory, and are faster to open, save, and calculate.
Formulas with external references to other workbooks are displayed in two ways, depending on whether the source workbook — the one that supplies data to a formula — is open or closed.
When the source is open, the external reference includes the workbook name in square brackets ( [ ]), followed by the worksheet name, an exclamation point ( !), and the cells that the formula depends on. For example, the following formula adds the cells C10:C25 from the workbook named Budget.xls.
When the source is not open, the external reference includes the entire path.
Note: If the name of the other worksheet or workbook contains spaces or non-alphabetical characters, you must enclose the name (or the path) within single quotation marks as in the example above. Excel will automatically add these for you when you select the source range.
Formulas that link to a defined name in another workbook use the workbook name followed by an exclamation point (!) and the name. For example, the following formula adds the cells in the range named Sales from the workbook named Budget.xlsx.
Select the cell or cells where you want to create the external reference.
Type = (equal sign).
If you want to use a function, such as SUM, then type the function name followed by an opening parenthesis. For example, =SUM(.
Switch to the worksheet that contains the cells that you want to link to.
Select the cell or cells that you want to link to and press Enter.
Note: If you select multiple cells (=Sheet1!A1:A10), and have a current version of Microsoft 365, then you can simply press ENTER to confirm the formula as a dynamic array formula. Otherwise, the formula must be entered as a legacy array formula by pressing CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER. For more information on array formulas, see Guidelines and examples of array formulas.
Excel will return to the original worksheet and display the values from the source worksheet.
Create an external reference between cells in different workbooks
Open the workbook that will contain the external reference (the destination workbook, also called the formula workbook) and the workbook that contains the data that you want to link to (the source workbook, also called the data workbook).
In the source workbook, select the cell or cells you want to link.
Press Ctrl+C or go to Home > Clipboard > Copy.
Switch to the destination workbook, and then click the worksheet where you want the linked data to be placed.
Select the cell where you want to place the linked data, then go to Home > Clipboard > Paste > Paste Link.
Excel will return the data you copied from the source workbook. If you change it, it will automatically change in the destination workbook when you refresh your browser window.
To use the link in a formula, type = in front of the link, choose a function, type (, and then type ) after the link.
Create a link to a worksheet in the same workbook
Select the cell or cells where you want to create the external reference.
Type = (equal sign).
If you want to use a function, such as SUM, then type the function name followed by an opening parenthesis. For example, =SUM(.
Switch to the worksheet that contains the cells that you want to link to.
Select the cell or cells that you want to link to and press Enter.
Excel will return to the original worksheet and display the values from the source worksheet.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Источник
Create or change a cell reference
A cell reference refers to a cell or a range of cells on a worksheet and can be used in a formula so that Microsoft Office Excel can find the values or data that you want that formula to calculate.
In one or several formulas, you can use a cell reference to refer to:
Data from one or more contiguous cells on the worksheet.
Data contained in different areas of a worksheet.
Data on other worksheets in the same workbook.
The value in cell C2.
Cells A1 through F4
The values in all cells, but you must press Ctrl+Shift+Enter after you type in your formula.
Note: This functionality doesn’t work in Excel for the web.
The cells named Asset and Liability
The value in the cell named Liability subtracted from the value in the cell named Asset.
The cell ranges named Week1 and Week2
The sum of the values of the cell ranges named Week1 and Week 2 as an array formula.
Cell B2 on Sheet2
The value in cell B2 on Sheet2.
Click the cell in which you want to enter the formula.
In the formula bar 
Do one of the following:
Reference one or more cells To create a reference, select a cell or range of cells on the same worksheet.
You can drag the border of the cell selection to move the selection, or drag the corner of the border to expand the selection.
Reference a defined name To create a reference to a defined name, do one of the following:
Press F3, select the name in the Paste name box, and then click OK.
Note: If there is no square corner on a color-coded border, the reference is to a named range.
Do one of the following:
If you are creating a reference in a single cell, press Enter.
If you are creating a reference in an array formula (such A1:G4), press Ctrl+Shift+Enter.
The reference can be a single cell or a range of cells, and the array formula can be one that calculates single or multiple results.
Note: If you have a current version of Microsoft 365, then you can simply enter the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, then press ENTER to confirm the formula as a dynamic array formula. Otherwise, the formula must be entered as a legacy array formula by first selecting the output range, entering the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, and then pressing CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER to confirm it. Excel inserts curly brackets at the beginning and end of the formula for you. For more information on array formulas, see Guidelines and examples of array formulas.
You can refer to cells that are on other worksheets in the same workbook by prepending the name of the worksheet followed by an exclamation point ( !) to the start of the cell reference. In the following example, the worksheet function named AVERAGE calculates the average value for the range B1:B10 on the worksheet named Marketing in the same workbook.
1. Refers to the worksheet named Marketing
2. Refers to the range of cells between B1 and B10, inclusively
3. Separates the worksheet reference from the cell range reference
Click the cell in which you want to enter the formula.
In the formula bar 
Click the tab for the worksheet to be referenced.
Select the cell or range of cells to be referenced.
Note: If the name of the other worksheet contains nonalphabetical characters, you must enclose the name (or the path) within single quotation marks ( ‘).
Alternatively, you can copy and paste a cell reference and then use the Link Cells command to create a cell reference. You can use this command to:
Easily display important information in a more prominent position. Let’s say that you have a workbook that contains many worksheets, and on each worksheet is a cell that displays summary information about the other cells on that worksheet. To make these summary cells more prominent, you can create a cell reference to them on the first worksheet of the workbook, which enables you to see summary information about the whole workbook on the first worksheet.
Make it easier to create cell references between worksheets and workbooks. The Link Cells command automatically pastes the correct syntax for you.
Click the cell that contains the data you want to link to.
Press Ctrl+C, or go to the Home tab, and in the Clipboard group, click Copy 
Press Ctrl+V, or go to the Home tab, in the Clipboard group, click Paste 
By default, the Paste Options 
Click the Paste Options button, and then click Paste Link 
Double-click the cell that contains the formula that you want to change. Excel highlights each cell or range of cells referenced by the formula with a different color.
Do one of the following:
To move a cell or range reference to a different cell or range, drag the color-coded border of the cell or range to the new cell or range.
To include more or fewer cells in a reference, drag a corner of the border.
In the formula bar 
Press F3, select the name in the Paste name box, and then click OK.
Press Enter, or, for an array formula, press Ctrl+Shift+Enter.
Note: If you have a current version of Microsoft 365, then you can simply enter the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, then press ENTER to confirm the formula as a dynamic array formula. Otherwise, the formula must be entered as a legacy array formula by first selecting the output range, entering the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, and then pressing CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER to confirm it. Excel inserts curly brackets at the beginning and end of the formula for you. For more information on array formulas, see Guidelines and examples of array formulas.
Frequently, if you define a name to a cell reference after you enter a cell reference in a formula, you may want to update the existing cell references to the defined names.
Do one of the following:
Select the range of cells that contains formulas in which you want to replace cell references with defined names.
Select a single, empty cell to change the references to names in all formulas on the worksheet.
On the Formulas tab, in the Defined Names group, click the arrow next to Define Name, and then click Apply Names.
In the Apply names box, click one or more names, and then click OK.
Select the cell that contains the formula.
In the formula bar 
Press F4 to switch between the reference types.
For more information about the different type of cell references, see Overview of formulas.
Click the cell in which you want to enter the formula.
In the formula bar 
Select a cell or range of cells on the same worksheet. You can drag the border of the cell selection to move the selection, or drag the corner of the border to expand the selection.
Do one of the following:
If you are creating a reference in a single cell, press Enter.
If you are creating a reference in an array formula (such A1:G4), press Ctrl+Shift+Enter.
The reference can be a single cell or a range of cells, and the array formula can be one that calculates single or multiple results.
Note: If you have a current version of Microsoft 365, then you can simply enter the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, then press ENTER to confirm the formula as a dynamic array formula. Otherwise, the formula must be entered as a legacy array formula by first selecting the output range, entering the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, and then pressing CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER to confirm it. Excel inserts curly brackets at the beginning and end of the formula for you. For more information on array formulas, see Guidelines and examples of array formulas.
You can refer to cells that are on other worksheets in the same workbook by prepending the name of the worksheet followed by an exclamation point ( !) to the start of the cell reference. In the following example, the worksheet function named AVERAGE calculates the average value for the range B1:B10 on the worksheet named Marketing in the same workbook.
1. Refers to the worksheet named Marketing
2. Refers to the range of cells between B1 and B10, inclusively
3. Separates the worksheet reference from the cell range reference
Click the cell in which you want to enter the formula.
In the formula bar 
Click the tab for the worksheet to be referenced.
Select the cell or range of cells to be referenced.
Note: If the name of the other worksheet contains nonalphabetical characters, you must enclose the name (or the path) within single quotation marks ( ‘).
Double-click the cell that contains the formula that you want to change. Excel highlights each cell or range of cells referenced by the formula with a different color.
Do one of the following:
To move a cell or range reference to a different cell or range, drag the color-coded border of the cell or range to the new cell or range.
To include more or fewer cells in a reference, drag a corner of the border.
In the formula bar 
Press Enter, or, for an array formula, press Ctrl+Shift+Enter.
Note: If you have a current version of Microsoft 365, then you can simply enter the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, then press ENTER to confirm the formula as a dynamic array formula. Otherwise, the formula must be entered as a legacy array formula by first selecting the output range, entering the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range, and then pressing CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER to confirm it. Excel inserts curly brackets at the beginning and end of the formula for you. For more information on array formulas, see Guidelines and examples of array formulas.
Select the cell that contains the formula.
In the formula bar 
Press F4 to switch between the reference types.
For more information about the different type of cell references, see Overview of formulas.
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
Источник
How to merge and center
- Highlight the cells you want to merge and center.
- Click on “Merge & Center,” which should be displayed in the “Alignment” section of the toolbar at the top of your screen. The top row of cells here is selected.
- The cells will now be merged with the data centered in the merged cell.
Contents
- 1 How do you link two cells in Excel?
- 2 Can you join cells in Excel?
- 3 How do you automatically link cells in Excel?
- 4 How do you link cells?
- 5 How do you merge cells in Excel without losing text?
- 6 How do I merge cells in a table in Excel?
- 7 How do I enable merge and center in Excel?
- 8 How do you link cells in sheets?
- 9 How do you share a link in Excel?
- 10 How do I link cells in the same worksheet in Excel?
- 11 How do I merge rows in Excel without losing data?
- 12 How do I merge rows but not columns?
- 13 Can cells be merged in a table?
- 14 How do I merge cells in Excel 2019?
- 15 Why won’t Excel let me merge cells?
- 16 How do you unlock merge cells in Excel?
- 17 What is the shortcut key to merge cells in Excel?
- 18 How do you reference a cell in another worksheet?
- 19 Why do you link the spreadsheet data?
- 20 What is a hyperlink in computer?
How do you link two cells in Excel?
Combine data with the Ampersand symbol (&)
- Select the cell where you want to put the combined data.
- Type = and select the first cell you want to combine.
- Type & and use quotation marks with a space enclosed.
- Select the next cell you want to combine and press enter. An example formula might be =A2&” “&B2.
Can you join cells in Excel?
To merge a group of cells:
Highlight or select a range of cells. Right-click on the highlighted cells and select Format Cells…. Click the Alignment tab and place a checkmark in the checkbox labeled Merge cells.
How do you automatically link cells in Excel?
Go to Sheet2, click in cell A1 and click on the drop-down arrow of Paste button on the Home tab and select Paste Link button. It will generate a link by automatically entering the formula =Sheet1! A1 .
How do you link cells?
Create a link to a worksheet in the same workbook
- Select the cell or cells where you want to create the external reference.
- Type = (equal sign).
- Switch to the worksheet that contains the cells that you want to link to.
- Select the cell or cells that you want to link to and press Enter.
How do you merge cells in Excel without losing text?
How to merge cells in Excel without losing data
- Select all the cells you want to combine.
- Make the column wide enough to fit the contents of all cells.
- On the Home tab, in the Editing group, click Fill > Justify.
- Click Merge and Center or Merge Cells, depending on whether you want the merged text to be centered or not.
How do I merge cells in a table in Excel?
Merge cells
- In the table, drag the pointer across the cells that you want to merge.
- Click the Layout tab.
- In the Merge group, click Merge Cells.
How do I enable merge and center in Excel?
Merge and Center Cells in Excel
- Select the adjacent cells you want a merge.
- On the Home button, go-to alignment group, click on merge and center cells in excel.
- Click on merge and center cell in excel to combine the data into one cell.
How do you link cells in sheets?
Link to data in a spreadsheet
- In Sheets, click the cell you want to add the link to.
- Click Insert. Link.
- In the Link box, click Select a range of cells to link.
- Highlight the cell or range of cells you want to link to.
- Click OK.
- (Optional) Change the link text.
- Click Apply.
Share a workbook in Excel for the web
- Select File > Share > Share with People (or select Share in the top right).
- In the Enter a name or email address box, type the email addresses of people you want to share with.
How do I link cells in the same worksheet in Excel?
Select a cell where you want to insert a hyperlink. Right-click on the cell and choose the Hyperlink option from the context menu. The Insert Hyperlink dialog window appears on the screen. Choose Place in This Document in the Link to section if your task is to link the cell to a specific location in the same workbook.
How do I merge rows in Excel without losing data?
Combine rows in Excel with Merge Cells add-in
- Select the range of cells where you want to merge rows.
- Go to the Ablebits Data tab > Merge group, click the Merge Cells arrow, and then click Merge Rows into One.
- This will open the Merge Cells dialog box with the preselected settings that work fine in most cases.
How do I merge rows but not columns?
Select the range of cells containing the values you need to merge, and expand the selection to the right blank column to output the final merged values. Then click Kutools > Merge & Split > Combine Rows, Columns or Cells withut Losing Data. 2.
Can cells be merged in a table?
You can combine two or more table cells located in the same row or column into a single cell.Select the cells that you want to merge. Under Table Tools, on the Layout tab, in the Merge group, click Merge Cells.
How do I merge cells in Excel 2019?
How to merge cells
- Highlight the cells you want to merge.
- Click on the arrow just next to “Merge and Center.”
- Scroll down to click on “Merge Cells”. This will merge both rows and columns into one large cell, with alignment intact.
- This will merge the content of the upper-left cell across all highlighted cells.
Why won’t Excel let me merge cells?
Actually, there are two conditions that can cause the Merge and Center tool to be unavailable. You should check, first, to see if your worksheet is protected.If you turn off sharing (if it is on) and disable protection (if the worksheet is protected), then the tool should once again be available.
How do you unlock merge cells in Excel?
1. Unlock all cells on the sheet.
- Press Ctrl + A or click the Select All button.
- Press Ctrl + 1 to open the Format Cells dialog (or right-click any of the selected cells and choose Format Cells from the context menu).
- In the Format Cells dialog, switch to the Protection tab, uncheck the Locked option, and click OK.
What is the shortcut key to merge cells in Excel?
How to Merge Cells in Excel Shortcut
- Merge Cells: ALT H+M+M.
- Merge & Center: ALT H+M+C.
- Merge Across: ALT H+M+A.
- Unmerge Cells: ALT H+M+U.
How do you reference a cell in another worksheet?
To reference a cell or range of cells in another worksheet in the same workbook, put the worksheet name followed by an exclamation mark (!) before the cell address. For example, to refer to cell A1 in Sheet2, you type Sheet2!A1. For example, to refer to cells A1:A10 in Sheet2, you type Sheet2!A1:A10.
Why do you link the spreadsheet data?
✦ Link Worksheet Data – Method Two ✦
As in the example above, we are bringing in the value of cell B6 from the Paris worksheet. The destination worksheet displays the formula value, and the link formula displays in the formula bar (figure 4).
What is a hyperlink in computer?
In a website, a hyperlink (or link) is an item like a word or button that points to another location. When you click on a link, the link will take you to the target of the link, which may be a webpage, document or other online content.
Learn how to link cells in the same or different Excel worksheets.
Linking saves a huge amount of time (and a huge amount of mistakes) in that it allows you to create connections from one cell to another.
For example, if I’m creating a personal cash flow worksheet and at the end of the month I have $4083.58 in my bank account. I can easily link the closing balance from the end of last month to the opening balance for this month. This saves me having to do double-entry, and it ensures the two figures are always the same.
When worksheets are linked, generally one worksheet contains a reference to data in another.
- The worksheet supplying the data is called the source worksheet.
- The worksheet containing the reference is termed the dependent worksheet.
- The actual reference is called an external reference.
As a simple example, consider the following.
There are two worksheets open, Monthly Actuals and Yearly Budget.
The worksheet Yearly Budget contains the following external reference, =MonthlyActuals!$B$6:$B$7.
Yearly Budget is the dependent worksheet relying on data from Monthly Actuals, and Monthly Actuals is the source worksheet, providing data for Yearly Budget.
Tip: links aren’t obvious and it can sometimes be frustrating trying to locate them within the worksheet. To quickly locate linked cells check out my blog post Find, modify and break links to an Excel workbook.
Linking a range of cells
The following techniques describe how to link cells from a source worksheet into a dependent worksheet.
Follow the same technique to link data between workbooks.
Option 1: Using Paste Link
1. In the source worksheet select the required cells.
2. Copy the selected data, e.g. CTRL + C or right-click, Copy.
3. Switch to the dependent worksheet and then select the upper left corner of the range where you want the linked data to appear.
4. To paste the link do one of the following:
- Right-click where you want to paste the link and then select Paste Link from the shortcut menu.
- From the Home tab, in the Clipboard group click on the arrow under the Paste option and select Paste Link.
5. The data will be pasted as a link through to the source worksheet.
Note: using this option may use an absolute cell reference to refer to the linked cell. If you would prefer a relative reference refer to the steps in Option 2.
Option 2: Create a link manually
You can manually create a link to any cell by inserting a reference to the source data.
1. In the dependent worksheet select the cell to hold the linked data and then type equals (=).
2. Switch to the source worksheet/workbook and select the cell holding the data to be linked.
3. Press ENTER.
Hint: you may like to have all source worksheets open before saving the dependent worksheet, as this will automatically update any external references if the source worksheet is saved in a different folder.
Identifying linked cells
You can easily identify where cells are linked as the link address will show in the Formula bar.
| Link type | Formula examples |
| Linking within the same workbook | =’Worksheet name’!Reference e.g. =Northern!B9 |
| Linking to an external workbook | =’Full pathname for worksheet’!Reference e.g. ='[C:DocumentsLink Between Worksheets.xlsx]Northern’!B9 |
Was this blog helpful? Let us know in the Comments below.
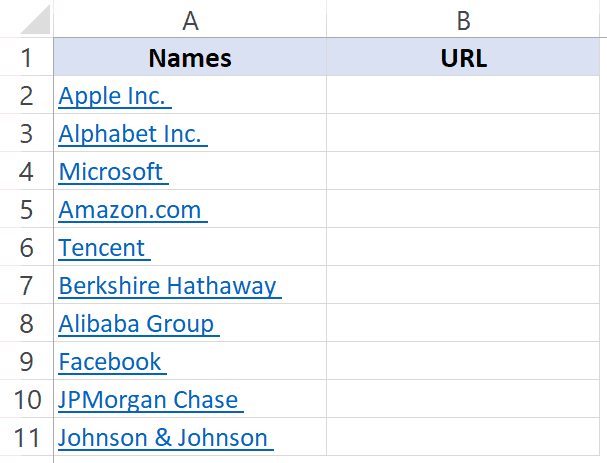
Excel allows having hyperlinks in cells which you can use to directly go to that URL.
For example, below is a list where I have company names which are hyperlinked to the company website’s URL. When you click on the cell, it will automatically open your default browser (Chrome in my case) and go to that URL.
There are many things you can do with hyperlinks in Excel (such as a link to an external website, link to another sheet/workbook, link to a folder, link to an email, etc.).
In this article, I will cover all you need to know to work with hyperlinks in Excel (including some useful tips and examples).
How to Insert Hyperlinks in Excel
There are many different ways to create hyperlinks in Excel:
- Manually type the URL (or copy paste)
- Using the HYPERLINK function
- Using the Insert Hyperlink dialog box
Let’s learn about each of these methods.
Manually Type the URL
When you manually enter a URL in a cell in Excel, or copy and paste it in the cell, Excel automatically converts it into a hyperlink.
Below are the steps that will change a simple URL into a hyperlink:
- Select a cell in which you want to get the hyperlink
- Press F2 to get into the edit mode (or double click on the cell).
- Type the URL and press enter. For example, if I type the URL – https://trumpexcel.com in a cell and hit enter, it will create a hyperlink to it.
Note that you need to add http or https for those URLs where there is no www in it. In case there is www as the prefix, it would create the hyperlink even if you don’t add the http/https.
Similarly, when you copy a URL from the web (or some other document/file) and paste it in a cell in Excel, it will automatically be hyperlinked.
Insert Using the Dialog Box
If you want the text in the cell to be something else other than the URL and want it to link to a specific URL, you can use the insert hyperlink option in Excel.
Below are the steps to enter the hyperlink in a cell using the Insert Hyperlink dialog box:
- Select the cell in which you want the hyperlink
- Enter the text that you want to be hyperlinked. In this case, I am using the text ‘Sumit’s Blog’
- Click the Insert tab.
- Click the links button. This will open the Insert Hyperlink dialog box (You can also use the keyboard shortcut – Control + K).
- In the Insert Hyperlink dialog box, enter the URL in the Address field.
- Press the OK button.
This will insert the hyperlink the cell while the text remains the same.
There are many more things you can do with the ‘Insert Hyperlink’ dialog box (such as create a hyperlink to another worksheet in the same workbook, create a link to a document/folder, create a link to an email address, etc.). These are all covered later in this tutorial.
Insert Using the HYPERLINK Function
Another way to insert a link in Excel can be by using the HYPERLINK Function.
Below is the syntax:
HYPERLINK(link_location, [friendly_name])
- link_location: This can be the URL of a web-page, a path to a folder or a file in the hard disk, place in a document (such as a specific cell or named range in an Excel worksheet or workbook).
- [friendly_name]: This is an optional argument. This is the text that you want in the cell that has the hyperlink. In case you omit this argument, it will use the link_location text string as the friendly name.
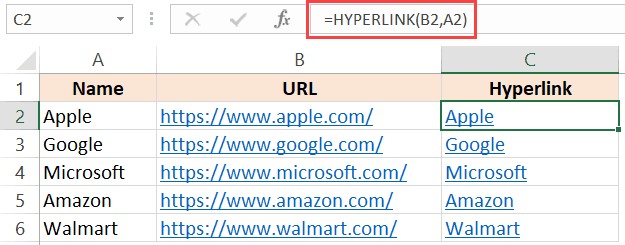
Below is an example where I have the name of companies in one column and their website URL in another column.
Below is the HYPERLINK function to get the result where the text is the company name and it links to the company website.
In the examples so far, we have seen how to create hyperlinks to websites.
But you can also create hyperlinks to worksheets in the same workbook, other workbooks, and files and folders on your hard disk.
Let’s see how it can be done.
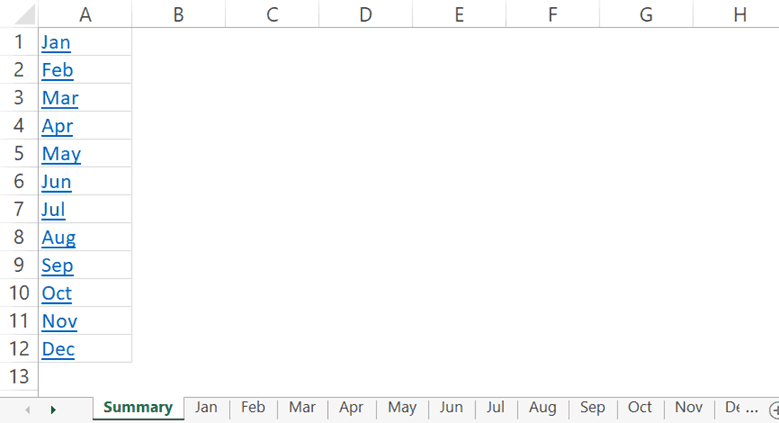
Create a Hyperlink to a Worksheet in the Same Workbook
Below are the steps to create a hyperlink to Sheet2 in the same workbook:
- Select the cell in which you want the link
- Enter the text that you want to be hyperlinked. In this example, I have used the text ‘Link to Sheet2’.
- Click the Insert tab.
- Click the links button. This will open the Insert Hyperlink dialog box (You can also use the keyboard shortcut – Control + K).
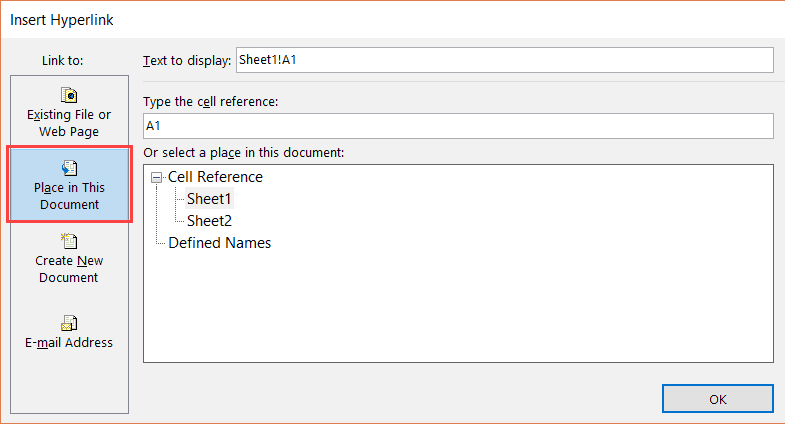
- In the Insert Hyperlink dialog box, select ‘Place in This Document’ option in the left pane.
- Enter the cell which you want to hyperlink (I am going with the default A1).
- Select the sheet that you want to hyperlink (Sheet2 in this case)
- Click OK.
Note: You can also use the same method to create a hyperlink to any cell in the same workbook. For example, if you want to link to a far off cell (say K100), you can do that by using this cell reference in step 6 and selecting the existing sheet in step 7.
You can also use the same method to link to a defined name (named cell or named range). If you have any named ranges (named cells) in the workbook, these would be listed in under the ‘Defined Names’ category in the ‘Insert Hyperlink’ dialog box.
Apart from the dialog box, there is also a function in Excel that allows you to create hyperlinks.
So instead of using the dialog box, you can instead use the HYPERLINK formula to create a link to a cell in another worksheet.
The below formula will do this:
=HYPERLINK("#"&"Sheet2!A1","Link to Sheet2")
Below is how this formula works:
- “#” would tell the formula to refer to the same workbook.
- “Sheet2!A1” tells the formula the cell that should be linked to in the same workbook
- “Link to Sheet2” is the text that appears in the cell.
Create a Hyperlink to a File (in the same or different folders)
You can also use the same method to create hyperlinks to other Excel (and non-Excel) files that are in the same folder or are in other folders.
For example, if you want to open a file with the Test.xlsx which is in the same folder as your current file, you can use the below steps:
- Select the cell in which you want the hyperlink
- Click the Insert tab.
- Click the links button. This will open the Insert Hyperlink dialog box (You can also use the keyboard shortcut – Control + K).
- In the Insert Hyperlink dialog box, select ‘Existing File or Webpage’ option in the left pane.
- Select ‘Current folder’ in the Look in options
- Select the file for which you want to create the hyperlink. Note that you can link to any file type (Excel as well as non-Excel files)
- [Optional] Change the Text to Display name if you want to.
- Click OK.
In case you want to link to a file which is not in the same folder, you can Browse the file and then select it. To Browse the file, click on the folder icon in the Insert Hyperlink dialog box (as shown below).
You can also do this using the HYPERLINK function.
The below formula will create a hyperlink that links to a file in the same folder as the current file:
=HYPERLINK("Test.xlsx","Test File")
In case the file is not in the same folder, you can copy the address of the file and use it as the link_location.
Create a Hyperlink to a Folder
This one also follows the same methodology.
Below are the steps to create a hyperlink to a folder:
- Copy the folder address for which you want to create the hyperlink
- Select the cell in which you want the hyperlink
- Click the Insert tab.
- Click the links button. This will open the Insert Hyperlink dialog box (You can also use the keyboard shortcut – Control + K).
- In the Insert Hyperlink dialog box, paste folder address
- Click OK.
You can also use the HYPERLINK function to create a hyperlink that points to a folder.
For example, the below formula will create a hyperlink to a folder named TEST on the desktop and as soon as you click on the cell with this formula, it will open this folder.
=HYPERLINK("C:UserssumitDesktopTest","Test Folder")
To use this formula, you will have to change the address of the folder to the one you want to link to.
Create Hyperlink to an Email Address
You can also have hyperlinks which open your default email client (such as Outlook) and have the recipients email and the subject line already filled in the send field.
Below are the steps to create an email hyperlink:
- Select the cell in which you want the hyperlink
- Click the Insert tab.
- Click the links button. This will open the Insert Hyperlink dialog box (You can also use the keyboard shortcut – Control + K).
- In the insert dialog box, click on ‘E-mail Address’ in the ‘Link to’ options
- Enter the E-mail address and the Subject line
- [Optional] Enter the text you want to be displayed in the cell.
- Click OK.
Now when you click on the cell which has the hyperlink, it will open your default email client with the email and subject line pre-filled.
You can also do this using the HYPERLINK function.
The below formula will open the default email client and have one email address already pre-filled.
=HYPERLINK("mailto:abc@trumpexcel.com","Send Email")
Note that you need to use mailto: before the email address in the formula. This tells the HYPERLINK function to open the default email client and use the email address that follows.
In case you want to have the subject line as well, you can use the below formula:
=HYPERLINK("mailto:abc@trumpexcel.com,?cc=&bcc=&subject=Excel is Awesome","Generate Email")
In the above formula, I have kept the cc and bcc fields as empty, but you can also these emails if needed.
Here is a detailed guide on how to send emails using the HYPERLINK function.
Remove Hyperlinks
If you only have a few hyperlinks, you can remove these manually, but if you have a lot, you can use a VBA Macro to do this.
Manually Remove Hyperlinks
Below are the steps to remove hyperlinks manually:
- Select the data from which you want to remove hyperlinks.
- Right-click on any of the selected cell.
- Click on the ‘Remove Hyperlink’ option.
The above steps would instantly remove hyperlinks from the selected cells.
In case you want to remove hyperlinks from the entire worksheet, select all the cells and then follow the above steps.
Remove Hyperlinks Using VBA
Below is the VBA code that will remove the hyperlinks from the selected cells:
Sub RemoveAllHyperlinks() 'Code by Sumit Bansal @ trumpexcel.com Selection.Hyperlinks.Delete End Sub
If you want to remove all the hyperlinks in the worksheet, you can use the below code:
Sub RemoveAllHyperlinks() 'Code by Sumit Bansal @ trumpexcel.com ActiveSheet.Hyperlinks.Delete End Sub
Note that this code will not remove the hyperlinks created using the HYPERLINK function.
You need to add this VBA code in the regular module in the VB Editor.
If you need to remove hyperlinks quite often, you can use the above VBA codes, save it in the Personal Macro Workbook, and add it to your Quick Access Toolbar. This will allow you to remove hyperlinks with a single click and it will be available in all the workbooks on your system.
Here is a detailed guide on how to remove hyperlinks in Excel.
Prevent Excel from Creating Hyperlinks Automatically
For some people, it’s a great feature that Excel automatically converts a URL text to a hyperlink when entered in a cell.
And for some people, it’s an irritation.
If you’re in the latter category, let me show you a way to prevent Excel from automatically creating URLs into hyperlinks.
The reason this happens as there is a setting in Excel that automatically converts ‘Internet and network paths’ into hyperlinks.
Here are the steps to disable this setting in Excel:
- Click the File tab.
- Click on Options.
- In the Excel Options dialog box, click on ‘Proofing’ in the left pane.
- Click on the AutoCorrect Options button.
- In the AutoCorrect dialog box, select the ‘AutoFormat As You Type’ tab.
- Uncheck the option – ‘Internet and network paths with hyperlinks’
- Click OK.
- Close the Excel Options dialog box.
If you’ve completed the following steps, Excel would not automatically turn URLs, email address, and network paths into hyperlinks.
Note that this change is applied to the entire Excel application, and would be applied to all the workbooks that you work with.
Extract Hyperlink URLs (using VBA)
There is no function in Excel that can extract the hyperlink address from a cell.
However, this can be done using the power of VBA.
For example, suppose you have a dataset (as shown below) and you want to extract the hyperlink URL in the adjacent cell.
Let me show you two techniques to extract the hyperlinks from the text in Excel.
Extract Hyperlink in the Adjacent Column
If you want to extract all the hyperlink URLs in one go in an adjacent column, you can so that using the below code:
Sub ExtractHyperLinks()
Dim HypLnk As Hyperlink
For Each HypLnk In Selection.Hyperlinks
HypLnk.Range.Offset(0, 1).Value = HypLnk.Address
Next HypLnk
End Sub
The above code goes through all the cells in the selection (using the FOR NEXT loop) and extracts the URLs in the adjacent cell.
In case you want to get the hyperlinks in the entire worksheet, you can use the below code:
Sub ExtractHyperLinks()
On Error Resume Next
Dim HypLnk As Hyperlink
For Each HypLnk In ActiveSheet.Hyperlinks
HypLnk.Range.Offset(0, 1).Value = HypLnk.Address
Next HypLnk
End Sub
Note that the above codes wouldn’t work for hyperlinks created using the HYPERLINK function.
Extract Hyperlink Using a Formula (created with VBA)
The above code works well when you want to get the hyperlinks from a dataset in one go.
But if you have a list of hyperlinks that keeps expanding, you can create a User Defined Function/formula in VBA.
This will allow you to quickly use the cell as the input argument and it will return the hyperlink address in that cell.
Below is the code that will create a UDF for getting the hyperlinks:
Function GetHLink(rng As Range) As String
If rng(1).Hyperlinks.Count <> 1 Then
GetHLink = ""
Else
GetHLink = rng.Hyperlinks(1).Address
End If
End Function
Note that this wouldn’t work with Hyperlinks created using the HYPERLINK function.
Also, in case you select a range of cells (instead of a single cell), this formula will return the hyperlink in the first cell only.
Find Hyperlinks with Specific Text
If you’re working with a huge dataset that has a lot of hyperlinks in it, it could be a challenge when you want to find the ones that have a specific text in it.
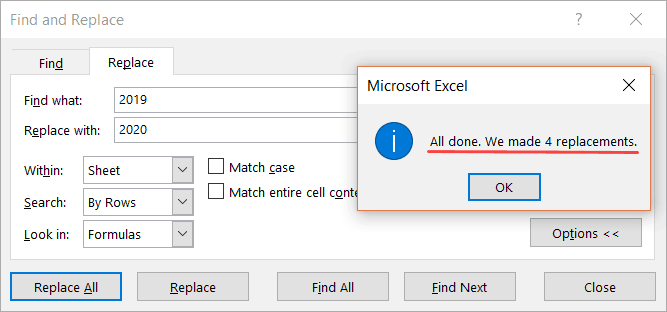
For example, suppose I have a dataset as shown below and I want to find all the cells with hyperlinks that have the text 2019 in it and change it to 2020.
And no.. doing this manually is not an option.
You can do that using a wonderful feature in Excel – Find and Replace.
With this, you can quickly find and select all the cells that have a hyperlink and then change the text 2019 with 2020.
Below are the steps to select all the cells with a hyperlink and the text 2019:
- Select the range in which you want to find the cells with hyperlinks with 2019. In case you want to find in the entire worksheet, select the entire worksheet (click on the small triangle at the top left).
- Click the Home tab.
- In the Editing group, click on Find and Select
- In the drop-down, click on Replace. This will open the Find and Replace dialog box.
- In the Find and Replace dialog box, click on the Options button.This will show more options in the dialog box.
- In the ‘Find What’ options, click on the little downward pointing arrow in the Format button (as shown below).
- Click on the ‘Choose Format From Cell’. This will turn your cursor into a plus icon with a format picker icon.
- Select any cell which has a hyperlink in it. You will notice that the Format gets visible in the box on the left of the Format button. This indicates that the format of the cell you selected has been picked up.
- Enter 2019 in the ‘Find What’ field and 2020 in the ‘Replace with’ field.
- Click on the Replace All button.
In the above data, it will change the text of four cells that have the text 2019 in it and also has a hyperlink.
You can also use this technique to find all the cells with hyperlinks and get a list of it. To do this, instead of clicking on Replace All, click on the Find All button. This will instantly give you a list of all the cell address that has hyperlinks (or hyperlinks with specific text depending on what you’ve searched for).
Note: This technique works as Excel is able to identify the formatting of the cell that you select and use that as a criterion to find cells. So if you’re finding hyperlinks, make sure you select a cell that has the same kind of formatting. If you select a cell that has a background color or any text formatting, it may not find all the correct cells.
Selecting a Cell that has a Hyperlink in Excel
While Hyperlinks are useful, there are a few things about it that irritate me.
For example, if you want to select a cell that has a hyperlink in it, Excel would automatically open your default web browser and try to open this URL.
Another irritating thing about it is that sometimes when you have a cell that has a hyperlink in it, it makes the entire cell clickable. So even if you’re clicking on the hyperlinked text directly, it still opens the browser and the URL of the text.
So let me quickly show you how to get rid of these minor irritants.
Select the Cell (without opening the URL)
This is a simple trick.
When you hover the cursor over a cell that has a hyperlink in it, you’ll notice the hand icon (which indicates if you click on it, Excel will open the URL in a browser)
Click the cell anyway and hold the left button of the mouse.
After a second, you’ll notice that the hand cursor icon changes into the plus icon, and now when you leave it, Excel will not open the URL.
Instead, it would select the cell.
Now, you can make any changes in the cell you want.
Neat trick… right?
Select a Cell by clicking on the blank space in the cell
This is another thing that might drive you nuts.
When there is a cell with the hyperlink in it as well as some blank space, and you click on the blank space, it still opens the hyperlink.
Here is a quick fix.
This happens when these cells have the wrap text enabled.
If you disable wrap text for these cells, you will be able to click on the white space on the right of the hyperlink without opening this link.
Some Practical Example of Using Hyperlink
There are useful things you can do when working with hyperlinks in Excel.
In this section, I am going to cover some examples that you may find useful and can use in your day-to-day work.
Example 1 – Create an Index of All Sheets in the Workbook
If you have a workbook with a lot of sheets, you can use a VBA code to quickly create a list of the worksheets and hyperlink these to the sheets.
This could be useful when you have 12-month data in 12 different worksheets and want to create one index sheet that links to all these monthly data worksheets.
Below is the code that will do this:
Sub CreateSummary()
'Created by Sumit Bansal of trumpexcel.com
'This code can be used to create summary worksheet with hyperlinks
Dim x As Worksheet
Dim Counter As Integer
Counter = 0
For Each x In Worksheets
Counter = Counter + 1
If Counter = 1 Then GoTo Donothing
With ActiveCell
.Value = x.Name
.Hyperlinks.Add ActiveCell, "", x.Name & "!A1", TextToDisplay:=x.Name, ScreenTip:="Click here to go to the Worksheet"
With Worksheets(Counter)
.Range("A1").Value = "Back to " & ActiveSheet.Name
.Hyperlinks.Add Sheets(x.Name).Range("A1"), "", _
"'" & ActiveSheet.Name & "'" & "!" & ActiveCell.Address, _
ScreenTip:="Return to " & ActiveSheet.Name
End With
End With
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Select
Donothing:
Next x
End Sub
You can place this code in the regular module in the workbook (in VB Editor)
This code also adds a link to the summary sheet in cell A1 of all the worksheets. In case you don’t want that, you can remove that part from the code.
You can read more about this example here.
Note: This code works when you have the sheet (in which you want the summary of all the worksheets with links) at the beginning. In case it’s not at the beginning, this may not give the right results).
Example 2 – Create Dynamic Hyperlinks
In most cases, when you click on a hyperlink in a cell in Excel, it will take you to a URL or to a cell, file or folder. Normally, these are static URLs which means that a hyperlink will take you to a specific predefined URL/location only.
But you can also use a little bit for Excel formula trickery to create dynamic hyperlinks.
By dynamic hyperlinks, I mean links that are dependent on a user selection and change accordingly.
For example, in the below example, I want the hyperlink in cell E2 to point to the company website based on the drop-down list selected by the user (in cell D2).
This can be done using the below formula in cell E2:
=HYPERLINK(VLOOKUP(D2,$A$2:$B$6,2,0), "Click here")
The above formula uses the VLOOKUP function to fetch the URL from the table on the left. The HYPERLINK function then uses this URL to create a hyperlink in the cell with the text – ‘Click here’.
When you change the selection using the drop-down list, the VLOOKUP result will change and would accordingly link to the selected company’s website.
This could be a useful technique when you’re creating a dashboard in Excel. You can make the hyperlinks dynamic depending on the user selection (which could be a drop-down list or a checkbox or a radio button).
Here is a more detailed article of using Dynamic Hyperlinks in Excel.
Example 3 – Quickly Generate Simple Emails Using Hyperlink Function
As I mentioned in this article earlier, you can use the HYPERLINK function to quickly create simple emails (with pre-filled recipient’s emails and the subject line).
Single Recipient Email Id
=HYPERLINK("mailto:abc@trumpexcel.com","Generate Email")
This would open your default email client with the email id abc@trumpexcel.com in the ‘To’ field.
Multiple Recipients Email Id
=HYPERLINK("mailto:abc@trumpexcel.com,def@trumpexcel.com","Generate Email")
For sending the email to multiple recipients, use a comma to separate email ids. This would open the default email client with all the email ids in the ‘To’ field.
Add Recipients in CC and BCC List
=HYPERLINK("mailto:abc@trumpexcel.com,def@trumpexcel.com?cc=123@trumpexcel.com&bcc=456@trumpexcel.com","Generate Email")
To add recipients to CC and BCC list, use question mark ‘?’ when ‘mailto’ argument ends, and join CC and BCC with ‘&’. When you click on the link in excel, it would have the first 2 ids in ‘To’ field, 123@trumpexcel.com in ‘CC’ field and 456@trumpexcel.com in the ‘BCC’ field.
Add Subject Line
=HYPERLINK("mailto:abc@trumpexcel.com,def@trumpexcel.com?cc=123@trumpexcel.com&bcc=456@trumpexcel.com&subject=Excel is Awesome","Generate Email")
You can add a subject line by using the &Subject code. In this case, this would add ‘Excel is Awesome’ in the ‘Subject’ field.
Add Single Line Message in Body
=HYPERLINK("mailto:abc@trumpexcel.com,def@trumpexcel.com?cc=123@trumpexcel.com&bcc=456@trumpexcel.com&subject=Excel is Awesome&body=I love Excel","Email Trump Excel")
This would add a single line ‘I love Excel’ to the email message body.
Add Multiple Lines Message in Body
=HYPERLINK("mailto:abc@trumpexcel.com,def@trumpexcel.com?cc=123@trumpexcel.com&bcc=456@trumpexcel.com&subject=Excel is Awesome&body=I love Excel.%0AExcel is Awesome","Generate Email")
To add multiple lines in the body you need to separate each line with %0A. If you wish to introduce two line breaks, add %0A twice, and so on.
Here is a detailed article on how to send emails from Excel.
Hope you found this article useful.
Let me know your thoughts in the comments section.
You May Also Like the Following Excel Tutorials:
- Excel AutoCorrect
- How to Find External Links and References in Excel
- 100+ Excel Interview Questions & Answers
- Excel Text to Columns
- Excel Sparklines

 .
. , open the web page that you want to link to, and then switch back to Excel without closing your browser.
, open the web page that you want to link to, and then switch back to Excel without closing your browser.
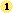 Name box
Name box
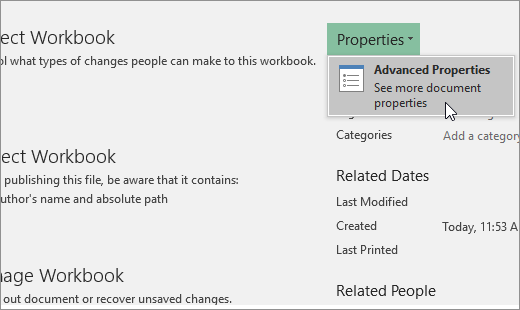
 , click Prepare, and then click Properties.
, click Prepare, and then click Properties.