Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel for iPad Excel for iPhone Excel for Android tablets Excel 2010 Excel 2007 Excel for Mac 2011 Excel for Android phones Excel Starter 2010 More…Less
The CELL function returns information about the formatting, location, or contents of a cell. For example, if you want to verify that a cell contains a numeric value instead of text before you perform a calculation on it, you can use the following formula:
=IF(CELL(«type»,A1)=»v»,A1*2,0)
This formula calculates A1*2 only if cell A1 contains a numeric value, and returns 0 if A1 contains text or is blank.
Note: Formulas that use CELL have language-specific argument values and will return errors if calculated using a different language version of Excel. For example, if you create a formula containing CELL while using the Czech version of Excel, that formula will return an error if the workbook is opened using the French version. If it is important for others to open your workbook using different language versions of Excel, consider either using alternative functions or allowing others to save local copies in which they revise the CELL arguments to match their language.
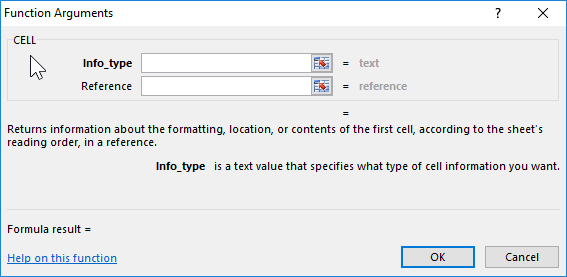
Syntax
CELL(info_type, [reference])
The CELL function syntax has the following arguments:
|
Argument |
Description |
|---|---|
|
info_type Required |
A text value that specifies what type of cell information you want to return. The following list shows the possible values of the Info_type argument and the corresponding results. |
|
reference Optional |
The cell that you want information about. If omitted, the information specified in the info_type argument is returned for cell selected at the time of calculation. If the reference argument is a range of cells, the CELL function returns the information for active cell in the selected range. Important: Although technically reference is optional, including it in your formula is encouraged, unless you understand the effect its absence has on your formula result and want that effect in place. Omitting the reference argument does not reliably produce information about a specific cell, for the following reasons:
|
info_type values
The following list describes the text values that can be used for the info_type argument. These values must be entered in the CELL function with quotes (» «).
|
info_type |
Returns |
|---|---|
|
«address» |
Reference of the first cell in reference, as text. |
|
«col» |
Column number of the cell in reference. |
|
«color» |
The value 1 if the cell is formatted in color for negative values; otherwise returns 0 (zero). Note: This value is not supported in Excel for the web, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
|
«contents» |
Value of the upper-left cell in reference; not a formula. |
|
«filename» |
Filename (including full path) of the file that contains reference, as text. Returns empty text («») if the worksheet that contains reference has not yet been saved. Note: This value is not supported in Excel for the web, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
|
«format» |
Text value corresponding to the number format of the cell. The text values for the various formats are shown in the following table. Returns «-» at the end of the text value if the cell is formatted in color for negative values. Returns «()» at the end of the text value if the cell is formatted with parentheses for positive or all values. Note: This value is not supported in Excel for the web, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
|
«parentheses» |
The value 1 if the cell is formatted with parentheses for positive or all values; otherwise returns 0. Note: This value is not supported in Excel for the web, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
|
«prefix» |
Text value corresponding to the «label prefix» of the cell. Returns single quotation mark (‘) if the cell contains left-aligned text, double quotation mark («) if the cell contains right-aligned text, caret (^) if the cell contains centered text, backslash () if the cell contains fill-aligned text, and empty text («») if the cell contains anything else. Note: This value is not supported in Excel for the web, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
|
«protect» |
The value 0 if the cell is not locked; otherwise returns 1 if the cell is locked. Note: This value is not supported in Excel for the web, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
|
«row» |
Row number of the cell in reference. |
|
«type» |
Text value corresponding to the type of data in the cell. Returns «b» for blank if the cell is empty, «l» for label if the cell contains a text constant, and «v» for value if the cell contains anything else. |
|
«width» |
Returns an array with 2 items. The 1st item in the array is the column width of the cell, rounded off to an integer. Each unit of column width is equal to the width of one character in the default font size. The 2nd item in the array is a Boolean value, the value is TRUE if the column width is the default or FALSE if the width has been explicitly set by the user. Note: This value is not supported in Excel for the web, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
CELL format codes
The following list describes the text values that the CELL function returns when the Info_type argument is «format» and the reference argument is a cell that is formatted with a built-in number format.
|
If the Excel format is |
The CELL function returns |
|---|---|
|
General |
«G» |
|
0 |
«F0» |
|
#,##0 |
«,0» |
|
0.00 |
«F2» |
|
#,##0.00 |
«,2» |
|
$#,##0_);($#,##0) |
«C0» |
|
$#,##0_);[Red]($#,##0) |
«C0-« |
|
$#,##0.00_);($#,##0.00) |
«C2» |
|
$#,##0.00_);[Red]($#,##0.00) |
«C2-« |
|
0% |
«P0» |
|
0.00% |
«P2» |
|
0.00E+00 |
«S2» |
|
# ?/? or # ??/?? |
«G» |
|
m/d/yy or m/d/yy h:mm or mm/dd/yy |
«D4» |
|
d-mmm-yy or dd-mmm-yy |
«D1» |
|
d-mmm or dd-mmm |
«D2» |
|
mmm-yy |
«D3» |
|
mm/dd |
«D5» |
|
h:mm AM/PM |
«D7» |
|
h:mm:ss AM/PM |
«D6» |
|
h:mm |
«D9» |
|
h:mm:ss |
«D8» |
Note: If the info_type argument in the CELL function is «format» and you later apply a different format to the referenced cell, you must recalculate the worksheet (press F9) to update the results of the CELL function.
Examples
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
See Also
Change the format of a cell
Create or change a cell reference
ADDRESS function
Add, change, find or clear conditional formatting in a cell
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
Very often, when working in Excel, you need to use data about addressing cells in a spreadsheet. For this was provided the function CELL. Consider its use on specific examples.
Function CELL value and properties in Excel
It should be noted that Excel uses several functions for addressing cells:
- — ROW;
- — COLUMN and others.
CELL function return information about the formatting, address, or contents of a cell. The function can return detailed information about the cell format, thereby eliminating the need to use VBA in some cases. The function is especially useful if you need to display the full path of the file in the cells.
How does the CELL function in Excel work?
Function in its work uses the syntax that consists of two arguments:
=CELL(info_type,[reference])
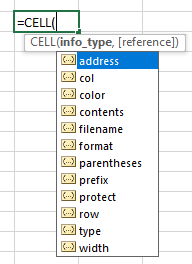
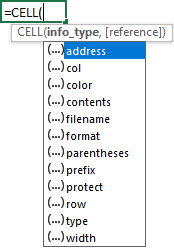
- Info_type is a text value that specifies the type of cell information that is required. When you enter a function manually, a drop-down list is displayed where all possible values of the “information type” argument are shown:
- [Reference] is an optional argument. The cell for which you want to receive information. If this argument is omitted, the information specified in the information_type argument is returned for the last cell changed. If the link argument points to a range of cells, function returns information only for the upper-left value of the range.
Examples of using the CELL function in Excel
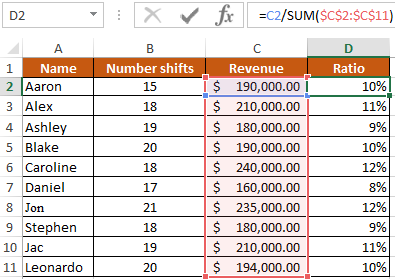
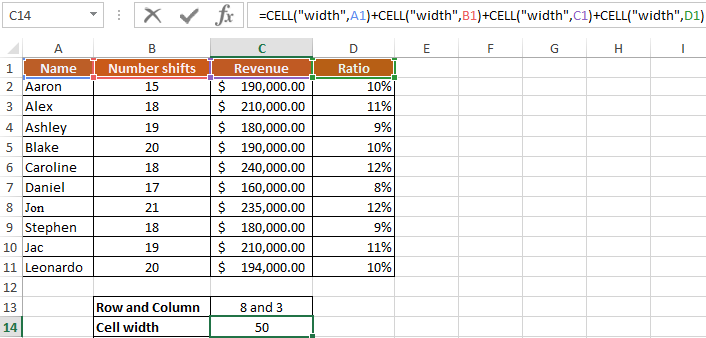
Example 1. Given the table of accounting work of employees of the organization of the form:
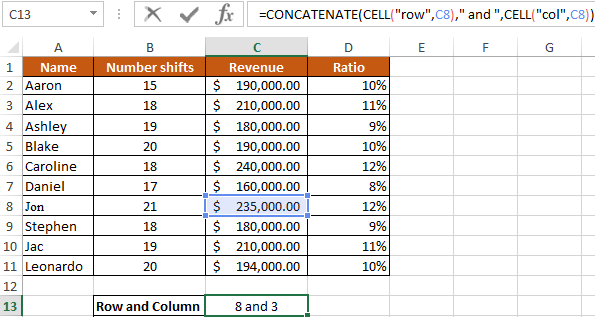
It is necessary with the help of the CELL function to calculate in which row and column the salary is in the amount of 235,000 dollars.
To do this, we introduce the following formula:
here:
- — «row» and «column» — output parameter;
- — C8 — address data with a salary.
As a result of the calculations, we obtain: row №8 and column № 3 (C).
How to know width of an Excel spreadsheet?
Example 2. It is necessary to calculate the width of the table in characters. Immediately it should be noted that in Excel, by default, the width of columns and cells is measured in the number of characters that they fit in their value are available for display in a cell without a line break.
Note. The height of lines and cells in Excel is by default measured in units of the basic font — in (pt) points. The larger the font, the higher the line for full display of characters in height.
Let’s enter into C14 the formula for calculating the sum of the width of each column of the table:
here:
- — «width» is a function parameter;
- — A1 — the width of a specific column.
How to get the value of the first value in the range
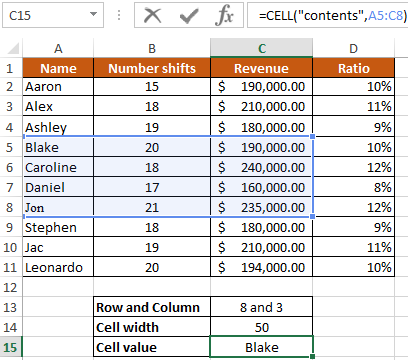
Example 3. In the condition of example 1, you need to display the contents of only the first (upper left) value from the range A5:C8.
We introduce the formula for calculating:
Download examples CELL function in Excel
Description of the formula is similar to the previous two examples.
This Tutorial demonstrates how to use the Excel CELL Function in Excel to get information about a cell.
CELL Function Overview
The CELL Function Returns information about a cell. Color, filename, contents, format, row, etc.
To use the CELL Excel Worksheet Function, select a cell and type:
(Notice how the formula inputs appear)
CELL function Syntax and inputs:
=CELL(info_type,reference)info_type – Text indicating what cell information you would like to return.
reference – The cell reference that you want information about.
How to use the CELL Function in Excel
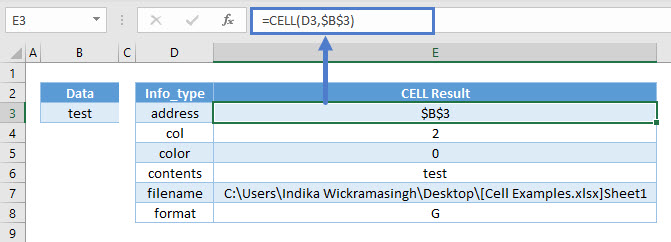
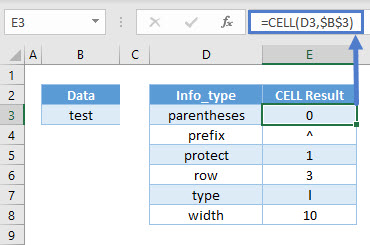
The CELL Function returns information about the formatting, location, or contents of cell.
=CELL(D3,$B$3)As seen above, the CELL Function returns all kinds of information from cell B3.
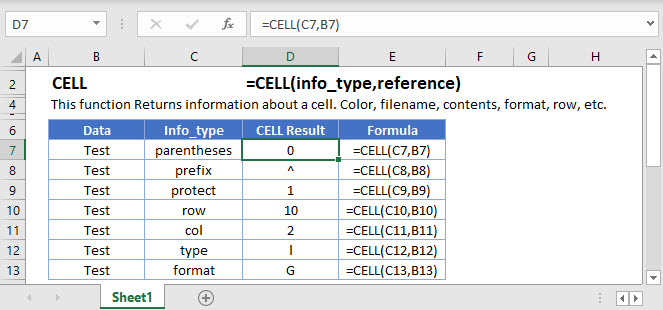
If you type =CELL(, you will be able to see 12 different types of information to retrieve.
Here are additional outputs of the CELL Function:
Overall View of Info_types
Some of the info_types are pretty straightforward and retrieves what you asked for, while the rest will be explained in the next few sections because of the complexity.
| Info_type | What it retrieves? |
| “address” | The cell reference/address. |
| “col” | The column number. |
| “color” | * |
| “contents” | The value itself or result of the formula. |
| “filename” | The full path, filename, and extension in square brackets, and sheet name. |
| “format” | * |
| “parentheses” | * |
| “prefix” | * |
| “protect” | * |
| “row” | The row number. |
| “type” | * |
| “width” | The column width rounded to the nearest integer. |
* Explained in the next few sections.
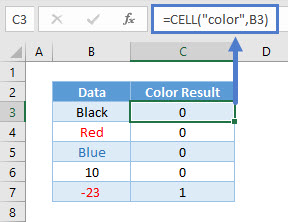
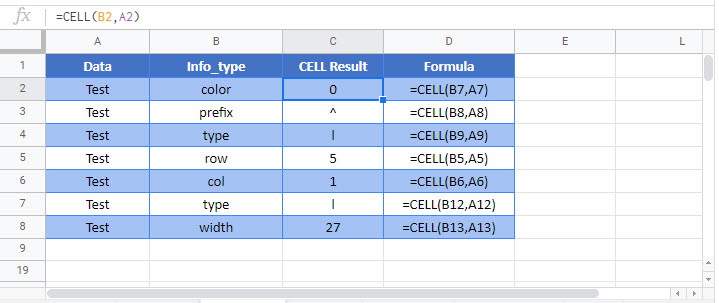
Color Info_type
Color will show all results as 0 unless the cell is formatted with color for negative values. The latter will show as 1.
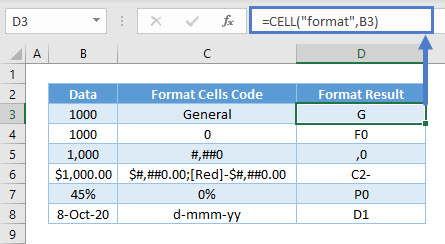
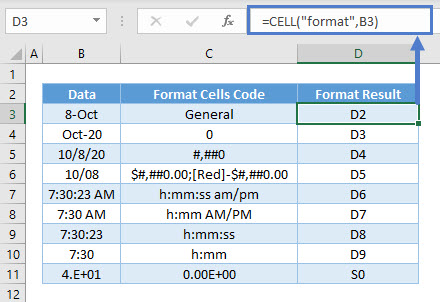
=CELL("color",B3)Format Info_type
Format shows the number format of the cell, but it might not be what you expect.
=CELL("format",B3)There are many kinds of different variations with formatting, but here are some guidelines to figure it out:
- “G” is for General, “C” for Currency, “P” for Percentage, “S” for Scientific (not shown above), “D” for Date.
- If the digits are with numbers, currencies, and percentages; it represents the decimal places. Eg. “F0” means 0 decimals in cell D4, and “C2-” means 2 decimals in cell D6. “D1” in cell D8 is simply a type of date format (there are D1 to D9 for different kinds of date and time formats).
- A comma at the beginning is for thousand separators (“,0” in cell D5 for eg).
- A minus sign is for formatting negative values with a color (“C2-” in cell D6 for eg).
Here are other examples of date formats and for scientific.
Parentheses Info_type
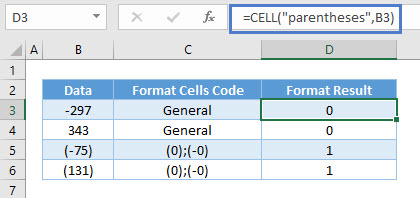
Parentheses shows 1 if the cell is formatted with parentheses (either or both positive and negative). Otherwise, it shows 0.
=CELL("parentheses",B3)Prefix Info_type
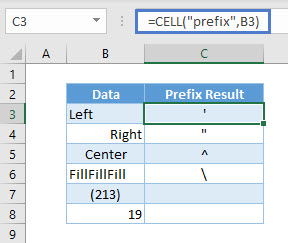
Prefix results in various symbols depending on how the text is aligned in the cell.
=CELL("prefix",B3)As seen above, a left alignment of the text is a single quote in cell C3.
A right alignment of the text shows double quotes in cell C4.
A center alignment of the text shows caret in cell C5.
A fill alignment of the text shows backslash in cell C6.
Numbers (cell C7 and C8) show as blank regardless of alignment.
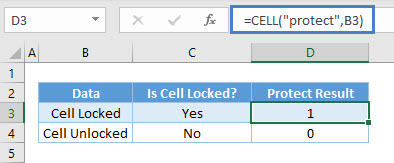
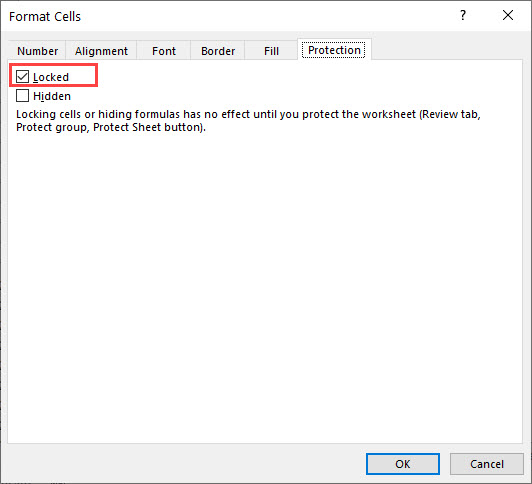
Protect Info_type
Protect results in 1 if the cell is locked, and 0 if it’s unlocked.
=CELL("protect",B3)Do note that all cells are locked by default. That is why you can’t edit any cells after you protect it. To unlock it, right-click on a cell and choose Format Cells.
Go to the Protection tab and you can uncheck “Locked” to unlock the cell.
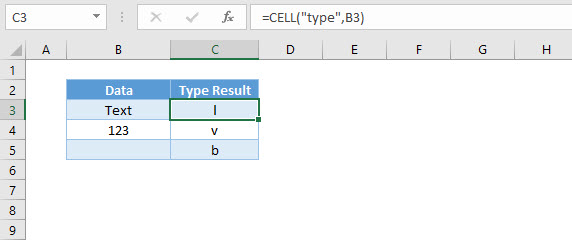
Type Info_type
Type results in three different alphabets dependent on the data type in the cell.
“l” stands for label in cell C3.
“v” stands for value in cell C4.
“b” stands for blank in cell C5.
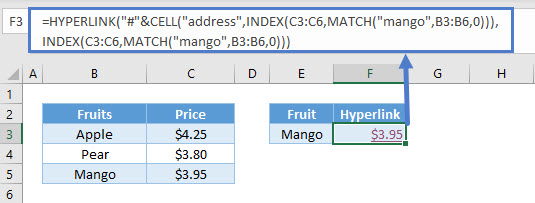
Create Hyperlink to Lookup Using Address
You can use the CELL Function along with HYPERLINK and INDEX / MATCH to hyperlink to a lookup result:
=HYPERLINK("#"&CELL("address",INDEX(C3:C6,MATCH("mango",B3:B6,0))),INDEX(C3:C6,MATCH("mango",B3:B6,0)))The INDEX and MATCH formula retrieves the price of Mango in cell C5: $3.95. The CELL Function, with “address” returns the cell location. The HYPERLINK function then creates the hyperlink.
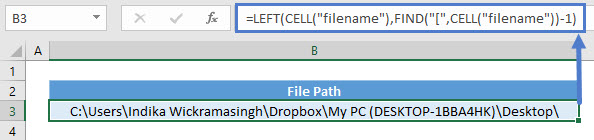
Retrieve File Path
To retrieve the file path where the particular file is stored, you can use:
=LEFT(CELL("filename"),FIND("[",CELL("filename"))-1)Since the filename will be the same using any cell reference, you can omit it. Use FIND function to obtain the position where “[“ starts and minus 1 to allow LEFT function to retrieve the characters before that.
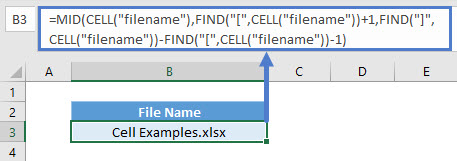
Retrieve File Name
To retrieve the file name, you can use:
=MID(CELL("filename"),FIND("[",CELL("filename"))+1,FIND("]",CELL("filename"))-FIND("[",CELL("filename"))-1)This uses a similar concept as above where FIND function obtains the position where “[“ starts and retrieves the characters after that. To know how many characters to extract, it uses the position of “]” minus “[“ and minus 1 as it includes the position of “]”.
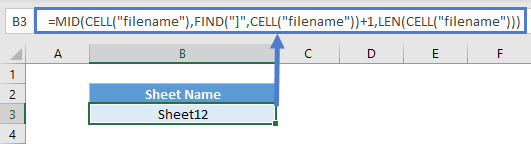
Retrieve Sheet Name
To retrieve the sheet name, you can use:
=MID(CELL("filename"),FIND("]",CELL("filename"))+1,LEN(CELL("filename")))Again, it’s similar to the above where FIND function obtains the position where “]“ starts and retrieves the characters after that. To know how many characters to extract, it uses the total length of what “filename” info_type returns.
CELL Function in Google Sheets
The CELL function works similarly in Google Sheets. It just doesn’t have the full range of info_type. It only includes “address”, “col”, “color”, “contents”, “prefix”, “row”, “type”, and “width”.
Additional Notes
The CELL Function returns information about a cell. The information that can be returned relates to cell location, formatting and contents.
Enter the type of information you want then enter the cell reference for the cell you want information about.
Return to the List of all Functions in Excel
Use the CELL function to return a wide range of information about a reference. The type of information returned is given as info_type, which must be enclosed in double quotes («»). CELL can return a cell’s address, the filename and path for a workbook, and information about the formatting used in the cell. See below for a full list of info types and format codes.
CELL is a volatile function, and can cause performance issues in large or complex worksheets.
The CELL function takes two arguments: info_type and reference. Info_type is a text string that indicates the type of information requested. See the table below for a full list of info types. Reference is a cell reference. Reference is typically a single cell. If reference refers to more than one cell, CELL returns information about the first cell in reference. For certain kinds of information (like filename) the cell address used for reference is optional and can be omitted. However, if reference is not supplied, CELL will return the name of the current «active sheet» which may or may not be the sheet where the formula exists, and might even be in a different workbook. To avoid confusion, use A1 for reference.
Note: the CELL function is a volatile function and may cause performance issues in large or complex worksheets.
Examples
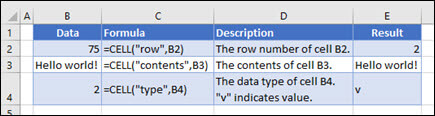
For example, to get the column number for C10:
=CELL("col", C10) // returns 3
To get the address of A1 as text:
=CELL("address",A1) // returns "$A$1"
To get the full path and workbook name for the current worksheet:
=CELL("filename",A1) // path + filename
CELL can also return format code information. For example, if A1 contains the number 100 with the currency number format applied, the CELL function will return «C2»:
=CELL("format",A1) // returns "C2"
When requesting the info_type «format» or «parentheses», a set of empty parentheses «()» is appended to the format returned if the number format uses parentheses for all values or for positive values. For example, if A1 uses the custom number format (0), then:
=CELL("format",A1) // returns "F0()"
Info types
The following info_types can be used with the CELL function:
| Info_type | Description |
|---|---|
| address | returns the address of the first cell in reference (as text). |
| col | returns the column number of the first cell in reference. |
| color | returns the value 1 if the first cell in reference is formatted using color for negative values; or zero if not. |
| contents | returns the value of the upper-left cell in reference. Formulas are not returned. Instead, the result of the formula is returned. |
| filename | returns the file name and full path as text. If the worksheet that contains reference has not yet been saved, an empty string is returned. |
| format | returns a code that corresponds to the number format of the cell. See below for a list of number format codes. If the first cell in reference is formatted with color for values < 0, then «-» is appended to the code. If the cell is formatted with parentheses, returns «() — at the end of the code value. |
| parentheses | returns 1 if the first cell in reference is formatted with parentheses and 0 if not. |
| prefix | returns a text value that corresponds to the label prefix — of the cell: a single quotation mark (‘) if the cell text is left-aligned, a double quotation mark («) if the cell text is right-aligned, a caret (^) if the cell text is centered text, a backslash () if the cell text is fill-aligned, and an empty string if the label prefix is anything else. |
| protect | returns 1 if the first cell in reference is locked or 0 if not. |
| row | returns the row number of the first cell in reference. |
| type | returns a text value that corresponds to the type of data in the first cell in reference: «b» for blank when the cell is empty, «l» for label if the cell contains a text constant, and «v» for value if the cell contains anything else. |
| width | returns the column width of the cell, rounded to the nearest integer. A unit of column width is equal to the width of one character in the default font size. Note: this value comes back as an array with two values {width,default} where width is the column width and default is a boolean value that indicates if the width is the default column width. |
Format codes
The table below shows the text codes returned by CELL when «format» is used for info_type.
| Format code returned | Format code meaning |
|---|---|
| G | General |
| F0 | 0 |
| ,0 | #,##0 |
| F2 | 0 |
| ,2 | #,##0.00 |
| C0 | $#,##0_);($#,##0) |
| C0- | $#,##0_);[Red]($#,##0) |
| C2 | $#,##0.00_);($#,##0.00) |
| C2- | $#,##0.00_);[Red]($#,##0.00) |
| P0 | 0% |
| P2 | 0.00% |
| S2 | 0.00E+00 |
| G | # ?/? or # ??/?? |
| D1 | d-mmm-yy or dd-mmm-yy |
| D2 | d-mmm or dd-mmm |
| D3 | mmm-yy |
| D4 | m/d/yy or m/d/yy h:mm or mm/dd/yy |
| D5 | mm/dd |
| D6 | h:mm:ss AM/PM |
| D7 | h:mm AM/PM |
| D8 | h:mm:ss |
Notes
- The CELL function is a volatile function and may cause performance issues in large or complex worksheets.
- Reference is optional for some info types, but use an address like A1 to avoid unexpected behavior.
This post will guide you how to use Excel CELL function with syntax and examples in Microsoft excel.
Description
The Excel CELL function returns information about the formatting, location, size, or contents of a cell.
The CELL function is a build-in function in Microsoft Excel and it is categorized as an Information Function.
The CELL function is available in Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2010, Excel 2007, Excel 2003, Excel XP, Excel 2000, Excel 2011 for Mac.
Syntax
The syntax of the CELL function is as below:
= CELL (info_type,[reference])
Where the CELL function arguments are:
Info_type -This is a required argument. The type of information that you want to get. The following types can be used.
From Microsoft site:
| info_type | Returns |
| “address” | Reference of the first cell in reference, as text. |
| “col” | Column number of the cell in reference. |
| “color” | The value 1 if the cell is formatted in color for negative values; otherwise returns 0 (zero).
NOTE: This value is not supported in Excel Online, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
| “contents” | Value of the upper-left cell in reference; not a formula. |
| “filename” | Filename (including full path) of the file that contains reference, as text. Returns empty text (“”) if the worksheet that contains reference has not yet been saved.
NOTE: This value is not supported in Excel Online, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
| “format” | Text value corresponding to the number format of the cell. The text values for the various formats are shown in the following table. Returns “-” at the end of the text value if the cell is formatted in color for negative values. Returns “()” at the end of the text value if the cell is formatted with parentheses for positive or all values.
NOTE: This value is not supported in Excel Online, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
| “parentheses” | The value 1 if the cell is formatted with parentheses for positive or all values; otherwise returns 0.
NOTE: This value is not supported in Excel Online, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
| “prefix” | Text value corresponding to the “label prefix” of the cell. Returns single quotation mark (‘) if the cell contains left-aligned text, double quotation mark (“) if the cell contains right-aligned text, caret (^) if the cell contains centered text, backslash () if the cell contains fill-aligned text, and empty text (“”) if the cell contains anything else.
NOTE: This value is not supported in Excel Online, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
| “protect” | The value 0 if the cell is not locked; otherwise returns 1 if the cell is locked.
NOTE: This value is not supported in Excel Online, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
| “row” | Row number of the cell in reference. |
| “type” | Text value corresponding to the type of data in the cell. Returns “b” for blank if the cell is empty, “l” for label if the cell contains a text constant, and “v” for value if the cell contains anything else. |
| “width” | Column width of the cell, rounded off to an integer. Each unit of column width is equal to the width of one character in the default font size.
NOTE: This value is not supported in Excel Online, Excel Mobile, and Excel Starter. |
Example
The below examples will show you how to use Excel CELL Function to retrieve information about a cell.
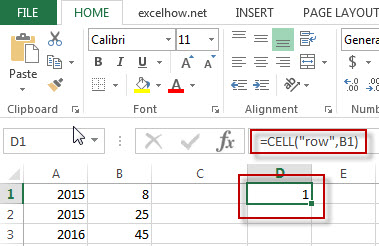
#1 =CELL(“row”,B1)
Note: the above excel formula will return the row number of Cell B1.
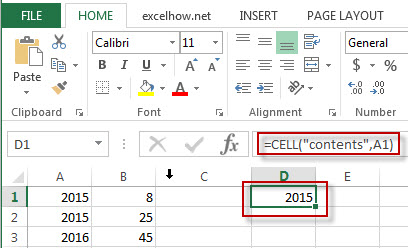
#2 =CELL(“contents”,A1)
Note: The above excel formula will return the content of cell A1.
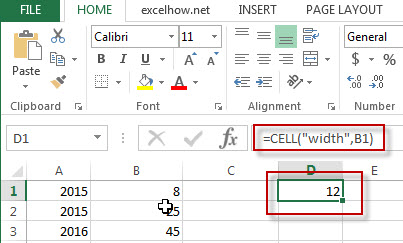
#3 =CELL(“width”,B1)
Note: the above excel formula will return the column width of the cell B1.
More CELL Function Examples
- Quickly Get Sheet Name
If you want to quickly get current worksheet name only, then inert it into one cell. You can use a formula based on the MID function in combination with the FIND function and the Cell function…… - Insert The File Path and Filename into Cell
If you want to insert a file path and filename into a cell in your current worksheet, you can use the CELL function to create a formual……..