Содержание
- Создание SQL запроса в Excel
- Способ 1: использование надстройки
- Способ 2: использование встроенных инструментов Excel
- Способ 3: подключение к серверу SQL Server
- Вопросы и ответы
SQL – популярный язык программирования, который применяется при работе с базами данных (БД). Хотя для операций с базами данных в пакете Microsoft Office имеется отдельное приложение — Access, но программа Excel тоже может работать с БД, делая SQL запросы. Давайте узнаем, как различными способами можно сформировать подобный запрос.
Читайте также: Как создать базу данных в Экселе
Язык запросов SQL отличается от аналогов тем, что с ним работают практически все современные системы управления БД. Поэтому вовсе не удивительно, что такой продвинутый табличный процессор, как Эксель, обладающий многими дополнительными функциями, тоже умеет работать с этим языком. Пользователи, владеющие языком SQL, используя Excel, могут упорядочить множество различных разрозненных табличных данных.
Способ 1: использование надстройки
Но для начала давайте рассмотрим вариант, когда из Экселя можно создать SQL запрос не с помощью стандартного инструментария, а воспользовавшись сторонней надстройкой. Одной из лучших надстроек, выполняющих эту задачу, является комплекс инструментов XLTools, который кроме указанной возможности, предоставляет массу других функций. Правда, нужно заметить, что бесплатный период пользования инструментом составляет всего 14 дней, а потом придется покупать лицензию.
Скачать надстройку XLTools
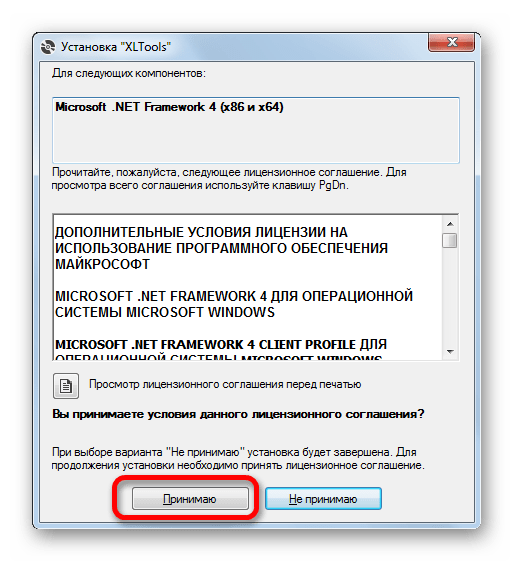
- После того, как вы скачали файл надстройки xltools.exe, следует приступить к его установке. Для запуска инсталлятора нужно произвести двойной щелчок левой кнопки мыши по установочному файлу. После этого запустится окно, в котором нужно будет подтвердить согласие с лицензионным соглашением на использование продукции компании Microsoft — NET Framework 4. Для этого всего лишь нужно кликнуть по кнопке «Принимаю» внизу окошка.
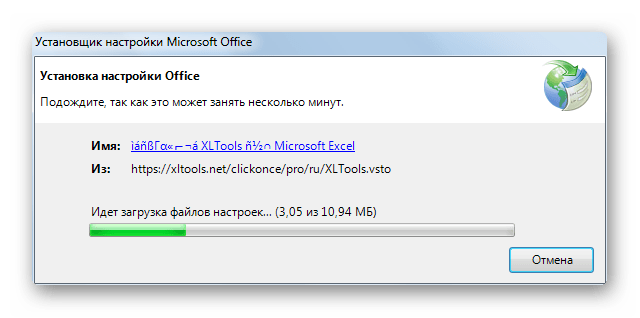
- После этого установщик производит загрузку обязательных файлов и начинает процесс их установки.
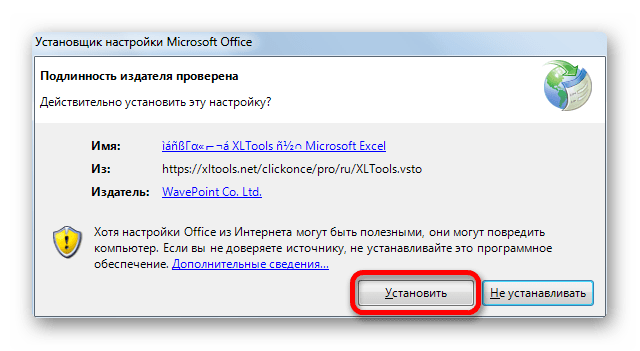
- Далее откроется окно, в котором вы должны подтвердить свое согласие на установку этой надстройки. Для этого нужно щелкнуть по кнопке «Установить».
- Затем начинается процедура установки непосредственно самой надстройки.
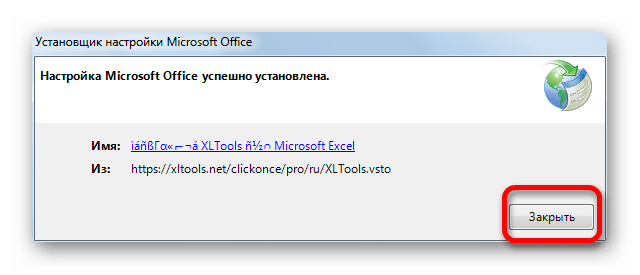
- После её завершения откроется окно, в котором будет сообщаться, что инсталляция успешно выполнена. В указанном окне достаточно нажать на кнопку «Закрыть».
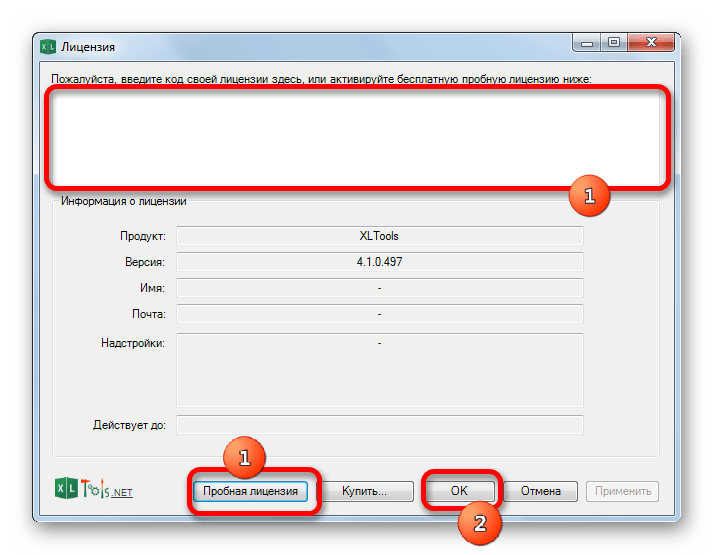
- Надстройка установлена и теперь можно запускать файл Excel, в котором нужно организовать SQL запрос. Вместе с листом Эксель открывается окно для ввода кода лицензии XLTools. Если у вас имеется код, то нужно ввести его в соответствующее поле и нажать на кнопку «OK». Если вы желаете использовать бесплатную версию на 14 дней, то следует просто нажать на кнопку «Пробная лицензия».
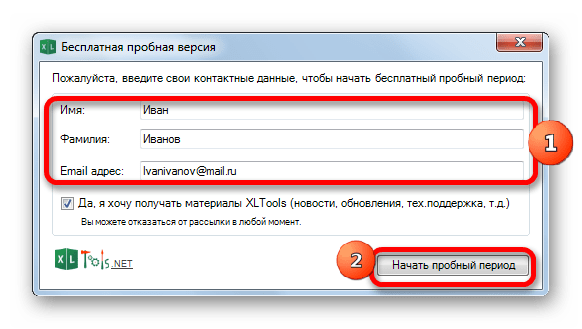
- При выборе пробной лицензии открывается ещё одно небольшое окошко, где нужно указать своё имя и фамилию (можно псевдоним) и электронную почту. После этого жмите на кнопку «Начать пробный период».
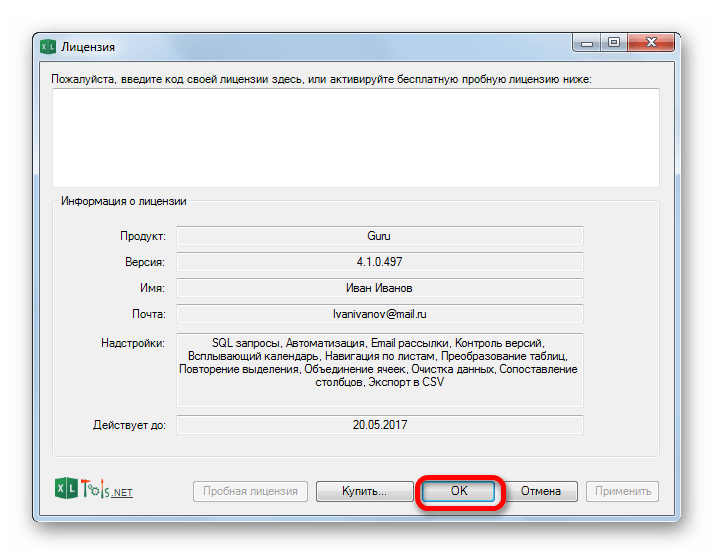
- Далее мы возвращаемся к окну лицензии. Как видим, введенные вами значения уже отображаются. Теперь нужно просто нажать на кнопку «OK».
- После того, как вы проделаете вышеуказанные манипуляции, в вашем экземпляре Эксель появится новая вкладка – «XLTools». Но не спешим переходить в неё. Прежде, чем создавать запрос, нужно преобразовать табличный массив, с которым мы будем работать, в так называемую, «умную» таблицу и присвоить ей имя.
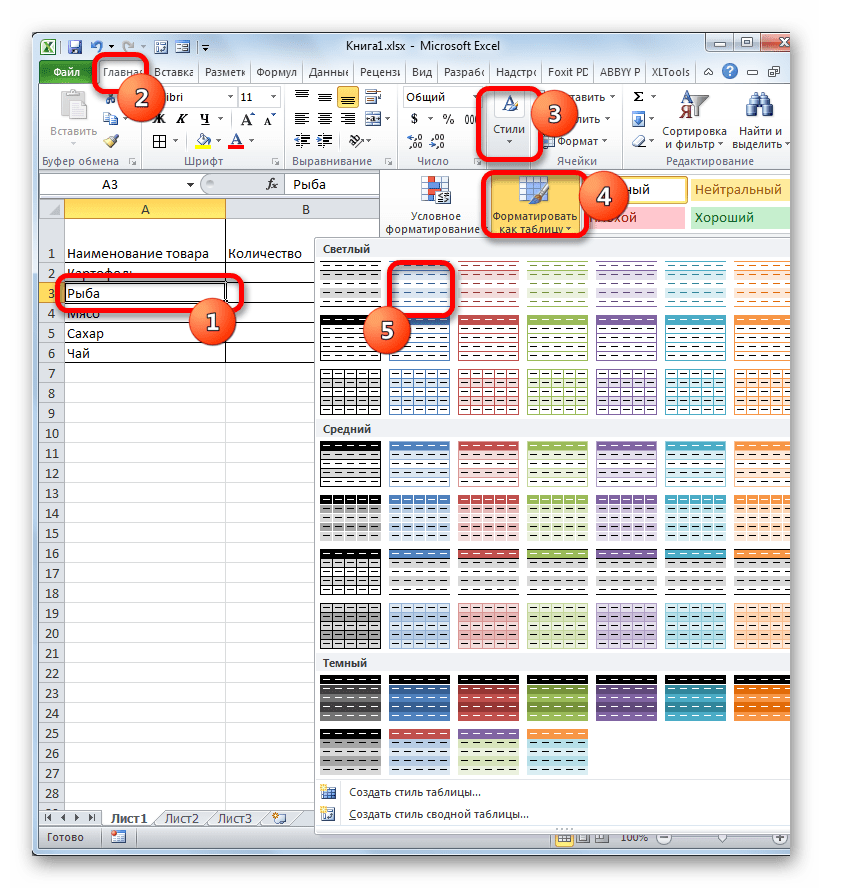
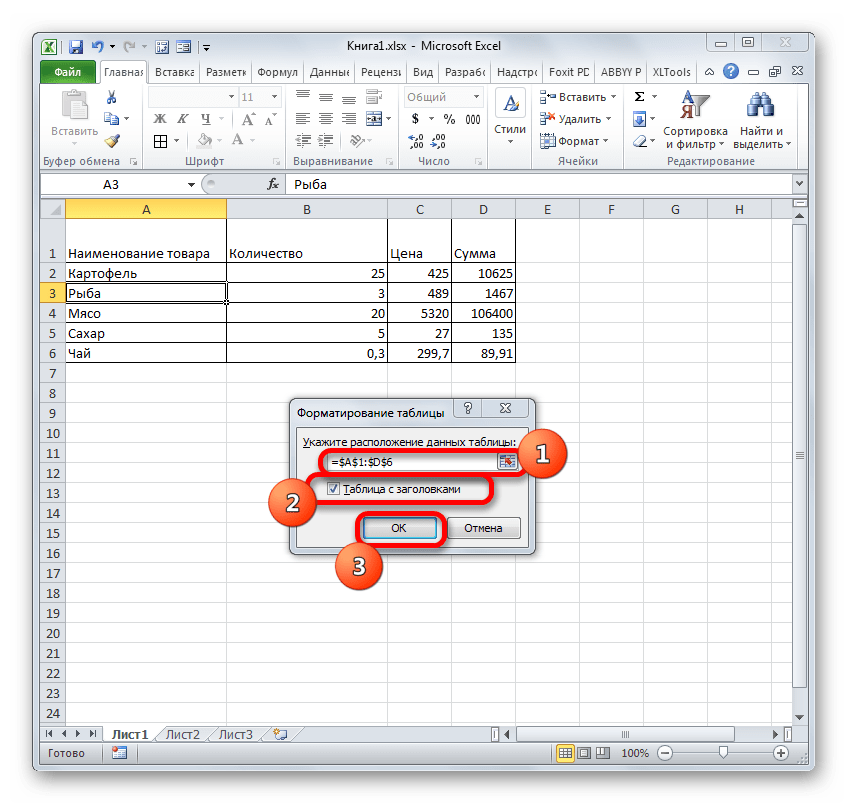
Для этого выделяем указанный массив или любой его элемент. Находясь во вкладке «Главная» щелкаем по значку «Форматировать как таблицу». Он размещен на ленте в блоке инструментов «Стили». После этого открывается список выбора различных стилей. Выбираем тот стиль, который вы считаете нужным. На функциональность таблицы указанный выбор никак не повлияет, так что основывайте свой выбор исключительно на основе предпочтений визуального отображения. - Вслед за этим запускается небольшое окошко. В нем указываются координаты таблицы. Как правило, программа сама «подхватывает» полный адрес массива, даже если вы выделили только одну ячейку в нем. Но на всякий случай не мешает проверить ту информацию, которая находится в поле «Укажите расположение данных таблицы». Также нужно обратить внимание, чтобы около пункта «Таблица с заголовками», стояла галочка, если заголовки в вашем массиве действительно присутствуют. Затем жмите на кнопку «OK».
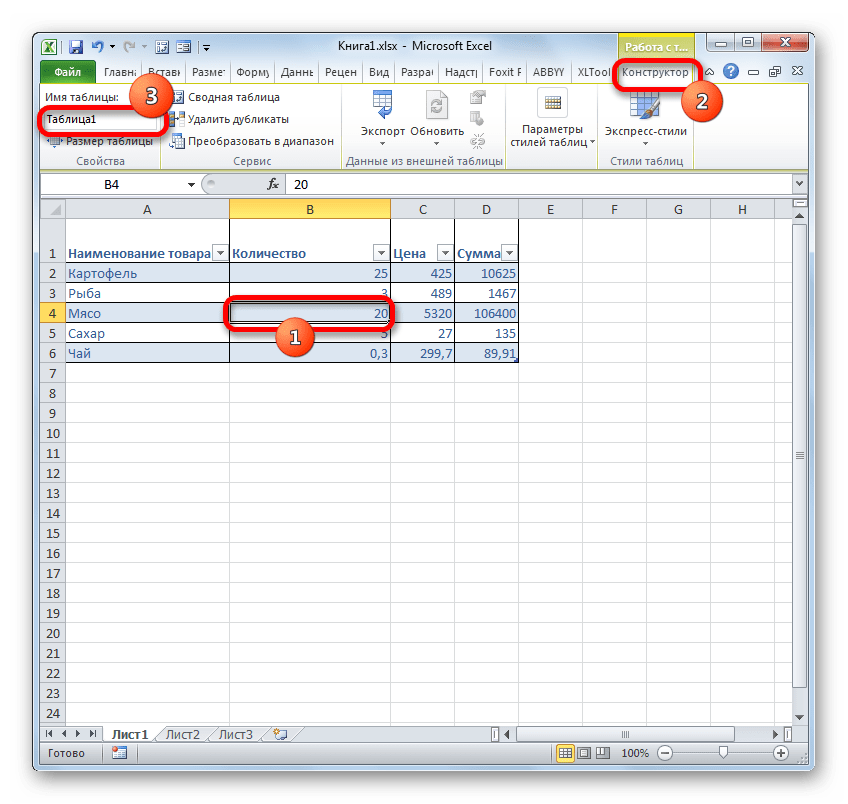
- После этого весь указанный диапазон будет отформатирован, как таблица, что повлияет как на его свойства (например, растягивание), так и на визуальное отображение. Указанной таблице будет присвоено имя. Чтобы его узнать и по желанию изменить, клацаем по любому элементу массива. На ленте появляется дополнительная группа вкладок – «Работа с таблицами». Перемещаемся во вкладку «Конструктор», размещенную в ней. На ленте в блоке инструментов «Свойства» в поле «Имя таблицы» будет указано наименование массива, которое ему присвоила программа автоматически.
- При желании это наименование пользователь может изменить на более информативное, просто вписав в поле с клавиатуры желаемый вариант и нажав на клавишу Enter.
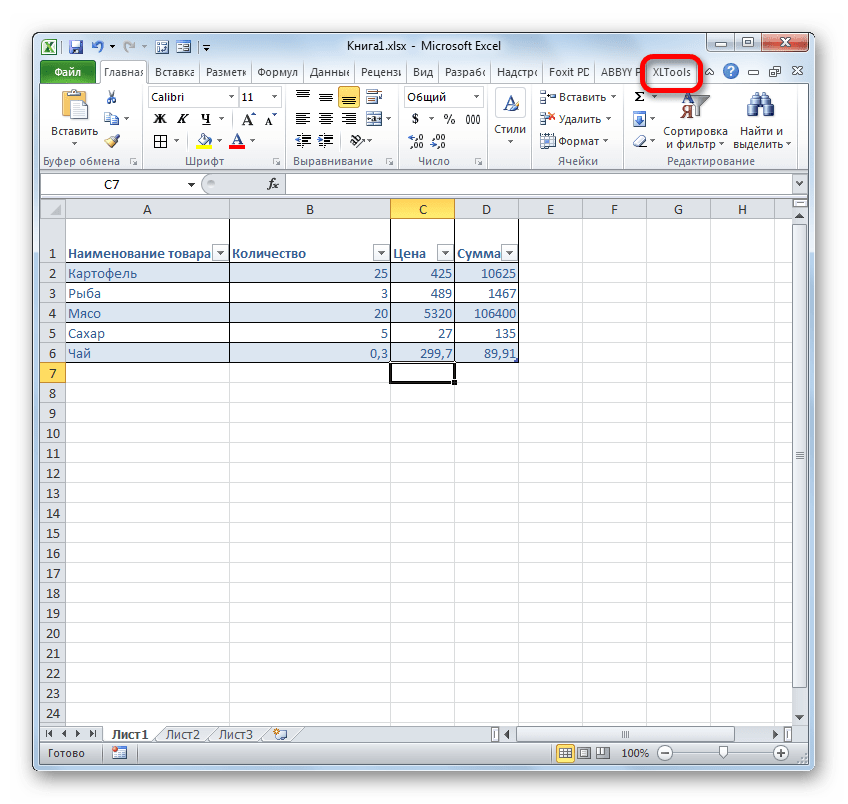
- После этого таблица готова и можно переходить непосредственно к организации запроса. Перемещаемся во вкладку «XLTools».
- После перехода на ленте в блоке инструментов «SQL запросы» щелкаем по значку «Выполнить SQL».
- Запускается окно выполнения SQL запроса. В левой его области следует указать лист документа и таблицу на древе данных, к которой будет формироваться запрос.
В правой области окна, которая занимает его большую часть, располагается сам редактор SQL запросов. В нем нужно писать программный код. Наименования столбцов выбранной таблицы там уже будут отображаться автоматически. Выбор столбцов для обработки производится с помощью команды SELECT. Нужно оставить в перечне только те колонки, которые вы желаете, чтобы указанная команда обрабатывала.
Далее пишется текст команды, которую вы хотите применить к выбранным объектам. Команды составляются при помощи специальных операторов. Вот основные операторы SQL:
- ORDER BY – сортировка значений;
- JOIN – объединение таблиц;
- GROUP BY – группировка значений;
- SUM – суммирование значений;
- DISTINCT – удаление дубликатов.
Кроме того, в построении запроса можно использовать операторы MAX, MIN, AVG, COUNT, LEFT и др.
В нижней части окна следует указать, куда именно будет выводиться результат обработки. Это может быть новый лист книги (по умолчанию) или определенный диапазон на текущем листе. В последнем случае нужно переставить переключатель в соответствующую позицию и указать координаты этого диапазона.
После того, как запрос составлен и соответствующие настройки произведены, жмем на кнопку «Выполнить» в нижней части окна. После этого введенная операция будет произведена.
Урок: «Умные» таблицы в Экселе
Способ 2: использование встроенных инструментов Excel
Существует также способ создать SQL запрос к выбранному источнику данных с помощью встроенных инструментов Эксель.
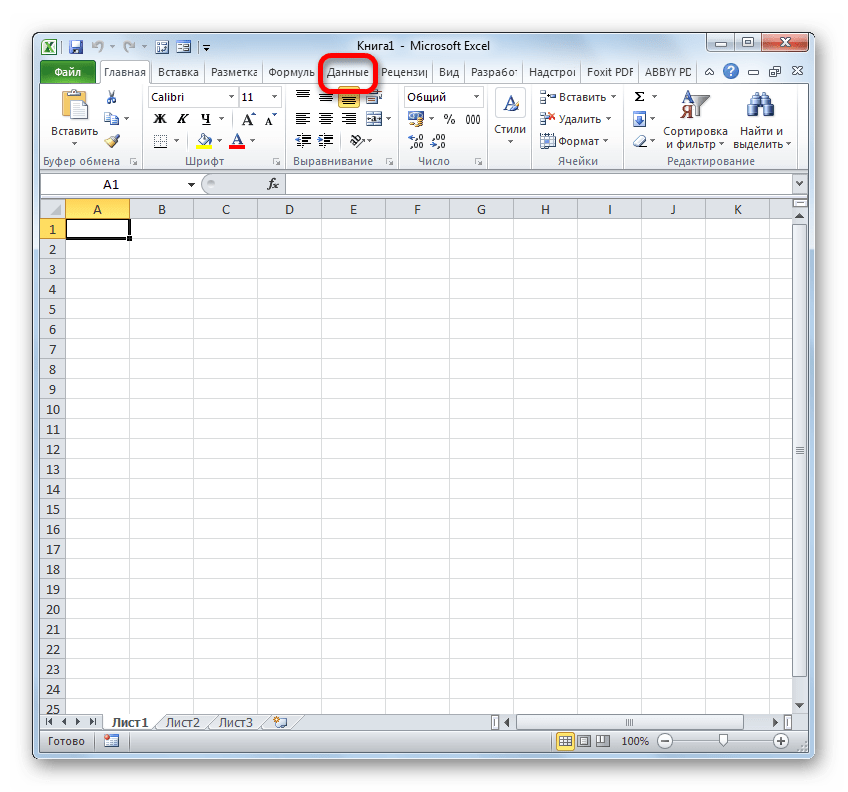
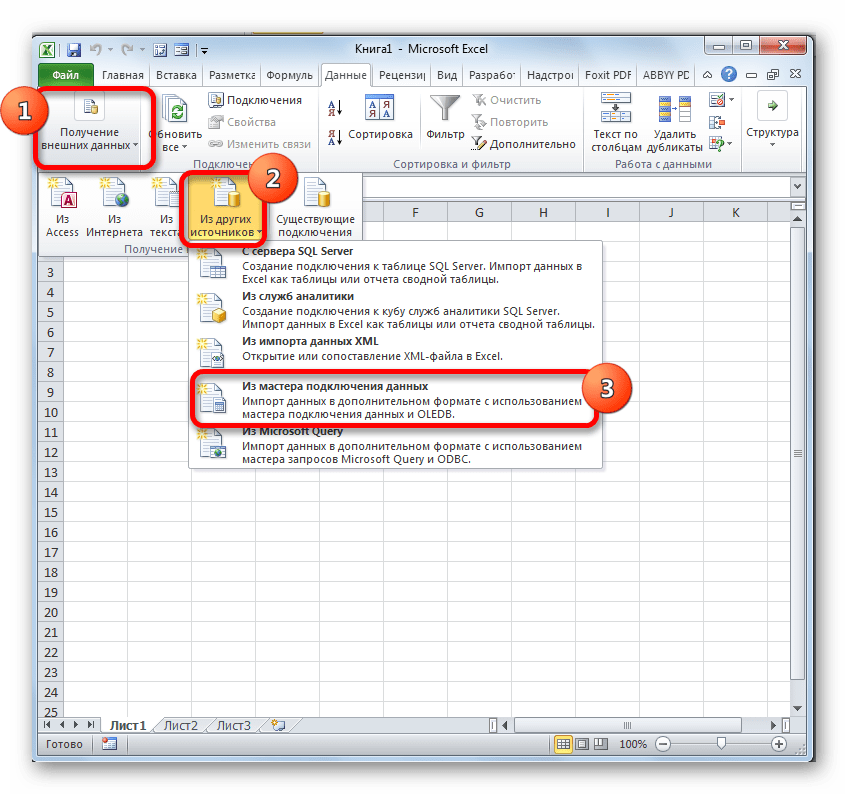
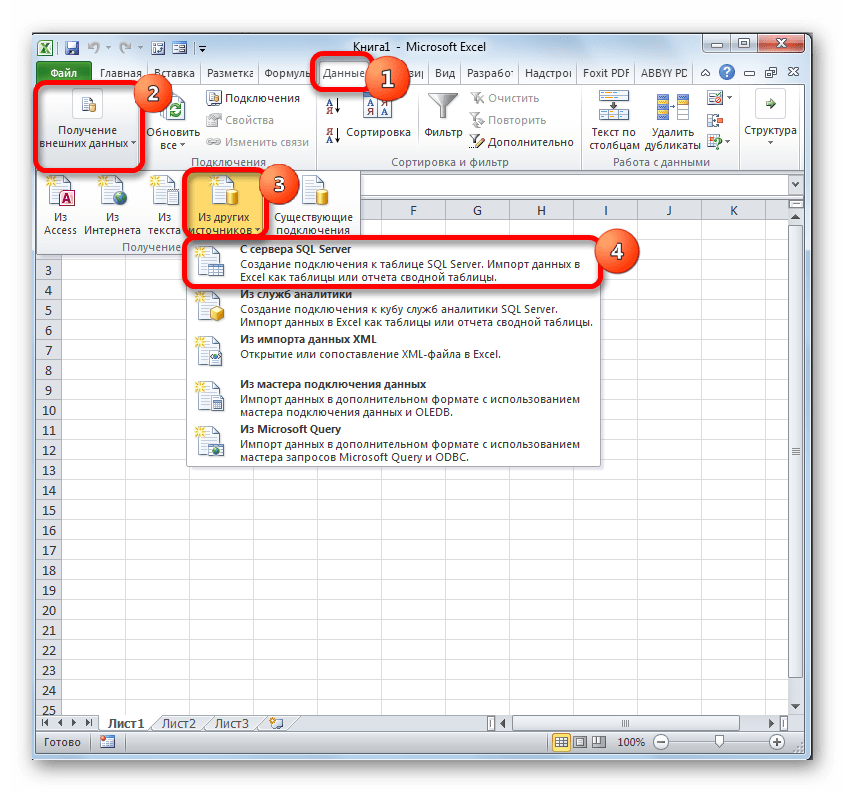
- Запускаем программу Excel. После этого перемещаемся во вкладку «Данные».
- В блоке инструментов «Получение внешних данных», который расположен на ленте, жмем на значок «Из других источников». Открывается список дальнейших вариантов действий. Выбираем в нем пункт «Из мастера подключения данных».
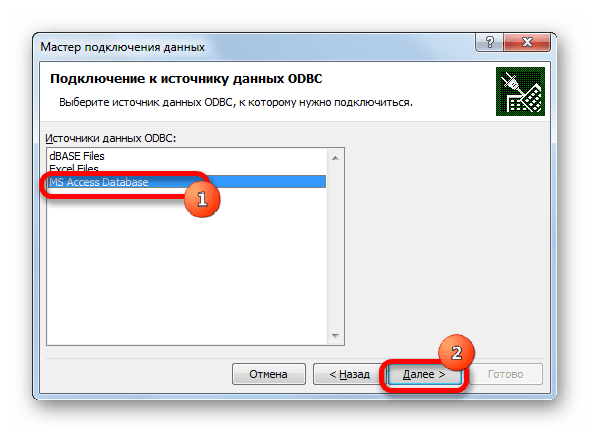
- Запускается Мастер подключения данных. В перечне типов источников данных выбираем «ODBC DSN». После этого щелкаем по кнопке «Далее».
- Открывается окно Мастера подключения данных, в котором нужно выбрать тип источника. Выбираем наименование «MS Access Database». Затем щелкаем по кнопке «Далее».
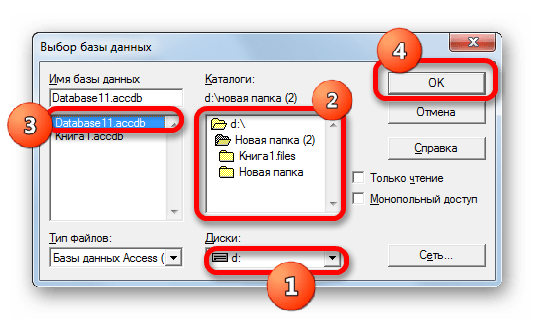
- Открывается небольшое окошко навигации, в котором следует перейти в директорию расположения базы данных в формате mdb или accdb и выбрать нужный файл БД. Навигация между логическими дисками при этом производится в специальном поле «Диски». Между каталогами производится переход в центральной области окна под названием «Каталоги». В левой области окна отображаются файлы, расположенные в текущем каталоге, если они имеют расширение mdb или accdb. Именно в этой области нужно выбрать наименование файла, после чего кликнуть на кнопку «OK».
- Вслед за этим запускается окно выбора таблицы в указанной базе данных. В центральной области следует выбрать наименование нужной таблицы (если их несколько), а потом нажать на кнопку «Далее».
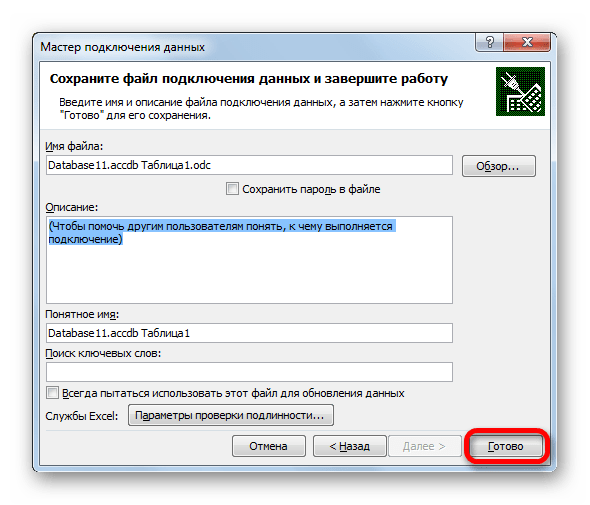
- После этого открывается окно сохранения файла подключения данных. Тут указаны основные сведения о подключении, которое мы настроили. В данном окне достаточно нажать на кнопку «Готово».
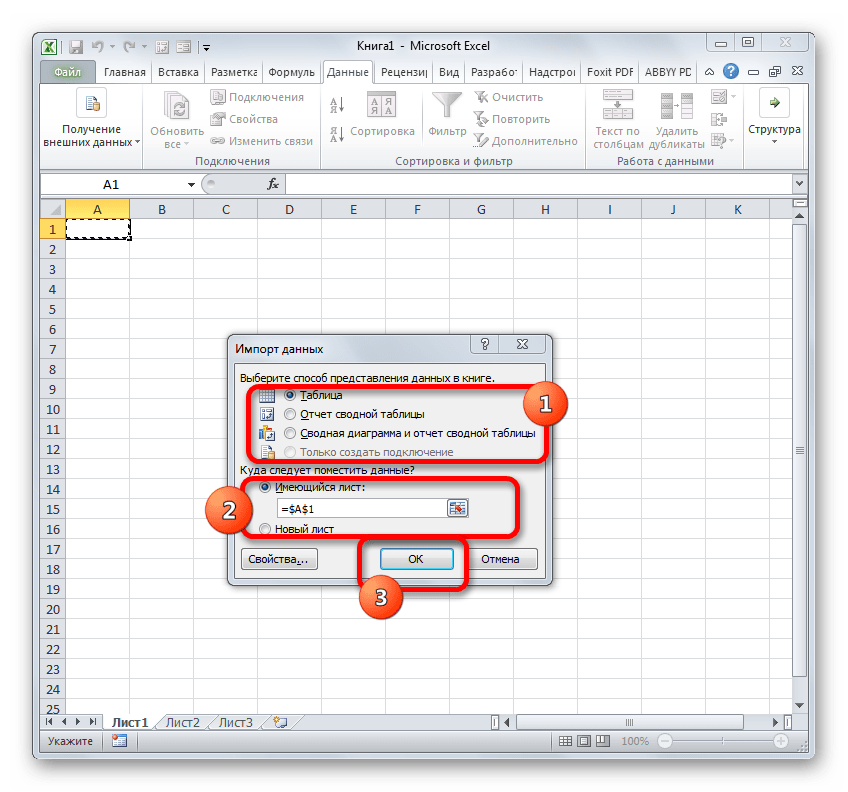
- На листе Excel запускается окошко импорта данных. В нем можно указать, в каком именно виде вы хотите, чтобы данные были представлены:
- Таблица;
- Отчёт сводной таблицы;
- Сводная диаграмма.
Выбираем нужный вариант. Чуть ниже требуется указать, куда именно следует поместить данные: на новый лист или на текущем листе. В последнем случае предоставляется также возможность выбора координат размещения. По умолчанию данные размещаются на текущем листе. Левый верхний угол импортируемого объекта размещается в ячейке A1.
После того, как все настройки импорта указаны, жмем на кнопку «OK».
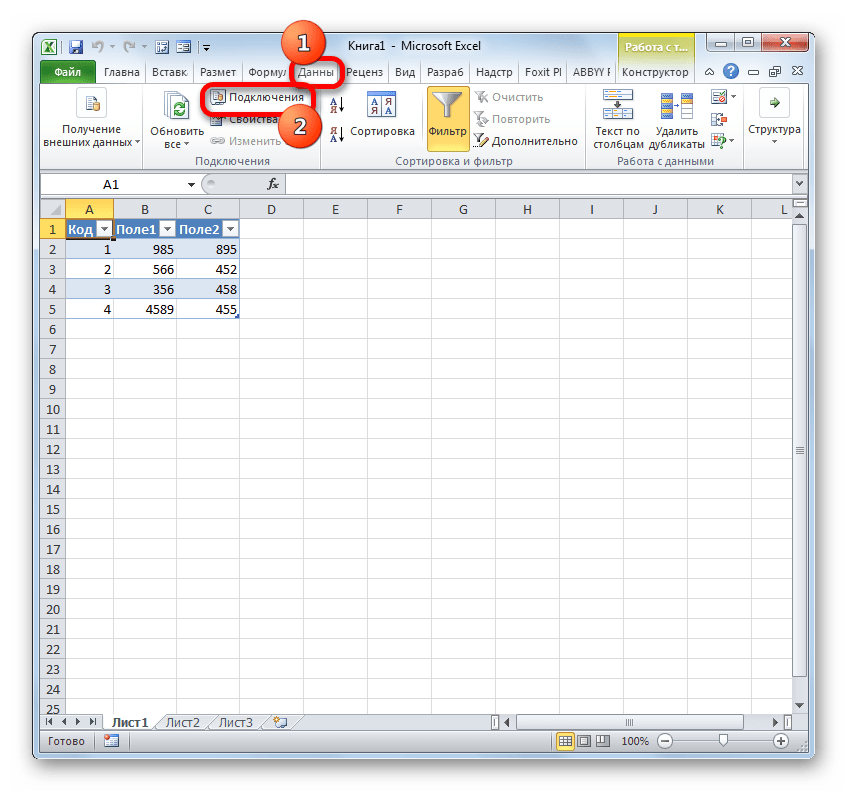
- Как видим, таблица из базы данных перемещена на лист. Затем перемещаемся во вкладку «Данные» и щелкаем по кнопке «Подключения», которая размещена на ленте в блоке инструментов с одноименным названием.
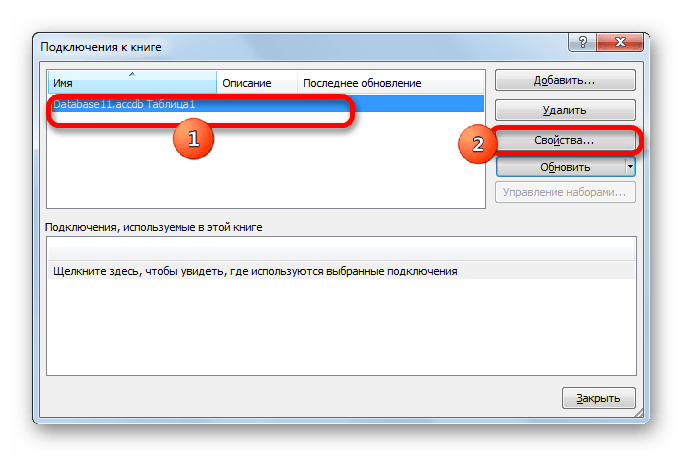
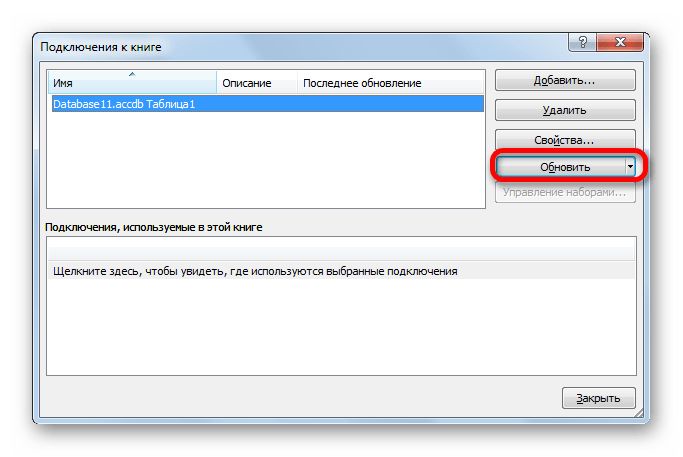
- После этого запускается окно подключения к книге. В нем мы видим наименование ранее подключенной нами базы данных. Если подключенных БД несколько, то выбираем нужную и выделяем её. После этого щелкаем по кнопке «Свойства…» в правой части окна.
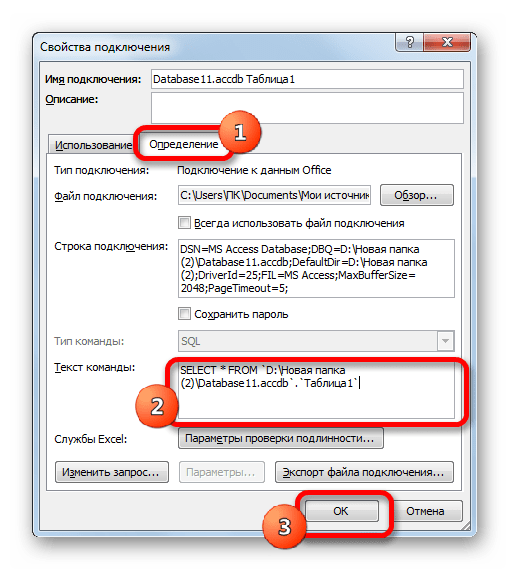
- Запускается окно свойств подключения. Перемещаемся в нем во вкладку «Определение». В поле «Текст команды», находящееся внизу текущего окна, записываем SQL команду в соответствии с синтаксисом данного языка, о котором мы вкратце говорили при рассмотрении Способа 1. Затем жмем на кнопку «OK».
- После этого производится автоматический возврат к окну подключения к книге. Нам остается только кликнуть по кнопке «Обновить» в нем. Происходит обращение к базе данных с запросом, после чего БД возвращает результаты его обработки назад на лист Excel, в ранее перенесенную нами таблицу.
Способ 3: подключение к серверу SQL Server
Кроме того, посредством инструментов Excel существует возможность соединения с сервером SQL Server и посыла к нему запросов. Построение запроса не отличается от предыдущего варианта, но прежде всего, нужно установить само подключение. Посмотрим, как это сделать.
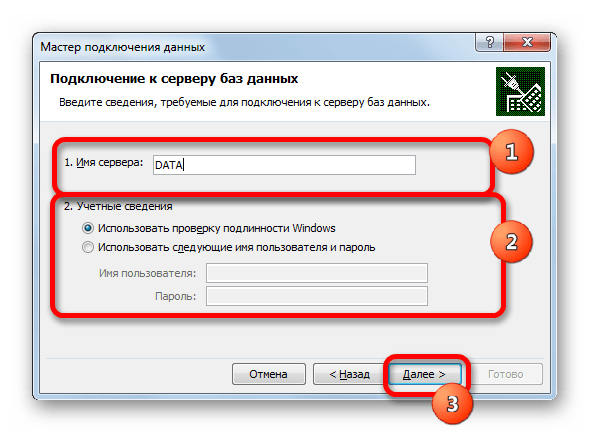
- Запускаем программу Excel и переходим во вкладку «Данные». После этого щелкаем по кнопке «Из других источников», которая размещается на ленте в блоке инструментов «Получение внешних данных». На этот раз из раскрывшегося списка выбираем вариант «С сервера SQL Server».
- Происходит открытие окна подключения к серверу баз данных. В поле «Имя сервера» указываем наименование того сервера, к которому выполняем подключение. В группе параметров «Учетные сведения» нужно определиться, как именно будет происходить подключение: с использованием проверки подлинности Windows или путем введения имени пользователя и пароля. Выставляем переключатель согласно принятому решению. Если вы выбрали второй вариант, то кроме того в соответствующие поля придется ввести имя пользователя и пароль. После того, как все настройки проведены, жмем на кнопку «Далее». После выполнения этого действия происходит подключение к указанному серверу. Дальнейшие действия по организации запроса к базе данных аналогичны тем, которые мы описывали в предыдущем способе.
Как видим, в Экселе SQL запрос можно организовать, как встроенными инструментами программы, так и при помощи сторонних надстроек. Каждый пользователь может выбрать тот вариант, который удобнее для него и является более подходящим для решения конкретно поставленной задачи. Хотя, возможности надстройки XLTools, в целом, все-таки несколько более продвинутые, чем у встроенных инструментов Excel. Главный же недостаток XLTools заключается в том, что срок бесплатного пользования надстройкой ограничен всего двумя календарными неделями.
Еще статьи по данной теме:
Помогла ли Вам статья?
26 Sep ’22 by Antonio Nakić-Alfirević
SQL Query function in Excel
If you’re reading this article you probably know that Google Sheets has a QUERY function that allows you to run SQL-like queries against data in the sheet. This function lets you do all sorts of gymnastics with the data in your sheet, be it filtering, aggregating, or pivoting data.
Being a fully-fledged desktop app, Excel tends to be more feature-rich than Google Sheets. This is especially true in the data analytics department where Excel shines with advanced Excel functions as well as Power Query functionality.
However, Excel doesn’t natively have a QUERY function that you can use in cells on the sheet.
In this blog post, I’m going to show you how to add a QUERY function to Excel and give a few examples of how to use it.
First look
Let’s start by taking a look at the function in action.
The function is pretty straightforward. It accepts the SQL query as the first parameter and returns a table with the results of the query.
The results automatically spill to the necessary amount of space. This spilling behavior relies on the dynamic array functionality that’s available in Excel 365 (but isn’t in earlier versions of Microsoft Excel).
Works with Excel tables
In Google Sheets, the QUERY function references data by address (e.g. “A1:B10”) while columns are referenced by letters (e.g. A, B, C…).
This works but has some drawbacks:
- It makes the query sensitive to the location of the data. If the data is moved or if columns are reordered, the query will break.
- It makes the query difficult to read since it uses range addresses and column letters instead of table and column names (e.g. Employees, DateOfBirth…)
- Adding or removing rows can break the query. For example, if the provided range is “A1:H10” the query will only take into account the first 10 rows. If additional rows are added, the query will not take them into account. You can get around this by omitting the end row number (e.g. “A1:H”), but this means that there must be no other content below the data range.
Excel, on the other hand, allows explicitly defining tables (aka ListObjects) that delineate the areas that hold data. Each Excel table has a name, as do its columns. This makes Excel tables very similar to database tables and makes them easier to work with from SQL.
Full SQL syntax support (SQLite)
Under the hood, the Windy.Query function is powered by SQLite – a small but powerful embedded database engine.
When called, the function passes the query to the built-in SQLite engine which has an adapter that lets it use Excel tables as its data source.
This means that the entire SQLite syntax is available for use in queries. In comparison, in Google Sheets, the query syntax is rather limited. It only supports a single table (no joins) and a very small set of built-in functions.
Examples of use
Since the engine under the hood is SQLite, queries can use all operations available in SQLite, including table joins, temp tables, column table expressions, window functions etc… Let’s go over some examples of how to use these in Excel.
Joining tables
Here’s an example of a simple one-to-many join:
The usual way of doing a simple operation such as this one in Excel would be to use xlookup or PowerQuery, but SQL is now another option. And if we needed anything more complex than a simple join, SQL would quickly shine as the most powerful and convenient option of the three.
Merging table rows (union)
Another way we might want to combine two (or more) tables is to combine their rows. We can do this with a SQL UNION operator.
The tables might have some rows in common. If we want to keep only one instance of such rows we would use the regular UNION operator. If we want to keep both versions of rows that are in common, we would use the UNION ALL operator.
Finding differences between two tables
In the previous example, we had two tables that had some rows in common and some rows not. Let’s assume, for example, that the first table contains last year’s list of employees and the second table is the new list of employees.
If we wanted to find out the differences between the two tables, we could easily do that with a bit of SQL.
All of the rows that are in the first table but not in the second one we will mark as “deleted”. All of the rows that are in the second table but not in the first one we will mark as “added”. Here’s what that SQL query looks like:
select id, name, 'deleted' from employees e where not exists (select * from Employees_New en where e.id == en.Id) union select id, name, 'added' from employees_new en where not exists (select * from Employees e where e.id == en.Id)
And here’s what the result looks like:
Ranking rows
Another useful thing we might want to do is rank rows based on some criteria. For example, suppose we have a table with a list of cities. For each city we have its population and the country it belongs to.
Our task is to find the top 3 cities in each country based on population. Here’s how we might do that in SQL.
-- we use this CTE so we can reference the calculated 'rank_pop' column in the where clause with cte as ( select city, country, population, -- using the RANK() window function RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY country ORDER BY population) as rank_pop from cities c) select * from cte where -- filtering by the 'rank_pop' column from the CTE rank_pop <= 3 order by country, rank_pop
This query is a bit more complex than the previous ones. It uses a common table expression and a window function (the rank function), and showcases the ability to write complex SQL in queries.
Queries can also make use of dozens of built-in SQLite functions. Various specialized extended functions such as RegexReplace, GPSDist (GPS distance between two points) and LevDist (fuzzy text matching) are also available.
Updating tables
OK, this next example is a bit of a hack, but a useful one… The query you supply doesn’t need to be a SELECT query. You can do UPDATE/INSERT/DELETE statements as well, and these will modify the data in the target Excel tables.
This can be a handy way to clean and transform data in your tables in place, without having to export/import the data to an external database (e.g. SQL Server, MySql, Postgres…).
This works because the SQLite engine isn’t copying the data. Rather, it’s using an adapter that lets it access live data in the Excel table.
How does the function see Excel tables?
At first glance, it might seem strange that the query can access your workbook tables. After all, we did not pass them in as parameters, and functions normally only work with parameters that are passed to them.
However, the Windy.Query function is aware of the workbook it’s being called from and it can read data from the workbook’s tables without the need for passing them in as parameters. This makes the function much easier to call especially when working with multiple tables.
Column Headers
Results returned by the Windy.Query function can optionally include headers. This is controlled by the second parameter of the function.
The texts in the column headers are determined by the SQL query itself. You can easily rename result columns by aliasing them in the select list.
Automatically refresh results
By default, the SQL query runs as a one-off operation when you enter the formula but does not refresh if the source tables change. However, if you want the query to refresh whenever one of the source tables changes, you can easily do so by setting the autoRefresh argument to true.
Note that the auto-refresh functionality relies on Excel’s RTD (Real-Time Data) server. The RTD server usually throttles updates so functions don’t overwhelm Excel with frequent updates. The default throttle interval is 2s meaning that the function will not update more than once every 2s. To improve responsiveness, you can lower this value to something like 20ms. The simplest way to do this is through the “Configure” dialog in the QueryStorm runtime’s ribbon.
Passing parameters
When needed, SQL queries can use values from cells as parameters. To use a cell as a parameter in a query, start by giving the cell a name (named range).
Once the cell has a name, you can reference it in the query using the @paramName or $paramName syntax.
If automatic refresh is turned on, results will automatically refresh whenever one of the parameter cells changes its value.
Performance
This is all well and good for small tables, you might think, but how does it handle large data sets? Well, it handles them quite well. The function can read source tables of 100k rows and 10 columns within a few milliseconds and can return this amount of data in a second or two. In addition to this, all columns are automatically indexed so searches and joins are extremely performant as well.
This makes the function perform very well, both from the data throughput standpoint as well as from the computational one.
OK, so is this better than the Google Sheets version of the QUERY function?
Yes, dah. Did you read the previous chapters? 😛
Installing the Windy.Query function
So how do you install this function into your Excel? It’s a simple 2-step process.
Step 1 is to install the QueryStorm Runtime add-in (if you don’t already have it). This is a free, 4MB add-in for Excel that lets you install and use various extensions for Excel. It’s basically an app store for Excel.
Step 2 is to click the “Extensions” button in the “QueryStorm” tab in the Excel ribbon, find the Windy.Query package in the “Online” tab, and install it.
What happens if I share the workbook with a user who doesn’t have the function?
Nothing bad. If the other user doesn’t have the function installed, they will see the last results of the query that were returned on your machine. They just won’t be able to refresh the results.
Advanced SQL query editor
Writing SQL queries in the formula bar can get a bit unwieldy. To make queries easier to write, it’s better to use a proper editor, preferably one that offers syntax highlighting and code completion for SQL and knows about the tables in your workbook.
For this purpose, I recommend using the QueryStorm IDE. This is an advanced IDE that lets you use SQL in Excel. You can write the query in the QueryStorm code editor and then paste the query into the Windy.Query function when you’re happy with it (if needed).
The IDE does more than just allow using SQL in Excel. You can use it to create and share functions and addins for Excel. In fact the QueryStorm IDE was used to create the Windy.Query function itself.
The IDE has a free community version for individuals and small companies, while users in larger companies can make use of the free trial license. For paid licenses, check out the pricing page.
You can read more in this blog post that’s dedicated to the QueryStorm SQL IDE.
Video demonstration
For a video demonstration of the Windy.Query function, take a look the following video:
Click and select the table in the data source that contains the fields you want to query with SQL and import into your Excel spreadsheet. Click the “>” button in the middle of the Query Wizard window to populate the Columns in Your Query pane with field names from the selected table in your data source.
Contents
- 1 How do I create a SQL query in Excel?
- 2 How do you write a query in Excel?
- 3 How do I get data from SQL query in Excel?
- 4 How do I write a SQL query?
- 5 What is SQL database?
- 6 What is VBA in Excel?
- 7 How do I create a query tab in Excel?
- 8 Can Excel run SQL query?
- 9 How do I run SQL VBA in Excel?
- 10 Is VBA same as SQL?
- 11 How do I open a query in Excel?
- 12 Where do you write SQL queries?
- 13 How do you write a query?
- 14 How do I write a query in Microsoft SQL Server?
- 15 What is SQL query example?
- 16 What are the 5 basic SQL commands?
- 17 How do you explain SQL queries?
- 18 What is SQL written in?
- 19 What is SQL IDE?
- 20 How do I write VBA in Excel?
How do I create a SQL query in Excel?
In Excel, select Data > Queries & Connections, and then select the Queries tab. In the list of queries, locate the query, right click the query, and then select Load To. The Import Data dialog box appears. Decide how you want to import the data, and then select OK.
How do you write a query in Excel?
With Microsoft Query, you can select the columns of data that you want and import only that data into Excel.
- On the Data tab, in the Get & Transform Data group, click Get Data.
- Click From Other Sources, From Microsoft Query.
- Select MS Access Database* and check ‘Use the Query Wizard to create/edit queries’.
- Click OK.
How do I get data from SQL query in Excel?
Open Microsoft Excel file and go to the Data tab on the Excel Ribbon (Under menu bar). Click “From other sources” icon in the “Get External Data” section and select “From SQL Server” on the dropdown menu. After the selection of “From SQL Server”, the Data Connection Wizard window opens.
How do I write a SQL query?
How to Create a SQL Statement
- Start your query with the select statement. select [all | distinct]
- Add field names you want to display. field1 [,field2, 3, 4, etc.]
- Add your statement clause(s) or selection criteria. Required:
- Review your select statement. Here’s a sample statement:
What is SQL database?
SQL stands for Structured Query Language. It’s used for relational databases. A SQL database is a collection of tables that stores a specific set of structured data. The SQL database has long been the tried and true workhorse of the backend enterprise and at the heart of everything we do in this electronic age.
What is VBA in Excel?
VBA stands for Visual Basic for Applications. Excel VBA is Microsoft’s programming language for Excel.and all the other Microsoft Office programs, like Word and PowerPoint. The Office suite programs all share a common programming language.
How do I create a query tab in Excel?
In Excel Select Data > Queries & Connections > Queries tab. In the Power Query Editor Select Data > Get Data > Launch Power Query Editor, and view the Queries pane on the left.
Can Excel run SQL query?
Read contents of an Excel spreadsheet
A more efficient way to retrieve specific values from spreadsheets is to treat Excel files as databases and execute SQL queries on them.SHEET with the name of the spreadsheet you want to access. COLUMN NAME with the column that contains the value you want to find.
How do I run SQL VBA in Excel?
Executing SQL Statements in VBA Code
- DoCmd. RunSQL.
- DoCmd. OpenQuery.
- [Querydef]. Execute.
- [Database]. Execute.
- dbFailOnError.
Is VBA same as SQL?
VBA & SQL are two languages and Excel is an application. VBA is Visual Basic code running on Excel. It is possible to automate Excel significantly using VBA. SQL is a special language for database queries which is used to communicate with a database.
How do I open a query in Excel?
To open a saved query from Excel:
- On the Data tab, in the Get External Data group, click From Other Sources, and then click From Microsoft Query. The Choose Data Source dialog box is displayed.
- In the Choose Data Source dialog box, click the Queries tab.
- Double-click the saved query that you want to open.
Where do you write SQL queries?
SQL queries can be written in the box located under the “Execute SQL” tab.
How do you write a query?
7 Query Letter Writing Dos
- Do make sure you have the correct contact information.
- Do research the agent you are querying.
- Do mention connections.
- Do personalize your letter.
- Do craft a compelling pitch.
- Do sell yourself.
- Do ask to see friends’ query letters.
How do I write a query in Microsoft SQL Server?
How to Write Basic SQL Statements in SQL Server
- SELECT – This command is used to retrieve information from a table.
- INSERT – This command is used to add information to a table.
- UPDATE – This command is used to modify information to a table.
- DELETE – This command is used to remove information from a table. Steps.
What is SQL query example?
An SQL SELECT statement retrieves records from a database table according to clauses (for example, FROM and WHERE ) that specify criteria. The syntax is: SELECT column1, column2 FROM table1, table2 WHERE column2=’value’;
What are the 5 basic SQL commands?
There are five types of SQL commands: DDL, DML, DCL, TCL, and DQL.
- Data Definition Language (DDL) DDL changes the structure of the table like creating a table, deleting a table, altering a table, etc.
- Data Manipulation Language.
- Data Control Language.
- Transaction Control Language.
- Data Query Language.
How do you explain SQL queries?
The EXPLAIN keyword is used throughout various SQL databases and provides information about how your SQL database executes a query. In MySQL, EXPLAIN can be used in front of a query beginning with SELECT , INSERT , DELETE , REPLACE , and UPDATE .
What is SQL written in?
If anyone ever asks you who wrote the first SQL database, you now know the answer: Oracle. So the answer is C – according to Burleson Consulting. Since SQL was originally written by IBM as part of System R, quoting what Oracle used to implement their variant of SQL is not entirely relevant.
What is SQL IDE?
What is an SQL IDE and Why do we Need It? SQL editors or SQL IDEs allow DBAs and web developers to perform and execute all kinds of SQL queries. These editors also help in establishing a connection to your database where you can access, control, and manipulate the data in the database.
How do I write VBA in Excel?
Insert VBA code to Excel Workbook
- Open your workbook in Excel.
- Press Alt + F11 to open Visual Basic Editor (VBE).
- Right-click on your workbook name in the “Project-VBAProject” pane (at the top left corner of the editor window) and select Insert -> Module from the context menu.
- Copy the VBA code (from a web-page etc.)
07 Aug 3 Ways to Perform an Excel SQL Query
Posted at 12:08h
in Excel VBA
0 Comments
Howdee! Excel is a great tool for performing data analysis. However, sometimes getting the data we need into Excel can be cumbersome and take a lot of time when going through other systems. You’re also at the mercy of how a disparate system exports data, and may need an additional step between exporting and getting the data into the format you need. If you have access to the database where the data is housed, you can circumvent these steps and create your own custom Excel SQL query.
To follow along with my below demos, you’ll need to have an instance of SQL server installed on your desktop. If you don’t, you can download the trial version, developer version, or free express version here. I’ll be working with the free developer version in this article. I’m also using a sample database that you can download here. The easiest way to install this is using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). That download is available here. Once you open SSMS, it should automatically detect your local server instance. You must ensure your SQL Server User is running as the “Local Client” and then you can create a blank database, and restore that database from the backup file. If you have issues accomplishing this, let me know in the comments and I’ll elaborate on how this is done.
If you are familiar enough with SQL and have access to your own data, you can skip these steps and use your data. Otherwise, I recommend downloading these tools before getting started. If you’re new to SQL, I highly recommend the SQL Essential Training courses on Lynda.com. Now, on to why you’re all here…
Excel SQL Query Using Get Data
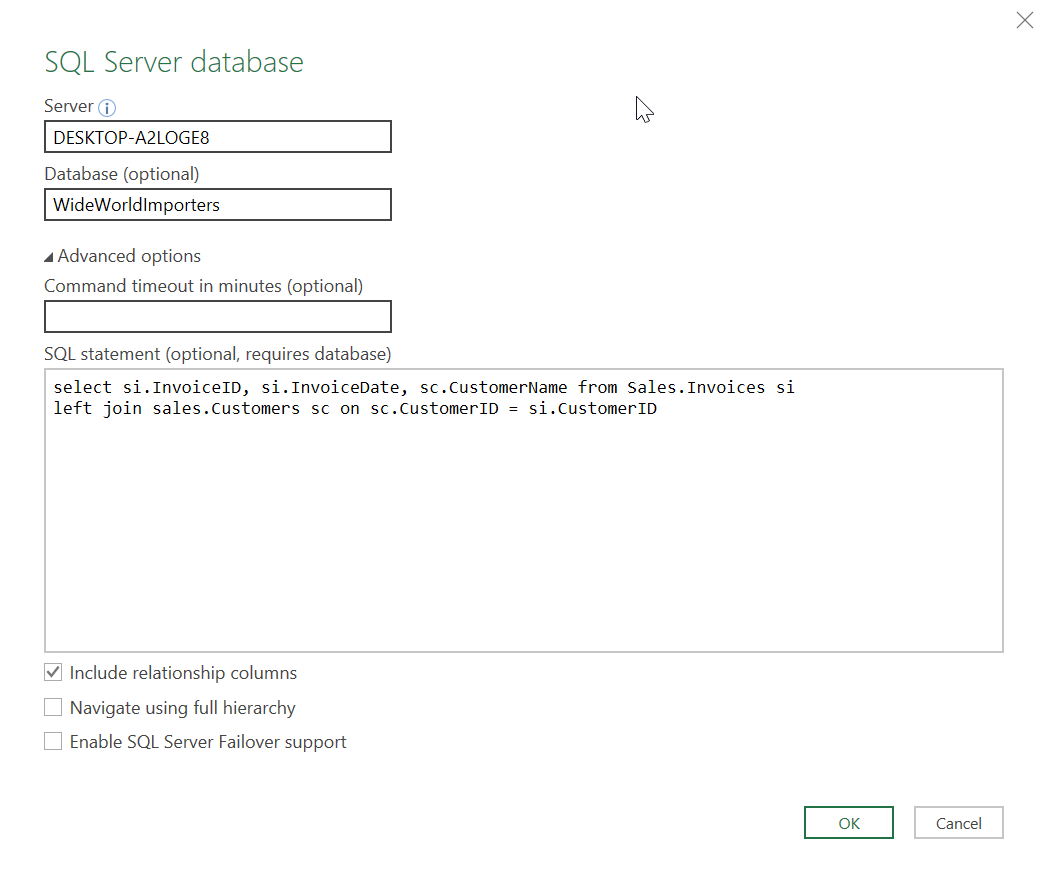
This option is the most straight forward approach to creating an Excel SQL query. However, it is important to note that this approach is only available in Excel 2013 and later and will not currently work on Mac OSX. To get started, select “Get Data” à “From Database” à “From SQL Server Database” as shown in the screen grab. At this point it will pop-up a prompt to enter your server name and the target database you’re wanting to query (you can get this information from SSMS). You can enter this information and then select “OK”. This will allow you to browse available tables from that database to import. You can remove columns and filter tables before importing. If you do not know how to write SQL queries yet, this is one approach you can take.
However, if you select the “Advanced” dropdown arrow, you can create your own custom Excel SQL query. I usually create my query in SSMS or Visual Studio and then just paste the final query in this window. That is because there is no intellisense in this window and it can be difficult to spot errors in your query. Once you select OK, it will ask you to confirm credentials and you may get an error about encryption. This is common when connecting to databases in this manner and nothing to worry about. The next screen will provide an example of your data and you can select “Load” to import it.
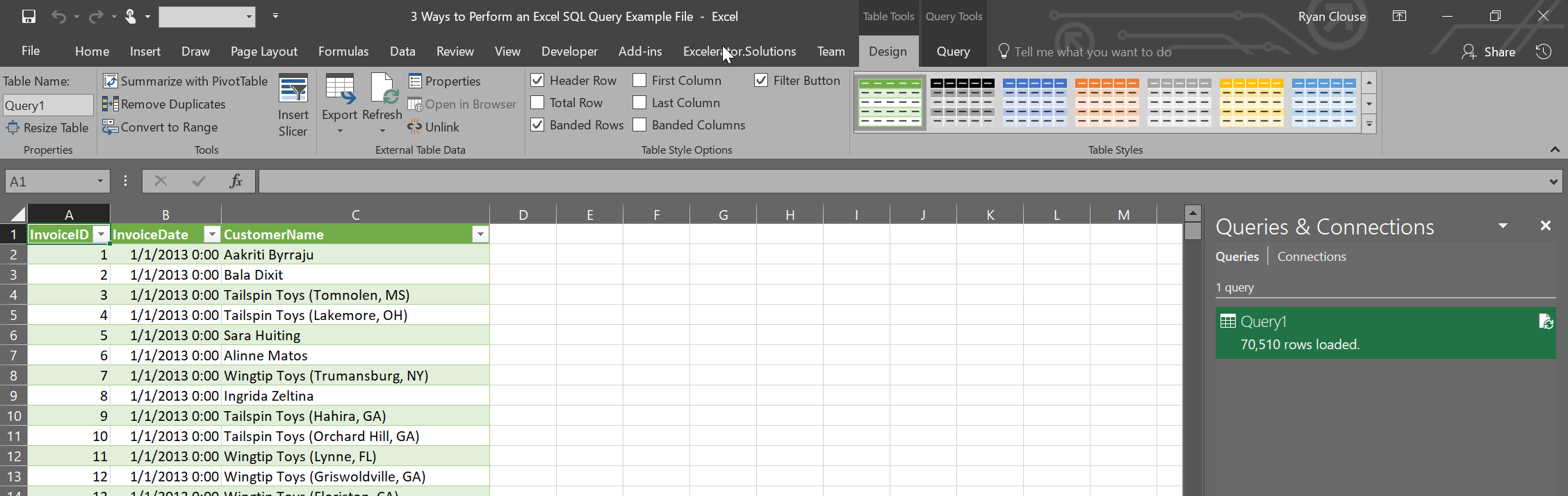
This will create a table on a new tab and you’ll also notice a new pane on the right titled “Connections & Queries”. It will display the name of your query (defaults to “Query1”, “Query2”, etc.) and you can rename the query by right-clicking and selecting “Rename”. You can also edit the query from this location as well. It will open up an interface with a sample of your data and you can add/remove columns, filter your data, or edit your source query from here.
Now that you’ve set up this Excel SQL query, you can simply refresh the data set with fresh data anytime by clicking “Refresh All” on the “Data” ribbon. A quick side note here. If you pivot this data, “Refresh All” will refresh pivot tables first and then the query. To update your pivot table, you’ll need to refresh all twice or update your pivot table manually. To me, one of the downsides of this approach is the results are always returned in a table. I personally do not like working with tables in Excel. That’s where using VBA for your SQL query can come in handy.
Excel SQL Query Using VBA
Using VBA to create your Excel SQL query is not as straight forward as the previous approach, but can still be an extremely useful method depending on your situation. I particularly like that the data is not returned to a table unless you designate it to be so. This technique will work on older versions of Microsoft Excel but will not work on Mac OSX versions of Excel since it uses and ADO connection.
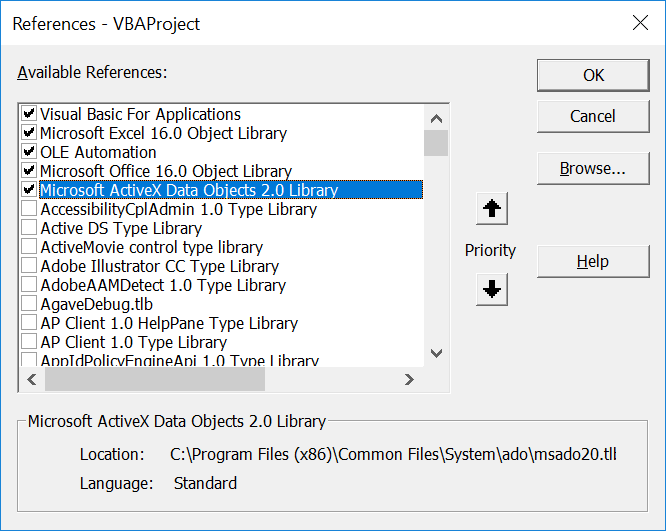
To get started, open up the VBA editor by pressing alt+F11. Before beginning to write your code, you’ll need to ensure that the “Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects 2.0 Library” is referenced from the VBA Project. To do this, click on “Tools” in the ribbon menu at the top of the VBA editor. In the popup, ensure the library is checked as shown below. This allows the project to use the ADO connectors to create the connection to your database. Next, let’s dimension a few variables.
Dim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim recset As New ADODB.Recordset
Dim sqlQry As String, sConnect As String
The Conn variable is will be used to represent the connection between our VBA project and the SQL database. The receset variable will represent a new record set through which we will give the command to perform our Excel SQL query using the connection we’ve established. Finally, the sqlQry variable will represent a string variable that is our SQL query command, and the sConnect variable will be a string representing the connection string the database requires. Let’s look at how to use these variables to perform a SQL query.
sqlQry = "select top 1000 si.InvoiceID, si.InvoiceDate, sc.CustomerName from Sales.Invoices si" & _
" left join sales.Customers sc on sc.CustomerID = si.CustomerID"
sConnect = "Driver={SQL Server};Server=[Your Server Name Here]; Database=[Your Database Here];Trusted_Connection=yes;"
Conn.Open sConnect
Set recset = New ADODB.Recordset
recset.Open sqlQry, Conn
Sheet2.Cells(2, 1).CopyFromRecordset recset
recset.Close
Conn.Close
Set recset = Nothing
While this may look complex, each step is relatively simple. Firstly, we set our sqlQry variable equal to a string that represents the syntax of our SQL query. We then create a connection string we can use in our next command to connect to the database. So, “Conn.Open” is the command to open the connection and “sConnect” is the string it uses to do so. “Trusted_Connection=yes” means that the connection will attempt to be established using your Microsoft credentials for the account you’re logged in as.
Now that the connection is open, we can open a new record set and pass it the sql command using the sqlQry variable, and tell it which connection to use by passing it the Conn variable. We can then use the VBA command “CopyFromRecordset” to paste the recordset anywhere in our workbook. It’s important to close both the record set and connection at this point. You also want to set your recset variable equal to nothing so it does not eat up valuable resources.
One of the downsides to using this method is that you must explicitly tell Excel some things that the previous approach did automatically. For example, this SQL query will not return any column headers. Therefore, you must explicitly tell Excel what to label your columns. Secondly, the data is not automatically cleared and the new query imported. You must also explicitly tell Excel to do this as well. Here is the final code with those commands added.
Sub SQL_Example()
Dim Conn As New ADODB.Connection
Dim recset As New ADODB.Recordset
Dim sqlQry As String, sConnect As String
Sheet2.Cells.ClearContents
sqlQry = "select top 1000 si.InvoiceID, si.InvoiceDate, sc.CustomerName from Sales.Invoices si" & _
" left join sales.Customers sc on sc.CustomerID = si.CustomerID"
sConnect = "Driver={SQL Server};Server=[Your Server Name Here]; Database=[Your Database Name Here];Trusted_Connection=yes;"
Conn.Open sConnect
Set recset = New ADODB.Recordset
recset.Open sqlQry, Conn
Sheet2.Cells(2, 1).CopyFromRecordset recset
recset.Close
Conn.Close
Set recset = Nothing
Sheet2.Cells(1, 1) = "Invoice ID"
Sheet2.Cells(1, 2) = "Invoice Date"
Sheet2.Cells(1, 3) = "Customer Name"
End Sub
My preference for using this approach is when I want the user to be able to pass parameters to my Excel SQL query. For example, I might have a dropdown of customer names the user could select. By using this tactic, I can easily add a dropdown of customer names the user can select, and pass that value to my SQL query in a where clause.
As you can see, both the built in Excel SQL query and the VBA method have pros and cons. I employ both in my everyday work depending on what situation I find myself in.
Excel SQL Query Using Microsoft Query
This option is likely the most complex option, but it has the added advantage of being compatible with some versions of Mac OSX. I won’t pretend to be an expert at creating Mac OSX compatible tools for Excel, but I have successfully used this implementation to create an embedded Excel SQL query for Macs in the past.
I also like this method because you can create popup style parameters. For example, you can prompt the user to input date range parameters at the time the SQL query is ran. Like the first example, running this query is as easy as clicking “Refresh All” on the Data ribbon. Let’s dive in to the details.
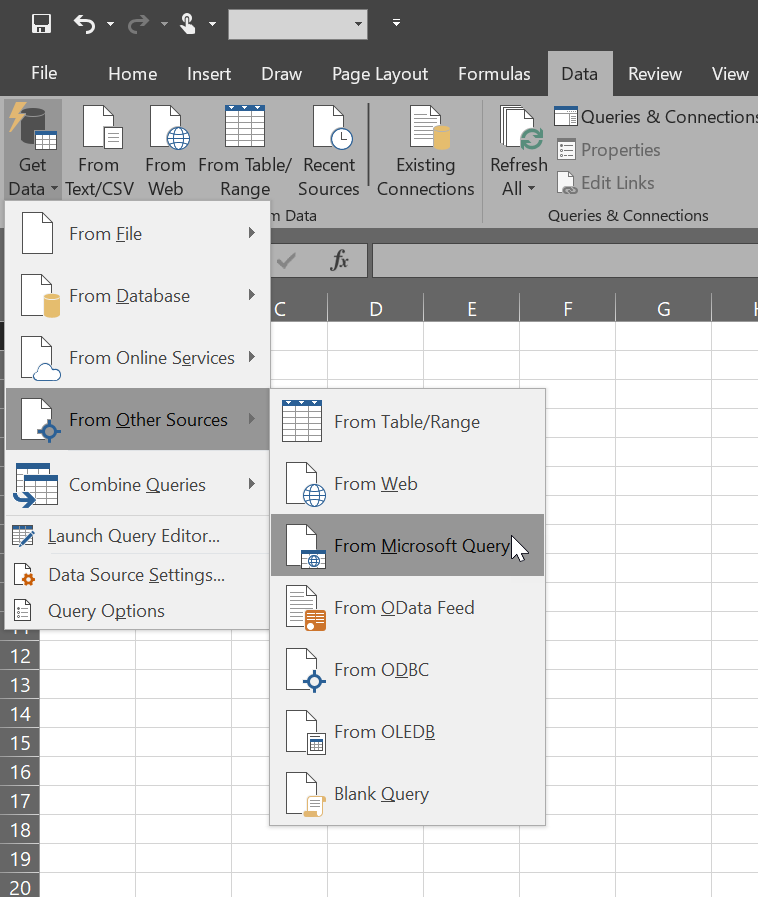
To get started here, click “Get Data” on the Data ribbon. In the menu that dropdowns select “From Other Sources” and, finally “From Microsoft Query”.
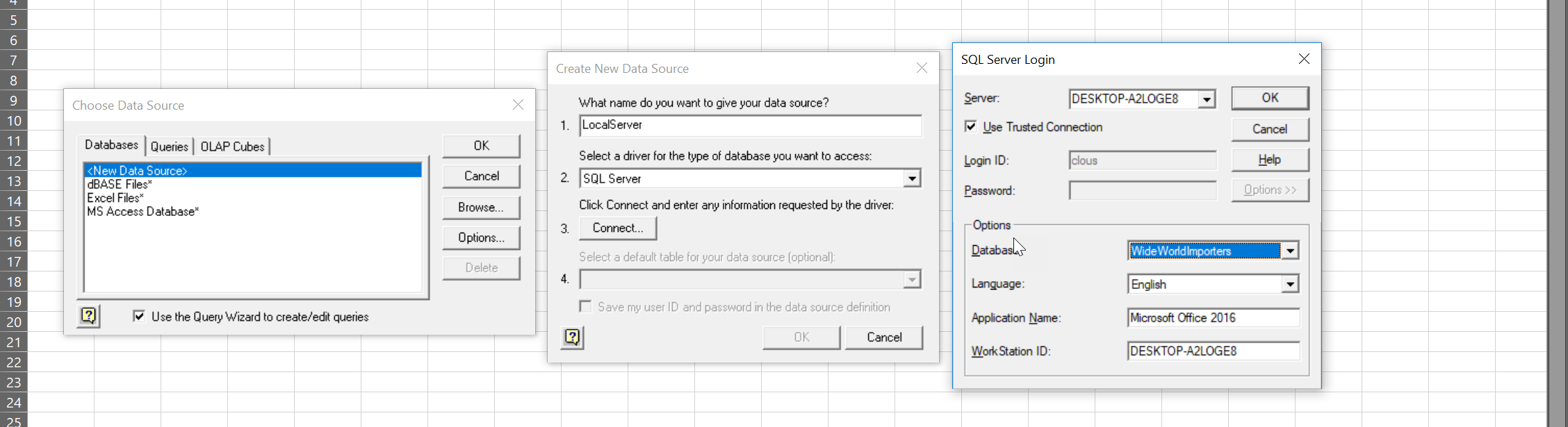
This will open a wizard for you to choose your data source. Double click “<New Data Source>” and you’ll be prompted to enter some information about your data source. Option 1 can be anything you wish that describes your data source. Option 2 should be “SQL Server”. Click “Connect” and it will pop up a third window where you can enter information about the server and login information. Be sure you select the “Options>>” dropdown so you can select the database you’re wanting to connect to.
You’ll now have a new data source in the original window. Double click the data source to bring up a table import wizard. If you want to import an entire table, you can do so here and even filter and sort the data using the import wizard. However, if you want to use your own custom query as we have been, just select any field and go through the wizard and import the data. When you come to screen that asks you if you want to return the data to Excel or edit in a query, return the data to Excel. It will then prompt you to select where you want the data returned in your workbook.
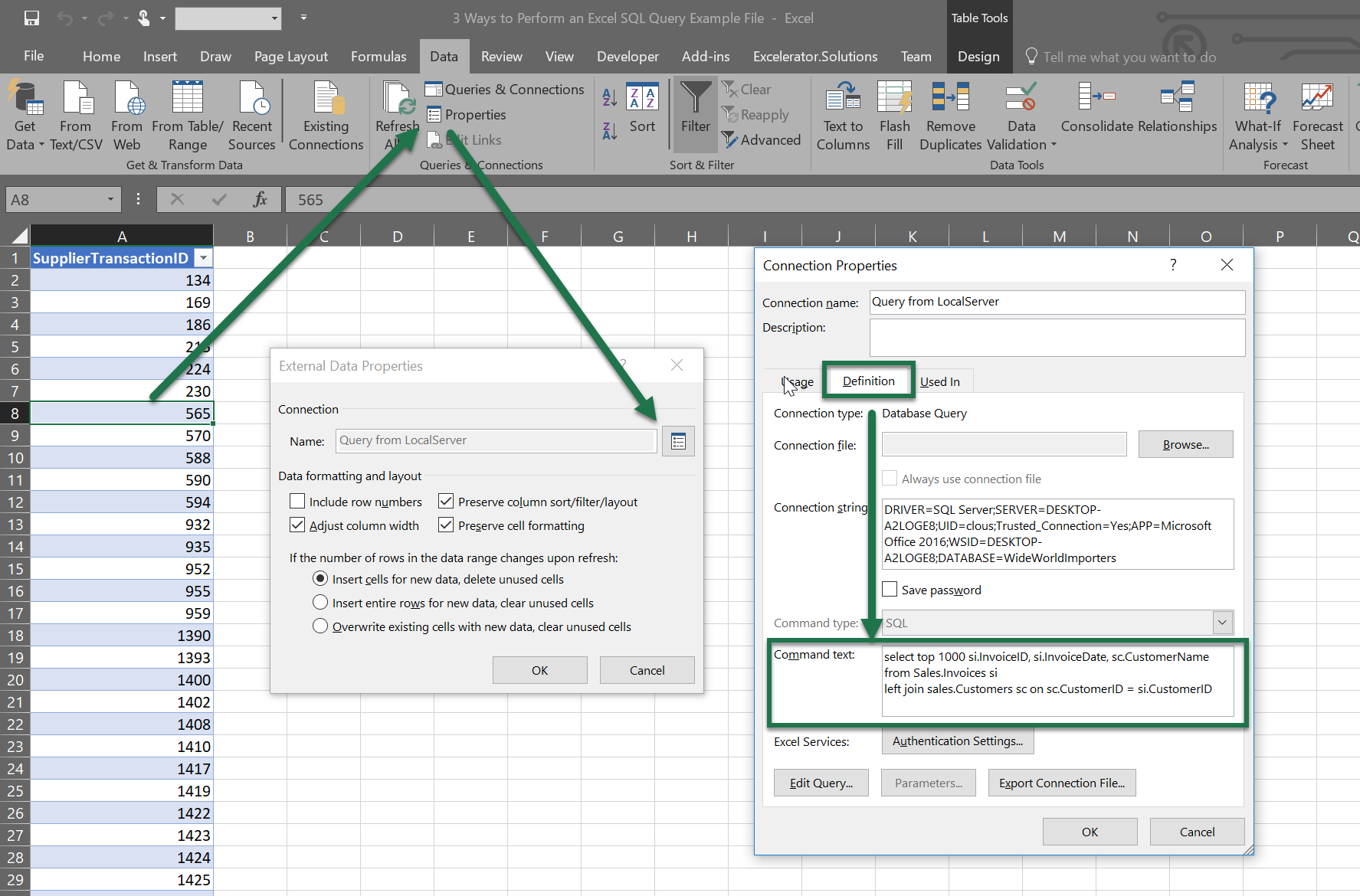
The query will return the data in a table format. To change it to your own custom SQL query, let’s follow these steps:
- Click anywhere in the data table.
- On the Excel Data Ribbon, in the “Queries & Connections” group, properties will no longer be grayed out like it normally is. Click this.
- In the popup – you’ll see another properties icon. Click this.
- In this popup, select the “Definition” tab and paste your SQL query in the “Command Text” input box.
Now you’ve built an Excel SQL Query that can be refreshed anytime the workbook is refreshed. In my screengrab, the “Parameters” button is greyed out. If you want to add parameters to your query, you do so by adding “?” in your command text. That looks like this.
This creates a parameter the end user can interact with. You can have the user be prompted to enter an input when the workbook is refreshed, select a default value, or have it linked to a cell in the workbook. Even though this option is cumbersome to set up, I really enjoy using it. It allows me a lot of flexibility to have the user interact with the data. As I touched on in the beginning, I’ve had success using this option on Microsoft Office for Mac OSX. I don’t want to say this will work 100% of the time on a Mac because I’ve also had it fail. If anyone has any input on this, I’d love to hear from you.
Let me know your thoughts on these approaches in the comments! What other ways do you creatively get data into Excel from SQL data sources?
Cheers!
R
Представьте себе ситуацию, Вы получили целевую выборку из одной базы данных, но для полноты картины, как всегда, нужны дополнительные данные. Проблема может быть в том, что нужная информация хранится в другой базе данных и возможности создать на ней свою таблицу нет, подключиться используя link тоже нельзя, да и количество элементов, по которым нужно получить данные, несколько больше, чем допустимое на данном источнике. Вот и получается, что возможность написать SQL запрос и получить нужные данные есть, но написать придется не один запрос, а потом потратить время на объединение полученных данных.
Выйти из подобной ситуации поможет Excel.
Уверен, что ни для кого не секрет, что MS Excel имеет встроенный модуль VBA и надстройки, позволяющие подключаться к внешним источникам данных, то есть по сути является мощным инструментом для аналитики, а значит идеально подходит для решения подобных задач.
Для того чтобы обойти проблему, нам потребуется таблица с целевой выборкой, в которой содержатся идентификаторы, по которым можно достаточно корректно получить недостающую информацию (это может быть уникальный идентификатор, назовем его ID, или набор из данных, находящихся в разных столбцах), ПК с установленным MS Excel, и доступом к БД с недостающей информацией и, конечно, желание получить ту самую информацию.
Создаем в MS Excel книгу, на листе которой размещаем таблицу с идентификаторами, по которым будем в дальнейшем формировать запрос (если у нас есть уникальный идентификатор, для обеспечения максимальной скорости обработки таблицу лучше представить в виде одного столбца), сохраняем книгу в формате *.xlsm, после чего приступаем к созданию макроса.
Через меню «Разработчик» открываем встроенный VBA редактор и начинаем творить.
Sub job_sql() — Пусть наш макрос называется job_sql.
Пропишем переменные для подключения к БД, записи данных и запроса:
Dim cn As ADODB.Connection
Dim rs As ADODB.Recordset
Dim sql As String
Опишем параметры подключения:
sql = «Provider=SQLOLEDB.1;Integrated Security=SSPI;Persist Security Info=True;Data Source=Storoge.company.ru Storoge.»
Объявим процедуру свойства, для присвоения значения:
Set cn = New ADODB.Connection
cn.Provider = » SQLOLEDB.1″
cn.ConnectionString = sql
cn.ConnectionTimeout = 0
cn.Open
Вот теперь можно приступать непосредственно к делу.
Организуем цикл:
For i = 2 To 1000
Как вы уже поняли конечное значение i=1000 здесь только для примера, а в реальности конечное значение соответствует количеству строк в Вашей таблице. В целях унификации можно использовать автоматический способ подсчета количества строк, например, вот такую конструкцию:
Dim LastRow As Long
LastRow = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Row — 1 + ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Rows.Count
Тогда открытие цикла будет выглядеть так:
For i = 2 To LastRow
Как я уже говорил выше MS Excel является мощным инструментом для аналитики, и возможности Excel VBA не заканчиваются на простом переборе значений или комбинаций значений. При наличии известных Вам закономерностей можно ограничить объем выгружаемой из БД информации путем добавления в макрос простых условий, например:
If Cells(i, 2) = «Ваше условие» Then
Итак, мы определились с объемом и условиями выборки, организовали подключение к БД и готовы формировать запрос. Предположим, что нам нужно получить информацию о размере ежемесячного платежа [Ежемесячный платеж] из таблицы [payments].[refinans_credit], но только по тем случаям, когда размер ежемесячного платежа больше 0
sql = «select [Ежемесячный платеж] from [PAYMENTS].[refinans_credit] » & _
«where [Ежемесячный платеж]>0 and [Номер заявки] ='» & Cells(i, 1) & «‘ «
Если значений для формирования запроса несколько, соответственно прописываем их в запросе:
«where [Ежемесячный платеж]>0 and [Номер заявки] = ‘» & Cells(i, 1) & «‘ » & _
» and [Дата платежа]='» & Cells(i, 2) & «‘»
В целях самоконтроля я обычно записываю сформированный макросом запрос, чтобы иметь возможность проверить его корректность и работоспособность, для этого добавим вот такую строчку:
Cells(i, 3) = sql
в третьем столбце записываются запросы.
Выполняем SQL запрос:
Set rs = cn.Execute(sql)
А чтобы хоть как-то наблюдать за выполнением макроса выведем изменение i в статус-бар
Application.StatusBar = «Execute script …» & i
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Теперь нам нужно записать полученные результаты. Для этого будем использовать оператор Do While:
j = 0
Do While Not rs.EOF
For ii = 0 To rs.Fields.Count — 1
Cells(i, 4 + j + ii) = rs.Fields(0 + ii) ‘& «;»
Указываем ячейки для вставки полученных данных (4 в примере это номер столбца с которого начинаем запись результатов)
Next ii
j = j + rs.Fields.Count
s.MoveNext
Loop
rs.Close
End If
— закрываем цикл If, если вводили дополнительные условия
Next i
cn.Close
Application.StatusBar = «Готово»
End Sub
— закрываем макрос.
В дополнение хочу отметить, что данный макрос позволяет обращаться как к БД на MS SQL так и к БД Oracle, разница будет только в параметрах подключения и собственно в синтаксисе SQL запроса.
В приведенном примере для авторизации при подключении к БД используется доменная аутентификация.
А как быть если для аутентификации необходимо ввести логин и пароль? Ничего невозможного нет. Изменим часть макроса, которая отвечает за подключение к БД следующим образом:
sql = «Provider= SQLOLEDB.1;Password=********;User ID=********;Data Source= Storoge.company.ru Storoge;APP=SFM»
Но в этом случае при использовании макроса возникает риск компрометации Ваших учетных данных. Поэтому лучше программно удалять учетные данные после выполнения макроса. Разместим поля для ввода пароля и логина на листе и изменим макрос следующим образом:
sql = «Provider= SQLOLEDB.1;Password=» & Sheets(«Лист аутентификации»).TextBox1.Value & «;User ID=» & Sheets(«Лист аутентификации «).TextBox2.Value & «;Data Source= Storoge.company.ru Storoge;APP=SFM»
Место для расположения текстовых полей не принципиально, можно расположить их на листе с таблицей в первых строках, но мне удобней размещать поля на отдельном листе. Чтобы введенные учетные данные не сохранялись вместе с результатом выполнения макроса в конце исполняемого кода дописываем:
Sheets(«Выгрузка»).TextBox1.Value = «« Sheets(»Выгрузка«).TextBox2.Value = »»
То есть просто присваиваем текстовым полям пустые значения, таким образом после выполнения макроса поля для ввода пароля и логина окажутся пустыми.
Вот такое вполне жизнеспособное решение, позволяющее сократить трудозатраты при получении и обработке данных, я использую. Надеюсь мой опыт применения SQL запросов в Excel будет полезен и вам в решении текущих задач.