Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel for Microsoft 365 for Mac Excel for the web Excel 2021 Excel 2021 for Mac Excel 2019 Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 Excel 2016 for Mac Excel 2013 Excel for Mac 2011 More…Less
This article describes the formula syntax and usage of the DAYS function in Microsoft Excel. For information about the DAY function, see DAY function.
Description
Returns the number of days between two dates.
Syntax
DAYS(end_date, start_date)
The DAYS function syntax has the following arguments.
-
End_date Required. Start_date and End_date are the two dates between which you want to know the number of days.
-
Start_date
Required. Start_date and End_date are the two dates between which you want to know the number of days.
Note: Excel stores dates as sequential serial numbers so that they can be used in calculations. By default, Jan 1, 1900 is serial number 1, and January 1, 2008 is serial number 39448 because it is 39447 days after January 1, 1900.
Remarks
-
If both date arguments are numbers, DAYS uses EndDate–StartDate to calculate the number of days in between both dates.
-
If either one of the date arguments is text, that argument is treated as DATEVALUE(date_text) and returns an integer date instead of a time component.
-
If date arguments are numeric values that fall outside the range of valid dates, DAYS returns the #NUM! error value.
-
If date arguments are strings that cannot be parsed as valid dates, DAYS returns the #VALUE! error value.
Example
Copy the example data in the following table, and paste it in cell A1 of a new Excel worksheet. For formulas to show results, select them, press F2, and then press Enter. If you need to, you can adjust the column widths to see all the data.
|
Data |
||
|---|---|---|
|
31-DEC-2021 |
||
|
1-JAN-2021 |
||
|
Formula |
Description |
Result |
|
=DAYS(«15-MAR-2021″,»1-FEB-2021») |
Finds the number of days between the end date (15-MAR-2021) and start date (1-FEB-2021). When you enter a date directly in the function, you need to enclose it in quotation marks. Result is 42. |
42 |
|
=DAYS(A2,A3) |
Finds the number of days between the end date in A2 and the start date in A3 (364). |
364 |
Top of Page
Need more help?
Summary
The Excel DAYS function returns the number of days between two dates. With a start date in A1 and end date in B1, =DAYS(B1,A1) will return the days between the two dates.
Purpose
Return value
A number representing days.
Arguments
- end_date — The end date.
- start_date — The start date.
Syntax
=DAYS(end_date, start_date)
Usage notes
The DAYS function returns the number of days between two dates. Both dates must be valid Excel dates or text values that can be coerced to dates. The DAYS function only works with whole numbers, fractional time values that might be part of a date are ignored. If start and end dates are reversed, DAYS returns a negative number. The DAYS function returns all days between two dates, to calculate working days between dates, see the NETWORKDAYS function.
Examples
With a start date in A1 and end date in A2:
=DAYS(A2,A1)
Will return the same result as:
=A2-A1
Unlike the simple formula above, the DAYS function can also handle dates in text format, as long as the date is recognized by Excel. For example:
=DAYS("7/15/2016","7/1/2016") // returns 14
The DAYS function returns the number of days between two dates. For example:
=DAYS("1-Mar-21","2-Mar-21") // returns 1
To include the end date in the count, add 1 to the result:
=DAYS("1-Mar-21","2-Mar-21")+1 // returns 2
Storing and parsing text values that represent dates should be avoided, because it can introduce errors and parsing problems. Working with native Excel dates (which are numbers) is a better approach. To create a numeric date from scratch in a formula, use the DATE function.
Notes
- The DAYS function only works with whole numbers and ignores time.
- If dates are not recognized, DAYS returns the #VALUE! error.
- If dates are out of range, DAYS returns the #NUM! error.
Author
Dave Bruns
Hi — I’m Dave Bruns, and I run Exceljet with my wife, Lisa. Our goal is to help you work faster in Excel. We create short videos, and clear examples of formulas, functions, pivot tables, conditional formatting, and charts.
Watch Video – Calculate the Number of Workdays Between Two Dates
Excel has some powerful functions to calculate the number of days between two dates in Excel. These are especially useful when you’re creating Gantt charts or timelines for a proposal/project.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to calculate the number of days between two dates (in various scenarios):
Calculating the Total Number of Days Between Two Dates in Excel
Excel has multiple ways to calculate the days between two dates.
Using the DAYS Function
Excel DAYS function can be used to calculate the total number of days when you have the start and the end date.
You need to specify the ‘Start Date’ and the ‘End Date’ in the Days function, and it will give you the total number of days between the two specified dates.
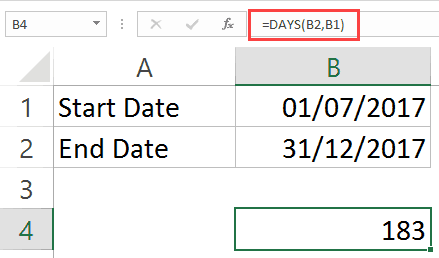
For example, suppose you have the start date is in cell B1 and End Date is in cell B2 (as shown below):
The following formula will give you the total number of days between the two dates:
=DAYS(B2,B1)
Note that you can also manually specify the dates in the Days function by putting it in double-quotes. Just make sure these dates in double-quotes is in an accepted date format in Excel.
Days function gives you the number of days between two dates. This means that if the dates are 1 Dec 2017 and 2 Dec 2017, it will return 1. If you want both the days to be counted, you need to add 1 to the result of Days function. You can read more about the Days function here.
Using the DATEDIF Function
DATEDIF function (derived from Date Difference) also allows you to quickly get the number of days between two dates. But unlike the DAYS function, it can do more than that.
You can also use the DATEDIF function to calculate the number of months or years that have elapsed in the two given dates.
Suppose you have the below dataset and you want to get the number of days between these two dates:
You can use the below DATEDIF formula to do this:
=DATEDIF(B1,B2,"D")
The above DATEDIF formula takes three arguments:
- The start date – B1 in this example
- The end date – B2 in this example
- “D” – the text string that tells the DATEDIF function what needs to be calculated.
Also note that unline the other Excel functions, when you type the DATEDIF function in Excel, it will not show the IntelliSense (the autocomplete option that helps you with the formula arguments).
If you only want to calculate the number of days between two given dates, then it’s better to use the DAYS function. DATEDIF is more suited when you want to calculate the total number of years or months that have passed in between two dates.
For example, the below formula would give you the total number of months between the two dates (in B1 and B2)
=DATEDIF(B1,B2,"M")
Similarly, the below formula will give you the total number of years between the two dates:
=DATEDIF(B1,B2,"Y")
You can read more about the DATEDIF function here. One of the common uses of this function is when you need to calculate age in Excel.
Number of Working Days Between Two Dates in Excel
Excel has two functions that will give you the total number of working days between two dates and will automatically account for weekends and specified holidays.
- Excel NETWORKDAYS function – you should use this when the weekend days are Saturday and Sunday.
- Excel NETWORKDAYS INTERNATIONAL function – use this when the weekend days are not Saturday and Sunday.
Let’s first quickly have a look at NETWORKDAYS Function syntax and arguments.
Excel NETWORKDAYS Function – Syntax & Arguments
=NETWORKDAYS(start_date, end_date, [holidays])
- start_date – a date value that represents the start date.
- end_date – a date value that represents the end date.
- [holidays] – (Optional) It is a range of dates that are excluded from the calculation. For example, these could be national/public holidays. This could be entered as a reference to a range of cells that contains the dates, an array of serial numbers that represent the dates, or a named range.
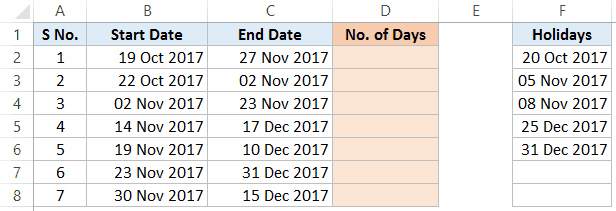
Let’s first look at an example where you want to calculate the number of working days (business days) between two dates with Saturday and Sunday as weekends.
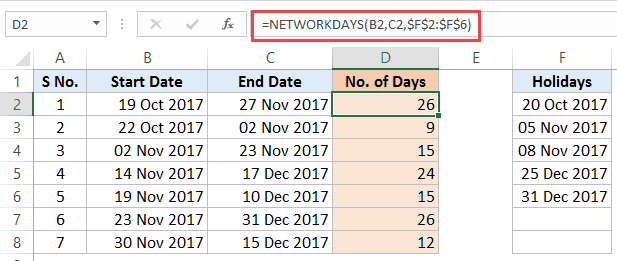
To calculate the number of working days (Column D) – when the start date, end date, and holidays are specified – use the below formula in D3 and copy for all cells:
=NETWORKDAYS(B2,C2,$F$2:$F$6)
This function works great in most cases, except the ones where the weekends are days other than Saturday and Sunday.
For example, in middle-eastern countries, the weekend is Friday and Saturday, or in some jobs, people may have a six-day workweek.
To tackle such cases, Excel has another function – NETWORKDAYS.INTL (introduced in Excel 2010).
Before I take you through the example, let’s quickly learn about the syntax and arguments of Excel NETWORKDAY INTERNATIONAL function
Excel NETWORKDAYS INTERNATIONAL Function – Syntax & Arguments
=NETWORKDAYS.INTL(start_date, end_date, [weekend], [holidays])
- start_date – a date value that represents the start date.
- end_date – a date value that represents the end date.
- [weekend] – (Optional) Here, you can specify the weekend, which could be any two days or any single day. If this is omitted, Saturday and Sunday are taken as the weekend.
- [holidays] – (Optional) It is a range of dates that are excluded from the calculations. For example, these could be national/public holidays. This could be entered as a reference to a range of cells that contains the dates or could be an array of serial numbers that represent the dates.
Now let’s see an example of calculating the number of working days between two dates where the weekend days are Friday and Saturday.
Suppose you have a dataset as shown below:
To calculate the number of working days (Column D) with the weekend as Friday and Saturday, use the following formula:
=NETWORKDAYS.INTL(B2,C2,7,$F$2:$F$6)
The third argument in this formula (the number 7) tells the formula to consider Friday and Saturday as the weekend.
Number of Weekends Between Two Dates in Excel
We can use the NETWORKDAYS function to calculate the number of weekends between two dates.
While the Networkdays function calculates the number of working days, we can also use to get the number of weekend days between two dates.
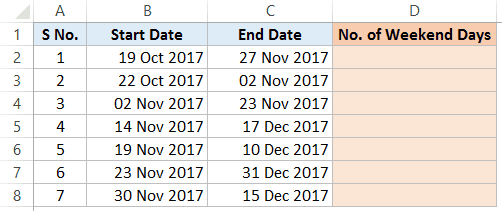
Suppose we have a dataset as shown below:
Here is the formula that will give you the total number of weekends days between the two dates:
=DAYS(C2,B2)+1-NETWORKDAYS(B2,C2)
Number of Work Days in a Part-time Job
You can use Excel NETWORKDAYS.INTL function to calculate the number of workdays in a part-time job as well.
Let’s take an example where you are involved in a project where you have to work part-time (Tuesday and Thursday only).
Here is the formula that will get this done:
=NETWORKDAYS.INTL($B$3,$C$3,"1010111",$E$3:$E$7)
Note that instead of choosing the weekend from the drop-down that’s inbuilt in the function, we have used “1010111” (in double quotes).
- 0 indicates a working day
- 1 indicates a non-working day
The first number of this series represents Monday and the last number represents Sunday.
So “0000011“ would mean that Monday to Friday are working days and Saturday and Sunday are non-working (weekend).
With the same logic, “1010111” indicates that only Tuesday and Thursday are working, and rest 5 days are non-working.
In case you have holidays (which you don’t want to get counted in the result), you can specify these holidays as the fourth argument.
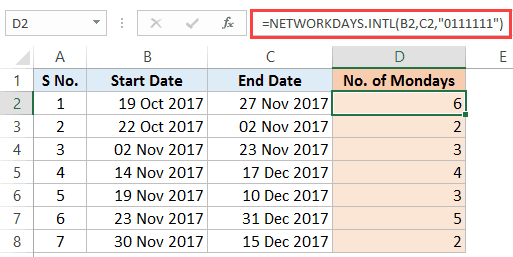
Number of Mondays Between Two Dates
To find the number of Mondays between two dates (or any other day), we can use the same logic as used above in calculating part-time jobs.
Suppose you have a dataset as shown below:
Here is the formula that will give you the number of Mondays between the two dates:
=NETWORKDAYS.INTL(B2,C2,"0111111")
In this formula, ‘0’ means a working day and ‘1’ means a non-working day.
This formula gives us the total number of working days considering that Monday is the only working day of the week.
Similarly, you can also calculate the number of any day between two given dates.
You May Also Like the Following Tutorials:
- Excel Timesheet Calculator Template.
- Convert Date to Text in Excel.
- How to Group Dates in Pivot Tables in Excel.
- How to Automatically Insert Date and Time Stamp in Excel.
- Convert Time to Decimal Number in Excel (Hours, Minutes, Seconds)
- How to SUM values between two dates in Excel
- Get Day Name from Date in Excel
- Check IF a Date is Between Two Given Dates in Excel
- How to Add Week to Date in Excel?
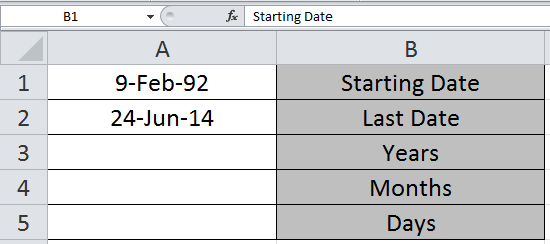
While working on Excel, Sometimes you need to calculate the number of Days, Months and Years between the two given dates.
To calculate the number of Days, Months and Years between the two given dates, we will use INT and MOD function in Excel 2016.
INT function returns the Integer part of the number.
Syntax:
MOD function returns the remainder of the number after dividing it with the divisor
Syntax:
Let’s get this by an example shown below.
We need to find the years, month and days between the two given dates in A1 and A2 cell.
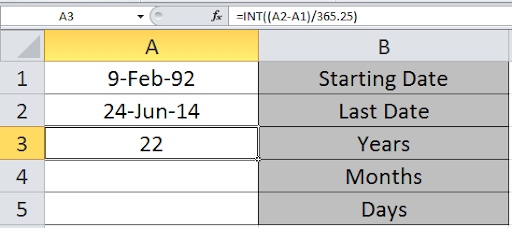
Write the formula in A3 cell to get the years between these two dates.
Formula
We can see the number of years in the A3 cell.
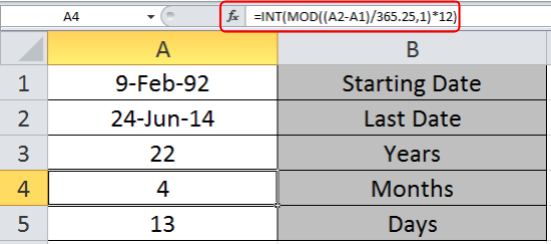
Now write the formula in A4 to get the months
=INT(MOD((A2-A1)/365.25,1)*12)
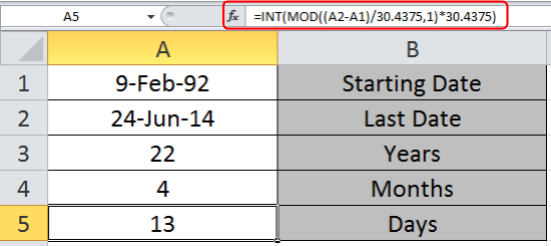
Use the Formula in A5 cell to get the days between the two dates.
=INT(MOD((A2-A1)/30.4375,1)*30.4375)
Explanation:
As we know there are 12 months in a year and an average of 365.25 days in 4-year interval.
Here INT function returns the Integer part of the mathematical formulation part.
Here as you can see you get the number of Days, Months and Years between the two given dates.
Previously in Excel 2010 and Excel 2013, MS used to provide a date function named DATEDIF. It was found that it had some errors and was prone to give wrong outputs. This is why in Excel 2016 it is not promoted. But the function is still useful to calculate age. When you type this formula, no help or suggestion will be shown. You have to type it whole…
DATEDIF Syntax
Syntax:
=DATEDIF(date1,date2, “Y”)
“Y” will return the difference of years. At the place “Y” we can also write “M” or “D”.
As you must have guessed that “M” will return the difference in Months and “D” will return difference of Days.
These basic formulas and its uses can improve your time and efficiency using MS Excel 2016. Hope you understood how to count the number of days between the two given dates. You can perform these tasks in Excel 2013 and 2010. Please share your views on this topic below in the comment box. We will help you.
Related Articles:
How to Calculate years between dates in Excel
How to Add Years to a Date in Excel
How to Convert Date and Time from GMT to CST in Excel
How to Get days between dates in Excel
Popular Articles:
50 Excel Shortcut to Increase Your Productivity
How to use the VLOOKUP Function in Excel
How to use the COUNTIF function in Excel 2016
How to use the SUMIF Function in Excel