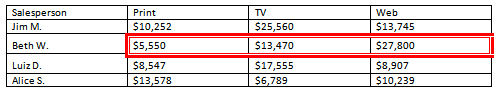If the document contains tables, it must be formatted according to the requirements accepted by your college, university, company, established on the project, etc. Most requirements, including accessibility, tell that tables should contain titles, column headers, alternate text, etc. In addition, tables must be correctly positioned on the page, using the pre-defined alignment, padding, and text-wrapping guidelines.
Usually, the table contains the following basic components:
- The table number (e.g., Table 1) and the title appear above the table body (see how to create a caption for tables).
- The table includes column headings, including a stub heading (heading for the leftmost, or stub, column). Some tables also include column spanners, decked heads, and table spanners. See how to format tables in a Word document.
- The table body contains all the rows and columns of a table (including the headings row). A cell is the point of intersection between a row and a column. See how to select and format table elements.
- All types of notes (general, specific, and probability) appear below the table if there are notes. Notes describe contents of the table that cannot be understood from the table title or body alone (e.g., definitions of abbreviations, copyright attribution, etc.).
See also how to create cross-references to a table.
Align the table on the page
By default, Word aligns the table to the Left. If you want to change an alignment of the table on the page, select it and do one of the following:
- On the Home tab, in the Paragraph group, select the alignment you prefer:
- Open the Table Properties dialog box by doing one of the following:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Table group, click the Properties button:
- Right-click the table and select Table Properties… in the popup menu:
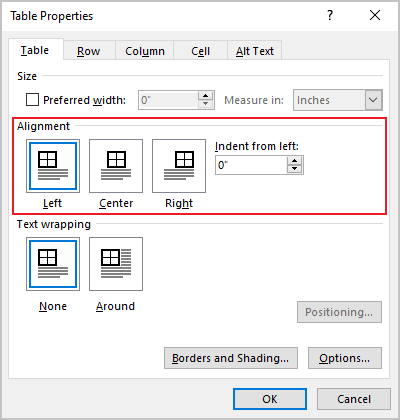
In the Table Properties dialog box, on the Table tab, in the Alignment section, select the option you prefer:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Table group, click the Properties button:
- Press the keyboard shortcuts:
- Ctrl+L to align a table to the Left (by default),
- Ctrl+E to Center the table,
- Ctrl+R to align a table to the Right.
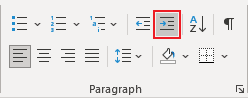
Add indent from left
The Indent from left controls the distance of the table from the left margin. To add the Indent from left, do one of the following:
- On the Home tab, in the Paragraph group, click the Increase Indent button:
- Open the Properties dialog box. In the Table Properties dialog box, on the Table tab, in the Alignment section, type or choose the value you need in the Indent from left field:
Note: The Indent from left field is active only for the Left alignment.
For example, the table with a left indent 0.5 inches:

Text Wrapping for a table
Word offers to customize the text wrapping style for a table, as well as for figures. To customize a text wrapping style, do the following:
1. Select a table.
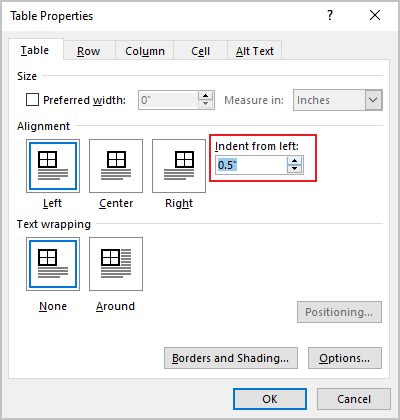
2. Open the Table Properties dialog box. In the Table Properties dialog box, on the Table tab, in the Text wrapping section:
- Select None to disable text wrapping for the table
- Select the Around option to have text wrapping around the table. Then click the Positioning… button for more customization:
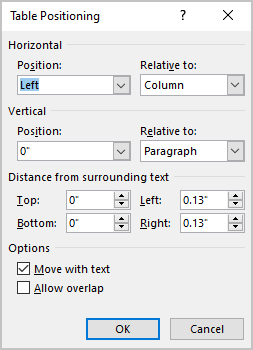
In the Table Positioning dialog box:
Position a table
- In the Horizontal sections, specify:
- Position to the Left, Right, Center, Inside, or Outside,
- Relative to the Margin, Page, or Column.
For example, with Position to the Right relative to Margin:
- In the Vertical section, specify:
- Position to the Top, Bottom, Center, Inside, or Outside,
- Relative to the Margin, Page, or Column.
For example, with Position to the Top relative to Page:
Increase the space between text and table
- In the Distance from surrounding text section, enter custom values for the distance between the text and the table independently for:
- Top (0 by default),
- Bottom (0 by default),
- Left (1.13 inches by default),
- Right (1.13 inches by default).
For example, with the 0.3-inch distance on all sides:
Note: See also how to change a distance within a table.
Text wrapping options
- In the Options section:
- The Move with text option moves the table along with the text in which it is located.
Select the Move with Text option if the text is directly related to the table data. The table is vertically aligned to the related paragraph around it. If the table data applies to the whole document, keep the Move with Text option unselected.
- Allow overlap allows to layer table on top of each other.
- The Move with text option moves the table along with the text in which it is located.
Position a large table
Control where a table is split
When working with a long table, or when a table needs to be placed at the bottom of the page, splitting up a table into two separate tables is necessary. By default, if a page break occurs within a large row, Microsoft Word allows a page break to split the line between two pages (see How to prevent a table break between pages).
To insert a table break at a specific location, position the cursor on the cell on the row, or select the row that should appear on the next page, then do one of the following:
- Press Ctrl+Enter.
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Merge group, click the Split Table button:
Be careful! Word applies the chosen style to the new table. If you Undo the table splitting, the formatting may not be Undone correctly.
Add an Alternative text (Alt Text)
Most requirements recommend adding alternative text for visual objects, including tables (see how to turn off automatically creating the Alternative text).
To add an alternative text for a table, do the following:
1. Select a table.
2. Do one of the following:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Table group, click the Properties button.
- Right-click the table and select Table Properties… in the popup menu.
3. In the Table Properties dialog box, on the Alt Text tab:
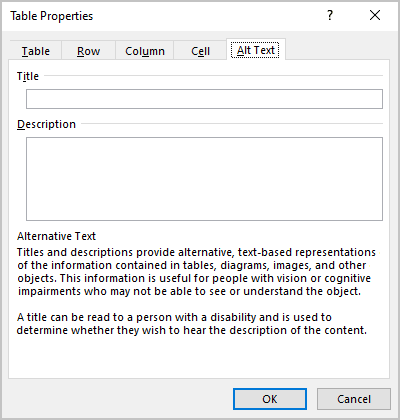
- In the Title field, type a title, if necessary.
- In the Description field, fill the description for the table.
- Click the OK button.
Lesson 21: Working with Tables
/en/word2010/reviewing-documents/content/
Introduction
A table is a grid of cells arranged in rows and columns. Tables can be customized and are useful for various tasks such as presenting text information and numerical data.
In this lesson, you will learn how to convert text to a table, apply table styles, format tables, and create blank tables.
Inserting and modifying tables
In Word, tables are useful for organizing and presenting data. You can create a blank table, convert text to a table, and apply a variety of styles and formats to existing tables.
Optional: You can download this example for extra practice.
To insert a blank table:
- Place your insertion point in the document where you want the table to appear.
- Select the Insert tab.
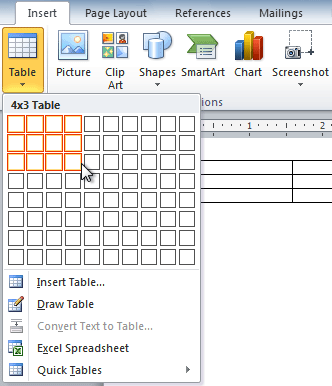
- Click the Table command.
- Hover your mouse over the diagram squares to select the number of columns and rows in the table.
Inserting a new table
- Click your mouse, and the table appears in the document.
- You can now place the insertion point anywhere in the table to add text.
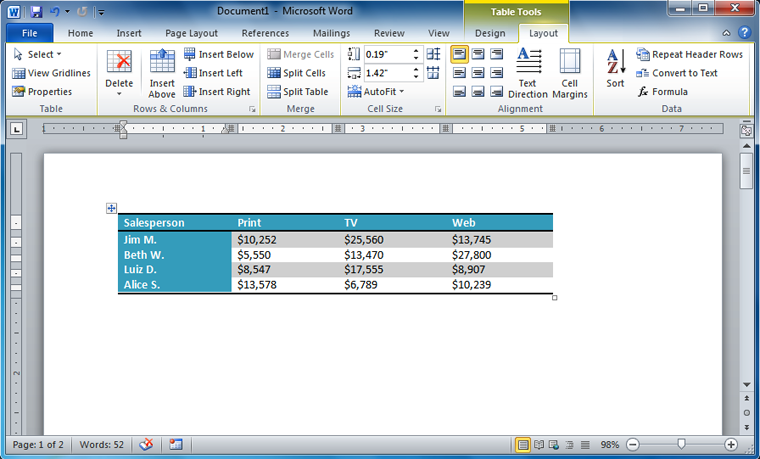
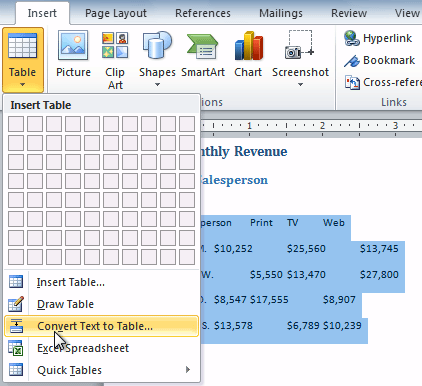
To convert existing text to a table:
- Select the text you want to convert.
- Select the Insert tab.
- Click the Table command.
- Select Convert Text to Table from the menu. A dialog box will appear.
Converting text to a table
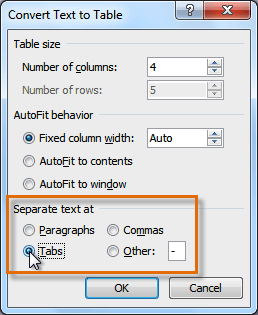
- Choose one of the options in the Separate text at: section. This is how Word knows what text to put in each column.
Separating text at Tabs
- Click OK. The text appears in a table.
The converted table
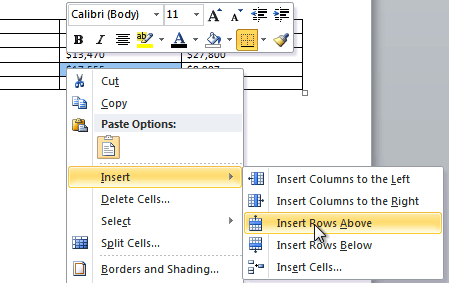
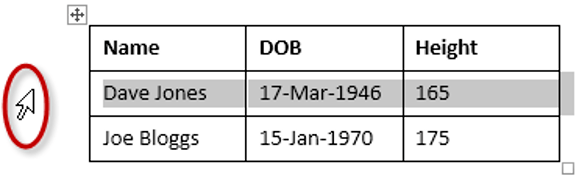
To add a row above an existing row:
- Place the insertion point in a row below the location where you want to add a row.
Placing the insertion point
- Right-click the mouse. A menu appears.
- Select Insert
Insert Rows Above.
Adding a row
- A new row appears above the insertion point.
The new row
You can also add rows below the insertion point. Follow the same steps, but select Insert Rows Below from the menu.
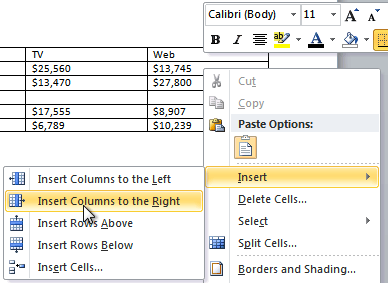
To add a column:
- Place the insertion point in a column adjacent to the location where you want the new column to appear.
- Right-click the mouse. A menu will appear.
Adding a column
- Select Insert
Insert Columns to the Left or Insert Columns to the Right. A new column appears.
The new column
To delete a row or column:
- Select the row or column.
- Right-click your mouse. A menu will appear.
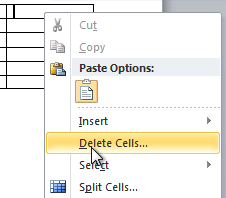
- Select Delete Cells.
Selecting Delete Cells
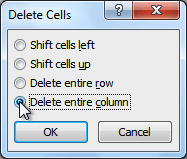
- Select Delete entire row or Delete entire column, then click OK.
Deleting a column
To apply a table style:
- Click anywhere on the table. The Design tab will appear on the Ribbon.
- Select the Design tab and locate the Table Styles.
- Click the More drop-down arrow to see all of the table styles.
Viewing the Table Styles
- Hover the mouse over the various styles to see a live preview.
- Select the desired style. The table style will appear in the document.
After adding a Table Style
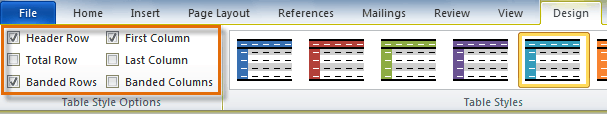
To change table style options:
Once you’ve chosen a table style, you can turn various options on or off to change the appearance of the table. There are six options: Header Row, Total Row, Banded Rows, First Column, Last Column, and Banded Columns.
- Click anywhere on the table. The Design tab will appear.
- From the Design tab, check or uncheck the desired options in the Table Style Options group.
Table Style Options
Depending on which table style you’re using, certain table style options may have a somewhat different effect. You may need to experiment to get the exact look you want.
To add borders to a table:
- Select the cells you want to add a border to.
Highlighted cells
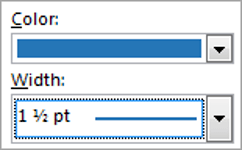
- From the Design tab, select the desired Line Style, Line Weight, and Pen Color.
Line Style, Line Weight, and Pen Color commands
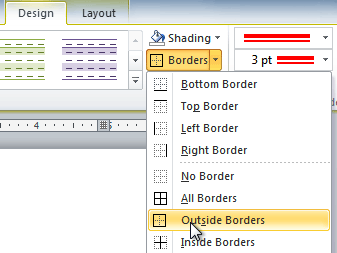
- Click the Borders drop-down arrow.
- From the drop-down menu, select the desired border type.
Selecting a border type
- The border will be added to the selected cells.
The finished border
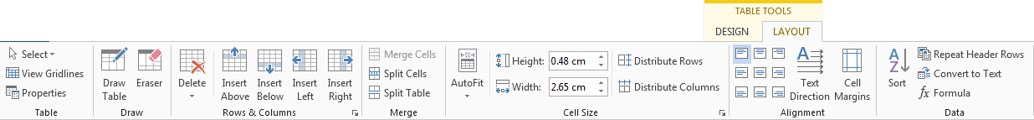
Modifying a table using the Layout tab
When you select a table in Word 2010, Design and Layout tabs appear under Table Tools on the Ribbon. Using commands on the Layout tab, you can make a variety of modifications to the table.
Click the buttons in the interactive below to learn about the different ways you can modify a table with the Layout tab.
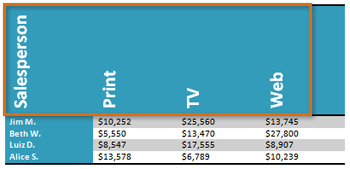
Change Text Direction
Making the text vertical can add style to your table and saves space, allowing you to fit more columns in your table.
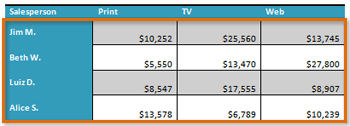
Align Cell Text
By changing the alignment of a cell, you can control exactly where the text is located. In the example below, the cell text is aligned to the bottom-right.
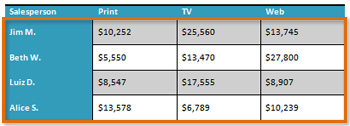
Distribute Rows/Columns
To keep your table looking neat and organized, you may want to distribute the rows or columns equally, which makes them all the same size. You can distribute the rows or columns for the entire table or just a portion of it.
Change Cell Size
You can type a desired row height or column width for your cells. If you prefer, you can click AutoFit, and it will automatically adjust column widths based on the text inside them.
Merge and Split Cells
Some tables require a layout that doesn’t conform to the standard grid. In these cases, you may need to merge or split cells.
Add Rows and Columns
You can insert or delete rows and columns in your table. This can be especially useful if you need to add something to the middle of your table.
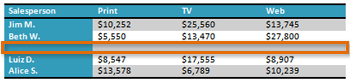
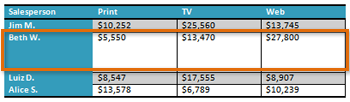
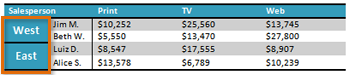
Challenge!
- Open an existing Word document. If you want, you can use this example.
- Convert some text into a table. If you are using the example, convert the text below By Client.
- Apply a table style, and experiment with the table style options. If you are using the example, see if you can make the table match the By Salesperson table above it.
- Delete a row from the table.
- Insert a blank table with five rows and four columns.
- Add borders to the blank table.
/en/word2010/smartart-graphics/content/
Insert and Edit a Table with Multiple Columns and Rows in Word
by Avantix Learning Team | Updated August 23, 2022
Applies to: Microsoft® Word® 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021 and 365 (Windows)
You can create a table in a Word document in 4 easy ways using the Ribbon. A table is a grid made up of columns and rows that intersect to form cells. You can insert text, numbers and images in a table. Once you have inserted a table, you can easily add and resize columns and rows and change table formatting.
It’s best to avoid using Draw Table to create a table since the table may not be created in a consistent way.
Note: Buttons and Ribbon tabs may display in a different way (with or without text) depending on your version of Word, the size of your screen and your Control Panel settings. For newer versions of Word, Ribbon tabs may appear with different names. For example, the Table Design tab may appear as Table Tools Design.
In the following example, a table with 4 columns and 5 rows has been inserted in a Word document:
Recommended article: 10 Microsoft Word Shortcuts for Moving Around in Tables
Do you want to learn more about Microsoft Word? Check out our virtual classroom or in-person classroom Word courses >
Create a table using the Table Grid
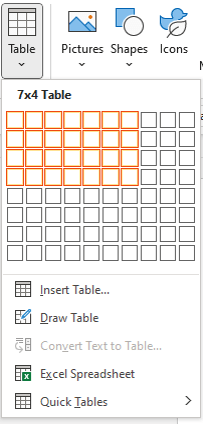
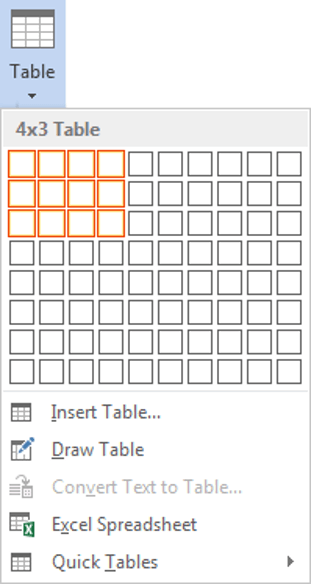
To insert a table using Insert Table and select columns and rows in the Table Grid:
- Click in the Word document where you want to insert a table.
- Click the Insert tab in the Ribbon.
- Click Table in the Tables group. A drop-down menu appears with a Table Grid.
- Hover over the grid until the number of columns and rows you want is selected.
- Click in the highlighted area of the grid to insert a table.
To insert a table, select cells in the Table Grid as follows:
Create a table using the Insert Table dialog box
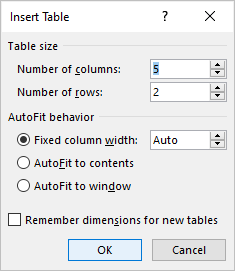
To insert a table using the Insert Table dialog box:
- Click in the Word document where you want to insert a table.
- Click the Insert tab in the Ribbon.
- Click Table in the Tables group. A drop-down menu appears.
- Select Insert Table. A dialog box appears.
- Enter the number of columns and rows you want to create.
- Select the desired options below AutoFit behavior (typically Fixed column width: Auto).
- Click OK.
The Insert Table dialog box appears with options to select the number of columns and rows:
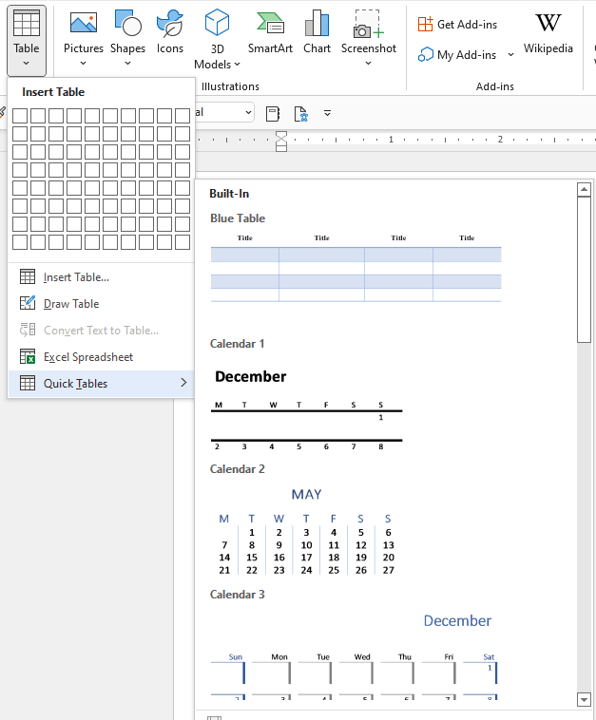
Create a table using Quick Tables
To insert a table using Quick Tables:
- Click in the Word document where you want to insert a table.
- Click the Insert tab in the Ribbon.
- Click Table in the Tables group. A drop-down menu appears.
- Select Quick Tables. A gallery appears.
- Click the table you want to insert.
Quick Tables appear in the Table drop-down menu:
Create a table by converting text to a table
If you have used tabs or other delimiters in paragraphs, you can convert the data into a table (if the delimiters are entered consistently). Wherever you have pressed Enter or Return to create a new paragraph, Word will create a new table row. You can use various delimiters to separate data but the most common are tabs, spaces or commas.
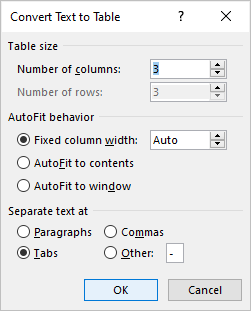
To convert delimited data to a table:
- Select the text that you want to convert.
- Click the Insert tab in the Ribbon.
- Click Table in the Tables group. A drop-down menu appears.
- Select Convert Text to Table. A dialog box appears.
- Enter the number of columns if necessary and ensure a delimiter is selected in the Separate text at area.
- Under AutoFit behavior, choose how you want your table to appear. Word chooses a width for the table columns by default. If you want a different column width, choose AutoFit to contents or AutoFit to window.
- Click OK.
In the Convert Text to Table dialog box, enter the number of columns as well as the delimiter:
Show table gridlines
Gridlines show the cell boundaries of a table on screen if table borders are not applied. Gridlines appear only on the screen and are not printed.
Gridlines are not visible when you view a document in a Web browser or in Print Preview.
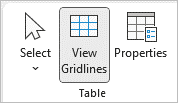
To show table gridlines in a Word document:
- Click in a table.
- Click the Table Layout or Table Tools Layout tab in the Ribbon.
- In the Table group, check View Gridlines.
View Gridlines appears on the Table Tools Layout or Table Layout tab in the Ribbon:
Move around in a table
You can use the following keys to move from one cell to another in a table:
- Tab to move to the next cell to the right.
- Shift-Tab to move to the cell to left.
- Ctrl-Tab to tab within a cell.
Add a row or a column
To add a row in a table:
- Click in a cell that is located above or below where you want to add a row.
- Click the Table Layout or Table Tools Layout tab in the Ribbon.
- To add a row above the cell you clicked in, click Insert Above in the Rows and Columns group. To add a row below the cell you clicked in, in the Rows and Columns group, click Insert Below.
The commands to insert rows or columns appear on the Table Tools Layout or Table Layout tab in the Ribbon:
You can also right-click in a row and choose Insert from the drop-down menu and insert options from the sub-menu.
If you click in the last cell in a table and press Tab, Word will automatically add a row.
To add a column in a table:
- Click in a cell that is located to the right or left of where you want to add a column.
- Click the Table Layout or Table Tools Layout tab in the Ribbon.
- To add a column to the left of the cell you clicked in, click Insert Left in the Rows and Columns group. To add a column to the right of the cell you clicked in, in the Rows and Columns group, click Insert Right.
You can also right-click in a row and choose Insert from the drop-down menu and insert options from the sub-menu.
Delete a column or row
To delete a row or column:
- Select the row or column (drag over the cells or click to the left of a row or above a column when the arrow appears).
- Click the Table Layout or Table Tools Layout tab in the Ribbon.
- In the Rows & Columns group, click Delete. A drop-down menu applears.
- Click Delete Rows or Delete Columns as appropriate.
You can also right-click in a row or column and choose Delete from the drop-down menu and delete options from the sub-menu.
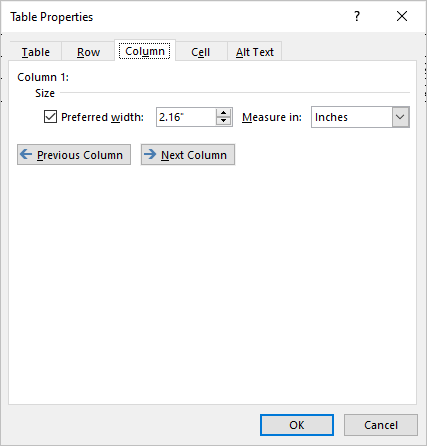
Change column width
To change column width:
- Select the column or columns you want to change.
- Click the Table Layout or Table Tools Layout tab in the Ribbon.
- Click Properties in the Table group. You can also right-click and choose Properties from the drop-down menu. A dialog box appears.
- Click the Column tab.
- Check Preferred Width.
- Type the new measurement for the column width. For example, typer 1.0″ or click the up and down arrows.
- Click OK.
The Table Properties dialog box appears as follows with the Column tab selected:
You can also drag the right line of a column to resize it.
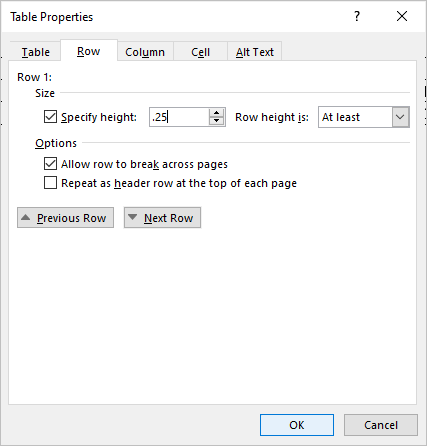
Change row height
To change row height:
- Select the row or rows you want to change.
- Click the Table Layout or Table Tools Layout tab in the Ribbon.
- Click Properties in the Table group. You can also right-click and choose Properties from the drop-down menu. A dialog box appears.
- Click the Row tab.
- Check Specify Height.
- Type the new measurement for the row height. For example, type 1.0″ or click the up and down arrows.
- Specify row height as At Least or Exactly.
- Click OK.
The Table Properties dialog box appears as follows with the Row tab selected:
You can also drag the bottom line of a row to resize it.
Distribute rows and columns evenly
To distribute rows and columns evenly:
- Select the entire table by clicking the four-arrows that appear on the top left of the table.
- Click the Table Layout or Table Tools Layout tab in the Ribbon.
- Click Distribute Rows and / or Distribute Columns in the Cell Size group.
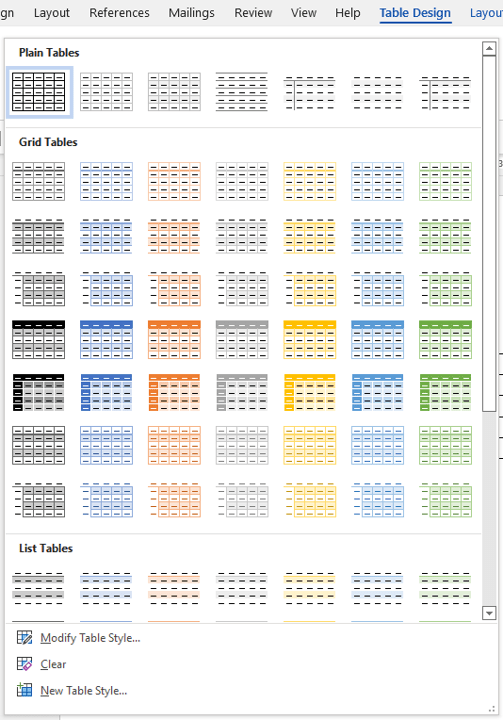
Apply a table style
To apply a table style:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Design or Table Tools Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click a table style or click the More arrow to display the Table Styles gallery and click a style.
Table Styles gallery appears on the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon:
To learn more about working with table styles, check out the article How to Format Microsoft Word Tables Using Table Styles (Ultimate Guide).
Subscribe to get more articles like this one
Did you find this article helpful? If you would like to receive new articles, JOIN our email list.
More resources
4 Ways to Delete a Table in Word
How to Make Columns in Word (Newspaper-style)
How to Insert Formulas and Functions in Word Tables
How to Keep a Microsoft Word Table Together on One Page
How to Delete a Page in Word (Remove Blank or Extra Pages)
Related courses
Microsoft Word: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft Excel: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft PowerPoint: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft Word: Long Documents Master Class
Microsoft Word: Styles, Templates and Tables of Contents
Microsoft Word: Designing Dynamic Word Documents Using Fields
VIEW MORE COURSES >
Our instructor-led courses are delivered in virtual classroom format or at our downtown Toronto location at 18 King Street East, Suite 1400, Toronto, Ontario, Canada (some in-person classroom courses may also be delivered at an alternate downtown Toronto location). Contact us at info@avantixlearning.ca if you’d like to arrange custom instructor-led virtual classroom or onsite training on a date that’s convenient for you.
Copyright 2023 Avantix® Learning
Microsoft, the Microsoft logo, Microsoft Office and related Microsoft applications and logos are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in Canada, US and other countries. All other trademarks are the property of the registered owners.
Avantix Learning |18 King Street East, Suite 1400, Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5C 1C4 | Contact us at info@avantixlearning.ca
F:PersonalDropboxEnglish WritingMyBlog at wordpressArrange tables and figures in word 2010.docx
In a thesis, it is quite common that we have to cite a table in another page. For example, on page 2 we have a paragraph:
“Study shows that 95% of the MS Word functions are not even known by 95% of the users (Table 1)”
The referred table (table 1) is on another page, page 3.
Later the thesis is revised, with more tables adding. The original Table 1 becomes table 3. In that case, it would be pain taking to manually update the reference ‘(Table 1)’ to ‘(Table 3)’.
Indeed MS Word offers a convenient way to automatically update references of the kind. Such function is called ‘Cross-reference“.
It is also common that a table/figure list should be created in the beginning of the thesis. Such table, similar to Tables of Contents, lists out the tables/figures in the thesis, with table title (also called table caption), and the page number of the page on which the tables locate. Instead of manual maintaining such lists, MS Word as well offers automatic update upon revision.
This document describes how to insert table and figure titles (captions) in an organized way, such that:
a) tables/figures can be cross-referred (cross-reference) in the same document, and the references can be updated automatically.
b) A list of table and figures can be generated to indicate the location of the tables/figures, automatically updated.
The method is introduced by the following example with one table.
Step 1, adding a table title
Suppose the following is the contents of table 1. To add a table title:
- Click the place where the table title is to be inserted.
- Click ‘reference’, and then click the icon ‘Insert Caption’.
- In the ‘Options’ section of pop-up box, select ‘Table’ (if it is a Figure, select ‘Figure’)
- Click ‘OK’
By default, the table caption is in a very ugly style, with ugly font, ugly color, and ugly font size. To customize the style, click ‘Home’. In the Style section, scroll down and find the style for ‘Caption’. Right click the style and select modify. In the pop-up box, change to the desired font, font size, and font color, as well as the paragraph, line space settings.
Table 1 inserting a new table 1
Table 2 now the second table
Step 2, insert a cross reference for table 1
To insert a cross-reference for the table [insert after this](Table 2):
- Click the place where the cross reference is to be inserted (in the above, click the place after the text ‘[insert after this]’. Note: it is not necessary to input the text ‘Table 1’, as the cross-reference setting will do the job automatically.
- Click ‘reference’
- Click ‘Cross-reference’
- In the pop-up box, in the section of ‘reference-type’, select ‘Table’ (if it is a Figure, select ‘Figure’). Usually, for citing the table, we only need to put it like ‘Table 1’ without the Table’s title. In that case, in the section of ‘Insert reference to:’, select ‘Only label and number’. Check ‘Insert as hyperlink’, and in the ‘For which caption’ section, select ‘Table 1 the first table’.
The cross-reference is thus done!
Later if a new table (Table 1) is inserted before the original table 1 and the new table’s title is set using the method in step 1, the table numbers will be arranged automatically. In that case, the original table 1 becomes table 2. To update the reference, simple click to select the whole field of the place of the original cross-reference for the old table 1, right-click again, and select ‘update field’.
What if there are figures, Such as (Figure 1)?
Figure 1 the WinWord logo

Step 3, inserting a list of tables.
To insert a list of tables:
- Click the place where the table list is to be inserted
- Click references
- Click ‘Insert Table of Figures’
- In the section of ‘general – Caption label’, select ‘Table’
Done! By the way, the style of the table list can be customized, but I have not figured out how.
Following is the place to insert table of tables:
Table 1 inserting a new table 1 1
Table 2 now the second table 2
It is the same to insert a table for all figures (in the section of ‘general-Caption label’, select ‘Figures’):
Figure 1 the WinWord logo 2
Are you struggling to get your message across? When your Microsoft Word project contains information, try presenting it in the form of a Word table. Learn how to make tables in Word quickly with a template.
A table is a kind of chart that organizes and presents data in rows and columns. It makes information easier to grasp, understand, and analyze at a glance, compared to explaining the same data through plain text.
Microsoft Word gives you various ways to insert or create a table. And you’ve got granular control over the formatting, layout, and appearance of Microsoft Word tables. Table charts are useful in different types of Word projects, whether for personal, educational, or business use.
This article will show you how to make a table in Word using a template. Then edit and format it to change its appearance.
(Note: The screenshots and instructions that follow are made using Microsoft Word for Mac version 16.4. If you’re using a different version of Word, then the interface and steps may be different.)
How to Make & Edit MS Word Tables (Video)
In this video, you’ll learn how to quickly make tables in Mircosoft Word. Find out how to start with a premium template. Quickly customize it to make an attractive, professional MS Word table you can use and reuse.
To learn even more about MS Word tables and about templates than can be used for tables, study the step-by-step tutorial below:
How to Make Basic Tables in Word
Let’s start by learning how to make a basic table in Microsoft Word:
1. Insert a Table
You can create a basic Microsoft Word table in one of two ways:
Method 1. The Insert Tab
Click on the Insert tab, then click the Table button on the ribbon.
The Insert Table panel appears. Drag the cursor over the squares to specify the number of columns and rows you want to create. Click to apply.
Method 2. The Insert Menu
Go to Insert > Table….
The Insert Table panel opens. Specify the number of columns and rows you need. (You can always add or remove columns and rows later.)
Also select the Autofit Behavior you want the table to have. You’ve got several options:
- Initial column width. The default setting is Auto, which divides the entire width of your page window across the number of columns in the table. Or, you can specify a different column width.
- AutoFit to contents. Resizes the column width based on the width of the content inside the column.
- AutoFit to window. Distributes the columns equally across the entire width of the page window.
- Set as default for new tables. Check this option if you want the settings to be applied globally to all new tables you create.
When you’re happy with the options you’ve selected, click OK.
2. Draw a Table
Or, you can draw a table in MS Word. This is a useful feature if you want to create an irregular or more complicated table with columns and/or rows of varying widths.
To draw a table, click Insert > Table > Draw Table.
With your mouse or trackpad, click and drag the cursor to start drawing your table. You can begin by drawing the outermost boundary of the table first.
Then, click and drag the cursor to create columns and rows inside the table. When you’re done, click anywhere outside the table.
Here’s an example of an “irregular” table you can draw using this feature.
If you make a mistake, click Layout > Eraser to erase a line from the table.
Click and drag the eraser along the line you wish to erase. The line that’ll be erased appears as a thick, red line. Release the mouse or trackpad to erase.
Click outside the table when you’re done.
3. Convert Text to Tables and Vice Versa
Another way to create a table is by converting text into a table. This means you can take non-tabular data from a CSV or plain TXT file and convert them into a table.
First, copy and paste the non-tabular data into your Word document.
With the text selected, go to Insert > Table > Convert Text to Table….
The Convert Text to Table panel opens. Specify the settings you wish to use. Click OK.
The text is then converted into a table.
You can also do the opposite, which is to convert a table into text.
Select the cells or entire table you want to convert. Next, click on the Layout tab then click the Convert Table to Text icon.
The Convert Table to Text panel opens. This is where you’ll decide how you want to separate text that’s currently in different columns. When you’ve made a selection, click OK.
For this example, I chose to separate text with commas. This is what the converted table looks like.
4. Advanced: How to Insert a Table from Excel
If you’ve already created a table in Excel, you can embed it into your Word document.
Open the Excel file. Click and drag the mouse to select the table.
Go back to your Word document. Go to Edit > Paste Special ….
In the Paste Special panel, select Microsoft Excel Binary Worksheet Object, then click OK.
This embeds the Excel table into Word. It’s still an Excel table, which means you can’t edit or format the table in MS Word. You’ve got to do so in Excel.
Double-click anywhere in the table to launch the source file in Excel. When you make any changes to the table in Excel, the table embedded in your Word project automatically updates to reflect those changes.
Now you know how to make a table in MS Word using various options.
How to Edit Tables
At any time after creating your table, you can edit and customize it to look the way you want it to. Here are some steps for editing tables in Microsoft Word:
1. Add a Column or Row
To add a row or column, click inside a table cell. Right-click on the mouse, then click Insert.
Select one of the following:
- Columns to the Left. Adds a column to the left of the current column
- Columns to the Right. Adds a column to the right of the current column
- Rows Above. Adds a row above the current row
- Rows Below. Adds a row below the current row
- Cells … Inserts a cell and shifts the rest of the cells either to the right or down from where the cursor is
- Table … Inserts a table inside the current cell
Or, with the cursor in one of the cells, you can click on the Layout tab.
Then choose of the following buttons on the ribbon:
- Insert Above. Inserts a row above the current cell
- Insert Below. Inserts a row below the current cell
- Insert Columns to the Left. Inserts a column to the left of the current cell
- Insert Columns to the Right. Inserts a column to the right of the current cell
Finally, you can add a new row when you’ve reached the last cell in the last row of your table. Simply press tab and a new row appears.
2. Delete a Column or Row
To delete a cell, column, row, or table, click on the Layout tab > Delete.
Select one of the options that appear:
- Delete Cells …
- Delete Columns
- Delete Rows
- Delete Table
You can use the same steps to edit a table you’ve drawn. Or, you can use the Layout tab to add or delete rows and columns.
Merge Cells
Sometimes you may want to merge cells to present information more clearly. To merge cells, click and drag the cursor to select the cells you wish to merge.
On the Layout tab, click on the Merge Cells button.
Or, after selecting the cells to be merged, right-click on your mouse, then click Merge Cells.
Now the cells have been merged into one.
Split Cells
After merging cells, you can always split them again into separate cells.
Place the cursor in the merged cell, then click Layout > Split Cells.
Or, right-click on your mouse, then click Split Cells….
Either way, the Split Cells panel pops up. Specify the number of columns and rows you want to split the cell into. Click OK.
Split Table
You may decide that it makes more sense to split up a table into two separate tables. Microsoft Word lets you do that easily, too.
In this example, I want to split the table right above the Accessories cell. And so, I’ll place the cursor in that cell. Next, click on the Layout tab, then click the Split Table button.
Now, we’ve got two separate tables.
Table Formatting
When you first create a table, it looks plain and boring. But Microsoft Word has many features so you can format tables to look exactly the way you want them. Here are some common ways to format tables:
1. Table Styles
The easiest way to format a table is by using one of the pre-formatted table styles. Put the cursor in any cell in the table. Click on the Table Design tab. Next, click on the arrow to expand the Table Styles group.
Click on a style you want to use and it’s applied immediately.
You can change any style you’ve selected. Again, click on Table Design, expand the Table Style group, then click Modify Style.
The Modify Style panel opens. Make the selections you want, then click OK.
2. Use Your Own Formatting
The Table Design tab gives you control over the appearance of every aspect of your table. Click on the Table Design tab and any of the appropriate buttons on the ribbon.
Resize a Table
You can also resize your table. Click on any cell to select the table, then click and drag one of the corners to resize it.
Or, you can use the Layout tab to resize individual cells, specific rows or columns, or the entire table. Select the columns or rows you wish to resize. Specify the height and/or width you wish to apply.
You can also adjust column width by hand by using the Table Ruler. Click inside a column you want to change. Then, drag the sliders in the Table Ruler to set to desired width.
Text Wrapping
If you want text to flow around the table, you can do so by changing its text wrapping.
Click in any cell to select the table. Click Table > Table Properties….
In the Table Properties panel and under Text Wrapping, click Around > OK.
Now the text flows around the table.
Take note that the Table Properties panel allows you to format other qualities of the table, including:
- Size
- Alignment
- Positioning
- Borders and Shading
On the other tabs, you can change:
- Column, Row, and Cell Size
- Allow row to break across pages
- Repeat as header row at the top of each page
- Cell Vertical Alignment
- Alt Text (Title and Description) — more information about the table, to help people with vision or cognitive impairment who may not see the table
Find Great Styles for Microsoft Word
You don’t have to start from scratch to create an impressive and effective Word document — even if you don’t have design skills. You can find great styles by using a template for Word.
One great source for great Microsoft Word templates and professional graphics is Envato Elements. For one low monthly subscription, you get unlimited downloads of templates, graphics, fonts, and other creative tools you need for your project. It’s a terrific option if you create plenty of materials.
For single projects, GraphicRiver is an outstanding source for templates for Word. This marketplace gives you access to thousands of creative elements on a pay-per-use basis.
Learn More
Microsoft Word has many robust features to help you realize the vision you’ve got for your document. But with power comes complexity. That’s why it’s a good idea to learn how to use Microsoft Word.
These articles will help you get started:
Visualize Your Data with Microsoft Word Tables
Make your information clearer and easier to understand by learning how to make a table in Microsoft Word. Tables organize data into rows and columns, which makes them easier to grasp at a glance. Follow the steps in this article to create, format, and customize tables in Word.
You can also use a premium Word template to get a premium design created by designers. Get Word templates from Envato Elements, if you want unlimited downloads of templates, graphics, and other creative tools you need — all for one flat monthly fee.
Or, get premium templates for Word from GraphicRiver if you prefer to pay for each use of an item. Both sources give you access to thousands of design elements created by professionals, so you can save time, energy, and effort while creating an outstanding Word document.
Did you find this post useful?
Marketing & Communications Professional and Lifelong Learner/Canada
Lexi Rodrigo is a marketing and communications professional, copywriter, and course creator who helps remarkable brands and people get seen, heard, and known. Writing for the web since 2008, she has over 100+ blog posts published on Envato Tuts, Acadium, Mirasee, Vero, Copyblogger, FreelanceFolder, Business2Community, and others.
Lexi has supported multimillion-dollar companies and nonprofits in various marketing and communication roles. She has driven results like tripling the organic search traffic of a blog in three months and generating over $65 million in revenues, donations, and sponsorships.
She has a Bachelor of Arts degree in communications. She is also the co-author of «Blog Post Ideas: 21 Proven Ways to Create Compelling Content and Kiss Writer’s Block Goodbye.» When she’s not reading or writing, Lexi bakes bread, grows food, and takes long walks.
Tables in Word are useful in so many situations. In this post you’ll discover how to create tables, then manipulate and design them in the quickest and easiest way to provide that visual punch.
Clickable Table of Contents
Enhance your Word tables with these advanced features
1. What are tables in Word good for?
Tables are useful for 2 distinct reasons.
- To show an actual table of data, or
- To organise and postion text, images and other elements on the page.
Many years ago, typewriters ruled the world. And a feature of a good typewriter was the tab stop, which was a device that essentially let you control indentation.
Over the years many people have continued to use tabs to indent text, because of its convenience, but they are hard work to set up properly.
Tables provide a much easier way to organise content on a page.
1. Select the Insert tab.
2. Click the Tables icon in the Tables group.
3. Move your mouse pointer into the table grid until the required number of rows and columns are highlighted orange, then left-click.
An empty table is inserted into the document.
Two new tabs, Design and Layout are also added to the ribbon area, under the banner of Table Tools.
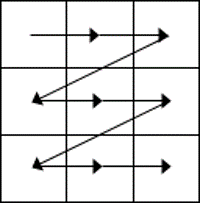
3. MOVING AROUND A Word TABLE
- While the table is empty, you can use the cursor keys to move around the cells. However, when the cells contain information, using the cursor keys will move through the cell content first before moving to the next cell
- You can left-click in any cell to position the cursor.
- Press Tab to move to the next cell. The cursor will move across and then down the table.
- Press Shift + Tab to move to the previous cell.
NB. Using Tab is better than using the cursors as it will move to the next/previous cell regardless of whether there is information in the cells.
NB2. If you press Tab while you are in the last cell, a new row will be added to the bottom of your table
4. SELECTING A CELL, ROW, COLUMN OR THE ENTIRE TABLE
To select a cell:
1. Position the mouse pointer inside the cell on the bottom-left corner of the cell.
The pointer will change shape to a solid black arrow that points up and right.
2. Left-click.
To select a row of a table:
1. Position the mouse pointer in the left margin in line with the row you want to select.
The mouse pointer will change to a white arrow that points up and right.
2. Left-click.
To select a column
1. Position the mouse pointer so that it rests on the top border of the table, above the column you want to select.
The mouse pointer will change to a solid black arrow pointing down.
2. Left-click.
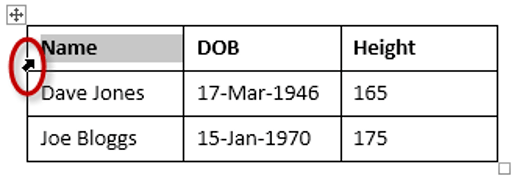
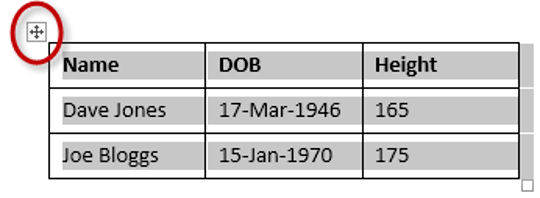
To select the entire table:
1. Position your mouse pointer over the 4-headed arrow icon situated at the top-left of the table.
2. Left-click.
5. INSERTING AN EXTRA ROW OR COLUMN
To insert an extra row:
1. Position the cursor in a cell.
2. Select the Layout tab, under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click Insert Above or Insert Below in the Rows and Columns group
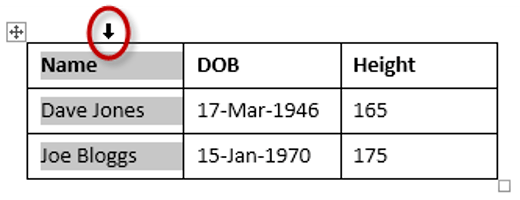
Here is a quick way to insert new rows:
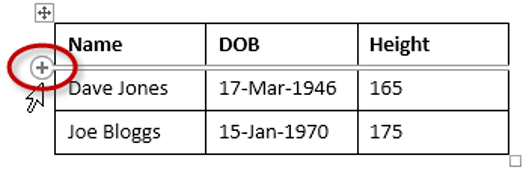
1. Position the cursor to the left of the table, but in close proximity.
2. A plus symbol will appear above or below the mouse pointer indicating where the new row will be added.
3. Nudge the mouse pointer up or down to move the plus sign above or below.
4. Left-click to insert the new row,
To insert an extra column:
1. Position the cursor in a cell.
2. Select the Layout tab, under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click Insert Left or Insert Right in the Rows and Columns group
Here is a quick way to insert a new column:
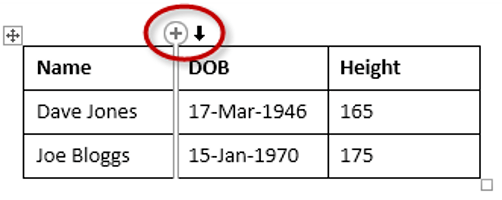
1. Position the cursor above a column, but in close proximity to the table.
2. A plus symbol will appear to the left or right of the mouse pointer indicating where the new column will be added.
3. Nudge the mouse pointer left or right to move the plus sign to the left or the right of the column.
4. Left-click to insert the new column,
6. DELETING A ROW OR COLUMN
To delete the current row or column:
1. Position the cursor in any cell of the row you want to delete.
2. Select the Layout tab, under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click the Delete icon in the Rows and Columns group.
4. Choose Delete Row or Delete Column from the drop-down menu.
7. Quickly fORMATTING tables in Word
Word provides you with a number of pre-set table designs. This means that it formats the headings and the data, applies a variety of borders and colours the cells in a way that makes it look like a professionally produced table. As a beginner this simple technique will give you a good-looking table.
1. Position the cursor in any cell in the table.
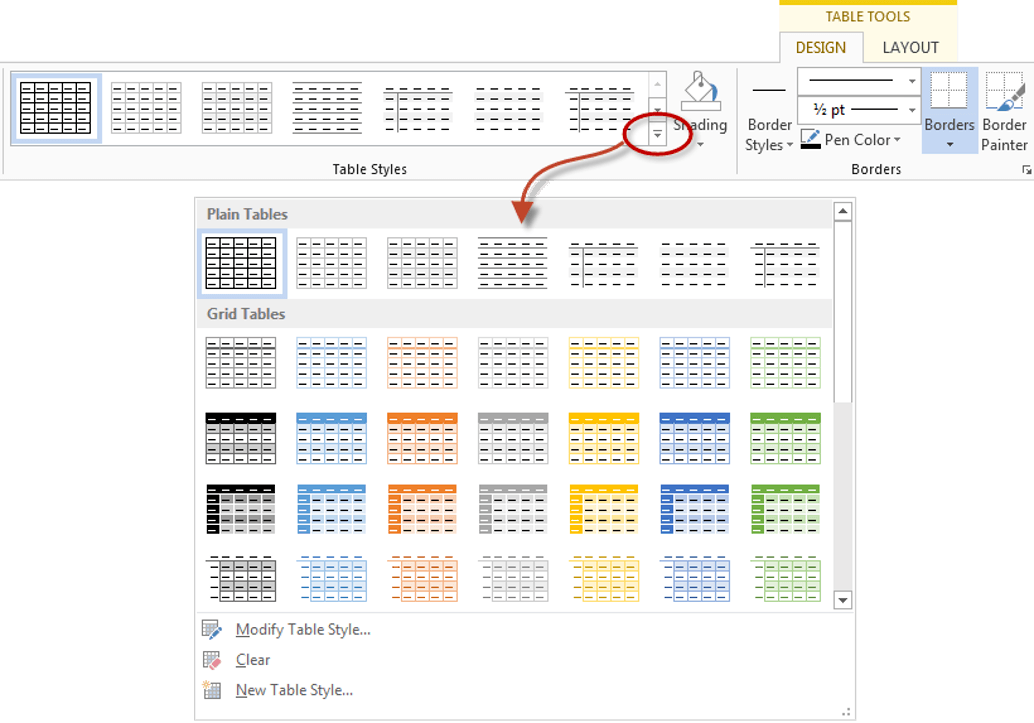
2. Select the Design tab under the Table Tools banner.
The Table Styles group lists a number of table designs. To get the full list, click the More button beneath the table styles scroll bar
The default table style is Table Grid in the Plain Tables category which adds simple gridlines but no shading to your table.
Live Preview allows you to hover over a design and see it applied to your table. If you like what you see, click to select the table design.
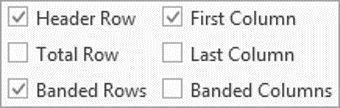
In the Table Style Options group of the Design tab, tick the components that you have in your table. For example, if your table has column headings, tick Header Row. In doing this, the various parts of your table are formatted accordingly
Header Row
This will emphasise the header row by making the text bold or applying a different cell colour (depending on the table style selected.
Total Row
This will emphasise the bottom table row by making the text bold or applying a different cell colour (depending on the table style selected.
First Column
This will emphasise the first column (for labels etc.) by making the text bold or applying a different cell colour (depending on the table style selected.
Last Column
This will emphasise the last column (for row totals etc.) by making the text bold or applying a different cell colour (depending on the table style selected.
Banded Rows
This will make odd rows one colour and even rows a different colour. This helps readability.
Banded Columns
This will make odd columns one colour and even columns a different colour. This helps readability.
8. SETTING THE BORDERS AND SHADING
The Table Styles Gallery allows you to completely format a table with one click. Whereas you used to need some nous, anybody can now create a professional looking design.
However, you will often still need to apply your own border and shading, and manually change a table design. With a little effort can add a lot of flavour to your page and dramatically enhance the overall appearance of the document.
To set the borders for tables in Word:
1. Select the portion of the table that you wish to set the borders for. This may be the entire table, a row or rows, a column or columns or a selection of cells.
2. Select the Design tab under the Table Tools banner.
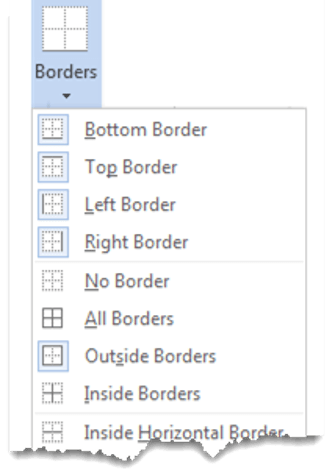
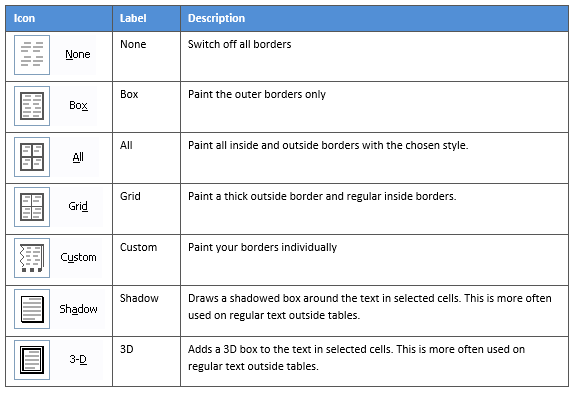
3. Select the Borders icon. A drop-down list appears. This list shows every combination of border that can be turned on or off. The icons with a shaded background are currently switched on. The rest are switched off.
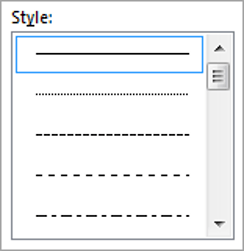
4. Click any icon to switch the border on or off. The border style that is applied is the default style (½ pt solid black line ) or the last style that was used.
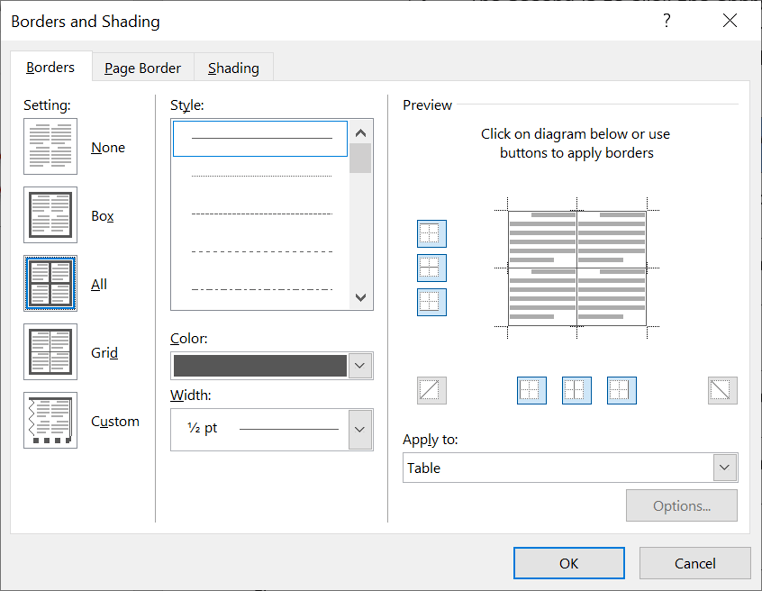
5. To apply customised borders, with different colours, styles and widths, click the Borders & Shading option at the bottom of the list to display the Borders and Shading dialog box.
Your selection will always have an outer border, and if you selected more than one cell, you will have some inside borders as well. The easiest way to use the dialog box is to start on the bottom-middle and work your way up and right.
1. Select the colour and width (thickness) that you would like for your border.
2. Choose a style (e.g. dotted, dashed, double, solid etc.)
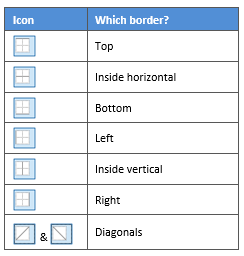
3. Paint your borders. There are two ways to do this.
- The first way is to click directly on a border in the Preview itself.
- The second way is to click the appropriate icon around the edge of the Preview section that represents each border. Depending on which cells you selected in your table, some of these icons may not be available.
On the left-hand side of the dialog box, there are some pre-defined border combinations which you can use to save yourself some time. Depending on your selection of cells, the pre-defined options may differ. Here’s a run-down:
To shade the cells of tables in Word:
1. Select the portion of the table that you wish to shade. This may be the entire table, a row or rows, a column or columns or a selection of cells.
2. Select the Design tab under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click the Shading icon.
The colours that you see displayed match the current them of the document. Themes were discussed earlier in the course.
4. Click a colour in the palette.
While you can pick any colour, it is recommended to stick with the light colour shades, otherwise your tables will appear very loud and ugly, like they’re shouting in your face. Subtle is the order of the day. The exception to this is column headings or other cells that you wish to differentiate. Under these circumstances, you can use a dark colour, but use a light font with it.
If you cannot find the exact colour you need,
- Click the More Colours link underneath the palette. This displays a larger, more accurate colour palette.
- And if that’s not enough, click the Custom tab and you’ll get a really fine selection of colours (you can even enter your own RGB settings if you know them)
9. REPEATING table HEADINGS ON EVERY PAGE WHEN PRINTING
When you have large tables that occupy two or more pages, many people insert manual page breaks, then copy and paste their table header rows at the top of each page.
When rows are added or removed from tables in Word, the table headers end up half way down the page.
There is a simple tool that will eliminate this problem
1. Ensure that the table is a single table, with no manual page breaks in the middle, and one header at the top. The table header may occupy more than one row, it doesn’t affect the way this feature works.
2. Position the cursor somewhere in the top row of the table.
3. Select the Layout tab under the Table Tools banner.
4. Click the Repeat Header Rows icon ion the Data group.
Now, it doesn’t matter how many rows tables in Word contain, if the table ever spills across into another page, the header row (which normally displays the column headings) will always appear at the top of the table.
10. All the key points again
- Tables in Word serve 2 distinct purpose: to display a table of data and to organise and position items on the page
- To create table, select 2 tabs — Design and Layout under the Table Tools banner.
- There are 2 tabs — Design and Layout under the Table Tools banner.
- You can press the TAB key to move direct to the next cell and SHIFT and TAB together to move backwards through a table.
- The four elements of a table are cells, rows, columns and the whole table. Each can be selected.
- Rows can be inserted by selecting the Layout tab under Table Tools, then clicking the Insert Above or Insert Below icons. Alternatively, hover to the left of a row and click the plus symbol that appears above or below the mouse pointer.
- Columns can be inserted by selecting the Layout tab under Table Tools, then clicking the Insert
Left or Insert Right icons. Alternatively, hover above a table column and click the plus symbol that appears to the left or right of the mouse pointer. - Columns and rows and be removed from the table, by positioning the cursor in the row or column to be removed, then clicking the Delete icon on the Layout tab of Table Tools and choosing Delete
Row or Delete Column. - Tables can be formatted using the Table Style gallery or by manually setting the shading and borders manually. Both sets of tools are found on the Design ribbon of the Table Tools.
- When using the Microsoft Table Styles, you can control the behaviour of the formatting by setting the Table Style options – 6 tick boxes that define the structure of your table.
- For long tables that spill across onto subsequent pages, the top row, which normally contains the column headings can be set to repeat automatically. So there is no excuse for cutting and pasting headings midway through your table or taping pages together to make sense of the table!
I hope you found plenty of value in this post. I’d love to hear your biggest takeaway in the comments below together with any questions you may have.
Have a fantastic day.
About the author
Jason Morrell
Jason loves to simplify the hard stuff, cut the fluff and share what actually works. Things that make a difference. Things that slash hours from your daily work tasks. He runs a software training business in Queensland, Australia, lives on the Gold Coast with his wife and 4 kids and often talks about himself in the third person!
SHARE
Microsoft Word is probably the most popular software there is for word processing. The program makes it possible for users to write texts very quickly and in a way that is (in most situations) straightforward. However, with the software you can also integrate additional elements into your document, including images and tables. If you would like to quickly create a well-arranged table, no need for Excel: Word itself has a feature for this.
Contents
- Creating a Table: Easy to Do in Word
- Customizing Tables
- Insert Excel Table in Word
Creating a Table: Easy to Do in Word
Word has a special feature with which you can quite easily create a table. To make use of it, click in your open Word document on the “Insert” tab and then select the “Table” item. Here Word already offers you a very easy-to-use tool: just click with the mouse pointer to select how many rows and columns your table should have. With one click, the program then inserts the selected matrix into the document.
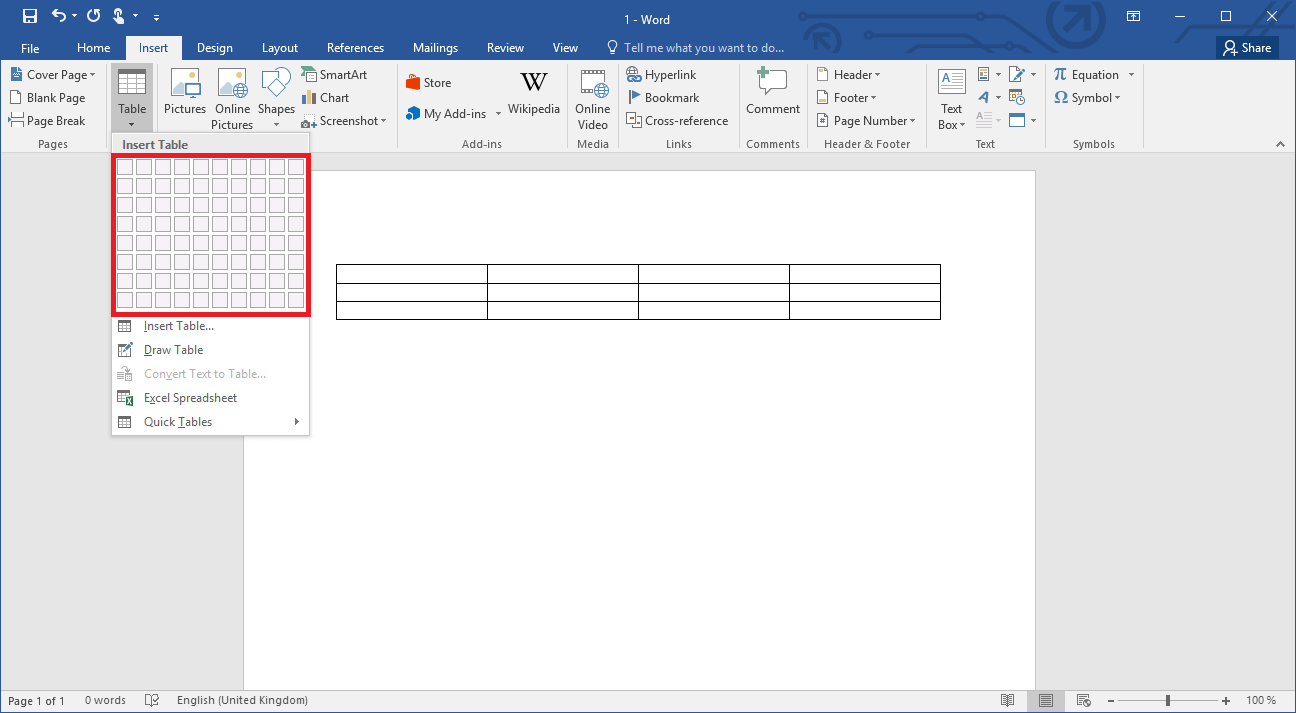
However, there are other options for creating tables in Word. Directly beneath the selection chart you’ll find the menu item “Insert Table…”. If you click on it, a menu will open with several options for customizing the table according to your preferences before it is created. For this as well, you must first determine the number of columns and rows but can then also specify the column width. You can determine if the column should be set to a specific width or you can leave the adjustment to Word. The program then configures the column width according to the content or window size.
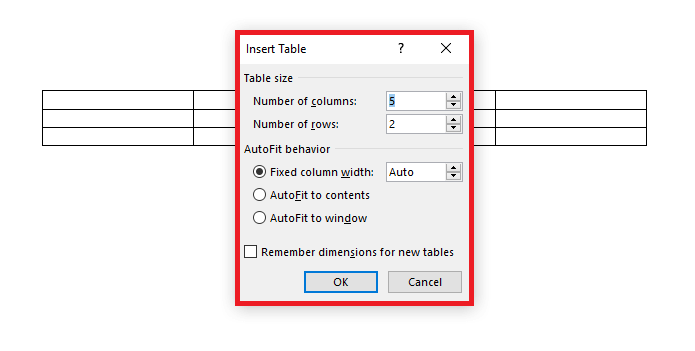
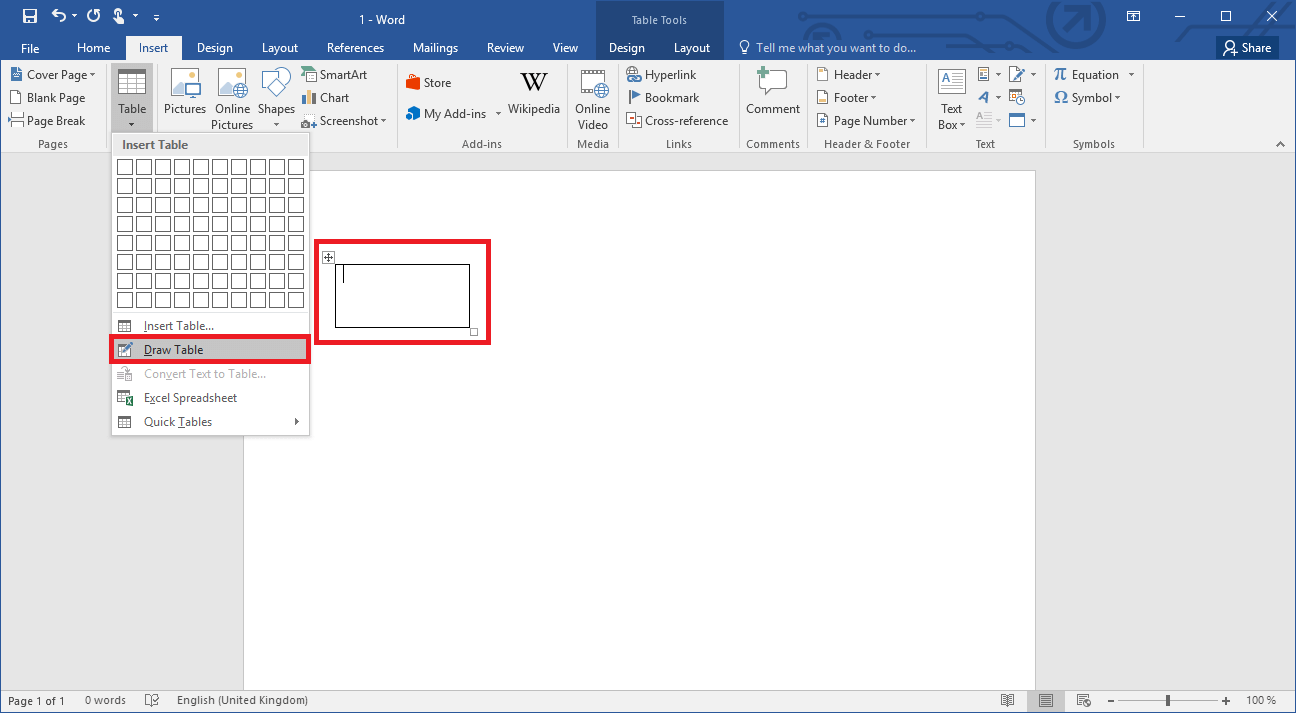
Another feature allows you to draw tables. This way, you can create a cell in the size of your choice and then insert additional rows and columns, structuring your table step-by-step.
If you already have the table content in your document but would just like to format it as a table, there is another feature that will let you do this. First, however, your individual cell entries must be pre-formatted. Arrange the words or numbers in different cells and separate the entries from each other using tabulators. In this way, Word can determine how the content must be distributed among the rows and columns. Therefore, select the section and click beneath “Table” on the menu item “Convert Text to Table…”. In the window that opens, check if Word correctly understood the distribution, then create the table.
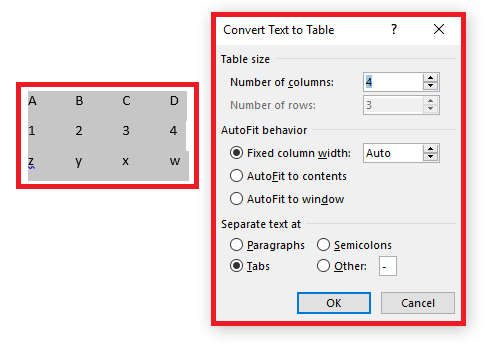
Note
You can also use other symbols in order to separate the entries from each other. In the menu of the appropriate feature, you can specify these so that Word correctly apportions the columns and rows.
Customizing Tables
If you have created your table in Word, it is usually not very visually appealing. However, you do have the option of customizing the layout. After you’ve created the table, the Table Tools open with two new tabs in the menu ribbon. Among other options, you can choose from different templates under “Design,” and in this way give your table a more professional design. If you find that the selection is insufficient, you have additional options for customization, such as adjusting the lines or coloring specific sections. Above the “Layout” tab you can also adjust the distribution of cells, rows and columns.
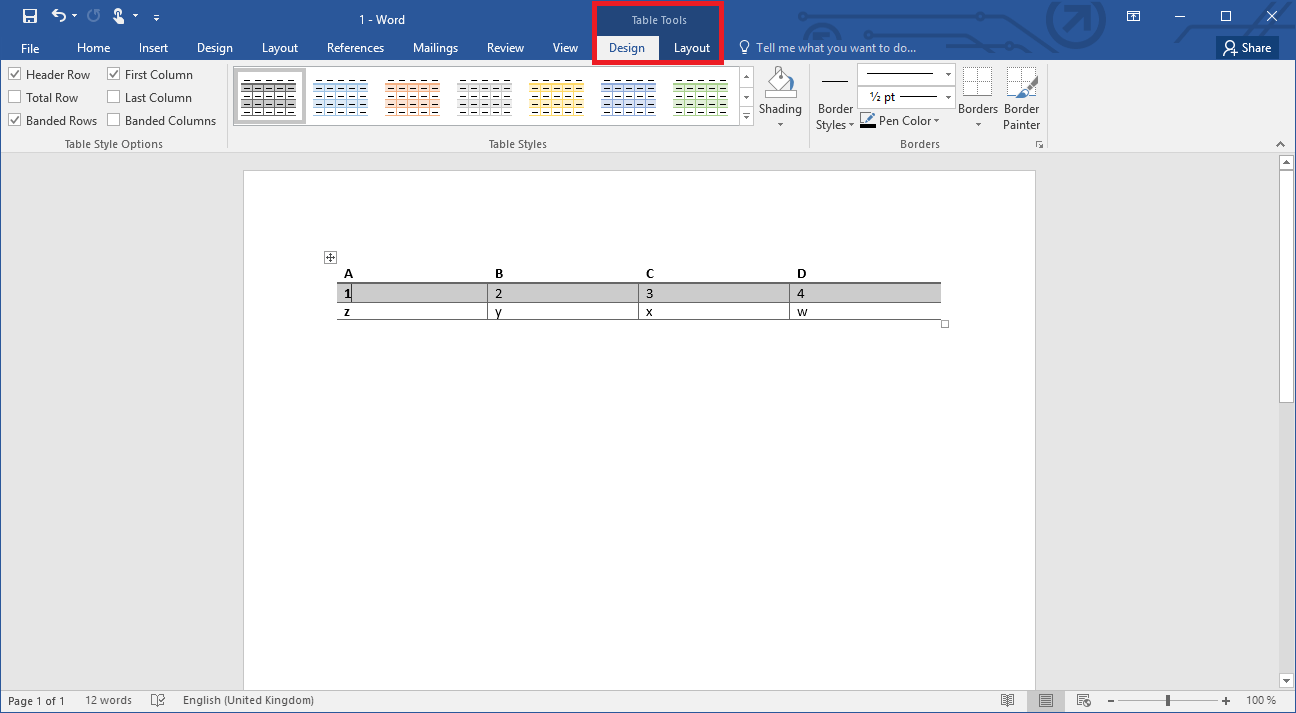
In addition, you also have the actual Word formatting options available. In this way you can make the content bold or italic, for example, or change the font size or text color.
Tip
If you would like to choose an appealing design when creating your table, you can try out the “Quick Table” option when inserting it. Here, Word provides you with tables that have already been formatted and that can be helpful in various situations.
Insert Excel Table in Word
For simple comparisons or lists, Word tables are enough. They can be created quickly and are easy to customize. However, if you have more complex requirements, and would like to, for example, have recourse to mathematical formulas and abundant data analyses, Excel would be more to your benefit. The Office suite’s table calculation software is specifically designed for such tasks. Its advantage is that it makes it possible to incorporate an Excel table into a Word document.
For this Microsoft provides you with two different versions: Either you integrate an existing Excel table into the document, or you create a new Excel table directly in Word. For the first approach, you must first create a table in the calculation program. Then you can select this table, copy it and insert it into Word. In word processing, you then format the table so that it is consistent with the rest of the document.
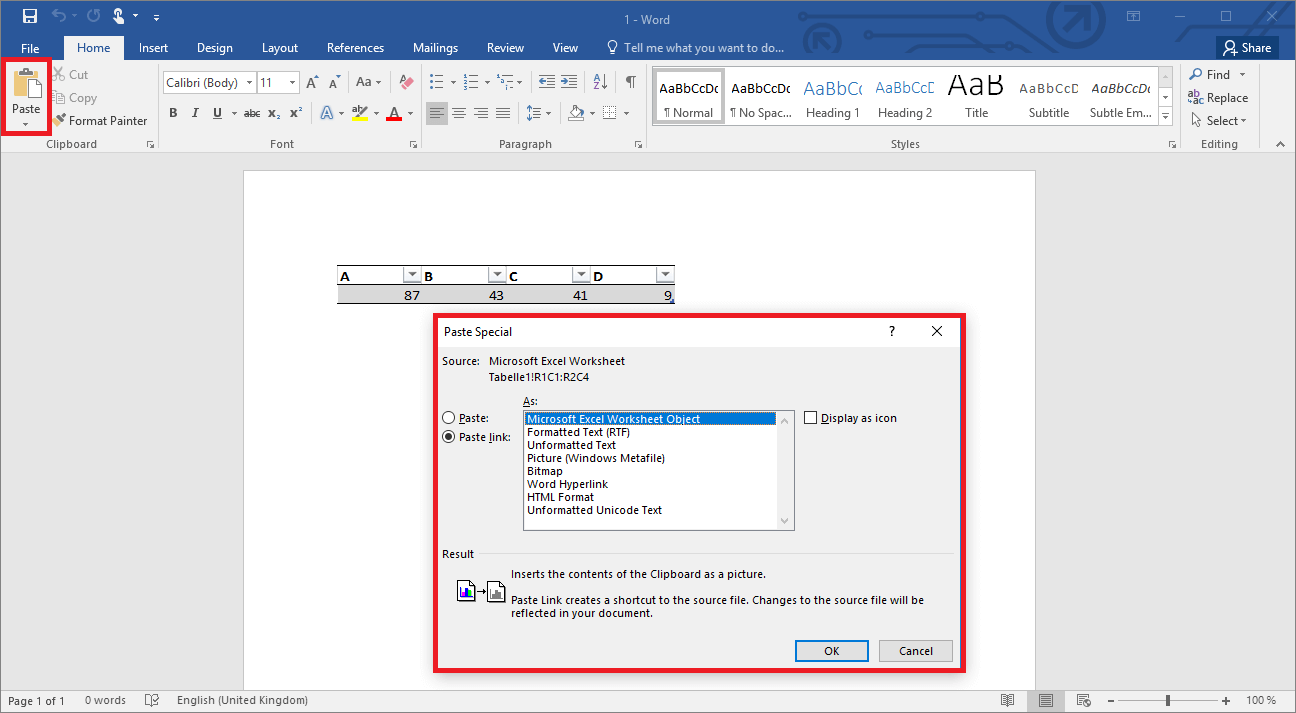
There is however another option that lets you incorporate an existing Excel table. If you link both files to each other, the table in the Word document inherits the changes that you make in Excel. For this as well, you select and copy the table in Excel. However, in the Word document you don’t simply paste the data as you normally would (for example, with the ctrl + V key combination), but instead use a special feature. In the “Start” tab you’ll see the “Insert” item all the way to the left. If you click here on the “Paste content…” option, you’ll be able to integrate the table as a link. Choose “Microsoft Excel Worksheet Object” from the list and confirm your decision.
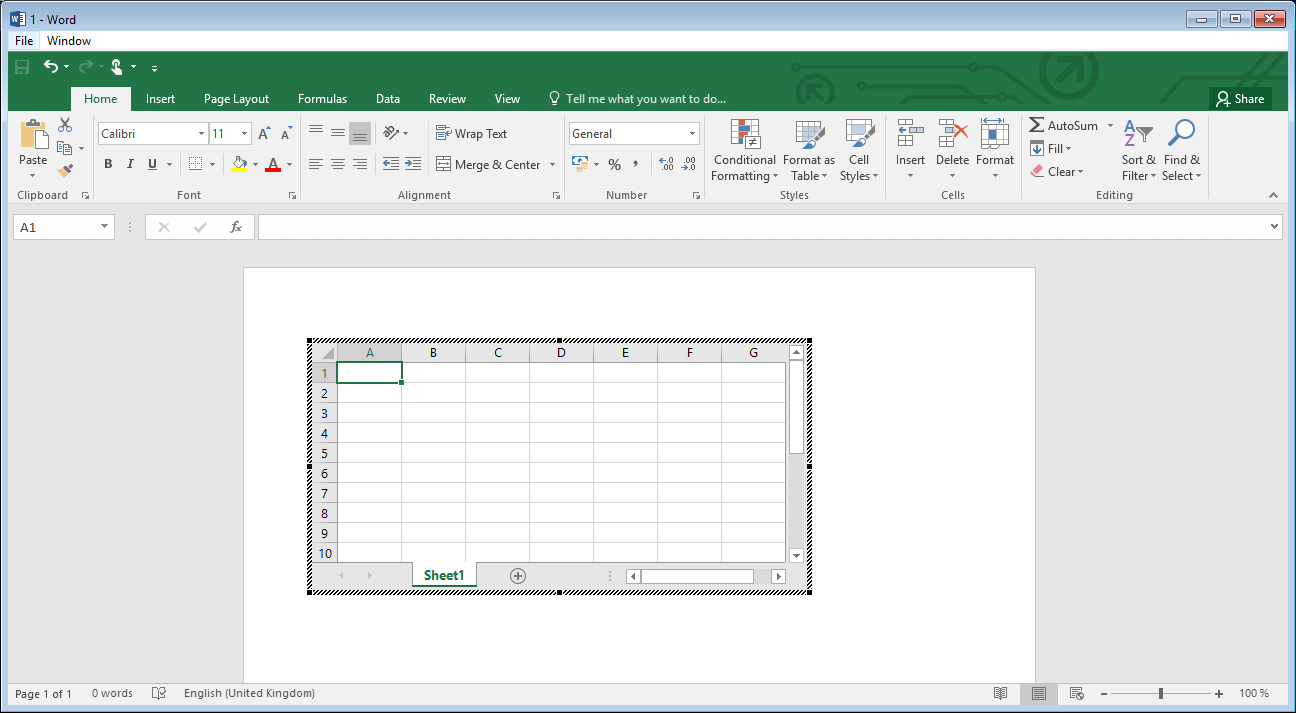
However, Word also gives you the option of creating an Excel table directly in the document—with all the features that one is also familiar with from table calculation. For this you’ll find the “Excel Calculation Table” feature in the table menu. Word now generates an Excel-style table and completely transposes its features: Word’s characteristic blue ribbon becomes the green Excel menu. You can make use of the Excel features if you have activated the table.
Note
Would you also like to take advantage of the Office suite’s wide range of features? With Microsoft 365, IONOS provides you with the complete Microsoft package in the cloud.

Word documents: how to save as a PDF file
If you want to send a Word document or prepare it for printing, it’s recommended you know how to save it as a PDF file. This way, you can be sure that the formatting of your document won’t change and that others will not be able to edit it without permission. For simple conversion tasks, the save function in Word is often sufficient. However, there are some dedicated tools which offer a wider…
Word documents: how to save as a PDF file

How to create a table of contents in Word
Microsoft Word makes it easy to create smart text documents with its diverse template styles. This includes pre-formatted table of contents templates. With our illustrated, step-by-step guide, we’ll show you how to find the templates and how to customize the design.
How to create a table of contents in Word

How to insert a watermark in Word
Sometimes you need to clearly label your document with words like “Sample,” “Draft,” “Example” or “Confidential”. In Microsoft Word, you can use watermarks to do this. This practical design tool allows you to display barely visible but impressive text or graphics that sit behind the actual text. In this tutorial, we will teach you how to insert a watermark in Word.
How to insert a watermark in Word

Create a table of figures in Word
Whether for school, university or the office, introducing tables or figures into a text makes it easier for the reader to grasp data or concepts. But if you’ve added lots of tables, it may be a good idea to insert a table of figures at the end of your Word document. A table of figures is a great way to help anyone quickly view and retrieve important information. Here’s how to insert and format a…
Create a table of figures in Word

Inserting Excel into Word
Want to learn how to insert an Excel table into Word and aren’t sure how to proceed? We’ll explain how to insert an Excel file into Word. The easiest way is to use the copy and paste commands. But if you want to edit the data later, it’s better to link the Excel spreadsheet in Word. You can do this quickly and easily with our simple step-by-step guide.
Inserting Excel into Word



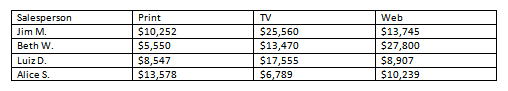
 Insert Rows Above.
Insert Rows Above.