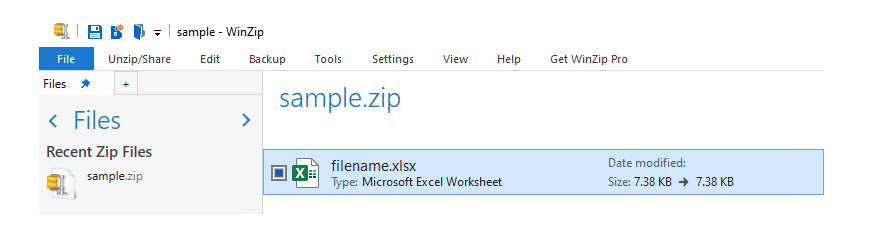
first of all, this post is the first piece of the solution, where you should specify startrow=:
Append existing excel sheet with new dataframe using python pandas
you might also consider header=False.
so it should look like:
df1.to_excel(writer, startrow = 2,index = False, Header = False)
if you want it to automatically get to the end of the sheet and append your df then use:
startrow = writer.sheets['Sheet1'].max_row
and if you want it to go over all of the sheets in the workbook:
for sheetname in writer.sheets:
df1.to_excel(writer,sheet_name=sheetname, startrow=writer.sheets[sheetname].max_row, index = False,header= False)
btw: for the writer.sheets you could use dictionary comprehension (I think it’s more clean, but that’s up to you, it produces the same output):
writer.sheets = {ws.title: ws for ws in book.worksheets}
so full code will be:
import pandas
from openpyxl import load_workbook
book = load_workbook('test.xlsx')
writer = pandas.ExcelWriter('test.xlsx', engine='openpyxl')
writer.book = book
writer.sheets = {ws.title: ws for ws in book.worksheets}
for sheetname in writer.sheets:
df1.to_excel(writer,sheet_name=sheetname, startrow=writer.sheets[sheetname].max_row, index = False,header= False)
writer.save()
Write Excel with Python Pandas. You can write any data (lists, strings, numbers etc) to Excel, by first converting it into a Pandas DataFrame and then writing the DataFrame to Excel.
To export a Pandas DataFrame as an Excel file (extension: .xlsx, .xls), use the to_excel() method.
Related course: Data Analysis with Python Pandas
installxlwt, openpyxl
to_excel() uses a library called xlwt and openpyxl internally.
- xlwt is used to write .xls files (formats up to Excel2003)
- openpyxl is used to write .xlsx (Excel2007 or later formats).
Both can be installed with pip. (pip3 depending on the environment)
1 |
$ pip install xlwt |
Write Excel
Write DataFrame to Excel file
Importing openpyxl is required if you want to append it to an existing Excel file described at the end.
A dataframe is defined below:
1 |
import pandas as pd |
You can specify a path as the first argument of the to_excel() method.
Note: that the data in the original file is deleted when overwriting.
The argument new_sheet_name is the name of the sheet. If omitted, it will be named Sheet1.
1 |
df.to_excel('pandas_to_excel.xlsx', sheet_name='new_sheet_name') |
Related course: Data Analysis with Python Pandas
If you do not need to write index (row name), columns (column name), the argument index, columns is False.
1 |
df.to_excel('pandas_to_excel_no_index_header.xlsx', index=False, header=False) |
Write multiple DataFrames to Excel files
The ExcelWriter object allows you to use multiple pandas. DataFrame objects can be exported to separate sheets.
As an example, pandas. Prepare another DataFrame object.
1 |
df2 = df[['a', 'c']] |
Then use the ExcelWriter() function like this:
1 |
with pd.ExcelWriter('pandas_to_excel.xlsx') as writer: |
You don’t need to call writer.save(), writer.close() within the blocks.
Append to an existing Excel file
You can append a DataFrame to an existing Excel file. The code below opens an existing file, then adds two sheets with the data of the dataframes.
Note: Because it is processed using openpyxl, only .xlsx files are included.
1 |
path = 'pandas_to_excel.xlsx' |
Related course: Data Analysis with Python Pandas
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
In this article, we will see how to export different DataFrames to different excel sheets using python.
Pandas provide a function called xlsxwriter for this purpose. ExcelWriter() is a class that allows you to write DataFrame objects into Microsoft Excel sheets. Text, numbers, strings, and formulas can all be written using ExcelWriter(). It can also be used on several worksheets.
Syntax:
pandas.ExcelWriter(path, date_format=None, mode=’w’)
Parameter:
- path: (str) Path to xls or xlsx or ods file.
- date_format: Format string for dates written into Excel files (e.g. ‘YYYY-MM-DD’). str, default None
- mode: {‘w’, ‘a’}, default ‘w’. File mode to use (write or append). Append does not work with fsspec URLs.
The to_excel() method is used to export the DataFrame to the excel file. To write a single object to the excel file, we have to specify the target file name. If we want to write to multiple sheets, we need to create an ExcelWriter object with target filename and also need to specify the sheet in the file in which we have to write. The multiple sheets can also be written by specifying the unique sheet_name. It is necessary to save the changes for all the data written to the file.
Syntax:
DataFrame.to_excel(excel_writer, sheet_name=’Sheet1′,index=True)
Parameter:
- excel_writer: path-like, file-like, or ExcelWriter object (new or existing)
- sheet_name: (str, default ‘Sheet1’). Name of the sheet which will contain DataFrame.
- index: (bool, default True). Write row names (index).
Create some sample data frames using pandas.DataFrame function. Now, create a writer variable and specify the path in which you wish to store the excel file and the file name, inside the pandas excelwriter function.
Example: Write Pandas dataframe to multiple excel sheets
Python3
import pandas as pd
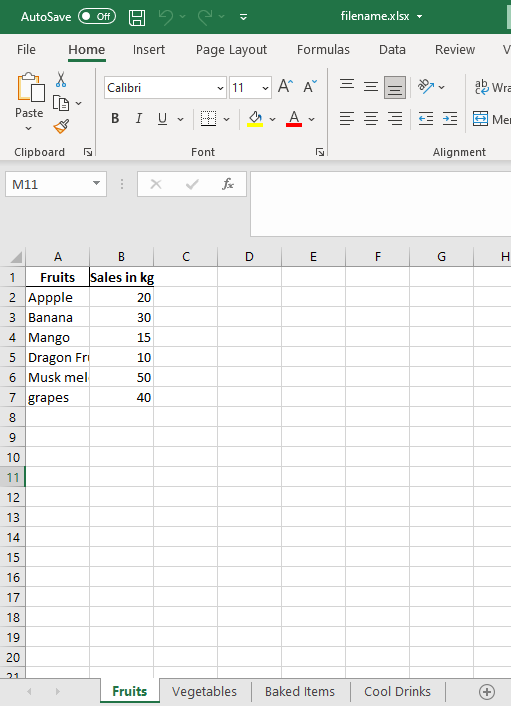
data_frame1 = pd.DataFrame({'Fruits': ['Appple', 'Banana', 'Mango',
'Dragon Fruit', 'Musk melon', 'grapes'],
'Sales in kg': [20, 30, 15, 10, 50, 40]})
data_frame2 = pd.DataFrame({'Vegetables': ['tomato', 'Onion', 'ladies finger',
'beans', 'bedroot', 'carrot'],
'Sales in kg': [200, 310, 115, 110, 55, 45]})
data_frame3 = pd.DataFrame({'Baked Items': ['Cakes', 'biscuits', 'muffins',
'Rusk', 'puffs', 'cupcakes'],
'Sales in kg': [120, 130, 159, 310, 150, 140]})
print(data_frame1)
print(data_frame2)
print(data_frame3)
with pd.ExcelWriter("path to filefilename.xlsx") as writer:
data_frame1.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="Fruits", index=False)
data_frame2.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="Vegetables", index=False)
data_frame3.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="Baked Items", index=False)
Output:
The output showing the excel file with different sheets got saved in the specified location.
Example 2: Another method to store the dataframe in an existing excel file using excelwriter is shown below,
Create dataframe(s) and Append them to the existing excel file shown above using mode= ‘a’ (meaning append) in the excelwriter function. Using mode ‘a’ will add the new sheet as the last sheet in the existing excel file.
Python3
import pandas as pd
data_frame1 = pd.DataFrame({'Fruits': ['Appple', 'Banana', 'Mango',
'Dragon Fruit', 'Musk melon', 'grapes'],
'Sales in kg': [20, 30, 15, 10, 50, 40]})
data_frame2 = pd.DataFrame({'Vegetables': ['tomato', 'Onion', 'ladies finger',
'beans', 'bedroot', 'carrot'],
'Sales in kg': [200, 310, 115, 110, 55, 45]})
data_frame3 = pd.DataFrame({'Baked Items': ['Cakes', 'biscuits', 'muffins',
'Rusk', 'puffs', 'cupcakes'],
'Sales in kg': [120, 130, 159, 310, 150, 140]})
data_frame4 = pd.DataFrame({'Cool drinks': ['Pepsi', 'Coca-cola', 'Fanta',
'Miranda', '7up', 'Sprite'],
'Sales in count': [1209, 1230, 1359, 3310, 2150, 1402]})
with pd.ExcelWriter("path_to_file.xlsx", mode="a", engine="openpyxl") as writer:
data_frame4.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="Cool drinks")
Output:
Writing Large Pandas DataFrame to excel file in a zipped format.
If the output dataframe is large, you can also store the excel file as a zipped file. Let’s save the dataframe which we created for this example. as excel and store it as a zip file. The ZIP file format is a common archive and compression standard.
Syntax:
ZipFile(file, mode=’r’)
Parameter:
- file: the file can be a path to a file (a string), a file-like object, or a path-like object.
- mode: The mode parameter should be ‘r’ to read an existing file, ‘w’ to truncate and write a new file, ‘a’ to append to an existing file, or ‘x’ to exclusively create and write a new file.
Import the zipfile package and create sample dataframes. Now, specify the path in which the zip file has to be stored, This creates a zip file in the specified path. Create a file name in which the excel file has to be stored. Use to_excel() function and specify the sheet name and index to store the dataframe in multiple sheets
Example: Write large dataframes in ZIP format
Python3
import zipfile
import pandas as pd
data_frame1 = pd.DataFrame({'Fruits': ['Appple', 'Banana', 'Mango',
'Dragon Fruit', 'Musk melon', 'grapes'],
'Sales in kg': [20, 30, 15, 10, 50, 40]})
data_frame2 = pd.DataFrame({'Vegetables': ['tomato', 'Onion', 'ladies finger',
'beans', 'bedroot', 'carrot'],
'Sales in kg': [200, 310, 115, 110, 55, 45]})
data_frame3 = pd.DataFrame({'Baked Items': ['Cakes', 'biscuits', 'muffins',
'Rusk', 'puffs', 'cupcakes'],
'Sales in kg': [120, 130, 159, 310, 150, 140]})
data_frame4 = pd.DataFrame({'Cool drinks': ['Pepsi', 'Coca-cola', 'Fanta',
'Miranda', '7up', 'Sprite'],
'Sales in count': [1209, 1230, 1359, 3310, 2150, 1402]})
with zipfile.ZipFile("path_to_file.zip", "w") as zf:
with zf.open("filename.xlsx", "w") as buffer:
with pd.ExcelWriter(buffer) as writer:
data_frame1.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="Fruits", index=False)
data_frame2.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="Vegetables", index=False)
data_frame3.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="Baked Items", index=False)
data_frame4.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="Cool Drinks", index=False)
Output:
Sample output of zipped excel file
Like Article
Save Article
Use pandas to_excel() function to write a DataFrame to an excel sheet with extension .xlsx. By default it writes a single DataFrame to an excel file, you can also write multiple sheets by using an ExcelWriter object with a target file name, and sheet name to write to.
Note that creating an ExcelWriter object with a file name that already exists will result in the contents of the existing file being erased.
Related: pandas read Excel Sheet
pandas to Excel key Points
- By default, it uses xlsxwriter if it is installed otherwise it uses openpyxl
- Supports saving multiple DataFrames to single sheet.
- Save multiple sheets, append existing sheet or file.
- Use ExcelWriter()
Let’s create a pandas DataFrame from list and explore usingto_excel() function by using multiple parameters.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Create multiple lists
technologies = ['Spark','Pandas','Java','Python', 'PHP']
fee = [25000,20000,15000,15000,18000]
duration = ['5o Days','35 Days',np.nan,'30 Days', '30 Days']
discount = [2000,1000,800,500,800]
columns=['Courses','Fee','Duration','Discount']
# Create DataFrame from multiple lists
df = pd.DataFrame(list(zip(technologies,fee,duration,discount)), columns=columns)
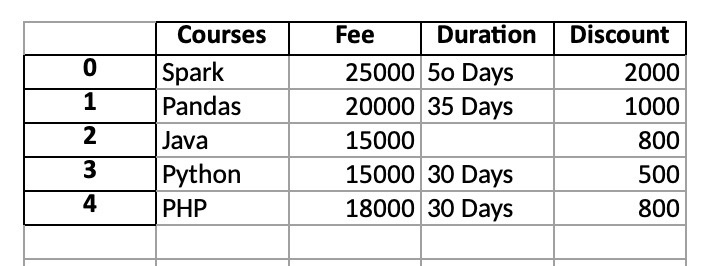
print(df)
# Outputs
# Courses Fee Duration Discount
#0 Spark 25000 5o Days 2000
#1 Pandas 20000 35 Days 1000
#2 Java 15000 NaN 800
#3 Python 15000 30 Days 500
#4 PHP 18000 30 Days 800
1. pandas DataFrame to Excel
Use to_excel() function to write or export pandas DataFrame to excel sheet with extension xslx. Using this you can write excel files to the local file system, S3 e.t.c. Not specifying any parameter it default writes to a single sheet.
to_excel() takes several optional params that can be used skip columns, skip rows, not to write index, set column names, formatting, and many more.
# Write DataFrame to Excel file
df.to_excel('Courses.xlsx')
This creates an excel file with the contents as below. By default, It exports column names, indexes, and data to a sheet named 'Sheet1'.
You can change the name of the sheet from Sheet1 to something that makes sense to your data by using sheet_name param. The below example exports it to the sheet named ‘Technologies‘.
# Write DataFrame to Excel file with sheet name
df.to_excel('Courses.xlsx', sheet_name='Technologies')
2. Write to Multiple Sheets
The ExcelWriter class allows you to write or export multiple pandas DataFrames to separate sheets. First, you need to create an object for ExcelWriter.
The below example writes data from df object to a sheet named Technologies and df2 object to a sheet named Schedule.
# Write to Multiple Sheets
with pd.ExcelWriter('Courses.xlsx') as writer:
df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name='Technologies')
df2.to_excel(writer, sheet_name='Schedule')
3. Append to Existing Excel File
ExcelWriter can be used to append DataFrame to an excel file. Use mode param with value 'a' to append. The code below opens an existing file and adds data from the DataFrame to the specified sheet.
# Append DataFrame to existing excel file
with pd.ExcelWriter('Courses.xlsx',mode='a') as writer:
df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name='Technologies')
4. Save Selected Columns
use param columns to save selected columns from DataFrame to excel file. The below example only saves columns Fee, Duration to excel file.
# Save Selected Columns to Excel File
df.to_excel('Courses.xlsx', columns = ['Fee','Duration'])
Use header param with a list of values if you wanted to write with different column names.
5. Skip Index
To skip Index from writing use index=False param. By default, it is set to True meaning write numerical Index to excel sheet.
# Skip Index
df.to_excel('Courses.xlsx', index = False)
Conclusion
In this article, you have learned how to write pandas DataFrame to excel file by using to_excel(). Also explored how to write to specific sheets, multiple sheets, and append to existing excel file.
Related Articles
- pandas ExcelWriter Usage with Examples
- pandas write CSV file
- pandas read Excel
- Pandas ExcelWriter Explained with Examples
- Pandas Read Multiple CSV Files into DataFrame
- How to Read Excel Multiple Sheets in Pandas
- Pretty Print Pandas DataFrame or Series?
- Pandas Handle Missing Data in Dataframe
- How to read CSV without headers in pandas
References
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/38074678/append-existing-excel-sheet-with-new-dataframe-using-python-pandas/38075046#38075046
В Pandas есть встроенная функция для сохранения датафрейма в электронную таблицу Excel. Все очень просто:
|
df.to_excel( path ) # где path это путь до файла, куда будем сохранять |
Как записать в лист с заданным именем
В этом случае будет создан xls / xlsx файл, а данные сохранятся на лист с именем Sheet1. Если хочется сохранить на лист с заданным именем, то можно использовать конструкцию:
|
df.to_excel( path, sheet_name=«Лист 1») # где sheet_name название листа |
Как записать в один файл сразу два листа
Но что делать, если хочется записать в файл сразу два листа? Логично было бы использовать две команды
df.to_excel друг за другом, но с одним путем до файла и разными
sheet_name , однако в Pandas это так не работает. Для решения этой задачи придется использовать конструкцию посложнее:
|
from pandas.io.excel import ExcelWriter with ExcelWriter(path) as writer: df.sample(10).to_excel(writer, sheet_name=«Лист 1») df.sample(10).to_excel(writer, sheet_name=«Лист 2») |
В результате будет создан файл Excel, где будет два листа с именами Лист 1 и Лист 2.
Как добавить ещё один лист у уже существующему файлу
Если использовать предыдущий код, то текущий файл будет перезаписан и в него будет записан новый лист. Старые данные при этом, ожидаемо, будут утеряны. Выход есть, достаточно лишь добавить модификатор «a» (append):
|
with ExcelWriter(path, mode=«a») as writer: df.sample(10).to_excel(writer, sheet_name=«Лист 3») |
Но что, если оставить этот код, удалить существующий файл Excel и попробовать выполнить код? Получим ошибку Файл не найден. В Python существует модификатор «a+», который создает файл, если его нет, и открывает его на редактирование, если файл существует. Но в Pandas такого модификатора не существует, поэтому мы должны выбрать модификатор для ExcelWriter в зависимости от наличия или отсутствия файла. Но это не сложно:
|
with ExcelWriter(path, mode=«a» if os.path.exists(path) else «w») as writer: df.sample().to_excel(writer, sheet_name=«Лист 4») |
К сожалению в Pandas, на момент написания поста, такого функционала нет. Но это можно реализовать с помощью пакета openpyxl. Вот пример такой функции:
|
def update_spreadsheet(path : str, _df, starcol : int = 1, startrow : int = 1, sheet_name : str =«ToUpdate»): »’ :param path: Путь до файла Excel :param _df: Датафрейм Pandas для записи :param starcol: Стартовая колонка в таблице листа Excel, куда буду писать данные :param startrow: Стартовая строка в таблице листа Excel, куда буду писать данные :param sheet_name: Имя листа в таблице Excel, куда буду писать данные :return: »’ wb = ox.load_workbook(path) for ir in range(0, len(_df)): for ic in range(0, len(_df.iloc[ir])): wb[sheet_name].cell(startrow + ir, starcol + ic).value = _df.iloc[ir][ic] wb.save(path) |
Как работает код и пояснения смотри в видео
Если у тебя есть вопросы, что-то не получается или ты знаешь как решить задачи в посте лучше и эффективнее (такое вполне возможно) то смело пиши в комментариях к видео.
Всем привет. Обрабатываю данные скриптом python:
import os
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_excel("ОБЩИЙ ЖУРНАЛ.xls")
for i in data:
if "Unnamed" in i:
del data[i]
else:
continue
for i in data["Протокол, №"]:
data_protocol = data[data["Протокол, №"] == i]
graphs_dir = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "Graphs")
writer = pd.ExcelWriter(f'{os.path.join(graphs_dir, f"{i}.xlsx")}', engine='xlsxwriter', mode='w')
try:
os.mkdir(graphs_dir)
except OSError:
pass
for j in data_protocol["T, °C"]:
data_temper = data_protocol[data_protocol["T, °C"] == j]
for k in data_temper["R"]:
data_R = data_temper[data_temper["R"] == k]
data_R.to_excel(writer, sheet_name=f'{i}_T={j}°C_R={k}')
else:
writer.save()Скрипт писал давно. По итогу у меня создавалось некоторое количество excel файлов. Теперь нужно снова обработать данные и дописать в ранее созданные файлы. В документации к pandas.ExcelWriter написано, что можно поменять mode=’w’ на mode=’a’. Но после запуска выходит ошибка:
ValueError: Append mode is not supported with xlsxwriter!
Пробовал убирать параметр engine=’xlsxwriter’, но он по умолчанию и та же сама ошибка вылетает.
У кого-нибудь есть идеи?
-
Вопрос заданболее двух лет назад
-
2972 просмотра
Pandas умеет добавлять в файлы с движком «openpyxl».
Если openpyxl не установлен — перед запуском скрипта установите его
writer = pd.ExcelWriter(f'{os.path.join(graphs_dir, f"{i}.xlsx")}', engine='openpyxl', mode='a')UPD. Если нужно добавить данные в уже существующий лист — вот сниппет со Stackoverflow
https://stackoverflow.com/a/38075046
Code
def append_df_to_excel(filename, df, sheet_name='Sheet1', startrow=None,
truncate_sheet=False,
**to_excel_kwargs):
"""
Append a DataFrame [df] to existing Excel file [filename]
into [sheet_name] Sheet.
If [filename] doesn't exist, then this function will create it.
Parameters:
filename : File path or existing ExcelWriter
(Example: '/path/to/file.xlsx')
df : dataframe to save to workbook
sheet_name : Name of sheet which will contain DataFrame.
(default: 'Sheet1')
startrow : upper left cell row to dump data frame.
Per default (startrow=None) calculate the last row
in the existing DF and write to the next row...
truncate_sheet : truncate (remove and recreate) [sheet_name]
before writing DataFrame to Excel file
to_excel_kwargs : arguments which will be passed to `DataFrame.to_excel()`
[can be dictionary]
Returns: None
"""
from openpyxl import load_workbook
import pandas as pd
# ignore [engine] parameter if it was passed
if 'engine' in to_excel_kwargs:
to_excel_kwargs.pop('engine')
writer = pd.ExcelWriter(filename, engine='openpyxl')
# Python 2.x: define [FileNotFoundError] exception if it doesn't exist
try:
FileNotFoundError
except NameError:
FileNotFoundError = IOError
try:
# try to open an existing workbook
writer.book = load_workbook(filename)
# get the last row in the existing Excel sheet
# if it was not specified explicitly
if startrow is None and sheet_name in writer.book.sheetnames:
startrow = writer.book[sheet_name].max_row
# truncate sheet
if truncate_sheet and sheet_name in writer.book.sheetnames:
# index of [sheet_name] sheet
idx = writer.book.sheetnames.index(sheet_name)
# remove [sheet_name]
writer.book.remove(writer.book.worksheets[idx])
# create an empty sheet [sheet_name] using old index
writer.book.create_sheet(sheet_name, idx)
# copy existing sheets
writer.sheets = {ws.title:ws for ws in writer.book.worksheets}
except FileNotFoundError:
# file does not exist yet, we will create it
pass
if startrow is None:
startrow = 0
# write out the new sheet
df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name, startrow=startrow, **to_excel_kwargs)
# save the workbook
writer.save()Пригласить эксперта
-
Показать ещё
Загружается…
13 апр. 2023, в 23:18
1000 руб./за проект
13 апр. 2023, в 22:24
6000 руб./за проект
13 апр. 2023, в 22:03
10000 руб./за проект
Минуточку внимания
In this tutorial, we will use an example to show you how to append data to excel using python pandas library.
In order to append data to excel, we should notice two steps:
- How to read data from excel using python pandas
- How to write data (python dictionary) to excel correctly
We will introduce these two steps in detail.
What data we will append?
We will append a python dictionary, here is an example:
data = {'Name':['Tom', 'Jack', 'Steve', 'Ricky'],'Age':[28,34,29,42],'City':['wuhan','chongqin','beijing','shanghai']}
Here Name, Age and City is the data header.
Then we can use this dictionary to create a DataFrame object to save.
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index= None)
In order to append data to excel, we should read an excel file to get original data, then append our data and save.
How to read excel data and append?
We can use example code below to read and append.
df_source = None
if os.path.exists(excel_name):
df_source = pd.DataFrame(pd.read_excel(excel_name, sheet_name=sheet_name))
if df_source is not None:
df_dest = df_source.append(df)
else:
df_dest = df
Then we can use to_excel() function to save data to excel.
df_dest.to_excel(writer, sheet_name=sheet_name, index = False, columns=columns)
The full code is below:
import pandas as pd
import os
#data = {'Name':['Tom', 'Jack', 'Steve', 'Ricky'],'Age':[28,34,29,42]}
def append_data_to_excel(excel_name, sheet_name, data):
with pd.ExcelWriter(excel_name) as writer:
columns = []
for k, v in data.items():
columns.append(k)
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index= None)
df_source = None
if os.path.exists(excel_name):
df_source = pd.DataFrame(pd.read_excel(excel_name, sheet_name=sheet_name))
if df_source is not None:
df_dest = df_source.append(df)
else:
df_dest = df
df_dest.to_excel(writer, sheet_name=sheet_name, index = False, columns=columns)
data = {'Name':['Tom', 'Jack', 'Steve', 'Ricky'],'Age':[28,34,29,42],'City':['wuhan','chongqin','beijing','shanghai']}
append_data_to_excel('test.xlsx', 'person',data)
data = {'Name':['Tom', 'Jack', 'Steve', 'Ricky'],'Age':[29,34,29,42]}
append_data_to_excel('test.xlsx', 'person',data)
append_data_to_excel('test.xlsx', 'person',data)
Run append_data_to_excel() function, we can append our data to existent excel file.
- Syntax of
pandas.DataFrame.to_excel() - Example Codes: Pandas
DataFrame.to_excel() - Example Codes: Pandas
DataFrame.to_excel()WithExcelWriter - Example Codes: Pandas
DataFrame.to_excelto Append to an Existing Excel File - Example Codes: Pandas
DataFrame.to_excelto Write Multiple Sheets - Example Codes: Pandas
DataFrame.to_excelWithheaderParameter - Example Codes: Pandas
DataFrame.to_excelWithindex=False - Example Codes: Pandas
DataFrame.to_excelWithindex_labelParameter - Example Codes: Pandas
DataFrame.to_excelWithfloat_formatParameter - Example Codes: Pandas
DataFrame.to_excelWithfreeze_panesParameter
Python Pandas DataFrame.to_excel(values) function dumps the dataframe data to an Excel file, in a single sheet or multiple sheets.
Syntax of pandas.DataFrame.to_excel()
DataFrame.to_excel(excel_writer,
sheet_name='Sheet1',
na_rep='',
float_format=None,
columns=None,
header=True,
index=True,
index_label=None,
startrow=0,
startcol=0,
engine=None,
merge_cells=True,
encoding=None,
inf_rep='inf',
verbose=True,
freeze_panes=None)
Parameters
excel_writer |
Excel file path or the existing pandas.ExcelWriter |
sheet_name |
Sheet name to which the dataframe dumps |
na_rep |
Representation of null values. |
float_format |
Format of floating numbers |
header |
Specify the header of the generated excel file. |
index |
If True, write dataframe index to the Excel. |
index_label |
Column label for index column. |
startrow |
The upper left cell row to write the data to the Excel. Default is 0 |
startcol |
The upper left cell column to write the data to the Excel. Default is 0 |
engine |
Optional parameter to specify the engine to use. openyxl or xlswriter |
merge_cells |
Merge MultiIndex to merged cells |
encoding |
Encoding of the output Excel file. Only necessary if xlwt writer is used, other writers support Unicode natively. |
inf_rep |
Representation of infinity. Default is inf |
verbose |
If True, error logs consist of more information |
freeze_panes |
Specify the bottommost and rightmost of the frozen pane. It is one-based, but not zero-based. |
Return
None
Example Codes: Pandas DataFrame.to_excel()
import pandas as pd
dataframe= pd.DataFrame({'Attendance': [60, 100, 80, 78, 95],
'Name': ['Olivia', 'John', 'Laura', 'Ben', 'Kevin'],
'Marks': [90, 75, 82, 64, 45]})
dataframe.to_excel('test.xlsx')
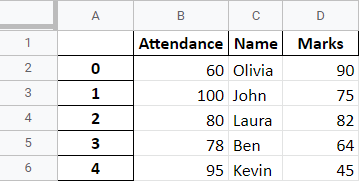
The caller DataFrame is
Attendance Name Marks
0 60 Olivia 90
1 100 John 75
2 80 Laura 82
3 78 Ben 64
4 95 Kevin 45
test.xlsx is created.
Example Codes: Pandas DataFrame.to_excel() With ExcelWriter
The above example uses the file path as the excel_writer, and we could also use pandas.Excelwriter to specify the excel file the dataframe dumps.
import pandas as pd
dataframe= pd.DataFrame({'Attendance': [60, 100, 80, 78, 95],
'Name': ['Olivia', 'John', 'Laura', 'Ben', 'Kevin'],
'Marks': [90, 75, 82, 64, 45]})
with pd.ExcelWriter('test.xlsx') as writer:
dataframe.to_excel(writer)
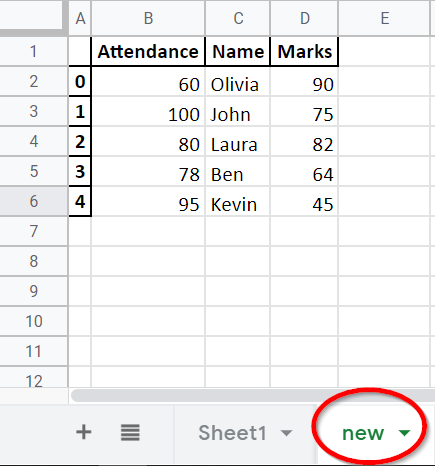
Example Codes: Pandas DataFrame.to_excel to Append to an Existing Excel File
import pandas as pd
import openpyxl
dataframe= pd.DataFrame({'Attendance': [60, 100, 80, 78, 95],
'Name': ['Olivia', 'John', 'Laura', 'Ben', 'Kevin'],
'Marks': [90, 75, 82, 64, 45]})
with pd.ExcelWriter('test.xlsx', mode='a', engine='openpyxl') as writer:
dataframe.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="new")
We should specify the engine as openpyxl but not default xlsxwriter; otherwise, we will get the error that xlswriter doesn’t support append mode.
ValueError: Append mode is not supported with xlsxwriter!
openpyxl shall be installed and imported because it is not part of pandas.
Example Codes: Pandas DataFrame.to_excel to Write Multiple Sheets
import pandas as pd
dataframe= pd.DataFrame({'Attendance': [60, 100, 80, 78, 95],
'Name': ['Olivia', 'John', 'Laura', 'Ben', 'Kevin'],
'Marks': [90, 75, 82, 64, 45]})
with pd.ExcelWriter('test.xlsx') as writer:
dataframe.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="Sheet1")
dataframe.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="Sheet2")
It dumps the dataframe object to both Sheet1 and Sheet2.
You could also write different data to multiple sheets if you specify the columns parameter.
import pandas as pd
dataframe= pd.DataFrame({'Attendance': [60, 100, 80, 78, 95],
'Name': ['Olivia', 'John', 'Laura', 'Ben', 'Kevin'],
'Marks': [90, 75, 82, 64, 45]})
with pd.ExcelWriter('test.xlsx') as writer:
dataframe.to_excel(writer,
columns=["Name","Attendance"],
sheet_name="Sheet1")
dataframe.to_excel(writer,
columns=["Name","Marks"],
sheet_name="Sheet2")
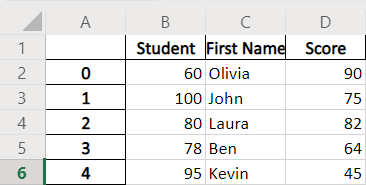
Example Codes: Pandas DataFrame.to_excel With header Parameter
import pandas as pd
dataframe= pd.DataFrame({'Attendance': [60, 100, 80, 78, 95],
'Name': ['Olivia', 'John', 'Laura', 'Ben', 'Kevin'],
'Marks': [90, 75, 82, 64, 45]})
with pd.ExcelWriter('test.xlsx') as writer:
dataframe.to_excel(writer, header=["Student", "First Name", "Score"])
The default header in the created Excel file is the same as dataframe’s column names. The header parameter specifies the new header to replace the default one.
Example Codes: Pandas DataFrame.to_excel With index=False
import pandas as pd
dataframe= pd.DataFrame({'Attendance': [60, 100, 80, 78, 95],
'Name': ['Olivia', 'John', 'Laura', 'Ben', 'Kevin'],
'Marks': [90, 75, 82, 64, 45]})
with pd.ExcelWriter('test.xlsx') as writer:
dataframe.to_excel(writer, index=False)
index = False specifies that DataFrame.to_excel() generates an Excel file without header row.
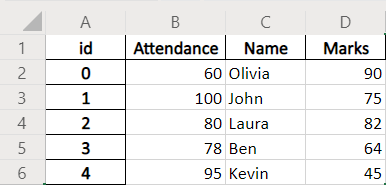
Example Codes: Pandas DataFrame.to_excel With index_label Parameter
import pandas as pd
dataframe= pd.DataFrame({'Attendance': [60, 100, 80, 78, 95],
'Name': ['Olivia', 'John', 'Laura', 'Ben', 'Kevin'],
'Marks': [90, 75, 82, 64, 45]})
with pd.ExcelWriter('test.xlsx') as writer:
dataframe.to_excel(writer, index_label='id')
index_label='id' sets the column name of the index column to be id.
Example Codes: Pandas DataFrame.to_excel With float_format Parameter
import pandas as pd
dataframe= pd.DataFrame({'Attendance': [60, 100, 80, 78, 95],
'Name': ['Olivia', 'John', 'Laura', 'Ben', 'Kevin'],
'Marks': [90, 75, 82, 64, 45]})
with pd.ExcelWriter('test.xlsx') as writer:
dataframe.to_excel(writer, float_format="%.1f")
float_format="%.1f" specifies the floating number to have two floating digits.
Example Codes: Pandas DataFrame.to_excel With freeze_panes Parameter
import pandas as pd
dataframe= pd.DataFrame({'Attendance': [60, 100, 80, 78, 95],
'Name': ['Olivia', 'John', 'Laura', 'Ben', 'Kevin'],
'Marks': [90, 75, 82, 64, 45]})
with pd.ExcelWriter('test.xlsx') as writer:
dataframe.to_excel(writer, freeze_panes=(1,1))
freeze_panes=(1,1) specifies that the excel file has the frozen top row and frozen first column.
Skip to content
Home » Python » Add new sheet to excel using pandas
A data frame can be added as a new sheet to an existing excel sheet. For this operation, the library required is openpyxl.
You can install this library using below command in Jupyter notebook. The same command can be executed in command prompt without the exclamation character “!”.
|
# Installing library for excel interaction using pandas !pip install openpyxl |
You can add the data from multiple DataFrames, each becoming one sheet.
Below snippet loads a pre-existing excel sheet and adds two more sheets to it using two different data frames.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
import pandas as pd import numpy as np from openpyxl import load_workbook # Defining the path which excel needs to be created # There must be a pre-existing excel sheet which can be updated FilePath = «/Users/farukh/Python ML IVY-May-2020/CarPricesData.xlsx» # Generating workbook ExcelWorkbook = load_workbook(FilePath) # Generating the writer engine writer = pd.ExcelWriter(FilePath, engine = ‘openpyxl’) # Assigning the workbook to the writer engine writer.book = ExcelWorkbook # Creating first dataframe DataSample1= [[10,‘value1’], [20,‘value2’], [30,‘value3’]] SimpleDataFrame1=pd.DataFrame(data=DataSample1, columns=[‘Col1’,‘Col2’]) print(SimpleDataFrame1) # Creating second dataframe DataSample2= [[100,‘A’], [200,‘B’], [300,‘C’]] SimpleDataFrame2=pd.DataFrame(data=DataSample2, columns=[‘colA’,‘colB’]) print(SimpleDataFrame2) # Adding the DataFrames to the excel as a new sheet SimpleDataFrame1.to_excel(writer, sheet_name = ‘Data1’) SimpleDataFrame2.to_excel(writer, sheet_name = ‘Data2’) writer.save() writer.close() |

Lead Data Scientist
Farukh is an innovator in solving industry problems using Artificial intelligence. His expertise is backed with 10 years of industry experience. Being a senior data scientist he is responsible for designing the AI/ML solution to provide maximum gains for the clients. As a thought leader, his focus is on solving the key business problems of the CPG Industry. He has worked across different domains like Telecom, Insurance, and Logistics. He has worked with global tech leaders including Infosys, IBM, and Persistent systems. His passion to teach inspired him to create this website!