Learn to read excel, write excel, evaluate formula cells and apply custom formatting to the generated excel files using Apache POI library with examples.
If we are building software for the HR or Finance domain, there is usually a requirement for generating excel reports across management levels. Apart from reports, we can also expect some input data for the applications coming in the form of excel sheets and the application is expected to support this requirement.
Apache POI is a well-trusted library among many other open-source libraries to handle such usecases involving excel files. Please note that, in addition, we can read and write MS Word and MS PowerPoint files also using the Apache POI library.
This Apache POI tutorial will discuss some everyday excel operations in real-life applications.
- 1. Maven Dependency
- 2. Important Classes in POI Library
- 3. Writing an Excel File
- 4. Reading an Excel File
- 5. Add and Evaluate Formula Cells
- 6. Formatting the Cells
- 7. Conclusion
1. Maven Dependency
If we are working on a maven project, we can include the Apache POI dependencies in pom.xml file using this:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2</version>
</dependency>2. Important Classes in POI Library
-
HSSF, XSSF and XSSF classes
Apache POI main classes usually start with either HSSF, XSSF or SXSSF.
- HSSF – is the POI Project’s pure Java implementation of the Excel 97(-2007) file format. e.g., HSSFWorkbook, HSSFSheet.
- XSSF – is the POI Project’s pure Java implementation of the Excel 2007 OOXML (.xlsx) file format. e.g., XSSFWorkbook, XSSFSheet.
- SXSSF (since 3.8-beta3) – is an API-compatible streaming extension of XSSF to be used when huge spreadsheets have to be produced and heap space is limited. e.g., SXSSFWorkbook, SXSSFSheet. SXSSF achieves its low memory footprint by limiting access to the rows within a sliding window, while XSSF gives access to all rows in the document.
-
Row and Cell
Apart from the above classes, Row and Cell interact with a particular row and a particular cell in an excel sheet.
-
Styling Related Classes
A wide range of classes like CellStyle, BuiltinFormats, ComparisonOperator, ConditionalFormattingRule, FontFormatting, IndexedColors, PatternFormatting, SheetConditionalFormatting etc. are used when you have to add formatting to a sheet, primarily based on some rules.
-
FormulaEvaluator
Another helpful class FormulaEvaluator is used to evaluate the formula cells in an excel sheet.
3. Writing an Excel File
I am taking this example first so we can reuse the excel sheet created by this code in further examples.
Writing excel using POI is very simple and involves the following steps:
- Create a workbook
- Create a sheet in workbook
- Create a row in sheet
- Add cells to sheet
- Repeat steps 3 and 4 to write more data
It seems very simple, right? Let’s have a look at the code doing these steps.
Java program to write an excel file using Apache POI library.
package com.howtodoinjava.demo.poi;
//import statements
public class WriteExcelDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//Blank workbook
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
//Create a blank sheet
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Employee Data");
//This data needs to be written (Object[])
Map<String, Object[]> data = new TreeMap<String, Object[]>();
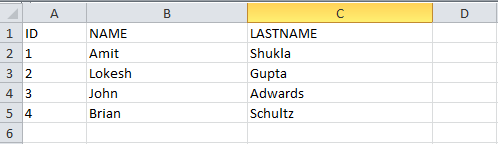
data.put("1", new Object[] {"ID", "NAME", "LASTNAME"});
data.put("2", new Object[] {1, "Amit", "Shukla"});
data.put("3", new Object[] {2, "Lokesh", "Gupta"});
data.put("4", new Object[] {3, "John", "Adwards"});
data.put("5", new Object[] {4, "Brian", "Schultz"});
//Iterate over data and write to sheet
Set<String> keyset = data.keySet();
int rownum = 0;
for (String key : keyset)
{
Row row = sheet.createRow(rownum++);
Object [] objArr = data.get(key);
int cellnum = 0;
for (Object obj : objArr)
{
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellnum++);
if(obj instanceof String)
cell.setCellValue((String)obj);
else if(obj instanceof Integer)
cell.setCellValue((Integer)obj);
}
}
try
{
//Write the workbook in file system
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("howtodoinjava_demo.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println("howtodoinjava_demo.xlsx written successfully on disk.");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
See Also: Appending Rows to Excel
4. Reading an Excel File
Reading an excel file using POI is also very simple if we divide this into steps.
- Create workbook instance from an excel sheet
- Get to the desired sheet
- Increment row number
- iterate over all cells in a row
- repeat steps 3 and 4 until all data is read
Let’s see all the above steps in code. I am writing the code to read the excel file created in the above example. It will read all the column names and the values in it – cell by cell.
Java program to read an excel file using Apache POI library.
package com.howtodoinjava.demo.poi;
//import statements
public class ReadExcelDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(new File("howtodoinjava_demo.xlsx"));
//Create Workbook instance holding reference to .xlsx file
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(file);
//Get first/desired sheet from the workbook
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//Iterate through each rows one by one
Iterator<Row> rowIterator = sheet.iterator();
while (rowIterator.hasNext())
{
Row row = rowIterator.next();
//For each row, iterate through all the columns
Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
while (cellIterator.hasNext())
{
Cell cell = cellIterator.next();
//Check the cell type and format accordingly
switch (cell.getCellType())
{
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue() + "t");
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue() + "t");
break;
}
}
System.out.println("");
}
file.close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Program Output:
ID NAME LASTNAME
1.0 Amit Shukla
2.0 Lokesh Gupta
3.0 John Adwards
4.0 Brian Schultz See Also: Apache POI – Read an Excel File using SAX Parser
5. Add and Evaluate Formula Cells
When working on complex excel sheets, we encounter many cells with formulas to calculate their values. These are formula cells. Apache POI also has excellent support for adding formula cells and evaluating already present formula cells.
Let’s see one example of how to add formula cells in excel?
The sheet has four cells in a row and the fourth one in the multiplication of all the previous 3 rows. So the formula will be: A2*B2*C2 (in the second row)
Java program to add formula in an excel file using Apache POI library.
public static void main(String[] args)
{
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Calculate Simple Interest");
Row header = sheet.createRow(0);
header.createCell(0).setCellValue("Pricipal");
header.createCell(1).setCellValue("RoI");
header.createCell(2).setCellValue("T");
header.createCell(3).setCellValue("Interest (P r t)");
Row dataRow = sheet.createRow(1);
dataRow.createCell(0).setCellValue(14500d);
dataRow.createCell(1).setCellValue(9.25);
dataRow.createCell(2).setCellValue(3d);
dataRow.createCell(3).setCellFormula("A2*B2*C2");
try {
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("formulaDemo.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println("Excel with foumula cells written successfully");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}Similarly, we want to read a file with formula cells and use the following logic to evaluate formula cells.
Java program to evaluate formula in an excel file using Apache POI library.
public static void readSheetWithFormula()
{
try
{
FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(new File("formulaDemo.xlsx"));
//Create Workbook instance holding reference to .xlsx file
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(file);
FormulaEvaluator evaluator = workbook.getCreationHelper().createFormulaEvaluator();
//Get first/desired sheet from the workbook
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//Iterate through each rows one by one
Iterator<Row> rowIterator = sheet.iterator();
while (rowIterator.hasNext())
{
Row row = rowIterator.next();
//For each row, iterate through all the columns
Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
while (cellIterator.hasNext())
{
Cell cell = cellIterator.next();
//Check the cell type after eveluating formulae
//If it is formula cell, it will be evaluated otherwise no change will happen
switch (evaluator.evaluateInCell(cell).getCellType())
{
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue() + "tt");
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue() + "tt");
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA:
//Not again
break;
}
}
System.out.println("");
}
file.close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}Program Output:
Pricipal RoI T Interest (P r t)
14500.0 9.25 3.0 402375.0 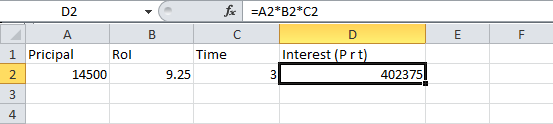
6. Formatting the Cells
So far we have seen examples of reading/writing and excel files using Apache POI. But, when creating a report in an excel file, it is essential to add formatting on cells that fit into any pre-determined criteria.
This formatting can be a different coloring based on a specific value range, expiry date limit etc.
In the below examples, we are taking a couple of such cell formatting examples for various purposes.
6.1. Cell value in a specific range
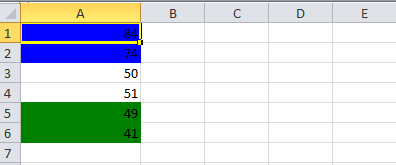
This code will color any cell in a range whose value is between a configured range. [e.g., between 50 and 70]
static void basedOnValue(Sheet sheet)
{
//Creating some random values
sheet.createRow(0).createCell(0).setCellValue(84);
sheet.createRow(1).createCell(0).setCellValue(74);
sheet.createRow(2).createCell(0).setCellValue(50);
sheet.createRow(3).createCell(0).setCellValue(51);
sheet.createRow(4).createCell(0).setCellValue(49);
sheet.createRow(5).createCell(0).setCellValue(41);
SheetConditionalFormatting sheetCF = sheet.getSheetConditionalFormatting();
//Condition 1: Cell Value Is greater than 70 (Blue Fill)
ConditionalFormattingRule rule1 = sheetCF.createConditionalFormattingRule(ComparisonOperator.GT, "70");
PatternFormatting fill1 = rule1.createPatternFormatting();
fill1.setFillBackgroundColor(IndexedColors.BLUE.index);
fill1.setFillPattern(PatternFormatting.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
//Condition 2: Cell Value Is less than 50 (Green Fill)
ConditionalFormattingRule rule2 = sheetCF.createConditionalFormattingRule(ComparisonOperator.LT, "50");
PatternFormatting fill2 = rule2.createPatternFormatting();
fill2.setFillBackgroundColor(IndexedColors.GREEN.index);
fill2.setFillPattern(PatternFormatting.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
CellRangeAddress[] regions = {
CellRangeAddress.valueOf("A1:A6")
};
sheetCF.addConditionalFormatting(regions, rule1, rule2);
}
6.2. Highlight Duplicate Values
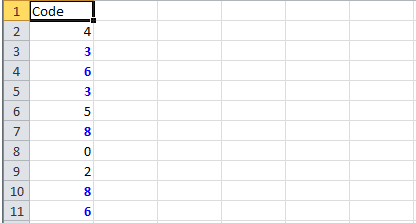
Highlight all cells which have duplicate values in observed cells.
static void formatDuplicates(Sheet sheet) {
sheet.createRow(0).createCell(0).setCellValue("Code");
sheet.createRow(1).createCell(0).setCellValue(4);
sheet.createRow(2).createCell(0).setCellValue(3);
sheet.createRow(3).createCell(0).setCellValue(6);
sheet.createRow(4).createCell(0).setCellValue(3);
sheet.createRow(5).createCell(0).setCellValue(5);
sheet.createRow(6).createCell(0).setCellValue(8);
sheet.createRow(7).createCell(0).setCellValue(0);
sheet.createRow(8).createCell(0).setCellValue(2);
sheet.createRow(9).createCell(0).setCellValue(8);
sheet.createRow(10).createCell(0).setCellValue(6);
SheetConditionalFormatting sheetCF = sheet.getSheetConditionalFormatting();
// Condition 1: Formula Is =A2=A1 (White Font)
ConditionalFormattingRule rule1 = sheetCF.createConditionalFormattingRule("COUNTIF($A$2:$A$11,A2)>1");
FontFormatting font = rule1.createFontFormatting();
font.setFontStyle(false, true);
font.setFontColorIndex(IndexedColors.BLUE.index);
CellRangeAddress[] regions = {
CellRangeAddress.valueOf("A2:A11")
};
sheetCF.addConditionalFormatting(regions, rule1);
sheet.getRow(2).createCell(1).setCellValue("<== Duplicates numbers in the column are highlighted. " +
"Condition: Formula Is =COUNTIF($A$2:$A$11,A2)>1 (Blue Font)");
}
6.3. Alternate Color Rows in Different Colors
A simple code to color each alternate row in a different color.
static void shadeAlt(Sheet sheet) {
SheetConditionalFormatting sheetCF = sheet.getSheetConditionalFormatting();
// Condition 1: Formula Is =A2=A1 (White Font)
ConditionalFormattingRule rule1 = sheetCF.createConditionalFormattingRule("MOD(ROW(),2)");
PatternFormatting fill1 = rule1.createPatternFormatting();
fill1.setFillBackgroundColor(IndexedColors.LIGHT_GREEN.index);
fill1.setFillPattern(PatternFormatting.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
CellRangeAddress[] regions = {
CellRangeAddress.valueOf("A1:Z100")
};
sheetCF.addConditionalFormatting(regions, rule1);
sheet.createRow(0).createCell(1).setCellValue("Shade Alternating Rows");
sheet.createRow(1).createCell(1).setCellValue("Condition: Formula Is =MOD(ROW(),2) (Light Green Fill)");
}
6.4. Color amounts that are going to expire in the next 30 days
A handy code for financial projects which keeps track of deadlines.
static void expiryInNext30Days(Sheet sheet)
{
CellStyle style = sheet.getWorkbook().createCellStyle();
style.setDataFormat((short)BuiltinFormats.getBuiltinFormat("d-mmm"));
sheet.createRow(0).createCell(0).setCellValue("Date");
sheet.createRow(1).createCell(0).setCellFormula("TODAY()+29");
sheet.createRow(2).createCell(0).setCellFormula("A2+1");
sheet.createRow(3).createCell(0).setCellFormula("A3+1");
for(int rownum = 1; rownum <= 3; rownum++) sheet.getRow(rownum).getCell(0).setCellStyle(style);
SheetConditionalFormatting sheetCF = sheet.getSheetConditionalFormatting();
// Condition 1: Formula Is =A2=A1 (White Font)
ConditionalFormattingRule rule1 = sheetCF.createConditionalFormattingRule("AND(A2-TODAY()>=0,A2-TODAY()<=30)");
FontFormatting font = rule1.createFontFormatting();
font.setFontStyle(false, true);
font.setFontColorIndex(IndexedColors.BLUE.index);
CellRangeAddress[] regions = {
CellRangeAddress.valueOf("A2:A4")
};
sheetCF.addConditionalFormatting(regions, rule1);
sheet.getRow(0).createCell(1).setCellValue("Dates within the next 30 days are highlighted");
}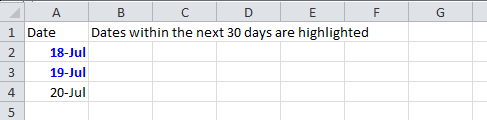
I am ending this apache poi tutorial here to keep the post within a limit.
7. Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned to read excel, write excel, set and evaluate formula cells, and format the cells with color codings using the Apache POI library.
Happy Learning !!
Source Code on Github
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet sheet
= workbook.createSheet("student Details");
Map<String, Object[]> data
= new TreeMap<String, Object[]>();
data.put("1",
new Object[] { "ID", "NAME", "LASTNAME" });
data.put("2",
new Object[] { 1, "Pankaj", "Kumar" });
data.put("3",
new Object[] { 2, "Prakashni", "Yadav" });
data.put("4", new Object[] { 3, "Ayan", "Mondal" });
data.put("5", new Object[] { 4, "Virat", "kohli" });
Set<String> keyset = data.keySet();
int rownum = 0;
for (String key : keyset) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(rownum++);
Object[] objArr = data.get(key);
int cellnum = 0;
for (Object obj : objArr) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellnum++);
if (obj instanceof String)
cell.setCellValue((String)obj);
else if (obj instanceof Integer)
cell.setCellValue((Integer)obj);
}
}
try {
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(
new File("gfgcontribute.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println(
"gfgcontribute.xlsx written successfully on disk.");
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- Details
- Written by
- Last Updated on 30 May 2019 | Print Email
In this tutorial, I’d love to share with you guys some examples of writing data to Excel files using the Apache POI library. If today is the first day you get to know Apache POI and you haven’t written any code snippet to read/write Excel files yet, I recommend you to read the sections 1 and 2 in the tutorial How to Read Excel Files in Java using Apache POI to understand the fundamentals of Apache POI.
Or if you are a kind of person who likes getting your hands-dirty first, let jump directly into the following examples.
1. Apache POI API Basics for Writing Excel Files
The fundamental interfaces include Workbook, Sheet, Row and Cell. For basic formatting, use the CellStyle and Font interfaces. Concrete implementing classes include:
- Excel 2003: HSSFWorkbook, HSSFSheet, HSSFRow, HSSFCell, etc.
- Excel 2007: XSSFWorkbook, XSSFSheet, XSSFRow, XSSFCell, etc.
But I recommend using the common interfaces for greater flexibility with both Excel formats 2003 (XLS) and 2007(XLSX).
Here are the basic steps for writing an Excel file:
- Create a Workbook.
- Create a Sheet.
- Repeat the following steps until all data is processed:
- Create a Row.
- Create Cellsin a Row. Apply formatting using CellStyle.
- Write to an OutputStream.
- Close the output stream.
Now, let’s see some examples that demonstrate writing a list of books to an Excel file.
2. A Simple Example to create an Excel file in Java
The following code snippet is a very simple program that demonstrates writing a list of books to an Excel file in the simplest and dirty form:
package net.codejava.excel;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
/**
* A very simple program that writes some data to an Excel file
* using the Apache POI library.
* @author www.codejava.net
*
*/
public class SimpleExcelWriterExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Java Books");
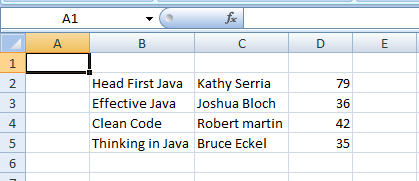
Object[][] bookData = {
{"Head First Java", "Kathy Serria", 79},
{"Effective Java", "Joshua Bloch", 36},
{"Clean Code", "Robert martin", 42},
{"Thinking in Java", "Bruce Eckel", 35},
};
int rowCount = 0;
for (Object[] aBook : bookData) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(++rowCount);
int columnCount = 0;
for (Object field : aBook) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(++columnCount);
if (field instanceof String) {
cell.setCellValue((String) field);
} else if (field instanceof Integer) {
cell.setCellValue((Integer) field);
}
}
}
try (FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("JavaBooks.xlsx")) {
workbook.write(outputStream);
}
}
}
This program creates an Excel 2007 document which looks like the following screenshot (File: JavaBooks.xlsx):
3. A More Object-Oriented Example to create an Excel file in Java
The following code snippets demonstrate a nicer program that focuses on OOP approach. That makes the program more flexible and easy to extend or upgrade in the future.
- Create the model class (Book.java):
package net.codejava.excel; public class Book { private String title; private String author; private float price; public Book() { } public Book(String title, String author, double price) { this.title = title; this.author = author; this.price = price; } // getters and setters } - The method that writes a list of books to an Excel file (in 2003 format):
public void writeExcel(List<Book> listBook, String excelFilePath) throws IOException { Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet(); int rowCount = 0; for (Book aBook : listBook) { Row row = sheet.createRow(++rowCount); writeBook(aBook, row); } try (FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(excelFilePath)) { workbook.write(outputStream); } } - The method that writes information of a book to cells:
private void writeBook(Book aBook, Row row) { Cell cell = row.createCell(1); cell.setCellValue(aBook.getTitle()); cell = row.createCell(2); cell.setCellValue(aBook.getAuthor()); cell = row.createCell(3); cell.setCellValue(aBook.getPrice()); } - The following method creates some dummy data (a list of books):
private List<Book> getListBook() { Book book1 = new Book("Head First Java", "Kathy Serria", 79); Book book2 = new Book("Effective Java", "Joshua Bloch", 36); Book book3 = new Book("Clean Code", "Robert Martin", 42); Book book4 = new Book("Thinking in Java", "Bruce Eckel", 35); List<Book> listBook = Arrays.asList(book1, book2, book3, book4); return listBook; } - And the following code snippet is for testing:
NiceExcelWriterExample excelWriter = new NiceExcelWriterExample(); List<Book> listBook = excelWriter.getListBook(); String excelFilePath = "NiceJavaBooks.xls"; excelWriter.writeExcel(listBook, excelFilePath);
4. Formatting Cells of the Excel file
Of course you may need to format the Excel file to make it looks nicely and professionally. Formatting is diversity and quite complex so in this introductory tutorial, I just show you how to format the basics like setting font style. Here are the steps:
- Create a CellStyle object what holds formatting information:
CellStyle cellStyle = sheet.getWorkbook().createCellStyle();
- Invoke the appropriate setters to apply the formatting you want. For example:
cellStyle.setAlignment(CellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER); cellStyle.setFont(font); cellStyle.setWrapText(true);
For example, the following method writes a header row for the document with font style bold and size is 16:
private void createHeaderRow(Sheet sheet) {
CellStyle cellStyle = sheet.getWorkbook().createCellStyle();
Font font = sheet.getWorkbook().createFont();
font.setBold(true);
font.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 16);
cellStyle.setFont(font);
Row row = sheet.createRow(0);
Cell cellTitle = row.createCell(1);
cellTitle.setCellStyle(cellStyle);
cellTitle.setCellValue("Title");
Cell cellAuthor = row.createCell(2);
cellAuthor.setCellStyle(cellStyle);
cellAuthor.setCellValue("Author");
Cell cellPrice = row.createCell(3);
cellPrice.setCellStyle(cellStyle);
cellPrice.setCellValue("Price");
}
You can see the complete program (FormattedExcelWriterExample.java) which can be found in the source code attached to this article.
5. Writing both Excel 2003 and Excel 2007 formats in Java
For better flexibility (supporting both common Excel formats), I recommend writing a factory method that either returns a HSSFWorkbook or XSSFWorkbook, depending on the extension of the file (.xls or .xlsx). Here’s the method:
private Workbook getWorkbook(String excelFilePath)
throws IOException {
Workbook workbook = null;
if (excelFilePath.endsWith("xlsx")) {
workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
} else if (excelFilePath.endsWith("xls")) {
workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The specified file is not Excel file");
}
return workbook;
}
You can see the complete program (FlexibleExcelWriterExample.java) which can be found in the source code attached to this article.
That’s how to read Excel files in Java programmatically. To learn more in-depth about Java programming, this Java software developers course would be good choice.
Related Java Excel Tutorials:
- How to Read Excel Files in Java using Apache POI
- Java Example to Read Password-protected Excel Files Using Apache POI
- Java Example to Update Existing Excel Files Using Apache POI
- Working with Formula Cells in Excel using Apache POI
References
- Apache POI — the Java API for Microsoft Documents
- POI API Documentation (Javadocs)
- Apache POI Quick Guide
- Apache POI HOWTO
About the Author:

Add comment
In this article, you will learn how to write Excel(XLS & XLSX) files in java using the Apache POI library. If you are new to the Apache POI library then we recommend you to learn the basics of Apache POI.
If you know the fundamentals of Apache POI already then directly move to follow this article now,
Apache POI Envirnment setup
There are two ways for installing Apache POI in Eclipse, based on your project type:
- Maven Project
- Stand alone Java Project (Non Maven)
Note: In this article, we have used the Apache POI-4.0.1 version of the library to demonstrate.
Maven Project
If you are going to create a maven project then you have to add the following maven dependency in the pom.xml file of your project:
<!-- Used for Excel 2003 or before (xls) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Used for Excel 2007 or later (xlsx) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
</dependency>
Stand alone Java Project (Non Maven)
If you are going to create a standalone java project then you have to add the following jar files into your java build path:
- poi-4.0.1.jar
- poi-ooxml-4.0.1.jar
- poi-ooxml-schemas-4.0.1.jar
- xmlbeans-3.0.2.jar
- curvesapi-1.05.jar
- commons-codec-1.11.jar
- commons-collections4-4.2.jar
- commons-compress-1.18.jar
- commons-math3-3.6.1.jar
You can easily download all the above jars in one place: Download Apache POI Jars
If you want to know the complete environment setup for Apache POI in Eclipse IDE, follow another article here: Apache POI – Getting Started
In the Apache POI, there are multiple interfaces and classes which are used to write the Excel files. Let’s see the basic interfaces and classes here:
The basic interfaces are Workbook, Sheet, Row, Cell, CellStyle, Font, etc. And there are specific concrete classes for specific file formats (.xls and .xlsx).
For Excel file format 2003 (XLS): HSSFWorkbook, HSSFSheet, HSSFRow, HSSFCell, etc.
For Excel file format 2007 (XLSX): XSSFWorkbook, XSSFSheet, XSSFRow, XSSFCell, etc.
HSSFWorkbook&XSSFWorkbook– used to create the workbookHSSFSheet&XSSFSheet– used to create the sheet for the excel fileHSSFRow&XSSFRow– used to create the row in the sheetHSSFCell&XSSFCell– used to create the cell in the row
We recommend you use common interfaces to support both Excel format XLS and XLSX.
The followings are the basic steps to write data in an Excel file:
- Create a
Workbook. - Create a
Sheet. - Create a
Row. - Create a
Cell. - Repeat the step-3 and step-4 until all data is processed.
- Write workbook to an
OutputStream. - Close the stream and workbook.
A Sample Example to write Excel 2003 format(xls)
The below java code demonstrates writing data to an Excel(.xls) file:
package com.javacodepoint.excel;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
public class WriteExcelFile {
// Main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a xlsfile object with specific file path
File xlsFile = new File("E:/Excel/employee.xls");
// Writing the xls file
writeXLSFile(xlsFile);
}
// Method to write xls file
public static void writeXLSFile(File xlsFile) {
try {
// Creating workbook
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
// Creating sheet
HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Employee Records");
// Creating header of the excel sheet
HSSFRow header = sheet.createRow(0);
// Creating cell and setting the cell value
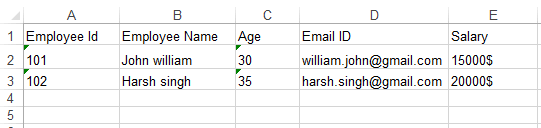
header.createCell(0).setCellValue("Employee Id");
header.createCell(1).setCellValue("Employee Name");
header.createCell(2).setCellValue("Age");
header.createCell(3).setCellValue("Email ID");
header.createCell(4).setCellValue("Salary");
// Creating the 1st row to insert employee record
HSSFRow row1 = sheet.createRow(1);
// Inserting 1st employee record
row1.createCell(0).setCellValue("101");
row1.createCell(1).setCellValue("John william");
row1.createCell(2).setCellValue("30");
row1.createCell(3).setCellValue("[email protected]");
row1.createCell(4).setCellValue("15000$");
// Creating the 2nd row
HSSFRow row2 = sheet.createRow(2);
// Inserting 2nd employee record
row2.createCell(0).setCellValue("102");
row2.createCell(1).setCellValue("Harsh singh");
row2.createCell(2).setCellValue("35");
row2.createCell(3).setCellValue("[email protected]");
row2.createCell(4).setCellValue("20000$");
// Creating file output stream to write the workbook data in to the file
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(xlsFile);
// Writing workbook
workbook.write(fos);
// Closing the output stream
fos.close();
// Closing the workbook
workbook.close();
// Printing the success message on the console
System.out.println("Excel(.xls) file has been created successfully.");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Exception while writting xls file");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Below is a screenshot of the created Excel file-
A Sample Example to write Excel 2007 format(xlsx)
The below java code demonstrates writing data to an Excel(.xlsx) file:
package com.javacodepoint.excel;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class WriteExcelFile {
// Main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a xlsxfile object with specific file path
File xlsxFile = new File("E:/Excel/employee.xlsx");
// Writing the xlsx file
writeXLSXFile(xlsxFile);
}
// Method to write xlsx file
public static void writeXLSXFile(File xlsxFile) {
try {
// Creating workbook
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
// Creating sheet
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Employee Records");
// Creating header of the excel sheet
XSSFRow header = sheet.createRow(0);
// Creating cell and setting the cell value
header.createCell(0).setCellValue("Employee Id");
header.createCell(1).setCellValue("Employee Name");
header.createCell(2).setCellValue("Age");
header.createCell(3).setCellValue("Email ID");
header.createCell(4).setCellValue("Salary");
// Creating the 1st row to insert employee record
XSSFRow row1 = sheet.createRow(1);
// Inserting 1st employee record
row1.createCell(0).setCellValue("101");
row1.createCell(1).setCellValue("John william");
row1.createCell(2).setCellValue("30");
row1.createCell(3).setCellValue("[email protected]");
row1.createCell(4).setCellValue("15000$");
// Creating the 2nd row
XSSFRow row2 = sheet.createRow(2);
// Inserting 2nd employee record
row2.createCell(0).setCellValue("102");
row2.createCell(1).setCellValue("Harsh singh");
row2.createCell(2).setCellValue("35");
row2.createCell(3).setCellValue("[email protected]");
row2.createCell(4).setCellValue("20000$");
// Creating file output stream to write the workbook data in to the file
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(xlsxFile);
// Writing workbook
workbook.write(fos);
// Closing the output stream
fos.close();
// Closing the workbook
workbook.close();
// Printing the success message on the console
System.out.println("Excel(.xlsx) file has been created successfully.");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Exception while writting xlsx file");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
A Generic Example to write both Excel format(.xls and .xlsx)
The following java code demonstrates writing data to an Excel(.xls and .xlsx) file to support both formats:
package com.javacodepoint.excel;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class WriteExcelFile {
// Main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a xlsxfile object with specific file path
File xlsxFile = new File("E:/Excel/employee.xlsx");
// Common method to write excel file based on file format
writeExcelFile(xlsxFile);
}
// Method to write both excel file xls & xlsx format
public static void writeExcelFile(File excelFile) {
try {
Workbook workbook = null;
// Creating workbook based on file format
if (excelFile.getName().endsWith(".xls")) {
workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
} else if (excelFile.getName().endsWith(".xlsx")) {
workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The specified file is not supported");
}
// Creating sheet
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Employee Records");
// Creating header of the excel sheet
Row header = sheet.createRow(0);
// Creating cell and setting the cell value
header.createCell(0).setCellValue("Employee Id");
header.createCell(1).setCellValue("Employee Name");
header.createCell(2).setCellValue("Age");
header.createCell(3).setCellValue("Email ID");
header.createCell(4).setCellValue("Salary");
// Creating the 1st row to insert employee record
Row row1 = sheet.createRow(1);
// Inserting 1st employee record
row1.createCell(0).setCellValue("101");
row1.createCell(1).setCellValue("John william");
row1.createCell(2).setCellValue("30");
row1.createCell(3).setCellValue("[email protected]");
row1.createCell(4).setCellValue("15000$");
// Creating the 2nd row
Row row2 = sheet.createRow(2);
// Inserting 2nd employee record
row2.createCell(0).setCellValue("102");
row2.createCell(1).setCellValue("Harsh singh");
row2.createCell(2).setCellValue("35");
row2.createCell(3).setCellValue("[email protected]");
row2.createCell(4).setCellValue("20000$");
// Creating file output stream to write the workbook data in to the file
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(excelFile);
// Writing workbook
workbook.write(fos);
// Closing the output stream
fos.close();
// Closing the workbook
workbook.close();
// Printing the success message on the console
System.out.println("Excel file has been created successfully.");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Exception while writting excel file");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Formatting Cells of the Excel sheet
To make the look and feel of an Excel sheet attractive, you may require to format the cells of the Excel file. Here we will show you the basic formatting ideas that help you to understand the fundamental of formatting the cells.
Let’s understand the following steps:
Step-1: Create a CellStyle object to holds formatting information.
CellStyle cellStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
Step-2: Now call the appropriate setters to apply the formatting you want.
cellStyle.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER); cellStyle.setFont(font); cellStyle.setWrapText(true);
Let’s see the complete example below-
CellStyleInExcelFile.java
package com.javacodepoint.excel;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.CellStyle;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Font;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.HorizontalAlignment;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class CellStyleInExcelFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a xlsxfile object with specific file path
File xlsxFile = new File("E:/Excel/employee.xlsx");
// Writing the xlsx file
writeFormattedXLSXFile(xlsxFile);
}
// Method to write formatted xlsx file
public static void writeFormattedXLSXFile(File xlsxFile) {
try {
// Creating workbook
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
// Creating sheet
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Employee Records");
// Creating cell style for header
CellStyle headerStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
Font font1 = workbook.createFont();
font1.setFontHeightInPoints((short)16);
font1.setBold(true);
headerStyle.setFont(font1);
headerStyle.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER);
XSSFRow header = sheet.createRow(0);
Cell cell= header.createCell(0);
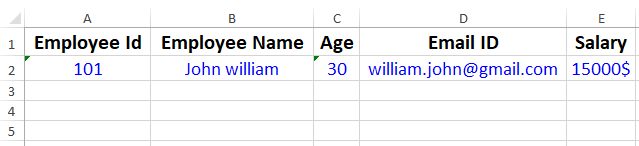
cell.setCellValue("Employee Id");
cell.setCellStyle(headerStyle); // applying the cell style
cell= header.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue("Employee Name");
cell.setCellStyle(headerStyle); // applying the cell style
cell= header.createCell(2);
cell.setCellValue("Age");
cell.setCellStyle(headerStyle); // applying the cell style
cell= header.createCell(3);
cell.setCellValue("Email ID");
cell.setCellStyle(headerStyle); // applying the cell style
cell= header.createCell(4);
cell.setCellValue("Salary");
cell.setCellStyle(headerStyle); // applying the cell style
// Creating a row to insert employee record
XSSFRow row = sheet.createRow(1);
//Creating cell style for row data
CellStyle dataCellStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
Font font2=workbook.createFont();
font2.setFontHeightInPoints((short)14);
font2.setColor((short)4);//blue color
dataCellStyle.setFont(font2);
dataCellStyle.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER);
cell= row.createCell(0);
cell.setCellValue("101");
cell.setCellStyle(dataCellStyle); // applying the cell style
cell= row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue("John william");
cell.setCellStyle(dataCellStyle); // applying the cell style
cell= row.createCell(2);
cell.setCellValue("30");
cell.setCellStyle(dataCellStyle); // applying the cell style
cell= row.createCell(3);
cell.setCellValue("[email protected]");
cell.setCellStyle(dataCellStyle); // applying the cell style
cell= row.createCell(4);
cell.setCellValue("15000$");
cell.setCellStyle(dataCellStyle); // applying the cell style
/* automatic adjust data in column using autoSizeColumn,
* autoSizeColumn should be made after populating the data into the excel.
* Calling before populating data will not have any effect.
*/
sheet.autoSizeColumn(0);
sheet.autoSizeColumn(1);
sheet.autoSizeColumn(2);
sheet.autoSizeColumn(3);
sheet.autoSizeColumn(4);
// Creating file output stream to write the workbook data in to the file
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(xlsxFile);
// Writing workbook
workbook.write(fos);
// Closing the output stream & workbook
fos.close();
workbook.close();
// Printing the success message on the console
System.out.println("Formatted Excel(.xlsx) file has been created successfully.");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Exception while writting formatted xlsx file");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
The below image is a screenshot of a formatted excel file:
Conclusion
In this article, you have seen how to write an Excel file using Apache POI API library in java. You have also seen how to format cells of the Excel file.
If you want to download the above example programs developed using maven and eclipse, download them from the below link.
Related Articles:
- Apache POI – Overview
- Apache POI – Getting Started
- How to read Excel files in java using Apache POI?
- How to create password-protected Excel in java?
- How to write data to an existing Excel file in java?
- [Java code] Convert Excel file to CSV with Apache POI
You may also like:
- How to create a Stopwatch in JavaScript?
- File upload validations in javascript
- Preview an image before uploading using Javascript
- Preview an image before uploading using jQuery