Рассказывает автор блога javarevisited.blogspot.ru
Из этой статьи вы сможете узнать о записи и чтении данных из Excel файлов в Java (будет рассмотрен как XLS, так и XLSX формат). Мы будем использовать библиотеку Apache POI и сосредоточимся на работе с типами String и Date, работа с последним происходит достаточно хитро. Напомню, что работу с числами мы уже рассмотрели в другой статье.
Библиотеку poi-XX.jar вы можете использовать для всех старых (xls, doc, ppt) файлов Microsoft Office, для новых (xlsx, docx, pptx) вам понадобится poi-ooxml-XX.jar. Очень важно понимать, что к чему относится, т.к. используемые классы тоже разные — для старых расширений это HSSFWorkbook, а для новых — XSSFWorkbook.
Подготовка: загрузка библиотек и зависимостей
Конечно, существует достаточно много открытых библиотек, которые позволяют работать с Excel файлами в Java, например, JXL, но мы будем использовать имеющую самый обширный API и самую популярную — Apache POI. Чтобы её использовать, вам нужно скачать jar файлы и добавить их через Eclipse вручную, или вы можете предоставить это Maven.
Во втором случае вам нужно просто добавить следующие две зависимости:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>3.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>3.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Самое удобное в Maven — что он загрузит не только указанные poi.jar и poi-ooxml.jar, но и все jar файлы, которые используются внутри, то есть xmlbeans-2.6.0.jar, stax-api-1.0.1.jar, poi-ooxml-schemas-3.12.jar и commons-codec-1.9.jar.
Если вы будете добавлять библиотеки вручную — не забудьте о вышеназванных файлах. Скачать всё можно отсюда. Помните — если вы загрузите только poi-XX.jar, то ваш код скомпилируется без ошибок, но потом упадёт с java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/apache/xmlbeans/XmlObject, так как внутри будет вызываться xmlbeans.jar.
Запись
В этом примере мы запишем в xls файл следующие данные: в первую ячейку — строку с именем, а во вторую — дату рождения. Вот пошаговая инструкция:
- Создаём объект
HSSFWorkBook; - Создаём лист, используя на объекте, созданном в предыдущем шаге,
createSheet(); - Создаём на листе строку, используя
createRow(); - Создаём в строке ячейку —
createCell(); - Задаём значение ячейки через
setCellValue(); - Записываем
workbookвFileчерезFileOutputStream; - Закрываем
workbook, вызываяclose().
Для записи строк или чисел этого вполне достаточно, но чтобы записать дату, нам понадобится сделать ещё кое-что:
- Создать
DateFormat; - Создать
CellStyle; - Записать
DateFormatвCellStyle; - Записать
CellStyleв ячейку; - Теперь в эту ячейку можно записать объект
Dateчерез всё тот жеsetCellValue; - Чтобы дата поместилась в ячейку, нам нужно добавить столбцу свойство автоматически менять размер:
sheet.autoSizeColumn(1).
Всё вместе это будет выглядеть так:
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static void writeIntoExcel(String file) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException{
Workbook book = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = book.createSheet("Birthdays");
// Нумерация начинается с нуля
Row row = sheet.createRow(0);
// Мы запишем имя и дату в два столбца
// имя будет String, а дата рождения --- Date,
// формата dd.mm.yyyy
Cell name = row.createCell(0);
name.setCellValue("John");
Cell birthdate = row.createCell(1);
DataFormat format = book.createDataFormat();
CellStyle dateStyle = book.createCellStyle();
dateStyle.setDataFormat(format.getFormat("dd.mm.yyyy"));
birthdate.setCellStyle(dateStyle);
// Нумерация лет начинается с 1900-го
birthdate.setCellValue(new Date(110, 10, 10));
// Меняем размер столбца
sheet.autoSizeColumn(1);
// Записываем всё в файл
book.write(new FileOutputStream(file));
book.close();
}
Чтение
Теперь мы считаем из только что созданного файла то, что мы туда записали.
- Для начала создадим
HSSFWorkBook, передав в конструкторFileInputStream; - Получаем лист, передавая в
getSheet()его номер или название; - Получаем строку, используя
getRow(); - Получаем ячейку, используя
getCell(); - Узнаём тип ячейки, используя на ней
getCellType(); - В зависимости от типа ячейки, читаем её значения, используя
getStringCellValue(),getNumericCellValue()илиgetDateCellValue(); - Закрываем
workbookиспользуяclose().
Напомню, что дату Excel хранит как числа, т.е. тип ячейки всё равно будет CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC.
В виде кода это будет выглядеть следующим образом:
public static void readFromExcel(String file) throws IOException{
HSSFWorkbook myExcelBook = new HSSFWorkbook(new FileInputStream(file));
HSSFSheet myExcelSheet = myExcelBook.getSheet("Birthdays");
HSSFRow row = myExcelSheet.getRow(0);
if(row.getCell(0).getCellType() == HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_STRING){
String name = row.getCell(0).getStringCellValue();
System.out.println("name : " + name);
}
if(row.getCell(1).getCellType() == HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC){
Date birthdate = row.getCell(1).getDateCellValue();
System.out.println("birthdate :" + birthdate);
}
myExcelBook.close();
}
В заключение
Как уже упомналось выше, чтение из xlsx файлов ничем принципиально не отличается — нужно только вместо HSSFWorkBook, HSSFSheet, HSSFRow (и прочих) из poi-XX.jar использовать XSSFWorkBook, XSSFSheet, XSSFRow из poi-ooxml-XX.jar. Это всё, что вам нужно знать для чтения и записи в файлы Excel. Разумеется, с помощью библиотеки Apache POI вы можете сделать гораздо больше, но эта статья должна помочь вам быстрее в ней освоиться.
Перевод статьи «How to Read Write Excel file in Java — POI Example»
Learn to read excel, write excel, evaluate formula cells and apply custom formatting to the generated excel files using Apache POI library with examples.
If we are building software for the HR or Finance domain, there is usually a requirement for generating excel reports across management levels. Apart from reports, we can also expect some input data for the applications coming in the form of excel sheets and the application is expected to support this requirement.
Apache POI is a well-trusted library among many other open-source libraries to handle such usecases involving excel files. Please note that, in addition, we can read and write MS Word and MS PowerPoint files also using the Apache POI library.
This Apache POI tutorial will discuss some everyday excel operations in real-life applications.
- 1. Maven Dependency
- 2. Important Classes in POI Library
- 3. Writing an Excel File
- 4. Reading an Excel File
- 5. Add and Evaluate Formula Cells
- 6. Formatting the Cells
- 7. Conclusion
1. Maven Dependency
If we are working on a maven project, we can include the Apache POI dependencies in pom.xml file using this:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2</version>
</dependency>2. Important Classes in POI Library
-
HSSF, XSSF and XSSF classes
Apache POI main classes usually start with either HSSF, XSSF or SXSSF.
- HSSF – is the POI Project’s pure Java implementation of the Excel 97(-2007) file format. e.g., HSSFWorkbook, HSSFSheet.
- XSSF – is the POI Project’s pure Java implementation of the Excel 2007 OOXML (.xlsx) file format. e.g., XSSFWorkbook, XSSFSheet.
- SXSSF (since 3.8-beta3) – is an API-compatible streaming extension of XSSF to be used when huge spreadsheets have to be produced and heap space is limited. e.g., SXSSFWorkbook, SXSSFSheet. SXSSF achieves its low memory footprint by limiting access to the rows within a sliding window, while XSSF gives access to all rows in the document.
-
Row and Cell
Apart from the above classes, Row and Cell interact with a particular row and a particular cell in an excel sheet.
-
Styling Related Classes
A wide range of classes like CellStyle, BuiltinFormats, ComparisonOperator, ConditionalFormattingRule, FontFormatting, IndexedColors, PatternFormatting, SheetConditionalFormatting etc. are used when you have to add formatting to a sheet, primarily based on some rules.
-
FormulaEvaluator
Another helpful class FormulaEvaluator is used to evaluate the formula cells in an excel sheet.
3. Writing an Excel File
I am taking this example first so we can reuse the excel sheet created by this code in further examples.
Writing excel using POI is very simple and involves the following steps:
- Create a workbook
- Create a sheet in workbook
- Create a row in sheet
- Add cells to sheet
- Repeat steps 3 and 4 to write more data
It seems very simple, right? Let’s have a look at the code doing these steps.
Java program to write an excel file using Apache POI library.
package com.howtodoinjava.demo.poi;
//import statements
public class WriteExcelDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//Blank workbook
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
//Create a blank sheet
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Employee Data");
//This data needs to be written (Object[])
Map<String, Object[]> data = new TreeMap<String, Object[]>();
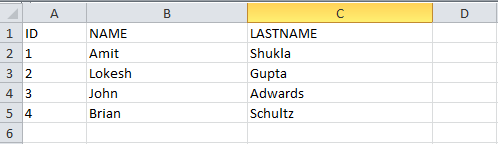
data.put("1", new Object[] {"ID", "NAME", "LASTNAME"});
data.put("2", new Object[] {1, "Amit", "Shukla"});
data.put("3", new Object[] {2, "Lokesh", "Gupta"});
data.put("4", new Object[] {3, "John", "Adwards"});
data.put("5", new Object[] {4, "Brian", "Schultz"});
//Iterate over data and write to sheet
Set<String> keyset = data.keySet();
int rownum = 0;
for (String key : keyset)
{
Row row = sheet.createRow(rownum++);
Object [] objArr = data.get(key);
int cellnum = 0;
for (Object obj : objArr)
{
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellnum++);
if(obj instanceof String)
cell.setCellValue((String)obj);
else if(obj instanceof Integer)
cell.setCellValue((Integer)obj);
}
}
try
{
//Write the workbook in file system
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("howtodoinjava_demo.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println("howtodoinjava_demo.xlsx written successfully on disk.");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
See Also: Appending Rows to Excel
4. Reading an Excel File
Reading an excel file using POI is also very simple if we divide this into steps.
- Create workbook instance from an excel sheet
- Get to the desired sheet
- Increment row number
- iterate over all cells in a row
- repeat steps 3 and 4 until all data is read
Let’s see all the above steps in code. I am writing the code to read the excel file created in the above example. It will read all the column names and the values in it – cell by cell.
Java program to read an excel file using Apache POI library.
package com.howtodoinjava.demo.poi;
//import statements
public class ReadExcelDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(new File("howtodoinjava_demo.xlsx"));
//Create Workbook instance holding reference to .xlsx file
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(file);
//Get first/desired sheet from the workbook
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//Iterate through each rows one by one
Iterator<Row> rowIterator = sheet.iterator();
while (rowIterator.hasNext())
{
Row row = rowIterator.next();
//For each row, iterate through all the columns
Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
while (cellIterator.hasNext())
{
Cell cell = cellIterator.next();
//Check the cell type and format accordingly
switch (cell.getCellType())
{
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue() + "t");
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue() + "t");
break;
}
}
System.out.println("");
}
file.close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Program Output:
ID NAME LASTNAME
1.0 Amit Shukla
2.0 Lokesh Gupta
3.0 John Adwards
4.0 Brian Schultz See Also: Apache POI – Read an Excel File using SAX Parser
5. Add and Evaluate Formula Cells
When working on complex excel sheets, we encounter many cells with formulas to calculate their values. These are formula cells. Apache POI also has excellent support for adding formula cells and evaluating already present formula cells.
Let’s see one example of how to add formula cells in excel?
The sheet has four cells in a row and the fourth one in the multiplication of all the previous 3 rows. So the formula will be: A2*B2*C2 (in the second row)
Java program to add formula in an excel file using Apache POI library.
public static void main(String[] args)
{
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Calculate Simple Interest");
Row header = sheet.createRow(0);
header.createCell(0).setCellValue("Pricipal");
header.createCell(1).setCellValue("RoI");
header.createCell(2).setCellValue("T");
header.createCell(3).setCellValue("Interest (P r t)");
Row dataRow = sheet.createRow(1);
dataRow.createCell(0).setCellValue(14500d);
dataRow.createCell(1).setCellValue(9.25);
dataRow.createCell(2).setCellValue(3d);
dataRow.createCell(3).setCellFormula("A2*B2*C2");
try {
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("formulaDemo.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println("Excel with foumula cells written successfully");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}Similarly, we want to read a file with formula cells and use the following logic to evaluate formula cells.
Java program to evaluate formula in an excel file using Apache POI library.
public static void readSheetWithFormula()
{
try
{
FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(new File("formulaDemo.xlsx"));
//Create Workbook instance holding reference to .xlsx file
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(file);
FormulaEvaluator evaluator = workbook.getCreationHelper().createFormulaEvaluator();
//Get first/desired sheet from the workbook
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//Iterate through each rows one by one
Iterator<Row> rowIterator = sheet.iterator();
while (rowIterator.hasNext())
{
Row row = rowIterator.next();
//For each row, iterate through all the columns
Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
while (cellIterator.hasNext())
{
Cell cell = cellIterator.next();
//Check the cell type after eveluating formulae
//If it is formula cell, it will be evaluated otherwise no change will happen
switch (evaluator.evaluateInCell(cell).getCellType())
{
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue() + "tt");
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue() + "tt");
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA:
//Not again
break;
}
}
System.out.println("");
}
file.close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}Program Output:
Pricipal RoI T Interest (P r t)
14500.0 9.25 3.0 402375.0 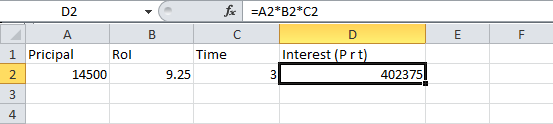
6. Formatting the Cells
So far we have seen examples of reading/writing and excel files using Apache POI. But, when creating a report in an excel file, it is essential to add formatting on cells that fit into any pre-determined criteria.
This formatting can be a different coloring based on a specific value range, expiry date limit etc.
In the below examples, we are taking a couple of such cell formatting examples for various purposes.
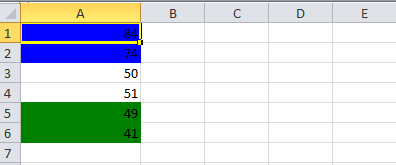
6.1. Cell value in a specific range
This code will color any cell in a range whose value is between a configured range. [e.g., between 50 and 70]
static void basedOnValue(Sheet sheet)
{
//Creating some random values
sheet.createRow(0).createCell(0).setCellValue(84);
sheet.createRow(1).createCell(0).setCellValue(74);
sheet.createRow(2).createCell(0).setCellValue(50);
sheet.createRow(3).createCell(0).setCellValue(51);
sheet.createRow(4).createCell(0).setCellValue(49);
sheet.createRow(5).createCell(0).setCellValue(41);
SheetConditionalFormatting sheetCF = sheet.getSheetConditionalFormatting();
//Condition 1: Cell Value Is greater than 70 (Blue Fill)
ConditionalFormattingRule rule1 = sheetCF.createConditionalFormattingRule(ComparisonOperator.GT, "70");
PatternFormatting fill1 = rule1.createPatternFormatting();
fill1.setFillBackgroundColor(IndexedColors.BLUE.index);
fill1.setFillPattern(PatternFormatting.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
//Condition 2: Cell Value Is less than 50 (Green Fill)
ConditionalFormattingRule rule2 = sheetCF.createConditionalFormattingRule(ComparisonOperator.LT, "50");
PatternFormatting fill2 = rule2.createPatternFormatting();
fill2.setFillBackgroundColor(IndexedColors.GREEN.index);
fill2.setFillPattern(PatternFormatting.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
CellRangeAddress[] regions = {
CellRangeAddress.valueOf("A1:A6")
};
sheetCF.addConditionalFormatting(regions, rule1, rule2);
}
6.2. Highlight Duplicate Values
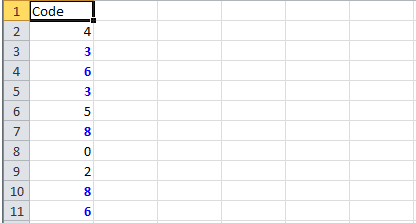
Highlight all cells which have duplicate values in observed cells.
static void formatDuplicates(Sheet sheet) {
sheet.createRow(0).createCell(0).setCellValue("Code");
sheet.createRow(1).createCell(0).setCellValue(4);
sheet.createRow(2).createCell(0).setCellValue(3);
sheet.createRow(3).createCell(0).setCellValue(6);
sheet.createRow(4).createCell(0).setCellValue(3);
sheet.createRow(5).createCell(0).setCellValue(5);
sheet.createRow(6).createCell(0).setCellValue(8);
sheet.createRow(7).createCell(0).setCellValue(0);
sheet.createRow(8).createCell(0).setCellValue(2);
sheet.createRow(9).createCell(0).setCellValue(8);
sheet.createRow(10).createCell(0).setCellValue(6);
SheetConditionalFormatting sheetCF = sheet.getSheetConditionalFormatting();
// Condition 1: Formula Is =A2=A1 (White Font)
ConditionalFormattingRule rule1 = sheetCF.createConditionalFormattingRule("COUNTIF($A$2:$A$11,A2)>1");
FontFormatting font = rule1.createFontFormatting();
font.setFontStyle(false, true);
font.setFontColorIndex(IndexedColors.BLUE.index);
CellRangeAddress[] regions = {
CellRangeAddress.valueOf("A2:A11")
};
sheetCF.addConditionalFormatting(regions, rule1);
sheet.getRow(2).createCell(1).setCellValue("<== Duplicates numbers in the column are highlighted. " +
"Condition: Formula Is =COUNTIF($A$2:$A$11,A2)>1 (Blue Font)");
}
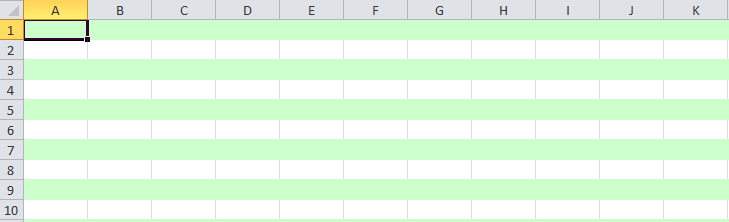
6.3. Alternate Color Rows in Different Colors
A simple code to color each alternate row in a different color.
static void shadeAlt(Sheet sheet) {
SheetConditionalFormatting sheetCF = sheet.getSheetConditionalFormatting();
// Condition 1: Formula Is =A2=A1 (White Font)
ConditionalFormattingRule rule1 = sheetCF.createConditionalFormattingRule("MOD(ROW(),2)");
PatternFormatting fill1 = rule1.createPatternFormatting();
fill1.setFillBackgroundColor(IndexedColors.LIGHT_GREEN.index);
fill1.setFillPattern(PatternFormatting.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
CellRangeAddress[] regions = {
CellRangeAddress.valueOf("A1:Z100")
};
sheetCF.addConditionalFormatting(regions, rule1);
sheet.createRow(0).createCell(1).setCellValue("Shade Alternating Rows");
sheet.createRow(1).createCell(1).setCellValue("Condition: Formula Is =MOD(ROW(),2) (Light Green Fill)");
}
6.4. Color amounts that are going to expire in the next 30 days
A handy code for financial projects which keeps track of deadlines.
static void expiryInNext30Days(Sheet sheet)
{
CellStyle style = sheet.getWorkbook().createCellStyle();
style.setDataFormat((short)BuiltinFormats.getBuiltinFormat("d-mmm"));
sheet.createRow(0).createCell(0).setCellValue("Date");
sheet.createRow(1).createCell(0).setCellFormula("TODAY()+29");
sheet.createRow(2).createCell(0).setCellFormula("A2+1");
sheet.createRow(3).createCell(0).setCellFormula("A3+1");
for(int rownum = 1; rownum <= 3; rownum++) sheet.getRow(rownum).getCell(0).setCellStyle(style);
SheetConditionalFormatting sheetCF = sheet.getSheetConditionalFormatting();
// Condition 1: Formula Is =A2=A1 (White Font)
ConditionalFormattingRule rule1 = sheetCF.createConditionalFormattingRule("AND(A2-TODAY()>=0,A2-TODAY()<=30)");
FontFormatting font = rule1.createFontFormatting();
font.setFontStyle(false, true);
font.setFontColorIndex(IndexedColors.BLUE.index);
CellRangeAddress[] regions = {
CellRangeAddress.valueOf("A2:A4")
};
sheetCF.addConditionalFormatting(regions, rule1);
sheet.getRow(0).createCell(1).setCellValue("Dates within the next 30 days are highlighted");
}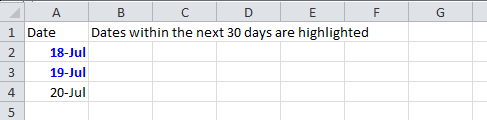
I am ending this apache poi tutorial here to keep the post within a limit.
7. Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned to read excel, write excel, set and evaluate formula cells, and format the cells with color codings using the Apache POI library.
Happy Learning !!
Source Code on Github
Афоризм
А в письмах Вы казались мне стройнее.
Наталья Резник
Поддержка проекта
Если Вам сайт понравился и помог, то будем признательны за Ваш «посильный» вклад в его поддержку и развитие
• Yandex.Деньги
410013796724260
• Webmoney
R335386147728
Z369087728698
Apache POI, взаимодействие с Excel
Apache POI представляет собой API, который позволяет использовать файлы MS Office в Java приложениях.
Данная библиотека разрабатывается и распространяется Apache Software Foundation и носит открытый характер.
Apache POI включает классы и методы для чтения и записи информации в документы MS Office.
Описание компонентов
| HSSF | Horrible Spreadsheet Format | Компонент чтения и записи файлов MS-Excel, формат XLS |
| XSSF | XML Spreadsheet Format | Компонент чтения и записи файлов MS-Excel, формат XLSX |
| HPSF | Horrible Property Set Format | Компонент получения наборов свойств файлов MS-Office |
| HWPF | Horrible Word Processor Format | Компонент чтения и записи файлов MS-Word, формат DOC |
| XWPF | XML Word Processor Format | Компонент чтения и записи файлов MS-Word, формат DOCX |
| HSLF | Horrible Slide Layout Format | Компонент чтения и записи файлов PowerPoint, формат PPT |
| XSLF | XML Slide Layout Format | Компонент чтения и записи файлов PowerPoint, формат PPTX |
| HDGF | Horrible DiaGram Format | Компонент работы с файлами MS-Visio, формат VSD |
| XDGF | XML DiaGram Format | Компонент работы с файлами MS-Visio, формат VSDX |
Список компонентов
| Наименование (артeфакт) | Необходимые компоненты |
|---|---|
| poi | commons-logging, commons-codec, commons-collections, log4j |
| poi-scratchpad | poi |
| poi-ooxml | poi, poi-ooxml-schemas |
| poi-ooxml-schemas | xmlbeans |
| poi-examples | poi, poi-scratchpad, poi-ooxml |
| ooxml-schemas | xmlbeans |
| ooxml-security | xmlbeans |
Подключение Apache POI к проекту
Для подключения Apache POI к проекту необходимо скачать соответствующие библиотеки с официального сайта
https://poi.apache.org/download.html.
Если в проекте используется фреймворк maven, то необходимо установить одну из
следующих зависимостей (версия может быть более новой) :
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.poi/poi -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>3.16</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.poi/poi-ooxml -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>3.16</version>
</dependency>
На странице описания примера чтения файлов Excel приведен проект, включающий
необходимый набор файлов библиотеки Apache POI (poi-3.16.jar, poi-ooxml-3.16.jar, poi-ooxml-schemas-3.16.jar) и
сопутствующих библиотек.
На странице рассматриваются следующие классы, используемые для работы с файлами Excel из приложений Java.
- рабочая книга — HSSFWorkbook, XSSFWorkbook
- лист книги — HSSFSheet, XSSFSheet
- строка — HSSFRow, XSSFRow
- ячейка — HSSFCell, XSSFCell
- стиль — стили ячеек HSSFCellStyle, XSSFCellStyle
- шрифт — шрифт ячеек HSSFFont, XSSFFont
Поскольку описание всех классов и методов не разместить на одной
странице, то ниже по тексту приводятся ссылки для перехода к исходной документации.
Классы и методы Apache POI для работы с файлами Excel
Рабочая книга HSSFWorkbook, XSSFWorkbook
- HSSFWorkbook
- org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel
- класс чтения и записи файлов Microsoft Excel в формате .xls, совместим
с версиями MS-Office 97-2003;
- XSSFWorkbook
- org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel
- класс чтения и записи файлов Microsoft Excel в формате .xlsx, совместим
с MS-Office 2007 или более поздней версии.
Конструкторы класса HSSFWorkbook
HSSFWorkbook ();
HSSFWorkbook (InternalWorkbook book);
HSSFWorkbook (POIFSFileSystem fs);
HSSFWorkbook (NPOIFSFileSystem fs);
HSSFWorkbook (POIFSFileSystem fs,
boolean preserveNodes);
HSSFWorkbook (DirectoryNode directory,
POIFSFileSystem fs,
boolean preserveNodes);
HSSFWorkbook (DirectoryNode directory,
boolean preserveNodes);
HSSFWorkbook (InputStream s);
HSSFWorkbook (InputStream s,
boolean preserveNodes);
preservenodes является необязательным параметром, который определяет необходимость сохранения
узлов типа макросы.
Конструкторы класса XSSFWorkbook
XSSFWorkbook (); // workbookType создать .xlsx или .xlsm XSSFWorkbook (XSSFWorkbookType workbookType); XSSFWorkbook (OPCPackage pkg ); XSSFWorkbook (InputStream is ); XSSFWorkbook (File file); XSSFWorkbook (String path);
Основные методы HSSFWorkbook, XSSFWorkbook
| Метод | Описание |
|---|---|
| createSheet () | Создание страницы книги HSSFSheet, XSSFSheet |
| createSheet (String name) | Создание страницы с определенным наименованием |
| CreateFont () | Создание шрифта |
| createCellStyle () | Создание стиля |
С полным перечнем всех методов класса XSSFWorkbook можно познакомиться на странице
http://poi.apache.org/apidocs/org/apache/poi/xssf/usermodel/XSSFWorkbook.html.
Классы листов книги, HSSFSheet, XSSFSheet
- org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet
- org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet
Классы HSSFSheet, XSSFSheet включают свойства и методы создания строк, определения размера колонок,
слияния ячеек в одну область и т.д.
Основные методы классов работы с листами
| Метод | Описание |
|---|---|
| addMergedRegion (CellRangeAddress) | Определение области слияния ячеек страницы |
| autoSizeColumn (int column) | Автоматическая настройка ширины колонки column (отсчет от 0) |
| setColumnWidth (int column, int width) | Настройка ширины колонки column (отсчет от 0) |
| createRow (int row) | Создание строки row (отсчет от 0) |
| getRow (int row) | Получение ссылки на строку row (отсчет от 0) |
С полным перечнем всех методов класса XSSFSheet можно познакомиться на странице
https://poi.apache.org/apidocs/org/apache/poi/xssf/usermodel/XSSFSheet.html
Классы строк HSSFRow, XSSFRow
- org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFRow
- org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRow
Классы HSSFRow, XSSFRow включают свойства и методы работы со строками, создания ячеек в строке и т.д.
Основные методы классов HSSFRow, XSSFRow
| Метод | Описание |
|---|---|
| setHeight (short) | Определение высоты строки |
| getHeight() | Получение значения высоты в twips’ах (1/20) |
| getHeightInPoints() | Получение значение высоты |
| createCell (int) | Создание ячейки в строке (отсчет от 0) |
| getCell(int) | Получение ссылки на ячейку |
| getFirstCellNum() | Получение номера первой ячейки в строке |
| setRowStyle(CellStyle) | Определение стиля всей строки |
С полным перечнем всех методов класса XSSFRow можно познакомиться на странице
http://poi.apache.org/apidocs/org/apache/poi/xssf/usermodel/XSSFRow.html
Классы ячеек HSSFCell, XSSFCell
Ячейки электронной таблицы используются для размещения информации. В ячейке может быть представлено
числовое значение, текст или формула. Также ячейка может содержать комментарий.
Классы HSSFCell, XSSFCell включают свойства и методы работы с ячейками таблицы.
- org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCell
- org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCell
Основные методы классов HSSFCell, XSSFCell
| Метод | Описание |
|---|---|
| getBooleanCellValue() | Чтение логического значения ячейки |
| getDateCellValue() | Чтение значения ячейки типа java.util.Date |
| getNumericCellValue() | Чтение числового значения ячейки типа double |
| getStringCellValue() | Чтение текстового значения ячейки (java.lang.String) |
| setCellValue(boolean) | Определение логического значения ячейки |
| setCellValue(java.util.Calendar) | Определение значения ячейки типа даты |
| setCellValue(java.util.Date) | Определение значения ячейки типа даты |
| getCellTypeEnum() | Чтение типа значения ячейки CellType |
| setCellComment(Comment) | Запись комментария в ячейку |
| getCellComment() | Чтение комментария ячейки |
| removeCellComment() | Удаление комментария ячейки |
| setHyperlink(Hyperlink) | Запись гиперссылки в ячейку |
| getHyperlink() | Чтение гиперссылки XSSFHyperlink в ячейке |
| removeHyperlink() | Удаления гиперссылки ячейки |
| getCellFormula() | Чтение формулы, например SUM(C4:E4) |
| setCellFormula(String) | Определение формулы, например =SUM(C4:E4) |
| getCellStyle() | Чтение стиля ячейки (XSSFCellStyle) |
| setCellStyle(CellStyle) | Определение стиля ячейки |
| getColumnIndex() | Определение индекса ячейки |
| setAsActiveCell() | Определение активности ячейки |
С полным перечнем всех методов класса XSSFCell можно познакомиться на странице
http://poi.apache.org/apidocs/org/apache/poi/xssf/usermodel/XSSFCell.html
Классы стилей ячеек HSSFCellStyle, XSSFCellStyle
С полным перечнем всех свойств и методов класса XSSFCellStyle можно познакомиться на странице
http://poi.apache.org/apidocs/org/apache/poi/ss/usermodel/CellStyle.html
Ниже в качестве примера представлен метод, формирующий стиль ячейки, в которой :
- текст центрируется по вертикали и горизонтали;
- обрамление ячейки представляет тонкую черную линию по периметру;
- текст переносится на следующую строку (не ячейку), если не вмещается в размер ячейки.
private XSSFCellStyle createCellStyle(XSSFWorkbook book)
{
BorderStyle thin = BorderStyle.THIN;
short black = IndexedColors.BLACK.getIndex();
XSSFCellStyle style = book.createCellStyle();
style.setWrapText(true);
style.setAlignment (HorizontalAlignment.CENTER);
style.setVerticalAlignment(VerticalAlignment .CENTER);
style.setBorderTop (thin);
style.setBorderBottom (thin);
style.setBorderRight (thin);
style.setBorderLeft (thin);
style.setTopBorderColor (black);
style.setRightBorderColor (black);
style.setBottomBorderColor(black);
style.setLeftBorderColor (black);
return style;
}
Метод setWrapText позволяет определить флаг переноса текста в ячейке согласно ее размеру (ширине). Чтобы перенести
текст принудительно, можно в текстовой строке установить символы CRCL, например «Разделительrnтекста».
Классы шрифтов HSSFFont, XSSFFont
С полным перечнем всех свойств и методов класса XSSFFont можно познакомиться на странице
http://poi.apache.org/apidocs/org/apache/poi/ss/usermodel/Font.html
Ниже в качестве примера представлен метод, формирующий шрифт типа «Times New Roman» :
private XSSFFont createCellFont(XSSFWorkbook book)
{
XSSFFont font = workBook.createFont();
font.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 12);
font.setBoldweight(XSSFFont.BOLDWEIGHT_BOLD);
font.setFontName("Times New Roman");
return(font);
}
. . .
HSSFCellStyle style = book.createCellStyle();
style.setFont(createCellFont(book));
Примеры создания файлов Excel и определение стилей ячеек рассмотрены
здесь.
Apache POI is a powerful Java library to work with different Microsoft Office file formats such as Excel, Power point, Visio, MS Word etc. The name POI was originally an acronym for Poor Obfuscation Implementation, referring humorously to the fact that the file formats seemed to be deliberately obfuscated, but poorly, since they were successfully reverse-engineered. In this tutorial we will use Apache POI library to perform different functions on Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. Let’s get started.
Tools & Technologies:
- Java JDK 1.5 or above
- Apache POI library v3.8 or above (download)
- Eclipse 3.2 above (optional)
1. Add Apache POI dependency
Make sure to include apache poi jar file to your project. If your project uses Maven as dependency management, add following in your Pom.xml file.
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId> <artifactId>poi</artifactId> <version>3.8</version> </dependency>
If you are not using Maven then you can directly add required JAR files in your classpath.
- Download
poi-2.5.1.jar(or in this case 3.8) jar file. - Include this file in your projects class path.
- Create new java project in eclipse with auto generated main function.
2. Read Excel File
To read an excel file, Apache POI provides certain easy-to-use APIs. In below sample code we use different classes from POI library to read content of cell from excel file. This is for quick reference.
Code language: Java (java)
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet; import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook; //.. FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(new File("C:\test.xls")); //Get the workbook instance for XLS file HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(file); //Get first sheet from the workbook HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0); //Get iterator to all the rows in current sheet Iterator<Row> rowIterator = sheet.iterator(); //Get iterator to all cells of current row Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
Notice how each class in POI library starts with HSSF prefix! e.g. HSSFWorkbook, HSSFSheet etc. HSSF stands for Horrible SpreadSheet Format! I’m not kidding.. It really is. Similar to HSSF, POI has different prefix for other file formats too:
- HSSF (Horrible SpreadSheet Format) – reads and writes Microsoft Excel (XLS) format files.
- XSSF (XML SpreadSheet Format) – reads and writes Office Open XML (XLSX) format files.
- HPSF (Horrible Property Set Format) – reads “Document Summary” information from Microsoft Office files.
- HWPF (Horrible Word Processor Format) – aims to read and write Microsoft Word 97 (DOC) format files.
- HSLF (Horrible Slide Layout Format) – a pure Java implementation for Microsoft PowerPoint files.
- HDGF (Horrible DiaGram Format) – an initial pure Java implementation for Microsoft Visio binary files.
- HPBF (Horrible PuBlisher Format) – a pure Java implementation for Microsoft Publisher files.
- HSMF (Horrible Stupid Mail Format) – a pure Java implementation for Microsoft Outlook MSG files
- DDF (Dreadful Drawing Format) – a package for decoding the Microsoft Office Drawing format.
Working with .xlsx files
The classes we used in above code snippet, HSSFWorkbook and HSSFSheet works for .xls format. In order to work with newer xls format viz .xlsx, you need to see newer POI classes like:
Code language: Java (java)
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet; import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet; //.. FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(new File("C:\test.xlsx")); //Get the workbook instance for XLS file XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook (file); //Get first sheet from the workbook XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0); //Get iterator to all the rows in current sheet Iterator<Row> rowIterator = sheet.iterator(); //Get iterator to all cells of current row Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
Use XSSFWorkbook and XSSFSheet class in all of the below examples in order to make them work with .xlsx files. Consider a sample excel file: test.xls
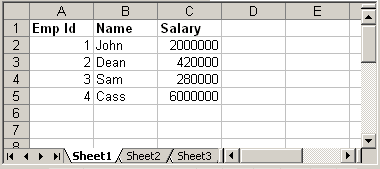
We will read above xls file using Apache POI and prints the data.
Code language: Java (java)
try { FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(new File("C:\test.xls")); //Get the workbook instance for XLS file HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(file); //Get first sheet from the workbook HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0); //Iterate through each rows from first sheet Iterator < Row > rowIterator = sheet.iterator(); while (rowIterator.hasNext()) { Row row = rowIterator.next(); //For each row, iterate through each columns Iterator < Cell > cellIterator = row.cellIterator(); while (cellIterator.hasNext()) { Cell cell = cellIterator.next(); switch (cell.getCellType()) { case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN: System.out.print(cell.getBooleanCellValue() + "tt"); break; case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC: System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue() + "tt"); break; case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING: System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue() + "tt"); break; } } System.out.println(""); } file.close(); FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\test.xls")); workbook.write(out); out.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
The above code is self explanatory. It read the sheet from workbook and iterate through each row and cell to print its values. Just note how we use different methods like getBooleanCellValue, getNumericCellValue etc to read cell value. Before reading a cell content, we need to first determine its type using method cell.getCellType() and then call appropriate method to read content. Output:
Code language: CSS (css)
Emp Id Name Salary 1.0 John 2000000.0 2.0 Dean 420000.0 3.0 Sam 280000.0 4.0 Cass 6000000.0
3. Create New Excel File
Let us create a new excel file and write data in it. Following is the API which we will use for this purpose.
Code language: Java (java)
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet; import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook; //.. HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Sample sheet"); //Create a new row in current sheet Row row = sheet.createRow(0); //Create a new cell in current row Cell cell = row.createCell(0); //Set value to new value cell.setCellValue("Blahblah");
Below is the complete code that writes a new excel with dummy data:
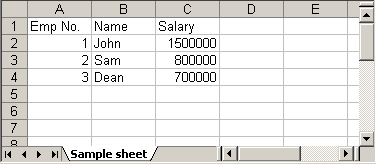
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Sample sheet"); Map < String, Object[] > data = new HashMap < String, Object[] > (); data.put("1", new Object[] { "Emp No.", "Name", "Salary" }); data.put("2", new Object[] { 1 d, "John", 1500000 d }); data.put("3", new Object[] { 2 d, "Sam", 800000 d }); data.put("4", new Object[] { 3 d, "Dean", 700000 d }); Set < String > keyset = data.keySet(); int rownum = 0; for (String key: keyset) { Row row = sheet.createRow(rownum++); Object[] objArr = data.get(key); int cellnum = 0; for (Object obj: objArr) { Cell cell = row.createCell(cellnum++); if (obj instanceof Date) cell.setCellValue((Date) obj); else if (obj instanceof Boolean) cell.setCellValue((Boolean) obj); else if (obj instanceof String) cell.setCellValue((String) obj); else if (obj instanceof Double) cell.setCellValue((Double) obj); } } try { FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\new.xls")); workbook.write(out); out.close(); System.out.println("Excel written successfully.."); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }Code language: Java (java)
Output:
new.xls
4. Update Existing Excel File
Updating an existing excel file is straight forward. Open the excel using different API that we discussed above and set the cell’s value. One thing we need to note here is that we can update the excel file only when we close it first.
update.xls
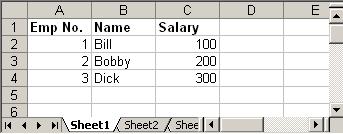
Following Java code read the above excel file and doubles the salary of each employee:
Code language: Java (java)
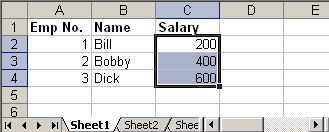
try { FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(new File("C:\update.xls")); HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(file); HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0); Cell cell = null; //Update the value of cell cell = sheet.getRow(1).getCell(2); cell.setCellValue(cell.getNumericCellValue() * 2); cell = sheet.getRow(2).getCell(2); cell.setCellValue(cell.getNumericCellValue() * 2); cell = sheet.getRow(3).getCell(2); cell.setCellValue(cell.getNumericCellValue() * 2); file.close(); FileOutputStream outFile = new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\update.xls")); workbook.write(outFile); outFile.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
Steps to update excel file will be:
- Open excel file in input mode (inputstream)
- Use POI API and read the excel content
- Update cell’s value using different
setCellValuemethods. - Close the excel input file (inputstream)
- Open same excel file in output mode (outputstream)
- Write content of updated workbook in output file
- Close output excel file
Output:
update.xls
5. Adding Formulas
Apache POI provides API to add excel formulas to cell programmatically. Following method that comes handy for this:
Code language: Java (java)
cell.setCellFormula("someformula")
For example:
Code language: Java (java)
cell.setCellFormula("A2*B2*C5") //or cell.setCellFormula("SUM(A1:A7)")
Note: Formula string should not start with equal sign (=) Thus, following is incorrect way of adding formula:
Code language: Java (java)
cell.setCellFormula("=A2*B2*C5") //Ops! Won't work
The above code will throw:
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
org.apache.poi.ss.formula.FormulaParseException: The specified formula '=A2*B2*C5' starts with an equals sign which is not allowed.
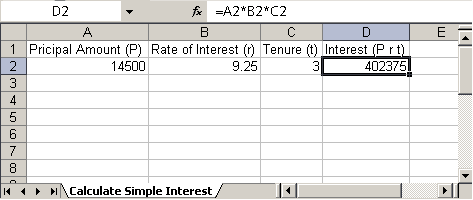
Following Java code creates a new excel sheet which calculates Simple Interest. It defines Principal amount, Rate of Interest and Tenure. We add an excel formula to calculate interest.
Code language: Java (java)
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Calculate Simple Interest"); Row header = sheet.createRow(0); header.createCell(0).setCellValue("Pricipal Amount (P)"); header.createCell(1).setCellValue("Rate of Interest (r)"); header.createCell(2).setCellValue("Tenure (t)"); header.createCell(3).setCellValue("Interest (P r t)"); Row dataRow = sheet.createRow(1); dataRow.createCell(0).setCellValue(14500 d); dataRow.createCell(1).setCellValue(9.25); dataRow.createCell(2).setCellValue(3 d); dataRow.createCell(3).setCellFormula("A2*B2*C2"); try { FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\formula.xls")); workbook.write(out); out.close(); System.out.println("Excel written successfully.."); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
Output:
formula.xls
Triggering Existing Excel Formulas
In certain cases your excel file might have formula defined and you may want to trigger those formulas since you updated it using POI. Following code snippet will do the trick.
Code language: Java (java)
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/somepath/test.xls"); Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook(fis); //or new XSSFWorkbook("C:\test.xls") FormulaEvaluator evaluator = wb.getCreationHelper().createFormulaEvaluator(); for (int sheetNum = 0; sheetNum < wb.getNumberOfSheets(); sheetNum++) { Sheet sheet = wb.getSheetAt(sheetNum); for (Row r: sheet) { for (Cell c: r) { if (c.getCellType() == Cell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA) { evaluator.evaluateFormulaCell(c); } } } }
We use FormulaEvaluator class to evaluate formula defined in each of the cell.
6. Adding Styles to Cell
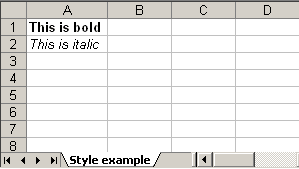
Adding style to a cell is also piece of cake. Check following example which creates two new cell one with bold font and another with italic and add text to it.
Code language: Java (java)
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Style example"); HSSFFont font = workbook.createFont(); font.setBoldweight(HSSFFont.BOLDWEIGHT_BOLD); HSSFCellStyle style = workbook.createCellStyle(); style.setFont(font); Row row = sheet.createRow(0); Cell cell = row.createCell(0); cell.setCellValue("This is bold"); cell.setCellStyle(style); font = workbook.createFont(); font.setItalic(true); style = workbook.createCellStyle(); style.setFont(font); row = sheet.createRow(1); cell = row.createCell(0); cell.setCellValue("This is italic"); cell.setCellStyle(style); try { FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\style.xls")); workbook.write(out); out.close(); System.out.println("Excel written successfully.."); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
Output:
style.xls
6.1 Add Background Color to the cell
Changing background color of the cell is a bit tricky. Ideally we assume setting background color will have some API like setFillBackgroundColor, but surprisingly to set background color of a cell, we have to set the foreground color :D. See below API.
cellStyle.setFillForegroundColor(HSSFColor.GREY_25_PERCENT.index);Code language: Java (java)
So use setFillForegroundColor method to set the background color of given cell. I hope this article is useful.
Learn how to create an Excel spreadsheet from within Java using Apache POI, a library for working with Microsoft Documents.
Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Maven Dependency
- 3. The Basics
- 4. The First Spreadsheet
- 5. Creating a Row and Cells
- 6. Auto Sizing Columns
- 7. Multi-Line Column
- 8. Adding Rows
- 9. Fixing “Number Stored As Text”
- 10. Using NumberFormat for Parsing
- 11. Setting Cell Style
- 12. Some More Formatting
- Summary
- See Also
- See Also
1. Introduction
Apache POI is a Java library to read and write Microsoft Documents including Word and Excel. Java Excel API can read and write Excel 97-2003 XLS files and also Excel 2007+ XLSX files. In this article, we show how to get going using the Apache POI library to work with Excel files.
2. Maven Dependency
You need the following maven dependency to work with Apache POI.
<poi.version>3.15</poi.version>
...
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>${poi.version}</version>
</dependency>
3. The Basics
Create an Excel 2007 XLSX file by using the class XSSFWorkbook as follows:
Workbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook();
To Work with the older Excel 97-2003 XLS format, use the following:
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
Once you have a Workbook, you can use the interfaces Sheet, Row, Cell, CellStyle to avoid tying your application to the version-specific interfaces.
4. The First Spreadsheet
Let’s say hello to a Hello-World spreadsheet created in Java. The code below creates an Excel spreadsheet with a single sheet named “Population”.
Workbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook();
String safeName = WorkbookUtil.createSafeSheetName("Population");
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet(safeName);
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("hello.xlsx");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
The WorkbookUtil.createSafeSheetName() is used since certain characters are invalid in a sheet name. This utility method replaces such characters with the space character.
5. Creating a Row and Cells
A Row object needs to be created inside a sheet before you can fill it with data. A sheet is considered to be comprised of a set or rows. Create a specific numbered row with the call:
int rowNum = 0; Row row = sheet.createRow((short)rowNum);
Let us now add some cells to this row. This row will serve as the header row since we will add some column titles to the row. There is no such concept of header row in Apache POI or Excel; we just treat the first row as such.
row.createCell(0).setCellValue(ch.createRichTextString("Rank"));
row.createCell(1).setCellValue(ch.createRichTextString("Country"));
row.createCell(2).setCellValue(ch.createRichTextString("Total(persons)"));
row.createCell(3).setCellValue(ch.createRichTextString("per sq.km"));
row.createCell(4).setCellValue(ch.createRichTextString("Date"));
Here is what the sheet looks like after adding the header row:
6. Auto Sizing Columns
You will notice that the columns are of equal size and some text in the columns is not visible. Wouldn’t it be nice to auto size the columns so all the text is visible? Here is how you can do it. Note that you should do this once just before writing the spreadsheet to a file to avoid having to resize columns when not required.
for (short i = sheet.getRow(0).getFirstCellNum(),
end = sheet.getRow(0).getLastCellNum() ; i < end ; i++) {
sheet.autoSizeColumn(i);
}
7. Multi-Line Column
In the above code, we might want to split the text in a column into multiple lines. This is not just a matter of inserting a new-line (or a carriage-return-new-line). You need to set the cell style to allow multi-line cells to show the data.
Assume we need to show a header cell in two lines:
Cell cell = row.createCell(2);
cell.setCellValue("Totalrn(persons)");
Once the data is inserted into the cell, set the cell style to allow wrapping.
CellStyle style = sheet.getWorkbook().createCellStyle(); style.setWrapText(true); cell.setCellStyle(style);
After this, the cell data shows multiple lines if required.
8. Adding Rows
Let us now add rows in a loop to our spreadsheet. The data we want to add looks like this:
List<List<String>> list = Arrays
.asList(Arrays.asList("1","China","1,378,020,000","147.75","2016"),
Arrays.asList("2","India","1,266,884,000","426.10","2016 WFB"),
Arrays.asList("3","United States of America","323,128,000","35.32","2016"),
Arrays.asList("4","Indonesia","257,453,000","142.12","2016"),
Arrays.asList("5","Brazil","206,081,000","24.66","2016"));
And here is the loop creating each row:
for (List<String> arr : list) {
row = sheet.createRow(rowNum); rowNum++;
row.createCell(0).setCellValue(arr.get(0));
row.createCell(1).setCellValue(arr.get(1));
row.createCell(2).setCellValue(arr.get(2));
row.createCell(3).setCellValue(arr.get(3));
row.createCell(4).setCellValue(arr.get(4));
}
The spreadsheet now looks like this. Notice that we have a few Excel errors: “Number Stored As Text”. That is because we are using Cell.setCellValue(String) method to set the cell value. Let us see how we can fix it.
9. Fixing “Number Stored As Text”
The solution is simple. Parse the text value to integer or double and use that to set the value. Pretty simple fix for the “Rank“.
int value = Integer.parseInt(arr.get(0)); row.createCell(0).setCellValue(value);
Similarly for the floating point value.
double value = Double.parseDouble(arr.get(3)); row.createCell(3).setCellValue(value);
After these changes, the error disappears on the two columns.
10. Using NumberFormat for Parsing
The fix for the Total field is a bit more involved. The numeric value is formatted with commas for the thousands-separator which we need to parse to obtain the value.
First we create a NumberFormat with the correct Locale. We store the NumberFormat for re-use (without recreating it every time).
private NumberFormat fmt = NumberFormat.getInstance(Locale.US);
We use the NumberFormat for parsing the string value into a double.
Cell cell = row.createCell(2);
String value = arr.get(2);
try {
Number n = fmt.parse(value);
cell.setCellValue(n.intValue());
} catch(java.text.ParseException ex) {
System.err.println("Row " + rowNum + ": " + value + ": " +
ex.getMessage());
}
With that update, the “Number Stored As Text” error has disappeared.
11. Setting Cell Style
However, we would still like to store the number with thousands-separator as before. For this, we need to tell Excel that the number is to be formatted with the correct formatter. This is done by setting the cell style. (The CellStyle is expensive to create and use. It should be created outside the loop and stored for reuse).
CellStyle popStyle = workbook.createCellStyle();
short format = (short)BuiltinFormats.getBuiltinFormat("#,##0");
popStyle.setDataFormat(format);
After the style is created, we need to set it on the cell.
Cell cell = row.createCell(2);
String value = arr.get(2);
try {
Number n = fmt.parse(value);
cell.setCellStyle(popStyle);
cell.setCellValue(n.intValue());
} catch(java.text.ParseException ex) {
System.err.println("Row " + rowNum + ": " + value + ": " +
ex.getMessage());
}
Now we can see that the numbers are formatted correctly.
12. Some More Formatting
The last bit of formatting we need is to eliminate the “Number Stored as Text” on the Date column. As you can see, some rows have an integer value and some have a non-numeric value mixed in. We handle that column as follows. Try to parse the value for a number to set it as a number, and if it fails set the value as a string.
String value = arr.get(4);
try {
int year = Integer.parseInt(value);
row.createCell(4).setCellValue(year);
} catch(NumberFormatException ex) {
row.createCell(4).setCellValue(value);
}
Looks like the spreadsheet is now all fixed up. Woo hoo!
Summary
And that was a beginner introduction to using the Apache POI library to create a spreadsheet. We have just scratched the surface of what the library can do. Hope you learned something useful today.
Check out the next part of this guide where we show you how to convert CSV to Excel along with more formatting examples.
See Also
- Apache POI Excel Example part 2








