Excel VBA AND Function
VBA AND function checks the provided statement whether it is true or false. AND function also evaluates the conditions with one another. If both the statements are true, the expression becomes true. Commonly this is associated with different decision-making loops to express the conditions. Comparing to all other logical operators AND returns true only if all the supplied conditions are true.
When you want to evaluate more than one expression and take decisions according to that then logical operators are the best option. AND operators connect two or more conditions together and evaluate the entire statement as a single expression. If all the statement is true, then the total expression returns true. If any expression evaluates false, then the entire statement will return false.
How to Use the AND Function in Excel VBA?
The logical AND can be used along with comparison operators, arithmetic operators, and text, etc. Any number of statements can be connected using AND. The logic behind AND operator is as follows.
| Condition 1 | Condition 2 | Result |
| TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| FALSE | TRUE | FALSE |
| FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
When more than two conditions are used, each condition should return true to make the entire expression true.
Syntax of VBA AND:
Format of VBA AND is expressed as,
[Condition1] And [Condition 2] And [Condition 3] And………. [Condition n]
- [Condition 1 to Condition n] can be a statement expressed using text and any operators.
You can download this VBA AND Excel Template here – VBA AND Excel Template
Example #1
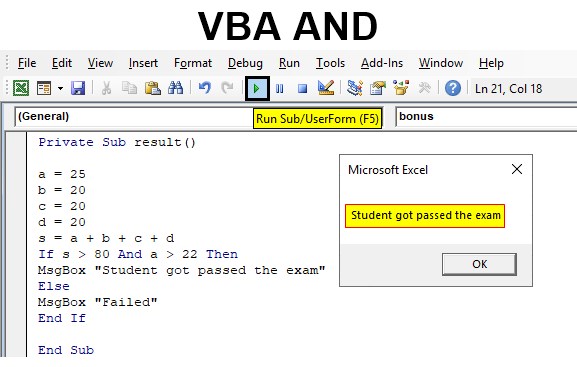
In this example, you can learn how to use AND function along with comparison operators. You have the marks scored by a student in a different subject. If the total comes more than 80 and 22 marks on the main subject the student got passed in the exam else fail. For this, follow the below steps:
Step 1: Insert a new module inside Visual Basic Editor (VBE). Click on Insert tab > select Module.
Step 2: Create a function named result in VBA to do the calculation and find the total mark of all subjects.
Code:
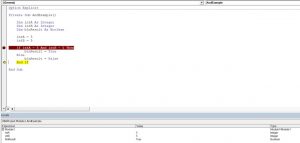
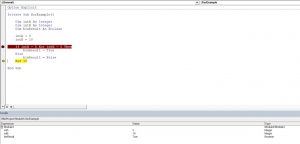
Private Sub result() End Sub
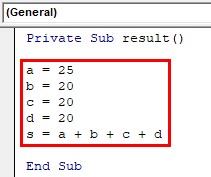
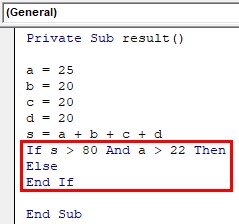
Step 3: Give the marks for different subjects. a, b, c, d are different subjects and the marks scored for each subject is as below. a is the main subject and s is the sum of all subjects a, b, c, d.
Code:
Private Sub result() a = 25 b = 20 c = 20 d = 20 s = a + b + c + d End Sub
Step 4: Now express the conditions as two statements and connect with AND function. IF …Else loop is used to execute the two different results according to the evaluation of the expression.
Code:
Private Sub result() a = 25 b = 20 c = 20 d = 20 s = a + b + c + d If s > 80 And a > 22 Then Else End If End Sub
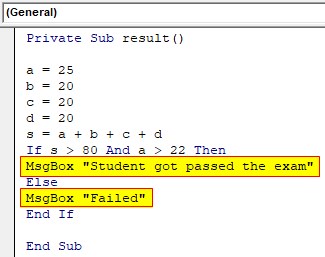
Step 5: Set the message to show according to the condition valuation. Where both conditions are true the entire expression becomes true and the true section of IF… Else loop will execute. Else the control will move to the false section.
Code:
Private Sub result() a = 25 b = 20 c = 20 d = 20 s = a + b + c + d If s > 80 And a > 22 Then MsgBox "Student got passed the exam" Else MsgBox "Failed" End If End Sub
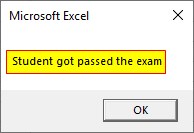
So if the sum is greater than 80 and the mark for the main subject ‘a’ is greater than 22 then the message “student got passed the exam” will show else fail is the result.
Step 6: Run this code by hitting the F5 or Run button which is placed on the topmost ribbon of VBE. The marks scored in the main subject is greater than 22 and the sum of all subject is greater than 80.
Here both the condition is true so the entire logical AND expression become true and the message in true section of IF… Else loop will be executed.
Example #2
There is no limit for giving the number of conditions with VBA AND. You can use ‘n’ number of conditions and VBA AND operator within a single expression. From an employee database, you have the attendance of a particular employee. You have the number of days that he was present in the office for the past 5 months. If the employee has 25 or more than 25 days’ attendance for every month, he is eligible for a bonus. For this, follow the below steps:
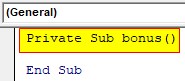
Step 1: In the same module let us start with another subprocedure.
Code:
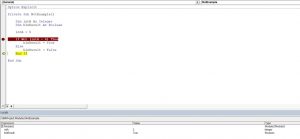
Private Sub bonus() End Sub
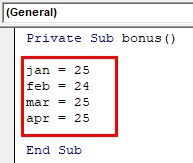
Step 2: To check the above conditions, start with a function ‘bonus’ and attendance for each month.
Private Sub bonus() jan = 25 feb = 24 mar = 25 apr = 25 End Sub
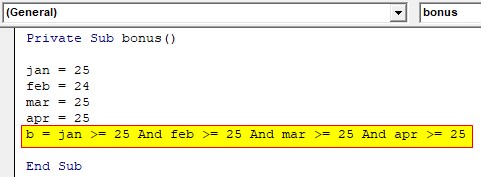
Step 3: Now, check each month’s attendance to confirm whether it is greater than or equal to 25. So multiple ‘AND’ operators are used to check the condition. The value of the entire expression is assigned to ‘b’ which returns a Boolean value.
Code:
Private Sub bonus() jan = 25 feb = 24 mar = 25 apr = 25 b = jan >= 25 And feb >= 25 And mar >= 25 And apr >= 25 End Sub
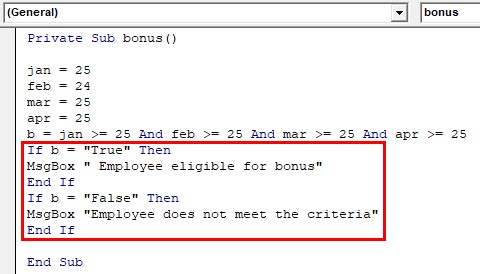
Step 4: According to this Boolean value, you can a loop. The value of ‘b’ should be true or false.
Code:
Private Sub bonus() jan = 25 feb = 24 mar = 25 apr = 25 b = jan >= 25 And feb >= 25 And mar >= 25 And apr >= 25 If b = "True" Then MsgBox " Employee eligible for bonus" End If If b = "False" Then MsgBox "Employee does not meet the criteria" End If End Sub
Two IF loops are set to execute according to the Boolean value of b. Here apart from Feb all month’s attendance is greater than or equal to 25. But even a single statement evaluates false the entire expression becomes false. ‘AND’ function returns false and the value of ‘b’ becomes false.
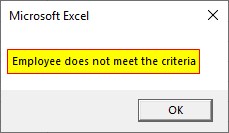
Step 5: So the second IF loop will be executed and the message within this will display as “Employee does not meet the criteria.
Here expression is evaluated as follows. First and last two conditions are true and the second condition is false. So while evaluating the entire expression, it becomes false.
Example #3
VBA AND to Evaluate User Credentials. Create a sign-in form using forms and controls in VBA which is available in the code window. For this, follow the below steps:
Step 1: Now Insert a new UserForm inside Visual Basic Editor (VBE). Click on Insert tab > select UserForm. Design a window using Toolbox with a user name, password and a sign-in button.
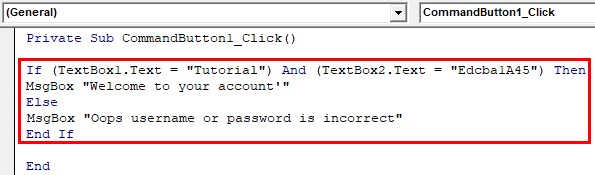
Step 2: Click the Sign-in button using the AND operator. Once the credentials are provided check the text value comes to both username and password textboxes, Textbox1 and Textbox 2. If the username is “Tutorial” and password is “Edcba1A45” then the credentials are correct and the user will be able to sign in and a welcome message will be displayed. Else error message is displayed.
Code:
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click() If (TextBox1.Text = "Tutorial") And (TextBox2.Text = "Edcba1A45") Then MsgBox "Welcome to your account'" Else MsgBox "Oops username or password is incorrect" End If End Sub
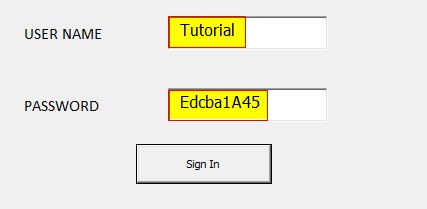
Step 3: Both conditions are expressed in an IF loop. AND operator evaluates these both conditions. Run the form using the run button and give username and password in the text field.
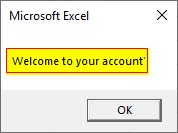
Since the username is “Tutorial” and password is “Edcba1A45” the AND operator returns a true and true block of IF loop will execute.
Things to Remember
- The logical AND function will always return a Boolean value true or false
- Commonly use with decision-making loops.
- Helps to compare ‘n’ number of expressions at a time by connecting with logical AND
- The entire statement returns true only if each statement is true.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the VBA AND. Here we discuss how to Use the AND Function in Excel VBA along with practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
- VBA PasteSpecial
- VBA Dynamic Array
- VBA ReDim Array
- VBA SubString
AND function is a logical function as well as a logical operator. We can have the “TRUE” result if all the conditions are fulfilled in this function. If any of the conditions fails, the output returns “FALSE.” We have a built-in AND command in VBA to use.
We hope you have reviewed our articles on “VBA OROr is a logical function in programming languages, and we have an OR function in VBA. The result given by this function is either true or false. It is used for two or many conditions together and provides true result when either of the conditions is returned true.read more” and “VBA IF ORIF OR is not a single statement; it is a pair of logical functions used together in VBA when we have more than one criteria to check, and when we use the if statement, we receive the true result if either of the criteria is met.read more.” This function is just the opposite of the OR function. In the OR function, to get the result as “TRUE,” we need any of the supplied logical conditions to be satisfied. But in the AND function, it is just the reverse. To get the “TRUE” result, all the supplied logical tests in excelA logical test in Excel results in an analytical output, either true or false. The equals to operator, “=,” is the most commonly used logical test.read more must be satisfied.
Look at the syntax of the AND function in excelThe AND function in Excel is classified as a logical function; it returns TRUE if the specified conditions are met, otherwise it returns FALSE.read more.
Table of contents
- Excel VBA AND Function
- Examples to Use VBA And Function
- Example #1
- Example #2
- Example #3
- Recommended Articles
- Examples to Use VBA And Function
[Logical Test] AND [Logical Test] AND [Logical Test]
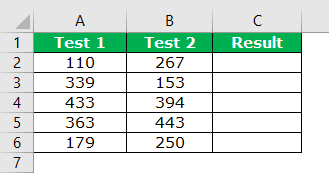
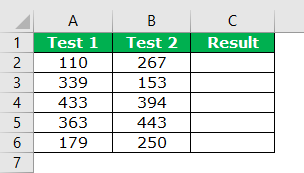
In the above, we have two test scores out of 600.
In the result column, we need to get the result as “TRUE” if the score of both the tests is greater than equal to 250.
For example, look at the below image.
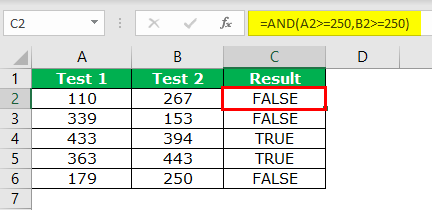
When we applied the logical function AND, we got the results. For example, in cells C4 and C5, we got the result as “TRUE” because Test 1 and Test 2 scores are greater than or equal to 250.
Look at the C6 cell here. We have got “FALSE” even though the score of Test 2 equals 250 because, in Test 1, the score is only 179.
Examples to Use VBA And Function
You can download this VBA AND Excel Template here – VBA AND Excel Template
Example #1
For example, we will test the numbers here, whether 25>=20 and 30<=31.
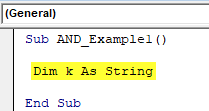
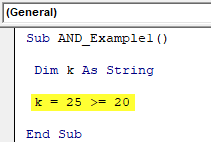
Step 1: Declare the variable as String.
Code:
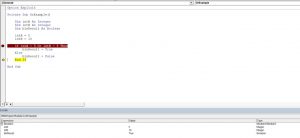
Sub AND_Example1() Dim K As String End Sub
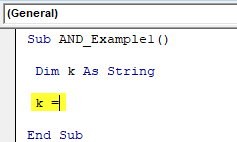
Step 2: For the variable “k,” we will assign the value by applying the AND function.
Code:
Sub AND_Example1() Dim K As String K = End Sub
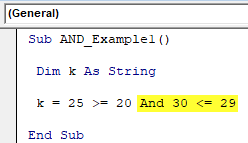
Step 3: Supply the first condition as 25>=20.
Code:
Sub AND_Example1() Dim K As String K = 25 >= 20 End Sub
Step 4: Now, open AND function and supply the second logical test, 30<=29.
Code:
Sub AND_Example1() Dim K As String K = 25 >= 20 And 30 <= 29 End Sub
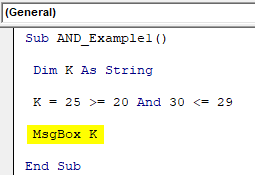
Step 5: Now, show the variable “k” result in the message box in VBAVBA MsgBox function is an output function which displays the generalized message provided by the developer. This statement has no arguments and the personalized messages in this function are written under the double quotes while for the values the variable reference is provided.read more.
Code:
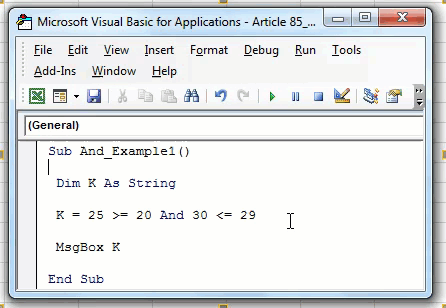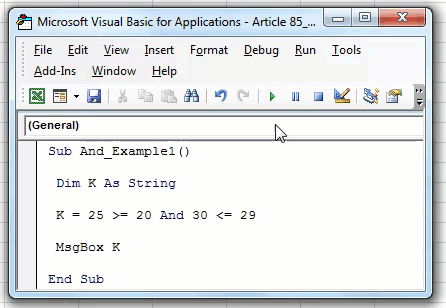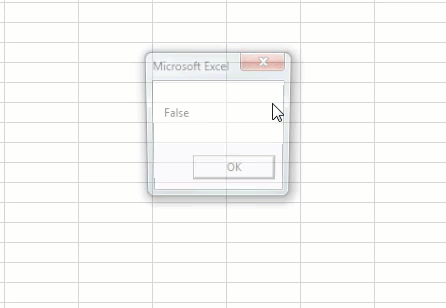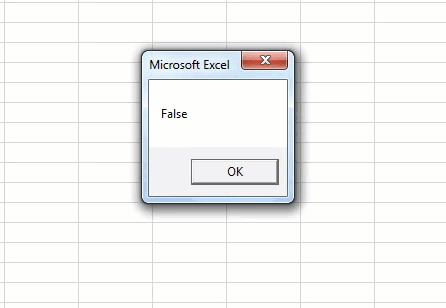
Sub AND_Example1() Dim K As String K = 25 >= 20 And 30 <= 29 MsgBox K End Sub
Run the macro to see what the result is.
We got the result as “FALSE” because we applied two conditions. The first condition 25>=20, this condition is satisfied, so the result is “TRUE.” However, the second condition, 30<=29, is not satisfied, so the result is “FALSE.” To get the result as TRUE, both the conditions should be satisfied.
Example #2
Now, we will change the logical test to “100>95 AND 100<200.”
Code:
Sub AND_Example2() Dim k As String k = 100 > 95 And 100 < 200 MsgBox k End Sub
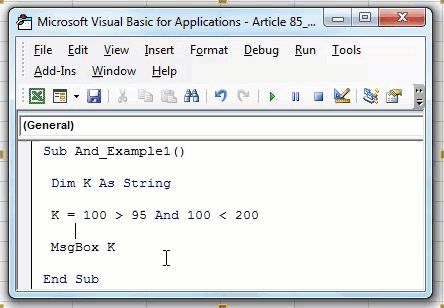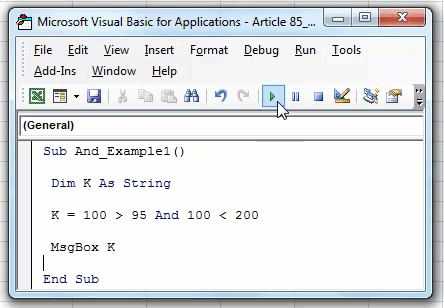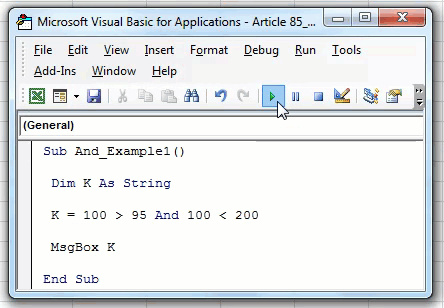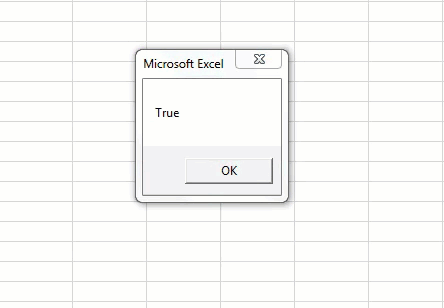
Run the code to see the result.
Here, we got “TRUE” as a result because:
1st Logical Test: 100 > 95 = TRUE
2nd Logical Test: 100 < 200 = TRUE
Our final result is “TRUE” since we got the “TRUE” results for both the logical tests.
Example #3
Now, we will see data from the worksheet. First, use the data we have used to show the example of the Excel AND function.
Here the condition is Test 1 Score >= 250 AND Test 2 Score >= 250.
Since we have more than one data cell, we need to use loops to avoid writing unnecessary and time-consuming lines of code. So, we have written the code below for you. The formula and logic are the same because we have only used “VBA For Next LoopAll programming languages make use of the VBA For Next loop. After the FOR statement, there is a criterion in this loop, and the code loops until the criteria are reached. read more.”
Code:
Sub AND_Example3() Dim k As Integer For k = 2 To 6 Cells(k, 3).Value = Cells(k, 1) >= 250 And Cells(k, 2) >= 250 Next k End Sub
It will give the same result as our worksheet function, but we will not get any formulas. We get only results.
Like this, we can apply the AND logical function to test multiple conditions, which should all be “TRUE” to arrive at the desired results.
It works opposite the OR function, where OR requires any supplied conditions to be “TRUE” to arrive at the results. But, AND function requires 100% result in a logical test to arrive at the results.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to VBA AND Function. Here, we learn how to use AND logical operator with practical examples and download an Excel template. You may also have a look at other articles related to Excel VBA: –
- Application.Match in VBA
- VBA Wait
- VBA DatePart
- Data Types in VBA
Содержание
- Оператор And (Visual Basic)
- Синтаксис
- Компоненты
- Комментарии
- Типы данных
- Пример 1
- Пример 2
- Оператор «И»
- Синтаксис
- Замечания
- Пример
- См. также
- Поддержка и обратная связь
- Logical Operators
- Logical Operator And
- Logical Operator Or
- Logical Operator Not
- VBA AND
- Excel VBA AND Function
- How to Use the AND Function in Excel VBA?
- Example #1
- Example #2
- Example #3
- Things to Remember
- Recommended Articles
Оператор And (Visual Basic)
Выполняет логическое соединение с двумя Boolean выражениями или побитовое соединение с двумя числовыми выражениями.
Синтаксис
Компоненты
result
Обязательный. Произвольное выражение типа Boolean или числового типа. Для логического сравнения result — это логическая комбинация двух Boolean значений. Для побитовых операций — это числовое значение, result представляющее побитовое соединение двух числовых битовых шаблонов.
expression1
Обязательный. Произвольное выражение типа Boolean или числового типа.
expression2
Обязательный. Произвольное выражение типа Boolean или числового типа.
Комментарии
Для логического сравнения имеет значение if и только в том случае, result если оба expression1 значения и expression2 имеют значение True . True В следующей таблице показано, как result определяется.
| Если expression1 имеет значение | И expression2 это | Значение равно result |
|---|---|---|
| True | True | True |
| True | False | False |
| False | True | False |
| False | False | False |
В логическом сравнении And оператор всегда вычисляет оба выражения, которые могут включать в себя вызовы процедур. Оператор AndAlso выполняет короткое замыкание, что означает, что если expression1 имеет значение False , то expression2 не вычисляется.
При применении к числовым значениям And оператор выполняет побитовое сравнение одинаково расположенных битов в двух числовых выражениях и задает соответствующий бит в в result соответствии со следующей таблицей.
| Если бит в имеет expression1 значение | И бит в expression2 является | Бит в result имеет значение |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
Так как логические и побитовые операторы имеют более низкий приоритет, чем другие арифметические и реляционные операторы, все побитовые операции должны быть заключены в круглые скобки, чтобы обеспечить точные результаты.
Типы данных
Если операнды состоят из одного Boolean выражения и одного числового выражения, Visual Basic преобразует Boolean выражение в числовое значение (–1 для True и 0 для False ) и выполняет побитовую операцию.
Для логического сравнения типом данных результата является Boolean . Для побитового сравнения результирующий тип данных является числовым типом, подходящим для типов expression1 данных и expression2 . См. таблицу «Реляционные и побитовые сравнения» в разделе Типы данных результатов оператора.
Оператор And может быть перегружен, что означает, что класс или структура могут переопределить свое поведение, если операнд имеет тип этого класса или структуры. Если код использует этот оператор для такого класса или структуры, убедитесь, что вы понимаете его переопределенное поведение. Для получения дополнительной информации см. Operator Procedures.
Пример 1
В следующем примере оператор используется And для выполнения логического соединения двух выражений. Результатом Boolean является значение, указывающее, являются ли оба выражения . True
В предыдущем примере приводятся результаты True и False соответственно.
Пример 2
В следующем примере оператор используется And для выполнения логического соединения с отдельными битами двух числовых выражений. Бит в результирующем шаблоне устанавливается, если для соответствующих битов в операндах задано значение 1.
Предыдущий пример дает результаты 8, 2 и 0 соответственно.
Источник
Оператор «И»
Используется для установления логической связи между двумя выражениями.
Синтаксис
Результат = expression1Иexpression2
Синтаксис оператора And состоит из таких частей:
| Part | Описание |
|---|---|
| result | Обязательный элемент; любая числовая переменная. |
| выражение1 | Обязательный элемент, любое допустимое выражение. |
| выражение2 | Обязательный элемент, любое допустимое выражение. |
Замечания
Если оба выражения будут оценены как True, result будет иметь значение True. Если любое из выражений имеет значение False, результат — False. В таблице ниже показано, как определяется значение result:
| Если expression1 равняется | И expression2 равняется | result представляет собой |
|---|---|---|
| True | False | False |
| True | Null | Null |
| False | True | False |
| False | False | False |
| False | Null | False |
| Null | True | Null |
| Null | False | False |
| Null | Null | Null |
Оператор And также выполняет побитовое сравнение аналогично расположенных битов двух числовых выражений и помещает соответствующий бит в result согласно этой таблице:
| Если бит в expression1 равняется | И бит в expression2 равняется | result представляет собой |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Пример
В примере показано, как оператор And логически соединяет два выражения.
См. также
Поддержка и обратная связь
Есть вопросы или отзывы, касающиеся Office VBA или этой статьи? Руководство по другим способам получения поддержки и отправки отзывов см. в статье Поддержка Office VBA и обратная связь.
Источник
Logical Operators
The three most used logical operators in Excel VBA are: And, Or and Not. As always, we will use easy examples to make things more clear.
Logical Operator And
Place a command button on your worksheet and add the following code lines:
Dim score1 As Integer , score2 As Integer , result As String
score1 = Range(«A1»).Value
score2 = Range(«B1»).Value
If score1 >= 60 And score2 > 1 Then
result = «pass»
Else
result = «fail»
End If
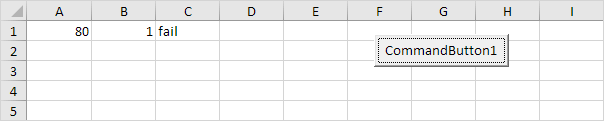
Explanation: if score1 is greater than or equal to 60 and score2 is greater than 1, Excel VBA returns pass, else Excel VBA returns fail.
Result when you click the command button on the sheet:
Conclusion: Excel VBA returns fail because score2 is not greater than 1.
Logical Operator Or
Place a command button on your worksheet and add the following code lines:
Dim score1 As Integer , score2 As Integer , result As String
score1 = Range(«A1»).Value
score2 = Range(«B1»).Value
If score1 >= 60 Or score2 > 1 Then
result = «pass»
Else
result = «fail»
End If
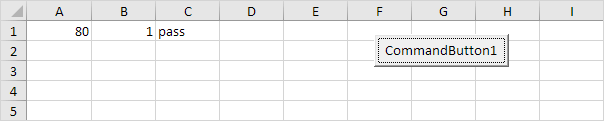
Explanation: if score1 is greater than or equal to 60 or score2 is greater than 1, Excel VBA returns pass, else Excel VBA returns fail.
Result when you click the command button on the sheet:
Conclusion: Excel VBA returns pass because score1 is greater than or equal to 60.
Logical Operator Not
Place a command button on your worksheet and add the following code lines:
Dim score1 As Integer , score2 As Integer , result As String
score1 = Range(«A1»).Value
score2 = Range(«B1»).Value
If score1 >= 60 And Not score2 = 1 Then
result = «pass»
Else
result = «fail»
End If
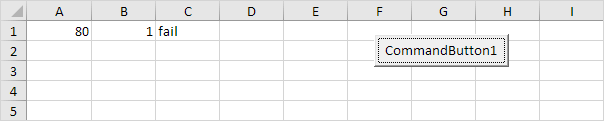
Explanation: if score1 is greater than or equal to 60 and score2 is not equal to 1, Excel VBA returns pass, else Excel VBA returns fail.
Result when you click the command button on the sheet:
Conclusion: Excel VBA returns fail because score2 is equal to 1.
Источник
VBA AND
Excel VBA AND Function
VBA AND function checks the provided statement whether it is true or false. AND function also evaluates the conditions with one another. If both the statements are true, the expression becomes true. Commonly this is associated with different decision-making loops to express the conditions. Comparing to all other logical operators AND returns true only if all the supplied conditions are true.
When you want to evaluate more than one expression and take decisions according to that then logical operators are the best option. AND operators connect two or more conditions together and evaluate the entire statement as a single expression. If all the statement is true, then the total expression returns true. If any expression evaluates false, then the entire statement will return false.
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Mobile Apps, Web Development & many more.
How to Use the AND Function in Excel VBA?
The logical AND can be used along with comparison operators, arithmetic operators, and text, etc. Any number of statements can be connected using AND. The logic behind AND operator is as follows.
| Condition 1 | Condition 2 | Result |
| TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| TRUE | FALSE | FALSE |
| FALSE | TRUE | FALSE |
| FALSE | FALSE | FALSE |
When more than two conditions are used, each condition should return true to make the entire expression true.
Syntax of VBA AND:
Format of VBA AND is expressed as,
[Condition1] And [Condition 2] And [Condition 3] And………. [Condition n]
- [Condition 1 to Condition n] can be a statement expressed using text and any operators.
Example #1
In this example, you can learn how to use AND function along with comparison operators. You have the marks scored by a student in a different subject. If the total comes more than 80 and 22 marks on the main subject the student got passed in the exam else fail. For this, follow the below steps:
Step 1: Insert a new module inside Visual Basic Editor (VBE). Click on Insert tab > select Module.
Step 2: Create a function named result in VBA to do the calculation and find the total mark of all subjects.
Code:
Step 3: Give the marks for different subjects. a, b, c, d are different subjects and the marks scored for each subject is as below. a is the main subject and s is the sum of all subjects a, b, c, d.
Code:
Step 4: Now express the conditions as two statements and connect with AND function. IF …Else loop is used to execute the two different results according to the evaluation of the expression.
Code:
Step 5: Set the message to show according to the condition valuation. Where both conditions are true the entire expression becomes true and the true section of IF… Else loop will execute. Else the control will move to the false section.
Code:
So if the sum is greater than 80 and the mark for the main subject ‘a’ is greater than 22 then the message “student got passed the exam” will show else fail is the result.
Step 6: Run this code by hitting the F5 or Run button which is placed on the topmost ribbon of VBE. The marks scored in the main subject is greater than 22 and the sum of all subject is greater than 80.
Here both the condition is true so the entire logical AND expression become true and the message in true section of IF… Else loop will be executed.
Example #2
There is no limit for giving the number of conditions with VBA AND. You can use ‘n’ number of conditions and VBA AND operator within a single expression. From an employee database, you have the attendance of a particular employee. You have the number of days that he was present in the office for the past 5 months. If the employee has 25 or more than 25 days’ attendance for every month, he is eligible for a bonus. For this, follow the below steps:
Step 1: In the same module let us start with another subprocedure.
Code:
Step 2: To check the above conditions, start with a function ‘bonus’ and attendance for each month.
Step 3: Now, check each month’s attendance to confirm whether it is greater than or equal to 25. So multiple ‘AND’ operators are used to check the condition. The value of the entire expression is assigned to ‘b’ which returns a Boolean value.
Code:
Step 4: According to this Boolean value, you can a loop. The value of ‘b’ should be true or false.
Code:
Two IF loops are set to execute according to the Boolean value of b. Here apart from Feb all month’s attendance is greater than or equal to 25. But even a single statement evaluates false the entire expression becomes false. ‘AND’ function returns false and the value of ‘b’ becomes false.
Step 5: So the second IF loop will be executed and the message within this will display as “Employee does not meet the criteria.
Here expression is evaluated as follows. First and last two conditions are true and the second condition is false. So while evaluating the entire expression, it becomes false.
Example #3
VBA AND to Evaluate User Credentials. Create a sign-in form using forms and controls in VBA which is available in the code window. For this, follow the below steps:
Step 1: Now Insert a new UserForm inside Visual Basic Editor (VBE). Click on Insert tab > select UserForm. Design a window using Toolbox with a user name, password and a sign-in button.
Step 2: Click the Sign-in button using the AND operator. Once the credentials are provided check the text value comes to both username and password textboxes, Textbox1 and Textbox 2. If the username is “Tutorial” and password is “Edcba1A45” then the credentials are correct and the user will be able to sign in and a welcome message will be displayed. Else error message is displayed.
Code:
Step 3: Both conditions are expressed in an IF loop. AND operator evaluates these both conditions. Run the form using the run button and give username and password in the text field.
Since the username is “Tutorial” and password is “Edcba1A45” the AND operator returns a true and true block of IF loop will execute.
Things to Remember
- The logical AND function will always return a Boolean value true or false
- Commonly use with decision-making loops.
- Helps to compare ‘n’ number of expressions at a time by connecting with logical AND
- The entire statement returns true only if each statement is true.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the VBA AND. Here we discuss how to Use the AND Function in Excel VBA along with practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –
Источник
This Excel tutorial explains how to use the Excel AND function (in VBA) with syntax and examples.
Description
The Microsoft Excel AND function returns TRUE if all conditions are TRUE. It returns FALSE if any of the conditions are FALSE.
The AND function is a built-in function in Excel that is categorized as a Logical Function. It can be used as a VBA function (VBA) in Excel. As a VBA function, you can use this function in macro code that is entered through the Microsoft Visual Basic Editor.
Please read our AND function (WS) page if you are looking for the worksheet version of the AND function as it has a very different syntax.
Syntax
The syntax for the AND function in Microsoft Excel is:
condition1 And condition2 [... And condition_n]
Parameters or Arguments
- condition1, condition2, … condition_n
- Expressions that you want to test that can either be TRUE or FALSE.
Returns
The AND function returns TRUE if all conditions are TRUE.
The AND function returns FALSE if any of the conditions are FALSE.
Applies To
- Excel for Office 365, Excel 2019, Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2011 for Mac, Excel 2010, Excel 2007, Excel 2003, Excel XP, Excel 2000
Type of Function
- VBA function (VBA)
Example (as VBA Function)
Let’s look at some Excel AND function examples and explore how to use the AND function in Excel VBA code.
This first example combines the AND function with the IF Statement in VBA code:
If LWebsite = "TechOnTheNet.com" And LPages <= 10 Then LBandwidth = "Low" Else LBandwidth = "High" End If
This would set the LBandwidth variable to the string value «Low» if both LWebsite was «TechOnTheNet.com» and LPages <= 10. Otherwise, it would set the LBandwidth variable to the string value «High».
This second example uses the AND function with the OR function in VBA, for example:
If (LWebsite = "TechOnTheNet.com" Or LWebsite = "CheckYourMath.com") And LPages <= 10 Then LBandwidth = "Low" Else LBandwidth = "High" End If
This would set the LBandwidth variable to the string value «Low» if LWebsite was either «TechOnTheNet.com» or «CheckYourMath.com» and LPages <= 10. Otherwise, it would set the LBandwidth variable to the string value «High».
In this Article
- Using the And Logical Operator
- Using the Or Logical Operator
- Using the Not Logical Operator
- Using the Xor Logical Operator
- Is Operator
- Like Operator
VBA allows you to use the logical operators And, Or, Not, Xor to compare values. The operators are considered “Boolean”, which means they return True or False as a result.
If you want to learn how to compare strings, click here: VBA Compare Strings – StrComp
If you want to learn how to use comparison operators, click here: VBA Comparison Operators – Not Equal to & More
Using the And Logical Operator
The And logical operator compares two or more conditions. If all the conditions are true, the operator will return True. If at least one of the conditions is not true, the operator will return False. Here is an example:
Dim intA As Integer
Dim intB As Integer
Dim blnResult As Boolean
intA = 5
intB = 5
If intA = 5 And intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfIn this example, we want to check if both intA and intB are equal to 5. If this is true, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set values of intA and intB to 5:
intA = 5
intB = 5After that, we use the And operator in the If statement to check if the values are equal to 5:
If intA = 5 And intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfAs both variables are equal to 5, the blnResult returns True:
Image 1. Using the And logical operator in VBA
Using the Or Logical Operator
The Or logical operator compares two or more conditions. If at least one of the conditions is true, it will return True. If none of the conditions are true, the operator will return False. Here is the code for the example:
Dim intA As Integer
Dim intB As Integer
Dim blnResult As Boolean
intA = 5
intB = 10
If intA = 5 Or intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfIn this example, we want to check if both intA is equal to 5. or intB is equal to 10. If any of these conditions is true, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set the value of intA to 5 and intB to 10:
intA = 5
intB = 10After that, we use the Or operator in the If statement to check if any of the values is equal to 5:
If intA = 5 Or intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfAs intA value is 5, the blnResult returns True:
Image 2. Using the Or logical operator in VBA
Using the Not Logical Operator
The Not logical operator checks one or more conditions. If the conditions are true, the operator returns False. Otherwise, it returns True. Here is the code for the example:
Dim intA As Integer
Dim blnResult As Boolean
intA = 5
If Not (intA = 6) Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfIn this example, we want to check if the value of intA is not equal to 6. If intA is different than 6, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set the value of intA to 5:
intA = 5After that, we use the Not operator in the If statement to check if the value of intA is different than 6:
If Not (intA = 6) Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfAs intA value is 5, the blnResult returns True:
Image 3. Using the Not logical operator in VBA
Using the Xor Logical Operator
The Xor logical operator compares two or more conditions. If exactly one of the conditions is true, it will return True. If none of the conditions are true, or more than one are true, it will return False. Here is the code for the example:
Dim intA As Integer
Dim intB As Integer
Dim blnResult As Boolean
intA = 5
intB = 10
If intA = 5 Xor intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfIn this example, we want to check if exactly one of the values (intA or IntB) are equal to 5. If only one condition is true, the value of Boolean blnResult will be True, otherwise, it will be False.
First, we set the value of intA to 5 and intB to 10:
intA = 5
intB = 10After that, we use the Or operator in the If statement to check if any of the values is equal to 5:
If intA = 5 Xor intB = 5 Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End IfAs intA value is 5 and intB is 10, the blnResult returns True:
Image 4. Using the Xor logical operator in VBA
Is Operator
The Is Operator tests if two object variables store the same object.
Let’s look at an example. Here we will assign two worksheets to worksheet objects rng1 and rng2, testing if the two worksheet objects store the same worksheet:
Sub CompareObjects()
Dim ws1 As Worksheet, ws2 As Worksheet
Set ws1 = Sheets("Sheet1")
Set ws2 = Sheets("Sheet2")
If ws1 Is ws2 Then
MsgBox "Same WS"
Else
MsgBox "Different WSs"
End If
End SubOf course the worksheet objects are not the same, so “Different WSs” is returned.
Like Operator
The Like Operator can compare two strings for inexact matches. This example will test if a string starts with “Mr.”
Sub LikeDemo()
Dim strName As String
Dim blnResult As Boolean
strName = "Mr. Michael James"
If strName Like "Mr*" Then
blnResult = True
Else
blnResult = False
End If
End SubVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!