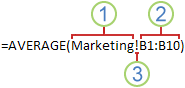Overview of formulas in Excel
Get started on how to create formulas and use built-in functions to perform calculations and solve problems.
Important: The calculated results of formulas and some Excel worksheet functions may differ slightly between a Windows PC using x86 or x86-64 architecture and a Windows RT PC using ARM architecture. Learn more about the differences.
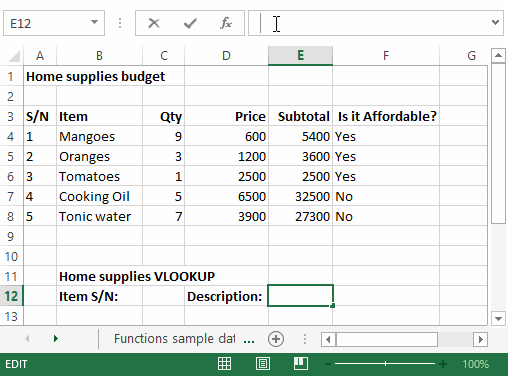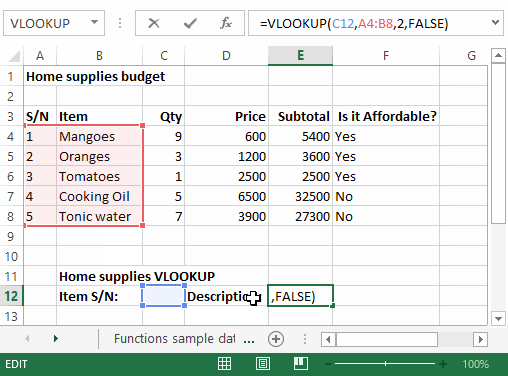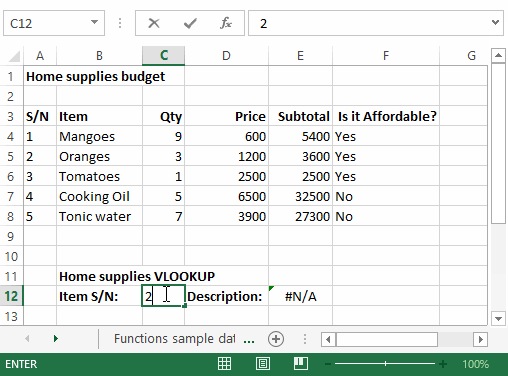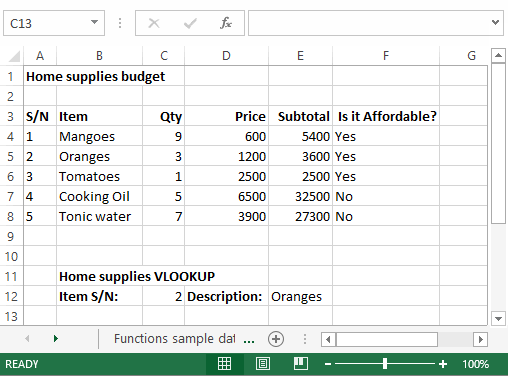
Important: In this article we discuss XLOOKUP and VLOOKUP, which are similar. Try using the new XLOOKUP function, an improved version of VLOOKUP that works in any direction and returns exact matches by default, making it easier and more convenient to use than its predecessor.
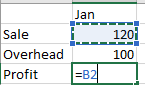
Create a formula that refers to values in other cells
-
Select a cell.
-
Type the equal sign =.
Note: Formulas in Excel always begin with the equal sign.
-
Select a cell or type its address in the selected cell.
-
Enter an operator. For example, – for subtraction.
-
Select the next cell, or type its address in the selected cell.
-
Press Enter. The result of the calculation appears in the cell with the formula.
See a formula
-
When a formula is entered into a cell, it also appears in the Formula bar.
-
To see a formula, select a cell, and it will appear in the formula bar.
Enter a formula that contains a built-in function
-
Select an empty cell.
-
Type an equal sign = and then type a function. For example, =SUM for getting the total sales.
-
Type an opening parenthesis (.
-
Select the range of cells, and then type a closing parenthesis).
-
Press Enter to get the result.
Download our Formulas tutorial workbook
We’ve put together a Get started with Formulas workbook that you can download. If you’re new to Excel, or even if you have some experience with it, you can walk through Excel’s most common formulas in this tour. With real-world examples and helpful visuals, you’ll be able to Sum, Count, Average, and Vlookup like a pro.
Formulas in-depth
You can browse through the individual sections below to learn more about specific formula elements.
A formula can also contain any or all of the following: functions, references, operators, and constants.
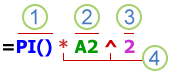
Parts of a formula
1. Functions: The PI() function returns the value of pi: 3.142…
2. References: A2 returns the value in cell A2.
3. Constants: Numbers or text values entered directly into a formula, such as 2.
4. Operators: The ^ (caret) operator raises a number to a power, and the * (asterisk) operator multiplies numbers.
A constant is a value that is not calculated; it always stays the same. For example, the date 10/9/2008, the number 210, and the text «Quarterly Earnings» are all constants. An expression or a value resulting from an expression is not a constant. If you use constants in a formula instead of references to cells (for example, =30+70+110), the result changes only if you modify the formula. In general, it’s best to place constants in individual cells where they can be easily changed if needed, then reference those cells in formulas.
A reference identifies a cell or a range of cells on a worksheet, and tells Excel where to look for the values or data you want to use in a formula. You can use references to use data contained in different parts of a worksheet in one formula or use the value from one cell in several formulas. You can also refer to cells on other sheets in the same workbook, and to other workbooks. References to cells in other workbooks are called links or external references.
-
The A1 reference style
By default, Excel uses the A1 reference style, which refers to columns with letters (A through XFD, for a total of 16,384 columns) and refers to rows with numbers (1 through 1,048,576). These letters and numbers are called row and column headings. To refer to a cell, enter the column letter followed by the row number. For example, B2 refers to the cell at the intersection of column B and row 2.
To refer to
Use
The cell in column A and row 10
A10
The range of cells in column A and rows 10 through 20
A10:A20
The range of cells in row 15 and columns B through E
B15:E15
All cells in row 5
5:5
All cells in rows 5 through 10
5:10
All cells in column H
H:H
All cells in columns H through J
H:J
The range of cells in columns A through E and rows 10 through 20
A10:E20
-
Making a reference to a cell or a range of cells on another worksheet in the same workbook
In the following example, the AVERAGE function calculates the average value for the range B1:B10 on the worksheet named Marketing in the same workbook.
1. Refers to the worksheet named Marketing
2. Refers to the range of cells from B1 to B10
3. The exclamation point (!) Separates the worksheet reference from the cell range reference
Note: If the referenced worksheet has spaces or numbers in it, then you need to add apostrophes (‘) before and after the worksheet name, like =’123′!A1 or =’January Revenue’!A1.
-
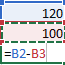
The difference between absolute, relative and mixed references
-
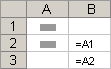
Relative references A relative cell reference in a formula, such as A1, is based on the relative position of the cell that contains the formula and the cell the reference refers to. If the position of the cell that contains the formula changes, the reference is changed. If you copy or fill the formula across rows or down columns, the reference automatically adjusts. By default, new formulas use relative references. For example, if you copy or fill a relative reference in cell B2 to cell B3, it automatically adjusts from =A1 to =A2.
Copied formula with relative reference
-
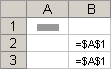
Absolute references An absolute cell reference in a formula, such as $A$1, always refer to a cell in a specific location. If the position of the cell that contains the formula changes, the absolute reference remains the same. If you copy or fill the formula across rows or down columns, the absolute reference does not adjust. By default, new formulas use relative references, so you may need to switch them to absolute references. For example, if you copy or fill an absolute reference in cell B2 to cell B3, it stays the same in both cells: =$A$1.
Copied formula with absolute reference
-
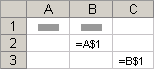
Mixed references A mixed reference has either an absolute column and relative row, or absolute row and relative column. An absolute column reference takes the form $A1, $B1, and so on. An absolute row reference takes the form A$1, B$1, and so on. If the position of the cell that contains the formula changes, the relative reference is changed, and the absolute reference does not change. If you copy or fill the formula across rows or down columns, the relative reference automatically adjusts, and the absolute reference does not adjust. For example, if you copy or fill a mixed reference from cell A2 to B3, it adjusts from =A$1 to =B$1.
Copied formula with mixed reference
-
-
The 3-D reference style
Conveniently referencing multiple worksheets If you want to analyze data in the same cell or range of cells on multiple worksheets within a workbook, use a 3-D reference. A 3-D reference includes the cell or range reference, preceded by a range of worksheet names. Excel uses any worksheets stored between the starting and ending names of the reference. For example, =SUM(Sheet2:Sheet13!B5) adds all the values contained in cell B5 on all the worksheets between and including Sheet 2 and Sheet 13.
-
You can use 3-D references to refer to cells on other sheets, to define names, and to create formulas by using the following functions: SUM, AVERAGE, AVERAGEA, COUNT, COUNTA, MAX, MAXA, MIN, MINA, PRODUCT, STDEV.P, STDEV.S, STDEVA, STDEVPA, VAR.P, VAR.S, VARA, and VARPA.
-
3-D references cannot be used in array formulas.
-
3-D references cannot be used with the intersection operator (a single space) or in formulas that use implicit intersection.
What occurs when you move, copy, insert, or delete worksheets The following examples explain what happens when you move, copy, insert, or delete worksheets that are included in a 3-D reference. The examples use the formula =SUM(Sheet2:Sheet6!A2:A5) to add cells A2 through A5 on worksheets 2 through 6.
-
Insert or copy If you insert or copy sheets between Sheet2 and Sheet6 (the endpoints in this example), Excel includes all values in cells A2 through A5 from the added sheets in the calculations.
-
Delete If you delete sheets between Sheet2 and Sheet6, Excel removes their values from the calculation.
-
Move If you move sheets from between Sheet2 and Sheet6 to a location outside the referenced sheet range, Excel removes their values from the calculation.
-
Move an endpoint If you move Sheet2 or Sheet6 to another location in the same workbook, Excel adjusts the calculation to accommodate the new range of sheets between them.
-
Delete an endpoint If you delete Sheet2 or Sheet6, Excel adjusts the calculation to accommodate the range of sheets between them.
-
-
The R1C1 reference style
You can also use a reference style where both the rows and the columns on the worksheet are numbered. The R1C1 reference style is useful for computing row and column positions in macros. In the R1C1 style, Excel indicates the location of a cell with an «R» followed by a row number and a «C» followed by a column number.
Reference
Meaning
R[-2]C
A relative reference to the cell two rows up and in the same column
R[2]C[2]
A relative reference to the cell two rows down and two columns to the right
R2C2
An absolute reference to the cell in the second row and in the second column
R[-1]
A relative reference to the entire row above the active cell
R
An absolute reference to the current row
When you record a macro, Excel records some commands by using the R1C1 reference style. For example, if you record a command, such as clicking the AutoSum button to insert a formula that adds a range of cells, Excel records the formula by using R1C1 style, not A1 style, references.
You can turn the R1C1 reference style on or off by setting or clearing the R1C1 reference style check box under the Working with formulas section in the Formulas category of the Options dialog box. To display this dialog box, click the File tab.
Top of Page
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
See Also
Switch between relative, absolute and mixed references for functions
Using calculation operators in Excel formulas
The order in which Excel performs operations in formulas
Using functions and nested functions in Excel formulas
Define and use names in formulas
Guidelines and examples of array formulas
Delete or remove a formula
How to avoid broken formulas
Find and correct errors in formulas
Excel keyboard shortcuts and function keys
Excel functions (by category)
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
MS Excel: Formulas and Functions — Listed by Category
Learn how to use all 300+ Excel formulas and functions including worksheet functions entered in the formula bar and VBA functions used in Macros.
Worksheet formulas are built-in functions that are entered as part of a formula in a cell. These are the most basic functions used when learning Excel. VBA functions are built-in functions that are used in Excel’s programming environment called Visual Basic for Applications (VBA).
Below is a list of Excel formulas sorted by category. If you would like an alphabetical list of these formulas, click on the following button:
Sort Alphabetically
(Enter a value in the field above to quickly find functions in the list below)
| ADDRESS (WS) | Returns a text representation of a cell address |
| AREAS (WS) | Returns the number of ranges in a reference |
| CHOOSE (WS, VBA) | Returns a value from a list of values based on a given position |
| COLUMN (WS) | Returns the column number of a cell reference |
| COLUMNS (WS) | Returns the number of columns in a cell reference |
| HLOOKUP (WS) | Performs a horizontal lookup by searching for a value in the top row of the table and returning the value in the same column based on the index_number |
| HYPERLINK (WS) | Creates a shortcut to a file or Internet address |
| INDEX (WS) | Returns either the value or the reference to a value from a table or range |
| INDIRECT (WS) | Returns the reference to a cell based on its string representation |
| LOOKUP (WS) | Returns a value from a range (one row or one column) or from an array |
| MATCH (WS) | Searches for a value in an array and returns the relative position of that item |
| OFFSET (WS) | Returns a reference to a range that is offset a number of rows and columns |
| ROW (WS) | Returns the row number of a cell reference |
| ROWS (WS) | Returns the number of rows in a cell reference |
| TRANSPOSE (WS) | Returns a transposed range of cells |
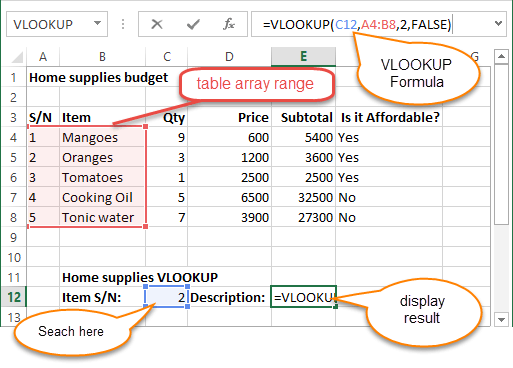
| VLOOKUP (WS) | Performs a vertical lookup by searching for a value in the first column of a table and returning the value in the same row in the index_number position |
| XLOOKUP (WS) | Performs a lookup (either vertical or horizontal) |
| ASC (VBA) | Returns ASCII value of a character |
| BAHTTEXT (WS) | Returns the number in Thai text |
| CHAR (WS) | Returns the character based on the ASCII value |
| CHR (VBA) | Returns the character based on the ASCII value |
| CLEAN (WS) | Removes all nonprintable characters from a string |
| CODE (WS) | Returns the ASCII value of a character or the first character in a cell |
| CONCAT (WS) | Used to join 2 or more strings together |
| CONCATENATE (WS) | Used to join 2 or more strings together (replaced by CONCAT Function) |
| CONCATENATE with & (WS, VBA) | Used to join 2 or more strings together using the & operator |
| DOLLAR (WS) | Converts a number to text, using a currency format |
| EXACT (WS) | Compares two strings and returns TRUE if both values are the same |
| FIND (WS) | Returns the location of a substring in a string (case-sensitive) |
| FIXED (WS) | Returns a text representation of a number rounded to a specified number of decimal places |
| FORMAT STRINGS (VBA) | Takes a string expression and returns it as a formatted string |
| INSTR (VBA) | Returns the position of the first occurrence of a substring in a string |
| INSTRREV (VBA) | Returns the position of the first occurrence of a string in another string, starting from the end of the string |
| LCASE (VBA) | Converts a string to lowercase |
| LEFT (WS, VBA) | Extract a substring from a string, starting from the left-most character |
| LEN (WS, VBA) | Returns the length of the specified string |
| LOWER (WS) | Converts all letters in the specified string to lowercase |
| LTRIM (VBA) | Removes leading spaces from a string |
| MID (WS, VBA) | Extracts a substring from a string (starting at any position) |
| NUMBERVALUE (WS) | Returns a text to a number specifying the decimal and group separators |
| PROPER (WS) | Sets the first character in each word to uppercase and the rest to lowercase |
| REPLACE (WS) | Replaces a sequence of characters in a string with another set of characters |
| REPLACE (VBA) | Replaces a sequence of characters in a string with another set of characters |
| REPT (WS) | Returns a repeated text value a specified number of times |
| RIGHT (WS, VBA) | Extracts a substring from a string starting from the right-most character |
| RTRIM (VBA) | Removes trailing spaces from a string |
| SEARCH (WS) | Returns the location of a substring in a string |
| SPACE (VBA) | Returns a string with a specified number of spaces |
| SPLIT (VBA) | Used to split a string into substrings based on a delimiter |
| STR (VBA) | Returns a string representation of a number |
| STRCOMP (VBA) | Returns an integer value representing the result of a string comparison |
| STRCONV (VBA) | Returns a string converted to uppercase, lowercase, proper case or Unicode |
| STRREVERSE (VBA) | Returns a string whose characters are in reverse order |
| SUBSTITUTE (WS) | Replaces a set of characters with another |
| T (WS) | Returns the text referred to by a value |
| TEXT (WS) | Returns a value converted to text with a specified format |
| TEXTJOIN (WS) | Used to join 2 or more strings together separated by a delimiter |
| TRIM (WS, VBA) | Returns a text value with the leading and trailing spaces removed |
| UCASE (VBA) | Converts a string to all uppercase |
| UNICHAR (WS) | Returns the Unicode character based on the Unicode number provided |
| UNICODE (WS) | Returns the Unicode number of a character or the first character in a string |
| UPPER (WS) | Convert text to all uppercase |
| VAL (VBA) | Returns the numbers found in a string |
| VALUE (WS) | Converts a text value that represents a number to a number |
| DATE (WS) | Returns the serial date value for a date |
| DATE (VBA) | Returns the current system date |
| DATEADD (VBA) | Returns a date after which a certain time/date interval has been added |
| DATEDIF (WS) | Returns the difference between two date values, based on the interval specified |
| DATEDIFF (VBA) | Returns the difference between two date values, based on the interval specified |
| DATEPART (VBA) | Returns a specified part of a given date |
| DATESERIAL (VBA) | Returns a date given a year, month, and day value |
| DATEVALUE (WS, VBA) | Returns the serial number of a date |
| DAY (WS, VBA) | Returns the day of the month (a number from 1 to 31) given a date value |
| DAYS (WS) | Returns the number of days between 2 dates |
| DAYS360 (WS) | Returns the number of days between two dates based on a 360-day year |
| EDATE (WS) | Adds a specified number of months to a date and returns the result as a serial date |
| EOMONTH (WS) | Calculates the last day of the month after adding a specified number of months to a date |
| FORMAT DATES (VBA) | Takes a date expression and returns it as a formatted string |
| HOUR (WS, VBA) | Returns the hours (a number from 0 to 23) from a time value |
| ISOWEEKNUM (WS) | Returns the ISO week number for a date |
| MINUTE (WS, VBA) | Returns the minutes (a number from 0 to 59) from a time value |
| MONTH (WS, VBA) | Returns the month (a number from 1 to 12) given a date value |
| MONTHNAME (VBA) | Returns a string representing the month given a number from 1 to 12 |
| NETWORKDAYS (WS) | Returns the number of work days between 2 dates, excluding weekends and holidays |
| NETWORKDAYS.INTL (WS) | Returns the number of work days between 2 dates, excluding weekends and holidays |
| NOW (WS, VBA) | Returns the current system date and time |
| SECOND (WS) | Returns the seconds (a number from 0 to 59) from a time value |
| TIME (WS) | Returns a decimal number given an hour, minute and second value |
| TIMESERIAL (VBA) | Returns a time given an hour, minute, and second value |
| TIMEVALUE (WS, VBA) | Returns the serial number of a time |
| TODAY (WS) | Returns the current system date |
| WEEKDAY (WS, VBA) | Returns a number representing the day of the week, given a date value |
| WEEKDAYNAME (VBA) | Returns a string representing the day of the week given a number from 1 to 7 |
| WEEKNUM (WS) | Returns the week number for a date |
| WORKDAY (WS) | Adds a specified number of work days to a date and returns the result as a serial date |
| WORKDAY.INTL (WS) | Adds a specified number of work days to a date and returns the result as a serial date (customizable weekends) |
| YEAR (WS, VBA) | Returns a four-digit year (a number from 1900 to 9999) given a date value |
| YEARFRAC (WS) | Returns the number of days between 2 dates as a year fraction |
| ABS (WS, VBA) | Returns the absolute value of a number |
| ACOS (WS) | Returns the arccosine (in radians) of a number |
| ACOSH (WS) | Returns the inverse hyperbolic cosine of a number |
| AGGREGATE (WS) | Apply functions such AVERAGE, SUM, COUNT, MAX or MIN and ignore errors or hidden rows |
| ASIN (WS) | Returns the arcsine (in radians) of a number |
| ASINH (WS) | Returns the inverse hyperbolic sine of a number |
| ATAN (WS) | Returns the arctangent (in radians) of a number |
| ATAN2 (WS) | Returns the arctangent (in radians) of (x,y) coordinates |
| ATANH (WS) | Returns the inverse hyperbolic tangent of a number |
| ATN (VBA) | Returns the arctangent of a number |
| CEILING (WS) | Returns a number rounded up based on a multiple of significance |
| CEILING.PRECISE (WS) | Returns a number rounded up to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance |
| COMBIN (WS) | Returns the number of combinations for a specified number of items |
| COMBINA (WS) | Returns the number of combinations for a specified number of items and includes repetitions |
| COS (WS, VBA) | Returns the cosine of an angle |
| COSH (WS) | Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a number |
| DEGREES (WS) | Converts radians into degrees |
| EVEN (WS) | Rounds a number up to the nearest even integer |
| EXP (WS, VBA) | Returns e raised to the nth power |
| FACT (WS) | Returns the factorial of a number |
| FIX (VBA) | Returns the integer portion of a number |
| FLOOR (WS) | Returns a number rounded down based on a multiple of significance |
| FORMAT NUMBERS (VBA) | Takes a numeric expression and returns it as a formatted string |
| INT (WS, VBA) | Returns the integer portion of a number |
| LN (WS) | Returns the natural logarithm of a number |
| LOG (WS) | Returns the logarithm of a number to a specified base |
| LOG (VBA) | Returns the natural logarithm of a number |
| LOG10 (WS) | Returns the base-10 logarithm of a number |
| MDETERM (WS) | Returns the matrix determinant of an array |
| MINVERSE (WS) | Returns the inverse matrix for a given matrix |
| MMULT (WS) | Returns the matrix product of two arrays |
| MOD (WS) | Returns the remainder after a number is divided by a divisor |
| MOD (VBA) | Returns the remainder after a number is divided by a divisor |
| ODD (WS) | Rounds a number up to the nearest odd integer |
| PI (WS) | Returns the mathematical constant called pi |
| POWER (WS) | Returns the result of a number raised to a given power |
| PRODUCT (WS) | Multiplies the numbers and returns the product |
| RADIANS (WS) | Converts degrees into radians |
| RAND (WS) | Returns a random number that is greater than or equal to 0 and less than 1 |
| RANDBETWEEN (WS) | Returns a random number that is between a bottom and top range |
| RANDOMIZE (VBA) | Used to change the seed value used by the random number generator for the RND function |
| RND (VBA) | Used to generate a random number (integer value) |
| ROMAN (WS) | Converts a number to roman numeral |
| ROUND (WS) | Returns a number rounded to a specified number of digits |
| ROUND (VBA) | Returns a number rounded to a specified number of digits |
| ROUNDDOWN (WS) | Returns a number rounded down to a specified number of digits |
| ROUNDUP (WS) | Returns a number rounded up to a specified number of digits |
| SGN (VBA) | Returns the sign of a number |
| SIGN (WS) | Returns the sign of a number |
| SIN (WS, VBA) | Returns the sine of an angle |
| SINH (WS) | Returns the hyperbolic sine of a number |
| SQR (VBA) | Returns the square root of a number |
| SQRT (WS) | Returns the square root of a number |
| SUBTOTAL (WS) | Returns the subtotal of the numbers in a column in a list or database |
| SUM (WS) | Adds all numbers in a range of cells |
| SUMIF (WS) | Adds all numbers in a range of cells based on one criteria |
| SUMIFS (WS) | Adds all numbers in a range of cells, based on a single or multiple criteria |
| SUMPRODUCT (WS) | Multiplies the corresponding items in the arrays and returns the sum of the results |
| SUMSQ (WS) | Returns the sum of the squares of a series of values |
| SUMX2MY2 (WS) | Returns the sum of the difference of squares between two arrays |
| SUMX2PY2 (WS) | Returns the sum of the squares of corresponding items in the arrays |
| SUMXMY2 (WS) | Returns the sum of the squares of the differences between corresponding items in the arrays |
| TAN (WS, VBA) | Returns the tangent of an angle |
| TANH (WS) | Returns the hyperbolic tangent of a number |
| TRUNC (WS) | Returns a number truncated to a specified number of digits |
| AVEDEV (WS) | Returns the average of the absolute deviations of the numbers provided |
| AVERAGE (WS) | Returns the average of the numbers provided |
| AVERAGEA (WS) | Returns the average of the numbers provided and treats TRUE as 1 and FALSE as 0 |
| AVERAGEIF (WS) | Returns the average of all numbers in a range of cells, based on a given criteria |
| AVERAGEIFS (WS) | Returns the average of all numbers in a range of cells, based on multiple criteria |
| BETA.DIST (WS) | Returns the beta distribution |
| BETA.INV (WS) | Returns the inverse of the cumulative beta probability density function |
| BETADIST (WS) | Returns the cumulative beta probability density function |
| BETAINV (WS) | Returns the inverse of the cumulative beta probability density function |
| BINOM.DIST (WS) | Returns the individual term binomial distribution probability |
| BINOM.INV (WS) | Returns the smallest value for which the cumulative binomial distribution is greater than or equal to a criterion |
| BINOMDIST (WS) | Returns the individual term binomial distribution probability |
| CHIDIST (WS) | Returns the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution |
| CHIINV (WS) | Returns the inverse of the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution |
| CHITEST (WS) | Returns the value from the chi-squared distribution |
| COUNT (WS) | Counts the number of cells that contain numbers as well as the number of arguments that contain numbers |
| COUNTA (WS) | Counts the number of cells that are not empty as well as the number of value arguments provided |
| COUNTBLANK (WS) | Counts the number of empty cells in a range |
| COUNTIF (WS) | Counts the number of cells in a range, that meets a given criteria |
| COUNTIFS (WS) | Counts the number of cells in a range, that meets a single or multiple criteria |
| COVAR (WS) | Returns the covariance, the average of the products of deviations for two data sets |
| FORECAST (WS) | Returns a prediction of a future value based on existing values provided |
| FREQUENCY (WS) | Returns how often values occur within a set of data. It returns a vertical array of numbers |
| GROWTH (WS) | Returns the predicted exponential growth based on existing values provided |
| INTERCEPT (WS) | Returns the y-axis intersection point of a line using x-axis values and y-axis values |
| LARGE (WS) | Returns the nth largest value from a set of values |
| LINEST (WS) | Uses the least squares method to calculate the statistics for a straight line and returns an array describing that line |
| MAX (WS) | Returns the largest value from the numbers provided |
| MAXA (WS) | Returns the largest value from the values provided (numbers, text and logical values) |
| MAXIFS (WS) | Returns the largest value in a range, that meets a single or multiple criteria |
| MEDIAN (WS) | Returns the median of the numbers provided |
| MIN (WS) | Returns the smallest value from the numbers provided |
| MINA (WS) | Returns the smallest value from the values provided (numbers, text and logical values) |
| MINIFS (WS) | Returns the smallest value in a range, that meets a single or multiple criteria |
| MODE (WS) | Returns most frequently occurring number |
| MODE.MULT (WS) | Returns a vertical array of the most frequently occurring numbers |
| MODE.SNGL (WS) | Returns most frequently occurring number |
| PERCENTILE (WS) | Returns the nth percentile from a set of values |
| PERCENTRANK (WS) | Returns the nth percentile from a set of values |
| PERMUT (WS) | Returns the number of permutations for a specified number of items |
| QUARTILE (WS) | Returns the quartile from a set of values |
| RANK (WS) | Returns the rank of a number within a set of numbers |
| SLOPE (WS) | Returns the slope of a regression line based on the data points identified by known_y_values and known_x_values |
| SMALL (WS) | Returns the nth smallest value from a set of values |
| STDEV (WS) | Returns the standard deviation of a population based on a sample of numbers |
| STDEVA (WS) | Returns the standard deviation of a population based on a sample of numbers, text, and logical values |
| STDEVP (WS) | Returns the standard deviation of a population based on an entire population of numbers |
| STDEVPA (WS) | Returns the standard deviation of a population based on an entire population of numbers, text, and logical values |
| VAR (WS) | Returns the variance of a population based on a sample of numbers |
| VARA (WS) | Returns the variance of a population based on a sample of numbers, text, and logical values |
| VARP (WS) | Returns the variance of a population based on an entire population of numbers |
| VARPA (WS) | Returns the variance of a population based on an entire population of numbers, text, and logical values |
| AND (WS) | Returns TRUE if all conditions are TRUE |
| AND (VBA) | Returns TRUE if all conditions are TRUE |
| CASE (VBA) | Has the functionality of an IF-THEN-ELSE statement |
| FALSE (WS) | Returns a logical value of FALSE |
| FOR…NEXT (VBA) | Used to create a FOR LOOP |
| IF (WS) | Returns one value if the condition is TRUE or another value if the condition is FALSE |
| IF (more than 7) (WS) | Nest more than 7 IF functions |
| IF (up to 7) (WS) | Nest up to 7 IF functions |
| IF-THEN-ELSE (VBA) | Returns a value if a specified condition evaluates to TRUE or another value if it evaluates to FALSE |
| IFERROR (WS) | Used to return an alternate value if a formula results in an error |
| IFNA (WS) | Used to return an alternate value if a formula results in #N/A error |
| IFS (WS) | Specify multiple IF conditions within 1 function |
| NOT (WS) | Returns the reversed logical value |
| OR (WS) | Returns TRUE if any of the conditions are TRUE |
| OR (VBA) | Returns TRUE if any of the conditions are TRUE |
| SWITCH (WS) | Compares an expression to a list of values and returns the corresponding result |
| SWITCH (VBA) | Evaluates a list of expressions and returns the corresponding value for the first expression in the list that is TRUE |
| TRUE (WS) | Returns a logical value of TRUE |
| WHILE…WEND (VBA) | Used to create a WHILE LOOP |
| CELL (WS) | Used to retrieve information about a cell such as contents, formatting, size, etc. |
| ENVIRON (VBA) | Returns the value of an operating system environment variable |
| ERROR.TYPE (WS) | Returns the numeric representation of an Excel error |
| INFO (WS) | Returns information about the operating environment |
| ISBLANK (WS) | Used to check for blank or null values |
| ISDATE (VBA) | Returns TRUE if the expression is a valid date |
| ISEMPTY (VBA) | Used to check for blank cells or uninitialized variables |
| ISERR (WS) | Used to check for error values except #N/A |
| ISERROR (WS, VBA) | Used to check for error values |
| ISLOGICAL (WS) | Used to check for a logical value (TRUE or FALSE) |
| ISNA (WS) | Used to check for #N/A error |
| ISNONTEXT (WS) | Used to check for a value that is not text |
| ISNULL (VBA) | Used to check for a NULL value |
| ISNUMBER (WS) | Used to check for a numeric value |
| ISNUMERIC (VBA) | Used to check for a numeric value |
| ISREF (WS) | Used to check for a reference |
| ISTEXT (WS) | Used to check for a text value |
| N (WS) | Converts a value to a number |
| NA (WS) | Returns the #N/A error value |
| TYPE (WS) | Returns the type of a value |
| ACCRINT (WS) | Returns the accrued interest for a security that pays interest on a periodic basis |
| ACCRINTM (WS) | Returns the accrued interest for a security that pays interest at maturity |
| AMORDEGRC (WS) | Returns the linear depreciation of an asset for each accounting period, on a prorated basis |
| AMORLINC (WS) | Returns the depreciation of an asset for each accounting period, on a prorated basis |
| DB (WS) | Returns the depreciation of an asset based on the fixed-declining balance method |
| DDB (WS, VBA) | Returns the depreciation of an asset based on the double-declining balance method |
| FV (WS, VBA) | Returns the future value of an investment |
| IPMT (WS, VBA) | Returns the interest payment for an investment |
| IRR (WS, VBA) | Returns the internal rate of return for a series of cash flows |
| ISPMT (WS) | Returns the interest payment for an investment |
| MIRR (WS, VBA) | Returns the modified internal rate of return for a series of cash flows |
| NPER (WS, VBA) | Returns the number of periods for an investment |
| NPV (WS, VBA) | Returns the net present value of an investment |
| PMT (WS, VBA) | Returns the payment amount for a loan |
| PPMT (WS, VBA) | Returns the payment on the principal for a particular payment |
| PV (WS, VBA) | Returns the present value of an investment |
| RATE (WS, VBA) | Returns the interest rate for an annuity |
| SLN (WS, VBA) | Returns the depreciation of an asset based on the straight-line depreciation method |
| SYD (WS, VBA) | Returns the depreciation of an asset based on the sum-of-years’ digits depreciation method |
| VDB (WS) | Returns the depreciation of an asset based on a variable declining balance depreciation method |
| XIRR (WS) | Returns the internal rate of return for a series of cash flows that may not be periodic |
| DAVERAGE (WS) | Averages all numbers in a column in a list or database, based on a given criteria |
| DCOUNT (WS) | Returns the number of cells in a column or database that contains numeric values and meets a given criteria |
| DCOUNTA (WS) | Returns the number of cells in a column or database that contains nonblank values and meets a given criteria |
| DGET (WS) | Retrieves from a database a single record that matches a given criteria |
| DMAX (WS) | Returns the largest number in a column in a list or database, based on a given criteria |
| DMIN (WS) | Returns the smallest number in a column in a list or database, based on a given criteria |
| DPRODUCT (WS) | Returns the product of the numbers in a column in a list or database, based on a given criteria |
| DSTDEV (WS) | Returns the standard deviation of a population based on a sample of numbers |
| DSTDEVP (WS) | Returns the standard deviation of a population based on the entire population of numbers |
| DSUM (WS) | Sums the numbers in a column or database that meets a given criteria |
| DVAR (WS) | Returns the variance of a population based on a sample of numbers |
| DVARP (WS) | Returns the variance of a population based on the entire population of numbers |
| BIN2DEC (WS) | Converts a binary number to a decimal number |
| BIN2HEX (WS) | Converts a binary number to a hexadecimal number |
| BIN2OCT (WS) | Converts a binary number to an octal number |
| COMPLEX (WS) | Converts coefficients (real and imaginary) into a complex number |
| CONVERT (WS) | Convert a number from one measurement unit to another measurement unit |
| CHDIR (VBA) | Used to change the current directory or folder |
| CHDRIVE (VBA) | Used to change the current drive |
| CURDIR (VBA) | Returns the current path |
| DIR (VBA) | Returns the first filename that matches the pathname and attributes specified |
| FILEDATETIME (VBA) | Returns the date and time of when a file was created or last modified |
| FILELEN (VBA) | Returns the size of a file in bytes |
| GETATTR (VBA) | Returns an integer that represents the attributes of a file, folder, or directory |
| MKDIR (VBA) | Used to create a new folder or directory |
| SETATTR (VBA) | Used to set the attributes of a file |
| CBOOL (VBA) | Converts a value to a boolean |
| CBYTE (VBA) | Converts a value to a byte (ie: number between 0 and 255) |
| CCUR (VBA) | Converts a value to currency |
| CDATE (VBA) | Converts a value to a date |
| CDBL (VBA) | Converts a value to a double |
| CDEC (VBA) | Converts a value to a decimal number |
| CINT (VBA) | Converts a value to an integer |
| CLNG (VBA) | Converts a value to a long integer |
| CSNG (VBA) | Converts a value to a single-precision number |
| CSTR (VBA) | Converts a value to a string |
| CVAR (VBA) | Converts a value to a variant |
More Lookup Functions
Other
In this post, you will find almost all excel functions and formulas in groups with short descriptions.
Function
You may find detailed information about certain formulas in our formulas section.
|
Lookup and Reference functions |
|
|
ADDRESS |
Returns a reference as text to a single cell in a worksheet |
|
AREAS |
Returns the number of areas in a reference |
|
CHOOSE |
Chooses a value from a list of values |
|
COLUMN |
Returns the column number of a reference |
|
COLUMNS |
Returns the number of columns in a reference |
|
HLOOKUP |
Looks in the top row of an array and returns the value of the indicated cell |
|
HYPERLINK |
Creates a shortcut or jump that opens a document stored on a network server, an intranet, or the Internet |
|
INDEX |
Uses an index to choose a value from a reference or array |
|
INDIRECT |
Returns a reference indicated by a text value |
|
LOOKUP |
Looks up values in a vector or array |
|
MATCH |
Looks up values in a reference or array |
|
OFFSET |
Returns a reference offset from a given reference |
|
ROW |
Returns the row number of a reference |
|
ROWS |
Returns the number of rows in a reference |
|
RTD |
Retrieves real-time data from a program that supports COM automation |
|
TRANSPOSE |
Returns the transpose of an array |
|
VLOOKUP |
Looks in the first column of an array and moves across the row to return the value of a cell |
|
Financial functions |
|
|
ACCRINT |
Returns the accrued interest for a security that pays periodic interest |
|
ACCRINTM |
Returns the accrued interest for a security that pays interest at maturity |
|
AMORDEGRC |
Returns the depreciation for each accounting period by using a depreciation coefficient |
|
AMORLINC |
Returns the depreciation for each accounting period |
|
COUPDAYBS |
Returns the number of days from the beginning of the coupon period to the settlement date |
|
COUPDAYS |
Returns the number of days in the coupon period that contains the settlement date |
|
COUPDAYSNC |
Returns the number of days from the settlement date to the next coupon date |
|
COUPNCD |
Returns the next coupon date after the settlement date |
|
COUPNUM |
Returns the number of coupons payable between the settlement date and maturity date |
|
COUPPCD |
Returns the previous coupon date before the settlement date |
|
CUMIPMT |
Returns the cumulative interest paid between two periods |
|
CUMPRINC |
Returns the cumulative principal paid on a loan between two periods |
|
DB |
Returns the depreciation of an asset for a specified period using the fixed-declining balance method |
|
DDB |
Returns the depreciation of an asset for a specified period using the double-declining balance method or some other method you specify |
|
DISC |
Returns the discount rate for a security |
|
DOLLARDE |
Converts a dollar price, expressed as a fraction, into a dollar price, expressed as a decimal number |
|
DOLLARFR |
Converts a dollar price, expressed as a decimal number, into a dollar price, expressed as a fraction |
|
DURATION |
Returns the annual duration of a security with periodic interest payments |
|
EFFECT |
Returns the effective annual interest rate |
|
FV |
Returns the future value of an investment |
|
FVSCHEDULE |
Returns the future value of an initial principal after applying a series of compound interest rates |
|
INTRATE |
Returns the interest rate for a fully invested security |
|
IPMT |
Returns the interest payment for an investment for a given period |
|
IRR |
Returns the internal rate of return for a series of cash flows |
|
ISPMT |
Calculates the interest paid during a specific period of an investment |
|
MDURATION |
Returns the Macauley modified duration for a security with an assumed par value of $100 |
|
MIRR |
Returns the internal rate of return where positive and negative cash flows are financed at different rates |
|
NOMINAL |
Returns the annual nominal interest rate |
|
NPER |
Returns the number of periods for an investment |
|
NPV |
Returns the net present value of an investment based on a series of periodic cash flows and a discount rate |
|
ODDFPRICE |
Returns the price per $100 face value of a security with an odd first period |
|
ODDFYIELD |
Returns the yield of a security with an odd first period |
|
ODDLPRICE |
Returns the price per $100 face value of a security with an odd last period |
|
ODDLYIELD |
Returns the yield of a security with an odd last period |
|
PMT |
Returns the periodic payment for an annuity |
|
PPMT |
Returns the payment on the principal for an investment for a given period |
|
PRICE |
Returns the price per $100 face value of a security that pays periodic interest |
|
PRICEDISC |
Returns the price per $100 face value of a discounted security |
|
PRICEMAT |
Returns the price per $100 face value of a security that pays interest at maturity |
|
PV |
Returns the present value of an investment |
|
RATE |
Returns the interest rate per period of an annuity |
|
RECEIVED |
Returns the amount received at maturity for a fully invested security |
|
SLN |
Returns the straight-line depreciation of an asset for one period |
|
SYD |
Returns the sum-of-years’ digits depreciation of an asset for a specified period |
|
TBILLEQ |
Returns the bond-equivalent yield for a Treasury bill |
|
TBILLPRICE |
Returns the price per $100 face value for a Treasury bill |
|
TBILLYIELD |
Returns the yield for a Treasury bill |
|
VDB |
Returns the depreciation of an asset for a specified or partial period using a declining balance method |
|
XIRR |
Returns the internal rate of return for a schedule of cash flows that is not necessarily periodic |
|
XNPV |
Returns the net present value for a schedule of cash flows that is not necessarily periodic |
|
YIELD |
Returns the yield on a security that pays periodic interest |
|
YIELDDISC |
Returns the annual yield for a discounted security; for example, a Treasury bill |
|
YIELDMAT |
Returns the annual yield of a security that pays interest at maturity |
|
Date and Time functions |
|
|
DATE |
Returns the serial number of a particular date |
|
DATEVALUE |
Converts a date in the form of text to a serial number |
|
DAY |
Converts a serial number to a day of the month |
|
DAYS360 |
Calculates the number of days between two dates based on a 360-day year |
|
EDATE |
Returns the serial number of the date that is the indicated number of months before or after the start date |
|
EOMONTH |
Returns the serial number of the last day of the month before or after a specified number of months |
|
HOUR |
Converts a serial number to an hour |
|
MINUTE |
Converts a serial number to a minute |
|
MONTH |
Converts a serial number to a month |
|
NETWORKDAYS |
Returns the number of whole workdays between two dates |
|
NOW |
Returns the serial number of the current date and time |
|
SECOND |
Converts a serial number to a second |
|
TIME |
Returns the serial number of a particular time |
|
TIMEVALUE |
Converts a time in the form of text to a serial number |
|
TODAY |
Returns the serial number of today’s date |
|
WEEKDAY |
Converts a serial number to a day of the week |
|
WEEKNUM |
Converts a serial number to a number representing where the week falls numerically with a year |
|
WORKDAY |
Returns the serial number of the date before or after a specified number of workdays |
|
YEAR |
Converts a serial number to a year |
|
YEARFRAC |
Returns the year fraction representing the number of whole days between start_date and end_date |
|
Math and Trigonometry functions |
|
|
ABS |
Returns the absolute value of a number |
|
ACOS |
Returns the arccosine of a number |
|
ACOSH |
Returns the inverse hyperbolic cosine of a number |
|
ASIN |
Returns the arcsine of a number |
|
ASINH |
Returns the inverse hyperbolic sine of a number |
|
ATAN |
Returns the arctangent of a number |
|
ATAN2 |
Returns the arctangent from x- and y-coordinates |
|
ATANH |
Returns the inverse hyperbolic tangent of a number |
|
CEILING |
Rounds a number to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance |
|
COMBIN |
Returns the number of combinations for a given number of objects |
|
COS |
Returns the cosine of a number |
|
COSH |
Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a number |
|
DEGREES |
Converts radians to degrees |
|
EVEN |
Rounds a number up to the nearest even integer |
|
EXP |
Returns e raised to the power of a given number |
|
FACT |
Returns the factorial of a number |
|
FACTDOUBLE |
Returns the double factorial of a number |
|
FLOOR |
Rounds a number down, toward zero |
|
GCD |
Returns the greatest common divisor |
|
INT |
Rounds a number down to the nearest integer |
|
LCM |
Returns the least common multiple |
|
LN |
Returns the natural logarithm of a number |
|
LOG |
Returns the logarithm of a number to a specified base |
|
LOG10 |
Returns the base-10 logarithm of a number |
|
MDETERM |
Returns the matrix determinant of an array |
|
MINVERSE |
Returns the matrix inverse of an array |
|
MMULT |
Returns the matrix product of two arrays |
|
MOD |
Returns the remainder from division |
|
MROUND |
Returns a number rounded to the desired multiple |
|
MULTINOMIAL |
Returns the multinomial of a set of numbers |
|
ODD |
Rounds a number up to the nearest odd integer |
|
PI |
Returns the value of pi |
|
POWER |
Returns the result of a number raised to a power |
|
PRODUCT |
Multiplies its arguments |
|
QUOTIENT |
Returns the integer portion of a division |
|
RADIANS |
Converts degrees to radians |
|
RAND |
Returns a random number between 0 and 1 |
|
RANDBETWEEN |
Returns a random number between the numbers you specify |
|
ROMAN |
Converts an arabic numeral to roman, as text |
|
ROUND |
Rounds a number to a specified number of digits |
|
ROUNDDOWN |
Rounds a number down, toward zero |
|
ROUNDUP |
Rounds a number up, away from zero |
|
SERIESSUM |
Returns the sum of a power series based on the formula |
|
SIGN |
Returns the sign of a number |
|
SIN |
Returns the sine of the given angle |
|
SINH |
Returns the hyperbolic sine of a number |
|
SQRT |
Returns a positive square root |
|
SQRTPI |
Returns the square root of (number * pi) |
|
SUBTOTAL |
Returns a subtotal in a list or database |
|
SUM |
Adds its arguments |
|
SUMIF |
Adds the cells specified by a given criteria |
|
SUMPRODUCT |
Returns the sum of the products of corresponding array components |
|
SUMSQ |
Returns the sum of the squares of the arguments |
|
SUMX2MY2 |
Returns the sum of the difference of squares of corresponding values in two arrays |
|
SUMX2PY2 |
Returns the sum of the sum of squares of corresponding values in two arrays |
|
SUMXMY2 |
Returns the sum of squares of differences of corresponding values in two arrays |
|
TAN |
Returns the tangent of a number |
|
TANH |
Returns the hyperbolic tangent of a number |
|
TRUNC |
Truncates a number to an integer |
|
Statistical functions |
|
|
AVEDEV |
Returns the average of the absolute deviations of data points from their mean |
|
AVERAGE |
Returns the average of its arguments |
|
AVERAGEA |
Returns the average of its arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
BETADIST |
Returns the beta cumulative distribution function |
|
BETAINV |
Returns the inverse of the cumulative distribution function for a specified beta distribution |
|
BINOMDIST |
Returns the individual term binomial distribution probability |
|
CHIDIST |
Returns the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution |
|
CHIINV |
Returns the inverse of the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution |
|
CHITEST |
Returns the test for independence |
|
CONFIDENCE |
Returns the confidence interval for a population mean |
|
CORREL |
Returns the correlation coefficient between two data sets |
|
COUNT |
Counts how many numbers are in the list of arguments |
|
COUNTA |
Counts how many values are in the list of arguments |
|
COUNTBLANK |
Counts the number of blank cells within a range |
|
COUNTIF |
Counts the number of nonblank cells within a range that meet the given criteria |
|
COVAR |
Returns covariance, the average of the products of paired deviations |
|
CRITBINOM |
Returns the smallest value for which the cumulative binomial distribution is less than or equal to a criterion value |
|
DEVSQ |
Returns the sum of squares of deviations |
|
EXPONDIST |
Returns the exponential distribution |
|
FDIST |
Returns the F probability distribution |
|
FINV |
Returns the inverse of the F probability distribution |
|
FISHER |
Returns the Fisher transformation |
|
FISHERINV |
Returns the inverse of the Fisher transformation |
|
FORECAST |
Returns a value along a linear trend |
|
FREQUENCY |
Returns a frequency distribution as a vertical array |
|
FTEST |
Returns the result of an F-test |
|
GAMMADIST |
Returns the gamma distribution |
|
GAMMAINV |
Returns the inverse of the gamma cumulative distribution |
|
GAMMALN |
Returns the natural logarithm of the gamma function, Γ(x) |
|
GEOMEAN |
Returns the geometric mean |
|
GROWTH |
Returns values along an exponential trend |
|
HARMEAN |
Returns the harmonic mean |
|
HYPGEOMDIST |
Returns the hypergeometric distribution |
|
INTERCEPT |
Returns the intercept of the linear regression line |
|
KURT |
Returns the kurtosis of a data set |
|
LARGE |
Returns the k-th largest value in a data set |
|
LINEST |
Returns the parameters of a linear trend |
|
LOGEST |
Returns the parameters of an exponential trend |
|
LOGINV |
Returns the inverse of the lognormal distribution |
|
LOGNORMDIST |
Returns the cumulative lognormal distribution |
|
MAX |
Returns the maximum value in a list of arguments |
|
MAXA |
Returns the maximum value in a list of arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
MEDIAN |
Returns the median of the given numbers |
|
MIN |
Returns the minimum value in a list of arguments |
|
MINA |
Returns the smallest value in a list of arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
MODE |
Returns the most common value in a data set |
|
NEGBINOMDIST |
Returns the negative binomial distribution |
|
NORMDIST |
Returns the normal cumulative distribution |
|
NORMINV |
Returns the inverse of the normal cumulative distribution |
|
NORMSDIST |
Returns the standard normal cumulative distribution |
|
NORMSINV |
Returns the inverse of the standard normal cumulative distribution |
|
PEARSON |
Returns the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient |
|
PERCENTILE |
Returns the k-th percentile of values in a range |
|
PERCENTRANK |
Returns the percentage rank of a value in a data set |
|
PERMUT |
Returns the number of permutations for a given number of objects |
|
POISSON |
Returns the Poisson distribution |
|
PROB |
Returns the probability that values in a range are between two limits |
|
QUARTILE |
Returns the quartile of a data set |
|
RANK |
Returns the rank of a number in a list of numbers |
|
RSQ |
Returns the square of the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient |
|
SKEW |
Returns the skewness of a distribution |
|
SLOPE |
Returns the slope of the linear regression line |
|
SMALL |
Returns the k-th smallest value in a data set |
|
STANDARDIZE |
Returns a normalized value |
|
STDEV |
Estimates standard deviation based on a sample |
|
STDEVA |
Estimates standard deviation based on a sample, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
STDEVP |
Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population |
|
STDEVPA |
Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
STEYX |
Returns the standard error of the predicted y-value for each x in the regression |
|
TDIST |
Returns the Student’s t-distribution |
|
TINV |
Returns the inverse of the Student’s t-distribution |
|
TREND |
Returns values along a linear trend |
|
TRIMMEAN |
Returns the mean of the interior of a data set |
|
TTEST |
Returns the probability associated with a Student’s t-test |
|
VAR |
Estimates variance based on a sample |
|
VARA |
Estimates variance based on a sample, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
VARP |
Calculates variance based on the entire population |
|
VARPA |
Calculates variance based on the entire population, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
WEIBULL |
Returns the Weibull distribution |
|
ZTEST |
Returns the one-tailed probability-value of a z-test |
|
Database and List Management functions |
|
|
DAVERAGE |
Returns the average of selected database entries |
|
DCOUNT |
Counts the cells that contain numbers in a database |
|
DCOUNTA |
Counts nonblank cells in a database |
|
DGET |
Extracts from a database a single record that matches the specified criteria |
|
DMAX |
Returns the maximum value from selected database entries |
|
DMIN |
Returns the minimum value from selected database entries |
|
DPRODUCT |
Multiplies the values in a particular field of records that match the criteria in a database |
|
DSTDEV |
Estimates the standard deviation based on a sample of selected database entries |
|
DSTDEVP |
Calculates the standard deviation based on the entire population of selected database entries |
|
DSUM |
Adds the numbers in the field column of records in the database that match the criteria |
|
DVAR |
Estimates variance based on a sample from selected database entries |
|
DVARP |
Calculates variance based on the entire population of selected database entries |
|
GETPIVOTDATA |
Returns data stored in a PivotTable |
|
Text and Data functions |
|
|
ASC |
Changes full-width (double-byte) English letters or katakana within a character string to half-width (single-byte) characters |
|
BAHTTEXT |
Converts a number to text, using the ß (baht) currency format |
|
CHAR |
Returns the character specified by the code number |
|
CLEAN |
Removes all nonprintable characters from text |
|
CODE |
Returns a numeric code for the first character in a text string |
|
CONCATENATE |
Joins several text items into one text item |
|
DOLLAR |
Converts a number to text, using the $ (dollar) currency format |
|
EXACT |
Checks to see if two text values are identical |
|
FIND |
Finds one text value within another (case-sensitive) |
|
FIXED |
Formats a number as text with a fixed number of decimals |
|
JIS |
Changes half-width (single-byte) English letters or katakana within a character string to full-width (double-byte) characters |
|
LEFT |
Returns the leftmost characters from a text value |
|
LEN |
Returns the number of characters in a text string |
|
LOWER |
Converts text to lowercase |
|
MID |
Returns a specific number of characters from a text string starting at the position you specify |
|
PHONETIC |
Extracts the phonetic (furigana) characters from a text string |
|
PROPER |
Capitalizes the first letter in each word of a text value |
|
REPLACE |
Replaces characters within text |
|
REPT |
Repeats text a given number of times |
|
RIGHT |
Returns the rightmost characters from a text value |
|
SEARCH |
Finds one text value within another (not case-sensitive) |
|
SUBSTITUTE |
Substitutes new text for old text in a text string |
|
T |
Converts its arguments to text |
|
TEXT |
Formats a number and converts it to text |
|
TRIM |
Removes spaces from text |
|
UPPER |
Converts text to uppercase |
|
VALUE |
Converts a text argument to a number |
|
Logical functions |
|
|
AND |
Returns TRUE if all its arguments are TRUE |
|
FALSE |
Returns the logical value FALSE |
|
IF |
Specifies a logical test to perform |
|
NOT |
Reverses the logic of its argument |
|
OR |
Returns TRUE if any argument is TRUE |
|
TRUE |
Returns the logical value TRUE |
|
Information functions |
|
|
CELL |
Returns information about the formatting, location, or contents of a cell |
|
ERROR.TYPE |
Returns a number corresponding to an error type |
|
INFO |
Returns information about the current operating environment |
|
ISBLANK |
Returns TRUE if the value is blank |
|
ISERR |
Returns TRUE if the value is any error value except #N/A |
|
ISERROR |
Returns TRUE if the value is any error value |
|
ISEVEN |
Returns TRUE if the number is even |
|
ISLOGICAL |
Returns TRUE if the value is a logical value |
|
ISNA |
Returns TRUE if the value is the #N/A error value |
|
ISNONTEXT |
Returns TRUE if the value is not text |
|
ISNUMBER |
Returns TRUE if the value is a number |
|
ISODD |
Returns TRUE if the number is odd |
|
ISREF |
Returns TRUE if the value is a reference |
|
ISTEXT |
Returns TRUE if the value is text |
|
N |
Returns a value converted to a number |
|
NA |
Returns the error value #N/A |
|
TYPE |
Returns a number indicating the data type of a value |
|
Engineering functions |
|
|
BESSELI |
Returns the modified Bessel function In(x) |
|
BESSELJ |
Returns the Bessel function Jn(x) |
|
BESSELK |
Returns the modified Bessel function Kn(x) |
|
BESSELY |
Returns the Bessel function Yn(x) |
|
BIN2DEC |
Converts a binary number to decimal |
|
BIN2HEX |
Converts a binary number to hexadecimal |
|
BIN2OCT |
Converts a binary number to octal |
|
COMPLEX |
Converts real and imaginary coefficients into a complex number |
|
CONVERT |
Converts a number from one measurement system to another |
|
DEC2BIN |
Converts a decimal number to binary |
|
DEC2HEX |
Converts a decimal number to hexadecimal |
|
DEC2OCT |
Converts a decimal number to octal |
|
DELTA |
Tests whether two values are equal |
|
ERF |
Returns the error function |
|
ERFC |
Returns the complementary error function |
|
GESTEP |
Tests whether a number is greater than a threshold value |
|
HEX2BIN |
Converts a hexadecimal number to binary |
|
HEX2DEC |
Converts a hexadecimal number to decimal |
|
HEX2OCT |
Converts a hexadecimal number to octal |
|
IMABS |
Returns the absolute value (modulus) of a complex number |
|
IMAGINARY |
Returns the imaginary coefficient of a complex number |
|
IMARGUMENT |
Returns the argument theta, an angle expressed in radians |
|
IMCONJUGATE |
Returns the complex conjugate of a complex number |
|
IMCOS |
Returns the cosine of a complex number |
|
IMDIV |
Returns the quotient of two complex numbers |
|
IMEXP |
Returns the exponential of a complex number |
|
IMLN |
Returns the natural logarithm of a complex number |
|
IMLOG10 |
Returns the base-10 logarithm of a complex number |
|
IMLOG2 |
Returns the base-2 logarithm of a complex number |
|
IMPOWER |
Returns a complex number raised to an integer power |
|
IMPRODUCT |
Returns the product of from 2 to 29 complex numbers |
|
IMREAL |
Returns the real coefficient of a complex number |
|
IMSIN |
Returns the sine of a complex number |
|
IMSQRT |
Returns the square root of a complex number |
|
IMSUB |
Returns the difference between two complex numbers |
|
IMSUM |
Returns the sum of complex numbers |
|
OCT2BIN |
Converts an octal number to binary |
|
OCT2DEC |
Converts an octal number to decimal |
|
OCT2HEX |
Converts an octal number to hexadecimal |
|
Lookup and Reference functions |
|
|
ADDRESS |
Returns a reference as text to a single cell in a worksheet |
|
AREAS |
Returns the number of areas in a reference |
|
CHOOSE |
Chooses a value from a list of values |
|
COLUMN |
Returns the column number of a reference |
|
COLUMNS |
Returns the number of columns in a reference |
|
HLOOKUP |
Looks in the top row of an array and returns the value of the indicated cell |
|
HYPERLINK |
Creates a shortcut or jump that opens a document stored on a network server, an intranet, or the Internet |
|
INDEX |
Uses an index to choose a value from a reference or array |
|
INDIRECT |
Returns a reference indicated by a text value |
|
LOOKUP |
Looks up values in a vector or array |
|
MATCH |
Looks up values in a reference or array |
|
OFFSET |
Returns a reference offset from a given reference |
|
ROW |
Returns the row number of a reference |
|
ROWS |
Returns the number of rows in a reference |
|
RTD |
Retrieves real-time data from a program that supports COM automation |
|
TRANSPOSE |
Returns the transpose of an array |
|
VLOOKUP |
Looks in the first column of an array and moves across the row to return the value of a cell |
|
Financial functions |
|
|
ACCRINT |
Returns the accrued interest for a security that pays periodic interest |
|
ACCRINTM |
Returns the accrued interest for a security that pays interest at maturity |
|
AMORDEGRC |
Returns the depreciation for each accounting period by using a depreciation coefficient |
|
AMORLINC |
Returns the depreciation for each accounting period |
|
COUPDAYBS |
Returns the number of days from the beginning of the coupon period to the settlement date |
|
COUPDAYS |
Returns the number of days in the coupon period that contains the settlement date |
|
COUPDAYSNC |
Returns the number of days from the settlement date to the next coupon date |
|
COUPNCD |
Returns the next coupon date after the settlement date |
|
COUPNUM |
Returns the number of coupons payable between the settlement date and maturity date |
|
COUPPCD |
Returns the previous coupon date before the settlement date |
|
CUMIPMT |
Returns the cumulative interest paid between two periods |
|
CUMPRINC |
Returns the cumulative principal paid on a loan between two periods |
|
DB |
Returns the depreciation of an asset for a specified period using the fixed-declining balance method |
|
DDB |
Returns the depreciation of an asset for a specified period using the double-declining balance method or some other method you specify |
|
DISC |
Returns the discount rate for a security |
|
DOLLARDE |
Converts a dollar price, expressed as a fraction, into a dollar price, expressed as a decimal number |
|
DOLLARFR |
Converts a dollar price, expressed as a decimal number, into a dollar price, expressed as a fraction |
|
DURATION |
Returns the annual duration of a security with periodic interest payments |
|
EFFECT |
Returns the effective annual interest rate |
|
FV |
Returns the future value of an investment |
|
FVSCHEDULE |
Returns the future value of an initial principal after applying a series of compound interest rates |
|
INTRATE |
Returns the interest rate for a fully invested security |
|
IPMT |
Returns the interest payment for an investment for a given period |
|
IRR |
Returns the internal rate of return for a series of cash flows |
|
ISPMT |
Calculates the interest paid during a specific period of an investment |
|
MDURATION |
Returns the Macauley modified duration for a security with an assumed par value of $100 |
|
MIRR |
Returns the internal rate of return where positive and negative cash flows are financed at different rates |
|
NOMINAL |
Returns the annual nominal interest rate |
|
NPER |
Returns the number of periods for an investment |
|
NPV |
Returns the net present value of an investment based on a series of periodic cash flows and a discount rate |
|
ODDFPRICE |
Returns the price per $100 face value of a security with an odd first period |
|
ODDFYIELD |
Returns the yield of a security with an odd first period |
|
ODDLPRICE |
Returns the price per $100 face value of a security with an odd last period |
|
ODDLYIELD |
Returns the yield of a security with an odd last period |
|
PMT |
Returns the periodic payment for an annuity |
|
PPMT |
Returns the payment on the principal for an investment for a given period |
|
PRICE |
Returns the price per $100 face value of a security that pays periodic interest |
|
PRICEDISC |
Returns the price per $100 face value of a discounted security |
|
PRICEMAT |
Returns the price per $100 face value of a security that pays interest at maturity |
|
PV |
Returns the present value of an investment |
|
RATE |
Returns the interest rate per period of an annuity |
|
RECEIVED |
Returns the amount received at maturity for a fully invested security |
|
SLN |
Returns the straight-line depreciation of an asset for one period |
|
SYD |
Returns the sum-of-years’ digits depreciation of an asset for a specified period |
|
TBILLEQ |
Returns the bond-equivalent yield for a Treasury bill |
|
TBILLPRICE |
Returns the price per $100 face value for a Treasury bill |
|
TBILLYIELD |
Returns the yield for a Treasury bill |
|
VDB |
Returns the depreciation of an asset for a specified or partial period using a declining balance method |
|
XIRR |
Returns the internal rate of return for a schedule of cash flows that is not necessarily periodic |
|
XNPV |
Returns the net present value for a schedule of cash flows that is not necessarily periodic |
|
YIELD |
Returns the yield on a security that pays periodic interest |
|
YIELDDISC |
Returns the annual yield for a discounted security; for example, a Treasury bill |
|
YIELDMAT |
Returns the annual yield of a security that pays interest at maturity |
|
Date and Time functions |
|
|
DATE |
Returns the serial number of a particular date |
|
DATEVALUE |
Converts a date in the form of text to a serial number |
|
DAY |
Converts a serial number to a day of the month |
|
DAYS360 |
Calculates the number of days between two dates based on a 360-day year |
|
EDATE |
Returns the serial number of the date that is the indicated number of months before or after the start date |
|
EOMONTH |
Returns the serial number of the last day of the month before or after a specified number of months |
|
HOUR |
Converts a serial number to an hour |
|
MINUTE |
Converts a serial number to a minute |
|
MONTH |
Converts a serial number to a month |
|
NETWORKDAYS |
Returns the number of whole workdays between two dates |
|
NOW |
Returns the serial number of the current date and time |
|
SECOND |
Converts a serial number to a second |
|
TIME |
Returns the serial number of a particular time |
|
TIMEVALUE |
Converts a time in the form of text to a serial number |
|
TODAY |
Returns the serial number of today’s date |
|
WEEKDAY |
Converts a serial number to a day of the week |
|
WEEKNUM |
Converts a serial number to a number representing where the week falls numerically with a year |
|
WORKDAY |
Returns the serial number of the date before or after a specified number of workdays |
|
YEAR |
Converts a serial number to a year |
|
YEARFRAC |
Returns the year fraction representing the number of whole days between start_date and end_date |
|
Math and Trigonometry functions |
|
|
ABS |
Returns the absolute value of a number |
|
ACOS |
Returns the arccosine of a number |
|
ACOSH |
Returns the inverse hyperbolic cosine of a number |
|
ASIN |
Returns the arcsine of a number |
|
ASINH |
Returns the inverse hyperbolic sine of a number |
|
ATAN |
Returns the arctangent of a number |
|
ATAN2 |
Returns the arctangent from x- and y-coordinates |
|
ATANH |
Returns the inverse hyperbolic tangent of a number |
|
CEILING |
Rounds a number to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance |
|
COMBIN |
Returns the number of combinations for a given number of objects |
|
COS |
Returns the cosine of a number |
|
COSH |
Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a number |
|
DEGREES |
Converts radians to degrees |
|
EVEN |
Rounds a number up to the nearest even integer |
|
EXP |
Returns e raised to the power of a given number |
|
FACT |
Returns the factorial of a number |
|
FACTDOUBLE |
Returns the double factorial of a number |
|
FLOOR |
Rounds a number down, toward zero |
|
GCD |
Returns the greatest common divisor |
|
INT |
Rounds a number down to the nearest integer |
|
LCM |
Returns the least common multiple |
|
LN |
Returns the natural logarithm of a number |
|
LOG |
Returns the logarithm of a number to a specified base |
|
LOG10 |
Returns the base-10 logarithm of a number |
|
MDETERM |
Returns the matrix determinant of an array |
|
MINVERSE |
Returns the matrix inverse of an array |
|
MMULT |
Returns the matrix product of two arrays |
|
MOD |
Returns the remainder from division |
|
MROUND |
Returns a number rounded to the desired multiple |
|
MULTINOMIAL |
Returns the multinomial of a set of numbers |
|
ODD |
Rounds a number up to the nearest odd integer |
|
PI |
Returns the value of pi |
|
POWER |
Returns the result of a number raised to a power |
|
PRODUCT |
Multiplies its arguments |
|
QUOTIENT |
Returns the integer portion of a division |
|
RADIANS |
Converts degrees to radians |
|
RAND |
Returns a random number between 0 and 1 |
|
RANDBETWEEN |
Returns a random number between the numbers you specify |
|
ROMAN |
Converts an arabic numeral to roman, as text |
|
ROUND |
Rounds a number to a specified number of digits |
|
ROUNDDOWN |
Rounds a number down, toward zero |
|
ROUNDUP |
Rounds a number up, away from zero |
|
SERIESSUM |
Returns the sum of a power series based on the formula |
|
SIGN |
Returns the sign of a number |
|
SIN |
Returns the sine of the given angle |
|
SINH |
Returns the hyperbolic sine of a number |
|
SQRT |
Returns a positive square root |
|
SQRTPI |
Returns the square root of (number * pi) |
|
SUBTOTAL |
Returns a subtotal in a list or database |
|
SUM |
Adds its arguments |
|
SUMIF |
Adds the cells specified by a given criteria |
|
SUMPRODUCT |
Returns the sum of the products of corresponding array components |
|
SUMSQ |
Returns the sum of the squares of the arguments |
|
SUMX2MY2 |
Returns the sum of the difference of squares of corresponding values in two arrays |
|
SUMX2PY2 |
Returns the sum of the sum of squares of corresponding values in two arrays |
|
SUMXMY2 |
Returns the sum of squares of differences of corresponding values in two arrays |
|
TAN |
Returns the tangent of a number |
|
TANH |
Returns the hyperbolic tangent of a number |
|
TRUNC |
Truncates a number to an integer |
|
Statistical functions |
|
|
AVEDEV |
Returns the average of the absolute deviations of data points from their mean |
|
AVERAGE |
Returns the average of its arguments |
|
AVERAGEA |
Returns the average of its arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
BETADIST |
Returns the beta cumulative distribution function |
|
BETAINV |
Returns the inverse of the cumulative distribution function for a specified beta distribution |
|
BINOMDIST |
Returns the individual term binomial distribution probability |
|
CHIDIST |
Returns the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution |
|
CHIINV |
Returns the inverse of the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution |
|
CHITEST |
Returns the test for independence |
|
CONFIDENCE |
Returns the confidence interval for a population mean |
|
CORREL |
Returns the correlation coefficient between two data sets |
|
COUNT |
Counts how many numbers are in the list of arguments |
|
COUNTA |
Counts how many values are in the list of arguments |
|
COUNTBLANK |
Counts the number of blank cells within a range |
|
COUNTIF |
Counts the number of nonblank cells within a range that meet the given criteria |
|
COVAR |
Returns covariance, the average of the products of paired deviations |
|
CRITBINOM |
Returns the smallest value for which the cumulative binomial distribution is less than or equal to a criterion value |
|
DEVSQ |
Returns the sum of squares of deviations |
|
EXPONDIST |
Returns the exponential distribution |
|
FDIST |
Returns the F probability distribution |
|
FINV |
Returns the inverse of the F probability distribution |
|
FISHER |
Returns the Fisher transformation |
|
FISHERINV |
Returns the inverse of the Fisher transformation |
|
FORECAST |
Returns a value along a linear trend |
|
FREQUENCY |
Returns a frequency distribution as a vertical array |
|
FTEST |
Returns the result of an F-test |
|
GAMMADIST |
Returns the gamma distribution |
|
GAMMAINV |
Returns the inverse of the gamma cumulative distribution |
|
GAMMALN |
Returns the natural logarithm of the gamma function, Γ(x) |
|
GEOMEAN |
Returns the geometric mean |
|
GROWTH |
Returns values along an exponential trend |
|
HARMEAN |
Returns the harmonic mean |
|
HYPGEOMDIST |
Returns the hypergeometric distribution |
|
INTERCEPT |
Returns the intercept of the linear regression line |
|
KURT |
Returns the kurtosis of a data set |
|
LARGE |
Returns the k-th largest value in a data set |
|
LINEST |
Returns the parameters of a linear trend |
|
LOGEST |
Returns the parameters of an exponential trend |
|
LOGINV |
Returns the inverse of the lognormal distribution |
|
LOGNORMDIST |
Returns the cumulative lognormal distribution |
|
MAX |
Returns the maximum value in a list of arguments |
|
MAXA |
Returns the maximum value in a list of arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
MEDIAN |
Returns the median of the given numbers |
|
MIN |
Returns the minimum value in a list of arguments |
|
MINA |
Returns the smallest value in a list of arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
MODE |
Returns the most common value in a data set |
|
NEGBINOMDIST |
Returns the negative binomial distribution |
|
NORMDIST |
Returns the normal cumulative distribution |
|
NORMINV |
Returns the inverse of the normal cumulative distribution |
|
NORMSDIST |
Returns the standard normal cumulative distribution |
|
NORMSINV |
Returns the inverse of the standard normal cumulative distribution |
|
PEARSON |
Returns the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient |
|
PERCENTILE |
Returns the k-th percentile of values in a range |
|
PERCENTRANK |
Returns the percentage rank of a value in a data set |
|
PERMUT |
Returns the number of permutations for a given number of objects |
|
POISSON |
Returns the Poisson distribution |
|
PROB |
Returns the probability that values in a range are between two limits |
|
QUARTILE |
Returns the quartile of a data set |
|
RANK |
Returns the rank of a number in a list of numbers |
|
RSQ |
Returns the square of the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient |
|
SKEW |
Returns the skewness of a distribution |
|
SLOPE |
Returns the slope of the linear regression line |
|
SMALL |
Returns the k-th smallest value in a data set |
|
STANDARDIZE |
Returns a normalized value |
|
STDEV |
Estimates standard deviation based on a sample |
|
STDEVA |
Estimates standard deviation based on a sample, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
STDEVP |
Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population |
|
STDEVPA |
Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
STEYX |
Returns the standard error of the predicted y-value for each x in the regression |
|
TDIST |
Returns the Student’s t-distribution |
|
TINV |
Returns the inverse of the Student’s t-distribution |
|
TREND |
Returns values along a linear trend |
|
TRIMMEAN |
Returns the mean of the interior of a data set |
|
TTEST |
Returns the probability associated with a Student’s t-test |
|
VAR |
Estimates variance based on a sample |
|
VARA |
Estimates variance based on a sample, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
VARP |
Calculates variance based on the entire population |
|
VARPA |
Calculates variance based on the entire population, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
WEIBULL |
Returns the Weibull distribution |
|
ZTEST |
Returns the one-tailed probability-value of a z-test |
|
Database and List Management functions |
|
|
DAVERAGE |
Returns the average of selected database entries |
|
DCOUNT |
Counts the cells that contain numbers in a database |
|
DCOUNTA |
Counts nonblank cells in a database |
|
DGET |
Extracts from a database a single record that matches the specified criteria |
|
DMAX |
Returns the maximum value from selected database entries |
|
DMIN |
Returns the minimum value from selected database entries |
|
DPRODUCT |
Multiplies the values in a particular field of records that match the criteria in a database |
|
DSTDEV |
Estimates the standard deviation based on a sample of selected database entries |
|
DSTDEVP |
Calculates the standard deviation based on the entire population of selected database entries |
|
DSUM |
Adds the numbers in the field column of records in the database that match the criteria |
|
DVAR |
Estimates variance based on a sample from selected database entries |
|
DVARP |
Calculates variance based on the entire population of selected database entries |
|
GETPIVOTDATA |
Returns data stored in a PivotTable |
|
Text and Data functions |
|
|
ASC |
Changes full-width (double-byte) English letters or katakana within a character string to half-width (single-byte) characters |
|
BAHTTEXT |
Converts a number to text, using the ß (baht) currency format |
|
CHAR |
Returns the character specified by the code number |
|
CLEAN |
Removes all nonprintable characters from text |
|
CODE |
Returns a numeric code for the first character in a text string |
|
CONCATENATE |
Joins several text items into one text item |
|
DOLLAR |
Converts a number to text, using the $ (dollar) currency format |
|
EXACT |
Checks to see if two text values are identical |
|
FIND |
Finds one text value within another (case-sensitive) |
|
FIXED |
Formats a number as text with a fixed number of decimals |
|
JIS |
Changes half-width (single-byte) English letters or katakana within a character string to full-width (double-byte) characters |
|
LEFT |
Returns the leftmost characters from a text value |
|
LEN |
Returns the number of characters in a text string |
|
LOWER |
Converts text to lowercase |
|
MID |
Returns a specific number of characters from a text string starting at the position you specify |
|
PHONETIC |
Extracts the phonetic (furigana) characters from a text string |
|
PROPER |
Capitalizes the first letter in each word of a text value |
|
REPLACE |
Replaces characters within text |
|
REPT |
Repeats text a given number of times |
|
RIGHT |
Returns the rightmost characters from a text value |
|
SEARCH |
Finds one text value within another (not case-sensitive) |
|
SUBSTITUTE |
Substitutes new text for old text in a text string |
|
T |
Converts its arguments to text |
|
TEXT |
Formats a number and converts it to text |
|
TRIM |
Removes spaces from text |
|
UPPER |
Converts text to uppercase |
|
VALUE |
Converts a text argument to a number |
|
Logical functions |
|
|
AND |
Returns TRUE if all its arguments are TRUE |
|
FALSE |
Returns the logical value FALSE |
|
IF |
Specifies a logical test to perform |
|
NOT |
Reverses the logic of its argument |
|
OR |
Returns TRUE if any argument is TRUE |
|
TRUE |
Returns the logical value TRUE |
|
Information functions |
|
|
CELL |
Returns information about the formatting, location, or contents of a cell |
|
ERROR.TYPE |
Returns a number corresponding to an error type |
|
INFO |
Returns information about the current operating environment |
|
ISBLANK |
Returns TRUE if the value is blank |
|
ISERR |
Returns TRUE if the value is any error value except #N/A |
|
ISERROR |
Returns TRUE if the value is any error value |
|
ISEVEN |
Returns TRUE if the number is even |
|
ISLOGICAL |
Returns TRUE if the value is a logical value |
|
ISNA |
Returns TRUE if the value is the #N/A error value |
|
ISNONTEXT |
Returns TRUE if the value is not text |
|
ISNUMBER |
Returns TRUE if the value is a number |
|
ISODD |
Returns TRUE if the number is odd |
|
ISREF |
Returns TRUE if the value is a reference |
|
ISTEXT |
Returns TRUE if the value is text |
|
N |
Returns a value converted to a number |
|
NA |
Returns the error value #N/A |
|
TYPE |
Returns a number indicating the data type of a value |
|
Engineering functions |
|
|
BESSELI |
Returns the modified Bessel function In(x) |
|
BESSELJ |
Returns the Bessel function Jn(x) |
|
BESSELK |
Returns the modified Bessel function Kn(x) |
|
BESSELY |
Returns the Bessel function Yn(x) |
|
BIN2DEC |
Converts a binary number to decimal |
|
BIN2HEX |
Converts a binary number to hexadecimal |
|
BIN2OCT |
Converts a binary number to octal |
|
COMPLEX |
Converts real and imaginary coefficients into a complex number |
|
CONVERT |
Converts a number from one measurement system to another |
|
DEC2BIN |
Converts a decimal number to binary |
|
DEC2HEX |
Converts a decimal number to hexadecimal |
|
DEC2OCT |
Converts a decimal number to octal |
|
DELTA |
Tests whether two values are equal |
|
ERF |
Returns the error function |
|
ERFC |
Returns the complementary error function |
|
GESTEP |
Tests whether a number is greater than a threshold value |
|
HEX2BIN |
Converts a hexadecimal number to binary |
|
HEX2DEC |
Converts a hexadecimal number to decimal |
|
HEX2OCT |
Converts a hexadecimal number to octal |
|
IMABS |
Returns the absolute value (modulus) of a complex number |
|
IMAGINARY |
Returns the imaginary coefficient of a complex number |
|
IMARGUMENT |
Returns the argument theta, an angle expressed in radians |
|
IMCONJUGATE |
Returns the complex conjugate of a complex number |
|
IMCOS |
Returns the cosine of a complex number |
|
IMDIV |
Returns the quotient of two complex numbers |
|
IMEXP |
Returns the exponential of a complex number |
|
IMLN |
Returns the natural logarithm of a complex number |
|
IMLOG10 |
Returns the base-10 logarithm of a complex number |
|
IMLOG2 |
Returns the base-2 logarithm of a complex number |
|
IMPOWER |
Returns a complex number raised to an integer power |
|
IMPRODUCT |
Returns the product of from 2 to 29 complex numbers |
|
IMREAL |
Returns the real coefficient of a complex number |
|
IMSIN |
Returns the sine of a complex number |
|
IMSQRT |
Returns the square root of a complex number |
|
IMSUB |
Returns the difference between two complex numbers |
|
IMSUM |
Returns the sum of complex numbers |
|
OCT2BIN |
Converts an octal number to binary |
|
OCT2DEC |
Converts an octal number to decimal |
|
OCT2HEX |
Converts an octal number to hexadecimal |
This is the list of all functions in Excel with a definition
of what they do.
The basics can be found
here for function on numbers,
here for functions on words.
A Formula is an expression that you create and which
calculates the value of a cell.
A Function is a predefined formula and is already available
in Excel (like Sinus, Logarithm, PMT, …) All the functions are listed here under.
In complex formulas, naming the cells is essential. Look
here how this is done. How to use the
name manager and have a readable spreadsheet.
- Date and Time Functions
- Lookup and reference function
- Engineering Functions
- Financial Functions
- Logical Functions
- Text Functions
- Math and trigonometry functions
- Statistical functions
- Database function
- Information functions
Date and time functions
Date and Time functions help you deal with dates and durations, and
birthdays and days until birthday, etc….. Beware it works only from 1
January 1900….. if you want to deal with the real past, then special tricks
and add in are needed.
DATE: The serial number of a particular date
DATEVALUE: Converts a date in the form of text to a serial number
DAY: Converts a serial number to a day of the month
DAYS360: Calculates the number of days between two dates based on a
360-day year
EDATE: The serial number of the date that is the indicated number of
months before or after the start date
EOMONTH: The serial number of the last day of the month before or after a
specified number of months
HOUR: Converts a serial number to an hour
MINUTE: Converts a serial number to a minute
MONTH: Converts a serial number to a month
NETWORKDAYS: The number of whole workdays between two dates
NOW: The serial number of the current date and time
SECOND: Converts a serial number to a second
TIME: The serial number of a particular time
TIMEVALUE: Converts a time in the form of text to a serial number
TODAY: The serial number of today’s date
WEEKDAY: Converts a serial number to a day of the week
WEEKNUM: Converts a serial number to a number representing where the week
falls numerically with a year
WORKDAY: The serial number of the date before or after a specified number
of workdays
YEAR: Converts a serial number to a year
YEARFRAC: The year fraction representing the number of whole days between
start_date and end_date
Lookup and reference function
In these functions, the most useful are VLookup and HLookup which allow
you to find items in rows or columns.
ADDRESS: A reference as text to a single cell in a worksheet:
AREAS: The number of areas in a reference (not so used)
CHOOSE: Chooses a value from a list of values
COLUMN: The column number of a reference
COLUMNS: The number of columns in a reference
GETPIVOTDATA: data stored in a PivotTable
HLOOKUP: Looks in the top row of an array and returns the value of the
indicated cell
HYPERLINK: Creates a shortcut or jump that opens a document stored on a
network server, an intranet, or the Internet
INDEX: Uses an index to choose a value from a reference or array
INDIRECT: A reference indicated by a text value.
Find the value of a cell by indicating its address in text form. Extremely useful.
LOOKUP: Looks up values in a vector or array
MATCH: Looks up values in a reference or array
OFFSET: A reference offset from a given reference. Here a good example to find the number of days in a month.
ROW: The row number of a reference
ROWS: The number of rows in a reference
RTD: Retrieves real-time data from a program that supports COM automation
TRANSPOSE: The transpose of an array
VLOOKUP: Looks in the first column of an array and moves across the row
to return the value of a cell
Logical functions or Boolean functions
Logical Functions are here to test statements like is this AND that both
TRUE and if this is the case then DO something…
AND: TRUE if all of its arguments are TRUE
FALSE: The logical value FALSE
IF: Specifies a logical test to perform
IFERROR: Handle if there is an error
NOT: Reverses the logic of its argument
OR: TRUE if any argument is TRUE
TRUE: The logical value TRUE
Text functions
These functions allow you to juggle with text. To convert, to extract, to
concatenate, to add and remove text from sentences, etc….Extremely useful.
ASC: Changes full-width (double-byte) English letters or katakana within
a character string to half-width (single-byte) characters
BAHTTEXT: Converts a number to text, using the ß (baht) currency format
CHAR: The character specified by the code number
CLEAN: Removes all nonprintable characters from text
CODE: A numeric code for the first character in a text string
CONCATENATE: Joins several text items into one text item. Second example of CONCATENATE in Excel is here.
DOLLAR: Converts a number to text, using the $ (dollar) currency format
EXACT: Checks to see if two text values are identical
FIND: Finds one text value within another (case-sensitive). Here another example.
FIXED: Formats a number as text with a fixed number of decimals
JIS: Changes half-width (single-byte) English letters or katakana within
a character string to full-width (double-byte) characters
LEFT(): The left most characters from a text value. Here some more on LEFT, LEFTB
LEN function: The number of characters in a text string, some other example of the LEN, LENB
LOWER: Converts text to lowercase. Another example for change to Lowercase is here.
MID, MIDB: A specific number of characters from a text string starting at
the position you specify. Here another example of MID, MIDB
PHONETIC: Extracts the phonetic (furigana) characters from a text string
PROPER: Capitalizes the first letter in each word of a text value
REPLACE, REPLACEB: Replaces characters within text
REPT: Repeats text a given number of times
RIGHT(): The rightmost characters from a text value: another example of RIGHT, RIGHTB
SEARCH, SEARCHB: Finds one text value within another (not case-sensitive). Another example here of the Search() function.
SUBSTITUTE: Substitutes new text for old text in a text string
T: Converts its arguments to text
TEXT: Formats a number and converts it to text
TRIM: Removes spaces from text
UPPER: Converts text to uppercase. Another example for changing to upper case in Excel is here.
VALUE: Converts a text argument to a number
Math and trigonometry functions
The math and trigonometry function are useful from early age math classes
for every student…. so use them wisely. You can trig, log, factorise and
inverse plus many more….
ABS: The absolute value of a number
ACOS: The arccosine of a number
ACOSH: The inverse hyperbolic cosine of a number
ACOT: inverse of the COT function
ACOTH: inverse hyperbolic cotangent of a number
ASIN: The arcsine of a number
ASINH: The inverse hyperbolic sine of a number
ATAN: The arctangent of a number
ATAN2: The arctangent from x- and y-coordinates
ATANH: The inverse hyperbolic tangent of a number
CSCH: Hyperbolic cosine of the number
CEILING: Rounds a number to the nearest integer or to the nearest
multiple of significance
COMBIN: The number of combinations for a given number of objects
COS: The cosine of an angle
COSH: The hyperbolic cosine of an angle
COT: returns the Cotangent of the angle
COTH: Hyperbolic cotangent of a number
CSC: Cosecant of an angle
DEGREES: Converts radians to degrees
EVEN: Rounds a number up to the nearest even integer
EXP: e raised to the power of a given number
FACT: The factorial of a number
FACTDOUBLE: The double factorial of a number
FLOOR: Rounds a number down, toward zero
GCD: The greatest common divisor
INT: Rounds a number down to the nearest integer
ISEVEN: boolean that determines if a number is even or odd
ISODD: boolean that determine if a number is odd (1, true) or even (0, false)
LCM: The least common multiple
LN: The natural logarithm of a number
LOG: The logarithm of a number to a specified base
LOG10: The base-10 logarithm of a number
MDETERM: The matrix determinant of an array
MINVERSE: The matrix inverse of an array
MMULT: The matrix product of two arrays
MOD: The remainder from division
MROUND: A number rounded to the desired multiple
MULTINOMIAL: The multinomial of a set of numbers
ODD: Rounds a number up to the nearest odd integer
PI: The value of pi. Used as PI().
POWER: The result of a number raised to a power
PRODUCT: Multiplies its arguments
QUOTIENT: The integer portion of a division
RADIANS: Converts degrees to radians
RAND: A random number between 0 and 1
RANDBETWEEN: A random number between the numbers you specify
ROMAN: Converts an arabic numeral to roman, as text
ROUND: Rounds a number to a specified number of digits
ROUNDDOWN: Rounds a number down, toward zero
ROUNDUP: Rounds a number up, away from zero
SEC: calculate the secant of an angle
SECH: Hyperbolic secant of the number
SERIESSUM: The sum of a power series based on the formula
SIGN: The sign of a number
SIN: The sine of the given angle
SINH: The hyperbolic sine of an angle
SQRT: A positive square root
SQRTPI: The square root of (number * pi)
SUBTOTAL: A subtotal in a list or database. Another example of Subtotal in Excel is here.
SUM: Adds its arguments
SUMIF: Adds the cells specified by a given criteria
SUMIFS: Adds the cells specified by more than one given criteria
SUMPRODUCT: The sum of the products of corresponding array components
SUMSQ: The sum of the squares of the arguments
SUMX2MY2: The sum of the difference of squares of corresponding values in
two arrays
SUMX2PY2: The sum of the sum of squares of corresponding values in two
arrays
SUMXMY2: The sum of squares of differences of corresponding values in two
arrays
TAN: The tangent of an angle
TANH: The hyperbolic tangent of an angle
TRUNC: Truncates a number to an integer
Statistical functions
Statistical function allow engineers, statistitian to calculate
probabilities of things happening or not….. you could use it to calculate
the next loto numbers…..
AVEDEV: The average of the absolute deviations of data points from their
mean
AVERAGE: The average of its arguments
AVERAGEA: The average of its arguments, including numbers, text, and
logical values
BETADIST: The beta cumulative distribution function
BETAINV: The inverse of the cumulative distribution function for a
specified beta distribution
BINOMDIST: The individual term binomial distribution probability
CHIDIST: The one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution
CHIINV: The inverse of the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared
distribution
CHITEST: The test for independence
CONFIDENCE: The confidence interval for a population mean
CORREL: The correlation coefficient between two data sets
COUNT: Counts how many numbers are in the list of arguments
COUNTA: Counts how many values are in the list of arguments
(does not count the empty cells)
COUNTBLANK: Counts the number of blank cells within a range
COUNTIF: Counts the number of nonblank cells within a range that meet the
given criteria (one only). A second example here.
COUNTIFS: Counts the number of nonblank cells within a range that meet multiple
given criteria
COVAR: covariance, the average of the products of paired deviations
CRITBINOM: The smallest value for which the cumulative binomial
distribution is less than or equal to a criterion value
DEVSQ: The sum of squares of deviations
EXPONDIST: The exponential distribution
FDIST: The F probability distribution
FINV: The inverse of the F probability distribution
FISHER: The Fisher transformation
FISHERINV: The inverse of the Fisher transformation
FORECAST: A value along a linear trend
FREQUENCY: A frequency distribution as a vertical array
FTEST: The result of an F-test
GAMMADIST: The gamma distribution
GAMMAINV: The inverse of the gamma cumulative distribution
GAMMALN: The natural logarithm of the gamma function, Γ(x)
GEOMEAN: The geometric mean
GROWTH: Values along an exponential trend
HARMEAN: The harmonic mean
HYPGEOMDIST: The hypergeometric distribution
INTERCEPT: The intercept of the linear regression line
KURT: The kurtosis of a data set
LARGE: The k-th largest value in a data set
LINEST: The parameters of a linear trend
LOGEST: The parameters of an exponential trend
LOGINV: The inverse of the lognormal distribution
LOGNORMDIST: The cumulative lognormal distribution
MAX: The maximum value in a list of arguments
MAXA: The maximum value in a list of arguments, including numbers, text,
and logical values
MEDIAN: The median of the given numbers
MIN: The minimum value in a list of arguments
MINA: The smallest value in a list of arguments, including numbers, text,
and logical values
MODE: The most common value in a data set
NEGBINOMDIST: The negative binomial distribution
NORMDIST: The normal cumulative distribution
NORMINV: The inverse of the normal cumulative distribution
NORMSDIST: The standard normal cumulative distribution
NORMSINV: The inverse of the standard normal cumulative distribution
PEARSON: The Pearson product moment correlation coefficient
PERCENTILE: The k-th percentile of values in a range
PERCENTRANK: The percentage rank of a value in a data set
PERMUT: The number of permutations for a given number of objects. Very useful for basic school statistic
POISSON: The Poisson distribution
PROB: The probability that values in a range are between two limits
QUARTILE: The quartile of a data set
RANK: The rank of a number in a list of numbers
RSQ: The square of the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient
SKEW: The skewness of a distribution
SLOPE: The slope of the linear regression line
SMALL: The k-th smallest value in a data set
STANDARDIZE: A normalized value based on mean and std
STDEV: Estimates standard deviation based on a sample
STDEVA: Estimates standard deviation based on a sample, including
numbers, text, and logical values
STDEVP: Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population
STDEVPA: Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population,
including numbers, text, and logical values
STEYX: The standard error of the predicted y-value for each x in the
regression
TDIST: The Student’s t-distribution
TINV: The inverse of the Student’s t-distribution
TREND: Values along a linear trend
TRIMMEAN: The mean of the interior of a data set
TTEST: The probability associated with a Student’s t-test
VAR: Estimates variance based on a sample
VARA: Estimates variance based on a sample, including numbers, text, and
logical values
VARP: Calculates variance based on the entire population
VARPA: Calculates variance based on the entire population, including
numbers, text, and logical values
WEIBULL: The Weibull distribution
ZTEST: The one-tailed probability-value of a z-test
Engineering functions
Engineering functions deal with tough stuff only engineers grasp (;-)….
Like complex number, binary numbers, conversions from binary to hexadecimal
(the base of computing)….
BESSELI: The modified Bessel function In(x)
BESSELJ: The Bessel function Jn(x)
BESSELK: The modified Bessel function Kn(x)
BESSELY: The Bessel function Yn(x)
BIN2DEC: Converts a binary number to decimal
BIN2HEX: Converts a binary number to hexadecimal
BIN2OCT: Converts a binary number to octal
COMPLEX: Converts real and imaginary coefficients into a complex number
CONVERT: Converts a number from one measurement system to another
DEC2BIN: Converts a decimal number to binary
DEC2HEX: Converts a decimal number to hexadecimal
DEC2OCT: Converts a decimal number to octal
DELTA: Tests whether two values are equal
ERF: The error function
ERFC: The complementary error function
GESTEP: Tests whether a number is greater than a threshold value
HEX2BIN: Converts a hexadecimal number to binary
HEX2DEC: Converts a hexadecimal number to decimal
HEX2OCT: Converts a hexadecimal number to octal
IMABS: The absolute value (modulus) of a complex number
IMAGINARY: The imaginary coefficient of a complex number
IMARGUMENT: The argument theta, an angle expressed in radians
IMCONJUGATE: The complex conjugate of a complex number
IMCOS: The cosine of a complex number
IMCOSH: The hyperbolic cosine of a complex number
IMCOT: the cotangent of an imaginary number or complex number
IMCSC: the cosecant of an imaginary number
IMCSCH: hyperbolic cosecant of an imaginary number
IMDIV: The quotient of two complex numbers
IMEXP: The exponential of a complex number
IMLN: The natural logarithm of a complex number
IMLOG10: The base-10 logarithm of a complex number
IMLOG2: The base-2 logarithm of a complex number
IMPOWER: A complex number raised to an integer power
IMPRODUCT: The product of from 2 to 29 complex numbers
IMREAL: The real coefficient of a complex number
IMSEC: the Secant of an imaginary number
IMSECH: the hyperbolic secant of an imaginary number or complex number
IMSIN: The sine of a complex number
IMSINH: the hyperbolic sinus of an complex number
IMSQRT: The square root of a complex number
IMSUB: The difference between two complex numbers
IMSUM: The sum of complex numbers
IMTAN: the tangent of an imaginary number
OCT2BIN: Converts an octal number to binary
OCT2DEC: Converts an octal number to decimal
OCT2HEX: Converts an octal number to hexadecimal
Financial functions
Financial functions help you deal with investment, budgets, interest,
loans….
ACCRINT : the accrued interest for a security that pays periodic interest
ACCRINTM : the accrued interest for a security that pays interest at
maturity
AMORDEGRC : the depreciation for each accounting period by using a
depreciation coefficient
AMORLINC : the depreciation for each accounting period
COUPDAYBS : the number of days from the beginning of the coupon period to
the settlement date
COUPDAYS : the number of days in the coupon period that contains the
settlement date
COUPDAYSNC : the number of days from the settlement date to the next
coupon date
COUPNCD : the next coupon date after the settlement date
COUPNUM : the number of coupons payable between the settlement date and
maturity date
COUPPCD : the previous coupon date before the settlement date
CUMIPMT : the cumulative interest paid between two periods
CUMPRINC : the cumulative principal paid on a loan between two periods
DB : the depreciation of an asset for a specified period by using the
fixed-declining balance method
DDB : the depreciation of an asset for a specified period by using the
double-declining balance method or some other method that you specify
DISC : the discount rate for a security
DOLLARDE : Converts a dollar price, expressed as a fraction, into a
dollar price, expressed as a decimal number
DOLLARFR : Converts a dollar price, expressed as a decimal number, into a
dollar price, expressed as a fraction
DURATION : the annual duration of a security with periodic interest
payments
EFFECT : the effective annual interest rate
FV : the future value of an investment
FVSCHEDULE : the future value of an initial principal after applying a
series of compound interest rates
INTRATE : the interest rate for a fully invested security
IPMT : the interest payment for an investment for a given period
IRR : the internal rate of return for a series of cash flows
ISPMT : Calculates the interest paid during a specific period of an
investment
MDURATION : the Macauley modified duration for a security with an assumed
par value of $100
MIRR : the internal rate of return where positive and negative cash flows
are financed at different rates
NOMINAL : the annual nominal interest rate
NPER : the number of periods for an investment
NPV : the net present value of an investment based on a series of
periodic cash flows and a discount rate
ODDFPRICE : the price per $100 face value of a security with an odd first
period
ODDFYIELD : the yield of a security with an odd first period
ODDLPRICE : the price per $100 face value of a security with an odd last
period
ODDLYIELD : the yield of a security with an odd last period
PMT : the periodic payment for an annuity
PPMT : the payment on the principal for an investment for a given period
PRICE : the price per $100 face value of a security that pays periodic
interest
PRICEDISC : the price per $100 face value of a discounted security
PRICEMAT : the price per $100 face value of a security that pays interest
at maturity
PV : the present value of an investment
RATE : the interest rate per period of an annuity
RECEIVED : the amount received at maturity for a fully invested security
SLN : the straight-line depreciation of an asset for one period
SYD : the sum-of-years’ digits depreciation of an asset for a specified
period
TBILLEQ : the bond-equivalent yield for a Treasury bill
TBILLPRICE : the price per $100 face value for a Treasury bill
TBILLYIELD : the yield for a Treasury bill
VDB : the depreciation of an asset for a specified or partial period by
using a declining balance method
XIRR : the internal rate of return for a schedule of cash flows that is
not necessarily periodic
XNPV : the net present value for a schedule of cash flows that is not
necessarily periodic
YIELD : the yield on a security that pays periodic interest
YIELDDISC : the annual yield for a discounted security
YIELDMAT : the annual yield of a security that pays interest at maturity
Database functions
Database in excel functions in Excel allow you to work on table and find
out some basic informations about the data entered.
DAVERAGE: The average of selected database entries
DCOUNT: Counts the cells that contain numbers in a database
DCOUNTA: Counts nonblank cells in a database
DGET: Extracts from a database a single record that matches the specified
criteria
DMAX: The maximum value from selected database entries
DMIN: The minimum value from selected database entries
DPRODUCT: Multiplies the values in a particular field of records that
match the criteria in a database
DSTDEV: Estimates the standard deviation based on a sample of selected
database entries
DSTDEVP: Calculates the standard deviation based on the entire population
of selected database entries
DSUM: Adds the numbers in the field column of records in the database
that match the criteria
DVAR: Estimates variance based on a sample from selected database entries
DVARP: Calculates variance based on the entire population of selected
database entries
Information functions
Information functions give you INFORMATION about the content of cells. Is
this a number, is there an error, etc….typically you can test for errors and
insteaf of having these errors like #NAME that have no meaning for the user,
then you can replace them with a text message.
CELL: Information about the formatting, location, or contents of a cell
ERROR.TYPE: A number corresponding to an error type
INFO: Information about the current operating environment
ISBLANK: TRUE if the value is blank
ISERR: TRUE if the value is any error value except #N/A
ISERROR: TRUE if the value is any error value
ISEVEN: TRUE if the number is even
ISFORMULA: checks if a cell contains a formula
ISLOGICAL: TRUE if the value is a logical value
ISNA: TRUE if the value is the #N/A error value
ISNONTEXT: TRUE if the value is not text
ISNUMBER: TRUE if the value is a number
ISODD: TRUE if the number is odd
ISREF: TRUE if the value is a reference
ISTEXT: TRUE if the value is text
N: A value converted to a number
NA: The error value #N/A
TYPE: A number indicating the data type of a value
So that’s it for the functions
in Excel.
These were only some basics. Now you will learn by doing.
Formulas and functions are the building blocks of working with numeric data in Excel. This article introduces you to formulas and functions.
In this article, we will cover the following topics.
- What is Formulas in Excel?
- Mistakes to avoid when working with formulas in Excel
- What is Function in Excel?
- The importance of functions
- Common functions
- Numeric Functions
- String functions
- Date Time functions
- V Lookup function
Tutorials Data
For this tutorial, we will work with the following datasets.
Home supplies budget
| S/N | ITEM | QTY | PRICE | SUBTOTAL | Is it Affordable? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mangoes | 9 | 600 | ||
| 2 | Oranges | 3 | 1200 | ||
| 3 | Tomatoes | 1 | 2500 | ||
| 4 | Cooking Oil | 5 | 6500 | ||
| 5 | Tonic Water | 13 | 3900 |
House Building Project Schedule
| S/N | ITEM | START DATE | END DATE | DURATION (DAYS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Survey land | 04/02/2015 | 07/02/2015 | |
| 2 | Lay Foundation | 10/02/2015 | 15/02/2015 | |
| 3 | Roofing | 27/02/2015 | 03/03/2015 | |
| 4 | Painting | 09/03/2015 | 21/03/2015 |
What is Formulas in Excel?
FORMULAS IN EXCEL is an expression that operates on values in a range of cell addresses and operators. For example, =A1+A2+A3, which finds the sum of the range of values from cell A1 to cell A3. An example of a formula made up of discrete values like =6*3.
=A2 * D2 / 2
HERE,
"="tells Excel that this is a formula, and it should evaluate it."A2" * D2"makes reference to cell addresses A2 and D2 then multiplies the values found in these cell addresses."/"is the division arithmetic operator"2"is a discrete value
Formulas practical exercise
We will work with the sample data for the home budget to calculate the subtotal.
- Create a new workbook in Excel
- Enter the data shown in the home supplies budget above.
- Your worksheet should look as follows.
We will now write the formula that calculates the subtotal
Set the focus to cell E4
Enter the following formula.
=C4*D4
HERE,
"C4*D4"uses the arithmetic operator multiplication (*) to multiply the value of the cell address C4 and D4.
Press enter key
You will get the following result
The following animated image shows you how to auto select cell address and apply the same formula to other rows.
Mistakes to avoid when working with formulas in Excel
- Remember the rules of Brackets of Division, Multiplication, Addition, & Subtraction (BODMAS). This means expressions are brackets are evaluated first. For arithmetic operators, the division is evaluated first followed by multiplication then addition and subtraction is the last one to be evaluated. Using this rule, we can rewrite the above formula as =(A2 * D2) / 2. This will ensure that A2 and D2 are first evaluated then divided by two.
- Excel spreadsheet formulas usually work with numeric data; you can take advantage of data validation to specify the type of data that should be accepted by a cell i.e. numbers only.
- To ensure that you are working with the correct cell addresses referenced in the formulas, you can press F2 on the keyboard. This will highlight the cell addresses used in the formula, and you can cross check to ensure they are the desired cell addresses.
- When you are working with many rows, you can use serial numbers for all the rows and have a record count at the bottom of the sheet. You should compare the serial number count with the record total to ensure that your formulas included all the rows.
Check Out
Top 10 Excel Spreadsheet Formulas
What is Function in Excel?
FUNCTION IN EXCEL is a predefined formula that is used for specific values in a particular order. Function is used for quick tasks like finding the sum, count, average, maximum value, and minimum values for a range of cells. For example, cell A3 below contains the SUM function which calculates the sum of the range A1:A2.
- SUM for summation of a range of numbers
- AVERAGE for calculating the average of a given range of numbers
- COUNT for counting the number of items in a given range
The importance of functions
Functions increase user productivity when working with excel. Let’s say you would like to get the grand total for the above home supplies budget. To make it simpler, you can use a formula to get the grand total. Using a formula, you would have to reference the cells E4 through to E8 one by one. You would have to use the following formula.
= E4 + E5 + E6 + E7 + E8
With a function, you would write the above formula as
=SUM (E4:E8)
As you can see from the above function used to get the sum of a range of cells, it is much more efficient to use a function to get the sum than using the formula which will have to reference a lot of cells.
Common functions
Let’s look at some of the most commonly used functions in ms excel formulas. We will start with statistical functions.
| S/N | FUNCTION | CATEGORY | DESCRIPTION | USAGE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | SUM | Math & Trig | Adds all the values in a range of cells | =SUM(E4:E8) |
| 02 | MIN | Statistical | Finds the minimum value in a range of cells | =MIN(E4:E8) |
| 03 | MAX | Statistical | Finds the maximum value in a range of cells | =MAX(E4:E8) |
| 04 | AVERAGE | Statistical | Calculates the average value in a range of cells | =AVERAGE(E4:E8) |
| 05 | COUNT | Statistical | Counts the number of cells in a range of cells | =COUNT(E4:E8) |
| 06 | LEN | Text | Returns the number of characters in a string text | =LEN(B7) |
| 07 | SUMIF | Math & Trig |
Adds all the values in a range of cells that meet a specified criteria. =SUMIF(range,criteria,[sum_range]) |
=SUMIF(D4:D8,”>=1000″,C4:C8) |
| 08 | AVERAGEIF | Statistical |
Calculates the average value in a range of cells that meet the specified criteria. =AVERAGEIF(range,criteria,[average_range]) |
=AVERAGEIF(F4:F8,”Yes”,E4:E8) |
| 09 | DAYS | Date & Time | Returns the number of days between two dates | =DAYS(D4,C4) |
| 10 | NOW | Date & Time | Returns the current system date and time | =NOW() |
Numeric Functions
As the name suggests, these functions operate on numeric data. The following table shows some of the common numeric functions.
| S/N | FUNCTION | CATEGORY | DESCRIPTION | USAGE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ISNUMBER | Information | Returns True if the supplied value is numeric and False if it is not numeric | =ISNUMBER(A3) |
| 2 | RAND | Math & Trig | Generates a random number between 0 and 1 | =RAND() |
| 3 | ROUND | Math & Trig | Rounds off a decimal value to the specified number of decimal points | =ROUND(3.14455,2) |
| 4 | MEDIAN | Statistical | Returns the number in the middle of the set of given numbers | =MEDIAN(3,4,5,2,5) |
| 5 | PI | Math & Trig | Returns the value of Math Function PI(π) | =PI() |
| 6 | POWER | Math & Trig |
Returns the result of a number raised to a power. POWER( number, power ) |
=POWER(2,4) |
| 7 | MOD | Math & Trig | Returns the Remainder when you divide two numbers | =MOD(10,3) |
| 8 | ROMAN | Math & Trig | Converts a number to roman numerals | =ROMAN(1984) |
String functions
These basic excel functions are used to manipulate text data. The following table shows some of the common string functions.
| S/N | FUNCTION | CATEGORY | DESCRIPTION | USAGE | COMMENT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | LEFT | Text | Returns a number of specified characters from the start (left-hand side) of a string | =LEFT(“GURU99”,4) | Left 4 Characters of “GURU99” |
| 2 | RIGHT | Text | Returns a number of specified characters from the end (right-hand side) of a string | =RIGHT(“GURU99”,2) | Right 2 Characters of “GURU99” |
| 3 | MID | Text |
Retrieves a number of characters from the middle of a string from a specified start position and length. =MID (text, start_num, num_chars) |
=MID(“GURU99”,2,3) | Retrieving Characters 2 to 5 |
| 4 | ISTEXT | Information | Returns True if the supplied parameter is Text | =ISTEXT(value) | value – The value to check. |
| 5 | FIND | Text |
Returns the starting position of a text string within another text string. This function is case-sensitive. =FIND(find_text, within_text, [start_num]) |
=FIND(“oo”,”Roofing”,1) | Find oo in “Roofing”, Result is 2 |
| 6 | REPLACE | Text |
Replaces part of a string with another specified string. =REPLACE (old_text, start_num, num_chars, new_text) |
=REPLACE(“Roofing”,2,2,”xx”) | Replace “oo” with “xx” |
Date Time Functions
These functions are used to manipulate date values. The following table shows some of the common date functions
| S/N | FUNCTION | CATEGORY | DESCRIPTION | USAGE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DATE | Date & Time | Returns the number that represents the date in excel code | =DATE(2015,2,4) |
| 2 | DAYS | Date & Time | Find the number of days between two dates | =DAYS(D6,C6) |
| 3 | MONTH | Date & Time | Returns the month from a date value | =MONTH(“4/2/2015”) |
| 4 | MINUTE | Date & Time | Returns the minutes from a time value | =MINUTE(“12:31”) |
| 5 | YEAR | Date & Time | Returns the year from a date value | =YEAR(“04/02/2015”) |
VLOOKUP function
The VLOOKUP function is used to perform a vertical look up in the left most column and return a value in the same row from a column that you specify. Let’s explain this in a layman’s language. The home supplies budget has a serial number column that uniquely identifies each item in the budget. Suppose you have the item serial number, and you would like to know the item description, you can use the VLOOKUP function. Here is how the VLOOKUP function would work.
=VLOOKUP (C12, A4:B8, 2, FALSE)
HERE,
"=VLOOKUP"calls the vertical lookup function"C12"specifies the value to be looked up in the left most column"A4:B8"specifies the table array with the data"2"specifies the column number with the row value to be returned by the VLOOKUP function"FALSE,"tells the VLOOKUP function that we are looking for an exact match of the supplied look up value
The animated image below shows this in action
Download the above Excel Code
Summary
Excel allows you to manipulate the data using formulas and/or functions. Functions are generally more productive compared to writing formulas. Functions are also more accurate compared to formulas because the margin of making mistakes is very minimum.
Here is a list of important Excel Formula and Function
- SUM function =
=SUM(E4:E8)
- MIN function =
=MIN(E4:E8)
- MAX function =
=MAX(E4:E8)
- AVERAGE function =
=AVERAGE(E4:E8)
- COUNT function =
=COUNT(E4:E8)
- DAYS function =
=DAYS(D4,C4)
- VLOOKUP function =
=VLOOKUP (C12, A4:B8, 2, FALSE)
- DATE function =
=DATE(2020,2,4)
Learning Excel formulas is a must when you work with data. Excel is used in all industries for its versatility and popularity. Excel is a go-to tool to store, manage, and retrieve data. Its versatility extends to generating reports and providing business insights.
Excel is used in the financial sector for financial modelling and analysis, in the banking sector, and in business for data analysis and forecasting. You can learn how to use this software with comprehensive Excel courses, such as those at Academy of Learning Career College.
One important feature of Excel is the Excel formulas feature. Learning a few frequently used formulas while working with large data sets is extremely valuable.
Excel Formulas – List and Guide for Beginners
What Are Excel Formulas?
An Excel formula is an expression that takes operands and operators. Operators show what action to perform. Operands show what item to apply the action to. For instance, a+b is a formula to calculate the sum of two numbers. Here, a and b are the operands, and + is the operator.
In other words, an Excel formula is an expression you use to make mathematical calculations in Excel. You can use a formula to add, subtract, divide, multiply, etc. For example, =1+1 is a formula to calculate the sum of two numbers. Note, you will always have = at the beginning of your formula in Excel.
A formula is one of a few ways you could add numbers in Excel. You could also use Excel’s built-in functions to quickly find the sum of two numbers, cells, or a range of cells. Functions are predefined formulas in Excel. They make calculations in Excel faster and easier, especially if you are working with large data sets. The Excel function to add two numbers together is =SUM(
- Example of Excel Formula:
- In a blank cell, type the = sign.
- Enter a number, cell address, or manually click a cell address to add it (In this case, we will enter 1).
- Type your operator (In this case we will use +).
- Enter another number, cell address, or manually click a cell address to add it (Again, we will use the number 1)
It should look like this: =1+1. - Hit enter, and your calculation will appear.
- Example of Excel Function:
- In a blank cell, type =SUM(
- To find the sum of cells A1 and A2, you can simply type =SUM(A1,A2)
- Hit enter and your calculation will appear.
Besides basic calculations, there are a wide variety of formulas you can use in Excel to aid your work. You can find a separate tab, Formulas, that contains all the Excel formulas list.
In the Formulas tab, in the Function Library group, you can also find Financial, Logical, Text, Date & Time, Lookup & Reference, and other functions.
- Financial Functions – This has a list of financial functions used to calculate interest rates, return depreciation amounts, and perform other functions related to finance.
- Logical Functions – This lists logical functions, such as TRUE, FALSE, IF, and IFNA.
- Text Functions – This covers all the functions needed to work with text.
- Date & Time Functions – This lists functions to work with date, time, and year.
- Lookup & Reference Functions – Lookup and reference functions help you find the value of a row or column.
- Math & Trig Functions – All mathematical and trigonometric functions are listed here.
- More Functions:
- Statistical
- Engineering
- Cube
- Information
- Compatibility
- Web
The below screenshot shows the functions listed in each category. When you hover your mouse over any function, it displays a dialogue box explaining what the function does. You can click on the option “Tell me more” to learn more about the function. This opens a separate window where the function is explained in detail.
Insert Function – You can pick any function from the list and get help working with the functions.
Insert function is another method of inserting a function in your selected cell. First, select a cell where you wish your Excel formula to appear. Then, click on Insert Function, select a category, and then select the appropriate function.
In the above example, the category Text is chosen. You can see that the functions used in the text are listed. Choose any function you would like to use. In this example, the CONCAT function is chosen, which combines two texts.
You can see the explanation of the function, which links a list or range of text or strings. When you click on that function, the Function Arguments dialogue opens. You are then prompted to enter the text. You must provide a text or a series of texts you wish to link in the text bar.
Click OK. You can find the result of the concatenated text at the bottom of the dialogue box, and the same concatenated text should also appear in the spreadsheet.
AutoSum – AutoSum automatically does a quick calculation of the numbers that you save in the spreadsheet.
Recently Used – This gives a list of functions that you recently used.
Difference Between Excel Functions and Formulas
An Excel function is a predefined piece of code that executes when you use it in a spreadsheet. It takes the specified number of arguments as defined by the source code. Since it is a predefined expression, you can select any cell in the worksheet where you wish the result to be displayed and enter ‘=’ followed by the function name.
As you enter the function name, you should see the list of all the Excel functions and what the function does. For instance, to calculate the sum of ‘n’ numbers, the predefined function in Excel is =SUM(number1, number2,…). Similarly, the function is =AVERAGE(number1, number2,…) to calculate the average.
An Excel formula is an expression that must contain the right operators and the operands as arguments. The user must take the utmost care to represent all the operations involved in the formula to arrive at the correct result.
For instance, to calculate the sum of ‘n’ numbers, the Excel formula is =(number1+number 2..) To find the average of these numbers, the formula is =(number1+number 2…)/n). Where ‘n’ is the total number in the list or table.
Let’s look at the most commonly used formulas you need to know when working in Excel. Mastering them can save you a lot of time and give you the confidence to be an expert.
1. IF()
The IF() function in Excel performs the logical operation. Select Formula → Function Library → Logical, and you find logical functions, like AND, OR, NOT, IF, IFNA, and other such functions. The IF() function checks for a condition and returns a positive value or text that you provide if the condition is satisfied. If it does not meet the condition, it returns the alternative negative value or text you provide along with the positive value or text.
Syntax =
IF(logical_test,[value_if_true],[value_if_false])
In the above example, the IF() function is entered in the formula bar, specifying the logical test that has to be performed on the values in the spreadsheet. Here, the condition is to check whether the person’s age is above 18 or not.
If the value in the table satisfies the condition, the value Yes is displayed, or else No is displayed.
Another method of using the function is to select the cell where you need to enter the formula and then select Formulas → Logical → IF. Now, enter the function arguments: the logical test, the value to display if the condition is true, and the value to return if the condition is false.
2. LEN()
The function LEN() returns the number of characters in a text string. It counts even the spaces and the special characters in the string.
=LEN(TEXT)
In the example above, the function is entered in two ways. One in the formula bar as =LEN(A2), and the other by selecting the options Formulas → Text → Len. The function takes the text string or the cell reference as an argument.
3. PROPER()
This function converts a text string to the proper case: the first letter in each word is converted to an uppercase letter and all other letters to lowercase. The function takes one argument that can accept the actual text enclosed in quotation marks, a formula that returns text, or a reference to the cell that contains the text.
Syntax
=PROPER(TEXT)
In the example above, the names are in small letters. The Excel formula, =PROPER() is chosen from the options: Formulas → Text → PROPER.
4. REPLACE( )
The Excel function, =REPLACE(), replaces part of a string with a different text string.
Syntax
=REPLACE(OLD_TEXT, START_NUM, NUM_CHARS,NEW_TEXT)
This function takes four arguments. The first argument is the old text. In the second argument, start_num, you must mention the text position where you need the new text to be entered. The third argument, NUM_CHARS, is the length of the new text, and the fourth argument is the new text that has to replace the old text.
In the example above, a new text, ‘er’, is included at the end of the old text. Both values in cells A2 and A3, Garden and Market, have 6 letters each. The function inserts the new and old text, displaying them as Gardener and Marketer.
5. SEARCH()
The SEARCH() function returns the number of characters at which a specific character or string is first found, reads it left to right, and is not case-sensitive.
Syntax
=SEARCH(FIND_TEXT,WITHIN_TEXT,[START_NUM])
This Excel function takes two mandatory arguments and one optional argument. The argument Find_Text finds the text that you have mentioned. It accepts wildcard characters, such as ~, ? and *. The argument Within_Text is the text in which you wish to search the Find_Text. Start_num is the character number in Within_text, counting from left, at which you want to start searching.
This function returns a default value of ‘1’ when the character to be searched is not mentioned. That’s why ‘1’ is returned as a result in cell C8 since the text to be searched is not mentioned in the table. The SEARCH() function is case-insensitive.
6. Date Functions
The Date function in Excel is used to find the date and days between the dates, months, and years. It is grouped under the category, Date and Time functions.
Syntax
DAY(SERIAL_NUMBER) – returns the day of the month, a number from 1 to 31.
DAYS(END_DATE, START_DATE) – returns the number of days between the two dates.
MONTH(SERIAL_NUMBER) – returns the month, a number from 1 (January) to 12 (December).
NOW() – returns the current date and time, formatted as a date and time.
YEAR(SERIAL_NUMBER) – returns the year of a date, an integer in the range 1900-9999.
TODAY() – returns the current date formatted as a date.
WEEKDAY(serial_number, return_type) – returns a number from 1 to 7 identifying the day of the week of a date.
The DATE() function takes the cell reference which contains the date as an argument and returns the result as a number. Excel considers the year 1900 as 1 and increments the number as the year proceeds.
In the example above, the functions =TODAY() and =NOW() do not take any arguments. The function TODAY() returns the current date as a result, and the function =NOW() returns the current date and time as a result.
7. VLOOKUP( )
VLOOKUP() function is categorized in Lookup and Reference and is used to search and find a corresponding value from the table.
Syntax
=VLOOKUP(LOOKUP_VALUE, TABLE_ARRAY,COL_INDEX_NUM,[RANGE_LOOKUP])
In the example above, to find the profession of a person, use the VLOOKUP function that searches vertically and returns the result. You can enter the formula directly in the formula bar, =VLOOKUP( A6, A3:C6,3 FALSE).
Cell A6 contains the lookupo_value, Sarah. It has to be searched in the table ranging in the cells A3:C6. The column index is in the 3rd position from the lookup_value. The range_lookup can either take TRUE or FALSE. A ‘FALSE’ returns the exact match, and a ‘TRUE’ returns an appropriate match.
Related: LOOKUPS in Excel Explained – A Beginner’s Guide
8. PRODUCT()
The PRODUCT() function is listed under the Mathematical and Trigonometric function library. It returns the product of the numbers that are mentioned within the function. It can also take the cell reference where the numbers are available.
Syntax
=PRODUCT(NUMBER1,NUMBER2)
9. ROUND( )
ROUND() function rounds a number to the specified number of digits. This is categorized under the Mathematical and Trigonometric function library.
Syntax
=ROUND(NUMBER, NUM_DIGITS)
In the example above, the values in cells A1 and A2 are multiplied, and the result is available in cell B4. Using the ROUND() function, it is rounded to the nearest 2 digits.
10. AutoSum Functions
The AutoSum functions allow you to perform quick calculations, such as sum, average, count, minimum, and maximum. All these functions operate upon a series of numbers and return the appropriate result.
Syntax
=SUM(NUMBER1, NUMBER2…)
In the example above, there are three different numbers for which the sum, average, count of numbers, min, and max is calculated, and the results are returned
11. CORREL()
CORREL() is a Statistical function grouped under More Functions. There are many Statistical functions available that can be used for different purposes. This function calculates the relationship between two different values.
The CORREL() function takes two data sets as arguments and returns the result as positive or negative. Statistical functions require operating data sets, and Excel formulas cannot calculate using a single value.
Syntax
=CORREL(ARRAY1, ARRAY2)
In the example above, there are two data sets, X and Y. To find the correlation between these two data sets, use the CORREL function. It can be accessed from Functions → More Functions → Statistical → Correl.
When you select that function, it prompts you to enter the values. Select the values in column A and input them in Array1 in the Function Arguments dialogue box. Similarly, select the values in column B and give them as input in Array2. Click OK. You get the value displayed in the spreadsheet.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the benefits of using Excel?
Excel is the best tool to do the following:
- Store data
- Perform calculations
- Create a table to organize and analyze data
- Visualize data using charts
- Predict the outcomes
2. What are the most valuable tools in Excel?
Excel offers built-in tools, such as:
- Functions
- Tables and Charts
- Pivot Table and Slicers
- Sort and Filter
- Data Validation
- Macros
3. How do I improve my Excel skills?
Follow these steps to improve your Excel skills:
- Learn basic formulas. This can help you to understand and work with complex ones.
- Use conditional formatting and other basic elements to organize your data.
- Learn how to sort and filter data.
- Learn keyboard shortcuts to work fast in Excel.
Closing Thoughts
Excel formulas are used in various calculations. All fields, such as business, research, and education, need a technique to store and work with numbers. The built-in Excel functions are capable of catering to every industry’s data storage and manipulation needs.
The above-listed functions are basic and easy to understand. When you start learning, you will be amazed at the kind of control you develop over data.
Are you motivated to learn more? Check out AOLCC’s courses in Excel and Microsoft Office Applications to learn everything from what a pivot table is in Excel to practical tips on how to make the most of Microsoft Office Applications. Also, you can learn what lookup functions are, and how to use them using our Lookups in Excel – Beginner’s Guide. You will also earn Micro-credentials on the completion of the course.