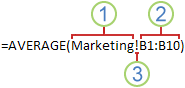Overview of formulas in Excel
Get started on how to create formulas and use built-in functions to perform calculations and solve problems.
Important: The calculated results of formulas and some Excel worksheet functions may differ slightly between a Windows PC using x86 or x86-64 architecture and a Windows RT PC using ARM architecture. Learn more about the differences.
Important: In this article we discuss XLOOKUP and VLOOKUP, which are similar. Try using the new XLOOKUP function, an improved version of VLOOKUP that works in any direction and returns exact matches by default, making it easier and more convenient to use than its predecessor.
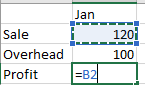
Create a formula that refers to values in other cells
-
Select a cell.
-
Type the equal sign =.
Note: Formulas in Excel always begin with the equal sign.
-
Select a cell or type its address in the selected cell.
-
Enter an operator. For example, – for subtraction.
-
Select the next cell, or type its address in the selected cell.
-
Press Enter. The result of the calculation appears in the cell with the formula.
See a formula
-
When a formula is entered into a cell, it also appears in the Formula bar.
-
To see a formula, select a cell, and it will appear in the formula bar.
Enter a formula that contains a built-in function
-
Select an empty cell.
-
Type an equal sign = and then type a function. For example, =SUM for getting the total sales.
-
Type an opening parenthesis (.
-
Select the range of cells, and then type a closing parenthesis).
-
Press Enter to get the result.
Download our Formulas tutorial workbook
We’ve put together a Get started with Formulas workbook that you can download. If you’re new to Excel, or even if you have some experience with it, you can walk through Excel’s most common formulas in this tour. With real-world examples and helpful visuals, you’ll be able to Sum, Count, Average, and Vlookup like a pro.
Formulas in-depth
You can browse through the individual sections below to learn more about specific formula elements.
A formula can also contain any or all of the following: functions, references, operators, and constants.
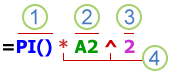
Parts of a formula
1. Functions: The PI() function returns the value of pi: 3.142…
2. References: A2 returns the value in cell A2.
3. Constants: Numbers or text values entered directly into a formula, such as 2.
4. Operators: The ^ (caret) operator raises a number to a power, and the * (asterisk) operator multiplies numbers.
A constant is a value that is not calculated; it always stays the same. For example, the date 10/9/2008, the number 210, and the text «Quarterly Earnings» are all constants. An expression or a value resulting from an expression is not a constant. If you use constants in a formula instead of references to cells (for example, =30+70+110), the result changes only if you modify the formula. In general, it’s best to place constants in individual cells where they can be easily changed if needed, then reference those cells in formulas.
A reference identifies a cell or a range of cells on a worksheet, and tells Excel where to look for the values or data you want to use in a formula. You can use references to use data contained in different parts of a worksheet in one formula or use the value from one cell in several formulas. You can also refer to cells on other sheets in the same workbook, and to other workbooks. References to cells in other workbooks are called links or external references.
-
The A1 reference style
By default, Excel uses the A1 reference style, which refers to columns with letters (A through XFD, for a total of 16,384 columns) and refers to rows with numbers (1 through 1,048,576). These letters and numbers are called row and column headings. To refer to a cell, enter the column letter followed by the row number. For example, B2 refers to the cell at the intersection of column B and row 2.
To refer to
Use
The cell in column A and row 10
A10
The range of cells in column A and rows 10 through 20
A10:A20
The range of cells in row 15 and columns B through E
B15:E15
All cells in row 5
5:5
All cells in rows 5 through 10
5:10
All cells in column H
H:H
All cells in columns H through J
H:J
The range of cells in columns A through E and rows 10 through 20
A10:E20
-
Making a reference to a cell or a range of cells on another worksheet in the same workbook
In the following example, the AVERAGE function calculates the average value for the range B1:B10 on the worksheet named Marketing in the same workbook.
1. Refers to the worksheet named Marketing
2. Refers to the range of cells from B1 to B10
3. The exclamation point (!) Separates the worksheet reference from the cell range reference
Note: If the referenced worksheet has spaces or numbers in it, then you need to add apostrophes (‘) before and after the worksheet name, like =’123′!A1 or =’January Revenue’!A1.
-
The difference between absolute, relative and mixed references
-
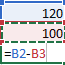
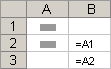
Relative references A relative cell reference in a formula, such as A1, is based on the relative position of the cell that contains the formula and the cell the reference refers to. If the position of the cell that contains the formula changes, the reference is changed. If you copy or fill the formula across rows or down columns, the reference automatically adjusts. By default, new formulas use relative references. For example, if you copy or fill a relative reference in cell B2 to cell B3, it automatically adjusts from =A1 to =A2.
Copied formula with relative reference
-
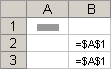
Absolute references An absolute cell reference in a formula, such as $A$1, always refer to a cell in a specific location. If the position of the cell that contains the formula changes, the absolute reference remains the same. If you copy or fill the formula across rows or down columns, the absolute reference does not adjust. By default, new formulas use relative references, so you may need to switch them to absolute references. For example, if you copy or fill an absolute reference in cell B2 to cell B3, it stays the same in both cells: =$A$1.
Copied formula with absolute reference
-
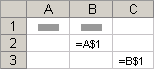
Mixed references A mixed reference has either an absolute column and relative row, or absolute row and relative column. An absolute column reference takes the form $A1, $B1, and so on. An absolute row reference takes the form A$1, B$1, and so on. If the position of the cell that contains the formula changes, the relative reference is changed, and the absolute reference does not change. If you copy or fill the formula across rows or down columns, the relative reference automatically adjusts, and the absolute reference does not adjust. For example, if you copy or fill a mixed reference from cell A2 to B3, it adjusts from =A$1 to =B$1.
Copied formula with mixed reference
-
-
The 3-D reference style
Conveniently referencing multiple worksheets If you want to analyze data in the same cell or range of cells on multiple worksheets within a workbook, use a 3-D reference. A 3-D reference includes the cell or range reference, preceded by a range of worksheet names. Excel uses any worksheets stored between the starting and ending names of the reference. For example, =SUM(Sheet2:Sheet13!B5) adds all the values contained in cell B5 on all the worksheets between and including Sheet 2 and Sheet 13.
-
You can use 3-D references to refer to cells on other sheets, to define names, and to create formulas by using the following functions: SUM, AVERAGE, AVERAGEA, COUNT, COUNTA, MAX, MAXA, MIN, MINA, PRODUCT, STDEV.P, STDEV.S, STDEVA, STDEVPA, VAR.P, VAR.S, VARA, and VARPA.
-
3-D references cannot be used in array formulas.
-
3-D references cannot be used with the intersection operator (a single space) or in formulas that use implicit intersection.
What occurs when you move, copy, insert, or delete worksheets The following examples explain what happens when you move, copy, insert, or delete worksheets that are included in a 3-D reference. The examples use the formula =SUM(Sheet2:Sheet6!A2:A5) to add cells A2 through A5 on worksheets 2 through 6.
-
Insert or copy If you insert or copy sheets between Sheet2 and Sheet6 (the endpoints in this example), Excel includes all values in cells A2 through A5 from the added sheets in the calculations.
-
Delete If you delete sheets between Sheet2 and Sheet6, Excel removes their values from the calculation.
-
Move If you move sheets from between Sheet2 and Sheet6 to a location outside the referenced sheet range, Excel removes their values from the calculation.
-
Move an endpoint If you move Sheet2 or Sheet6 to another location in the same workbook, Excel adjusts the calculation to accommodate the new range of sheets between them.
-
Delete an endpoint If you delete Sheet2 or Sheet6, Excel adjusts the calculation to accommodate the range of sheets between them.
-
-
The R1C1 reference style
You can also use a reference style where both the rows and the columns on the worksheet are numbered. The R1C1 reference style is useful for computing row and column positions in macros. In the R1C1 style, Excel indicates the location of a cell with an «R» followed by a row number and a «C» followed by a column number.
Reference
Meaning
R[-2]C
A relative reference to the cell two rows up and in the same column
R[2]C[2]
A relative reference to the cell two rows down and two columns to the right
R2C2
An absolute reference to the cell in the second row and in the second column
R[-1]
A relative reference to the entire row above the active cell
R
An absolute reference to the current row
When you record a macro, Excel records some commands by using the R1C1 reference style. For example, if you record a command, such as clicking the AutoSum button to insert a formula that adds a range of cells, Excel records the formula by using R1C1 style, not A1 style, references.
You can turn the R1C1 reference style on or off by setting or clearing the R1C1 reference style check box under the Working with formulas section in the Formulas category of the Options dialog box. To display this dialog box, click the File tab.
Top of Page
Need more help?
You can always ask an expert in the Excel Tech Community or get support in the Answers community.
See Also
Switch between relative, absolute and mixed references for functions
Using calculation operators in Excel formulas
The order in which Excel performs operations in formulas
Using functions and nested functions in Excel formulas
Define and use names in formulas
Guidelines and examples of array formulas
Delete or remove a formula
How to avoid broken formulas
Find and correct errors in formulas
Excel keyboard shortcuts and function keys
Excel functions (by category)
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
[icon name=”calendar” class=”” unprefixed_class=””] DATE & TIME
DateDif
EndOfMonth
Time
Weekday
Weeknum
Workday
Year
[icon name=”lightbulb-o” class=”” unprefixed_class=””] LOGICAL
And
If
If, And
Iferror
[icon name=”arrow-circle-up” class=”” unprefixed_class=””] LOOKUP
Array, Lookup
Hlookup
Iferror, Vlookup
Index
Index, Match
Indirect
Match
Multiple Criteria, Vlookup
Offset
Pivot Table, GetPivotData
Sum, Lookup
Vlookup
Xlookup
[icon name=”calculator” class=”” unprefixed_class=””] MATH
Average
Count
CountA
CountBlank
CountIf
CountIfs
Mathematical Formulas
Mod
Percentage
Rand
Randbetween
Round
Subtotal
Sumifs
Sumproduct
[icon name=”delicious” class=”” unprefixed_class=””] OTHER
3D
Array
Chart
Convert, Values
Evaluate
Find & Select
FV
Reference
Show, Hide
Transpose
Type
Value
[icon name=”wpforms” class=”” unprefixed_class=””] TEXT
Between
Clean
Concatenate
Data Cleansing, Trim
Extract, Find, Left
Left
Len, Length
Proper
Remove
Remove, Substitute
Replace
Replace, Cleanup
Right
Substitute
Substitute, Trim
Text
Upper
[icon name=”wpforms” class=”” unprefixed_class=””] OFFICE 365
Filter
Sort
Sortby
Unique
Click on any Excel formula & function link below and it will take you to the advanced Excel formulas with examples in Excel sheet free download for you to practice!
Description of the functions in Excel with pictures and examples of their application in practice.
Functions for efficient settlement
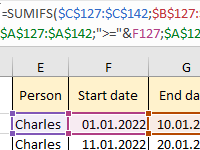
A template with examples of how to effectively use the broad capabilities of the SUMMESLYMN function under different conditions. How to use the function if there are many conditions with dates?
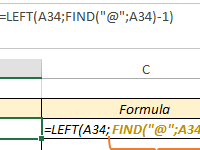
Practical examples of the FIND function with pictures, a description and a file of ready-made solutions. Formulas for using the FIND function to find values in columns of tables.
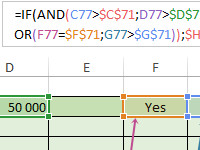
How to work with the formula of logical functions AND OR IF to automate the analysis of table data. Examples in pictures and with a detailed description of a sample file of tables or formulas.
MS Excel: Formulas and Functions — Listed by Category
Learn how to use all 300+ Excel formulas and functions including worksheet functions entered in the formula bar and VBA functions used in Macros.
Worksheet formulas are built-in functions that are entered as part of a formula in a cell. These are the most basic functions used when learning Excel. VBA functions are built-in functions that are used in Excel’s programming environment called Visual Basic for Applications (VBA).
Below is a list of Excel formulas sorted by category. If you would like an alphabetical list of these formulas, click on the following button:
Sort Alphabetically
(Enter a value in the field above to quickly find functions in the list below)
| ADDRESS (WS) | Returns a text representation of a cell address |
| AREAS (WS) | Returns the number of ranges in a reference |
| CHOOSE (WS, VBA) | Returns a value from a list of values based on a given position |
| COLUMN (WS) | Returns the column number of a cell reference |
| COLUMNS (WS) | Returns the number of columns in a cell reference |
| HLOOKUP (WS) | Performs a horizontal lookup by searching for a value in the top row of the table and returning the value in the same column based on the index_number |
| HYPERLINK (WS) | Creates a shortcut to a file or Internet address |
| INDEX (WS) | Returns either the value or the reference to a value from a table or range |
| INDIRECT (WS) | Returns the reference to a cell based on its string representation |
| LOOKUP (WS) | Returns a value from a range (one row or one column) or from an array |
| MATCH (WS) | Searches for a value in an array and returns the relative position of that item |
| OFFSET (WS) | Returns a reference to a range that is offset a number of rows and columns |
| ROW (WS) | Returns the row number of a cell reference |
| ROWS (WS) | Returns the number of rows in a cell reference |
| TRANSPOSE (WS) | Returns a transposed range of cells |
| VLOOKUP (WS) | Performs a vertical lookup by searching for a value in the first column of a table and returning the value in the same row in the index_number position |
| XLOOKUP (WS) | Performs a lookup (either vertical or horizontal) |
| ASC (VBA) | Returns ASCII value of a character |
| BAHTTEXT (WS) | Returns the number in Thai text |
| CHAR (WS) | Returns the character based on the ASCII value |
| CHR (VBA) | Returns the character based on the ASCII value |
| CLEAN (WS) | Removes all nonprintable characters from a string |
| CODE (WS) | Returns the ASCII value of a character or the first character in a cell |
| CONCAT (WS) | Used to join 2 or more strings together |
| CONCATENATE (WS) | Used to join 2 or more strings together (replaced by CONCAT Function) |
| CONCATENATE with & (WS, VBA) | Used to join 2 or more strings together using the & operator |
| DOLLAR (WS) | Converts a number to text, using a currency format |
| EXACT (WS) | Compares two strings and returns TRUE if both values are the same |
| FIND (WS) | Returns the location of a substring in a string (case-sensitive) |
| FIXED (WS) | Returns a text representation of a number rounded to a specified number of decimal places |
| FORMAT STRINGS (VBA) | Takes a string expression and returns it as a formatted string |
| INSTR (VBA) | Returns the position of the first occurrence of a substring in a string |
| INSTRREV (VBA) | Returns the position of the first occurrence of a string in another string, starting from the end of the string |
| LCASE (VBA) | Converts a string to lowercase |
| LEFT (WS, VBA) | Extract a substring from a string, starting from the left-most character |
| LEN (WS, VBA) | Returns the length of the specified string |
| LOWER (WS) | Converts all letters in the specified string to lowercase |
| LTRIM (VBA) | Removes leading spaces from a string |
| MID (WS, VBA) | Extracts a substring from a string (starting at any position) |
| NUMBERVALUE (WS) | Returns a text to a number specifying the decimal and group separators |
| PROPER (WS) | Sets the first character in each word to uppercase and the rest to lowercase |
| REPLACE (WS) | Replaces a sequence of characters in a string with another set of characters |
| REPLACE (VBA) | Replaces a sequence of characters in a string with another set of characters |
| REPT (WS) | Returns a repeated text value a specified number of times |
| RIGHT (WS, VBA) | Extracts a substring from a string starting from the right-most character |
| RTRIM (VBA) | Removes trailing spaces from a string |
| SEARCH (WS) | Returns the location of a substring in a string |
| SPACE (VBA) | Returns a string with a specified number of spaces |
| SPLIT (VBA) | Used to split a string into substrings based on a delimiter |
| STR (VBA) | Returns a string representation of a number |
| STRCOMP (VBA) | Returns an integer value representing the result of a string comparison |
| STRCONV (VBA) | Returns a string converted to uppercase, lowercase, proper case or Unicode |
| STRREVERSE (VBA) | Returns a string whose characters are in reverse order |
| SUBSTITUTE (WS) | Replaces a set of characters with another |
| T (WS) | Returns the text referred to by a value |
| TEXT (WS) | Returns a value converted to text with a specified format |
| TEXTJOIN (WS) | Used to join 2 or more strings together separated by a delimiter |
| TRIM (WS, VBA) | Returns a text value with the leading and trailing spaces removed |
| UCASE (VBA) | Converts a string to all uppercase |
| UNICHAR (WS) | Returns the Unicode character based on the Unicode number provided |
| UNICODE (WS) | Returns the Unicode number of a character or the first character in a string |
| UPPER (WS) | Convert text to all uppercase |
| VAL (VBA) | Returns the numbers found in a string |
| VALUE (WS) | Converts a text value that represents a number to a number |
| DATE (WS) | Returns the serial date value for a date |
| DATE (VBA) | Returns the current system date |
| DATEADD (VBA) | Returns a date after which a certain time/date interval has been added |
| DATEDIF (WS) | Returns the difference between two date values, based on the interval specified |
| DATEDIFF (VBA) | Returns the difference between two date values, based on the interval specified |
| DATEPART (VBA) | Returns a specified part of a given date |
| DATESERIAL (VBA) | Returns a date given a year, month, and day value |
| DATEVALUE (WS, VBA) | Returns the serial number of a date |
| DAY (WS, VBA) | Returns the day of the month (a number from 1 to 31) given a date value |
| DAYS (WS) | Returns the number of days between 2 dates |
| DAYS360 (WS) | Returns the number of days between two dates based on a 360-day year |
| EDATE (WS) | Adds a specified number of months to a date and returns the result as a serial date |
| EOMONTH (WS) | Calculates the last day of the month after adding a specified number of months to a date |
| FORMAT DATES (VBA) | Takes a date expression and returns it as a formatted string |
| HOUR (WS, VBA) | Returns the hours (a number from 0 to 23) from a time value |
| ISOWEEKNUM (WS) | Returns the ISO week number for a date |
| MINUTE (WS, VBA) | Returns the minutes (a number from 0 to 59) from a time value |
| MONTH (WS, VBA) | Returns the month (a number from 1 to 12) given a date value |
| MONTHNAME (VBA) | Returns a string representing the month given a number from 1 to 12 |
| NETWORKDAYS (WS) | Returns the number of work days between 2 dates, excluding weekends and holidays |
| NETWORKDAYS.INTL (WS) | Returns the number of work days between 2 dates, excluding weekends and holidays |
| NOW (WS, VBA) | Returns the current system date and time |
| SECOND (WS) | Returns the seconds (a number from 0 to 59) from a time value |
| TIME (WS) | Returns a decimal number given an hour, minute and second value |
| TIMESERIAL (VBA) | Returns a time given an hour, minute, and second value |
| TIMEVALUE (WS, VBA) | Returns the serial number of a time |
| TODAY (WS) | Returns the current system date |
| WEEKDAY (WS, VBA) | Returns a number representing the day of the week, given a date value |
| WEEKDAYNAME (VBA) | Returns a string representing the day of the week given a number from 1 to 7 |
| WEEKNUM (WS) | Returns the week number for a date |
| WORKDAY (WS) | Adds a specified number of work days to a date and returns the result as a serial date |
| WORKDAY.INTL (WS) | Adds a specified number of work days to a date and returns the result as a serial date (customizable weekends) |
| YEAR (WS, VBA) | Returns a four-digit year (a number from 1900 to 9999) given a date value |
| YEARFRAC (WS) | Returns the number of days between 2 dates as a year fraction |
| ABS (WS, VBA) | Returns the absolute value of a number |
| ACOS (WS) | Returns the arccosine (in radians) of a number |
| ACOSH (WS) | Returns the inverse hyperbolic cosine of a number |
| AGGREGATE (WS) | Apply functions such AVERAGE, SUM, COUNT, MAX or MIN and ignore errors or hidden rows |
| ASIN (WS) | Returns the arcsine (in radians) of a number |
| ASINH (WS) | Returns the inverse hyperbolic sine of a number |
| ATAN (WS) | Returns the arctangent (in radians) of a number |
| ATAN2 (WS) | Returns the arctangent (in radians) of (x,y) coordinates |
| ATANH (WS) | Returns the inverse hyperbolic tangent of a number |
| ATN (VBA) | Returns the arctangent of a number |
| CEILING (WS) | Returns a number rounded up based on a multiple of significance |
| CEILING.PRECISE (WS) | Returns a number rounded up to the nearest integer or to the nearest multiple of significance |
| COMBIN (WS) | Returns the number of combinations for a specified number of items |
| COMBINA (WS) | Returns the number of combinations for a specified number of items and includes repetitions |
| COS (WS, VBA) | Returns the cosine of an angle |
| COSH (WS) | Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a number |
| DEGREES (WS) | Converts radians into degrees |
| EVEN (WS) | Rounds a number up to the nearest even integer |
| EXP (WS, VBA) | Returns e raised to the nth power |
| FACT (WS) | Returns the factorial of a number |
| FIX (VBA) | Returns the integer portion of a number |
| FLOOR (WS) | Returns a number rounded down based on a multiple of significance |
| FORMAT NUMBERS (VBA) | Takes a numeric expression and returns it as a formatted string |
| INT (WS, VBA) | Returns the integer portion of a number |
| LN (WS) | Returns the natural logarithm of a number |
| LOG (WS) | Returns the logarithm of a number to a specified base |
| LOG (VBA) | Returns the natural logarithm of a number |
| LOG10 (WS) | Returns the base-10 logarithm of a number |
| MDETERM (WS) | Returns the matrix determinant of an array |
| MINVERSE (WS) | Returns the inverse matrix for a given matrix |
| MMULT (WS) | Returns the matrix product of two arrays |
| MOD (WS) | Returns the remainder after a number is divided by a divisor |
| MOD (VBA) | Returns the remainder after a number is divided by a divisor |
| ODD (WS) | Rounds a number up to the nearest odd integer |
| PI (WS) | Returns the mathematical constant called pi |
| POWER (WS) | Returns the result of a number raised to a given power |
| PRODUCT (WS) | Multiplies the numbers and returns the product |
| RADIANS (WS) | Converts degrees into radians |
| RAND (WS) | Returns a random number that is greater than or equal to 0 and less than 1 |
| RANDBETWEEN (WS) | Returns a random number that is between a bottom and top range |
| RANDOMIZE (VBA) | Used to change the seed value used by the random number generator for the RND function |
| RND (VBA) | Used to generate a random number (integer value) |
| ROMAN (WS) | Converts a number to roman numeral |
| ROUND (WS) | Returns a number rounded to a specified number of digits |
| ROUND (VBA) | Returns a number rounded to a specified number of digits |
| ROUNDDOWN (WS) | Returns a number rounded down to a specified number of digits |
| ROUNDUP (WS) | Returns a number rounded up to a specified number of digits |
| SGN (VBA) | Returns the sign of a number |
| SIGN (WS) | Returns the sign of a number |
| SIN (WS, VBA) | Returns the sine of an angle |
| SINH (WS) | Returns the hyperbolic sine of a number |
| SQR (VBA) | Returns the square root of a number |
| SQRT (WS) | Returns the square root of a number |
| SUBTOTAL (WS) | Returns the subtotal of the numbers in a column in a list or database |
| SUM (WS) | Adds all numbers in a range of cells |
| SUMIF (WS) | Adds all numbers in a range of cells based on one criteria |
| SUMIFS (WS) | Adds all numbers in a range of cells, based on a single or multiple criteria |
| SUMPRODUCT (WS) | Multiplies the corresponding items in the arrays and returns the sum of the results |
| SUMSQ (WS) | Returns the sum of the squares of a series of values |
| SUMX2MY2 (WS) | Returns the sum of the difference of squares between two arrays |
| SUMX2PY2 (WS) | Returns the sum of the squares of corresponding items in the arrays |
| SUMXMY2 (WS) | Returns the sum of the squares of the differences between corresponding items in the arrays |
| TAN (WS, VBA) | Returns the tangent of an angle |
| TANH (WS) | Returns the hyperbolic tangent of a number |
| TRUNC (WS) | Returns a number truncated to a specified number of digits |
| AVEDEV (WS) | Returns the average of the absolute deviations of the numbers provided |
| AVERAGE (WS) | Returns the average of the numbers provided |
| AVERAGEA (WS) | Returns the average of the numbers provided and treats TRUE as 1 and FALSE as 0 |
| AVERAGEIF (WS) | Returns the average of all numbers in a range of cells, based on a given criteria |
| AVERAGEIFS (WS) | Returns the average of all numbers in a range of cells, based on multiple criteria |
| BETA.DIST (WS) | Returns the beta distribution |
| BETA.INV (WS) | Returns the inverse of the cumulative beta probability density function |
| BETADIST (WS) | Returns the cumulative beta probability density function |
| BETAINV (WS) | Returns the inverse of the cumulative beta probability density function |
| BINOM.DIST (WS) | Returns the individual term binomial distribution probability |
| BINOM.INV (WS) | Returns the smallest value for which the cumulative binomial distribution is greater than or equal to a criterion |
| BINOMDIST (WS) | Returns the individual term binomial distribution probability |
| CHIDIST (WS) | Returns the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution |
| CHIINV (WS) | Returns the inverse of the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution |
| CHITEST (WS) | Returns the value from the chi-squared distribution |
| COUNT (WS) | Counts the number of cells that contain numbers as well as the number of arguments that contain numbers |
| COUNTA (WS) | Counts the number of cells that are not empty as well as the number of value arguments provided |
| COUNTBLANK (WS) | Counts the number of empty cells in a range |
| COUNTIF (WS) | Counts the number of cells in a range, that meets a given criteria |
| COUNTIFS (WS) | Counts the number of cells in a range, that meets a single or multiple criteria |
| COVAR (WS) | Returns the covariance, the average of the products of deviations for two data sets |
| FORECAST (WS) | Returns a prediction of a future value based on existing values provided |
| FREQUENCY (WS) | Returns how often values occur within a set of data. It returns a vertical array of numbers |
| GROWTH (WS) | Returns the predicted exponential growth based on existing values provided |
| INTERCEPT (WS) | Returns the y-axis intersection point of a line using x-axis values and y-axis values |
| LARGE (WS) | Returns the nth largest value from a set of values |
| LINEST (WS) | Uses the least squares method to calculate the statistics for a straight line and returns an array describing that line |
| MAX (WS) | Returns the largest value from the numbers provided |
| MAXA (WS) | Returns the largest value from the values provided (numbers, text and logical values) |
| MAXIFS (WS) | Returns the largest value in a range, that meets a single or multiple criteria |
| MEDIAN (WS) | Returns the median of the numbers provided |
| MIN (WS) | Returns the smallest value from the numbers provided |
| MINA (WS) | Returns the smallest value from the values provided (numbers, text and logical values) |
| MINIFS (WS) | Returns the smallest value in a range, that meets a single or multiple criteria |
| MODE (WS) | Returns most frequently occurring number |
| MODE.MULT (WS) | Returns a vertical array of the most frequently occurring numbers |
| MODE.SNGL (WS) | Returns most frequently occurring number |
| PERCENTILE (WS) | Returns the nth percentile from a set of values |
| PERCENTRANK (WS) | Returns the nth percentile from a set of values |
| PERMUT (WS) | Returns the number of permutations for a specified number of items |
| QUARTILE (WS) | Returns the quartile from a set of values |
| RANK (WS) | Returns the rank of a number within a set of numbers |
| SLOPE (WS) | Returns the slope of a regression line based on the data points identified by known_y_values and known_x_values |
| SMALL (WS) | Returns the nth smallest value from a set of values |
| STDEV (WS) | Returns the standard deviation of a population based on a sample of numbers |
| STDEVA (WS) | Returns the standard deviation of a population based on a sample of numbers, text, and logical values |
| STDEVP (WS) | Returns the standard deviation of a population based on an entire population of numbers |
| STDEVPA (WS) | Returns the standard deviation of a population based on an entire population of numbers, text, and logical values |
| VAR (WS) | Returns the variance of a population based on a sample of numbers |
| VARA (WS) | Returns the variance of a population based on a sample of numbers, text, and logical values |
| VARP (WS) | Returns the variance of a population based on an entire population of numbers |
| VARPA (WS) | Returns the variance of a population based on an entire population of numbers, text, and logical values |
| AND (WS) | Returns TRUE if all conditions are TRUE |
| AND (VBA) | Returns TRUE if all conditions are TRUE |
| CASE (VBA) | Has the functionality of an IF-THEN-ELSE statement |
| FALSE (WS) | Returns a logical value of FALSE |
| FOR…NEXT (VBA) | Used to create a FOR LOOP |
| IF (WS) | Returns one value if the condition is TRUE or another value if the condition is FALSE |
| IF (more than 7) (WS) | Nest more than 7 IF functions |
| IF (up to 7) (WS) | Nest up to 7 IF functions |
| IF-THEN-ELSE (VBA) | Returns a value if a specified condition evaluates to TRUE or another value if it evaluates to FALSE |
| IFERROR (WS) | Used to return an alternate value if a formula results in an error |
| IFNA (WS) | Used to return an alternate value if a formula results in #N/A error |
| IFS (WS) | Specify multiple IF conditions within 1 function |
| NOT (WS) | Returns the reversed logical value |
| OR (WS) | Returns TRUE if any of the conditions are TRUE |
| OR (VBA) | Returns TRUE if any of the conditions are TRUE |
| SWITCH (WS) | Compares an expression to a list of values and returns the corresponding result |
| SWITCH (VBA) | Evaluates a list of expressions and returns the corresponding value for the first expression in the list that is TRUE |
| TRUE (WS) | Returns a logical value of TRUE |
| WHILE…WEND (VBA) | Used to create a WHILE LOOP |
| CELL (WS) | Used to retrieve information about a cell such as contents, formatting, size, etc. |
| ENVIRON (VBA) | Returns the value of an operating system environment variable |
| ERROR.TYPE (WS) | Returns the numeric representation of an Excel error |
| INFO (WS) | Returns information about the operating environment |
| ISBLANK (WS) | Used to check for blank or null values |
| ISDATE (VBA) | Returns TRUE if the expression is a valid date |
| ISEMPTY (VBA) | Used to check for blank cells or uninitialized variables |
| ISERR (WS) | Used to check for error values except #N/A |
| ISERROR (WS, VBA) | Used to check for error values |
| ISLOGICAL (WS) | Used to check for a logical value (TRUE or FALSE) |
| ISNA (WS) | Used to check for #N/A error |
| ISNONTEXT (WS) | Used to check for a value that is not text |
| ISNULL (VBA) | Used to check for a NULL value |
| ISNUMBER (WS) | Used to check for a numeric value |
| ISNUMERIC (VBA) | Used to check for a numeric value |
| ISREF (WS) | Used to check for a reference |
| ISTEXT (WS) | Used to check for a text value |
| N (WS) | Converts a value to a number |
| NA (WS) | Returns the #N/A error value |
| TYPE (WS) | Returns the type of a value |
| ACCRINT (WS) | Returns the accrued interest for a security that pays interest on a periodic basis |
| ACCRINTM (WS) | Returns the accrued interest for a security that pays interest at maturity |
| AMORDEGRC (WS) | Returns the linear depreciation of an asset for each accounting period, on a prorated basis |
| AMORLINC (WS) | Returns the depreciation of an asset for each accounting period, on a prorated basis |
| DB (WS) | Returns the depreciation of an asset based on the fixed-declining balance method |
| DDB (WS, VBA) | Returns the depreciation of an asset based on the double-declining balance method |
| FV (WS, VBA) | Returns the future value of an investment |
| IPMT (WS, VBA) | Returns the interest payment for an investment |
| IRR (WS, VBA) | Returns the internal rate of return for a series of cash flows |
| ISPMT (WS) | Returns the interest payment for an investment |
| MIRR (WS, VBA) | Returns the modified internal rate of return for a series of cash flows |
| NPER (WS, VBA) | Returns the number of periods for an investment |
| NPV (WS, VBA) | Returns the net present value of an investment |
| PMT (WS, VBA) | Returns the payment amount for a loan |
| PPMT (WS, VBA) | Returns the payment on the principal for a particular payment |
| PV (WS, VBA) | Returns the present value of an investment |
| RATE (WS, VBA) | Returns the interest rate for an annuity |
| SLN (WS, VBA) | Returns the depreciation of an asset based on the straight-line depreciation method |
| SYD (WS, VBA) | Returns the depreciation of an asset based on the sum-of-years’ digits depreciation method |
| VDB (WS) | Returns the depreciation of an asset based on a variable declining balance depreciation method |
| XIRR (WS) | Returns the internal rate of return for a series of cash flows that may not be periodic |
| DAVERAGE (WS) | Averages all numbers in a column in a list or database, based on a given criteria |
| DCOUNT (WS) | Returns the number of cells in a column or database that contains numeric values and meets a given criteria |
| DCOUNTA (WS) | Returns the number of cells in a column or database that contains nonblank values and meets a given criteria |
| DGET (WS) | Retrieves from a database a single record that matches a given criteria |
| DMAX (WS) | Returns the largest number in a column in a list or database, based on a given criteria |
| DMIN (WS) | Returns the smallest number in a column in a list or database, based on a given criteria |
| DPRODUCT (WS) | Returns the product of the numbers in a column in a list or database, based on a given criteria |
| DSTDEV (WS) | Returns the standard deviation of a population based on a sample of numbers |
| DSTDEVP (WS) | Returns the standard deviation of a population based on the entire population of numbers |
| DSUM (WS) | Sums the numbers in a column or database that meets a given criteria |
| DVAR (WS) | Returns the variance of a population based on a sample of numbers |
| DVARP (WS) | Returns the variance of a population based on the entire population of numbers |
| BIN2DEC (WS) | Converts a binary number to a decimal number |
| BIN2HEX (WS) | Converts a binary number to a hexadecimal number |
| BIN2OCT (WS) | Converts a binary number to an octal number |
| COMPLEX (WS) | Converts coefficients (real and imaginary) into a complex number |
| CONVERT (WS) | Convert a number from one measurement unit to another measurement unit |
| CHDIR (VBA) | Used to change the current directory or folder |
| CHDRIVE (VBA) | Used to change the current drive |
| CURDIR (VBA) | Returns the current path |
| DIR (VBA) | Returns the first filename that matches the pathname and attributes specified |
| FILEDATETIME (VBA) | Returns the date and time of when a file was created or last modified |
| FILELEN (VBA) | Returns the size of a file in bytes |
| GETATTR (VBA) | Returns an integer that represents the attributes of a file, folder, or directory |
| MKDIR (VBA) | Used to create a new folder or directory |
| SETATTR (VBA) | Used to set the attributes of a file |
| CBOOL (VBA) | Converts a value to a boolean |
| CBYTE (VBA) | Converts a value to a byte (ie: number between 0 and 255) |
| CCUR (VBA) | Converts a value to currency |
| CDATE (VBA) | Converts a value to a date |
| CDBL (VBA) | Converts a value to a double |
| CDEC (VBA) | Converts a value to a decimal number |
| CINT (VBA) | Converts a value to an integer |
| CLNG (VBA) | Converts a value to a long integer |
| CSNG (VBA) | Converts a value to a single-precision number |
| CSTR (VBA) | Converts a value to a string |
| CVAR (VBA) | Converts a value to a variant |