Adjective Suffixes in English
Contents
If you’re a non-native English speaker, you may find it tough to understand the various rules of English adjectives. Forming adjectives. is a tough, but important aspect of the language.
The good news is that English has many ways of making adjectives, and if you understand suffixes, you can do it with ease. In this reference, we’ll explore the concept of suffixes, provide a list of some of the most common ones, and explain the meaning of each adjectival suffix in English.
What is an Adjective Suffix?
An adjective suffix is a group of letters that are added to the end of a word to change the word’s meaning or to make it an adjective. Adjective suffixes are a great way to add more description to a sentence without having to use too many words. For example, when you add the suffix “-able” to the word “trust”, you can create the adjective “trustable” which means that something is able to be trusted.
The use of adjective suffixes can be quite complicated and it’s important to understand which suffixes can be added to which words. For example, the suffix “-ful” can be added to words such as “care” and “beauty” to create the adjectives “careful” and “beautiful”, but it cannot be added to the word “happy” as the word “happiness” already exists in the English language.
In addition to understanding which suffixes can be added to which words, it’s also important to know the meaning of each suffix so that you can use them correctly. For example, the suffix “-ous” is used to describe something full of a certain quality, such as in the word “dangerous”. Knowing the meaning of each suffix can help you to use them correctly and effectively in your writing.
Now that you know what an adjective suffix is, let’s take a look at some of the most common ones. Here’s a full list of adjective suffixes in English:
- —able: able to be done or able to be used
- —al: related to a certain thing
- —ful: full of a certain quality
- —ic: pertaining to a certain thing
- —ive: having a certain quality
- —less: without a certain quality
- —ous: full of a certain quality
- —y: having the characteristics of something
- —ish: similar to a certain quality
7
Common Adjective Suffixes
Let’s take a look at each of the adjective suffixes and explain the meaning and see 10 example words for each one.
Suffix -able (iable)
The suffix “-able” means that something is able to be done or that it is capable of being done. Here are 10 example words that use the suffix “-able”:
- Adaptable
- Changeable
- Dependable
- Drinkable
- Enjoyable
- Lovable
- Notable
- Reliable
- Tolerable
- Wearable
You can use the suffix -able to create many more words. Another version of this same suffix is -ible, which also means “able to be done.” For example:
- Accessible
- Collapsible
- Edible
- Flexible
- Invisible
You normally choose -ible for words that end in “-ss” or “-ct.”
Suffix -al (ial)
The suffix “-al” means that something is related to or pertaining to a particular thing or person. Here are 10 example words that use the suffix “-al”:
- Annual
- Critical
- Cultural
- Universal
- Musical
- Political
- Regional
- Social
- Spiritual
- Brutal
Other versions of this suffix are -ial and -ical, which also mean “related to or pertaining to a particular thing.” For example:
- Financial
- Historical
- Metaphysical
- Physical
- Practical
You normally choose -ial for words that end in “-t” or “-s.”
-ical is a bit more complicated and is normally used for words with a Greek root. For example, the word «Paradox» has a Greek root, so it is usually written as «Paradoxical.»
Suffix -ful
The suffix “-ful” means that something is full of a certain quality or attribute. Here are 10 example words that use the suffix “-ful”:
- Careful
- Cheerful
- Clueless
- Fearful
- Hopeful
- Joyful
- Painful
- Skillful
- Thankful
- Thoughtful
You can also use the suffix “-ful” to create adjectives that describe a person or thing. For example, the word “colorful” means that something is full of color.
Suffix -ic
The suffix “-ic” means that something is related to a certain action, process, or thing. Here are 10 example words that use the suffix “-ic”:
- Automatic
- Basic
- Dramatic
- Fantastic
- Historic
- Lyrical
- Panic
- Romantic
- Scientific
- Tragic
You can also use the suffix “-ic” to create adjectives that describe a person or thing. For example, the word “energetic” means that someone is full of energy. We choose -ic and not -ful here because energy is a process or action, not an attribute.
Suffix -ive
The suffix “-ive” means that something is characterized by a certain quality or attribute. Here are 10 example words that use the suffix “-ive”:
- Active
- Aggressive
- Creative
- Decisive
- Expressive
- Imaginative
- Positive
- Protective
- Responsive
- Sensitive
You can also use the suffix “-ive” to create adjectives that describe a person or thing. For example, the word “adaptive” means that someone is able to adapt quickly to new situations. At the same time, «adaptable» means that something is capable of being adapted or changed. We choose -ive here if we want to specify that the quality of being able to adapt or change is an attribute.
Suffix -less
The suffix “-less” means that something is without a certain quality or attribute. Here are 10 example words that use the suffix “-less”:
- Careless
- Fearless
- Heartless
- Hopeless
- Motionless
- Peerless
- Reckless
- Skilless
- Useless
- Worthless
This is one of the easiest suffixes to use. Just add “-less” to the end of a word to create a negative adjective. For example, you can make the word “careful” into the negative adjective “careless” by adding the suffix “-less.” We would choose -less here if we want to specify that there is a lack of energy or activity.
Suffix -ous
The suffix “-ous” means that something is marked by a certain quality or attribute. Here are 10 example words that use the suffix “-ous”:
- Famous
- Glorious
- Harmful
- Joyous
- Nervous
- Religious
- Serious
- Spontaneous
- Tenacious
- Victorious
As you can see, -ous sometimes turns into -ious. We use -ious because the word ends with vowel. For example, “glory” can be turned into “glorious,” and so on. This is one of the most common suffixes and it is often used to create adjectives. For example, you can make the word “fame” into the adjective “famous” by adding the suffix “-ous.”
Suffix -y
The suffix “-y” means that something is full of a certain quality or attribute. Here are 10 example words that use the suffix “-y”:
- Airy
- Brainy
- Dirty
- Greedy
- Moody
- Pretty
- Rocky
- Smelly
- Tiny
- Windy
This is another very common suffix and it is often used to create adjectives. For example, you can make the word “rock” into the adjective “rocky” by adding the suffix “-y.” We would choose -y here if we want to specify that something is abundant.
Suffix -ish
The suffix “-ish” means that something is similar or approximate to a certain quality or attribute. Here are 10 example words that use the suffix “-ish”:
- Childish
- Foolish
- Sheepish
- Bookish
- Boyish
- Yellowish
- Selfish
- Feverish
- Brutish
- Squeamish
This is a good suffix if you want to show the existence of some quality without certainty. For example, you can make the word “green” into the adjective “greenish” by adding the suffix “-ish.” We would choose -ish here if we want to specify that something is similar to the green color, but is not quite the same thing.
Summary
In this reference, we’ve explored the concept of adjective suffixes, provided a list of the most common ones, and explained the meaning and 10 example words for each common adjective suffix in English. We hope that this helped you to understand the concept and apply it in your own life.
Check out more references if you’re interested in adjectives and different rules of using them.
Суффиксы прилагательных, встречающиеся в заданиях ЕГЭ и ОГЭ:
-able/ible, -al, -ent/ant, -free, -ful, -less, -ic/ical, -ive, -ous, -proof
-able/ible
Служит для образования прилагательных от сущ. и глаголов (возможность, способность осуществления чего-либо):
to change (менять) – changeable (переменчивый)
to compare (сравнивать) – comparable (сравнимый)
to desire (желать) – desirable (желательный)
to read (читать) – readable (удобочитаемый)
to comfort (успокаивать) – comfortable (удобный)
to respect (уважать) – respectable (респектабельный)
to forget (забывать) – unforgettable (незабываемый)
to believe (верить) – unbelievable (невероятный)
vision (видение) – visible (видимый)
to access (иметь доступ)– accessible (доступный)
to flex (сгибать) – flexible (гибкий)
to eat (есть) – edible (съедобный)
-al
Для образования прилагательных от абстрактных существительных:
theatre (театр) – theatrical (театральный)
nature (природа) – natural (природный)
profession (профессия) – professional (профессиональный)
function (функция) – functional (функциональный)
mechanic (механик) – mechanical (механический)
culture (культура) – cultural (культурный)
biology (биология) – biological (биологический)
psychology (психология) – psychological (психологический)
addition (добавление) – additional (добавочный)
fiction (вымысел) – fictional (вымышленный)
-ent/ant
Служат для образования прилагательных, обозначающих качество или состояние:
to differ (различаться)– different (разный)
to depend (зависеть) – (in)dependent (независимый/зависимый)
to resist (сопротивляться) – resistant (устойчивый)
to ignore (игнорировать) – ignorant (невежественный)
to please (угождать) – pleasant (приятный)
to suffice (быть достаточным) – sufficient (достаточный)
to signify (значить) – significant (значимый)
to tolerate (терпеть) – tolerant (терпимый)
-free
Значение: отсутствие чего-либо, свобода от чего-либо:
sugar (сахар) – sugar-free (без сахара)
drug (наркотик) – drug-free (без наркотиков)
smoke (курить) – smoke-free (для некурящих
ice (лед) – ice-free (безо льда)
care (забота) – carefree (беззаботный)
-ful/less
Значение: ful – наличие какого-то качества
less – отсутствие какого-либо качества
help (помощь) – helpful/helpless (отзывчивый/беспомощный)
thought (мысль) – thoughtful/thoughtless (думающий/бездумный)
care (забота) – careful/careless (осторожный/беспечный)
pain (боль) – painful/painless (болезненный/безболезненный)
harm (вред) – harmful/harmless (вредный/безвредный)
power (власть)– powerful/powerless (мощный/бессильный)
use (польза) – useful/useless (полезный/бесполезный)
colour (цвет) – colourful/colourless (красочный/бесцветный)
meaning (значение) – meaningful/meaningless (значимый/бессмысленный)
taste (вкус) – tasteful/tasteless (вкусный/безвкусный)
fear (страх) – fearful/fearless (напуганный/бесстрашный)
Прилагательные с ful/less без пары антонимов:
beautiful – красивый
awful – ужасный
skillful – умелый
brainless – безмозглый
countless – бессчетный
endless – бесконечный
priceless – бесценный
timeless – вечный
worthless – ничего не стоящий
grateful – благодарный
homeless – бездомный
peaceful – мирный
successful – успешный
playful – игривый
dreadful – ужасный
-ic/ical
history (история) – historic/historical (исторический)
economy (экономика) – economic/economical (экономический/экономичный)
magic (магия) – magic/magical (волшебный/магический)
classic (классика) – classic/classical (классический)
academy (академия) – academic (академический)
artist (художник) – artistic (художественный)
drama (драма) – dramatic (драматический)
energy (энергия) – energetic (энергичный)
fantasy (фантазия) – fantastic (фантастический)
critic (критик) – critical (критический)
grammar (грамматика) – grammatical (грамматический)
music (музыка) – musical (музыкальный)
-ive
Значение: имеющий качество, способность
to effect (осуществлять) – effective (эффективный)
to act (действовать) – active (активный)
to impress (впечатлять) – impressive (впечатляющий)
to attract (привлекать) – attractive (привлекательный)
to communicate (общаться) – communicative (общительный)
-ous
Значение: указание на наличие признака или качества
to vary (различаться)– various (различный)
danger (опасность) – dangerous (опасный)
monster (монстр) – monstrous (ужасный)
disaster (бедствие) – disastrous (разрушительный)
humour (юмор) – humorous (юмористический)
caution (осторожность) – cautious (осторожный)
delicacy (лакомство) – delicious (вкусный)
fame (слава)– famous (знаменитый)
adventure (приключение)- adventurous (авантюрный)
-proof
Значение: устойчивость предмета, его защищенность
water (вода) – waterproof (водонепроницаемый)
fire (огонь) – fireproof (огнеупорный)
bullet (пуля) – bulletproof (пуленепробиваемый)
sound (звук) – soundproof (звуконепроницаемый)
air (воздух) – airproof (герметический, воздухонепроницаемый)
wind (ветер) – windproof (ветронепродуваемый)
В данной статье мы рассмотрели все основные суффиксы прилагательных, необходимые для успешной подготовки к экзаменам по английскому языку.
Авторский курс по написанию эссе
Adjectives Suffixes List and Examples
ESL students, do you know how to make your adjectives sound more interesting? By adding suffixes, you can change the meaning and pronunciation of words. In this blog post, we will provide a list of common adjective suffixes with examples. So put on your learning hat and let’s get started!!
List of Adjectives Suffixes and Examples
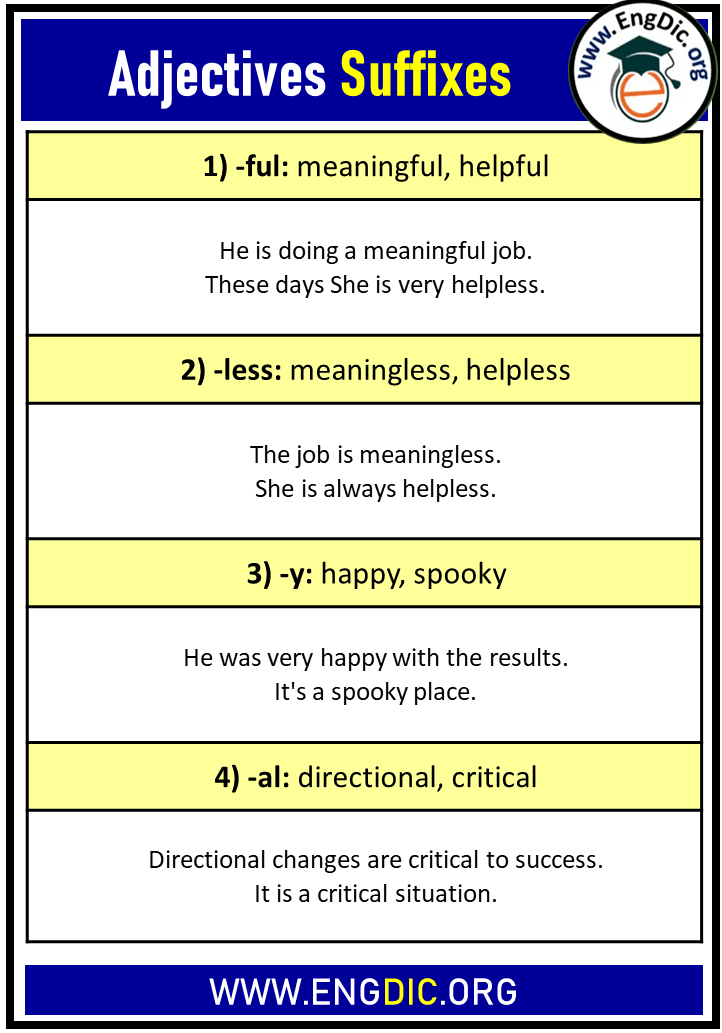
1) -ful: meaningful, helpful
- He is doing a meaningful job.
- These days She is very helpless.
2) -less: meaningless, helpless
- The job is meaningless.
- She is always helpless.
3) -y: happy, spooky
- He was very happy with the results.
- It’s a spooky place.
4) -al: directional, critical
- Directional changes are critical to success.
5) -ous: dangerous, curious
- It’s a dangerous thing to do.
- She is very curious about everything.
6) -able: changeable, lovable
- His moods are changeable.
- She is very lovable.
7) -ic: electric, poetic
- The electric lightbulb was invented by Edison.
- He has a poetic soul.

- He is German.
- She is African.
9) -ish: English, Spanish
- She has a bit of an English accent.
- He sounds a bit more Spanish than usual today.
10) -en: broken, shaken
- The cup is broken.
- His nerves were shaken by the experience.
11) -ty: guilty, pretty
- He is guilty of a serious crime.
- She is pretty in a simple way.
12) -ic: cubic, romantic
- He has a cubic shape.
- Their love is very romantic.
13) -al: criminal, territorial
- He committed a criminal act.
- She was territorial about her property.
14) -ic: fantastic, volcanic
- The party was fantastic.
- She has a volcanic temper.
15) -ive: constructive, defensive
- He is a very constructive person.
- She became very defensive at the accusation.
16) -ment: excellent
- He did an excellent job.
17) -ty: honesty, fertility
- Her honesty can never be doubted.
- The fertility of this soil is amazing.
18) -ful: careful, grateful
- He was very careful with the equipment.
- She was grateful for his help.
19) -less: careless
- He was careless with the equipment.
20) -al: postal
- The postal service is very reliable.
21) -ic: fantastic, photographic
- She has a fantastic memory.
- He has a photographic memory.
22) -ar: cellular, lunar
- She has a cellular structure.
- Is this the lunar calendar?
23) -ic: cubic, electric
- His head was growing cubic in shape.
- The electric company is very reliable.
24) -ine: marine, canine
- He is very marine, having served in the navy.
- She is a canine, being a dog.
25) -ive: additive, divisive
- The additive process is used to make new colors.
- Their relationship was very divisive.
Letters positioned at the end of a word are known as suffixes. These endings can convert the class of a word. For example, adding a particular suffix to a word can change it from a noun to an adjective. Such a group of endings is called adjective suffixes. They turn words into adjectives.
An adjective is something that describes a noun. You can add adjective suffixes to verbs and nouns to create an adjective. Therefore, adjective suffixes change the root word’s grammatical function. For instance, adding -able to the verb cure produces a new adjective that is curable.
The new adjective created will carry the meaning of the original word, but the meaning will function to describe a noun rather than work as a noun or verb itself.
- Adjective Suffixes List PDF
- Key Points to Remember While Adding an Adjective Suffix
- How to Use an Adjective Suffix?
- What are Adjective Suffixes?
- Which are some of the commonly used adjective suffixes?
- Give examples for the adjective suffix ‘ish’?
Adjective Suffixes List PDF
Given below is a list of some of the commonly used adjective suffixes:
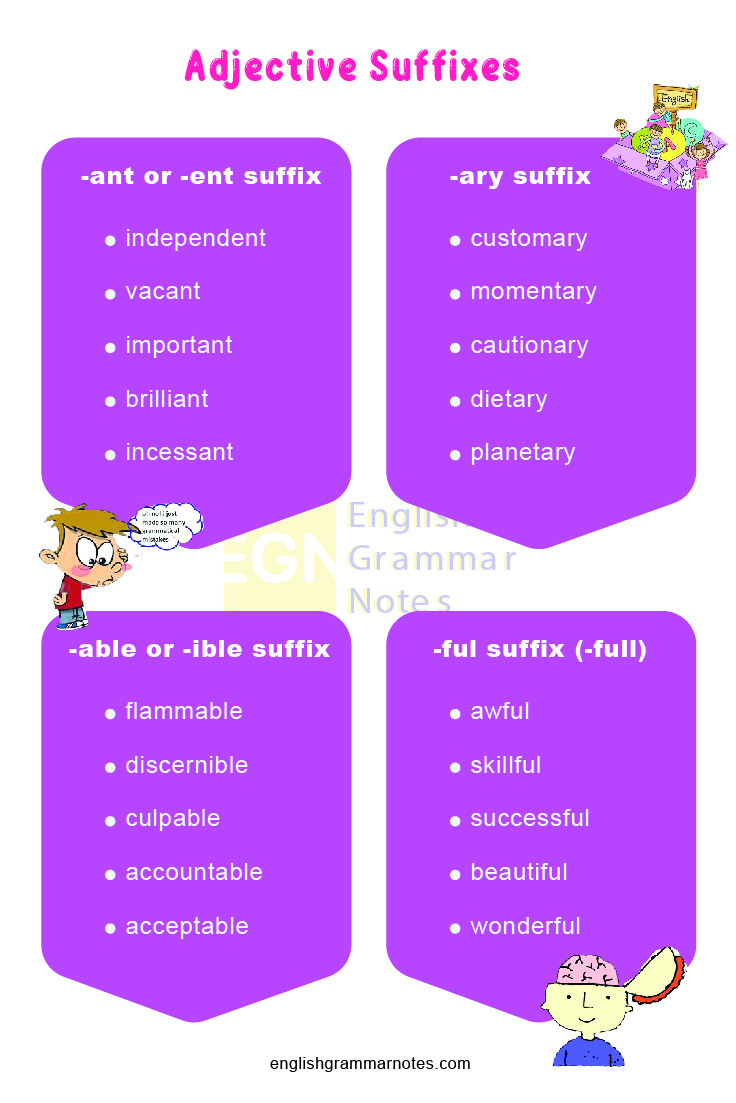
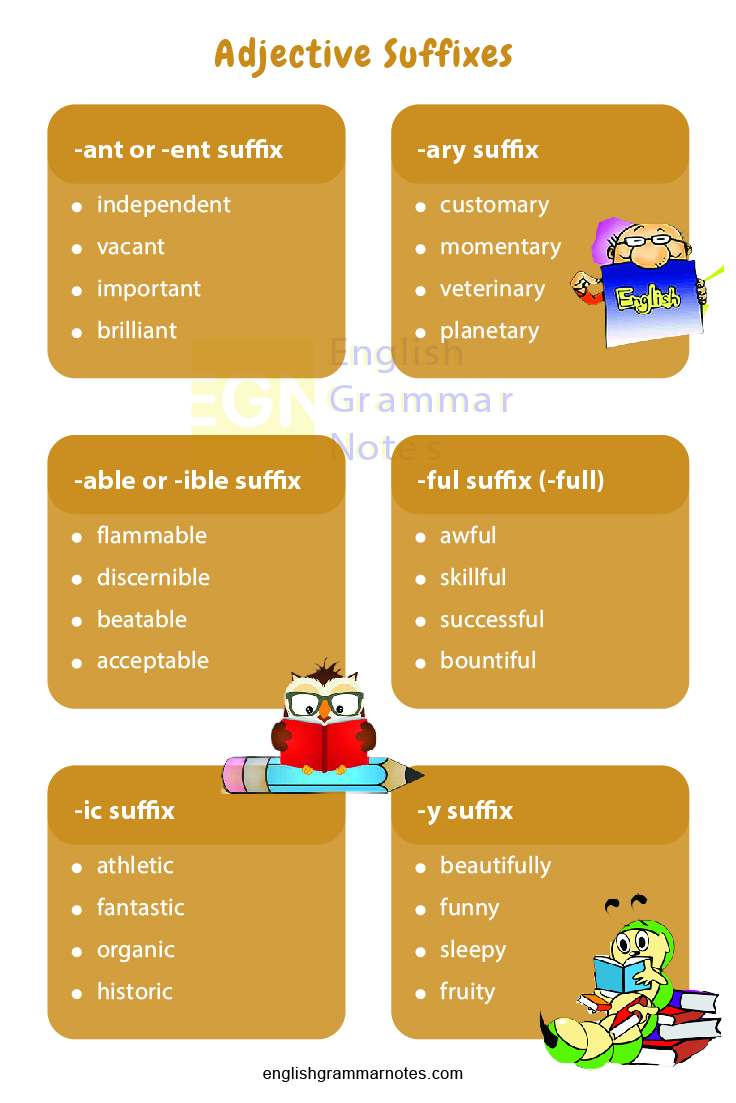
-ant or -ent suffix: Refers to performing or being, inclined towards something/ someone
- independent
- vacant
- important
- brilliant
- incessant
-ary suffix: Relates to something, relating to quality or place
- customary
- momentary
- cautionary
- dietary
- veterinary
- planetary
-able or -ible suffix: (capable of being, capable or worthy of, tending to)
- flammable
- discernible
- culpable
- accountable
- beatable
- acceptable
- edible
-al suffix (-al, -ial, -ical): Means about something, relating to or having the quality of
- accidental
- educational
- brutal
- historical
- regional
- social
- universal
- personal
- experimental
- mental
- universal
-ful suffix (-full): Full of, tending, or liable to
- awful
- skillful
- successful
- bountiful
- beautiful
- wonderful
- careful
-ic suffix: Pertaining or relating to
- athletic
- scenic
- fantastic
- organic
- acidic
- historic
- scenic
-y suffix: Characterized by, tending to
- rainy
- funny
- dirty
- messy
- sleepy
- beautifully
- brainy
- fruity
-like suffix:
- lifelike
- warlike
- childlike
- lifelike
- ladylike
- birdlike
– ish suffix: Origin, nature
- selfish
- sheepish
- pinkish
- bookish
- childish
- boyish
- foolish
– ile suffix: Tending to, capable of
- futile
- gentile
- senile
- fragile
-ive suffix: Performing or tending toward, the nature of
- cooperative
- sensitive
- supportive
- pensive
- creative
-ious or -ous suffix: Full of, relating to, qualities of
- dangerous
- nervous
- gracious
- mysterious
- poisonous
- victorious
-less suffix: Without, lacking, unable to act
- powerless
- friendless
- worthless
- useless
- homeless
- careless
- breathless
- faithless
- fearless
-an, -ian suffix: Refers to one who is or does, related to
- agrarian
- simian
Key Points to Remember While Adding an Adjective Suffix
In certain cases when a suffix gets added to a root word the spelling of the root word transforms. The adjective suffix, ‘-ness’, when combined with words that end with ‘y’ a spelling change occurs. Take the example of the word heavy. Adding the suffix –ness turns the y into i before you get the new word heaviness.
It is necessary to be aware of whether a suffix transforms the spelling of the root word. Learning such common spelling alterations will make sure that you spell a word in the right way.
How to Use an Adjective Suffix?
- Pick a noun or verb to use as the root word. Root word: Home
- Secondly, choose a suffix to attach to the root word Suffix: less.
- Add the suffix to the root to form the adjective. Home+less= Homeless.
Also, See:
- Dis Prefix
- In Prefix
- Prefixes
FAQs on Adjective Suffixes
1. What are Adjective Suffixes?
An adjective is something that describes a noun. An adjective suffix is added to verbs and nouns to create an adjective. Therefore, adjective suffixes change the root word’s grammatical function. For instance, adding -able to the verb cure produces a new adjective that is curable.
2. Which are some of the commonly used adjective suffixes?
An adjective suffix is added to verbs and nouns to create an adjective. Common adjective suffixes include ious, ish, less, I’ve, etc.
3. Give examples for the adjective suffix ‘ish’?
An adjective is that which describes a noun. An adjective suffix is added to verbs and nouns to create an adjective. Therefore, adjective suffixes change the root word’s grammatical function.’ish’ is a commonly used adjective suffix. Examples include: childish, boyish, girlish, bookish, etc.
Conclusion
Understanding what adjective suffixes are will help you convert nouns and verbs into adjectives. Learning these word-endings will help you distinguish between a noun, adjective, verb, or adverb. Having an idea of adjective suffixes that alter the spellings of words will make sure that you spell them the right way. So make sure to familiarise yourself with the common adjective suffixes. You can even check our other articles on English Vocabulary Words.
|
ADJECTIVE
|
||
| Suffix |
Original word |
Derived word |
| -able, -ible |
accept adapt afford access admit allow apply avail avoid believe change collect comfort comprehensive convert depend desire digest eat enjoy force notice present profit question recycle rely rent respond suit tax understand value |
acceptable adaptable affordable accessible admissible allowable applicable available avoidable believable changeable collectible comfortable comprehensible convertible dependable desirable digestible edible enjoyable forcible noticeable presentable printable profitable questionable recyclable reliable rentable responsible suitable taxable understandable valuable |
| -al |
accident benefit economy electricity emotion environment ethic face fanatic globe industry influence logic music nation office origin politics part person practice profession psycology region sentiment tide toxic typic use |
accidental beneficial economical electrical emotional environmental ethical facial anatical global industrial influential logical musica national official original political (im)partial (im)personal practical professional psycological regional sentimental tidal toxical typical (un)usual |
| -ary |
aliment — — imagine literate militar necessity revolution second — |
alimentary auxiliary contrary imaginary literary military necessary revolutionary secondary temporary |
| -esque |
— — — |
burlesque grotesque picturesque |
| -ful |
beauty care cheer colour fancy forget — harm help hope joy law pain peace power sin sorrow success thank thought use wonder |
beautiful careful cheerful colourful fanciful forgetful grateful harmful helpful hopeful joyful lawful painful peaceful powerful sinful sorrowful successful thankful thoughtful useful wonderful |
| -ic |
academy air alcohol dynamo economy electricity electron gen language mith toxin tragedy |
academic aerobic alcoholic dynamic economic electric electronic genetic linguistic mythic toxic tragic |
| -ious, -ous |
ambition anxiety caution conscience courtesy curiosity danger delight fame fury generosity glamour glory harmony infection jealousy luxury miracle mystery nerve — prestige — prodigy religion ridicule seriousness suspicion (n), suspect (v) vary (v), variety (n) vice |
ambitious anxious cautious conscious courteous curious dangerous delicious famous furious generous glamourous glorious harmonious infectious jealous luxurious miraculous mysterious nervous obvious prestigious previous prodigious religious ridiculous serious suspicions various vicious |
| -ish |
child England fiend new self short |
childish English fiendish newish selfish shortish |
| -ive |
abort abuse act addict adopt affirmation attract compare compete create decide description destroy education effect excess expend explode mass narration negation produce support |
abortive abusive active addictive adoptive affirmative attractive comparative competitive creative decisive descriptive destructive educative effective excessive expensive explosive massive narrative negative productive supportive |
| -less |
breath care colour end harm help home hope pain power reck sleep smoke speech stain sugar taste thought use |
breathless careless colourless endless harmless helpless homeless hopeless painless powerless reckless sleepless smokeless speechless stainless sugarless tasteless thoughtless useless |
| -ly |
alone body brother coward cost day dead — elder friend ghost heaven — home hour joy kind — live love month night order sick — week wool wrink year |
lonely bodily brotherly cowardly costly daily deadly early elderly (un)friendly ghostly heavenly holy homely hourly jolly kindly (un)likely lively lovely (bi)montly night orderly sickly ugly (bi)weekly woolly wrinkly yearly |
| -y |
bag cheek chill cloud — curl ease fog freak fruit hill might salt scare shag sleep smell smoke sugar |
baggy cheeky chilly cloudy cosy (Br) / cozy (US) curly easy foggy freaky fruity hilly mighty salty scary shaggy sleepy smelly smoky sugary |
Common Suffixes in English with meaning and Examples!
What are Suffixes in english Grammar?
A suffix is a letter or group of letters, for example ‘-ly’ or ‘-ness,’ which is added to the end of a word in order to form a different word, often of a different word class.
Learn Common Noun Suffixes in English with Pictures. How to use suffixes to create nouns from adjectives and verbs. Our suffix word lists are the second part of our comprehensive root word tables.
Common Suffixes in English
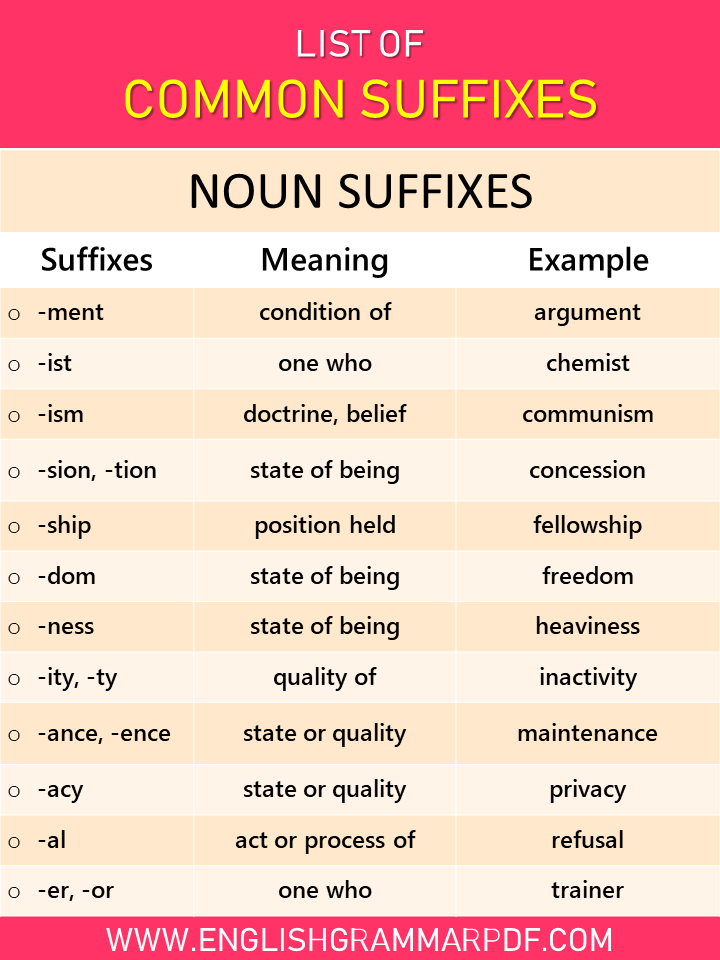
Noun Suffixes |
||
| Suffixes | Meaning | Example |
| -ment | condition of | argument, government, punishment |
| -ist | one who | chemist, racist, plagiarist |
| -ism | doctrine, belief | communism, feminism, skepticism |
| -sion, -tion | state of being | concession, transcription, abbreviation |
| -ship | position held | fellowship, scholarship, kinship, internship |
| -dom | state of being | freedom, boredom |
| -ness | state of being | heaviness, sadness, testiness |
| -ity, -ty | quality of | inactivity, veracity, parity, serenity |
| -ance, -ence | state or quality | maintenance, eminence, assurance |
| -acy | state or quality | privacy, fallacy, delicacy |
| -al | act or process of | refusal, recital, rebuttal |
| -er, -or | one who | trainer, protector, narrator |
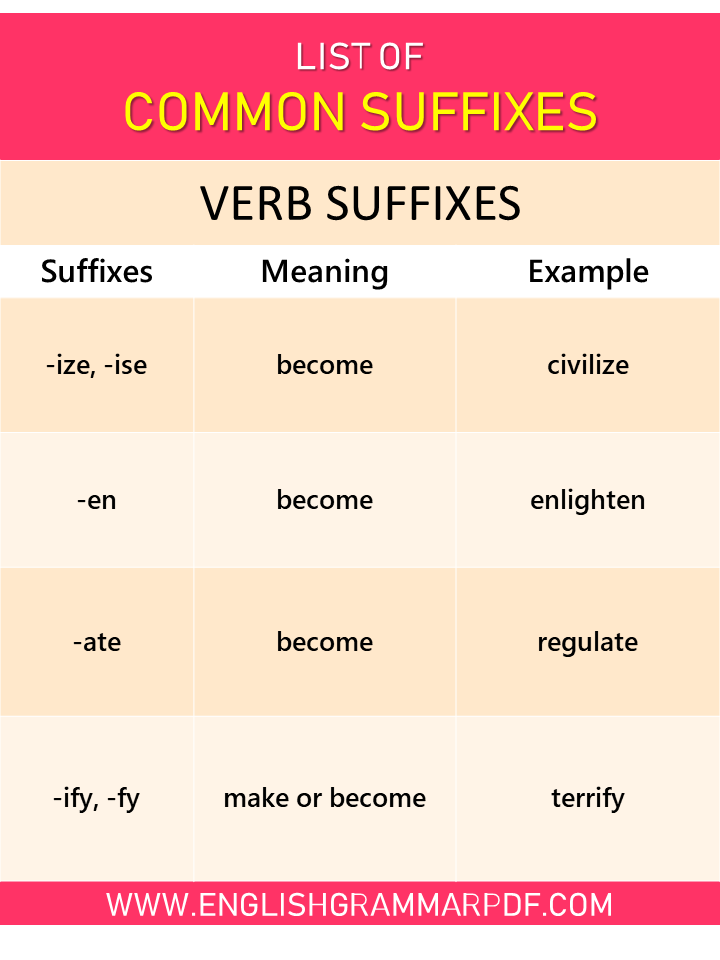
Verb Suffixes |
||
| Suffixes | Meaning | Example |
| -ize, -ise* | become | civilize, humanize, socialize, valorize |
| -en | become | enlighten, awaken, strengthen |
| -ate | become | regulate, eradicate, enunciate, repudiate |
| -ify, -fy | make or become | terrify, satisfy, rectify, exemplify |
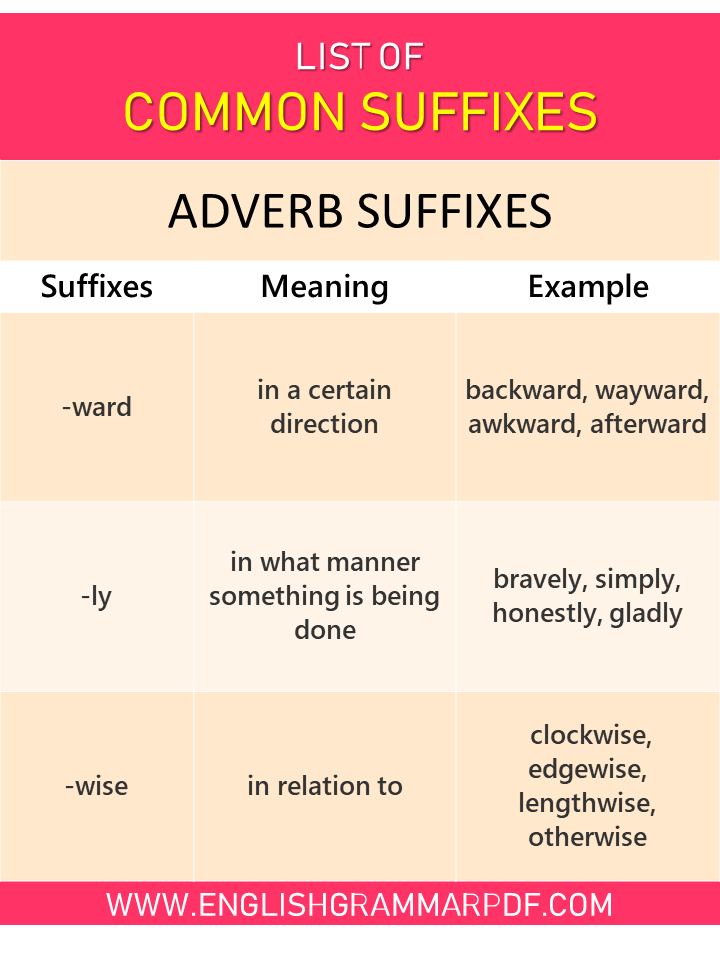
Adverb Suffixes |
||
| Suffixes | Meaning | Example |
| -ward | in a certain direction | backward, wayward, awkward, afterward |
| -ly | in what manner something is being done | bravely, simply, honestly, gladly |
| -wise | in relation to | clockwise, edgewise, lengthwise, otherwise |
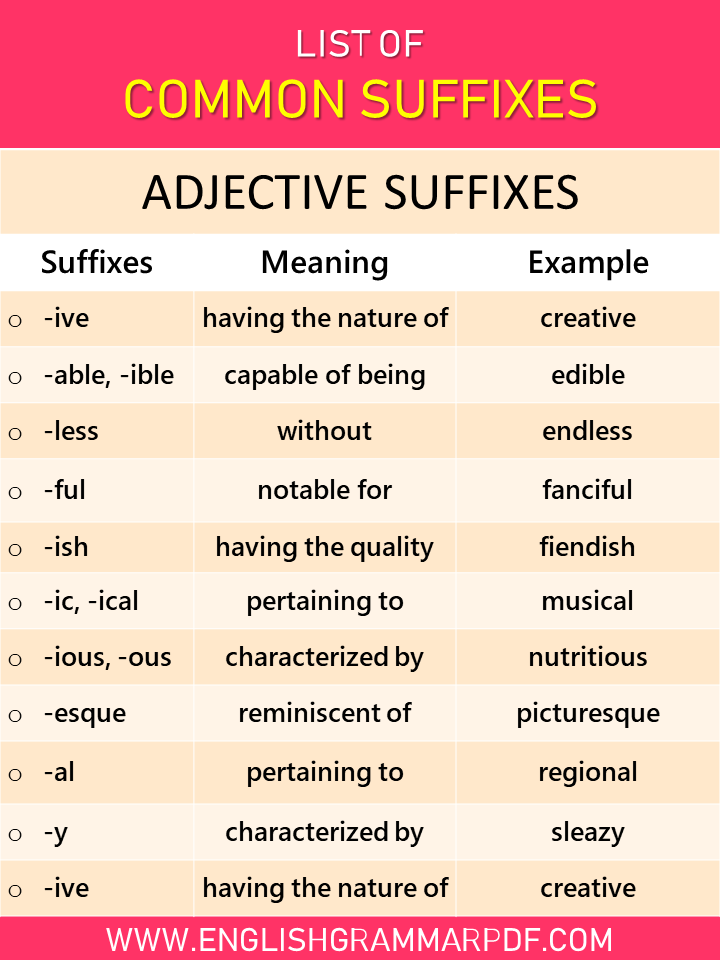
Adjective Suffixes |
||
| Suffixes | Meaning | Example |
| -ive | having the nature of | creative, punitive, divisive, decisive |
| -able, -ible | capable of being | edible, presentable, abominable, credible |
| -less | without | endless, ageless, lawless, effortless |
| -ful | notable for | fanciful, resentful, woeful, doubtful |
| -ish | having the quality of | fiendish, childish, snobbish |
| -ic, -ical | pertaining to | musical, mythic, domestic, chiastic |
| -ious, -ous | characterized by | nutritious, portentous, studious |
| -esque | reminiscent of | picturesque, statuesque, burlesque |
| -al | pertaining to | regional, grammatical, emotional, coastal |
| -y | characterized by | sleazy, hasty, greasy, nerdy, smelly |
Related: Prefixes List a to z
Infographics (Common Suffixes in English)
Download this List of Common Suffixes in English PDF (Download PDF)
About The Author
Производные (derived) прилагательные образуются путем прибавления суффиксов к глаголам, существительным и другим прилагательным.
Наиболее употребительные суффиксы производных имен прилагательных. Таблица 1-2.
| Суффикс | Значение | Примеры и комментарии |
| глагол + -able; —ible | выполнимый (но не выполняемый), способный поддаваться действию
(можно переводить придаточным предложением, начиная со слов: который можно + исходный глагол) |
eat — eatable (съедобный — который можно съесть) enjoy — enjoyable (приятный — который доставляет удовольствие) read — readable (читабельный — который можно читать) detect — detectable (обнаружимый — который можно обнаружить) observe — observable (который можно наблюдать, а не наблюдаемый) predict — predictable (предсказуемый — который можно предсказать) comprehend — comprehensible (понимаемый — который можно понять) convert — convertible (превращаемый — который можно превратить) vision — visible (видимый — который можно увидеть) |
| существительное + -able; —ible | наличие признака, свойства или качества, выраженного основой | comfort — comfortable (удобный) fashion — fashionable (модный) knowledge — knowledgeable (умный) value — valuable (ценный) access — accessible (доступный) |
| существительное + —al | имеющий природу, относящийся к тому, что выражено основой | centre — central (центральный) emotion — emotional (эмоциональный) norm — normal (нормальный) nature — natural (природный) season — seasonal (сезонный) |
| -an; -ian | территориальная или национальная принадлежность; язык | America — American (американский) Mexico — Mexican (мексиканский) Russia — Russian (русский) |
| -ese | территориальная или национальная принадлежность; язык | China — Chinese (китайский) Japan — Japanese (японский) Portugal — Portuguese (португальский) |
| существительное + -ish | территориальная или национальная принадлежность; язык | Denmark — Danish (датский) England — English (английский) Poland — Polish (польский) Scotland — Scottish (шотландский) |
| глагол + -ant существительное на -ance + -ant существительное на -ence + -ant |
характеризуют лица или предметы как имеющие или проявляющие определенные качества | arrogance — arrogant (высокомерный) relevance — relevant (уместный, относящийся к делу) ignore — ignorant (невежественный) importance — important (важный) significance — significant (значительный) observe — observant (наблюдательный) |
| глагол + -ent существительноена -ence + -ent |
характеризуют лица или предметы как имеющие или проявляющие определенные качества | dependence — dependent (зависимый) difference — different (различный) evidence — evident очевидный exist — existent (существующий) persist — persistent (настойчивый) intelligence — intelligent (умный) |
| существительное + -ary прилагательное + -ary; -ory |
качество | advise — advisory (рекомендательный) contradict — contradictory (противоречивый) diet — dietary (диетический) document — documentary (документальный) element — elementary (элементарный) imagine — imaginary (воображаемый) second — secondary (вторичный) revolution — revolutionary (революционный) |
| глагол + -ate | разнообразные значения | adequacy — adequate (адекватный) affection — affectionate (любящий) consider — considerate (внимательный) literacy — literate (грамотный) moderation — moderate (умеренный) passion — passionate (страстный) |
Adjective Suffixes. List of Adjective Suffixes with rules and examples
Suffix is a group or words which can be added at the end of a word for changing its parts of speech. It can change a noun into adjective, an adjective into adverb and verb into adjective depending upon the requirements. There are some specific suffixes which turn nouns into adjectives and they are called adjective suffixes. Adjectives including suffixes also modify and qualify noun just like other adjectives.
There are certain suffixes which are added to only adjectives. Those suffixes can be added at the end of any noun or verb to transform into adjectives for changing a word’s grammatical usage in a sentence. After viewing some definite suffixes students will be able to identify adjectives just by looking into those suffixes. They can also use adjectives in correct form within a text. Adding able to verb move becomes adjective moveable which produces a new word. So, it is clear that able can be added to noun or verb for making those into adjective form.
List of Adjective Suffixes with Examples
Students should also notice that after adding certain suffixes to words the spelling also changed. The common suffix ness is added to the word sleep will be sleepiness in adjective. Not all root words’ spelling are changed due to suffix but some specific words are changed. For that students must follow the formation of adjectives including suffixes for different words. We have provided all common adjectives suffixes with explanation for students below:
i) Suffix –able and –ible:
These two suffixes are added to nouns or verbs for transforming those into adjectives. This kind of adjectives explains if a noun is capable of something, worthy or just by being there.
Ex.
Accountable, acceptable, edible, flammable, beatable, discernible etc.
His behaviour in office hours was quite accountable to us.
We eat vegetarian food because this is edible for us.
ii) Suffix –al, -ical, -ial:
When we need to specify someone is relating to something, pertaining to some other thing and have the particular quality these suffixes are added.
Ex.
Universal, personal, accidental, regional, educational, historical, mental, social etc.
We should always focus on our personal growth.
The part in the road is quite accidental.
We went to some historical places in our last trip.
She must know the regional language for getting the job.
iii) Suffix –ent and –ant:
It refers to performing or being somewhere, inclined to something for nouns.
Ex.
Brilliant, important, independent, vacant etc.
iv) Suffix -ary:
This suffix refers to relation with something for place and quality.
Ex.
Cautionary, planetary, veterinary, momentary, dietary etc.
v) Suffix –ful or –full:
It means something full of, liable to something and tending.
Ex.
Beautiful, careful, respectful, skilful, wonderful, successful etc.
vi) Suffix –ic:
This suffix express something pertaining to and relative to someone.
Ex.
Historic, scenic, acidic, athletic, organic, fantastic etc.
vii) Suffix –ive:
With this suffix adjectives refer someone or somethibg tending or performing to, to explain nature of persons.
Ex.
Sensitive, creative, respective, supportive, cooperative etc.
viii) Suffix –ious and –ous:
It also mentions something full of, explains the quality and relation with something.
Ex.
Mysterious, poisonous, victorious, generous, dangerous etc.
ix) Suffix –less:
It generally used for explaining negative sense like lack of something, without something and inability.
Ex.
Homeless, jobless, priceless, powerless, shameless, careless, fearless, useless, worthless etc.
x) Suffix –y:
It refers to characterisation and tending to something.
Ex.
Rainy, cloudy, messy, sleepy, dirty, brainy, funny etc.
xi) Suffix –like:
To mentions something likewise.
Ex.
Childlike, birdlike, lifelike, warlike etc.
xii) Suffix –ish:
To explain someone’s origin and nature.
Ex.
Foolish, boyish, selfish, bookish, childish etc.
xiii) Suffix –ile:
To refer someone capable os something significant.
Ex.
Futile, fragile, senile etc.
xiv) Suffix –ian and –an:
With this suffix adjectives explain something related to, some person who does.
Ex.
Simian, agrarian etc.
FAQs:
- What is the purpose of learning adjective suffix?
Answer. After learning adjective suffixes students will be able to identify adjectives correctly and use them in proper places.
- From where students will get learning resources of adjective suffixes?
Answer. Students should rely on this article where all common adjective suffixes have been explained with perfect examples.
For more update follow net explanations page