Свойство ActiveCell объекта Application, применяемое в VBA для возвращения активной ячейки, расположенной на активном листе в окне приложения Excel.
Свойство ActiveCell объекта Application возвращает объект Range, представляющий активную ячейку на активном листе в активном или указанном окне приложения Excel. Если окно не отображает лист, применение свойства Application.ActiveCell приведет к ошибке.
Если свойство ActiveCell применяется к активному окну приложения Excel, то идентификатор объекта (Application или ActiveWindow) можно в коде VBA Excel не указывать. Следующие выражения, скопированные с сайта разработчиков, являются эквивалентными:
|
ActiveCell Application.ActiveCell ActiveWindow.ActiveCell Application.ActiveWindow.ActiveCell |
Но если нам необходимо возвратить активную ячейку, находящуюся в неактивном окне приложения Excel, тогда без указания идентификатора объекта на обойтись:
|
Sub Primer1() With Windows(«Книга2.xlsx») .ActiveCell = 325 MsgBox .ActiveCell.Address MsgBox .ActiveCell.Value End With End Sub |
Программно сделать ячейку активной в VBA Excel можно с помощью методов Activate и Select.
Различие методов Activate и Select
Выберем программно диапазон «B2:E6» методом Select и выведем адрес активной ячейки:
|
Sub Primer2() Range(«B2:E6»).Select ActiveCell = ActiveCell.Address End Sub |
Результат:
Как видим, активной стала первая ячейка выбранного диапазона, расположенная слева вверху. Если мы поменяем местами границы диапазона (Range("E6:B2").Select), все равно активной станет та же первая ячейка.
Теперь сделаем активной ячейку «D4», расположенную внутри выделенного диапазона, с помощью метода Activate:
|
Sub Primer3() Range(«E6:B2»).Select Range(«D4»).Activate ActiveCell = ActiveCell.Address End Sub |
Результат:
Как видим, выбранный диапазон не изменился, а активная ячейка переместилась из первой ячейки выделенного диапазона в ячейку «D4».
И, наконец, выберем ячейку «D4», расположенную внутри выделенного диапазона, с помощью метода Select:
|
Sub Primer4() Range(«E6:B2»).Select Range(«D4»).Select ActiveCell = ActiveCell.Address End Sub |
Результат:
Как видим, ранее выбранный диапазон был заменен новым, состоящим из одной ячейки «D4». Такой же результат будет и при активации ячейки, расположенной вне выбранного диапазона, методом Activate:
|
Sub Primer5() Range(«E6:B2»).Select Range(«A3»).Activate ActiveCell = ActiveCell.Address End Sub |
Аналогично ведут себя методы Activate и Select при работе с выделенной группой рабочих листов.
Свойство Application.ActiveCell используется для обращения к одной ячейке, являющейся активной, а для работы со всеми ячейками выделенного диапазона используется свойство Application.Selection.
Home / VBA / How to use ActiveCell in VBA in Excel
In VBA, the active cell is a property that represents the cell that is active at the moment. When you select a cell or navigate to a cell and that green box covers that cell you can use ACTIVECELL property to refer to that cell in a VBA code. There are properties and methods that come with it.

Use the Active Cell Property
- Type the keyword “ActiveCell”.
- Type a dot (.) to get the list properties and methods.
- Select the property or method that you want to use.
- Run the code to perform the activity to the active cell.

Important Points
- When you use the active cell property VBA refers to the active cell of the active workbook’s active sheet’s, irrespective of how many workbooks are open at the moment.
- ActiveCell is ultimately a cell that comes with all the properties and methods that a normal cell comes with.
Activate a Cell from the Selected Range
To activate a cell using a VBA code there are two ways that you can use one “Activate” method and “Select” method.
Sub vba_activecell()
'select and entire range
Range("A1:A10").Select
'select the cell A3 from the selected range
Range("A3").Activate
'clears everything from the active cell
ActiveCell.Clear
End SubThe above code, first of all, selects the range A1:A10 and then activates the cell A3 out of that and in the end, clears everything from the active cell i.e., A3.
Return Value from the Active Cell
The following code returns the value from the active cell using a message box.
MsgBox ActiveCell.ValueOr if you want to get the value from the active cell and paste it into a separate cell.
Range("A1") = ActiveCell.ValueSet Active Cell to a Variable
You can also set the active cell to the variable, just like the following example.
Sub vba_activecell()
'declares the variable as range
Dim myCell As Range
'set active cell to the variable
Set myCell = ActiveCell
'enter value in the active cell
myCell.Value = Done
End SubGet Row and Column Number of the ActiveCell
With the active cell there comes a row and column property that you can use to get the row and column number of the active cell.
MsgBox ActiveCell.Row
MsgBox ActiveCell.ColumnGet Active Cell’s Address
You can use the address property to get the address of the active cell.
MsgBox ActiveCell.AddressWhen you run the above code, it shows you a message box with the cell address of the active cell of the active workbook’s active sheet (as I mentioned earlier).
Move from the Active Cell using Offset
With offset property, you can move to a cell which is a several rows and columns away from the active cell.
ActiveCell.Offset(2, 2).SelectSelect a Range from the Active Cell
And you can also select a range starting from the active cell.
Range(ActiveCell.Offset(1, 1), ActiveCell.Offset(5, 5)).SelectMore Tutorials
- Count Rows using VBA in Excel
- Excel VBA Font (Color, Size, Type, and Bold)
- Excel VBA Hide and Unhide a Column or a Row
- Excel VBA Range – Working with Range and Cells in VBA
- Apply Borders on a Cell using VBA in Excel
- Find Last Row, Column, and Cell using VBA in Excel
- Insert a Row using VBA in Excel
- Merge Cells in Excel using a VBA Code
- Select a Range/Cell using VBA in Excel
- SELECT ALL the Cells in a Worksheet using a VBA Code
- Special Cells Method in VBA in Excel
- UsedRange Property in VBA in Excel
- VBA AutoFit (Rows, Column, or the Entire Worksheet)
- VBA ClearContents (from a Cell, Range, or Entire Worksheet)
- VBA Copy Range to Another Sheet + Workbook
- VBA Enter Value in a Cell (Set, Get and Change)
- VBA Insert Column (Single and Multiple)
- VBA Named Range | (Static + from Selection + Dynamic)
- VBA Range Offset
- VBA Sort Range | (Descending, Multiple Columns, Sort Orientation
- VBA Wrap Text (Cell, Range, and Entire Worksheet)
- VBA Check IF a Cell is Empty + Multiple Cells
⇠ Back to What is VBA in Excel
Helpful Links – Developer Tab – Visual Basic Editor – Run a Macro – Personal Macro Workbook – Excel Macro Recorder – VBA Interview Questions – VBA Codes
Активная ячейка в Excel VBA
Активная ячейка — это текущая выбранная ячейка на листе, активная ячейка в VBA может использоваться как ссылка для перехода к другой ячейке или изменения свойств той же активной ячейки или ссылки на ячейки, предоставленной из активной ячейки, активная ячейка в VBA может можно получить с помощью метода application.property с ключевым словом active cell.
Для эффективной работы с кодированием VBA важно понимать концепцию объекта диапазона и свойств ячеек в VBA. В этих концепциях есть еще одна концепция, которую вам нужно изучить, это «активная ячейка VBA».
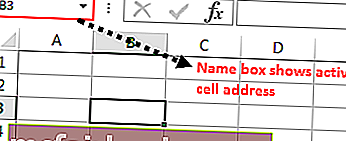
В Excel есть миллионы ячеек, и вы наверняка сомневаетесь, какая из них является активной. Для примера посмотрите на изображение ниже.
На самом изображении выше у нас есть много ячеек, чтобы определить, какая из них является активной ячейкой, очень просто, какая бы ячейка не была выбрана прямо сейчас, она называется «Активная ячейка» в VBA.
Если ваша активная ячейка не видна в вашем окне, посмотрите на поле имени, оно покажет вам адрес активной ячейки, на приведенном выше изображении адрес активной ячейки — B3.
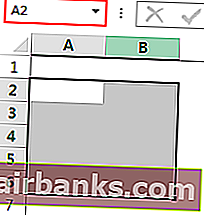
Даже когда в качестве диапазона ячеек выбрано множество ячеек, любая первая ячейка в выделении становится активной ячейкой. Например, посмотрите на изображение ниже.
# 1 — Ссылки в Excel VBA
В наших предыдущих статьях мы видели, как ссылаться на ячейки в VBA. По свойству Active Cell мы можем ссылаться на ячейку.
Например, если мы хотим выбрать ячейку A1 и вставить значение «Hello», мы можем записать его двумя способами. Ниже приведен способ выбора ячейки и вставки значения с помощью объекта VBA «RANGE».
Код:
Sub ActiveCell_Example1 () Диапазон ("A1"). Выберите диапазон ("A1"). Value = "Hello" End Sub
Сначала будет выбрана ячейка A1 « Диапазон (« A1 »). Выбрать»
Затем он вставит значение «Hello» в диапазон ячейки A1 («A1»). Value = «Hello»
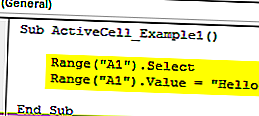
Теперь я удалю строку Range («A1»). Value = «Hello» и использую свойство Active Cell для вставки значения.
Код:
Sub ActiveCell_Example1 () Диапазон ("A1"). Выберите ActiveCell.Value = "Hello" End Sub
Точно так же сначала он выберет ячейку A1 « Диапазон (« A1 »). Выбрать»
Но здесь я использовал ActiveCell.Value = «Hello» вместо Range («A1»). Value = «Hello»
Причина, по которой я использовал свойство Active Cell, потому что в тот момент, когда я выбираю ячейку A1, она становится активной ячейкой. Таким образом, мы можем использовать свойство Excel VBA Active Cell для вставки значения.
# 2 — Активный адрес ячейки, значение, строка и номер столбца
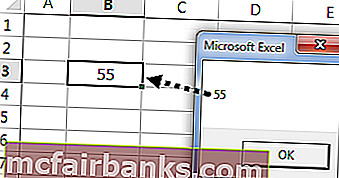
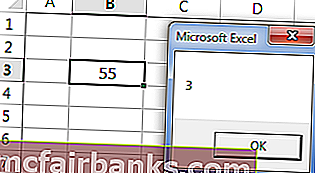
Чтобы понять это еще лучше, давайте покажем адрес активной ячейки в окне сообщения. Теперь посмотрите на изображение ниже.
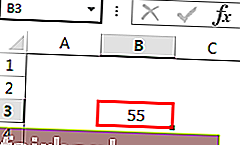
На изображении выше активной ячейкой является «B3», а значение — 55. Давайте напишем код на VBA, чтобы получить адрес активной ячейки.
Код:
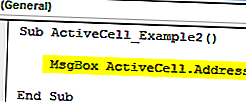
Sub ActiveCell_Example2 () MsgBox ActiveCell.Address End Sub
Запустите этот код с помощью клавиши F5 или вручную, тогда он покажет адрес активной ячейки в окне сообщения.
Выход:
Точно так же код ниже покажет значение активной ячейки.
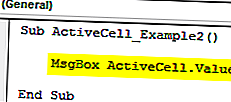
Код:
Sub ActiveCell_Example2 () MsgBox ActiveCell.Value End Sub
Выход:
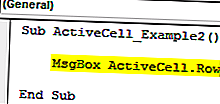
Код ниже покажет номер строки активной ячейки.
Код:
Sub ActiveCell_Example2 () MsgBox ActiveCell.Row End Sub
Выход:
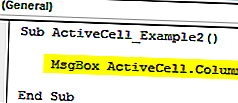
Код ниже покажет номер столбца активной ячейки.
Код:
Подложка ActiveCell_Example2 () MsgBox ActiveCell.Column End Sub
Выход:
# 3 — Параметры активной ячейки в Excel VBA
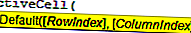
Свойство Active Cell также имеет параметры. После ввода свойства ActiveCell откройте скобку, чтобы увидеть параметры.
Используя этот параметр, мы также можем ссылаться на другую ячейку.
Например, ActiveCell (1,1) означает, какая ячейка активна. Если вы хотите переместиться на одну строку ниже, вы можете использовать ActiveCell (2,1), здесь 2 не означает, что нужно переместиться на две строки вниз, а не только на одну строку вниз. Аналогично, если вы хотите переместить один столбец вправо, тогда это код ActiveCell (2,2)
Для примера посмотрите на изображение ниже.
На изображении выше активной ячейкой является A2, чтобы вставить значение в активную ячейку, вы пишете этот код.
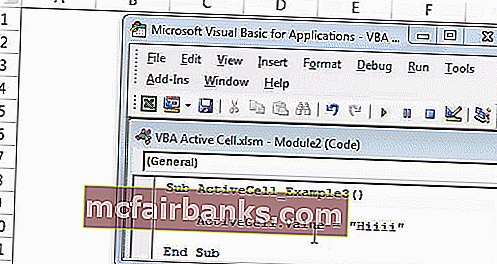
Код:
ActiveCell.Value = «Hiiii» или ActiveCell (1,1) .Value = «Hiiii»
Запустите этот код вручную или с помощью клавиши F5, это вставит значение «Hiiii» в ячейку.
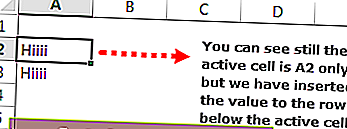
Теперь, если вы хотите вставить то же значение в ячейку ниже, вы можете использовать этот код.
Код:
ActiveCell (2,1) .Value = «Hiiii»
Это вставит значение в ячейку под активной ячейкой.
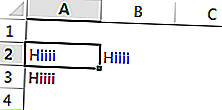
Если вы хотите вставить значение в один столбец справа, вы можете использовать этот код.
Код:
ActiveCell (1,2) .Value = «Hiiii»
Это вставит «Hiiii» в следующую ячейку столбца активной ячейки.
Таким образом, мы можем ссылаться на ячейки в VBA, используя свойство Active Cell.
Надеюсь, вам понравилось. Спасибо, что уделили нам время.
Вы можете скачать шаблон VBA Active Cell Excel здесь: — VBA Active Cell Template
‘Active Cell’ is an important concept in Excel.
While you don’t have to care about the active cell when you’re working on the worksheet, it’s an important thing to know when working with VBA in Excel.
Proper use of the active cell in Excel VBA can help you write better code.
In this tutorial, I first explained what is an active cell, and then show you some examples of how to use an active cell in VBA in Excel.
What is an Active Cell in Excel?
An active cell, as the name suggests, is the currently active cell that will be used when you enter any text or formula in Excel.
For example, if I select cell B5, then B5 becomes my active cell in the worksheet. Now if I type anything from my keyboard, it would be entered in this cell, because this is the active cell.
While this may sound obvious, here is something not that obvious – when you select a range of cells, even then you would only have one active cell.
For example, if I select A1:B10, although I have 20 selected cells, I still have only one single active cell.
So now, if I start typing any text or formula, it would only be entered in the active cell.
You can identify the active cell by looking at the difference in color between the active cell in all the other cells in the selection. You would notice that the active cell is of a lighter shade than the other selected cells.

Another quick way to know which cell is the active cell is by looking at the Name box (the field that is next to the formula bar). The cell reference of the active cell would be shown in the Name Box.

Using Active Cell in VBA in Excel
Now that I’ve explained what is an active cell in a worksheet in excel, let’s learn how an Active cell can be used in Excel VBA.
Active Cell Properties and Methods
In VBA, you can use an active cell in two ways:
- To get the information about it (these are called Properties)
- To perform some action on it (these are called Methods)
Here is how you can access all the properties and methods of an active cell in VBA:
- Open a Module in Excel VBA editor
- Type the phrase ‘ActiveCell’
- Enter a dot (.) after the word ActiveCell
As soon as you do this, you would notice that a set of properties and methods appear as a drop-down (this is called an IntelliSense in Excel VBA).
In the drop-down that appears, you would see two types of options – the one that has a green icon and the one that has a gray icon (with a hand).
The one with the grey icons is the Properties, and the one with the green icons is the Methods.
Some examples of Methods would include Activate, AddComment, Cut, Delete, Clear, etc. As you can notice, these are actions that can be performed on the active cell.
Some examples of Properties would include Address, Font, HasFormula, Interior.Color. All these are properties of the active cell that gives you information about that active cell.
For example, you can use this to get the cell address of the active cell or change the interior cell color of the cell.
Now let’s have a few simple VBA code examples that you can use in your day-to-day work when working with active cell in excel
Making a Cell the Active Cell
To make any cell the active cell, you first have to make sure that it is selected.
If you only have one single cell selected, it by default becomes the active cell.
Below is the VBA code to make cell B5 the active cell:
Sub Change_ActiveCell()
Range("B5").Activate
End Sub
In the above VBA code, I have first specified the cell address of the cell that I want to activate (which is B5), and then I use the activate method to make it the active cell.
When you only want to make one single cell the active cell, you can also use the select method (code below):
Sub Change_ActiveCell()
Range("B5").Select
End Sub
As I mentioned earlier, you can only have one active cell even if you have a range of cell selected.
With VBA, you can first select a range of cells, and then make any one of those cells the active cell.
Below the VBA code that would first select range A1:B10, and then make cell A5 the active cell:
Sub Select_ActiveCell()
Range("A1:B10").Select
Range("A5").Activate
End Sub
Clear the Active Cell
Below is the VBA code that would first make cell A5 the active cell, and then clear its content (cell content as well any formatting applied to the cell).
Sub Clear_ActiveCell()
Range("A5").Activate
ActiveCell.Clear
End Sub
Note that I have shown you the above code just to show you how the clear method work with active cell. In VBA, you don’t need to always select or activate the cell to perform any method on it.
For example, you can also clear the content of cell A5 using the below code:
Sub Clear_CellB5()
Range("A5").Clear
End Sub
Get the Value from the Active Cell
Below the VBA code that could show you a message box displaying the value in the active cell:
Sub Show_ActiveCell_Value()
MsgBox ActiveCell.Value
End Sub
Similarly, you can also use a simple VBA code to show the cell address of the active cell (code below):
Sub Show_ActiveCell_Address() MsgBox ActiveCell.Address End Sub
The above code would show the address in absolute reference (such as $A$5).

Formating the Active Cell (Color, Border)
Below the VBA code that would make the active cell blue in color and change the font color to white.
Sub Format_ActiveCell() 'Makes the active cell blue in color ActiveCell.Interior.Color = vbBlue 'Changes the cell font color to white ActiveCell.Font.Color = vbWhite End Sub
Note that I have used the inbuilt color constant (vbBlue and vbWhite). You can also use the RGB constant. For example, instead of vbRed, you can use RGB(255, 0, 0)
Offsetting From the Active Cell
VBA in Excel allows you to refer to cells relative to the position of the active cell (this is called offsetting).
For example, if my active cell is cell A1, I can use the offset property on the active cell and refer to the cell below it by specifying the position of that row corresponding to the active cell.
Let me show you an example.
Sub Offset_From_ActiveCell()
'Make cell A1 the Active Cell
Range("A1").Activate
'Goes One cell Below the Actice Cell and Enters the text Test in it
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 0).Value = "Test"
End Sub
The above code first activate cell A1 and makes it the active cell. It then uses the offset property on the active cell, to refer to the cell which is one row below it.
And in the same line in the code, I have also assigned a value “Test” to that cell which is one row below the active cell.
Let me show you another example where offsetting from the active cell could be used in a practical scenario.
Below I have a VBA code that first activates cell A1, and then uses the offset property to cover 10 cells below the active cell and enter numbers from 1 to 10 in cell A1:A10.
Sub Offset_From_ActiveCell()
'Activates cell A1
Range("A1").Activate
'Loop to go through 10 cells below the active cell and enter sequential numbers in it
For i = 1 To 10
ActiveCell.Offset(i - 1, 0).Value = i
Next i
End Sub
The above code uses a For Next loop that runs 10 times (and each time the value of the variable ‘i’ increases by 1). And since I am also using ‘i’ in the offset property, it keeps going one cell down with each iteration.
Get ActiveCell Row or Column Number
Below the VBA code that will show you the row number of the active cell in message box:
Sub ActiveCell_RowNumber() MsgBox ActiveCell.Row End Sub
And the below code will show you the column number in a message box:
Sub ActiveCell_ColumnNumber()
MsgBox ActiveCell.Column
End Sub
Assign Active Cell Value to a Variable
You can also use VBA to assign the active cell to a variable. Once this is done, you can use this variable instead of the active cell in your code.
And how does this help? Good Question!
When you assign the active cell to a variable, you can continue to use this variable instead of the active cell. The benefit here is that unlike the active cell (which can change when other sheets or workbooks are activated) your variable would continue to refer to the original active cell it was assigned to.
So if you are writing a VBA code that cycles through each worksheet and activates these worksheets, while your active cell would change as new sheets are activated, the variable to which you assigned the active cell initially wouldn’t change.
Below is an example code that defines a variable ‘varcell’ and assigns the active cell to this variable.
Sub Assign_ActiveCell() Dim varcell As Range Set varcell = ActiveCell MsgBox varcell.Value End Sub
Select a Range of Cells Starting from the Active Cell
And the final thing I want to show you about using active cell in Excel VBA is to select an entire range of cells starting from the active cell.
A practical use case of this could be when you want to quickly format a set of cells in every sheet in your workbook.
Below is the VBA code that would select cells in 10 rows and 10 columns starting from the active cell:
Sub Select_from_Activecell()
Range(ActiveCell, ActiveCell.Offset(10, 10)).Select
End Sub
When we specify two cell references inside the Range property, VBA refers to the entire range covered between there two references.
For example, Range(Range(“A1”), Range(“A10”)).Select would select cell A1:A10.
Similarly, I have used it with active cell, Where the first reference is the active cell itself, and the second reference offsets the active cell by 10 rows and 10 columns.
I hope this tutorial has been useful for you in understanding how active cell works in Excel VBA.
Other Excel tutorials you may also find useful:
- Highlight the Active Row and Column in a Data Range in Excel
- 24 Useful Excel Macro Examples for VBA Beginners (Ready-to-use)
- How to Filter Cells with Bold Font Formatting in Excel (An Easy Guide)
- How to Delete Entire Row in Excel Using VBA
- Copy and Paste Multiple Cells in Excel (Adjacent & Non-Adjacent)
- Working with Worksheets using Excel VBA (Explained with Examples)
- Using Workbook Object in Excel VBA (Open, Close, Save, Set)
- Excel VBA Events – An Easy (and Complete) Guide
- How to Edit Cells in Excel? (Shortcuts)
Return to VBA Code Examples
This tutorial will demonstrate how to get the Active Cell’s column or row.
Active Cell Column
This procedure will return the ActiveCell’s column in a MessageBox:
Public Sub ActiveColumn()
MsgBox ActiveCell.Column
End SubActive Cell Row
This will return the ActiveCell’s row:
Public Sub ActiveRow()
MsgBox ActiveCell.Row
End SubVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro – A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More!

VBA Code Examples Add-in
Easily access all of the code examples found on our site.
Simply navigate to the menu, click, and the code will be inserted directly into your module. .xlam add-in.
(No installation required!)
Free Download