Antonym: now. Similar words: when, by then, and then, hence, now and then, kitchen, even when, strengthen. Meaning: [ðen] n. that time; that moment. adj. at a specific prior time. adv. 1. subsequently or soon afterward (often used as sentence connectors) 2. in that case or as a consequence 3. at that time.
1 First think, and then speak.
2 When war begins, then hell openeth.
3 Custom, then is the great guide of human life.
4 First catch your hare then cook him.
5 When war begins then hell opens.
6 Half a loaf is better then no bread.
7 When the fox preacheth, then beware your geese.
8 First try, and then trust.
9 Deliberate before you begin, then execute with vigour.
10 In delay there lies no plenty , Then come kiss me , sweet and twenty , Youth’s a stuff that will not endure .
11 If the mountain won’t come to Mohammed, then Mohammed must go to the mountain.
12 When Greek meets Greek, then comes the tug of war.
13 Carrion crows bewail the dead sheep and then eat them.
14 We first make our habits, and then our habits make us.
15 When Greek meet Greek, then comes the tug of war.
16 If there be neither snow nor rain, then will be dear all sorts of grain.
17 When Greeks joined Greeks,(www.Sentencedict.com) then was the tug of war.
18 Do you love life ? Then do not squander time ; for that’s the stuff5 life is made of .
19 If you doubt yourself, then indeed you stand on shaky11 ground.
20 Some persons do first, think afterwards, and then repent for ever.
21 When the oak is before the ash, then you will only get a splash; when the ash is before the oak, then you may expect a soak.
22 We were living in Wales then.
23 The minister preaches a sermon now and then.
24 Can’t help sadness, then slowly learned to hide.
25 She started to sing,and then the others chimed in.
26 The cuckoo comes in April, and stays the month of May; sings a song at midsummer, and then goes away.
27 We should put aside and postpone all other reforms; that we have but one task——the istruction of the people, the diffusion of education, the ecourgement of science—-on that day a great step will have then been taken in our rgenerion.
28 When you want knowledge like you wanted air under water then you will get it.
29 The cuckoo comes in April, and stays the month of May; sings a song at Midsummer, and then goes away.
30 Let early education be a sort of a musement; you will then be bette able to find out the natural bent.
Even Native English speakers mess up than and then because of their similar spelling and pronunciations. However, their meanings significantly vary.
This guide will show you nuanced differences between then vs. than. Learn when to use the two words in the sentence before the self-anointed grammar policemen point out your grammar error.
Then vs. Than: What’s The Difference?
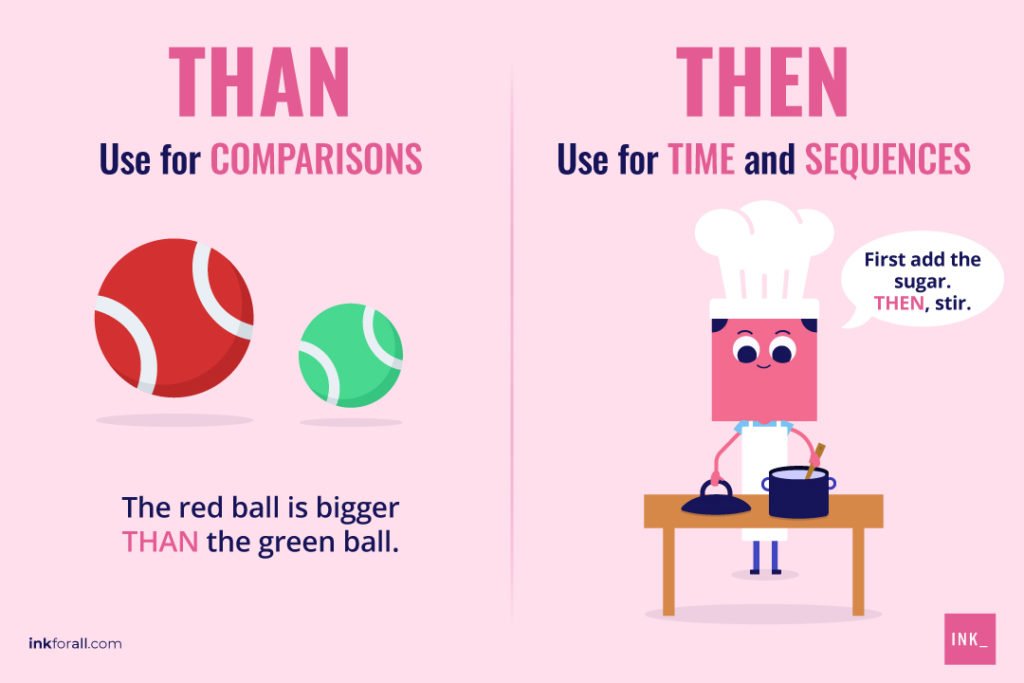
Then is an adverb, noun, or adjective that indicates a previous time. Meanwhile, than is a conjunction used when comparing two items or people.
Use then in writing or events when there is an element of time. In the English language, then means at that time, at that point, or next. You’ll find it in phrases like since then and until then to show a reference of time.
Use than in common phrases like better than, further than, taller than, or broader than. You’ll find this word after terms like other, less, more, and rather.
In Middle English, then and than used to be the same word used for all their meanings. People used them to show relationships with time and for comparison purposes. However, modern writing now treats them differently.
That’s why the two words are now homophones people get confused with. Homophones are words that show an essential difference in spelling but similarities in sound.
When to Use Then
You can use then as an adverb to replace at that time in question to make grammatical sense. This adverb helps you place events in time in order, such as when relating to a future time.
Examples:
- But by then, Shannon might be tired.
- Let’s buy ice cream and then watch a movie.
Here’s a longer, multilayered example of then relating to the future.
My first subject is Chemistry, then French, then Science. Then, I’ll have lunch, go to Math class, and go home.
Then can also mean previous or former. Some English speakers use the term if they can’t recall the exact time of an event in the past. Here are some sentences that use then relating to a previous time.
Examples:
- The then president visited our small town.
- We lived in San Diego then.
Aside from using then in terms of time, you can also use it to show consequence or mean in that case.
Examples:
- If you had taken care of the cat, then we wouldn’t be in this situation.
- I slept late, so then I woke up dizzy.
When to Use Than
Making an unequal comparison requires using a particular word in the English language. Than is the conjunction that expresses a form of comparison in a sentence. Use it to introduce the second item or person to make direct comparisons.
For instance, when you say “truth is stranger than fiction,” it means that real events are more unnatural than imagination.
Examples:
- My mother told me that a curious person is better than a know-it-all.
Is it Earlier Than or Earlier Then?
Both phrases are correct but have different meanings. The more common phrase you might be looking for is earlier than. For example, you might arrive at school earlier than usual. However, you used to come earlier then.
Is it Later Then or Later Than?
The correct phrase is later than if you want to show a comparison between two late items, people, or events.
Is it Rather Then or Rather Than?
The correct term is rather than since rather is used to show preference in a specific matter. For instance, you might know someone who wants wine rather than a martini.
Is it Other Than or Other Then?
Other than is the appropriate phrase as it means apart from or except.
Is it Better Than or Better Then?
Better than is one of the most popular phrases with the word than. To be better than something or someone means you’re superior or more excellent.
Is it More Than or Then?
The appropriate phrase is more than, which indicates a bigger value or amount. It can also mean extremely, as in more than gratefulto be reading this post.
Is it Less Then or Less Than?
Use less than as a synonym for far from or certainly not.
It is Well Then or Well Than?
The correct phrase is well then to indicate that what someone said was unexpected or inappropriate. Well than is a wrong phrase because well is not in its comparative form.
Than Me or Than I?
The traditional rule is to use than I because the longer version of the sentence is typically than I am. However, it can lead to outdated-sounding language, especially if you use a different pronoun.
Example:
- He is smarter than she.
- He is smarter than I.
Can You Start a Sentence With Then?
You can start a sentence using then when showing a list of events or a chronology of events.
Example:
- I read a book last night. Then I got hungry and ordered food.
How Do You Use Than in a Sentence?
Here are plenty of examples of how you can use than in a sentence.
An asteroid wider than two football fields will zoom past Earth in the wee hours of Thursday (Aug. 4). The asteroid is set to pass at 12:23 a.m. (ET). [Live Science].
Indeed, it may have been no more than a coincidence that Tsai Chi-chang, deputy speaker of Taiwan’s legislature, appeared to respond to Pelosi’s suit by wearing a pink tie to meet her on Wednesday morning. [CNN].
She recalls one episode in which a former employer chastised her and two other assistants, each of whom made more than $150,000 a year, she says, for putting bananas in the refrigerator, instead of on the kitchen counter. [Wall Street Journal].
The arrests on Tuesday near Krugersdorp, a city northwest of Johannesburg, bring the total number of people detained since the attack to more than 120. [The Guardian].
How Do You Use Then in a Sentence?
Let’s take a look at these examples of then in sentences.
Shark! Man in New Jersey catches, then releases a 7-foot sand tiger shark. [Fox News].
Speaking to CNN, the congresswoman Carolyn Maloney said sorry for broaching the issue in a debate – but then said again she thought Biden would not run. [The Guradian].
No, because smartphones bring these three features into one product. Then why should organizations pay for three different products, when it is indeed possible to bring all these aspects into one smart product? [Forbes]
The Real Difference Between Than vs. Then
One of the writing issues that English speakers and writers face is the confusion between than vs. then. Using the two words interchangeably can be annoying for grammar perfectionists, even in informal writing. Remember:
- Use then in a sentence when referring to a sense of time, whether past or future. You can also use it to show consequences.
- Use than to feature comparisons between two unequal items, places, persons, or events.
Answer the worksheet below to test your knowledge of this homophone.
Are these sentences correct in terms of punctuation and grammar?
She asked, «Could I have a drink of your water?» Then she walked away when I said, «No, you can’t.»
Thanks so much for the first three responses, but I guess I should have continued by telling you that this is part of a transcription, so I can’t change the order of the words. Given that information, is ‘Then’ best capitalized and starting its own sentence, or would you leave it lowercase as a continuation of the prior sentence?
asked Mar 31, 2015 at 15:31
gnmorrgnmorr
911 gold badge1 silver badge4 bronze badges
4
Yes, you can start a sentence with then. However, the clause that begins with then should go last:
She asked, «Could I have a drink of your water?» I said, «No, you can’t.» Then she walked away.
Then indicates a consequence or a result, which is why it should go at the end of any group of sentences that describe actions that create that consequence.
Think of then as a result of if, where if always comes first:
If she may not have a drink of your water, then she will walk away.
answered Mar 31, 2015 at 15:45
SnapmanSnapman
6033 silver badges7 bronze badges
4
He read the letter and began to cry. His huge old saltwater aquarium burst.Then the room was flooded with saltwater.
or:
He read the letter and began to cry. Then the room was flooded with saltwater.
His huge old saltwater aquarium had burst.
There is a rhyme and reason to where and when «then» appears. The second example is clearly superior because «then» is placed «incorrectly». In the second example the placement of «then» gives us the impression that the room was flooded with tears, before we are told the more mundane cause. In the first example, the flooding clearly follows, and is a consequence of, the bursting aquarium. This is much drier.
My point is that grammar is meant to serve the story, to make things more clear (or deliberately ambiguous), to create tension and release. If you keep your eyes on the prize, so to speak, you will make fewer errors without having to memorize rules, and the errors you do make will be different in kind than the errors of sloppy writing.
answered Mar 31, 2015 at 17:00
bobrobobro
1,70411 silver badges10 bronze badges
3
I would rephrase it entirely and say:
When I said, «No, you can’t,» she walked away.
That sounds better in my humble opinion. You could add an adverb before ‘walked’ to make the sentence more interesting.
answered Mar 31, 2015 at 17:54
BuzzBuzz
4144 silver badges6 bronze badges
1
- 0
- 40,869
Hello,
I’d like to know if it’s possible to start a sentence with ‘then’.
For example:
Then, he walked away.
Or is it:
He then walked away.
Thanks!
- DutchGirl
- answer
Comments
I think most of the time this sentence would be incorporated into another sentence. For example,
John gave his condolences to the family and then he walked away.
I don’t know that it is technically incorrect to start a sentence with then (perhaps another poster will answer that), but it seems ackward to me and incomplete. The second sentence also sounds like it needs something before it, e.g.:
Having given his condolences, he then walked away.
- sam1947
- add a comment
DutchGirlI’d like to know if it’s possible to start a sentence with ‘then’.
Yes. And a comma is not necessary.
Then he walked away.
CJ
- CalifJim
- add a comment
It is perfectly acceptable to start a sentence with the word
then
. The word
then
is a conjunctive adverb. It is in the same family as
however
,
therefore
, and
consequently
. So,
Peter approached the cliff. Then, he walked away. (correct)
Peter approached the cliff; then, he walked away. (correct)
Peter approached the cliff; he then walked away. (correct)
Peter approached the cliff, then he walked away. (INCORRECT — Comma Splice)
Peter approached the cliff, and then he walked away (correct)
- GrammarWorks
- add a comment
Then, he walked away. (This is NOT correct. There should not be a comma after then in this sentence.)
- anonymous
- add a comment
DutchGirlI’d like to know if it’s possible to start a sentence with ‘then’.
You can start a sentence with anything – even ‘and’ or ‘but’.
- Rover_KE
- add a comment
Thank you to Jose Blanco, for your comprehensive answer based on rules of grammar rather than opinion or guesswork.
-Betsy
- anonymous
- add a comment
That is not true. You can’t start a sentence with ’cause. (In American Standard English that is…)
- anonymous
- add a comment
You surprise me. Are you sure?
(Standard English is because, not ’cause)
- Clive
- add a comment
Show more
Answer this Question

Main Than vs. Then Takeaways:
- Then and than are homophones. This means that they sound almost identical when spoken but have different meanings and spellings.
- When you think of then, think of time.
- When you think of than, think of comparisons.
- Sometimes, than can be used to indicate time, but it is still typically a comparison.
- Then can be an adverb, adjective, or noun.
- Than is a conjunction.
Like affect vs. effect and to vs. too, than vs. then cause a lot of confusion. While many use these homophones interchangeably, they are not the same. Choosing the wrong word may mean that you don’t communicate your message clearly or correctly. In fact, than and then have different functions and meanings. But, there are, of course, some exceptions. Here, we’ll make sure you have everything you need to keep them straight, once and for all.
Then vs. Than Rule
Here’s the best way to tell the difference between then vs. than: associate then with time and than with comparisons. For example, use then for clarifying a sequence of events like writing a recipe or retelling a story (“We went to the supermarket and then headed home.”). Try remembering that the “e” in “then” stands for “events.”
Conversely, use than when making a comparison (“We like going to the smaller shop nearby more than going to the supermarket.”).
You might see then in a comparison, but always about time (“Back then, we were less timid than we are now.”).
Than vs. Then Exception: Comparisons About Time
There is one exception. Sometimes, than can appear in comparisons about time. But in these cases, there is still a comparison involved.
In this example, we’re dealing with time, but it’s secondary. The main function of than here remains the same: to make a comparison.
“He” is comparing his meeting time to 12 pm. He’ll be there no later than noon. In other words, other times are being compared to that one particular time-related target.
This may be confusing because we’re not drawing a 1:1 comparison between two individual things (he arrived earlier than I arrived); instead, we’re comparing one individual thing (12 pm) to a group (all times before 12 pm). Nevertheless, this is ultimately a comparison and as a result, should use then.
What Type of Word is Then?
Then usually refers to time and can function as three types of speech. First, then is usually an adverb (“If you leave, then turn off the lights”). Second, then can be an adjective (“Jackie Kennedy, then Jacqueline Onassis, studied literature“). Finally, it can be a noun (“See you then?” or “We’ll wait until then”). Conversely, than is a conjunction and is for making comparisons (“This cake is sweeter than that brownie”).
How is Then Used in a Sentence?
Then vs.than breaks down to time vs. comparisons. For instance, there are several ways to use then, and they all indicate time. Most often, then is an adverb to help clarify a sequence of events (“Wash then dry the dishes”). What’s more, then helps describe a condition and then a consequence (“If it rains, then we’ll eat inside”). Additionally, then can also be an adjective (“The then CEO”). Finally, then can be a noun (“I’ll see you then!”).
Then can function as several parts of speech. Most often, it’s found working as an adverb in sentences where time is involved, but can also be an adjective or noun. Use then to:
- Clarify a sequence or indicate the order in which certain actions occurred
- Illustrate the relationship between several actions or items
- Illustrate the consequences of a certain action
- Indicate a previously held position
Clarify a Sequence (Adverb)
Describe the Relationship Between a Condition and Consequence (Adverb)
You could also use then to tell the reader when something caused something else to happen. Those examples typically frame the second action as a consequence of the first. In that case, you’ll probably use an if/then construction, making it clear the connection between the two actions.
Indicate a Previously Held Position (Adjective)
Remember, then can be an adjective, an adverb, or a noun. It’s most often used in sentences that are discussing time. You might be demonstrating a series of events, indicating a relationship between several actions.
Refer to Past or Future Time (Noun)
How is Than Used in a Sentence?
Than is a conjunction used for comparisons (“She is taller than I am”).However, then is an adverb, adjective, or noun related to time. A point of overlap is that than can appear in comparisons about time (“Please arrive no later than 9 a.m.”).
Overall, than is important because it helps enrich the level of clarity and detail in your writing.
When the relationship between the nouns, verbs, and adjectives in a sentence isn’t equal, you can use than to indicate that one takes precedence. This helps clarify status, physical stature, order of operations, and other important information.
Like other conjunctions, than is used to connect two clauses or two words within the same clause. Unlike other conjunctions, than is specifically used to compare and contrast.
Than helps us understand which is bigger, better, louder, or simply more favored. For example, using “than” is a good way to paint a picture of how items contrast each other.
Here are easy examples of how to use than vs. then in a sentence:
Use the phrase “other than” when describing exceptions. You can replace other than with alternatives like except for and besides.
How to use Less Than and More Than
How to use More Than in a Sentence
How to Use Less Than in a Sentence
Common Expressions: Than vs. Then
Is it Other Than or Other Then?
The correct phrase is “other than” and not “other then.” Use “other than” to indicate an exception (“Other than cats, she’s not a fan of animals”). The item or situation that comes directly after “other than” is the only example mentioned that doesn’t fit into the described scenario. In this way, this structure compares the exception to the rule. Therefore, “other than” expresses a comparison. Since we use than for comparisons and then for time, “other then” doesn’t make sense here.
Is it Well Then or Well Than?
The correct phrase is “well then“, not “well than.” Use the phrase well then to switch topics. Similarly, use this phrase to start concluding a conversation or saying goodbye (Well then, I have to go. See you tomorrow!). Moreover, if a person says something strange or interesting, the response well then indicates that you’re surprised and unsure of what else to say. For this reason, some use it sarcastically.
For instance, say your friend has a history of jumping and hitting their head. You might ask them whether they think that’s a good idea. When they reluctantly say, No…, you could respond with, Well then….?! to suggest they should know better.
If someone makes a strong display of emotion or a comment that you find surprising, provocative, or offensive comment, you might respond with well then.
Notice that because “well” is an interjection in these examples, there’s often a comma between “well” and “then.”
Is it Rather Than or Rather Then?
The correct phrase is “rather than“, not “rather then.” This is because than is most commonly used in comparisons (“He’s taller than her”) while then is more for discussing time (“Sal went to the store then stopped by the post office”). Since “rather than” compares two actions or choices, it only makes sense to use “rather than” instead of “rather then.”
Is it Older Than or Older Then?
Both “older than” and “older then” are correct. But, they are not interchangeable because they mean different things. Usually, we use then for time and than for comparisons. However, this question is confusing because both “older than” and “older then” deal with time and comparisons, but in different ways. Use “older than” to compare the age of one person to that of another person (“My sister is older than I am”). On the other hand, we use “older then” to refer to a time other than the present (“See you then!” Let’s wait a week and buy it then”).
Technically both options are correct. Which one you choose to use depends on your message and the surrounding context.
Rather than accidentally making a mistake with then or than in the future, bookmark this page and review as needed. Happy writing!
Is it Better Than or Better Then?
The answer will depend on the context of your statement. If you’re comparing two things in your sentence, then the correct phrase is “better than.” However, if you are referring to a certain time in the past as better, then “better then” is the right phrase. See examples below:
Let’s see if Then and Than Still Confuse you
Then vs Than Question #1
A. The word “then” mostly functions as an adverb in a sentence.
B. Then can function as an adjective, adverb, or noun.
C. You can use “then” and “than” interchangeably in a sentence.
D. Then is often used in sentences that are discussing time.
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is C. “Then” suggests the order in which specific actions occurred, while “than” is used for comparison.
Then and Than Question #2
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is TRUE. Although both words sound alike, they have different meanings.
Than Question #3
Preposition
Conjunction
Both
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is BOTH. “Than” is a conjunction or preposition, depending on how it is used in a sentence.
Than or Then Question #4
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is THAN. “Than” is commonly used in comparisons.
Then or Than Question #5
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is THEN. “Then” is used to indicate time.
Then vs Than Question #6
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is THAN. “Rather than” compares two actions or choices, with the person in question opting for one over the other.
Than vs. Then Quiz Result
Expert!
Not bad!
Almost got it! Review the article and try again.
Read More: What’s The Difference Between Yea, Yeah, and Yay?
-
#1
A lot of my students start sentences as follows….
«Then, I will visit…….»
«Then, She will eat lunch»
I can’t quote an exact grammar rule but it sounds clumsy and unnatural.
Any tips?
-
#2
Hello Japaholic
I can agree with starting a sentence with «then» can sound clumsy. I would say that two things could be quick ways of fixing it. #1 You can say «After» or «Later» instead. OR #2 You can tell them to add to the sentence before E.G. I will visit my sister, then I will eat lunch. I would try getting them to say these if you truly wish to try getting them to change this. I truly believe that these situations could fixed by the second solution unless it is a sentence on it’s own, and that I would merely just try getting them to use a better word choice. I hope that this helped you, and if you have anymore questions please ask.
-
#3
There is no rule about starting—or not starting—a sentence with the word «then», nor is there anything «clumsy» about it. It depends on context. (What was the sentence before that one?) It would be perfectly normal to say to a child, «You must finish your homework. Then, you may go out and play.»
-
#4
A lot of my students start sentences as follows….
«Then, I will visit…….»
«Then, She will eat lunch»
I can’t quote an exact grammar rule but it sounds clumsy and unnatural.
Any tips?
Yes, my tip is: do not go burdening your students with more rules than they need. We get a steady stream of over-ruled students in here, maybe this is how it starts!
Last edited: Dec 22, 2014
English has a lot of confusing words, especially those words that look alike and sound alike. The two words I want to talk about today are no exception.
Choosing between then or than can be difficult since they are only a single letter apart and they sound pretty close to each other, but if you’re not sure which word to use and when, don’t worry. I get this question from a lot of readers.
What is the Difference Between Then and Than?
Today, I want to discuss the differences between then vs. than, their functions in a sentence, and give you a few tricks to remember them for the future. After reading this post, you shouldn’t have any trouble when choosing than or then.
When to Use Then

- At that time.
- I was at work then.
- Come over this afternoon; I’ll be ready then.
- Next in time, space, or order; immediately afterward.
- We saw a movie and then went out for dinner.
- We filled up the car and then began the trip.
- In addition; moreover; besides.
- The glasses are $100, and then there is sales tax.
- First you need a license, and then you can drive.
- In that case, accordingly.
- If the weather is bad, then my flight will get canceled.
- If there is heavy traffic, then I might be late.
All four of these uses are uses of then as an adverb. The use of then as an adjective is much more limited.
- Being so at the time.
- The decision was made by then chairman Bill Gates.
- The bill was signed by then President Ronald Reagan.
As you can see, most of the uses of then have to do with time. It can mean next in time or at the time. Keep this in mind for later when I give you the trick to remember.
When to Use Than

- He is taller than I am.
- She can run faster than I can.
- Your meal looks better than mine does.
- Coca-Cola is better than Pepsi.
In all of these examples, than is used to introduce a comparison between two things. This is important to keep in mind. No matter what you are comparing, whether it be time, money, speed, if a comparison is taking place, than is the correct word choice.
Popular Phrases Using Than

- More than less than; less than more than. (Less then or less than?)
- He has less than I have. (Correct)
- He has less then I have. (Wrong).
- She has more than I have. (Correct)
- She has more then I have. (Wrong)
- Rather than or rather then?
- I would rather eat than sleep. (Correct)
- I would rather eat then sleep. (Wrong)
In the above example using rather then or than, the two sentences communicate different meanings. The first sentence says you prefer (right now at least) eating to sleeping. The second says you prefer to eat first and sleep second. So, the second sentence isn’t necessarily wrong in all meanings, it’s just wrong when your intended meaning is a comparison, not an ordered list of events.
- Sooner rather than later.
- I would prefer to eat sooner rather than later. (Correct)
- I would prefer to eat sooner rather then later. (Wrong)

This means that sentences such as Jack is taller than Jill should be construed as an elliptical version of the sentence Jack is taller than Jill is. In this sentence, the name Jill is standing in for the full clause Jill is.
In other words, the pronoun that follows than is determined by whether it serves as the subject or object of the verb “understood.”
The traditional rule, therefore, requires the sentence Jack is taller than I (not me), since the full sentence is understood to be Jack is taller than I am. But it does allow for sentences like this one, The report shocked Jack more than me, since this sentence is understood to be The report shocked Jack more than it shocked me. In this sentence Jack is acting as an object of shocked, whereas in the first sentence he was the subject.
It’s probably best to hold to this traditional rule if you are writing an academic paper for school or a book for publishing, but understand that it can lead to some cumbersome, outdated sounding language.
- He is taller than she.
- You are taller than I.
In informal writing and speech, sentences like he is smaller than her are widely used and almost universally accepted.
Remembering When to Use Then and Than
We’ve spent so much time talking about than that we almost forgot about the word then, so now it’s the time to come full circle on using then and than.
A good trick to keep track of these words is that then is usually used to indicate time. Both then and time have a letter “E” in them.
Than is used to make comparisons. Both than and comparison have a letter “A” in them.
Summary
These two words are very close in their appearance, but than vs. then have very different uses.
Then is commonly used to express a sense of time or what comes next or used to be.
Than is used to form comparisons between two things.
Contents
- 1 What is the Difference Between Then and Than?
- 2 When to Use Then
- 3 When to Use Than
- 4 Popular Phrases Using Than
- 5 Than Me vs. Than I
- 6 Remembering When to Use Then and Than
- 7 Summary